Submitted:
15 March 2024
Posted:
18 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture
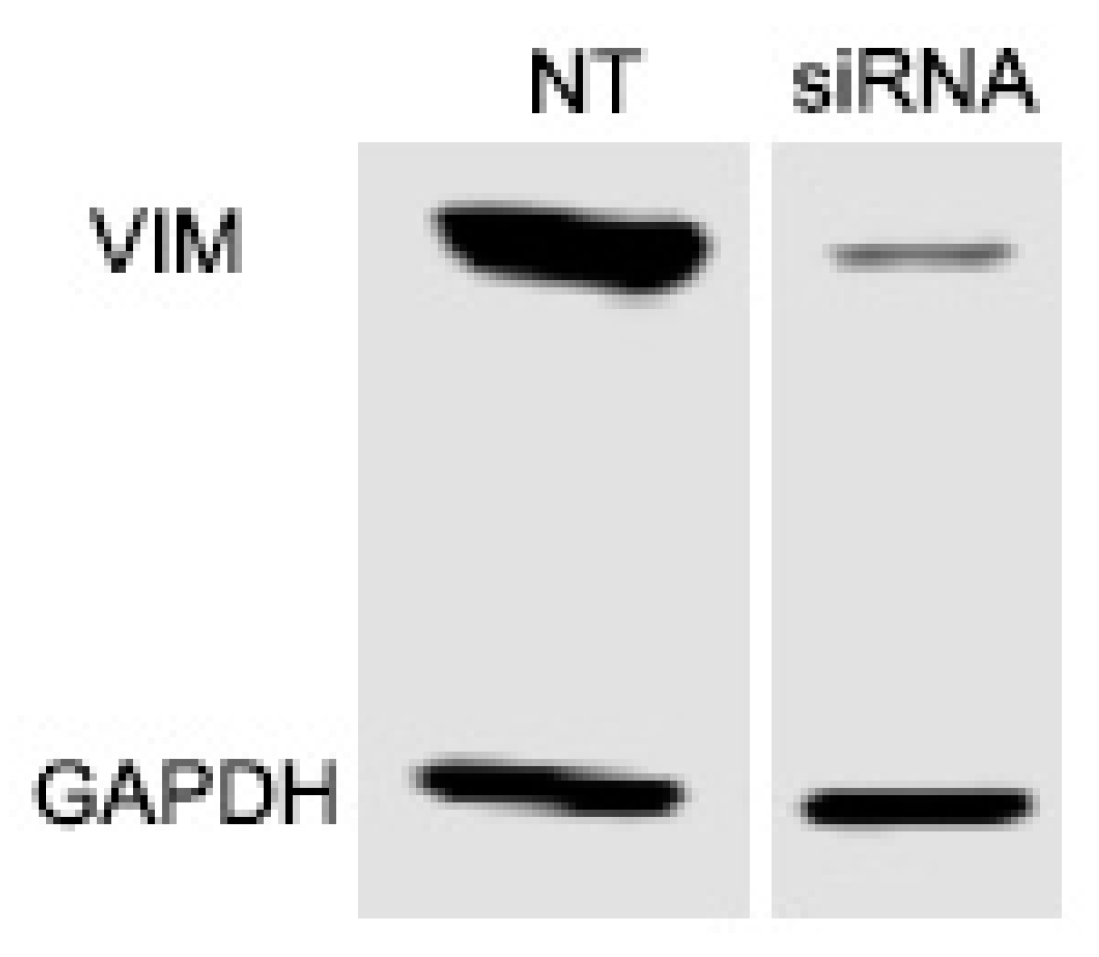
2.3. Vimentin Knockdown
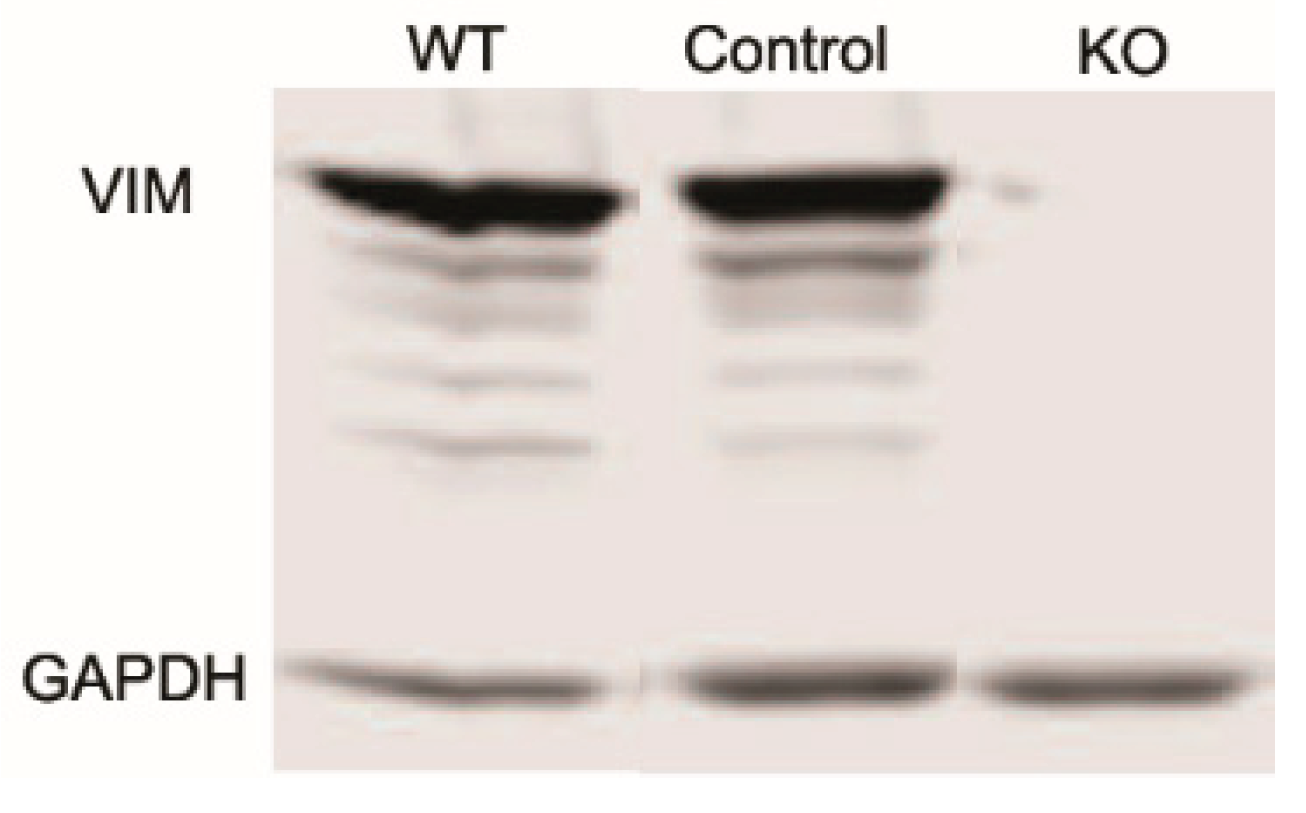
2.4. Vimentin Knockout
2.5. 3D Collagen Matrix Model
2.6. Collagen Matrix Contraction
2.7. Immunostaining
2.8. Immunoblotting
2.9. Image Processing and Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
2.11. Proteomics
3. Results
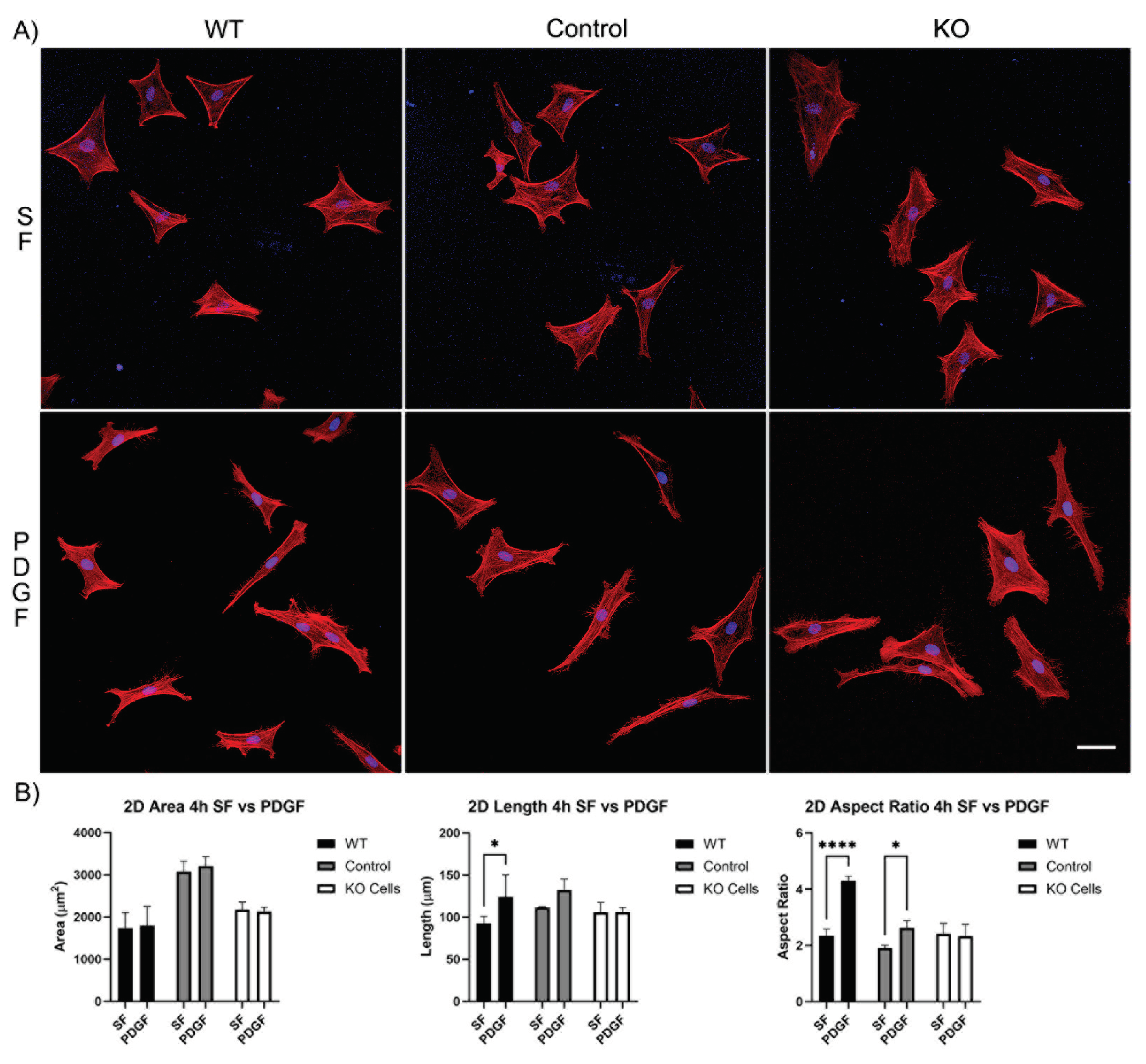
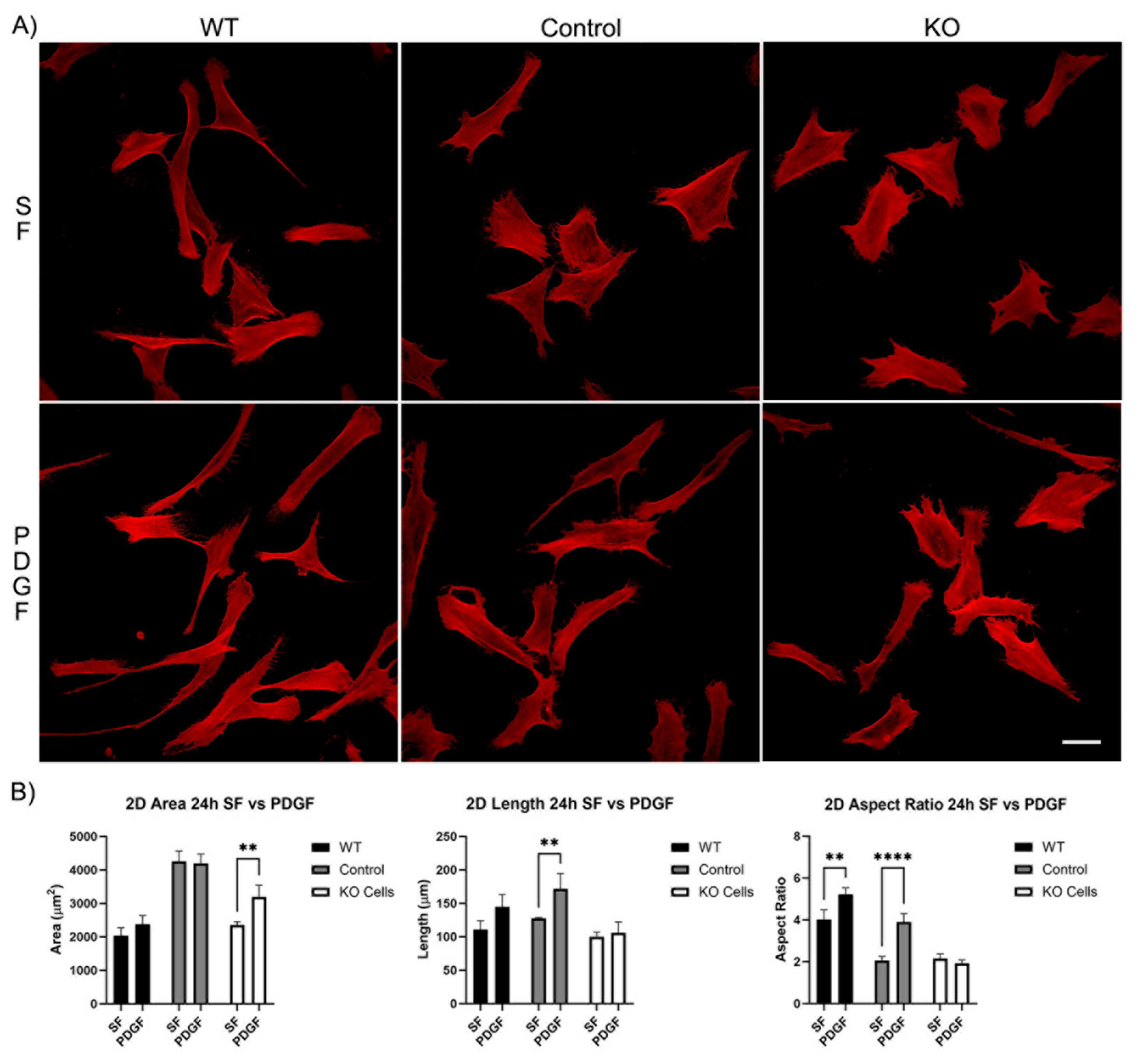
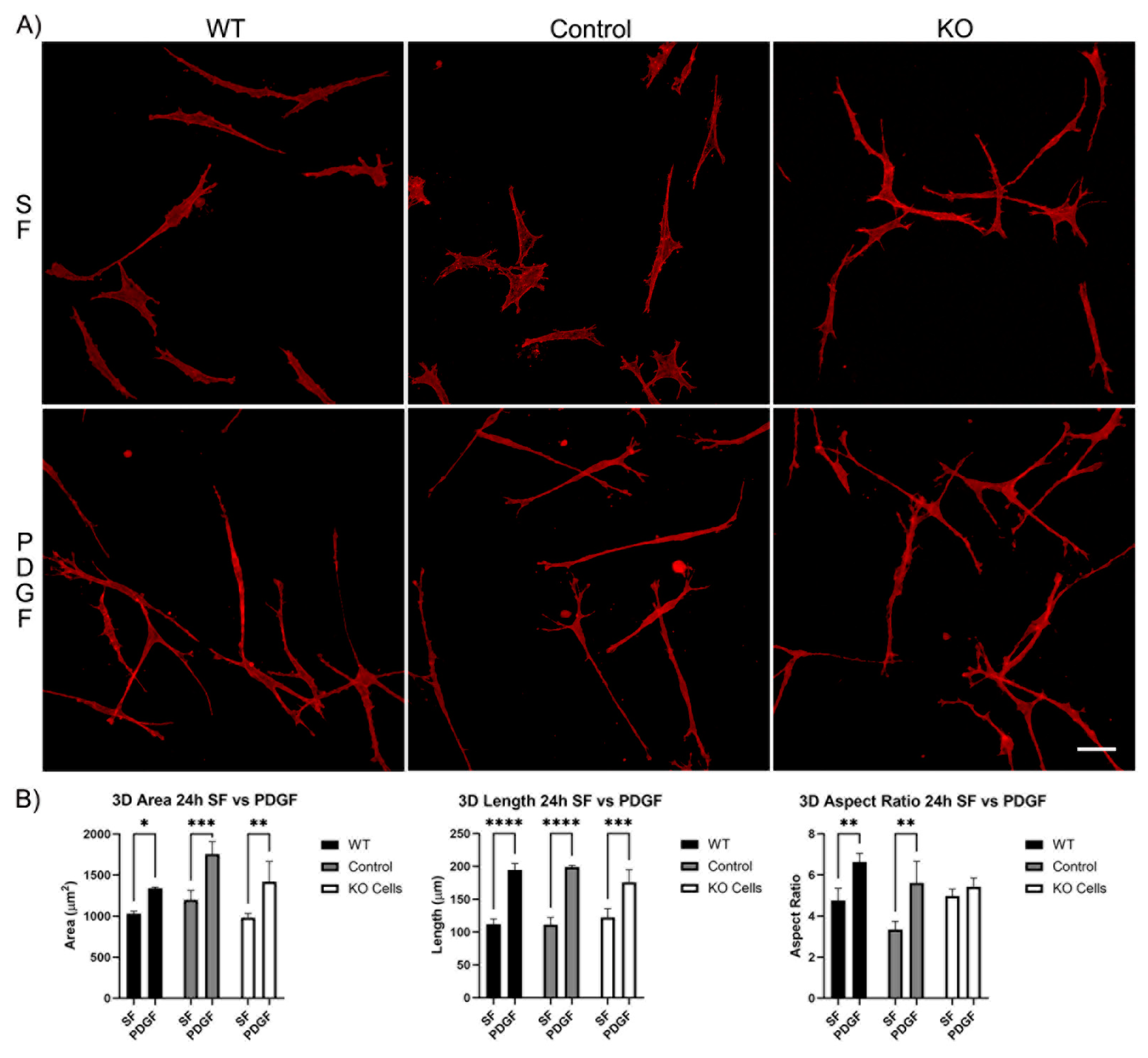
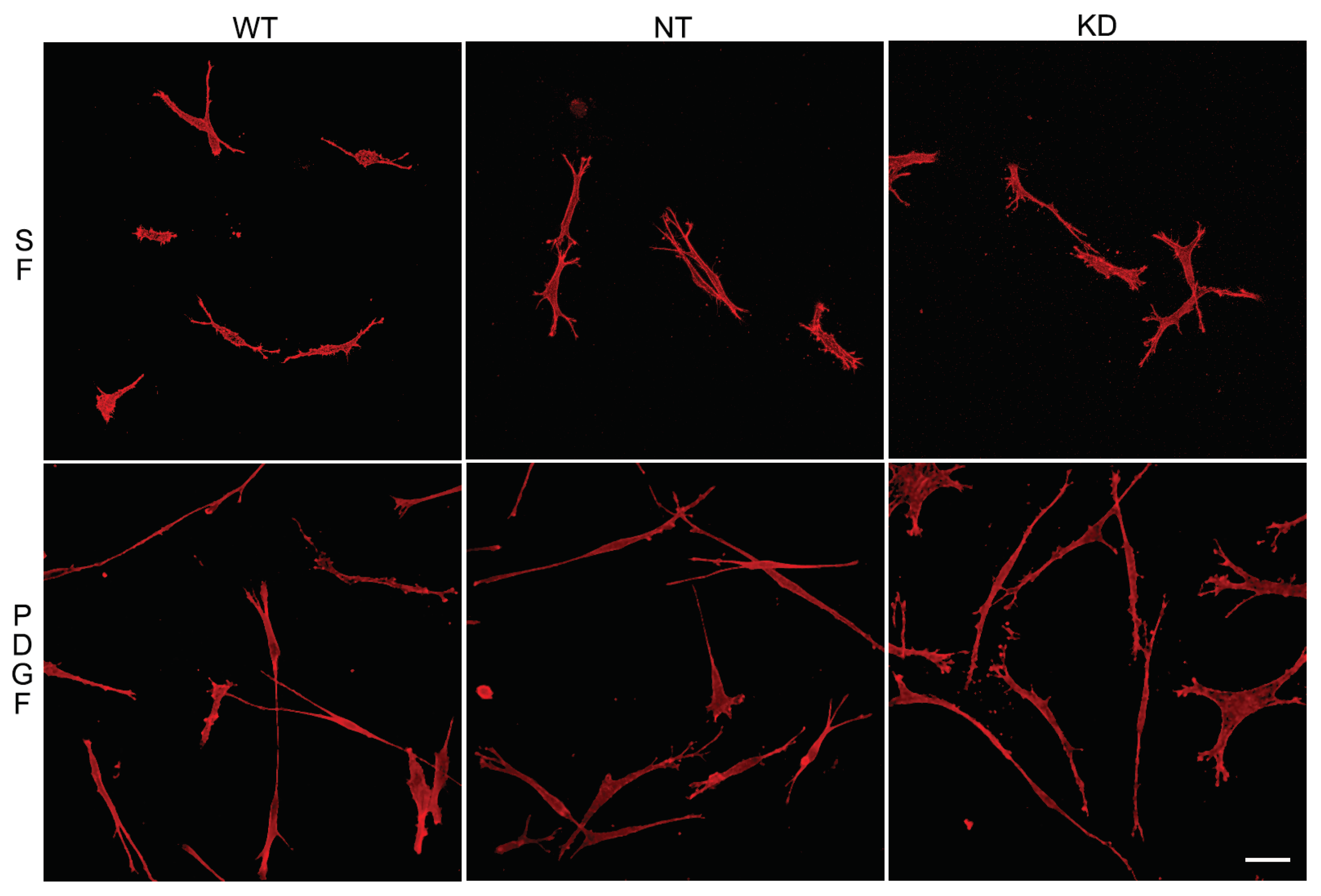
3.1. Knockout of Vimentin alters PDGF-Induced Elongation of Corneal Fibroblasts
3.1.1. Corneal Fibroblast Spreading on 2D Substrates
3.1.2. Corneal Fibroblast Spreading in 3D Collagen Matrices
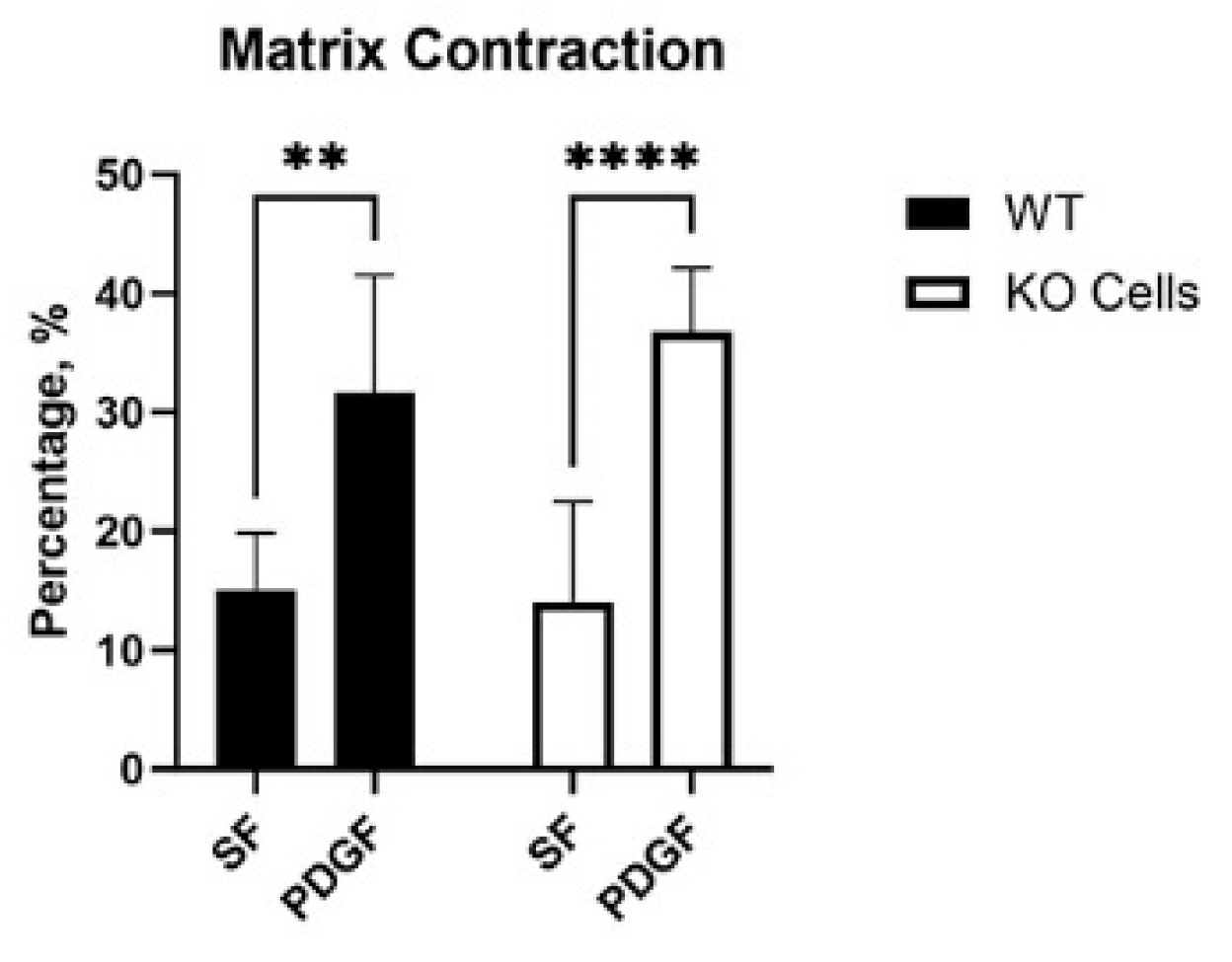
3.2. Vim KO and Wild-Type Cells Produce Similar Amounts of Matrix Reorganization
3.3. Knockdown of Vimentin Does not Alter Corneal Fibroblast Spreading
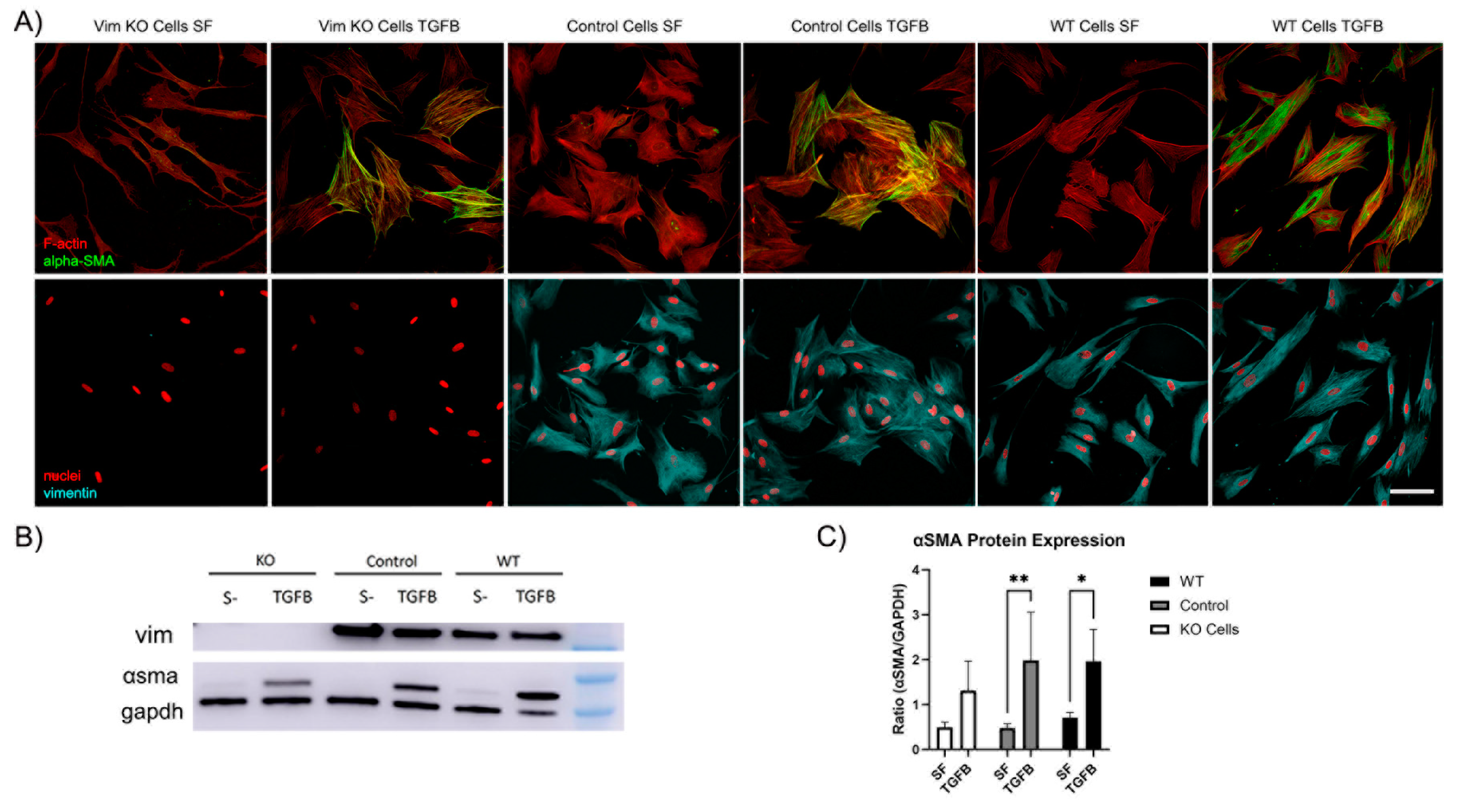
3.4. Vimentin Is not Requred for Myofibroblast Transformation of Corneal Keratocytes
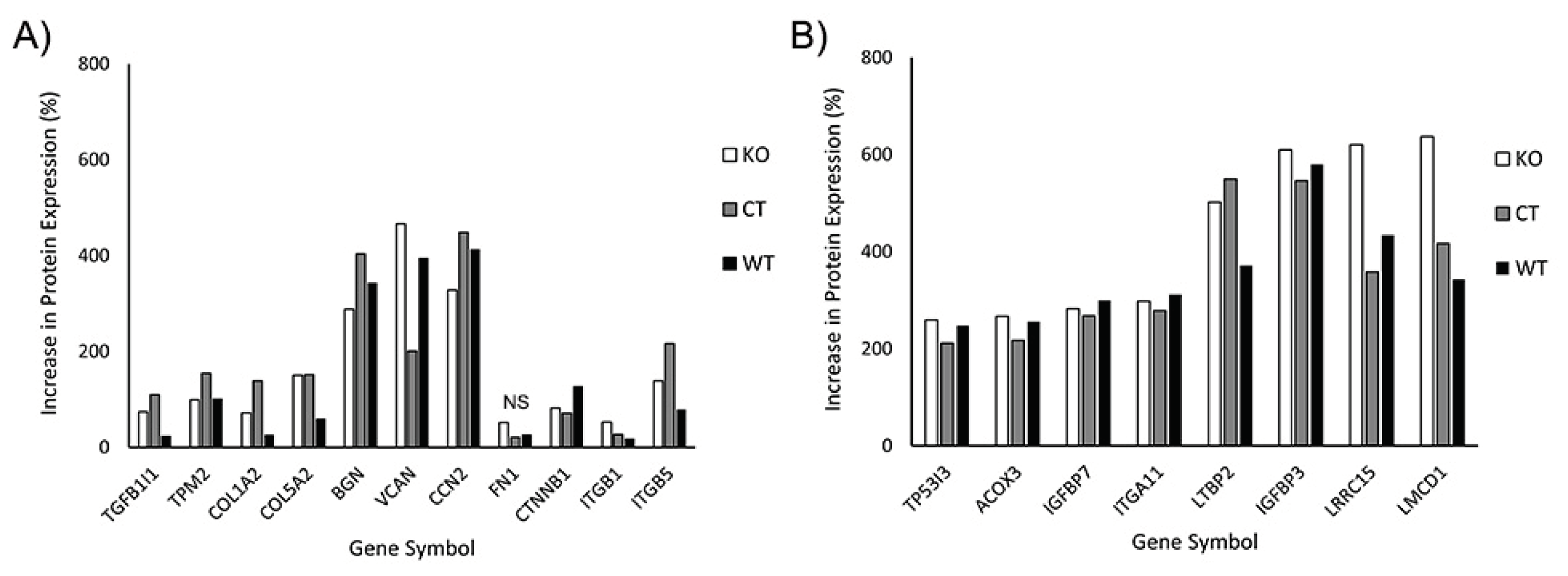
3.5. Proteomics Shows Similar Expression Profiles for KO and Wild Type Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hohmann, T.; Dehghani, F. The Cytoskeleton-A Complex Interacting Meshwork. Cells 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingber, D. E. Tensegrity and mechanotransduction. J Bodyw Mov Ther 2008, 12, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, J. E.; Haugh, J. M. Directed migration of mesenchymal cells: where signaling and the cytoskeleton meet. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2014, 30, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, J. R. Mitosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seetharaman, S.; Etienne-Manneville, S. Cytoskeletal Crosstalk in Cell Migration. Trends Cell Biol 2020, 30, 720–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Manzanares, M.; Horwitz, A. R. Adhesion dynamics at a glance. J Cell Sci 2011, 124 Pt 23, 3923–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, K. A.; Donato, D. M.; Balcioglu, H. E.; Schmidt, T.; Danen, E. H.; Koenderink, G. H. A guide to mechanobiology: Where biology and physics meet. Biochim Biophys Acta 2015, 1853, 3043–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etienne-Manneville, S. Cytoplasmic Intermediate Filaments in Cell Biology. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2018, 34, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridge, K. M.; Shumaker, D.; Robert, A.; Hookway, C.; Gelfand, V. I.; Janmey, P. A.; Lowery, J.; Guo, M.; Weitz, D. A.; Kuczmarski, E.; et al. Methods for Determining the Cellular Functions of Vimentin Intermediate Filaments. Methods Enzymol 2016, 568, 389–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plikus, M. V.; Wang, X.; Sinha, S.; Forte, E.; Thompson, S. M.; Herzog, E. L.; Driskell, R. R.; Rosenthal, N.; Biernaskie, J.; Horsley, V. Fibroblasts: Origins, definitions, and functions in health and disease. Cell 2021, 184, 3852–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J. J.; Feramisco, J. R. Disruption of the in vivo distribution of the intermediate filaments in fibroblasts through the microinjection of a specific monoclonal antibody. Cell 1981, 24, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, I.; Ostrowska-Podhorodecka, Z.; Lee, W.; Liu, R. S. C.; Carneiro, K.; Janmey, P. A.; McCulloch, C. A. Cooperative roles of PAK1 and filamin A in regulation of vimentin assembly and cell extension formation. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 2020, 1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoii, D. H.; Azizi, H.; Amirian, M. Signaling Pathways and Protein-Protein Interaction of Vimentin in Invasive and Migration Cells: A Review. Cell Reprogram 2022, 24, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowska-Podhorodecka, Z.; McCulloch, C. A. Vimentin regulates the assembly and function of matrix adhesions. Wound Repair Regen 2021, 29, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, M. G.; Restle, D.; Janmey, P. A. Vimentin enhances cell elastic behavior and protects against compressive stress. Biophys J 2014, 107, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivanany, P. B.; Grose, K. C.; Tippani, M.; Su, S.; Petroll, W. M. Assessment of Corneal Stromal Remodeling and Regeneration after Photorefractive Keratectomy. Sci Rep 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netto, M. V.; Mohan, R. R.; Sinha, S.; Sharma, A.; Dupps, W.; Wilson, S. E. Stromal haze, myofibroblasts, and surface irregularity after PRK. Exp Eye Res 2006, 82, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivanany, P. B.; Grose, K. C.; Petroll, W. M. Temporal and spatial analysis of stromal cell and extracellular matrix patterning following lamellar keratectomy. Exp Eye Res 2016, 153, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S. K.; Gupta, I.; Cho, Y. K.; Zhang, X.; Uehara, H.; Muddana, S. K.; Bernhisel, A. A.; Archer, B.; Ambati, B. K. Vimentin knockdown decreases corneal opacity. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2014, 55, 4030–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargagna-Mohan, P.; Lei, L.; Thompson, A.; Shaw, C.; Kasahara, K.; Inagaki, M.; Mohan, R. Vimentin Phosphorylation Underlies Myofibroblast Sensitivity to Withaferin A In Vitro and during Corneal Fibrosis. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0133399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jester, J. V.; Huang, J.; Fisher, S.; Spiekerman, J.; Chang, J. H.; Wright, W. E.; Shay, J. W. Myofibroblast differentiation of normal human keratocytes and hTERT, extended-life human corneal fibroblasts. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2003, 44, 1850–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron-Mendoza, M.; Lin, X.; Ma, L.; Ririe, P.; Petroll, W. M. Individual versus collective fibroblast spreading and migration: regulation by matrix composition in 3D culture. Exp Eye Res 2012, 99, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younesi, F. S.; Son, D. O.; Firmino, J.; Hinz, B. Myofibroblast Markers and Microscopy Detection Methods in Cell Culture and Histology. Methods Mol Biol 2021, 2299, 17–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K. K.; Sheppard, D.; Chapman, H. A. TGF-beta1 Signaling and Tissue Fibrosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmstrom, J.; Lindberg, H.; Lindberg, C.; Bratt, C.; Wieslander, E.; Delander, E. L.; Sarnstrand, B.; Burns, J. S.; Mose-Larsen, P.; Fey, S.; et al. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 specifically induce proteins involved in the myofibroblast contractile apparatus. Mol Cell Proteomics 2004, 3, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzavlaki, K.; Moustakas, A. TGF-beta Signaling. Biomolecules 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prunotto, M.; Bruschi, M.; Gunning, P.; Gabbiani, G.; Weibel, F.; Ghiggeri, G. M.; Petretto, A.; Scaloni, A.; Bonello, T.; Schevzov, G.; et al. Stable incorporation of alpha-smooth muscle actin into stress fibers is dependent on specific tropomyosin isoforms. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken) 2015, 72, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagihara, T.; Tsubouchi, K.; Gholiof, M.; Chong, S. G.; Lipson, K. E.; Zhou, Q.; Scallan, C.; Upagupta, C.; Tikkanen, J.; Keshavjee, S.; et al. Connective-Tissue Growth Factor Contributes to TGF-beta1-induced Lung Fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2022, 66, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layton, T. B.; Williams, L.; McCann, F.; Zhang, M.; Fritzsche, M.; Colin-York, H.; Cabrita, M.; Ng, M. T. H.; Feldmann, M.; Sansom, S. N.; et al. Cellular census of human fibrosis defines functionally distinct stromal cell types and states. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taipale, J.; Keski-Oja, J. Growth factors in the extracellular matrix. FASEB J 1997, 11, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschumperlin, D. J. Matrix, mesenchyme, and mechanotransduction. Ann Am Thorac Soc 2015, 1 (Suppl 1), S24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carracedo, S.; Lu, N.; Popova, S. N.; Jonsson, R.; Eckes, B.; Gullberg, D. The fibroblast integrin alpha11beta1 is induced in a mechanosensitive manner involving activin A and regulates myofibroblast differentiation. J Biol Chem 2010, 285, 10434–10445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElhinney, K.; Irnaten, M.; O'Brien, C. p53 and Myofibroblast Apoptosis in Organ Fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogatkevich, G. S.; Atanelishvili, I.; Bogatkevich, A. M.; Silver, R. M. Critical Role of LMCD1 in Promoting Profibrotic Characteristics of Lung Myofibroblasts in Experimental and Scleroderma-Associated Lung Fibrosis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2023, 75, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, J. Fibroblasts-Warriors at the Intersection of Wound Healing and Disrepair. Biomolecules 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munger, J. S.; Huang, X.; Kawakatsu, H.; Griffiths, M. J.; Dalton, S. L.; Wu, J.; Pittet, J. F.; Kaminski, N.; Garat, C.; Matthay, M. A.; et al. The integrin alpha v beta 6 binds and activates latent TGF beta 1: a mechanism for regulating pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis. Cell 1999, 96, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurty, A. T.; Shyer, J. A.; Thai, M.; Gandham, V.; Buechler, M. B.; Yang, Y. A.; Pradhan, R. N.; Wang, A. W.; Sanchez, P. L.; Qu, Y.; et al. LRRC15(+) myofibroblasts dictate the stromal setpoint to suppress tumour immunity. Nature 2022, 611, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoloudaki, G.; Snider, P.; Simmons, O.; Conway, S. J.; Hamilton, D. W. Periostin and matrix stiffness combine to regulate myofibroblast differentiation and fibronectin synthesis during palatal healing. Matrix Biol 2020, 94, 31–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargagna-Mohan, P.; Paranthan, R. R.; Hamza, A.; Zhan, C. G.; Lee, D. M.; Kim, K. B.; Lau, D. L.; Srinivasan, C.; Nakayama, K.; Nakayama, K. I.; et al. Corneal antifibrotic switch identified in genetic and pharmacological deficiency of vimentin. J Biol Chem 2012, 287, 989–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaurasia, S. S.; Kaur, H.; de Medeiros, F. W.; Smith, S. D.; Wilson, S. E. Dynamics of the expression of intermediate filaments vimentin and desmin during myofibroblast differentiation after corneal injury. Exp Eye Res 2009, 89, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Z.; Ding, L.; Burckhardt, C. J.; Lowery, J.; Zaritsky, A.; Sitterley, K.; Mota, A.; Costigliola, N.; Starker, C. G.; Voytas, D. F.; et al. Vimentin Intermediate Filaments Template Microtubule Networks to Enhance Persistence in Cell Polarity and Directed Migration. Cell Syst 2016, 3, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costigliola, N.; Ding, L.; Burckhardt, C. J.; Han, S. J.; Gutierrez, E.; Mota, A.; Groisman, A.; Mitchison, T. J.; Danuser, G. Vimentin fibers orient traction stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2017, 114, 5195–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, M. E.; Mendez, M. G.; Janmey, P. A. Substrate stiffness regulates solubility of cellular vimentin. Mol Biol Cell 2014, 25, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patteson, A. E.; Pogoda, K.; Byfield, F. J.; Mandal, K.; Ostrowska-Podhorodecka, Z.; Charrier, E. E.; Galie, P. A.; Deptula, P.; Bucki, R.; McCulloch, C. A.; et al. Loss of Vimentin Enhances Cell Motility through Small Confining Spaces. Small 2019, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Loosdregt, I.; Weissenberger, G.; van Maris, M.; Oomens, C. W. J.; Loerakker, S.; Stassen, O.; Bouten, C. V. C. The Mechanical Contribution of Vimentin to Cellular Stress Generation. J Biomech Eng 2018, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron-Mendoza, M.; Seemann, J.; Grinnell, F. The differential regulation of cell motile activity through matrix stiffness and porosity in three dimensional collagen matrices. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 6425–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miron-Mendoza, M.; Vazquez, D.; Garcia-Ramila, N.; Ikebe, H. R.; Petroll, W. M. Coupling of Fibrin Reorganization and Fibronectin Patterning by Corneal Fibroblasts in Response to PDGF BB and TGFbeta1. Bioengineering (Basel) 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndiaye, A. B.; Koenderink, G. H.; Shemesh, M. Intermediate Filaments in Cellular Mechanoresponsiveness: Mediating Cytoskeletal Crosstalk From Membrane to Nucleus and Back. Front Cell Dev Biol 2022, 10, 882037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, R.; Gonzalez, A. M.; Debiase, P. J.; Trejo, H. E.; Goldman, R. D.; Flitney, F. W.; Jones, J. C. Recruitment of vimentin to the cell surface by beta3 integrin and plectin mediates adhesion strength. J Cell Sci 2009, 122 Pt 9, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckes, B.; Colucci-Guyon, E.; Smola, H.; Nodder, S.; Babinet, C.; Krieg, T.; Martin, P. Impaired wound healing in embryonic and adult mice lacking vimentin. J Cell Sci 2000, 113 ( Pt 13) Pt 13, 2455–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaki, M.; Zhu, G.; Haseba, T.; Shafer, S. S.; Kao, W. W. Expression of collagen I, smooth muscle alpha-actin, and vimentin during the healing of alkali-burned and lacerated corneas. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1993, 34, 3320–3328. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan, R.; Bargagna-Mohan, P. The Use of Withaferin A to Study Intermediate Filaments. Methods Enzymol 2016, 568, 187–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwa, V.; Oh, Y.; Rosenfeld, R. G. The insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP) superfamily. Endocr Rev 1999, 20, 761–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilewski, J. M.; Liu, L.; Henry, A. C.; Knauer, A. V.; Feghali-Bostwick, C. A. Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 3 and 5 are overexpressed in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and contribute to extracellular matrix deposition. Am J Pathol 2005, 166, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Castillo, M.; Rosique-Oramas, D.; Medina-Avila, Z.; Perez-Hernandez, J. L.; Higuera-De la Tijera, F.; Santana-Vargas, D.; Montalvo-Jave, E. E.; Sanchez-Avila, F.; Torre, A.; Kershenobich, D.; et al. Differential production of insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins in liver fibrosis progression. Mol Cell Biochem 2020, 469, (1–2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, K.; Kurosaka, D.; Iwata, T.; Oguchi, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Mashima, Y.; Tsubota, K. Involvement of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in corneal fibroblasts during corneal wound healing. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2006, 47, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, N.; Zenzmaier, C.; Heitz, M.; Hermann, M.; Plas, E.; Schafer, G.; Klocker, H.; Berger, P. Stromal insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (IGFBP3) is elevated in the diseased human prostate and promotes ex vivo fibroblast-to-myofibroblast differentiation. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 2586–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talior-Volodarsky, I.; Connelly, K. A.; Arora, P. D.; Gullberg, D.; McCulloch, C. A. alpha11 integrin stimulates myofibroblast differentiation in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Res 2012, 96, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Zou, J.; Hu, X.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, Z. Latent Transforming Growth Factor-beta Binding Protein-2 Regulates Lung Fibroblast-to-Myofibroblast Differentiation in Pulmonary Fibrosis via NF-kappaB Signaling. Front Pharmacol 2021, 12, 788714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieging, K. T.; Mello, S. S.; Attardi, L. D. Unravelling mechanisms of p53-mediated tumour suppression. Nat Rev Cancer 2014, 14, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoschek, M.; Oskolkov, N.; Bocci, M.; Lovrot, J.; Larsson, C.; Sommarin, M.; Madsen, C. D.; Lindgren, D.; Pekar, G.; Karlsson, G.; et al. Spatially and functionally distinct subclasses of breast cancer-associated fibroblasts revealed by single cell RNA sequencing. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, C. X.; Muller, S.; Keerthivasan, S.; Koeppen, H.; Hung, J.; Gierke, S.; Breart, B.; Foreman, O.; Bainbridge, T. W.; Castiglioni, A.; et al. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals Stromal Evolution into LRRC15(+) Myofibroblasts as a Determinant of Patient Response to Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancer Discov 2020, 10, 232–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.; Tian, M.; He, P.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B. Suppression of LMCD1 ameliorates renal fibrosis by blocking the activation of ERK pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 2022, 1869, 119200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




