Submitted:
18 March 2024
Posted:
19 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
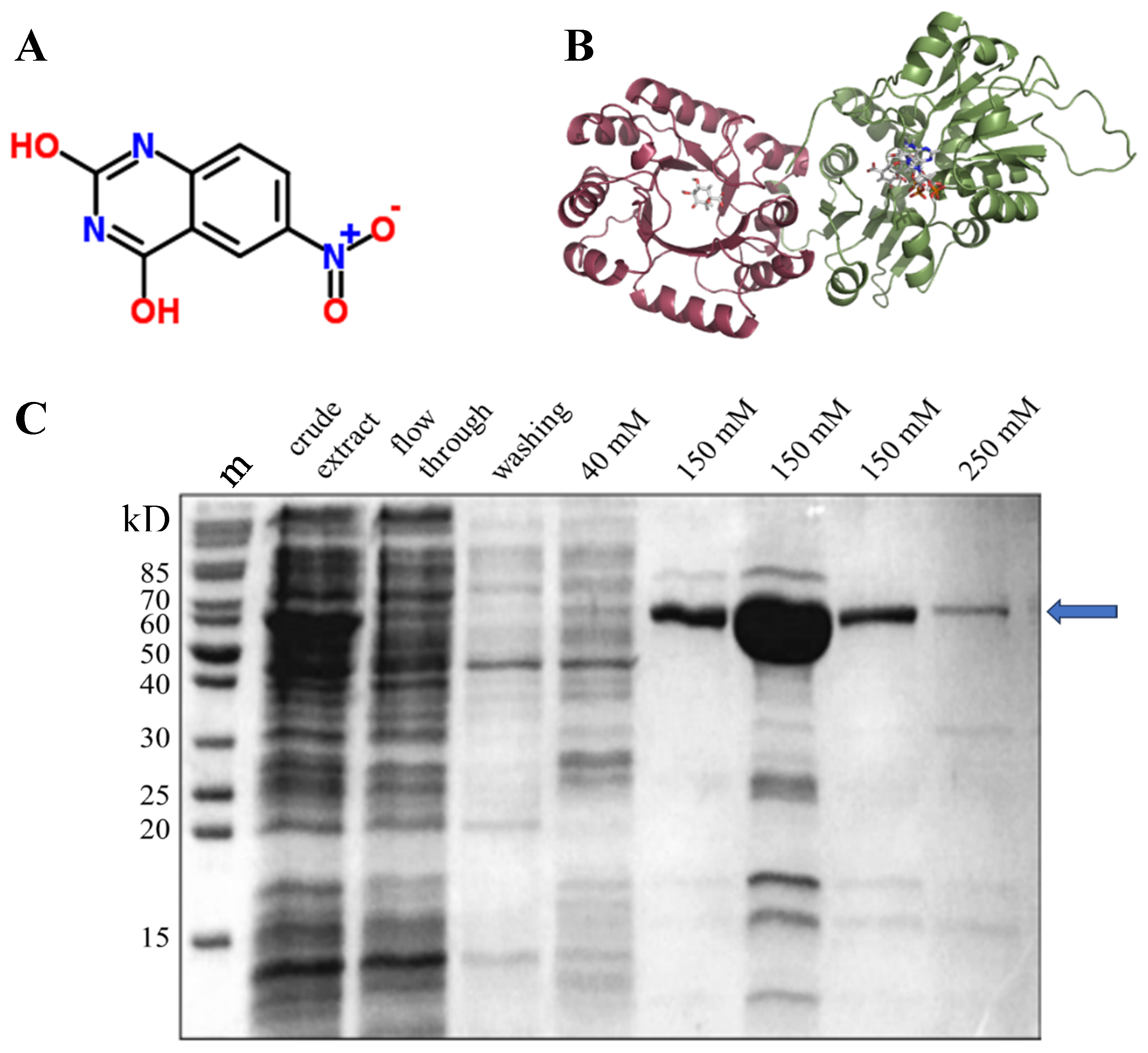
2.1. Three-dimensional structure of AtDHQD/SDH
2.2. Docking simulations and virtual scanning
2.3. Expression and purification of the DHQD/SDH protein
2.4. In vitro SDH activity
2.5. Germination and seedling growth
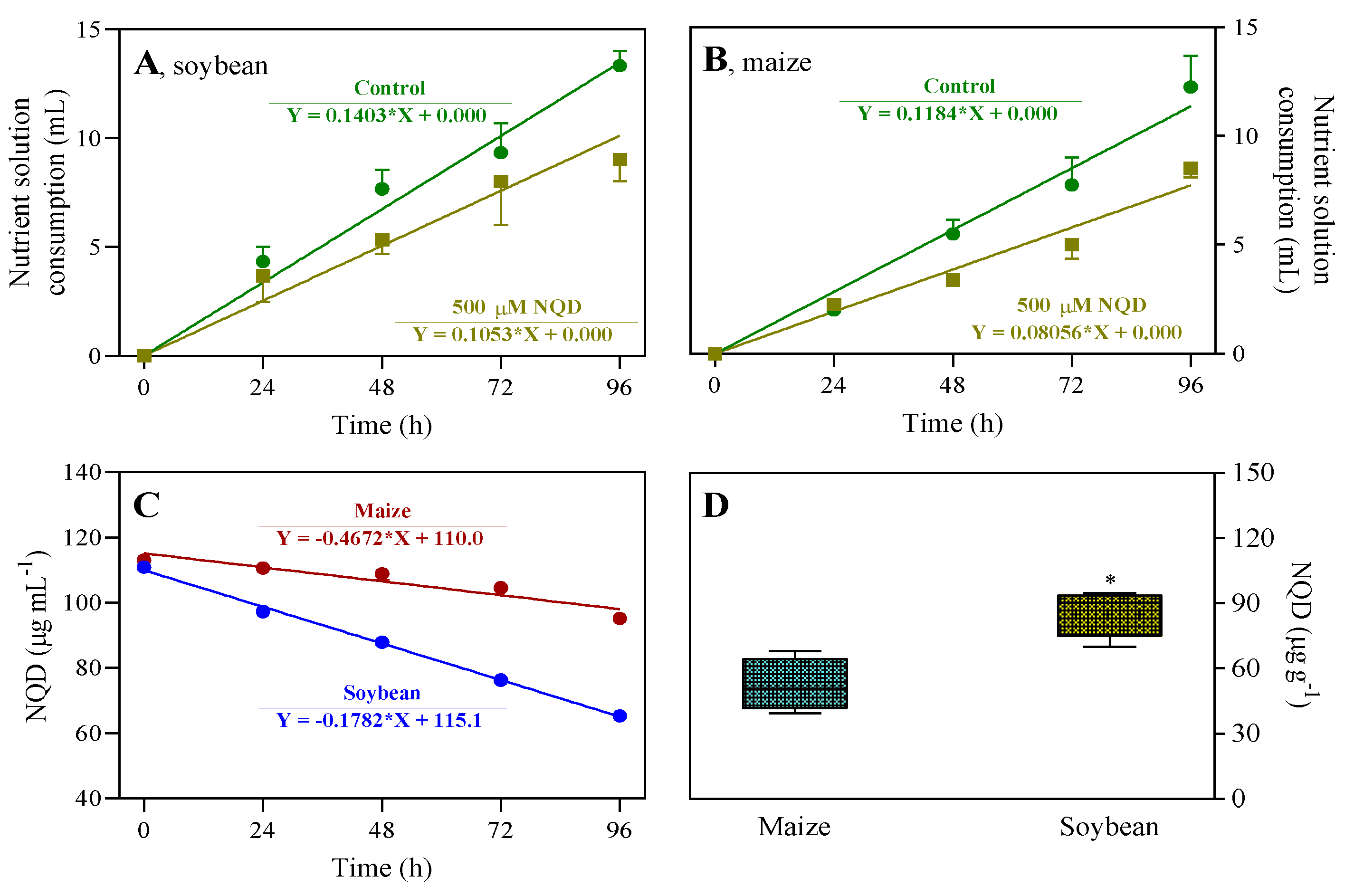
2.6. Nutrient solution consumption and NQD absorption by the seedlings
2.7. Quantification of total proteins, amino acids, phenolic acids, and lignin
2.8. Glyphosate effects on shikimate levels
2.9. Statistical analysis
3. Results
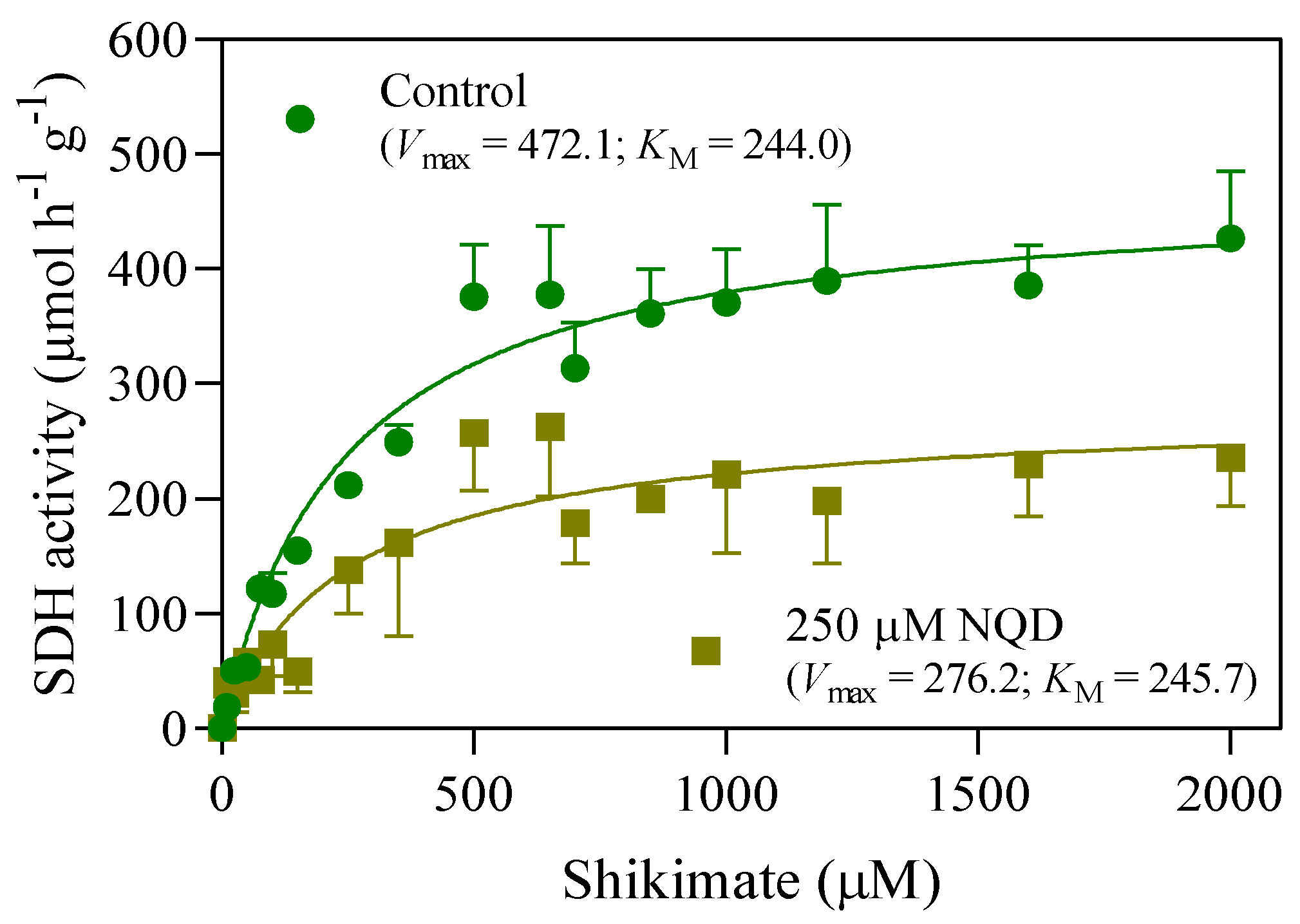
3.1. In silico and in vitro analyses reveal NQD as a potential inhibitor of SDH
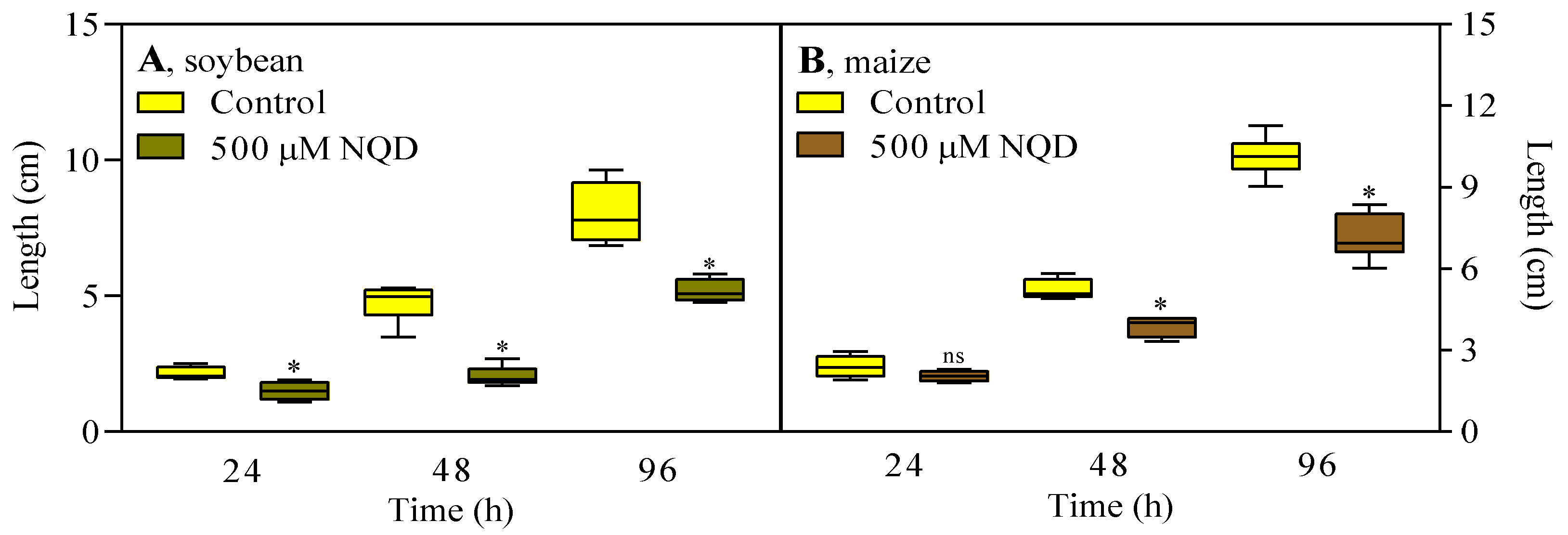
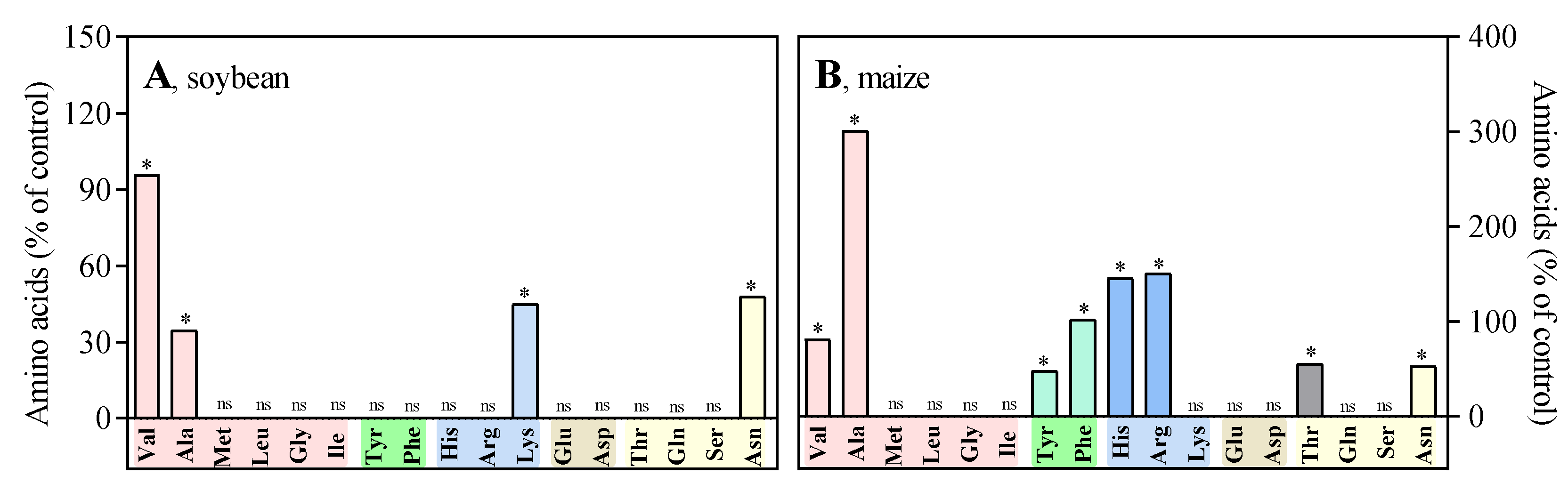
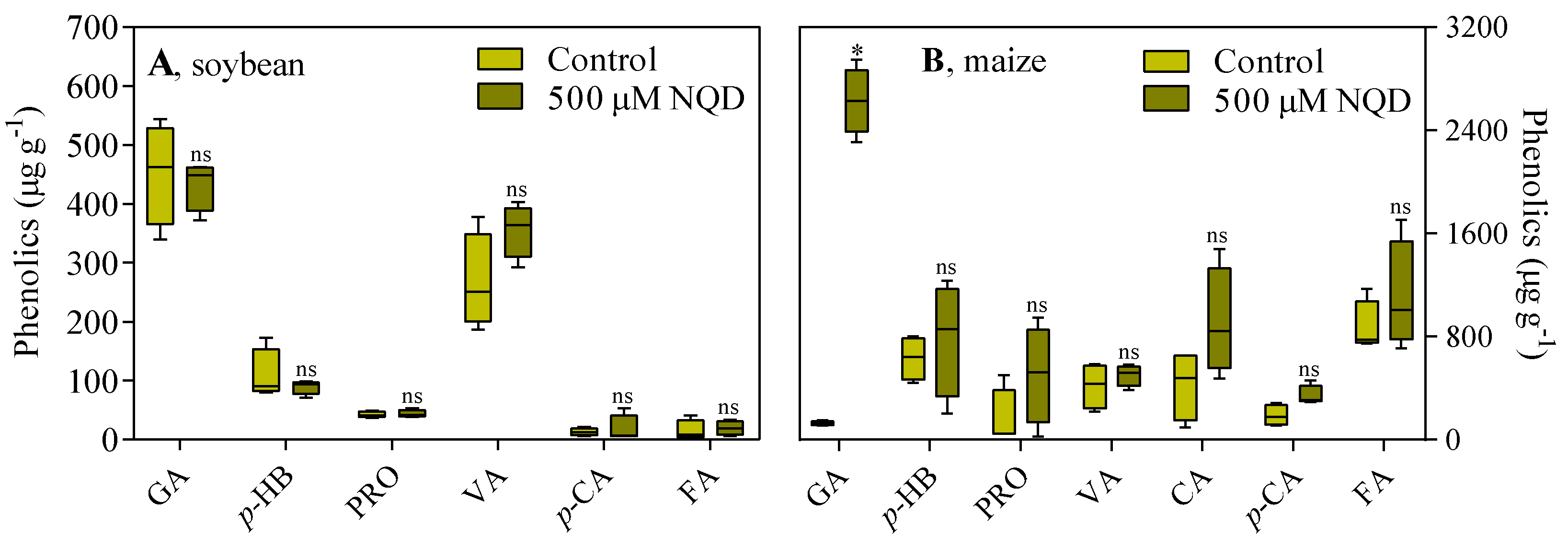
3.2. In vivo, NQD has an impact on the root growth of soybean and maize
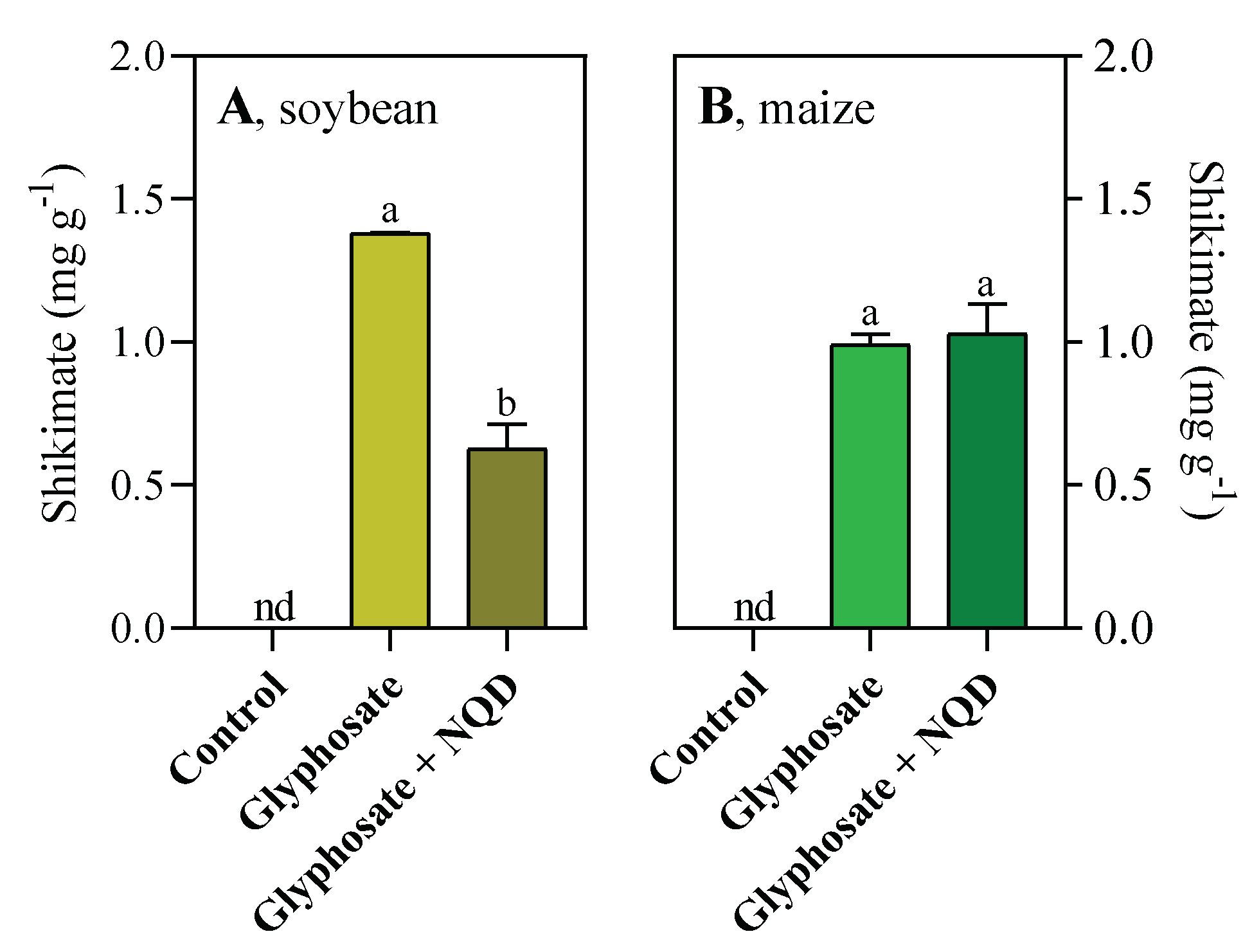
3.3. Glyphosate assays confirm that NQD inhibits SDH
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Tohge, T.; Watanabe, M.; Hoefgen, R.; Fernie, A.R. Shikimate and Phenylalanine Biosynthesis in the Green Lineage. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzin, V.; Galili, G. New Insights into the Shikimate and Aromatic Amino Acids Biosynthesis Pathways in Plants. Mol. Plant 2010, 3, 956–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Dudareva, N. The Shikimate Pathway and Aromatic Amino Acid Biosynthesis in Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2012, 63, 73–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coruzzi, G.; Last, R.; Dudareva, N.; Amrhein, N. Amino Acids. In Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Plants; Bob B. Buchanan, Wilhelm Gruissem, R.L.J., Ed.; Chichester, UK, 2015; pp. 289–336 ISBN 9780470714225.
- Francenia Santos-Sánchez, N.; Salas-Coronado, R.; Hernández-Carlos, B.; Villanueva-Cañongo, C. Shikimic Acid Pathway in Biosynthesis of Phenolic Compounds. In Plant Physiological Aspects of Phenolic Compounds; IntechOpen, 2019; Vol. 32, pp. 137–144.
- Marchiosi, R.; dos Santos, W.D.; Constantin, R.P.; de Lima, R.B.; Soares, A.R.; Finger-Teixeira, A.; Mota, T.R.; de Oliveira, D.M.; Foletto-Felipe, M. de P.; Abrahão, J.; et al. Biosynthesis and Metabolic Actions of Simple Phenolic Acids in Plants. Phytochem Rev. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Mousdale, D.M.; Coggins, J.R. Subcellular Localization of the Common Shikimate-Pathway Enzymes in Pisum Sativum L. Planta 1985, 163, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, F.; Roberts, C.W.; Johnson, J.J.; Kyle, D.E.; Krell, T.; Coggins, J.R.; Coombs, G.H.; Milhous, W.K.; Tzipor, S.; Ferguson, D.J.P.; et al. Evidence for the Shikimate Pathway in Apicomplexan Parasites. Nature 1998, 393, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gientka, I.; Duszkiewicz-Reinhard, W. Shikimate Pathway in Yeast Cells: Enzymes, Functioning, Regulation – A Review. Polish J. food Nutr. Sci. 2009, 59, 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Heap, I. International Herbicide-Resistant Weed Database Available online:. Available online: https://www.weedscience.org/Home.aspx (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Ramella, J.R.P.; Barbosa, J. de A.; Ferreira, S.D.; Fey, E.; da Costa, N.V. Weed Interference on Nutrient Accumulation in the Leaves of Cassava under No-Tillage or Conventional Tillage. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2020, 55, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönbrunn, E.; Eschenburg, S.; Shuttleworth, W.A.; Schloss, J. V; Amrhein, N.; Evans, J.N.; Kabsch, W. Interaction of the Herbicide Glyphosate with Its Target Enzyme 5-Enolpyruvylshikimate 3-Phosphate Synthase in Atomic Detail. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2001, 98, 1376–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.A.; Christendat, D. Structure of Arabidopsis Dehydroquinate Behydratase-Shikimate Dehydrogeoase and Implications for Metabolic Channeling in the Shikimate Pathway. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 7787–7796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Meng, J.; Liu, Y.; Guan, Y.; Xiao, C. IMB-SD62, a Triazolothiadiazoles Derivative with Promising Action against Tuberculosis. Tuberculosis 2018, 112, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avitia-Domínguez, C.; Sierra-Campos, E.; Salas-Pacheco, J.; Nájera, H.; Rojo-Domínguez, A.; Cisneros-Martínez, J.; Téllez-Valencia, A. Inhibition and Biochemical Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Shikimate Dehydrogenase: An in Silico and Kinetic Study. Molecules 2014, 19, 4491–4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enríquez-Mendiola, D.; Téllez-Valencia, A.; Sierra-Campos, E.; Campos-Almazán, M.; Valdez-Solana, M.; Palacio-Gastélum, M.G.; Avitia-Domínguez, C. Kinetic and Molecular Dynamic Studies of Inhibitors of Shikimate. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2019, 94, 1504–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peek, J.; Castiglione, G.; Shi, T.; Christendat, D. Isolation and Molecular Characterization of the Shikimate Dehydrogenase Domain from the Toxoplasma gondii AROM Complex. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2014, 194, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baillie, A.C.; Corbett, J.R.; Dowsett, J.R.; McCloskey, P. Inhibitors of Shikimate Dehydrogenase as Potential Herbicides. Pestic. Sci. 1972, 3, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peek, J.; Shi, T.; Christendat, D. Identification of Novel Polyphenolic Inhibitors of Shikimate Dehydrogenase (AroE). J. Biomol. Screen. 2014, 19, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Yu, H.; Wang, M.; Cui, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Dong, J. Natural Product Drupacine Acting on a Novel Herbicidal Target Shikimate Dehydrogenase. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 194, 105480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H. long; Tian, C.; Shen, R. yan; Zhao, H.; Yang, J.; Dong, J. gao; Zhang, L. hui; Ma, S. jie Herbicidal Activity and Biochemical Characteristics of the Botanical Drupacine against Amaranthus retroflexus L. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 1434–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, M.C.; Constantin, R.P.; Abrahão, J.; de Paiva Foletto-Felipe, M.; Grizza, L.H.E.; Constantin, R.P.; dos Santos, W.D.; Ferrarese-Filho, O.; Marchiosi, R. Inhibitory Effect of 3-Cyanobenzoic Acid on Initial Growth of Maize Seedlings and Its Biochemical Impacts on Antioxidant and Energy Metabolisms. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Bortolo, T.S.C.; Marchiosi, R.; Viganó, J.; Siqueira-soares, R.D.C.; Ferro, A.P.; Barreto, G.E.; Bido, G.D.S.; Abrahão, J.; Dantas, W.; Ferrarese-filho, O. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry Trans-Aconitic Acid Inhibits the Growth and Photosynthesis of Glycine max. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 132, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchiosi, R.; Lucio Ferrarese, M. de L.; Bonini, E.A.; Fernandes, N.G.; Ferro, A.P.; Ferrarese-Filho, O. Glyphosate-Induced Metabolic Changes in Susceptible and Glyphosate-Resistant Soybean (Glycine max L.) Roots. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2009, 93, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchiosi, R.; Graciene de Souza Bido, B.; Paulo Alfredo Feitoza Böhm, B.; Ricardo Soares, A.; Hingrid Ariane da Silva, B.; Ana Paula Ferro, B.; de Lourdes Lucio Ferrarese, M.; Osvaldo Ferrarese-Filho, B. Photosynthetic Response of Soybean to L-DOPA and Aqueous Extracts of Velvet Bean. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.A.; Christendat, D. The DHQ-Dehydroshikimate-SDH-Shikimate-NADP(H) Complex: Insights into Metabolite Transfer in the Shikimate Pathway. Cryst. Growth Des. 2007, 7, 2153–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Comparative Protein Structure Modeling Using MODELLER. Curr. Protoc. Bioinforma. 2016, 2016, 5.6.1–5.6.37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborative Computational Project, N. 4 The CCP4 Suite: Programs for Protein Crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1994, 50, 760–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.C.; Braun, R.; Wang, W.; Gumbart, J.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Villa, E.; Chipot, C.; Skeel, R.D.; Kalé, L.; Schulten, K. Scalable Molecular Dynamics with NAMD. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1781–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackerell, A.D.; Feig, M.; Brooks, C.L. Extending the Treatment of Backbone Energetics in Protein Force Fields: Limitations of Gas-Phase Quantum Mechanics in Reproducing Protein Conformational Distributions in Molecular Dynamics Simulation. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1400–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoete, V.; Cuendet, M.A.; Grosdidier, A.; Michielin, O. SwissParam: A Fast Force Field Generation Tool for Small Organic Molecules. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 2359–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M. , M.G.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodseel, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated Docking with Selective Receptor Flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 32, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, R.; Christensen, M.H. MolDock: A New Technique for High-Accuracy Molecular Docking. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3315–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauren, K. Wolf New Software and Websites for the Chemical Enterprise. Chem. Eng. News 2009, 87, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villén, J.; Gygi, S.P. The SCX/IMAC Enrichment Approach for Global Phosphorylation Analysis by Mass Spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1630–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foletto-Felipe, M. de P. O-Acetilserina(Tiol) Liase: Estudos in Silico, in Vitro e in Vivo, Universidade Estadual de Maringá, 2021.
- Dong, J.; Wu, F.; Zhang, G. Influence of Cadmium on Antioxidant Capacity and Four Microelement Concentrations in Tomato Seedlings (Lycopersicon esculentum). Chemosphere 2006, 64, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, R.A.; Alas, R.M.; Smith, R.J.; Lea, P.J. Response of Antioxidant Enzymes to Transfer from Elevated Carbon Dioxide to Air and Ozone Fumigation, in the Leaves and Roots of Wild-Type and a Catalase-Deficient Mutant of Barley. Physiol. Plant. 1998, 104, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astarita, L. V.; Floh, E.I.S.; Handro, W. Free Amino Acid, Protein and Water Content Changes Associated with Seed Development in Araucaria angustifolia. Biol. Plant. 2003, 47, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieruzzi, F.P. Quantificação de Aminoácidos, Poliaminas, AIA e ABA e Marcadores Protéicos Na Germinação de Sementes de Ocotea odorifera Vell. (Lauraceae), Universidade de São Paulo, 2009.
- Benson, J.R.; Hare, P.E. O Phthalaldehyde: Fluorogenic Detection of Primary Amines in the Picomole Range. Comparison with Fluorescamine and Ninhydrin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1975, 72, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira-Vilar, F.C.; Siqueira-Soares, R.D.C.; Finger-Teixeira, A.; De Oliveira, D.M.; Ferro, A.P.; Da Rocha, G.J.; Ferrarese, M.D.L.L.; Dos Santos, W.D.; Ferrarese-Filho, O. The Acetyl Bromide Method Is Faster, Simpler and Presents Best Recovery of Lignin in Different Herbaceous Tissues than Klason and Thioglycolic Acid Methods. PLoS One 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonini, E.A.; Ferrarese, M.L.L.; Marchiosi, R.; Zonetti, P.C.; Ferrarese-Filho, O. A Simple Chromatographic Assay to Discriminate between Glyphosate-Resistant and Susceptible Soybean (Glycine max) Cultivars. Eur. J. Agron. 2009, 31, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Hofius, D.; Hajirezaei, M.R.; Fernie, A.R.; Börnke, F.; Sonnewald, U. Functional Analysis of the Essential Bifunctional Tobacco Enzyme 3-Dehydroquinate Dehydratase/Shikimate Dehydrogenase in Transgenic Tobacco Plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 2053–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, R.A. Enzymes: A Practical Introduction to Structure, Mechanism, and Data Analysis; Third edit.; Wiley: New York, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Blat, Y. Non-competitive Inhibition by Active Site Binders. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2010, 75, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornish-Bowden, A. Fundamentals of Enzyme Kinetics; Fourth edi.; Wiley-Blackwell: Singapore, 2012; ISBN 978-3-527-33074-4. [Google Scholar]
- Noureldin, N.A.; Kothayer, H.; Lashine, E.S.M.; Baraka, M.M.; Huang, Y.; Li, B.; Ji, Q. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Quinazoline-2,4-Diones Conjugated with Different Amino Acids as Potential Chitin Synthase Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 152, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangjee, A.; Vidwans, A.P.; Vasudevan, A.; Queener, S.F.; Kisliuk, R.L.; Cody, V.; Li, R.; Galitsky, N.; Luft, J.R.; Pangborn, W. Structure-Based Design and Synthesis of Lipophilic 2,4-Diamino-6- Substituted Quinazolines and Their Evaluation as Inhibitors of Dihydrofolate Reductases and Potential Antitumor Agents. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 3426–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Hofius, D.; Hajirezaei, M.-R.; Fernie, A.R.; Börnke, F.; Sonnewald, U. Functional Analysis of the Essential Bifunctional Tobacco Enzyme 3-Dehydroquinate Dehydratase/Shikimate Dehydrogenase in Transgenic Tobacco Plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 2053–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amir, R. Current Understanding of the Factors Regulating Methionine Content in Vegetative Tissues of Higher Plants. Amino Acids 2010, 39, 917–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Jander, G. Abscisic Acid-Regulated Protein Degradation Causes Osmotic Stress-Induced Accumulation of Branched-Chain Amino Acids in Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 2017, 246, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista-Silva, W.; Heinemann, B.; Rugen, N.; Nunes-Nesi, A.; Araújo, W.L.; Braun, H.P.; Hildebrandt, T.M. The Role of Amino Acid Metabolism during Abiotic Stress Release. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 1630–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brilisauer, K.; Rapp, J.; Rath, P.; Schöllhorn, A.; Bleul, L.; Weiß, E.; Stahl, M.; Grond, S.; Forchhammer, K. Cyanobacterial Antimetabolite 7-Deoxy-Sedoheptulose Blocks the Shikimate Pathway to Inhibit the Growth of Prototrophic Organisms. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, T.M. Synthesis versus Degradation: Directions of Amino Acid Metabolism during Arabidopsis Abiotic Stress Response. Plant Mol. Biol. 2018, 98, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista-Silva, W.; Heinemann, B.; Rugen, N.; Nunes-Nesi, A.; Araújo, W.L.; Braun, H.P.; Hildebrandt, T.M. The Role of Amino Acid Metabolism during Abiotic Stress Release. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 1630–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossipov, V.; Salminen, J.P.; Ossipova, S.; Haukioja, E.; Pihlaja, K. Gallic Acid and Hydrolysable Tannins Are Formed in Birch Leaves from an Intermediate Compound of the Shikimate Pathway. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2003, 31, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Carrington, Y.; Alber, A.; Ehlting, J. Molecular Characterization of Quinate and Shikimate Metabolism in Populus trichocarpa. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 23846–23858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bontpart, T.; Marlin, T.; Vialet, S.; Guiraud, J.L.; Pinasseau, L.; Meudec, E.; Sommerer, N.; Cheynier, V.; Terrier, N. Two Shikimate Dehydrogenases, VvSDH3 and VvSDH4, Are Involved in Gallic Acid Biosynthesis in Grapevine. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 3537–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, G.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Y.; Dai, X.; Xia, T.; et al. Functional Analysis of 3-Dehydroquinate Dehydratase/Shikimate Dehydrogenases Involved in Shikimate Pathway in Camellia sinensis. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, K.; Nishiguchi, M.; Funke, E.; Miyazawa, S.-I.; Miyama, T.; Milkowski, C. Dehydroquinate Dehydratase/Shikimate Dehydrogenases Involved in Gallate Biosynthesis of the Aluminum-Tolerant Tree Species Eucalyptus camaldulensis. Planta 2021, 253, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeeman, S.C. Carbohydrate Metabolism. In Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Plants; Buchanan, B.B., Gruissem, W., Jones, R.L., Eds.; Wiley Blackwell, 2015; pp. 567–609 ISBN 9780470714218.
- Steinrücken, H.C.; Amrhein, N. The Herbicide Glyphosate Is a Potent Inhibitor of 5-Enolpyruvyl-Shikimic Acid-3-Phosphate Synthase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1980, 4, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke, S.O.; Powles, S.B. Glyphosate: A Once-in-a-century Herbicide. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Luo, L.; Zheng, L. Lignins: Biosynthesis and Biological Functions in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Crystallographic binder | Zinc database binder | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autodock | Molegro | Autodock | Molegro | |||||
| mean score | rmsd (Å) |
mean score | rmsd (Å) |
mean score | mean score | |||
| DHQ | -7.98 ± 0.09 | 0.32 ± 0.02 | -81.38 ± 0.02 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | -7.88 ± 0.10 | -79.69 ± 0.24 | ||
| DHK | -8.25 ± 0.02 | 0.22 ± 0.03 | -67.35 ± 0.01 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | -7.26 ± 0.21 | -62.63 ± 0.00 | ||
| Name | Structure | xlogP | Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AutoDock | Molegro | |||
| DHK endo | 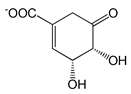 |
-1.97 | -7.43 | - |
| DHK exo | -6.56 | -79.83 | ||
| 6-Nitroquinazoline-2,4-diol (NQD) | 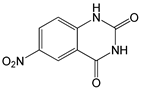 |
0.56 | -7.70 | -94.92 |
| 4-Bromo-3-cyanobenzoic acid | 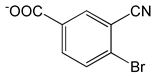 |
2.34 | -7.39 | -90.80 |
| 1,3-Dioxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-isoindole-5-carboxylic acid | 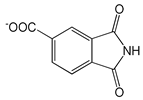 |
1.34 | -7.29 | -104.27 |
| 2-Mercapto-5-benzimidazolecarboxylic acid | 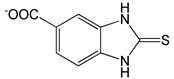 |
1.30 | -7.18 | -100.97 |
| Methyl 3-bromo-4-hydroxybenzoate | 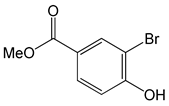 |
2.63 | -6.76 | -81.74 |
| 2-Chloro-4-nitro-n-methylaniline | 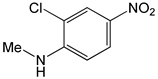 |
2.36 | -6.74 | -86.25 |
| 4-Chlorothieno[2,3-D]pyrimidine-6-carboxylic acid | 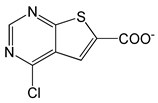 |
1.91 | -6.73 | -85.02 |
| 2-Amino-5-nitrobenzamide | 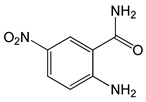 |
0.13 | -6.67 | -88.97 |
| NQD (µM) | Vmax (µmol h-1 g-1) | KM (µM) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 472.1 | 244.0 |
| 250 | 276.2 | 245.7 |
| Control | 500 µM NQD | Difference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soybean | 334 ± 16.52 | 465.6 ± 19.51* | 39% |
| Maize | 222.9 ± 7.91 | 303.0 ± 27.20* | 36% |
| NQD (µM) | Soybean | Maize |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 68.73 ± 2.436 | 144.3 ± 3.036 |
| 500 | 66.56 ± 1.401 | 149.9 ± 2.819 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





