Submitted:
12 March 2024
Posted:
14 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. The Regulation of Post-Transcriptional RNA Processing in Land Plant Mitochondria
2. RNA Helicases as Key Players in Organellar RNA Metabolism
3. The Splicing of Plant Mitochondrial Group II Introns Relies on the Activities of Different Subset Nuclear-Encoded RNA Binding Cofactors
4. Mitochondrial RNA Helicases Factors in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Yeast)
5. Mitochondrial RNA Helicases Factors in Arabidopsis thaliana Plants
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gualberto, J. M.; Newton, K. J. , Plant mitochondrial genomes: Dynamics and mechanisms of mutation. Annu Rev Plant Biol 2017, 68, 225–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmudjak, M.; Ostersetzer-Biran, O., RNA Metabolism and Transcript Regulation. In Annu Plant Rev online, 2018; pp 143-184.
- Small, I.; Melonek, J.; Bohne, A.-V.; Nickelsen, J.; Schmitz-Linneweber, C. , Plant organellar RNA maturation. Plant Cell 2023, 35(6), 1727–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, C.; Mizrahi, R.; Ostersetzer-Biran, O. , Why so complex? The intricacy of genome structure and gene expression, associated with angiosperm mitochondria, may relate to the regulation of embryo quiescence or dormancy - intrinsic blocks to early plant life. Plants 2020, 9(5), 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, P.; Rugen, N.; Carrie, C.; Elsasser, M.; Finkemeier, I.; Giese, J.; Hildebrandt, T. M.; Kuhn, K.; Maurino, V. G.; Ruberti, C.; Schallenberg-Rudinger, M.; Steinbeck, J.; Braun, H. P.; Eubel, H.; Meyer, E. H.; Muller-Schussele, S. J.; Schwarzlander, M. , Single organelle function and organization as estimated from Arabidopsis mitochondrial proteomics. Plant J 2020, 101(2), 420–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Jian, Y.; Vosoughi, S.; Zeng, C.; Zhao, Y. , Evaluating native-like structures of RNA-protein complexes through the deep learning method. Nat Comm 2023, 14(1), 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C. S.; Tseng, C. K.; Lai, Y. H.; Wang, H. F.; Newman, A. J.; Cheng, S. C. , Dynamic protein-RNA interactions in mediating splicing catalysis. Nucleic Acids Res 2019, 47(2), 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glisovic, T.; Bachorik, J. L.; Yong, J.; Dreyfuss, G. , RNA-binding proteins and post-transcriptional gene regulation. FEBS Lett 2008, 582(14), 1977–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licatalosi, D. D.; Darnell, R. B. , RNA processing and its regulation: global insights into biological networks. Nat Rev Genet 2010, 11(1), 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitale, R. C.; Incarnato, D. , Probing the dynamic RNA structurome and its functions. Nat Rev Genet 2023, 24(3), 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assmann, S. M.; Chou, H.-L.; Bevilacqua, P. C. , Rock, scissors, paper: How RNA structure informs function. Plant Cell 2023, 35(6), 1671–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, J. A.; Westhof, E. , The Dynamic Landscapes of RNA Architecture. Cell 2009, 136(4), 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeois, C. F.; Mortreux, F.; Auboeuf, D. , The multiple functions of RNA helicases as drivers and regulators of gene expression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2016, 17(7), 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowsky, E. , RNA helicases at work: binding and rearranging. Trends Biochem Scie 2011, 36(1), 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owttrim, G. W. , RNA helicases: diverse roles in prokaryotic response to abiotic stress. RNA biol 2013, 10(1), 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairman-Williams, M. E.; Guenther, U. P.; Jankowsky, E. , SF1 and SF2 helicases: family matters. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2010, 20(3), 313–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammani, K.; Giege, P. , RNA metabolism in plant mitochondria. Trends Plant Sci 2014, 19(6), 380–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawaz, G.; Kang, H. , Chloroplast- or Mitochondria-Targeted DEAD-Box RNA Helicases Play Essential Roles in Organellar RNA Metabolism and Abiotic Stress Responses. Front Plant Sci 2017, 8, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colas des Francs-Small, C.; Small, I. , Surrogate mutants for studying mitochondrially encoded functions. Biochimie 2014, 100(0), 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, W.; Koonin, E. V. , Introns and the origin of nucleus-cytosol compartmentalization. Nature 2006, 440(7080), 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz-Linneweber, C.; Lampe, M.-K.; Sultan, L. D.; Ostersetzer-Biran, O., Organellar maturases: A window into the evolution of the spliceosome. BBA - Bioenergetics 2015, 1847, (9), 798-808. [CrossRef]
- Cech, T. R. , The RNA worlds in context. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2012, 4(7), a006742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerly, S.; Semper, C. , Evolution of group II introns. Mobile DNA 2015, 6(1), 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambowitz, A. M.; Belfort, M. , Mobile bacterial group II introns at the crux of eukaryotic evolution. Microbiol spect 2015, 3(1), 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Catania, F.; Lynch, M. , Where do introns come from? PLoS Biol 2008, 6(11), e283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cech, T. R. , The generality of self-splicing RNA: Relationship to nuclear messenger-RNA splicing. Cell 1986, 44(2), 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ambowitz, A. M.; Caprara, M. G.; Zimmerly, S.; Perlman, P., Group I and Group II Ribozymes as RNPs: Clues to the Past and Guides to the Future. In The RNA World, R. Gesteland, T. Cech, and J. Atkins, eds (Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press). 1999, pp. 451-485.
- Pyle, A. M.; Lambowitz, A. M., Group II Introns: Ribozymes that splice RNA and invade DNA. In: The RNA World, R. Gesteland, TR. Cech, and J. Atkins (eds), 3rd eddition. Cold Spring Harbor:. 1999.
- Michel, F.; Umesono, K.; Ozeki, H. , Comparative and functional anatomy of group II catalytic introns — a review. Gene 1989, 82(1), 5–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferat, J. L.; Michel, F. , Group-II Self-Splicing Introns in Bacteria. Nature 1993, 364(6435), 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonen, L.; Vogel, J. , The ins and outs of group II introns. Trends Genet 2001, 17(6), 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonen, L. , Cis- and trans-splicing of group II introns in plant mitochondria. Mitochondrion 2008, 8(1), 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G. G.; Colas des Francs-Small, C.; Ostersetzer-Biran, O. , Group II intron splicing factors in plant mitochondria. Front Plant Sci 2014, 5(35), 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, P. A. , On the origin of RNA splicing and introns. Cell 1985, 42(2), 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmudjak, M.; Shevtsov, S.; Sultan, L. D.; Keren, I.; Ostersetzer-Biran, O. , Analysis of the roles of the Arabidopsis nMAT2 and PMH2 proteins provided with new insights into the regulation of group II intron splicing in land-plant mitochondria. Int J Mol Sci 2017, 18(11), 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, I. M.; Rasmusson, A. G.; Van Aken, O. , Plant mitochondria – past, present and future. Plant J 2021, 108(4), 912–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizrahi, R.; Shevtsov-Tal, S.; Ostersetzer-Biran, O. , Group II intron-encoded proteins (IEPs/maturases) as key regulators of Nad1 expression and Complex I biogenesis in land plant mitochondria. Genes 2022, 13(7), 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohr, G.; Lambowitz, A. M. , Putative proteins related to group II intron reverse transcriptase/maturases are encoded by nuclear genes in higher plants. Nucleic Acids Res 2003, 31(2), 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, I. D.; Peeters, N. , The PPR motif - a TPR-related motif prevalent in plant organellar proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 2000, 25(2), 46–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Silva, P.; Martinez-Azorin, F.; Micol, V.; Attardi, G. , The human mitochondrial transcription termination factor (mTERF) is a multizipper protein but binds to DNA as a monomer, with evidence pointing to intramolecular leucine zipper interactions. EMBO J 1997, 16(5), 1066–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleine, T. , Arabidopsis thaliana mTERF proteins: evolution and functional classification. Front Plant Sci 2012, 3, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, P.; Micol, J. L.; Quesada, V. , Unveiling Plant mTERF Functions. Mol Plant 2012, 5(2), 294–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedman, T.; Gaidutšik, I.; Villemson, K.; Hou, Y.; Sedman, J. , Double-stranded DNA-dependent ATPase Irc3p is directly involved in mitochondrial genome maintenance. Nucleic Acids Res 2014, 42(21), 13214–13227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, D.; Fontanesi, F.; Barrientos, A. , The DEAD box protein Mrh4 functions in the assembly of the mitochondrial large ribosomal subunit. Cell Metabol 2013, 18(5), 712–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.-R.; Rowe, C. E.; Mohr, S.; Jiang, Y.; Lambowitz, A. M.; Perlman, P. S. , The splicing of yeast mitochondrial group I and group II introns requires a DEAD-box protein with RNA chaperone function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005, 102(1), 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conrad-Webb, H.; Perlman, P. S.; Zhu, H.; Butow, R. A. , The nuclear SUV3-1 mutation affects a variety of post-transcriptional processes in yeast mitochondria. Nucleic Acids Res 1990, 18, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepien, P. P.; Margossian, S. P.; Landsman, D.; Butow, R. A. , The yeast nuclear gene suv3 affecting mitochondrial post-transcriptional processes encodes a putative ATP-dependent RNA helicase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1992, 89(15), 6813–6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Duan, Y.; Hua, D.; Fan, G.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Han, L.; Qu, L.-J.; Gong, Z. , DEXH box RNA helicase–mediated mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production in Arabidopsis mediates crosstalk between abscisic acid and auxin signaling. Plant Cell 2012, 24(5), 1815–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stonebloom, S.; Burch-Smith, T.; Kim, I.; Meinke, D.; Mindrinos, M.; Zambryski, P. , Loss of the plant DEAD-box protein ISE1 leads to defective mitochondria and increased cell-to-cell transport via plasmodesmata. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009, 106(40), 17229–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthes, A.; Schmidt-Gattung, S.; Köhler, D.; Forner, J.; Wildum, S.; Raabe, M.; Urlaub, H.; Binder, S. , Two DEAD-box proteins may be part of RNA-dependent high-molecular-mass protein complexes in Arabidopsis mitochondria. Plant Physiol 2007, 145(4), 1637–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, D.; Schmidt-Gattung, S.; Binder, S., The DEAD-box protein PMH2 is required for efficient group II intron splicing in mitochondria of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 2010, 72, (4-5), 459-67. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. Z.; Ding, S.; Liu, X. Y.; Xu, C.; Sun, F.; Tan, B. C. , The DEAD-box RNA helicase ZmRH48 is required for the splicing of multiple mitochondrial introns, mitochondrial complex biosynthesis, and seed development in maize. J Integr Plant Biol 2023, 65(11), 2456–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliardi, D.; Kuhn, J.; Spadinger, U.; Brennicke, A.; Leaver, C. J.; Binder, S. , An RNA helicase (AtSUV3) is present in Arabidopsis thaliana mitochondria. FEBS Letters 1999, 458(3), 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuteja, N.; Tarique, M.; Tuteja, R. , Rice SUV3 is a bidirectional helicase that binds both DNA and RNA. BMC Plant Biol 2014, 14, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, R. K.; Ansari, M. W.; Tuteja, R.; Tuteja, N., OsSUV3 transgenic rice maintains higher endogenous levels of plant hormones that mitigates adverse effects of salinity and sustains crop productivity. Rice (N Y) 2014, 7, (1), 17. [CrossRef]
- Wallet, C.; Le Ret, M.; Bergdoll, M.; Bichara, M.; Dietrich, A.; Gualberto, J. M. , The RECG1 DNA Translocase Is a Key Factor in Recombination Surveillance, Repair, and Segregation of the Mitochondrial DNA in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2015, 27(10), 2907–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, C. M.; Castleden, I. R.; Tanz, S. K.; Aryamanesh, N.; Millar, A. H. , SUBA4: the interactive data analysis centre for Arabidopsis subcellular protein locations. Nucleic Acids Res 2017, 45(D1), D1064–D1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almagro Armenteros, J. J.; Salvatore, M.; Emanuelsson, O.; Winther, O.; von Heijne, G.; Elofsson, A.; Nielsen, H., Detecting sequence signals in targeting peptides using deep learning. Life Sci Alliance 2019, 2, (5). [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, G. , The petite mutation in yeast. Trends Biochem Sci 1979, 4(9), 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, A. M.; Pape, L. K.; Tzagoloff, A. , Mitochondrial protein synthesis is required for maintenance of intact mitochondrial genomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J 1985, 4(8), 2087–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, K. A.; Kaniak-Golik, A.; Golik, P., Maintenance and expression of the S. cerevisiae mitochondrial genome—from genetics to evolution and systems biology. BBA-Bioenergetics 2010, 1797, (6-7), 1086-1098.
- Duvezin-Caubet, S.; Rak, M.; Lefebvre-Legendre, L.; Tetaud, E.; Bonnefoy, N.; di Rago, J.-P. , A "petite obligate" mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: functional mtDNA is lethal in cells lacking the delta subunit of mitochondrial F1-ATPase. J Biol Chem 2006, 281(24), 16305–16313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, D. M. , Partial Assembly of the Yeast Mitochondrial ATP Synthase1. J Bioenerg Biomem 2000, 32(4), 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczesny, R. J.; Wojcik, M. A.; Borowski, L. S.; Szewczyk, M. J.; Skrok, M. M.; Golik, P.; Stepien, P. P., Yeast and human mitochondrial helicases. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Gene Reg Mechan 2013, 1829, (8), 842-853.
- de la Cruz, J.; Kressler, D.; Linder, P. , Unwinding RNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: DEAD-box proteins and related families. Trends Biochem Sci 1999, 24(5), 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, S.; Westermann, B. , Genome-wide deletion mutant analysis reveals genes required for respiratory growth, mitochondrial genome maintenance and mitochondrial protein synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genome Biol 2009, 10(9), 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, U.; Lehmann, K.; Stahl, U. , A novel mitochondrial DEAD box protein (Mrh4) required for maintenance of mtDNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Yeast Res 2002, 2(3), 267–276. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Conrad-Webb, H.; Sheng Liao, X.; Perlman, P. S.; Butow, R. A. , Functional Expression of a Yeast Mitochondrial Intron-Encoded Protein Requires RNA Processing at a Conserved Dodecamer Sequence at the 3′ End of the Gene. Mol Cell Biol 1989, 9(4), 1507–1512. [Google Scholar]
- Conrad-Webb, H.; Perlman, P. S.; Zhu, H.; Butow, R. A. , The nuclear SUV3-1 mutation affects a variety of post-transcriptional processes in yeast mitochondria. Nucleic Acids Res 1990, 18(6), 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margossian, S. P.; Li, H.; Zassenhaus, H. P.; Butow, R. A. , The DExH box protein Suv3p is a component of a yeast mitochondrial 3′-to-5′ exoribonuclease that suppresses group I intron toxicity. Cell 1996, 84(2), 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepien, P. P.; Kokot, L.; Leski, T.; Bartnik, E. , The suv3 nuclear gene product is required for the in vivo processing of the yeast mitochondrial 21 s rRNA transcripts containing the r1 intron. Curr Genet 1995, 27, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golik, P.; Szczepanek, T.; Bartnik, E.; Stepien, P. P.; Lazowska, J. , The S. cerevisiae nuclear gene SUV3 encoding a putative RNA helicase is necessary for the stability of mitochondrial transcripts containing multiple introns. Curr Genet 1995, 28, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziembowski, A.; Piwowarski, J.; Hoser, R.; Minczuk, M.; Dmochowska, A.; Siep, M.; van der Spek, H.; Grivell, L.; Stepien, P. P. , The yeast mitochondrial degradosome: its composition, interplay between RNA helicase and RNase activities and the role in mitochondrial RNA metabolism. J Biol Chem 2003, 287(3), 1603–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogowska, A. T.; Puchta, O.; Czarnecka, A. M.; Kaniak, A.; Stepien, P. P.; Golik, P. , Balance between transcription and RNA degradation is vital for Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondria: reduced transcription rescues the phenotype of deficient RNA degradation. Mol Biol Cell 2006, 17(3), 1184–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Séraphin, B.; Simon, M.; Boulet, A.; Faye, G. , Mitochondrial splicing requires a protein from a novel helicase family. Nature 1989, 337(6202), 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bifano, A. L.; Caprara, M. G. , A DExH/D-box protein coordinates the two steps of splicing in a group I intron. J Mol Biol 2008, 383(3), 667–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkowitsch, L.; Chen, D.; Stampfl, S.; Semrad, K.; Waldsich, C.; Mayer, O.; Jantsch, M. F.; Konrat, R.; Bläsi, U.; Schroeder, R. , RNA Chaperones, RNA Annealers and RNA Helicases. RNA Biol 2007, 4(3), 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.; Jarmoskaite, I.; Lambowitz, A. M. , Toward a molecular understanding of RNA remodeling by DEAD-box proteins. RNA Biol 2013, 10(1), 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solem, A.; Zingler, N.; Pyle, A. M. , A DEAD protein that activates intron self-splicing without unwinding RNA. Mol Cell 2006, 24(4), 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, G.; Del Campo, M.; Mohr, S.; Yang, Q.; Jia, H.; Jankowsky, E.; Lambowitz, A. M. , Function of the C-terminal domain of the DEAD-box protein Mss116p analyzed in vivo and in vitro. J Mol Biol 2008, 375(5), 1344–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Campo, M.; Lambowitz, A. M. , Structure of the Yeast DEAD box protein Mss116p reveals two wedges that crimp RNA. Mol Cell 2009, 35(5), 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halls, C.; Mohr, S.; Del Campo, M.; Yang, Q.; Jankowsky, E.; Lambowitz, A. M., Involvement of DEAD-box proteins in group I and group II intron splicing. Biochemical characterization of Mss116p, ATP hydrolysis-dependent and-independent mechanisms, and general RNA chaperone activity. J Mol Biol 2007, 365, (3), 835-855. [CrossRef]
- Linder, P.; Owttrim, G. W. , Plant RNA helicases: linking aberrant and silencing RNA. Trends Plant Sci 2009, 14(6), 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umate, P.; Tuteja, R.; Tuteja, N. , Genome-wide analysis of helicase gene family from rice and Arabidopsis: a comparison with yeast and human. Plant Mol Biol 2010, 73(4), 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lallemand, T.; Leduc, M.; Landès, C.; Rizzon, C.; Lerat, E., An Overview of Duplicated Gene Detection Methods: Why the Duplication Mechanism Has to Be Accounted for in Their Choice. Genes 2020, 11, (9). [CrossRef]
- Keren, I.; Bezawork-Geleta, A.; Kolton, M.; Maayan, I.; Belausov, E.; Levy, M.; Mett, A.; Gidoni, D.; Shaya, F.; Ostersetzer-Biran, O. , AtnMat2, a nuclear-encoded maturase required for splicing of group-II introns in Arabidopsis mitochondria. RNA 2009, 15(12), 2299–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostersetzer-Biran, O. , Respiratory complex I and embryo development. J Exp Bot 2016, 67(5), 1205–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, K.; Obata, T.; Feher, K.; Bock, R.; Fernie, A. R.; Meyer, E. H. , Complete mitochondrial complex I deficiency induces an up-regulation of respiratory fluxes that is abolished by traces of functional complex I. Plant Physiol 2015, 168(4), 1537–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, H.-P.; Binder, S.; Brennicke, A.; Eubel, H.; Fernie, A. R.; Finkemeier, I.; Klodmann, J.; König, A.-C.; Kühn, K.; Meyer, E.; Obata, T.; Schwarzländer, M.; Takenaka, M.; Zehrmann, A. , The life of plant mitochondrial complex I. Mitochondrion 2014, 19, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, M.; Sugiyama, M. , Genetic analysis of adventitious root formation with a novel series of temperature-sensitive mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana. Development 2003, 130(23), 5637–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, M.; Sugiyama, M. , A novel plant-specific family gene, ROOT PRIMORDIUM DEFECTIVE 1, is required for the maintenance of active cell proliferation. Plant Physiol 2006, 140(2), 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edris, R.; Sultan, L. D.; Best, C.; Mizrahi, R.; Weinstein, O.; Chen, S.; Kamennaya, N. A.; Keren, N.; Zer, H.; Zhu, H.; Ostersetzer-Biran, O. , Root Primordium Defective 1 Encodes an Essential PORR Protein Required for the Splicing of Mitochondria Encoded Group II Introns and for Respiratory Complex I Biogenesis. Plant Cell Physiol 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y. H. , How effective is T-DNA insertional mutagenesis in Arabidopsis? Journal of Biochemical Technology 2008, 1(1), 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Castandet, B.; Choury, D.; Bégu, D.; Jordana, X.; Araya, A. , Intron RNA editing is essential for splicing in plant mitochondria. Nucleic Acids Res 2010, 38(20), 7112–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldenkott, B.; Yamaguchi, K.; Tsuji-Tsukinoki, S.; Knie, N.; Knoop, V. , Chloroplast RNA editing going extreme: more than 3400 events of C-to-U editing in the chloroplast transcriptome of the lycophyte Selaginella uncinata. RNA 2014, 20(10), 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, I. D.; Schallenberg-Rudinger, M.; Takenaka, M.; Mireau, H.; Ostersetzer-Biran, O. , Plant organellar RNA editing: what 30 years of research has revealed. Plant J 2020, 101(5), 1040–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, A.; Kindgren, P.; Colas des Francs-Small, C.; Kazama, T.; Tanz, S. K.; Toriyama, K.; Small, I. , AEF1/MPR25 is implicated in RNA editing of plastid atpF and mitochondrial nad5, and also promotes atpF splicing in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant J 2015, 81(5), 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambowitz, A. M.; Zimmerly, S. , Mobile group II introns. Annu Rev Genet 2004, 38(1), 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, F.; Lang, B. F. , Mitochondrial class II introns encode proteins related to the reverse transcriptases of retroviruses. Nature 1985, 306(6029), 641–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
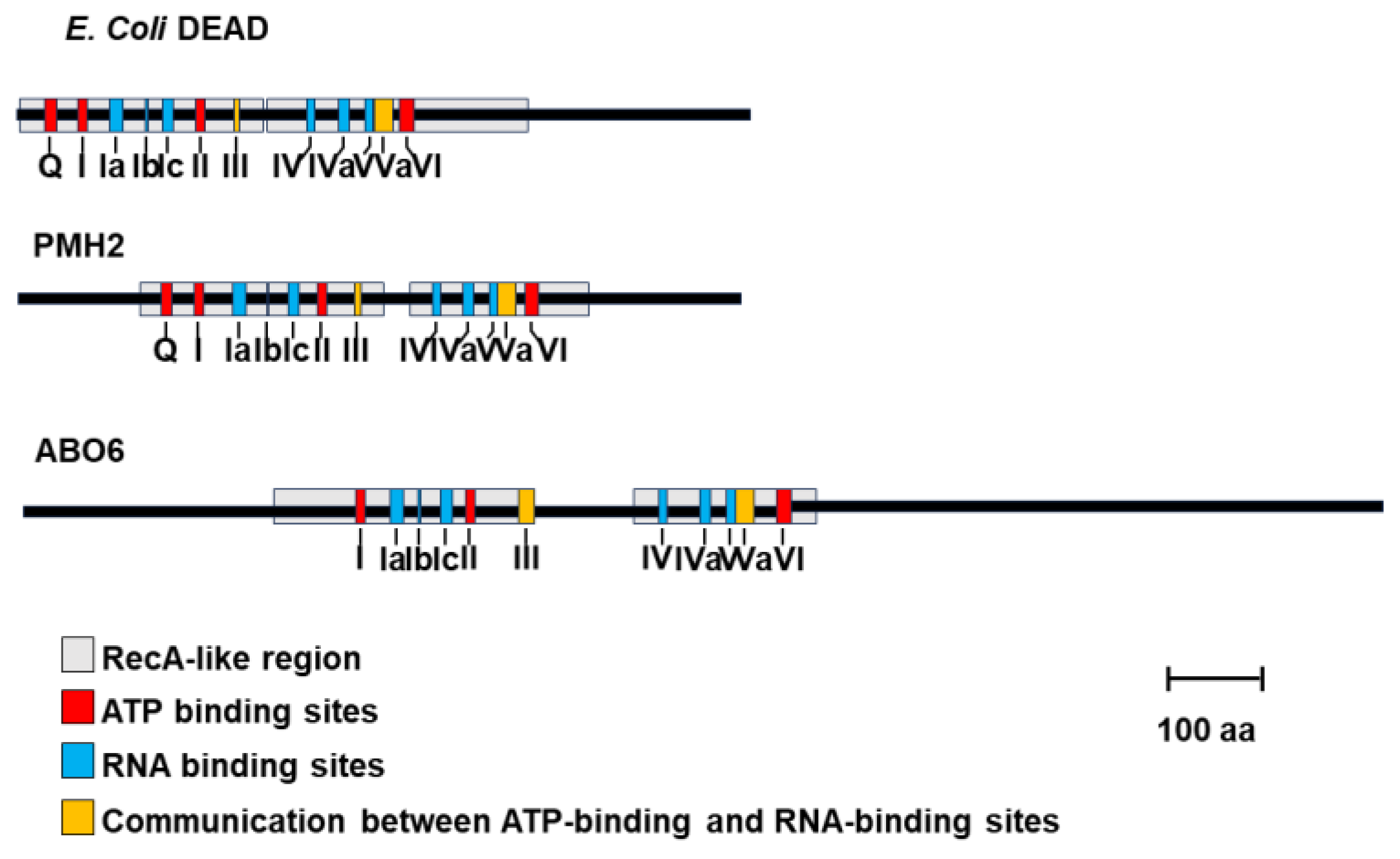
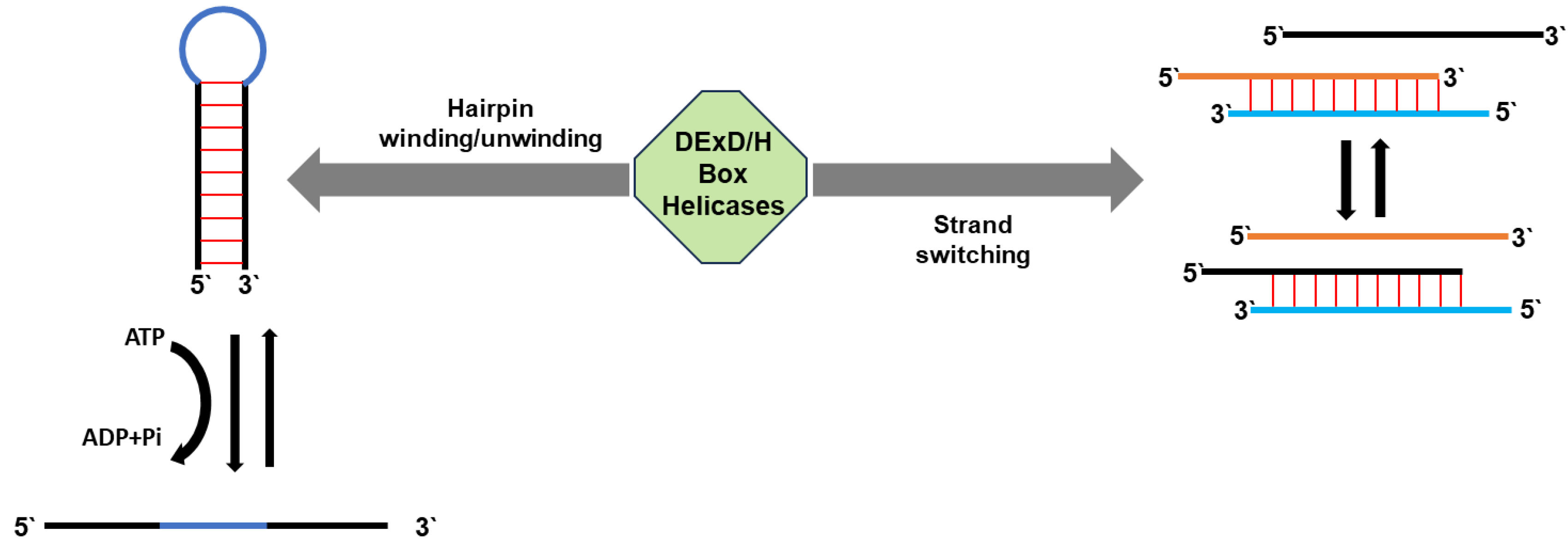
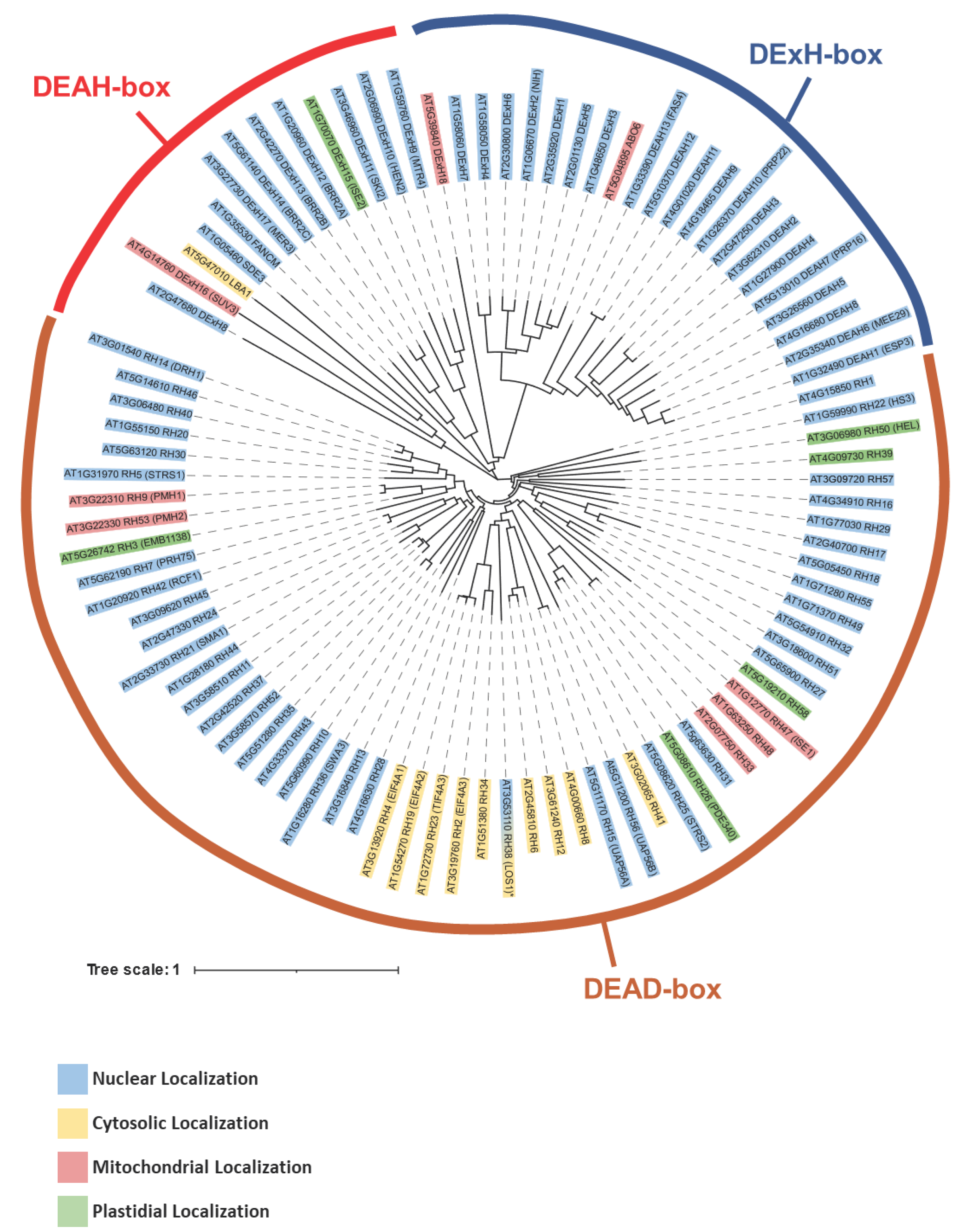
| RNA helicase | Gene I.D. | Organism*1 | Specific role(s) in mt-RNA metabolism | REFs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRC3 | S000002740 | S.c. | mtDNA maintenance or stability | [43] |
| MRH4 | S000003032 | S.c. | Translation, ribosome biogenesis | [44] |
| MSS116 | S000002602 | S.c. | Splicing (group I and II introns) | [45] |
| SUV3 | S000005950 | S.c. | Nucleolysis (degredosomal factor) | [46,47] |
| ABO6 | At5g04895 | A.t. | Splicing (group II introns) | [48] |
| ISE1/EMB1586 | At1g12770 | A.t. | T.B.D*2., affects mitochondria biogenesis | [49] |
| DExH8 | At5g39640 | A.t. | T.B.D., predicted to the mitochondria*3 | --- |
| PMH1 | At3g22310 | A.t. | T.B.D., found in large RNP complexes*4 | [50] |
| PMH2 | At3g22330 | A.t. | Splicing (group II introns) | [35,50,51] |
| RH33 | At2g07750 | A.t. | Splicing (group II introns) | This study |
| RH48 | At1g63250 | A.t. | T.B.D., homolog of Zm-RH48 | --- |
| RH48 | GRMZM2G171801 | Z.m. | Splicing (group II introns) | [52] |
| SUV3 (At) | At4g14790 | A.t. | T.B.D., RNA metabolisms | [53] |
| SUV3 (Os) | GQ982584 | O.s. | T.B.D., DNA/RNA metabolisms | [54,55] |
| RECG1 | At2g01440 | A.t. | T.B.D., mtDNA and cpDNA maintenance | [56] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





