Submitted:
14 March 2024
Posted:
14 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
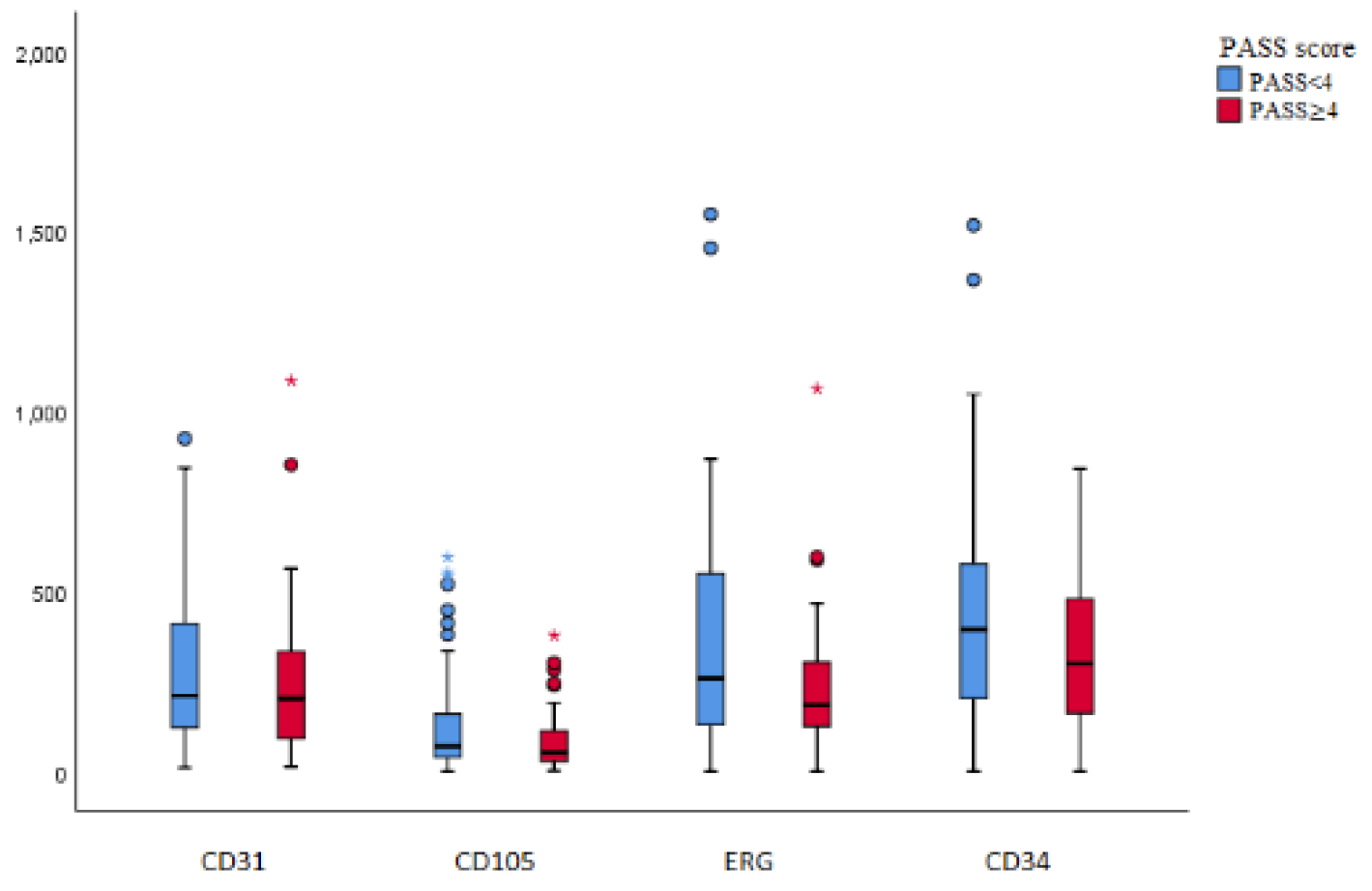
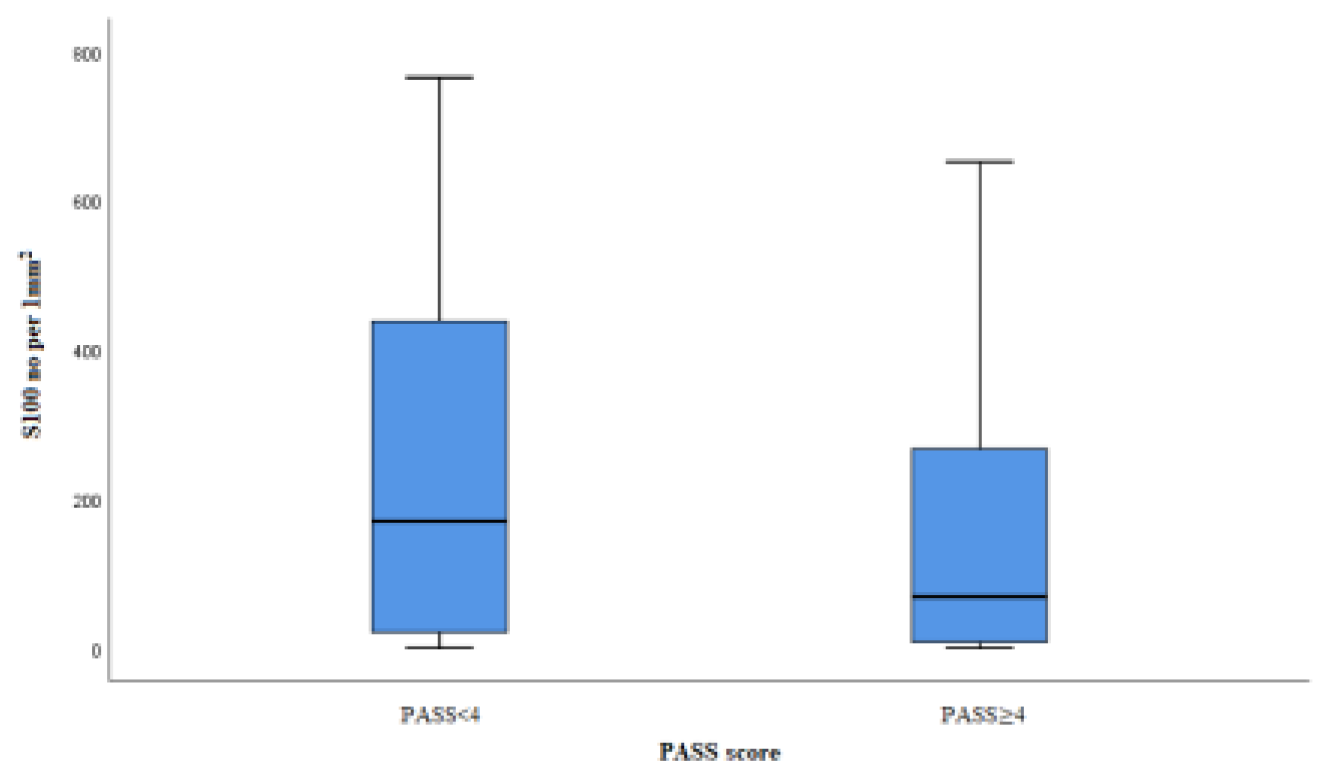
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and macroscopic findings
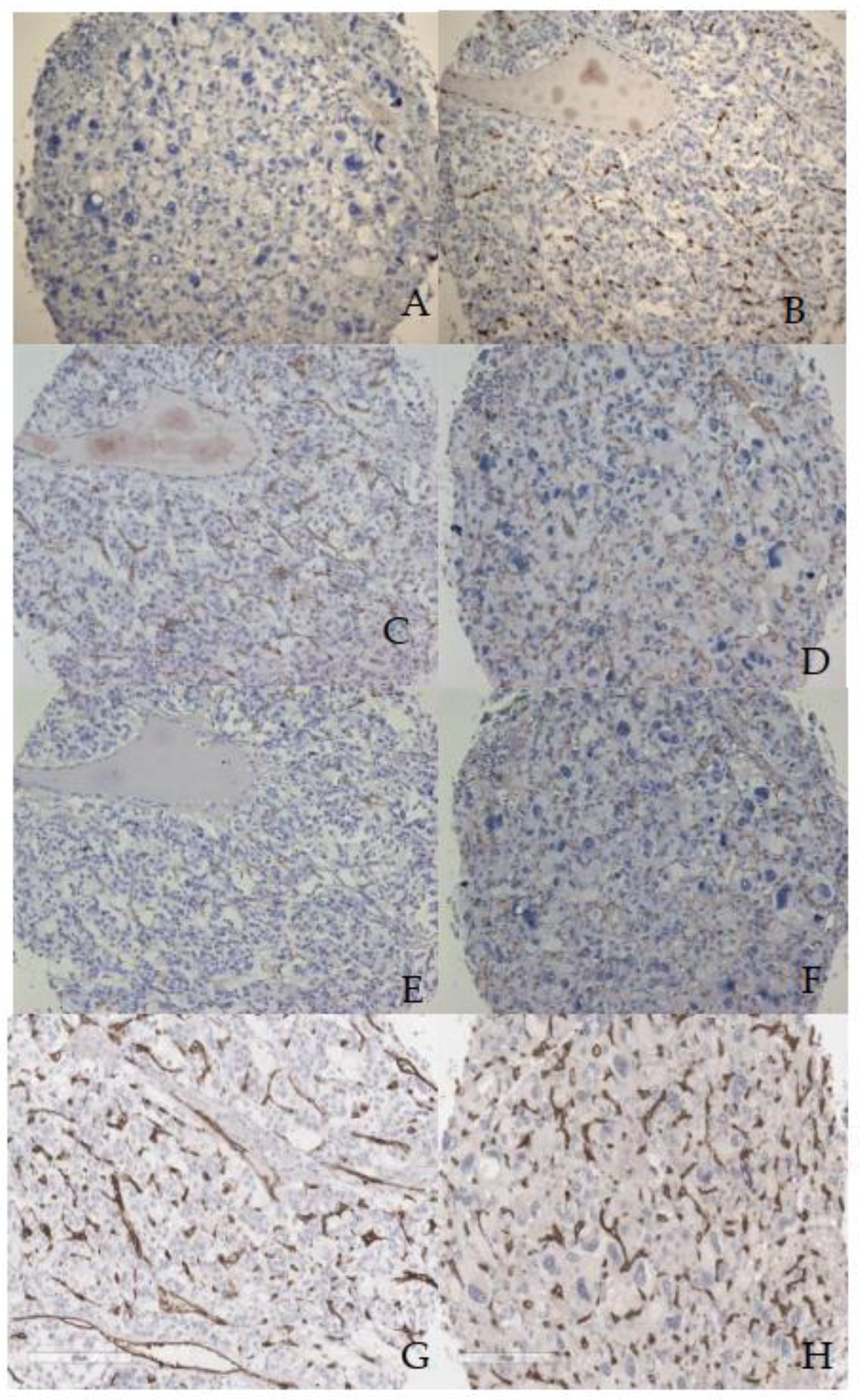
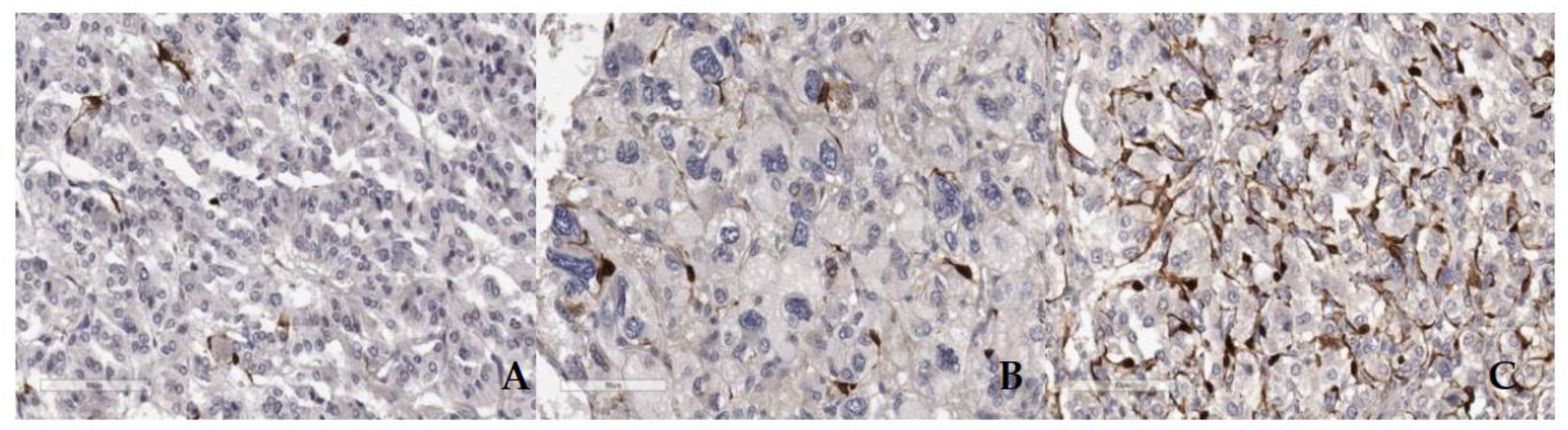
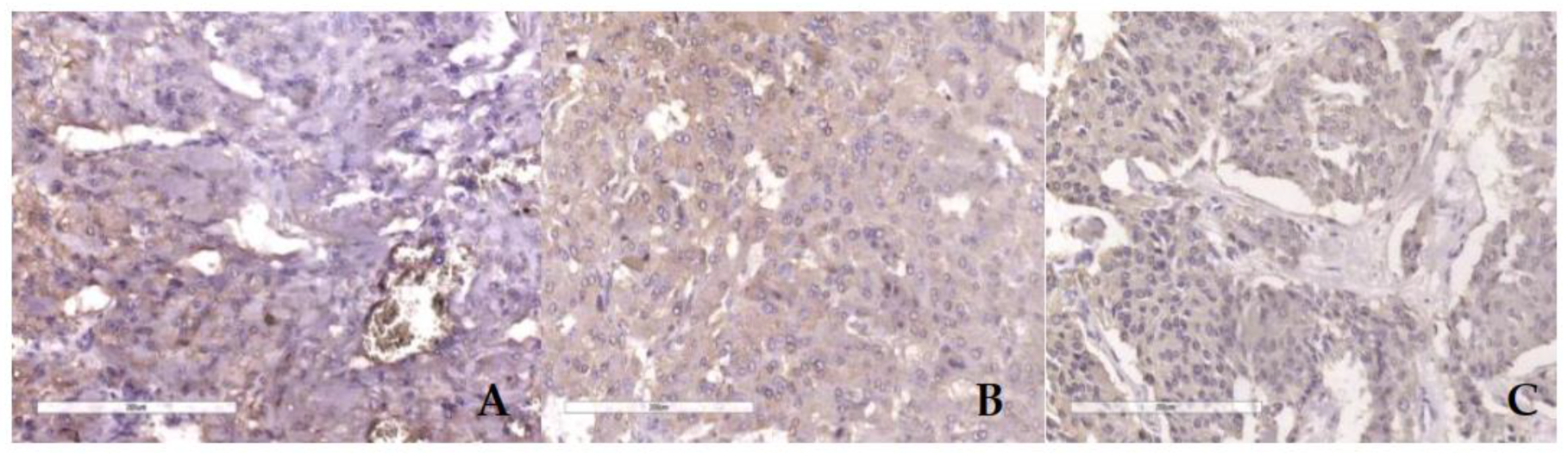
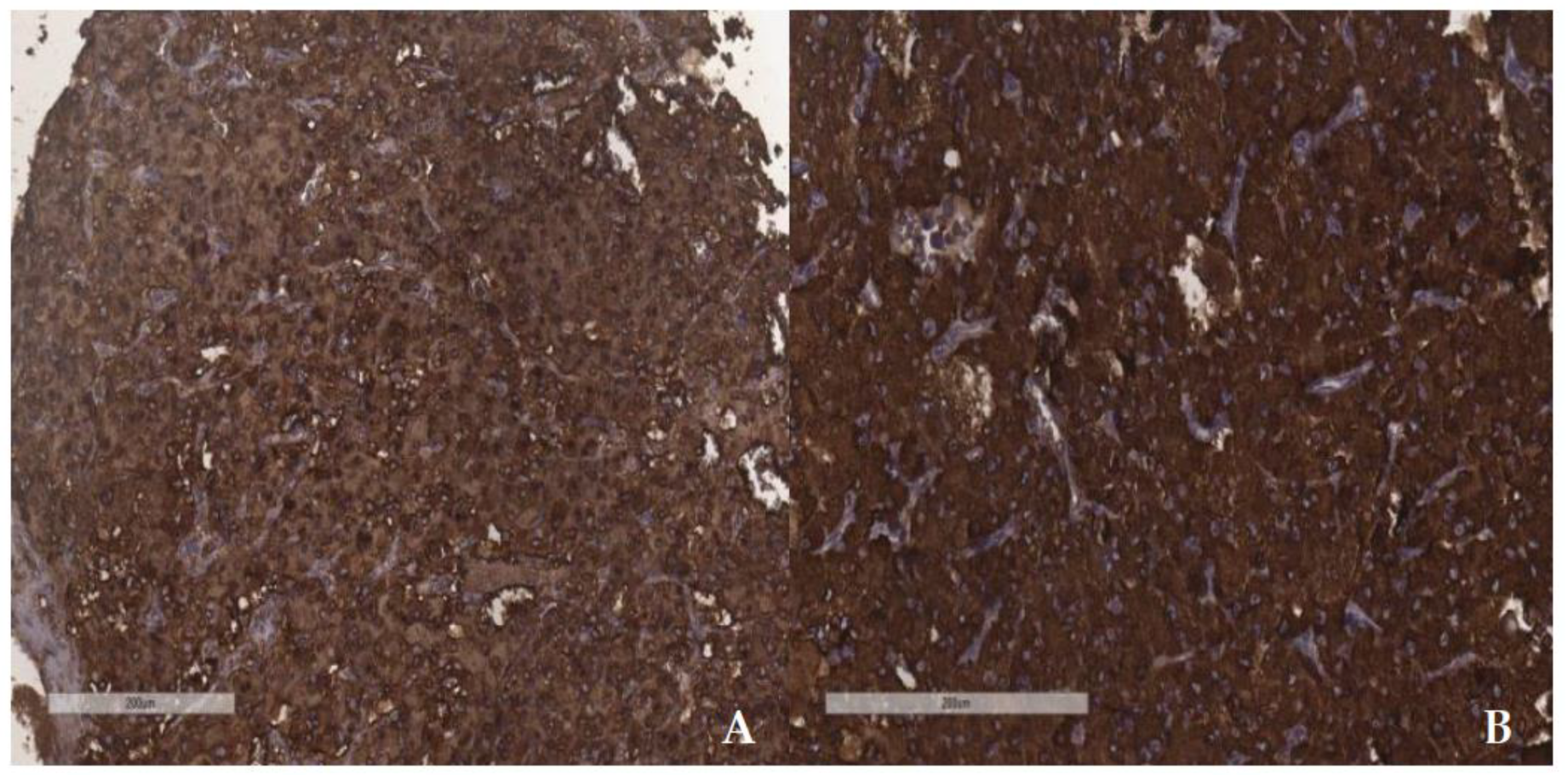
3.2. Microscopic and immunohistochemical findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mete, O.; Asa, S.L.; Gill, A.J.; Kimura, N.; de Krijger, R.R.; Tischler, A. Overview of the 2022 WHO Classification of Paragangliomas and Pheochromocytomas. Endocr Pathol 2022, 33, 90–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, A.K-Y. Update on Adrenal Tumors in 2017 World Health Organisation (WHO) of Endocrine Tumours. Endocr Pathol 2017, 28, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, R.V.; Osamura, R.Y.; Kloppel, G.; Rosai, J. Tumors of the adrenal medulla and extra-adrenal paraganglia. In WHO classification of tumours of endocrine organs: pathology and genetics of tumours of endocrine organ, 4th ed.; Lloyd, R.V., Osamura, R.Y., Kloppel, G., Rosai, J., Eds.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2017; pp. 179–192. [Google Scholar]
- Fishbein, L.; Merrill, S.; Fraker, D.L.; Cohen, D.L.; Nathanson, K.L. Inherited mutations in pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma: why all patients should be offered genetic testing. Ann Surg Oncol 2013, 20, 1444–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahia, P.L.M. Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma pathogenesis: learning from genetic heterogeneity. Nat Rev Cancer 2014, 14, 108–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenders, J.W.M.; Duh, Q-Y. ; Eisenhofer, G.; Gimenez-Roqueplo, A-P.; Grebe, S.K.G.; Murad, M.H.; Naruse, M.; Pacak, K.; Young Jr, W.F. Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma: an endocrine society clinical and practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2014, 99, 1915–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grogan, R.H.; Mitmaker, E.J.; Duh, Q-Y. Changing paradigms in the treatment of malignant pheochromocytoma. Cancer control 2011, 18, 104–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druce, M.R.; Kaltsas, G.A.; Fraenkel, M.; Gross, D.J.; Grossman, A.B. Novel and evolving therapies in the treatment of malignant pheochromocytoma: experience with the mTOR inhibitor everolimus (RAD001). Horm Metab Res 2009, 41, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edstrom Elder, E.; Hjelm Skog, A.-L.; Hoog, A.; Hamberger, B. The management of benign and malignant pheochromocytoma and abdominal paraganglioma. Eur J Surg Oncol 2003, 29, 278–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tischler, A.S. Pheochromocytoma and extra-adrenal paraganlioma: updates. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2008, 132, 1272–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Ramirez, M.; Feng, L.; Johnson, M.M.; Ejaz, S.; Habra, M.A.; Rich, T.; Busaidy, N.; Cote, G.J.; Perrier, N.; Phan, A.; Patel, S.; Waguespack, S.; Jimenez, C. Clinical risk factors for malignancy and overall survival in patients with pheochromocytomas and sympathetic paragangliomas; primary tumor size and primary tumor location as prognostic indicators. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011, 96, 717–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, O.; Young Jr, W.F.; Iniguez-Ariza, N.M.; Kittah, N.E.; Gruber, L.; Bancos, C.; Tamhane, S.; Bancos, I. Malignant Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma: 272 Patients Over 55 Years. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2017, 102, 3296–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasim, S.; Jimenez, C. Metastatic pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma: Management of endocrine manifestations, surgery and ablative procedures, and systemic therapies. Best Prac Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2020, 34, 101354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenhofer, G.; Tischler, A.S.; de Krijger, R.R. Diagnostic tests and biomarkers for pheochromocytoma and extra-adrenal paraganglioma: from routine laboratory methods to disease stratification. Endocr Pathol 2012, 23, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, L.D.R. Pheochromocytoma of the Adrenal gland Scaled Score (PASS) to separate benign from malignant neoplasms: a clinicopathologic and immunophenotypic study of 100 cases. Am J Surg Path 2002, 26, 551–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Yamazaki, Y.; Pecori, A.; Tezuka, Y.; Ono, Y.; Omata, K.; Morimoto, R.; Nakamura, Y.; Satoh, F.; Sasano, H. Histopatological Analysis of Tumor Microinviroment and Angiogenesis in Pheochromocytoma. Front Endocrinol 2020, 10, 587779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Tischler, A.S.; Lloyd, R.V.; DeLellis, R.A.; de Krijger, R.; van Nederveen, F.; Nose, V. Observer variation in the application of the Pheochromocytoma of the Adrenal Gland Scaled Score. Am J Surg Pathol 2009, 33, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strong, V.E.; Kennedy, T.; Al-Ahmadie, H.; Tang, L.; Coleman, J.; Fong, Y.; Brennan, M.; Ghossein, R.A. Prognostic indicators of malignancy in adrenal pheochromocytomas: clinical, histopathologic and cell cycle/apoptosis gene expression analysis. Surgery 2008, 143, 759–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkman, J.; Shing, Y. Angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 1992, 267, 10931–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Djuricin, G.; Staren, E.D.; Gattuso, P.; Gould, V.E.; Shen, J.; Saclarides, T.; Rubin, D.B.; Prinz, R.A. Tumor angiogenesis in pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas. Surgery 1996, 120, 938–42, discussion 942-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohji, H.; Sasagawa, I.; Iciyanagi, O.; Suzuki, Y.; Nakada, T. Tumour angiogenesis and Ki67 expression in phaeochromocytoma. BJU Int 2001, 87, 381–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, C.; Junsheng, M.; Gonzalez, A.R.; Varghese, J.; Zhang, M.; Perrier, N.; Habra, M.A.; Graham, P.; Waguespack, S.G. TNM Staging and Overall Survival in Patients With Pheochromocytoma and Sympathetic Paraganglioma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2023, 108, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skacel, M.; Skilton, B.; Pettay, J.D.; Tubbs, R.R. Tissue microarrays: a powerful tool for high-throughput analysis of clinical specimens: a review of the method with validation data. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2002, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, C.R.; Rudbeck, L. The Staining Proscess. In Immunohistochemical Staining Methods, 6th ed.; Taylor, C.R., Rudbeck, L., Eds.; Dako Denmark A/S: Glostrup, Denmark, 2013; pp. 20–91. [Google Scholar]
- Schnidein, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; Tinevez, J-Y.; White, D.J.; Hartenstein, V.; Eliceiri, K.; Tomancak, P.; Cardona, A. Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat Methods 2012, 9, 676–82. [Google Scholar]
- https://www.studocu.com/en-gb/document/the-open-university/cell-biology/cell-counts-histology-guidance-sxhl288/6880909.
- https://pdf4pro.com/view/exercise-3-biology-105-estimating-the-size-of-cells-4aac9.html. Exercise 3.
- Yao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Chen, J.; Sun, X.; Qiu, Y.; Ding, Y. Endoglin (CD105) expression in angiogenesis of primary hepatocellular carcinomas: analysis using tissue microarrays and comparisons with CD34 and VEGF. Ann Clin Lab Sci 2007, 37, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tanigawa, N.; Lu, C.; Mitsui, T.; Miura, S. Quantitation of sinusoid-like vessels in hepatocellular carcinoma: its clinical and prognostic significance. Hepatology 1997, 26, 1216–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weidner, N. Current pathologic methods for measuring intratumoral microvessel density within breast carcinoma and other solid tumors. Breast Cancer Res Treat 1995, 36, 169–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlumberger, M.; Gicquel, C.; Lumbroso, J.; Tenenbaum, F.; Comoy, E.; Bosq, J.; Foncesa, E.; Ghillani, P.P.; Aubert, B.; Travagli, J.P.; Gardet, P.; Parmentier, C. Malignant pheochromocytoma: clinical, biological, histologic and therapeutic data in a series of 20 patients with distant metastases. J Endocrinol Invest 1992, 15, 631–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattarino, F.; Bouloux, P.M. The diagnosis of malignancy in phaeochromocytoma. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1996, 44, 239–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialas, M.; Dyduch, G.; Dudala, J.; Bereza-Buziak, M.; Hubalewska-Dydejczyk, A.; Budzynski, A.; Okon, K. Study of microvessel density and the expression of vascular endothelial growth factors in adrenal gland pheochromocytomas. Int J Endocrinol 2014, 2014, 104129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favier, J.; Plouin, P-F.; Corvol, P.; Gasc, J-M. Angiogenesis and vascular architecture in pheochromocytomas: distinctive traits in malignant tumors. Am J Pathol 2002, 161, 1235–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudijk, L.; van Nederveen, F.; Badoual, C.; Tissier, F.; Tischler, A.S.; Smid, M.; Gaal, J.; Lepoutre-Lussey, C.; Gimenez-Roqueplo, A-P.; Dinjens, W.N.M.; Korpershoek, E.; de Krijger, R.; Favier, J. Vascular pattern analysis for the prediction of clinical behaviour in pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas. PLoS One 2015, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seon, B.K.; Matsuno, F.; Haruta, Y.; Kondo, M.; Barcos, M. Long-lasting complete inhibition of human solid tumors in SCID mice by targeting endothelial cells of tumor vasculature with antihuman endoglin immunotoxin. Clin Cancer Res 1997, 3, 1031–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Westphal, J.R.; Willems, H.W.; Schalkwijk, C.J.; Ruiter, D.J.; de Waal, R.M. Characteristics and possible function of endoglin, a TGF-beta binding protein. Behring Inst Mitt 1993, (92), 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Saad, R.S.; Jasnosz, K.M.; Tung, M.Y.; Silverman, J.F. Endoglin (CD105) expression in endometrial carcinoma. Int J Gynecol Pathol 2003, 22, 248–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrem, S.; Zarkovic, K.; Eskinja, N.; Jonjic, N. Endoglin is a better marker than CD31 in evaluation of angiogenesis in glioblastoma. Croat Med J. 2005, 46, 417–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Birdsey, G.M.; Dryden, N.H.; Amsellem, V.; Gebhardt, F.; Sahnan, K.; Haskard, D.O.; Dejana, E.; Mason, J.C.; Randi, A.M. Transcription factor Erg regulates angiogenesis and endothelial apoptosis through VE-cadherin. Blood. 2008, 111, 3498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favier, J.; Gimenez-Roqueplo, A-P. Pheochromocytomas: the (pseudo)-hypoxia hypothesis. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010, 24, 957–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amorim-Pires, D.; Peixoto, J.; Lima, J. Hypoxia Pathway Mutations in Pheochromocytomas and Paragangliomas. Cytogenet Genome Res 2016, 150, 227–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wailly, P.; Oragano, L.; Rade, F.; Beaulieu, A.; Arnault, V.; Levillain, P.; Kraimps, J.L. Malignant pheochromocytoma: new malignancy criteria. Langenbecks Arch Surg 2012, 397, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagura, S.; Katoh, R.; Kawaoi, A.; Kobayashi, M.; Obara, T.; Omata, K. Immunohistohemical estimation of growth activity to predict biological behavior of pheochromocytomas. Mod Pathol 1999, 12, 1107–11. [Google Scholar]
- August, C.; August, K.; Schroeder, S.; Bahn, H.; Hinze, R.; Baba, H.A.; Kersting, C.; Buerger, H. CGH and CD44/MIB-1 immunohistochemisty are helpful to distinguish metastasized from nonmetastasized sporadic pheochromocytomas. Mod Pathol 2004, 17, 1119–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elder, E.E.; Xu, D.; Hoog, A.; Enberg, U.; Hou, M.; Pisa, P.; Gruber, A.; Larsson, C.; Backdahl, M. KI67 AND hTERT expression can aid in distinction between malignant and benign pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma. Mod Pathl 2003, 16, 246–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavangar, S.M.; Shojaee, A.; Tabriz, M.H.; Haghpanah, V.; Larijani, B.; Heshmat, R.; Lashkari, A.; Azimi, S. Immunohistochemical expression of Ki-67, c-erbB-2, and c-kit antigens in benign and malignant pheochromocytoma. Pathol Res Pract 2010, 206, 305–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T-H.; Chen, Y-J.; Wu, S-F.; Gao, J.; Jiang, W-J.; Lu, Z-H.; Guan, J.; Wei, S-Z.; Luo, Y-F.; Cao, J-L.; Wan, J-W. Distinction between benign and malignant pheochromocytomas. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 2004, 33, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Unger, P.; Hoffman, K.; Pertsemlidis, D.; Thung, S.; Wolfe, D.; Kaneko, M. S100 protein-positive sustentacular cells in malignant and locally aggressive adrenal pheochromocytomas. Arch Path Lab Med 1991, 115, 484–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schlumberg, M.; Gicquel, C.; Lumbroso, J.; Tenenbaum, F.; Comoy, E.; Bosq, J. Fonseca, E.; Ghillani, P.P.; Aubert, B.; Travagli, J.P.; Gardet, P.; Parmentier, C. Malignant pheochromocytoma: clinical, biological, histologic and therapeutic data in a series of 20 patients with distant metastases. J Endocinol Invest 1992, 15, 631–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffet, A.; Burnichon, N.; Favier, J.; Gimenez-Roqueplo, A-P. An overview of 20 years of genetic studies in pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2020, 34, 101416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysal, B.E.; Willett-Brozick, J.E.; Lawrence, E.C.; Drovdlic, C.M.; Savul, S.A.; McLeod, D.R.; Yee, H.A.; Brackmann, D.E.; Slattery 3rd, W.H; Myers, E.N.; Farrell, R.E.; Rubinsterin, W.S. Prevalence of SDHB, SDHC, and SDHD germline mutations in clinic patients with head and neck paragangliomas. J Med Genet 2002, 39, 178–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffet, A.; Venisse, A.; Nau, V.; Roncellin, I.; Boccio, V.; Le Pottier, N.; Boussion, M.; Travers, C.; Simian, C.; Burnichon, N.; Abermil, N.; Favier, J.; Jeunemaitre, X.; Gimenez-Roqueplo, A-P. A decade (2001–2010) of genetic testing for pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma. Horm Metab Res 2012, 44, 359–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benn, D.E.; Robinson, B.G.; Clifton-Bligh, R.J. 15 YEARS OF PARAGANGLIOMA: Clinical manifestations of paraganglioma syndromes types 1-5. Endocr Relat Cancer 2015, 22, T91–T103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plouin, P.F.; Amar, L.; Dekkers, O.M.; Fassnacht, M.; Gimenez-Roqueplo, A-P.; Lenders, J.W.M.; Lussey-Lepoutre, C.; Steichen, O. European Society of Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline for long-term follow-up of patients operated on for a phaeochromocytoma or a paraganglioma. Eur J Endocrinol 2016, 174, G1–G10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antibody | Dilution | Source |
|---|---|---|
| CD31 | 1:100 | BIO SB |
| CD34 | 1:200 | NOVOCASTRA |
| CD105 | 1:100 | Termo Fisher |
| ERG | 1:100 | ABCAM |
| SDHB | 1:50 | ABCAM |
| S-100 | 1:100 | NOVOCASTRA |
| Ki67 | 1:200 | DAKO |
| Feature | PASS<4 | PASS≥4 |
|---|---|---|
| Total number (%)a (m,f) b | 61 (53%) (17m, 44f) | 54 (47%) (23m, 31f) |
| Age at resection mean/range | 48,4 (22-78) | 48,8 (19-73) |
| Site of tumor | ||
| Intraadrenal total/percentages | 55 (47,83%) | 52 (45,22%) |
| extraadrenal total/percentages | 6 (5,22%) | 2 (1,74%) |
| Tumor weight in grams mean/range | 31,7 (3-159) | 89,7 (2-361) |
| Tumor size in mm mean/range | 44 (4-110) | 61 (20-130) |
| Catecholamines/metabolites | ||
| elevated total/percentages | 47 (40,87%) | 46 (40%) |
| normal total/percentages | 9 (7,83%) | 7 (6,08%) |
| unknown data total/percentages | 5 (4,35%) | 1 (0,87%) |
| Blood pressure/spikes | ||
| elevated total/percentages | 47 (40,87%) | 44 (38,26%) |
| normal total/percentages | 13 (11,3%) | 10 (8,7%) |
| unknown data total/percentages | 1 (0,87%) | |
| MIBI scintigraphy | ||
| increased accumulation | 24 (20,87%) | 16 (13,91%) |
| normal distribution | 8 (6,96%) | 4 (3,49%) |
| unknown data | 29 (25,22%) | 34 (29,56%) |
| Genetic testing | ||
| mutation present | 16 (13,91%) | 16 (13,91%) |
| mutation excluded | 8 (6,96%) | 8 (6,09%) |
| unknown data | 37 (32,17%) | 31 (26,96%) |
| TNM | ||
| T1 tumor < 5cmc | 37 | 13 |
| T2 tumor ≥ 5cmd | 22 | 24 |
| T3 tumor of any size with invasion | 2 | 16 |
| Syndrome | Number (m,f)x | Age mean/range | PASS mean/range |
|---|---|---|---|
| VHL | 10 (6m, 4f) | 37,7 (19-55) | 4,2 (1-12) |
| MEN2a | 17 (6m; 11f) | 42,6 (22-64) | 3,1 (1-8) |
| NF1 | 4 (1m; 3f) | 44,3 (34-53) | 6,3 (4-9) |
| SDHB | 1(1f) | 51 | 9 |
| Without mutation | 15 (3m; 11f) | 45 (29-64) | 5,1 (1-10) |
| Not available | 68 (24m; 44f) | 52,5 (23-78) | 3,7 (1-10) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





