Submitted:
18 March 2024
Posted:
22 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
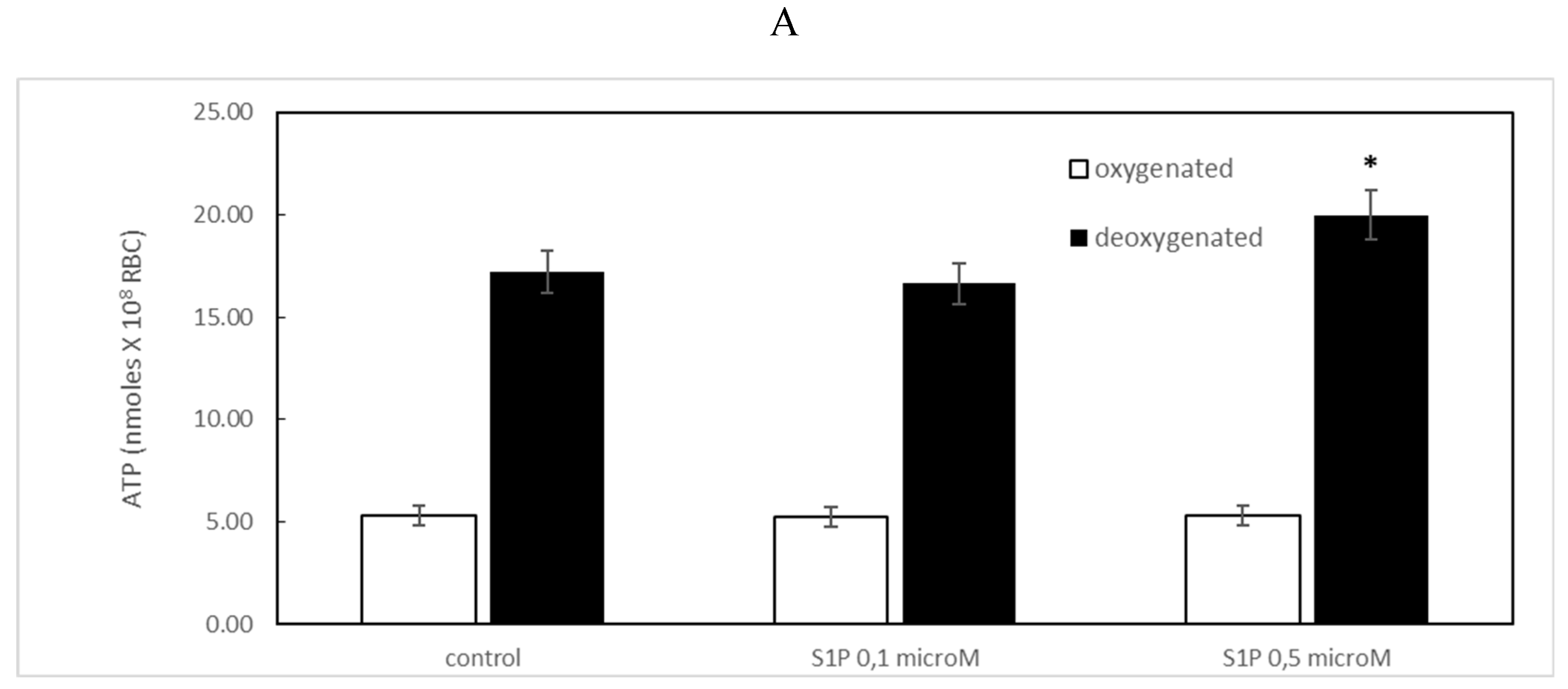
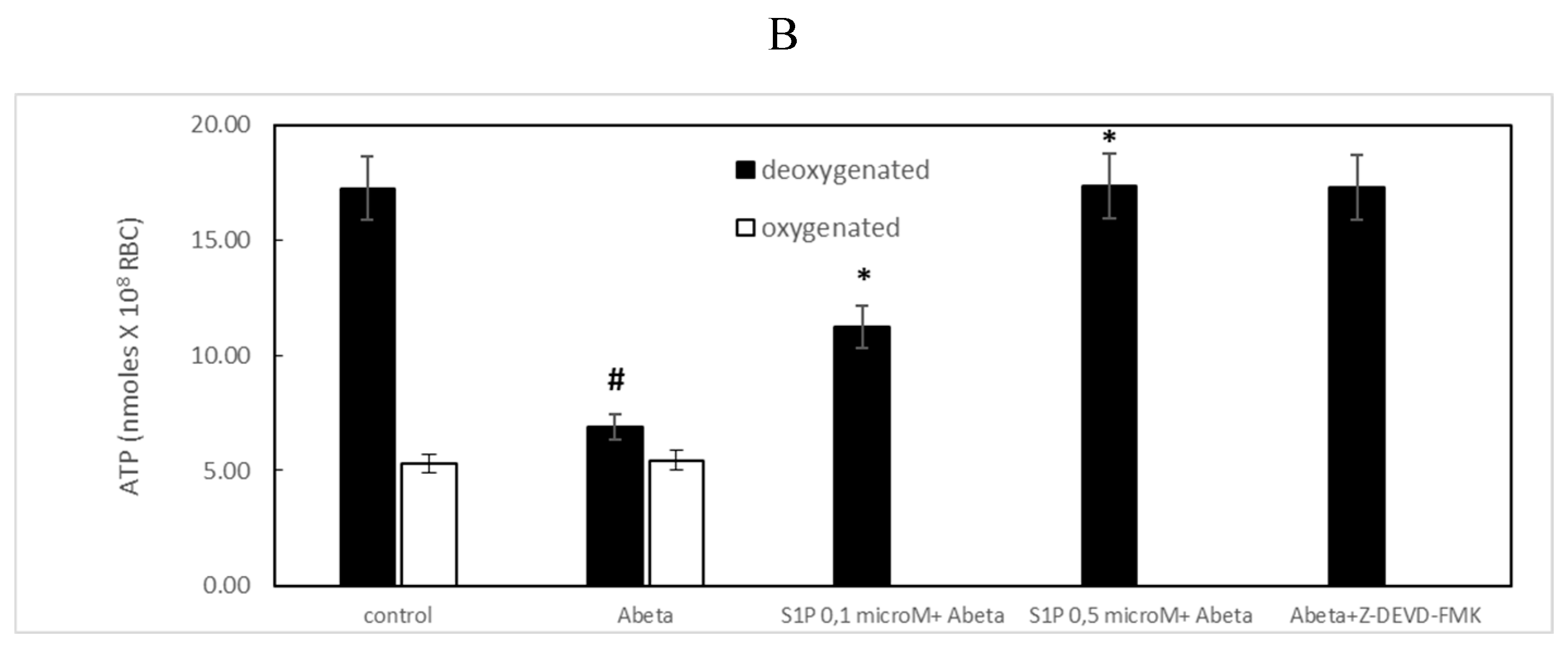
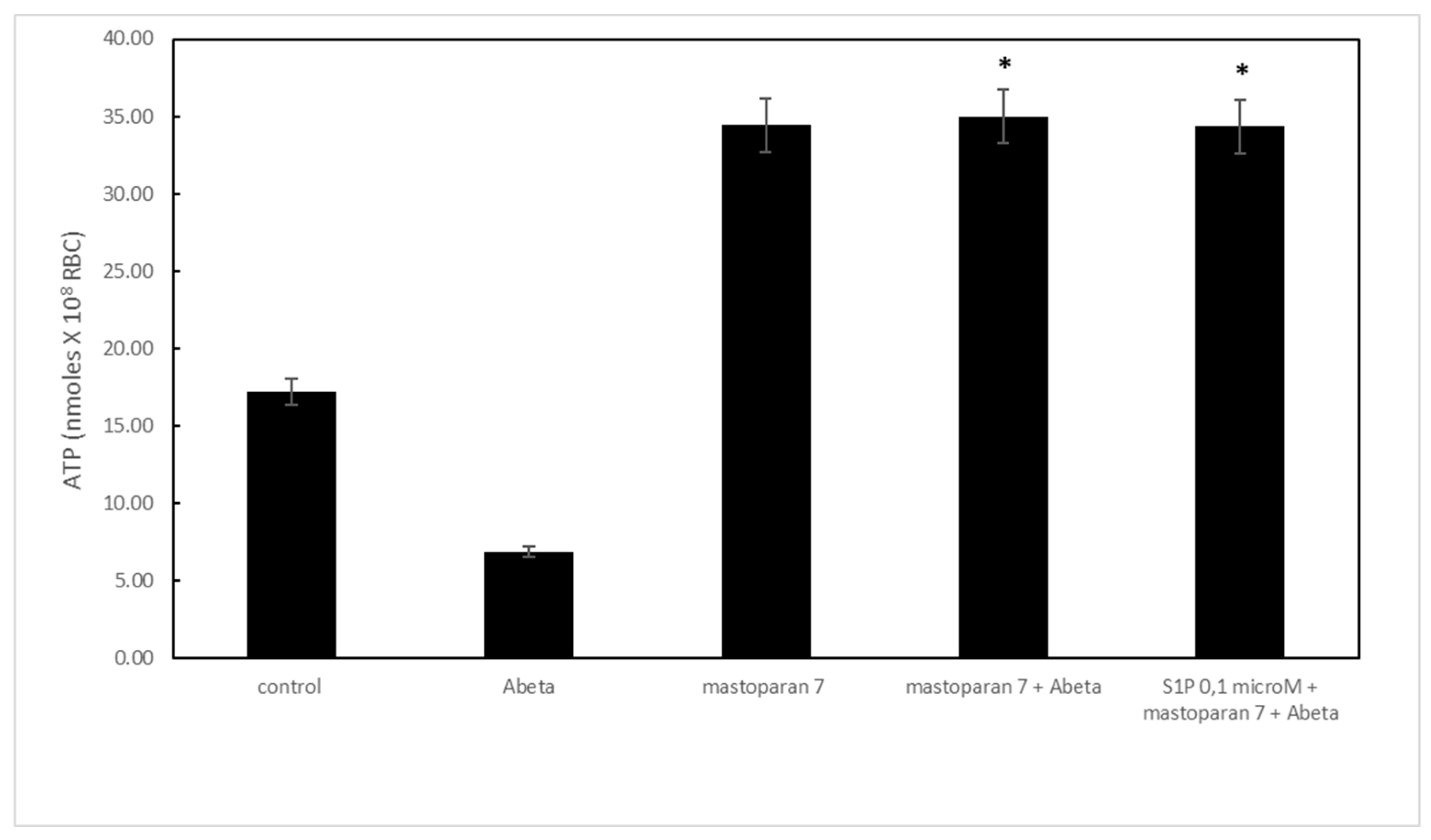
2.1. Protective Role of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate on ATP Release
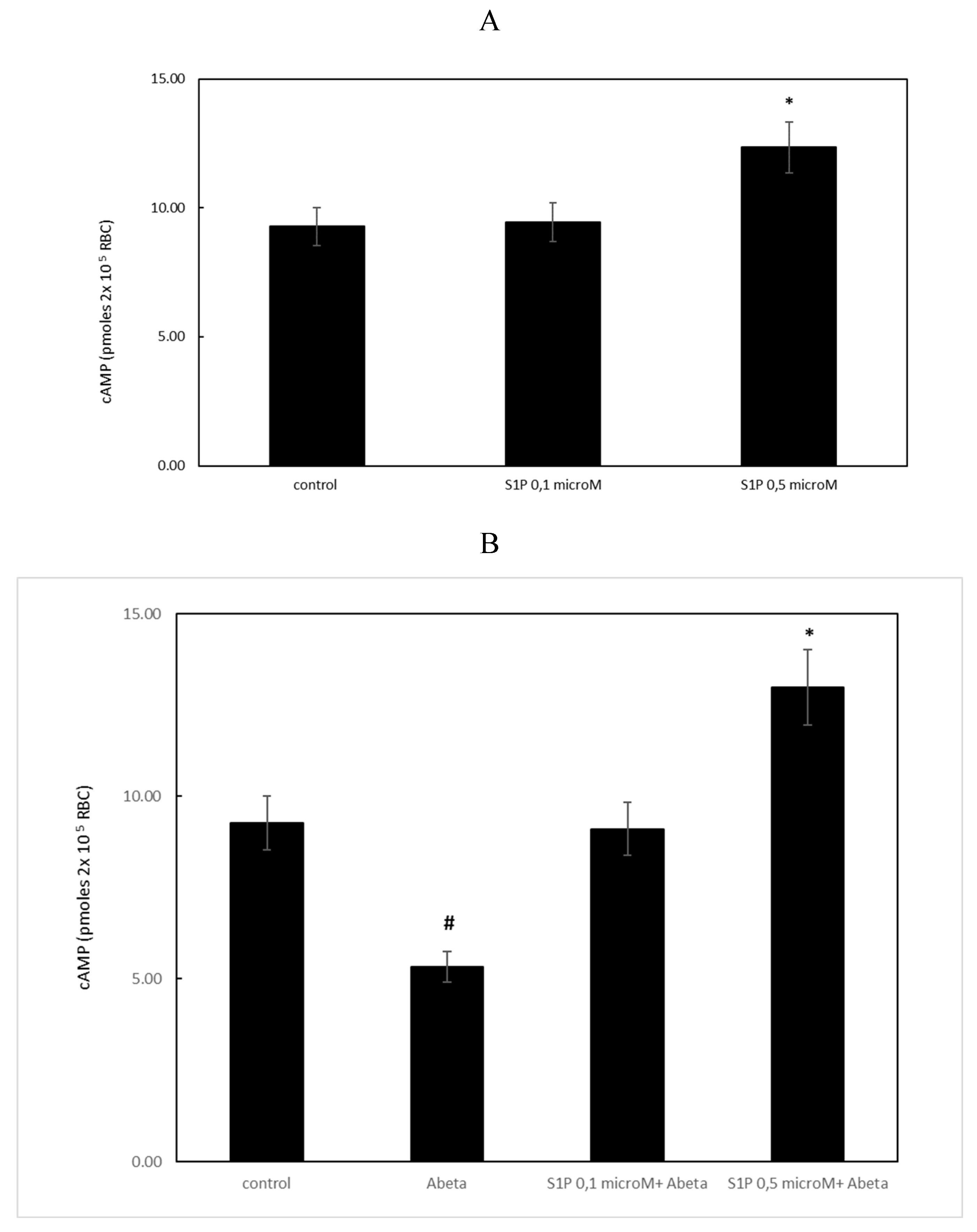
2.2. Effect of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate on the Accumulation of cAMP
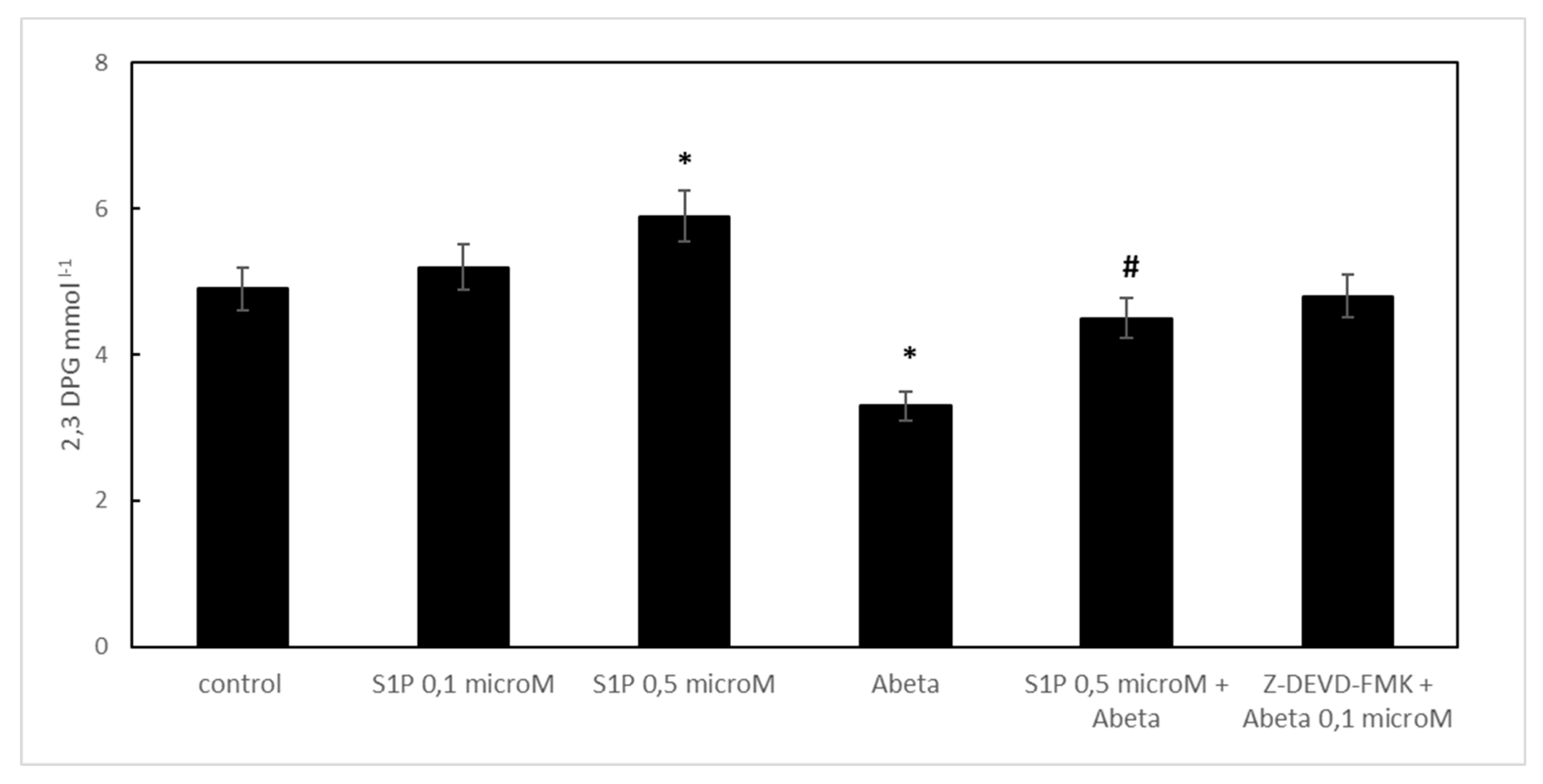
2.3. Effect of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate on 2,3 DPG Levels
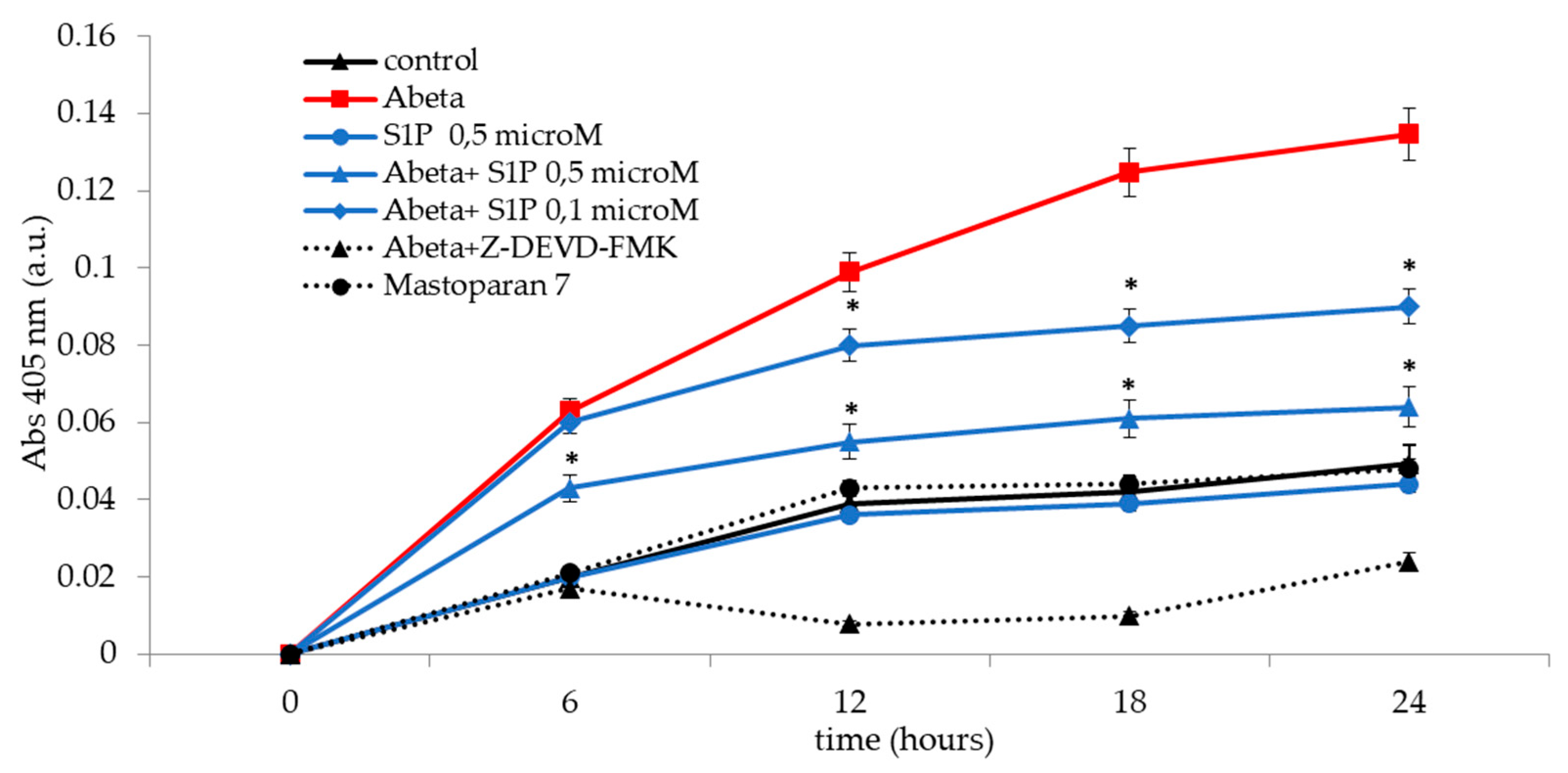
2.4. Effect of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate on Caspase-3 Activity
2.5. Hemolysis Degree
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Preparation of Red Blood Cells and Incubation Conditions
4.3. ATP Assay
4.4. Measurement of cAMP
4.5. Determination of 2,3 DPG
4.6. Caspase-3 Activity Determination
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yatomi, Y. Sphingosine 1-phosphate in vascular biology: possible therapeutic strategies to control vascular diseases. Curr Pharm Des 2006, 12, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Stunff, H.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Generation and metabolism of bioactive sphingosine-1-phosphate. J Cell Biochem 2004, 92, 882–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanel, P.; Andreani, P.; Graler M., H. Erythrocytes store and release sphingosine 1-phosphate in blood. FASEB J 2007, 21, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, C.; Sensken, S.C.; Peest, U. Erythrocytes serve as a reservoir for cellular and extracellular sphingosine 1-phosphate. J Cell Biochem 2010, 109, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.Q.; Vu, T.M.; Tukijan, F. Erythrocytes efficiently utilize exogenous sphingosines for S1P synthesis and export via Mfsd2b. J Biol Chem 2022, 96, 100201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Anada, Y.; Tani, M.; Ikeda, M.; Sano, T.; Kihara, A. Lack of sphingosine 1-phosphate-degrading enzymes in erythrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2007, 357, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappu, R.; Schwab, SR.; Cornelissen, I.; Pereira, JP.; Regard, JB.; Xu, Y.; et al. Promotion of lymphocyte egress into blood and lymph by distinct sources of sphingosine-1-phosphate. Science 2007, 316, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatomi, Y.; Ruan, F.; Hakomori, S.; Igarashi, Y. Sphingosine-1-phosphate: a platelet-activating sphingolipid released from agonist-stimulated human platelets. Blood 1995, 86, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, K.; Le, YM.; Michaud, J.; Thangada, S.; Ai Y Bonkovsky, HL.; et al. Vascular endothelium is a contributor to plasma sphingosine 1-phosphate. Circ Res 2008, 102, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuhara, S.; Simmons, S.; Kawamura, S.; Inoue, A.; Orba, Y.; Tokudome, T. The sphingosine-1-phosphate transporter Spns2 expressed on endothelial cells regulates lymphocyte trafficking in mice. J Clin Investig, 2012; 122, 1416–1426. [Google Scholar]
- Cuvillier, O.; Pirianov, G.; Kleuser, B.; Vanek, P.G.; Coso, O.A.; Gutkind, S.; et al. Suppression of ceramide-mediated programmed cell death by sphingosine-1-phosphate. Nature 1996, 381, 800–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, A.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate as a second messenger in cell proliferation induced by PDGF and FCS mitogens. Nature 1993, 365, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupperman, E.; An, S.; Osborne, N.; Waldron, S.; Stainier, D.Y. A sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor regulates cell migration during vertebrate heart development. Nature 2000, 406, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, S.; Milstien, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate: an enigmatic signalling lipid. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2003, 4, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, M.S.; Claus, R.A.; Schilder, M.; Pöhlmann, S.; Coldewey, S.M.; Grundmann, J.; Fricke, T.; Moerer, O.; Meissner, K.; Bauer, M.; Hofmann-Winkler, H.; Gräler, MH. Erythrocytes increase endogenous sphingosine 1-phosphate levels as an adaptive response to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Clin Sci (Lond) 2021, 135, 2781–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Zhang, Y.; D'Alessandro, A.; Nemkov, T.; Song, A.; Wu, H.; Liu, H.; Adebiyi, M.; Huang, A.; Wen, Y.E.; Bogdanov, M.V.; Vila, A.; O'Brien, J.; Kellems, R.E.; Dowhan, W.; Subudhi, A.W.; Jameson-Van Houten, S.; Julian, C.G.; Lovering, A.T.; Safo, M.; Hansen, K.C.; Roach, R.C.; Xia, Y. Sphingosine-1-phosphate promotes erythrocyte glycolysis and oxygen release for adaptation to high-altitude hypoxia. Nat Commun 2016, 7, 12086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiti, F. Sphingosine Increases ATP Release from Red Blood Cells. The Open Biochem J 2022, 16, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellsworth, M.L.; Ellis, C.G.; Sprague, R.S. Role of erythrocyte-released ATP in the regulation of microvascular oxygen supply in skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2016, 216, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Stephenson, A.H.; Lonigro, A.J.; Sprague, R.S. Erythrocytes of humans with cystic fibrosis fail to stimulate nitric oxide synthesis in isolated rabbit lungs. Am J Physiol 2004, 288, H1580–H1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Locovei, S.; Dahl, G. Pannexin membrane channels are mechanosensitive conduits for ATP. FEBS Lett 2004, 572, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkoe, D. A central role for amyloid. Journal of neuropathology and experimental neurology. J. Alzheimer’s Disease 1994, 53, 438–447. [Google Scholar]
- Pike C., J.; Walencewicz-Wasserman A., J.; Kosmosi, J.; Cribbs, D.H.; Glabe C., G.; Cotman, C.W. Structure–activity analyses of beta-amyloid peptides: Contributions of the b35-35 region to aggregation and neurotoxicity. Journal of Neurochemistry 1995, 64, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillot, T.; Drouet, B.; Queille, S.; Labeur, C.; Vandekerchkhove, J.; Rosseneu, M.; et al. The nonfibrillar amyloid betapeptide induces apoptotic neuronal cell death: Involvement of its C-terminal fusogenic domain. Journal of Neurochemistry 1999, 73, 1626–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim H., J.; Chae S., C.; Lee, D. K:; Chromy B.; Lee S. C.; Park Y. C. et al. Selective neuronal degeneration induced by soluble oligomeric amyloid beta protein. The FASEB Journal 2003, 17, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiko, T.; Nakagava, K.; Satoh, A.; Tsuduki, T.; Furukawa, K.; Arai, H.; Miyazawa, T. Amyloid b levels in human red blood cells. PLoS One 2012, e49620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammas, P.; Yamada, M.; Zlokovic, B. The cerebromicrovasculature: a key player in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. J. Alzheimers Dis 2002, 4, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.M.; Kokjohn, T.A.; Beach, T.G.; Sue, L.I.; Brune, D.; Lopez, J.C. Comparative analysis of amyloid-beta chemical structure and amyloid plaque morphology of transgenic mouse and Alzheimer's disease brains. J. Biol. Chem 2001, 276, 12991–12998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carelli-Alinovi, C.; Dinarelli, S.; Sampaolese, B.; Misiti, F.; Girasole, M. Morphological changes induced in erythrocyte by amyloid beta peptide and glucose depletion: A combined atomic force microscopy and biochemical study. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 2019, 1861, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carelli-Alinovi, C.; Pirolli, D.; Giardina, B.; Misiti, F. Protein kinase C mediates caspase 3 activation: a role for erythrocyte morphology changes. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc 2015, 59, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiti, F.; Carelli-Alinovi, C.; Sampaolese, B.; Giardina, B. b-amyloid decreases detectable endothelial nitric oxide synthase in human erythrocytes: a role for membrane acetylcholinesterase. Cell Biochem. Funct 2012, 30, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiti, F.; Orsini, F.; Clementi, M.E.; Masala, D.; Tellone, E.; Galtieri, A.; Giardina, B. Amyloid peptide inhibits ATP release from human erythrocytes. Biochem. Cell Biol 2008, 86, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosenko, E.A.; Solomadin, I.N.; Tikhonova, L.A.; Ready, V.P.; Aliev, G.; Kaminsky, Y.G. Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease: role of oxidative stress,amyloid-b peptides, systemic ammonia, and RBC energy metabolism. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2014, 13, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, R. : Kusiak J.W.; Chrest F.J.;Femehin A.A.; Murali J. West R.P. Red cell perturbations by amyloid beta-protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1622, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clementi, M.E.; Giardina, B.; Colucci, D.; Galtieri, A.; Misiti, F. Amyloid-beta peptide affects the oxygen dependence of RBC metabolism: a role for caspase 3. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol 2007, 39, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, D.; Baudin-Creuza, V.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Pathak, S.; Delaunay, J.; Kundu, M.; Basu, J. Caspase 3-mediated proteolysis of the N-terminal cytoplasmic domain of the human erythroid anion exchanger 1 (band 3). J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 52551–52558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carelli-Alinovi, C.; Giardina, B.; Misiti, F. Amyloid beta peptide (1-42)-mediated antioxidant imbalance is associated with activation of protein kinase C in red blood cells. Cell Biochem. Funct 2015, 33, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesman, RF.; Albert, MS.; Alonso, A.; Coker, LH.; Coresh, J.; Davis, SM.; Deal, JA.; McKhann, GM.; Mosley, TH.; Sharrett, AR.; Schneider, ALC.; Windham, BG.; Wruck, LM.; Knopman, DS. Associations between midlife vascular risk factors and 25-year incident dementia in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) cohort. JAMA Neurol 2017, 74, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iadecola, C.; Gottesman, RF. Cerebrovascular Alterations in Alzheimer Disease. Circ Res 2018, 123, 406–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Huang Y Li, B.; Gong, C.X.; Schuchman, E.H. Deregulation of sphingolipid metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 2010, 2, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oizumi, H.; Sugimura, Y.; Totsune, T.; Kawasaki, I.; Ohshiro, S.; Baba, T.; Kimpara, T.; Sakuma, H.; Hasegawa, T.; Kawahata, I.; Fukunaga, K.; Takeda, A. Plasma sphingolipid abnormalities in neurodegenerative diseases. PLoS One 2022, 16, e0279315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edsall, L.C.; Cuvillier, O.; Twitty, S.; Spiegel, S.; Milstien, S. Sphingosine kinase expression regulates apoptosis and caspase activation in PC12 cells. J Neurochem 2001, 2, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Brouchet, A.; Pchejetski, D.; Let, B. Critical role for sphingosine kinase-1 in regulating survival of neuroblastoma cells exposed to amyloid-beta peptide. Mol Pharmacol 2007, 2, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigi, A.; Cascella, R.; Fani, G.; Bernacchioni, C.; Cencetti, F.; Bruni, P.; Chiti, F.; Donati, C.; Cecchi, C. Sphingosine 1-phosphate attenuates neuronal dysfunction induced by amyloid-β oligomers through endocytic internalisation of NMDA receptors. FEBS J 2023, 290, 112–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, S.; Mauri, L.; Prioni, S.; Cabitta, L.; Sonnino, S.; Prinetti, A.; Giussani, P. Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptors and Metabolic Enzymes as Druggable Targets for Brain Diseases. Front Pharmacol 2019, 23, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asle-Rousta, M.; Oryan, S.; Ahmadiani, A.; Rahnema, M. Activation of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor-1 by SEW2871 improves cognitive function in Alzheimer's disease model rats. Excli J 2013, 3, 449–461. [Google Scholar]
- Zijlstra, W.G.; Buursma, A.; Meeuwsen-van der Roest, W.P. Absorption spectra of human fetal and adult oxyhemoglobin, de-oxyhemoglobin, carboxyhemoglobin, and methemoglobin. Clin Chem 1991, 37, 37,1633–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, B.; D'Alessandro, A.; Ramundo, N.; Zolla, L. Red blood cell storage and cell morphology. Transfus Med 2012, 22, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergfeld, G. R, Forrester T. Release of ATP from human erythrocytes in response to a brief period of hypoxia and hypercapnia. Cardiovasc. Res 1992, 26, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprague, R.S.; Stephenson, A.H.; Bowles, E.A.; Stumpf, M.S.; Lonigro, A.J. Reduced expression of G(i) in erythrocytes of humans with type 2 diabetes is associated with impairment of both cAMP generation and ATP release. Diabetes 2006, 55, 3588–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficarra, S.; Misiti, F.; Russo, A.; Carelli-Alinovi, C.; Bellocco, E.; Barreca, D.; Laganà, G.; Leuzzi, U.; Toscano, G.; Giardina, B.; Galtieri, A.; Tellone, E. Antiepileptic carbamazepine drug treatment induces alteration of membrane in red blood cells: possible positive effects on metabolism and oxidative stress. Biochimie 2013, 95, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, F.; Dargahi, L.; Nasoohi, S.; Omidbakhsh, R.; Mohamed, Z.; Chik, Z. Neurorestorative effect of FTY720 in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease: comparison with memantine. Behav Brain Res 2013, 252, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




