Submitted:
13 March 2024
Posted:
14 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
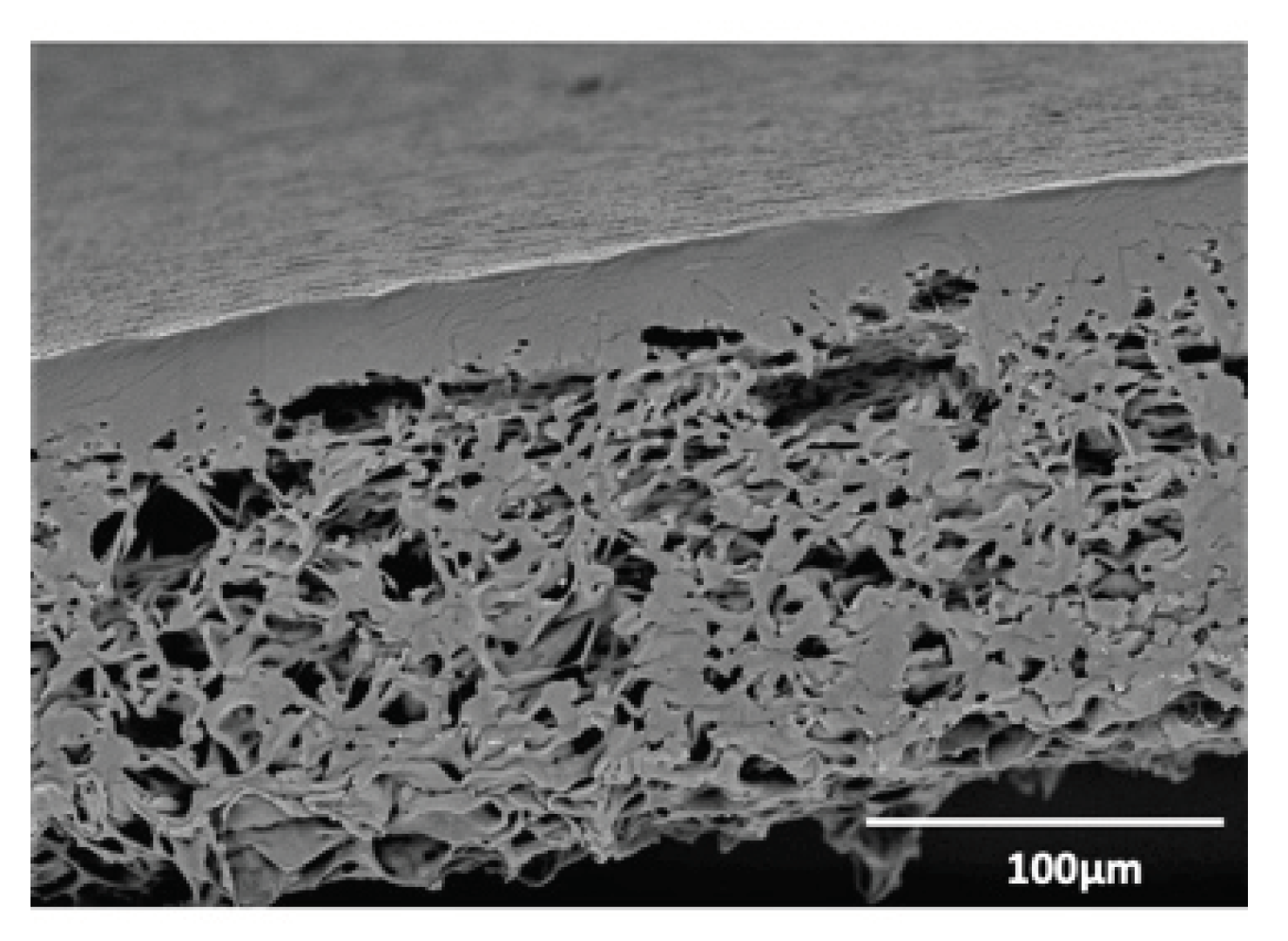
2.1. Biomaterials
2.2. Animal Experiment
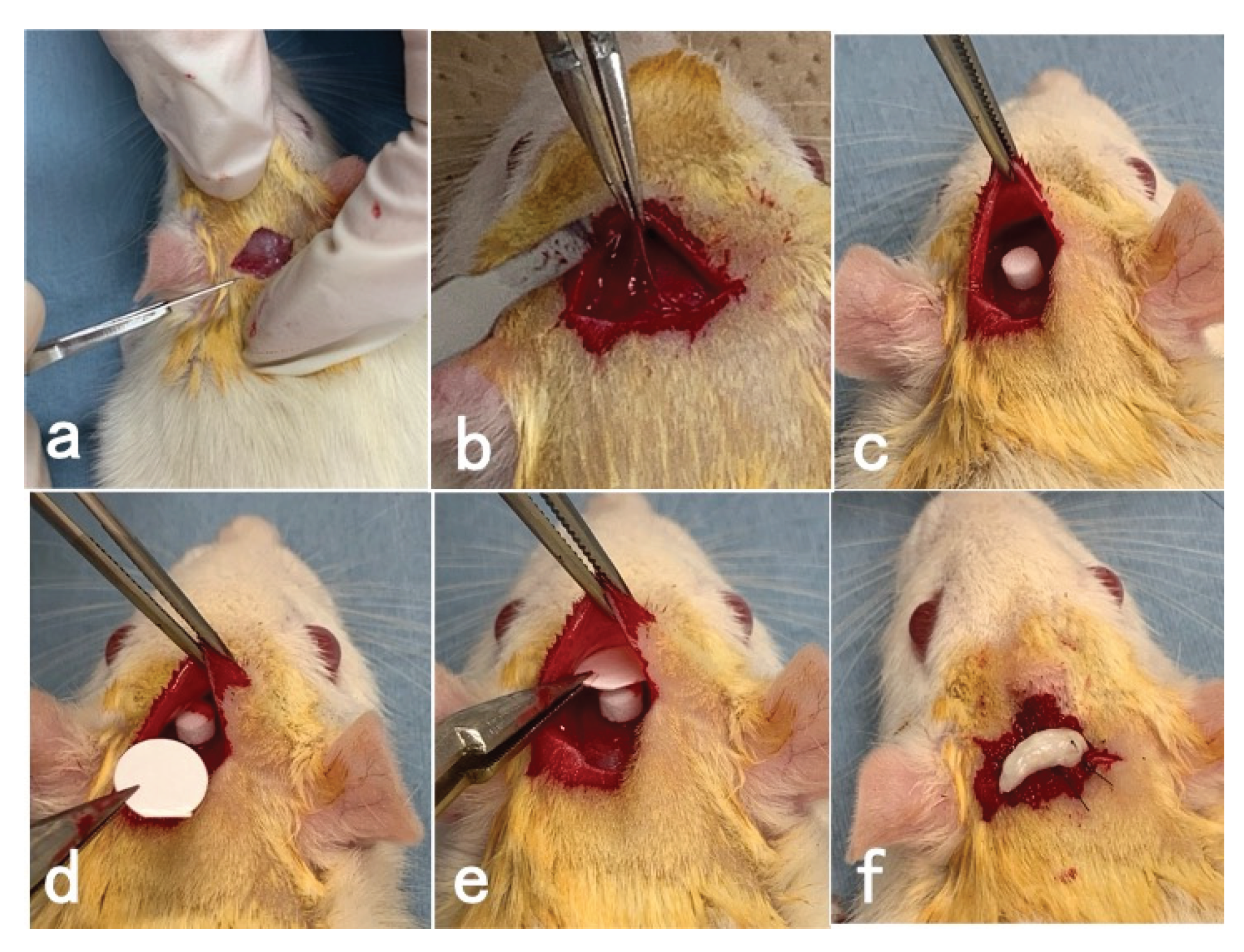
2.3. Surgical Procedures
2.4. Histological Examination
3. Results
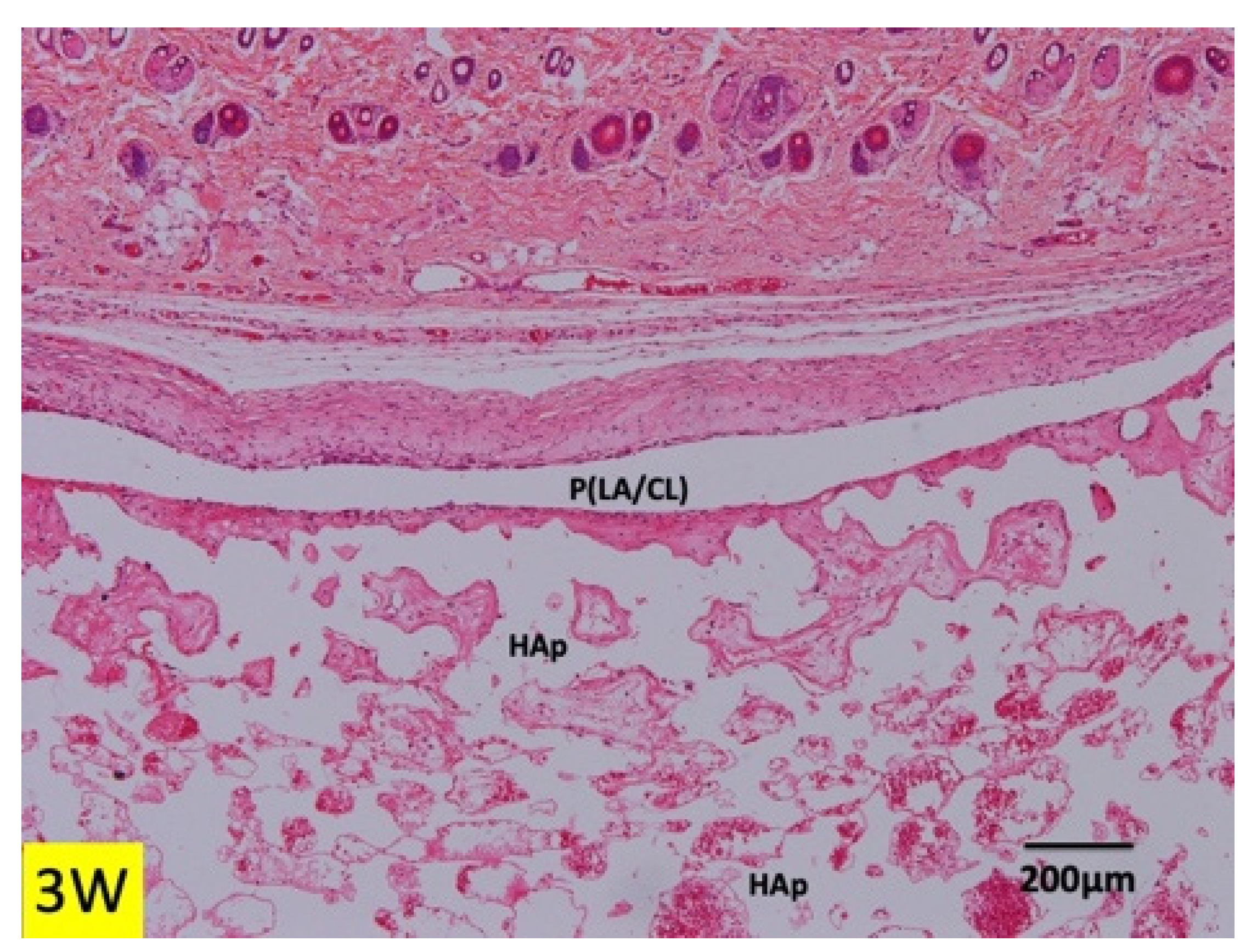
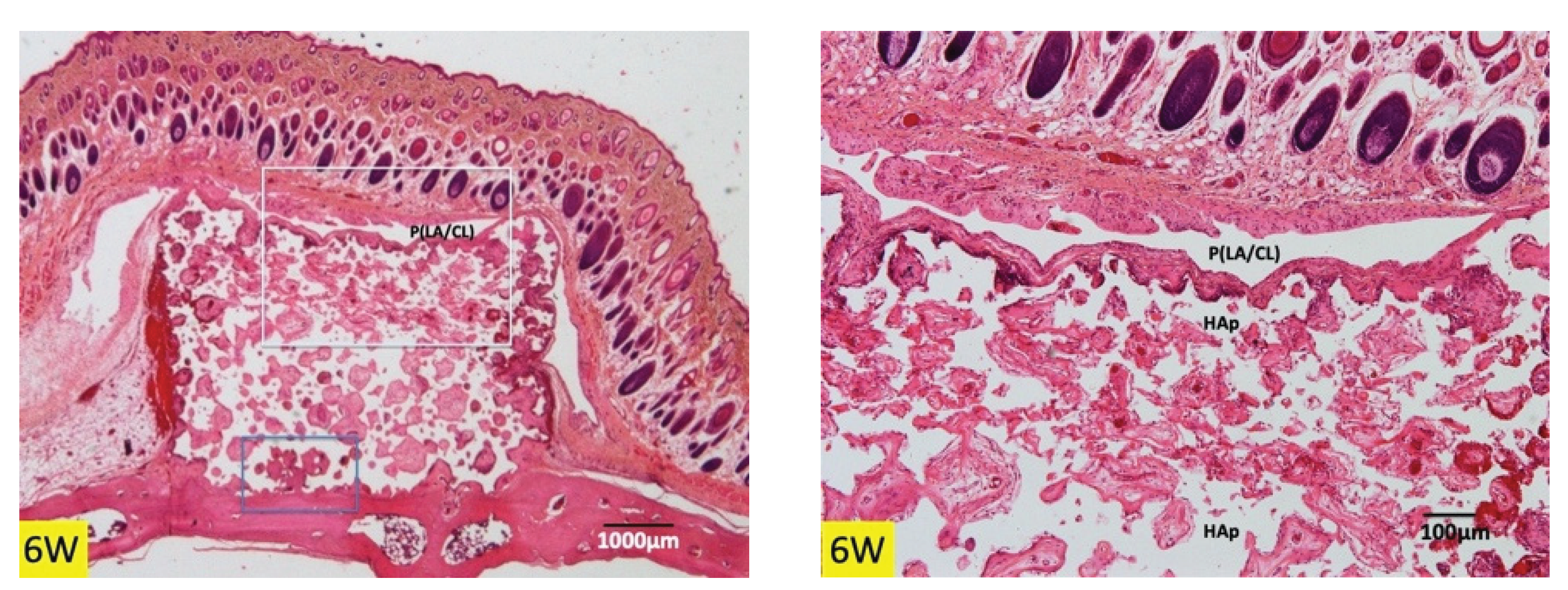
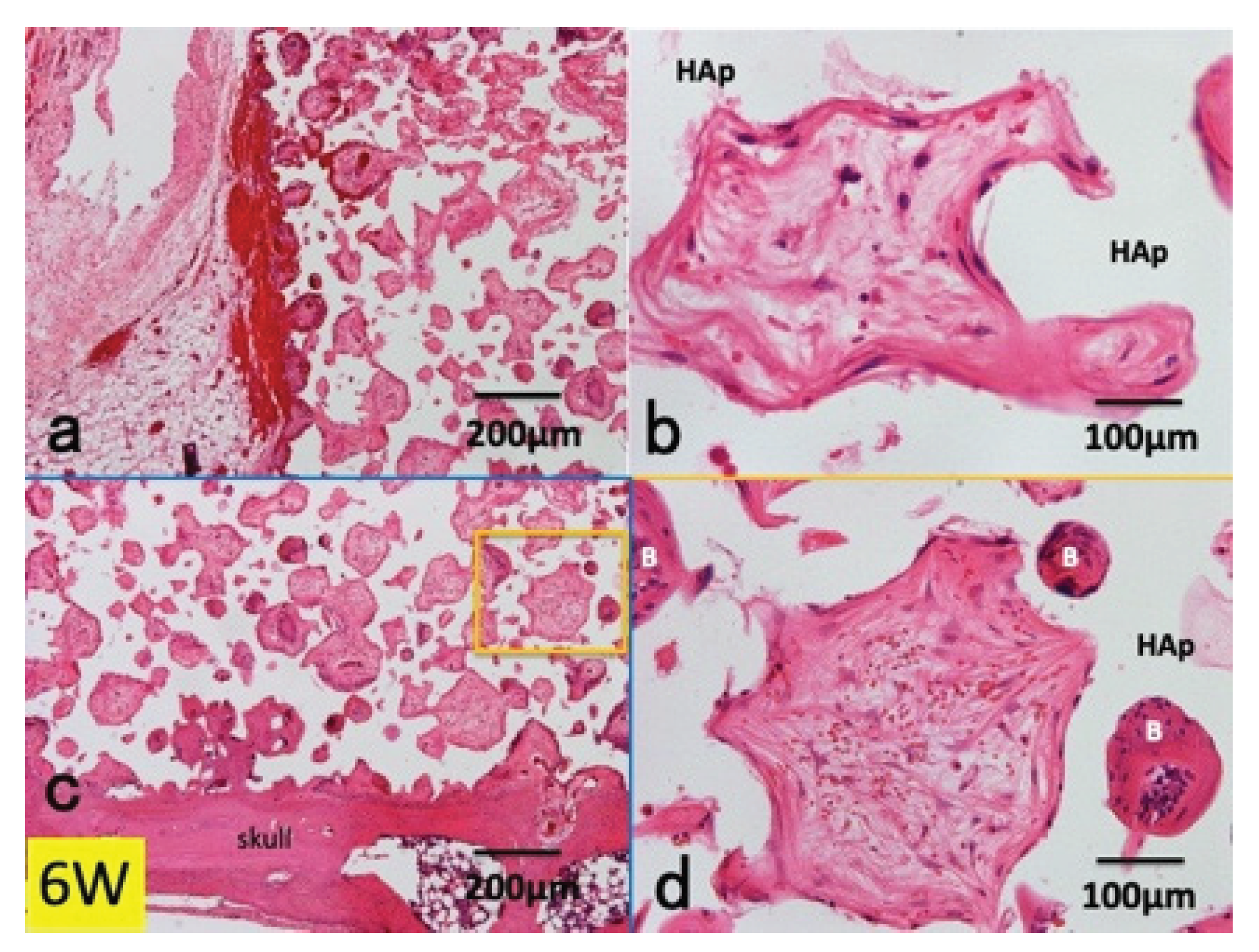
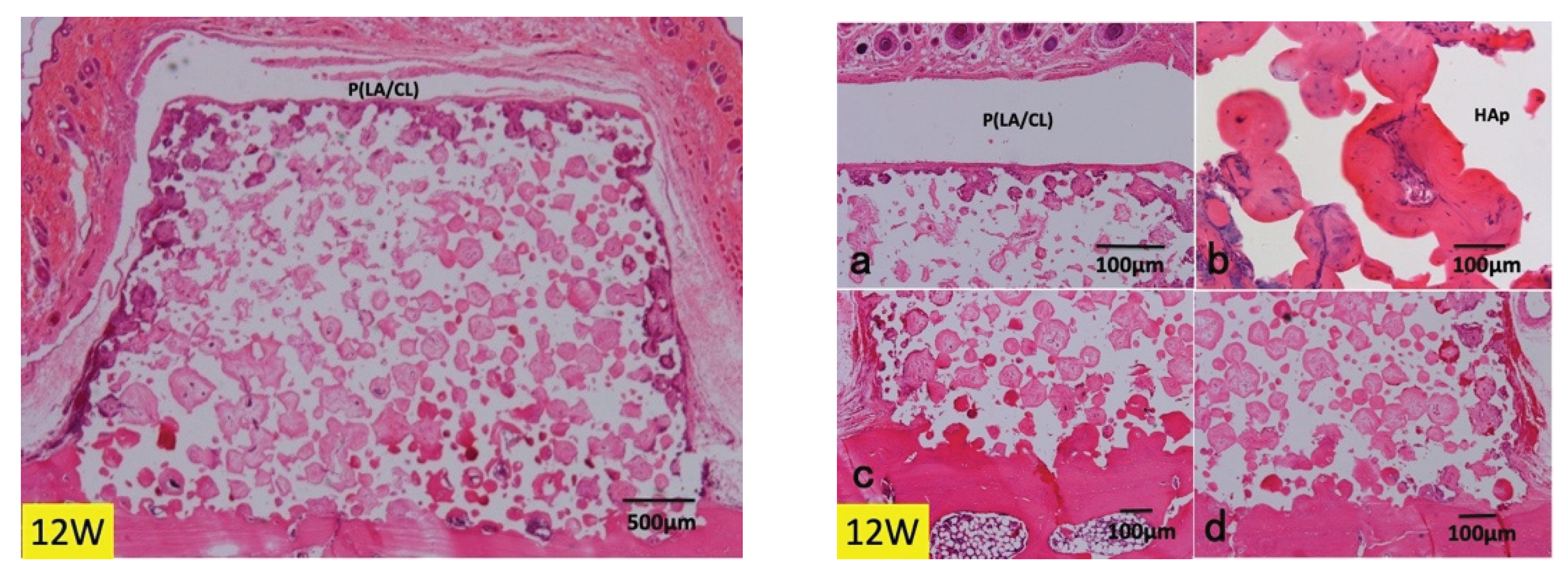
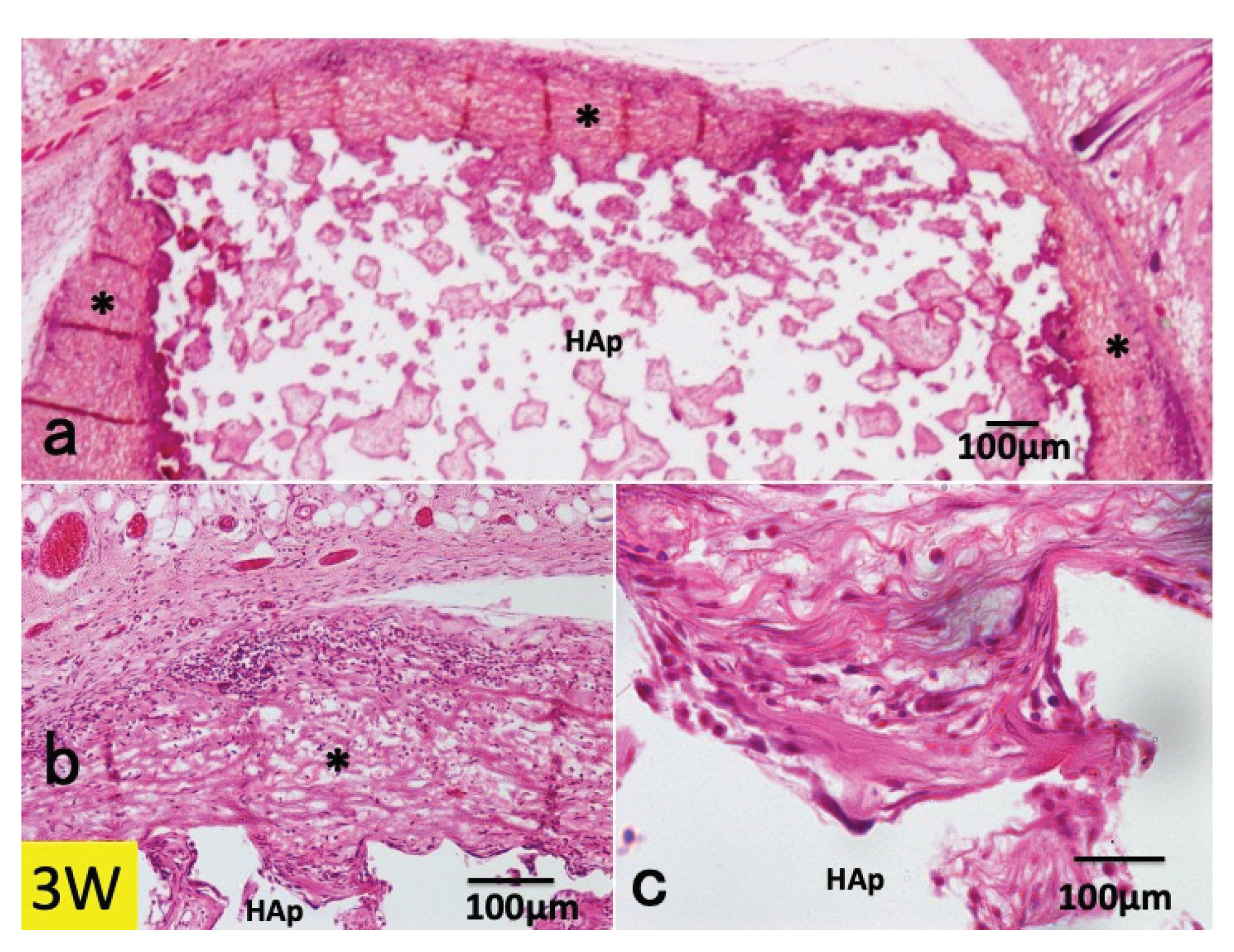
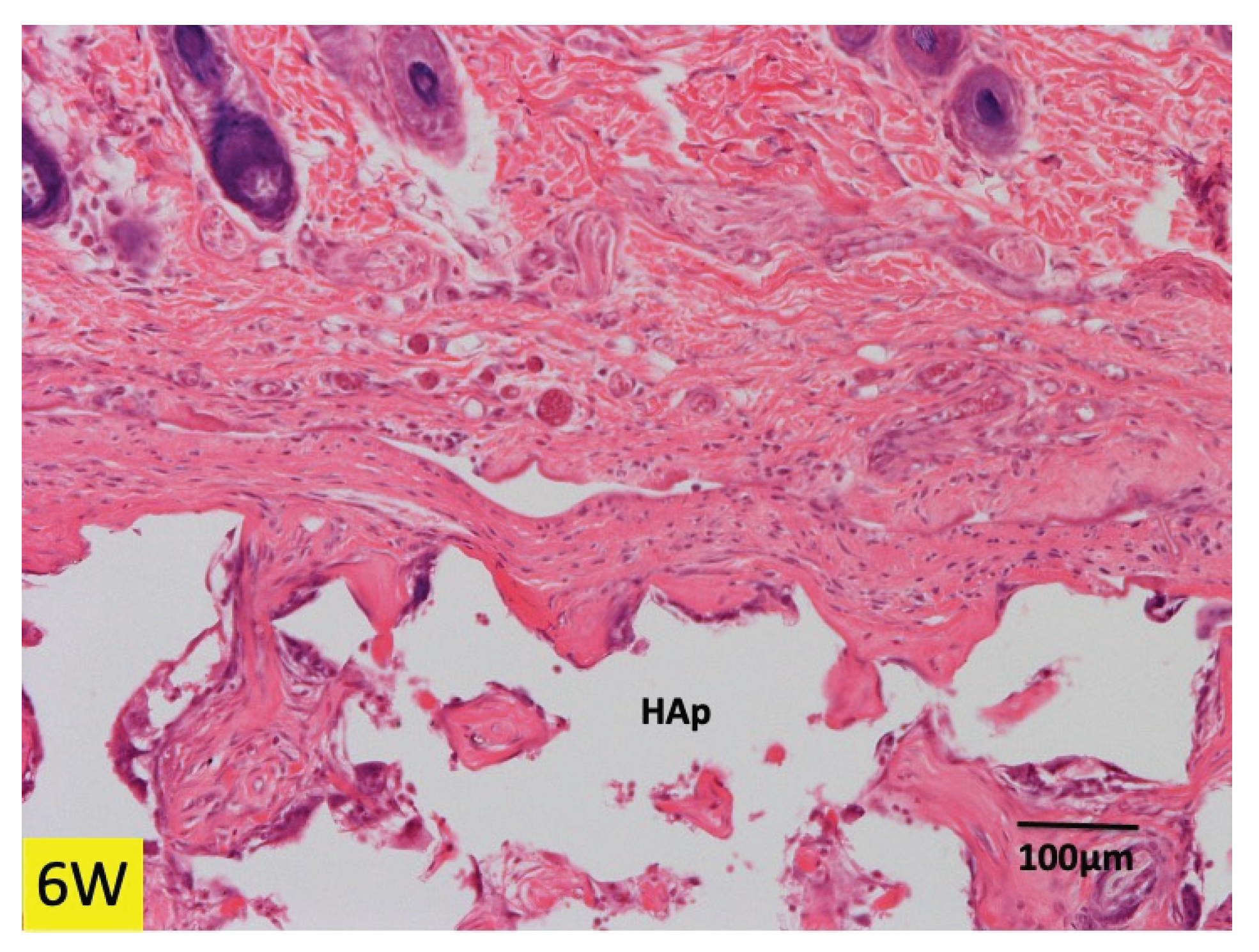
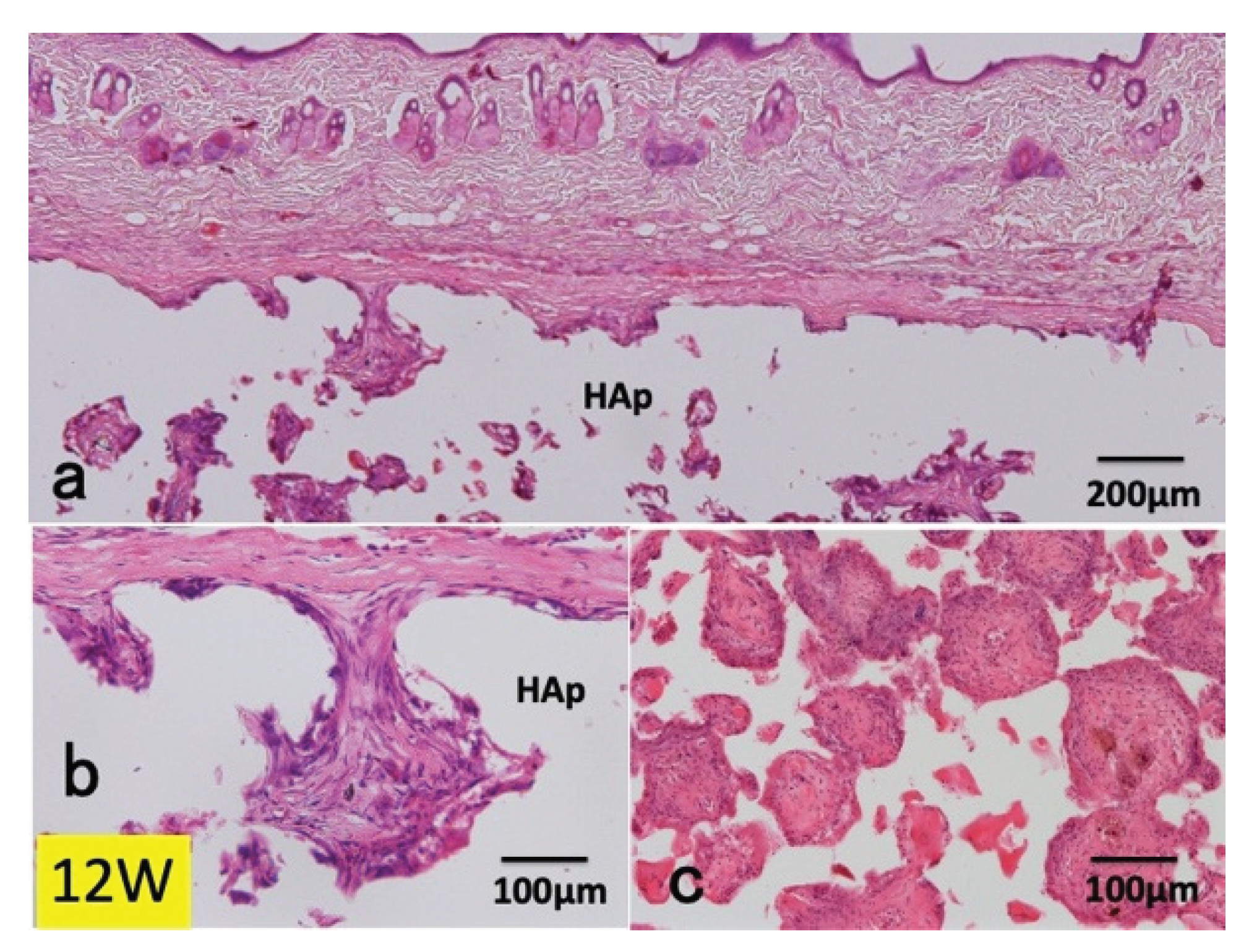
3.1. Histological Findings in P(LA/CL) /HAp on Skull without Periosteum
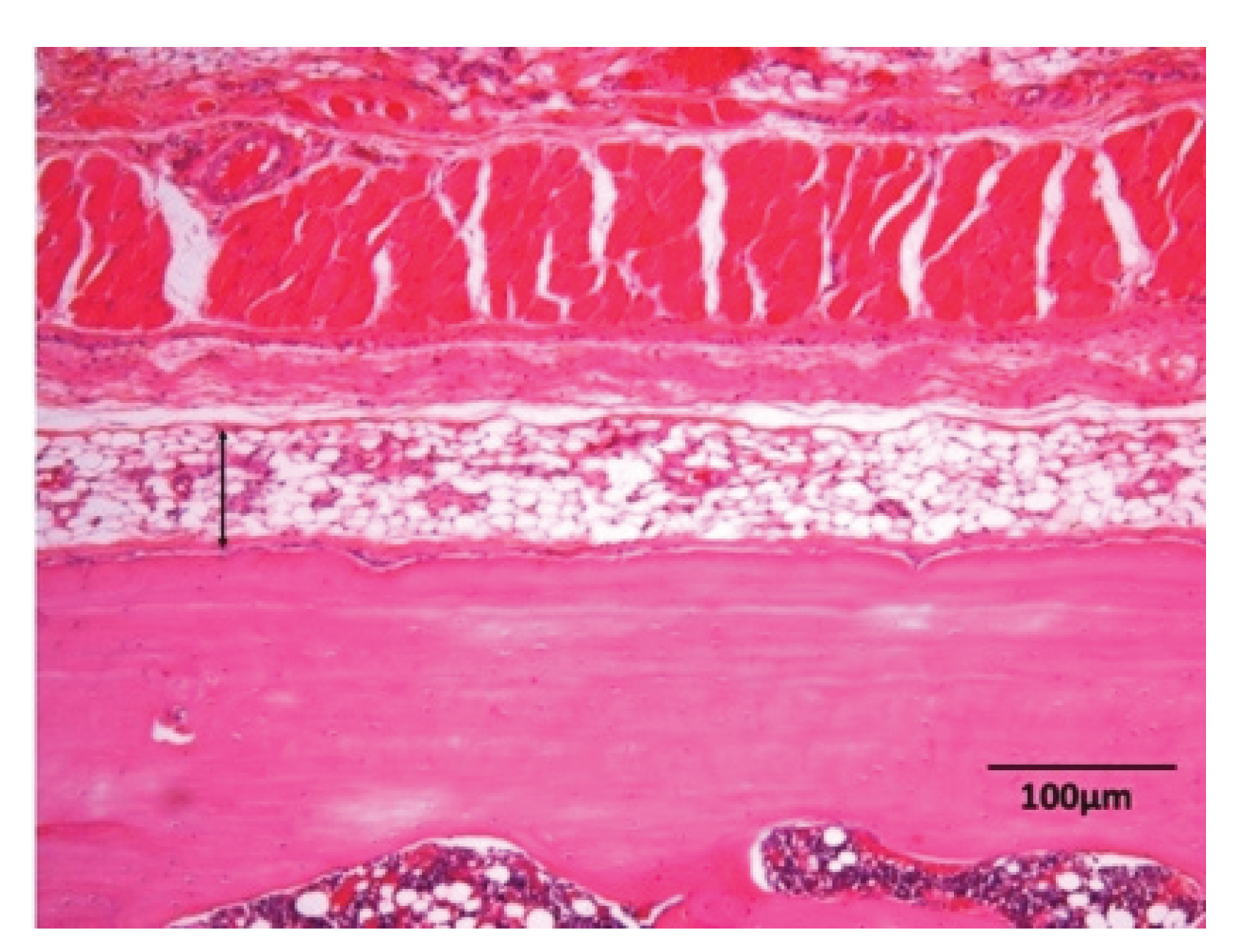
3.2. Histological Findings in Collagen /HAp on Skull without Periosteum
4. Discussion
4.1. Animal Model
4.2. Barrier Membranes
4.3. Bone Managements for Bone Formation in Porous Scaffolds
4.4. Limitation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scantlebury T.V. 1982-1992: A decade of technology development for guided tissue regeneration. J Periodontol. 1993; Nov;64 Suppl 11S:1129-1137. [CrossRef]
- Sheikh Z., Qureshi J., Alshahrani A.M., Nassar H., Ikeda Y., Glogauer M., Ganss B. Collagen based barrier membranes for periodontal guided bone regeneration applications. Odontology. 2017; Jan;105(1):1-12. [CrossRef]
- Lee S.W., Kim S.G. Membranes for the guided bone regeneration. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014; 36:239–246. [CrossRef]
- Selvig K.A., Kersten B.G., Chamberlain A.D., Wikesjö U.M., Nilvéus R.E. Regenerative surgery of intrabony periodontal defects using ePTFE barrier membranes: Scanning electron microscopic evaluation of retrieved membranes versus clinical healing. J. Periodontol. 1992; 63:974–978. [CrossRef]
- Zellin G., Gritli-Linde A., Linde A. Healing of mandibular defects with different biodegradable and non-biodegradable membranes: An experimental study in rats. Biomaterials. 1995; 16:601–609. [CrossRef]
- McGinnis M., Larsen P., Miloro M., Beck M. Comparison of resorbable and nonresorbable guided bone regeneration materials: A preliminary study. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implant. 1998; 13:30–35.
- Bornstein M.M., Bosshardt D., Buser D. Effect of two different bioabsorbable collagen membranes on guided bone regeneration: A comparative histomorphometric study in the dog mandible. J. Periodontol. 2007; 78:1943–1953. [CrossRef]
- Ren Y., Fan L., Alkildani S., Liu L., Emmert S., Najman S., Rimashevskiy D., Schnettler R., Jung O., Xiong X., Barbeck M. Barrier membranes for guided bone regeneration (GBR): A focus on recent advances in collagen membranes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022; Nov 29;23(23):14987. [CrossRef]
- Allan B., Ruan R., Landao-Bassonga E., Gillman N., Wang T., Gao J., Ruan Y., Xu Y., Lee C., Goonewardene M., Zheng M. Collagen membrane for guided bone regeneration in dental and orthopedic applications. Tissue Eng. Part A. 2021; Mar;27(5-6):372-381.
- Abe G.L., Sasaki J., Katata C., Hohno T., Tsuboi R., Kitagawa H., Imazato S. Fabricarion of novel poly (l-lactic acid/ε-caprolactone) bilayer membrane for GBR. Dent. Mater. 2020; 36:626–634.
- Abe G.L., Tsuboi R., Kitagawa H., Sasaki J., Li A., Kohno T., Imazato S. Poly (lactic acid/caprolactone) bilayer membrane blocks bacterial penetration. J. Periodont. Res. 2022; 57:510–518. [CrossRef]
- Ogata K., Ohba S., Sumita Y., Asahina I. Safety and feasibility assessment of biodegradable poly (l-lactic acid/ε-caprolactone) membrane for guided bone regeneration: A case series of first-in-human pilot study. J. Dent. Sci. 2022; 17:368–376. [CrossRef]
- Shido R., Ohba S., Tominaga R., Sumita Y., Asahina I. A prospective study of the assessment of the efficacy of a biodegradable poly (l-lactic acid/ε-caprolactone) membrane for guided bone regeneration. J. Clin. Med. 2023; 15;12(18):5994. [CrossRef]
- Murata M., Maki F., Sato D., Shibata T., Arisue M. Bone augmentation by onlay implant using recombinant human BMP-2 and collagen on adult rat skull without periosteum. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2000; 11(4):289-95. [CrossRef]
- Okubo N., Ishikawa M., Shakya M., Hosono H., Maehara O., Ohkawara T., Ohnishi S., Akazawa T., Murata M. Autograft of demineralized dentin matrix prepared immediately after extraction for horizontal bone augmentation of the anterior atrophic maxilla: A first case of non-vital tooth-derived dentin. J. Hard Tissue Biol., 2022; 31(1) 47-54. [CrossRef]
- Baek Y.J., Kim J.H., Song J.M., Yoon S.Y., Kim H.S., Shin S.H. Chitin-fibroin-hydroxyapatite membrane for guided bone regeneration: micro-computed tomography evaluation in a rat model. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016; Mar 22;38(1):14. [CrossRef]
- Ikumi R., Miyahara T., Akino N., Tachikawa N., Kasugai S. Guided bone regeneration using a hydrophilic membrane made of unsintered hydroxyapatite and poly (L-lactic acid) in a rat bone-defect model. Dent. Mater. J. 2018; Nov 30;37(6):912-918. [CrossRef]
- Sengupta P. The laboratory rat: Relating its age with human's. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013; Jun;4(6):624-30.
- Schlegel A.K., Möhler H., Busch F., Mehl A. Preclinical and clinical studies of a collagen membrane (Bio-Gide). Biomaterials. 1997; Apr;18(7):535-8. [CrossRef]
- Tal H., Kozlovsky A., Artzi Z., Nemcovsky C.E., Moses O. Cross-linked and non-cross-linked collagen barrier membranes disintegrate following surgical exposure to the oral environment: a histological study in the cat. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2008; Aug;19(8):760-6. [CrossRef]
- Murata M. Collagen biology for bone regenerative surgery. J. Korean Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013; 38(32), 1-5. [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay S., Raines R.T. Review collagen-based biomaterials for wound healing. Biopolymers. 2014; 101:821–833. [CrossRef]
- Kabir M.A., Murata M., Shakya M., Yamada K., Akazawa T. Bio-absorption of human dentin-derived biomaterial in sheep critical-size iliac defects. Materials (Basel). 2021; Jan 5;14(1):223. [CrossRef]
- Murata M., Nezu T., Takebe H., Hirose Y., Okubo N., Saito T., Akazawa T. Human dentin materials for minimally invasive bone regeneration: Animal studies and clinical cases. J. Oral Biosci. 2023; Mar;65(1):13-18. [CrossRef]
- Tal H., Kozlovsky A., Artzi Z., Nemcovsky C.E., Moses O. Long-term bio-degradation of cross-linked and non-cross-linked collagen barriers in human guided bone regeneration. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2008; Mar;19(3):295-302. [CrossRef]
- Wang W., Nie W., Liu D., Du H., Zhou X., Chen L., Wang H., Mo X., Li L., He C. Macroporous nanofibrous vascular scaffold with improved biodegradability and smooth muscle cells infiltration prepared by dual phase separation technique. Int. J. Nanomedicine. 2018; Nov 1;13:7003-7018. [CrossRef]
- Ripamonti U., Ma S., Reddi A.H. The critical role of geometry of porous hydroxyapatite delivery system in induction of bone by osteogenin, a bone morphogenetic protein. Matrix. 1992; Jun;12(3):202-12.. [CrossRef]
- Kuboki Y., Takita H., Kobayashi D., Tsuruga E., Inoue M., Murata M., Nagai N., Dohi Y., Ohgushi H. BMP-induced osteogenesis on the surface of hydroxyapatite with geometrically feasible and nonfeasible structures: topology of osteogenesis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1998; Feb;39(2):190-9.
- Toosi S., Javid-Naderi M.J., Tamayol A., Ebrahimzadeh M.H., Yaghoubian S., Mousavi Shaegh S.A. Additively manufactured porous scaffolds by design for treatment of bone defects. Front Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024; Jan 19; 11:1252636. [CrossRef]
- Alvira-González J., De Stavola L. The role of cortical perforations in bone regeneration: a systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020; Jul;49(7):945-951. [CrossRef]
- Shakya, M.; Murata, M.; Yokozeki, K.; Akazawa, T.; Nagayasu, H.; Adhikari, B. R.; Upadhyaya, C. Accelerated bone induction of adult rat compact bone plate scratched by ultrasonic scaler using acidic electrolyzed water. Materials (Basel). 2021; 14(12), 3347. [CrossRef]
- Zhu B., Yokozeki K., Kabir M.A., Todoh M., Akazawa T, Murata M. Chemical properties of human dentin blocks and vertical augmentation by ultrasonically demineralized dentin matrix blocks on scratched skull without periosteum of adult-aged rats. Materials (Basel). 2021; Dec 24;15(1):105. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




