1. Introduction
Apis mellifera, western honeybee, play a crucial role in the process of pollination and stability of the ecosystem [
1,
2]. Basically, they produce economic and health benefit products such as honey, royal jelly, propolis, and beeswax. Unfortunately, the rate of honeybee colony losses has been increasing annually in many countries in the world [
3,
4,
5]. According to a collaborative survey conducted by the Rural Development Administration, Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency, local authorities, and Korean Beekeeping Association in the Republic of Korea (ROK), 416,409 beehives disappeared between October 2021 and March 2022. Numerous factors influence the health of honeybee colonies, and one of devastating factors to colony loss is parasitic infection, especially mite species [
1,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12]. In the ROK, significant harm to honeybee colonies is attributed to
Varroa mite [
1,
11,
13,
14]. Other harmful mite species have been identified morphologically and/or genetically, including
Tropilaelaps mercedesae,
Tyrophagus curvipenis, and
Acarapis mites in the ROK [
12,
14]. However, there has been no research about detecting
Carpoglyphus lactis within the Korean honeybee population.
C. lactis, commonly known as the cheese mite or milk mite, belongs to the genus
Carpoglyphus within the family Carpoglyphidae of Astigmata [
15,
16,
17]. This mite is primarily associated with cheese and other milk products [
16]. The previous reports mainly focus on the relationship between the mite and milk products, as well as its impact on cheese quality. The
C. lactis species has been observed in the Holarctic, Oriental, Australian, and Indian regions [
15,
18,
19,
20,
21]. Additionally,
C. lactis mites are known to be relatively common in beehives among the observed regions. They are primarily found in stored pollen and aged beehives, potentially posing a threat to stored honey [
22]. Moreover, they are present in beehive debris, in hive materials, on dead bees, and on beehive frames, serving as a source of pollen, honey, and essential bee substances stored in queen bee cells [
23,
24]. The damage caused by these mites is particularly severe for beehives stored during the winter season. Germany and the United States highlight widespread cases of beehive destruction due to
C. lactis mites during winter storage [
20,
25,
26]. In Zander, Germany, in 1947, 250 beehives were destroyed by
C. lactis mites in a single winter storage area [
27]. In Alabama, the US, beehives were found heavily infected with
C. lactis mite after winter storage by Baker and Delfinado, 1978 [
21].
C. lactis mites devastate honeybee combs, consuming stored pollen and polluting the hive with a brownish-yellow powder composed of mite carcasses, debris, and pollen. Research on the detection rate and prevalence of this mite on honeybees is still limited. Considering the severity of
C. lactis mite on honeybees, understanding their presence and prevalence in honeybee colonies is crucial for beekeepers.
This study aimed to identify the emergence of C. lactis in honeybee colonies in the ROK in 2023. The detection rate of this mite was surveyed across 9 provinces in the ROK. This marks the initiation of investigations for future reference and encourages the development of effective management strategies against C. lactis in honeybee colonies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Samples and Detection of Astigmatid Mites in Honeybees
Honeybee samples were collected from 9 provinces (Gangwon, Gyeonggi, Chungcheonnam, Chungcheonbuk, Gyeongsangnam, Gyeongsangbuk, Jeollanam, Jeollabuk, and Jeju) in the ROK (
Figure 1). The honeybee samples were regularly collected throughout the year 2023 from non-migrating honeybee colonies. Honeybee samples were collected from the hive of each opened colony; subsequently, the comb was taken out after carefully observing the comb without the queen bee. A total of 615 honeybee colonies from 124 apiaries were sampled to investigate the presence of Astigmatid mites. The worker bees (
n = 10~30) were collected in 50 mL Falcon tubes from colonies in each apiary. Larvae sampling was collected from three random locations within the hive using forceps, checking 10 larvae at each site. Samples were collected using sterile tools to prevent contamination and directly placed into 50 mL Falcon tubes. Each tube was labelled with a unique identifier to ensure sample traceability throughout the testing process. To preserve the integrity of the collected samples, they were promptly transferred to a temperature-controlled storage facility at –20 °C. The honeybee samples were used to assess temperature-dependent appearance patterns. Concurrently, these samples were used to evaluate the prevalence, diversity, and simultaneous occurrence of pathogens and Astigmatid mites. The samples were divided into two portions; the first was used for Astigmatid mite examination under a dissecting microscope, and the remained one was used for total nucleic extraction in polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The comb was collected in positive honeybee colonies for mite examination under a dissecting microscope. As this study only involved honeybees, which are invertebrates not covered by most ethical regulations related to animal research, formal ethical approval was not required.
2.2. Total Nucleic Acid Extraction
The honeybee samples were homogenized using a Precellys 24 tissue homogenizer (Bertin Instruments, Montigny-le-Bretonneux, France) in three cycles of 15 s at a speed of 5,000 rpm in 1 mL of phosphate-buffered saline solution. Subsequently, a mixture of 200 μL of lysis buffer and 20 μL of proteinase K solution was added to the homogenized sample, and the resulting mixture was incubated at 56 °C for 10 min. The total nucleic acids were extracted using the Maxwell® RSC automated system according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Finally, 60 μL of purified total nucleic acids were employed to detect honeybee pathogens. The total nucleic acids from the honeybee and control samples were stored at –20 °C until further analysis.
2.3. Amplification of Astigmatid Mite-Specific Genes Using Polymerase Chain Reaction
DNA sequence-based identification has proven to be the most reliable approach for the species determination. Cytochrome
c oxidase subunit I (
COI) gene has been successfully used in the species identification and phylogenetic studies of mites [
28]. The primer pairs used in this experiment were described in
Table 1.
The total reaction volume (20 µL), including 1 µL of DNA, 1 µL of each primer (10 pmol), and 17 µL ddH2O, was used by AccuPower® PCR PreMix and Master Mix (Bioneer Corp., Daejeon, ROK). The PCR thermal cycling conditions were as per those by Nguyen et al. [
12]: 94°C (5 min); 5 cycles of 94°C (20 s), 52°C (30 s), and 68°C (30 s); followed by 5 cycles of 94°C (20 s), 50°C (30 s), and 68°C (30 s); 30 cycles of 94°C (20 s), 48°C (30 s), and 68°C (30 s); 30 cycles of 94°C (20 s), 46°C (30 s), and 68°C (30 s); and a final extension step at 68°C (5 min). The amplified products corresponding to the
COI gene segment of
C. lactis in the honeybee colonies were visualized using 1% agarose gel electrophoresis, with a determined size of 1,242 bp. Subsequently, the PCR products were purified and sequenced by Cosmogenetech Co., Ltd. (Seoul, ROK). To verify the presence of
C. lactis mite and assess its genetic diversity within Korean honeybees, the positive control was specifically designed by cloning the
COI gene from a known Korean
C. lactis mite.
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis and Statistical Analysis
The sequences of the
COI gene segments of
C. lactis mites amplified from different regions were sequenced and compared with the
COI gene of this mite available in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Subsequently, the sequences were aligned using ClustalW multiple alignment in BioEdit version 7.2.5 [
29]. A species phylogenetic tree was constructed using MEGA11 based on the nucleotide sequences of the
COI gene [
30]. Simultaneously, a phylogenetic tree was built according to the calculated values obtained from Kimura’s two-parameter distance method by neighbour-joining with 1,000 bootstrap replicates and maximum-likelihood method. Three sequences of
C. lactis mites isolated from China (NCBI accession nos.: NC_048990.1 and MN073839.1) and the UK (NCBI accession no. KY922482.1) were chosen as representative sequences.
The values were evaluated using the likelihood ratio Chi-square test to measure the strength between the variables of the two groups. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Identification of Carpoglyphus lactis Mites in Honeybee Colonies
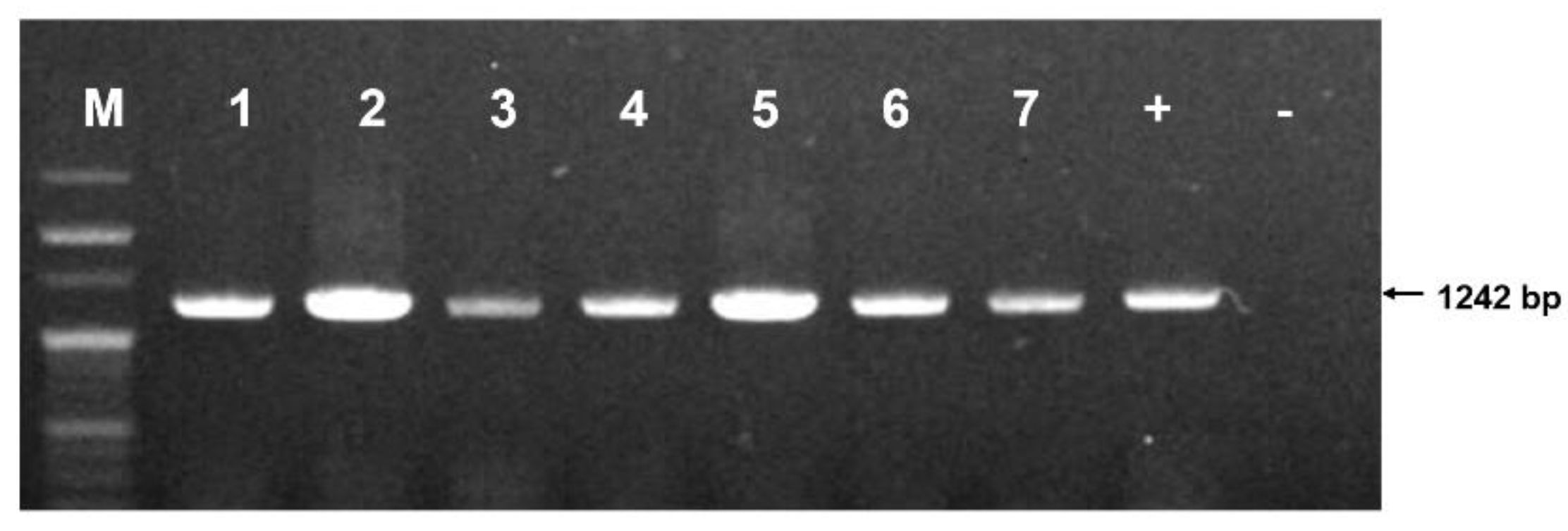
Among 615 honeybee colonies sampled from 124 apiaries, PCR analysis successfully identified the presence of the
C. lactis mite in a subset of colonies. The characteristic 1,242 bp PCR product confirmed the presence of the mite (
Figure 2).
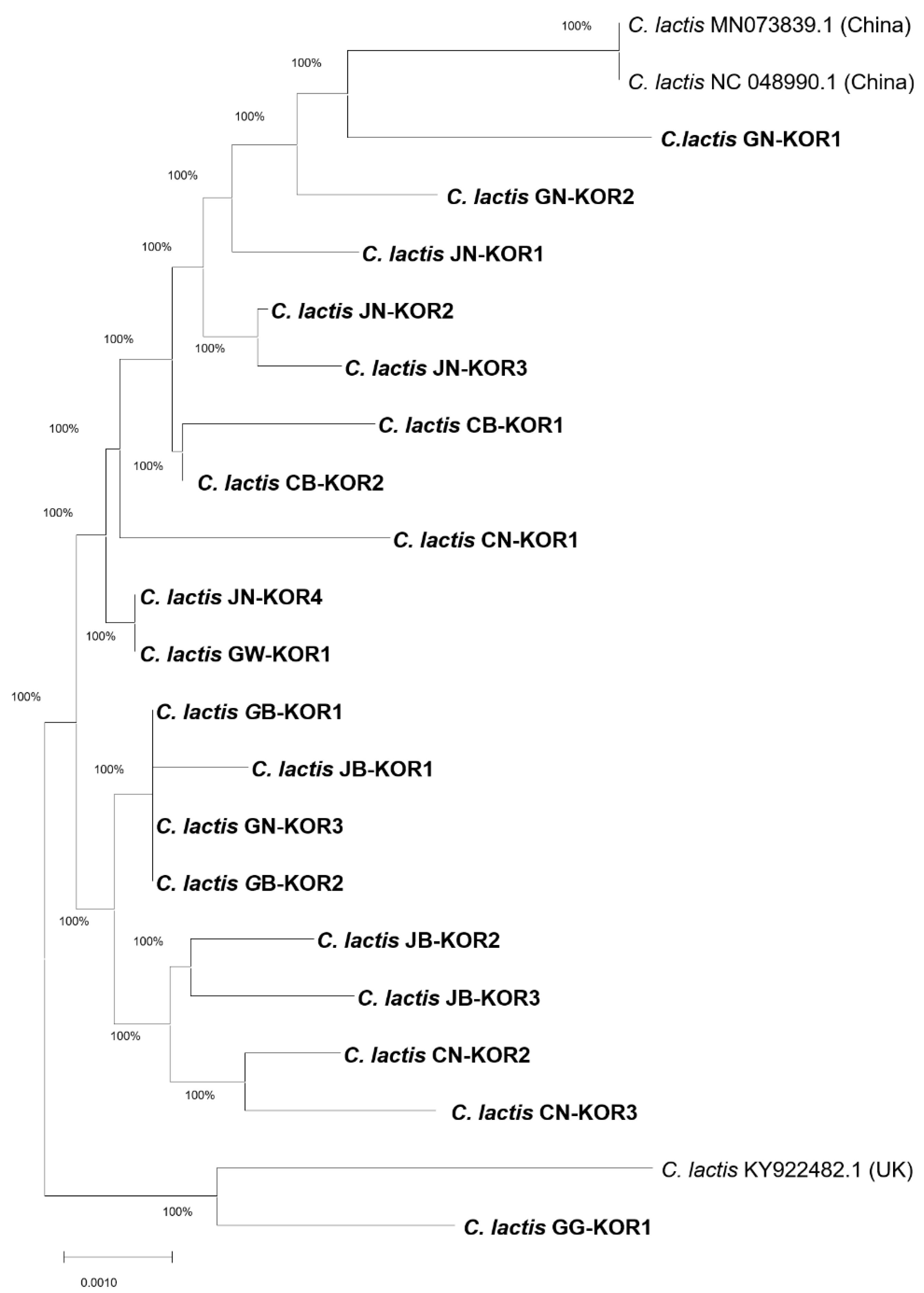
Comparative analysis of the gene segment sequences of
C. lactis mites compared with the GenBank database (blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi) unveiled a significant level of nucleotide similarity (99.1~99.5%) between those from this study and those from China (NCBI accession No. NC_048990.1) and the UK (NCBI accession no. KY922482.1) (
Figure S1). Variations in the
COI gene sequence of
C. lactis, involving A to G and C to T at identical positions from the UK, were identified. These mutation positions exhibited remarkable consistency among strains isolated nationwide, resembling those from the UK (
Figure S1). A phylogenetic tree, constructed by the
COI gene sequence of
C. lactis (
Figure 3), demonstrated high similarity (99.1~99.5%) between
COI gene sequences isolated in Korean honeybee colonies and those from the UK and China. Our analysis of the
COI gene sequence in honeybee samples revealed the widespread presence of
C. lactis in honeybee colonies across 9 provinces in the ROK.
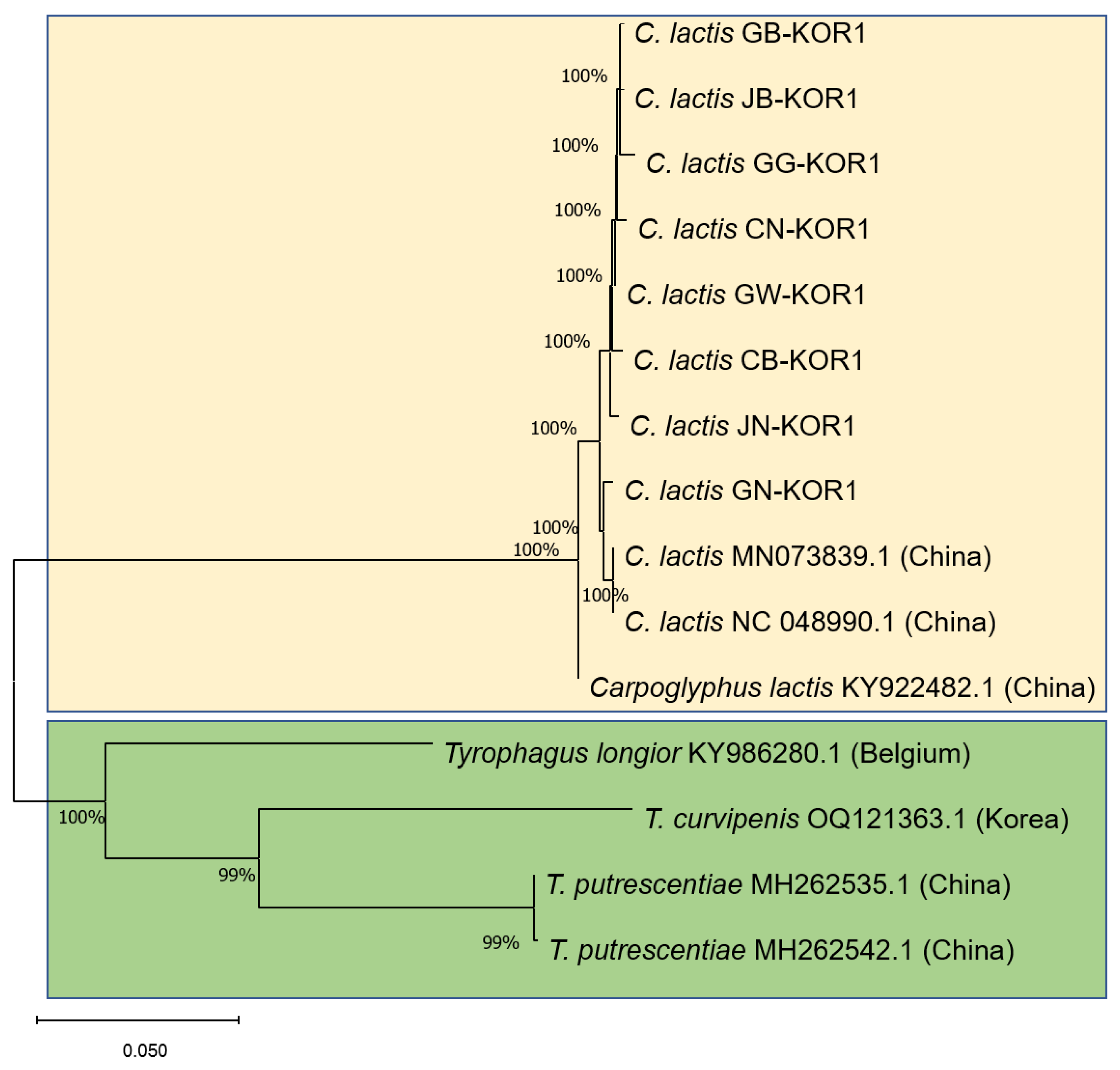
3.2. Similarities of COI Gene Sequence of Astigmatid Mites in Honeybee Colonies
Astigmatid mites are characterized by their tiny size and detrimental impact on honeybee colonies. Species identification was conducted by analysing the phylogeny, utilizing the
COI gene sequences of
C. lactis compared to confirm mite species found in honeybee colonies (
Figure 4). Our phylogenetic analysis, based on the
COI gene sequences belonging to two families, aligns closely with current morphological classifications. The mites found in honeybee apiaries belong to the hyporder Astigmatid; however, within this order, the
C. lactis mite forms a distinct and separate branch with
Tyrophagus mites. The first branch contains
C. lactis of the family Carpoglyphidae, while the remaining three species,
T. longior in Belgium (NCBI accession no. KY986280.1),
T. putrescentiae in China (NCBI accession nos.: MH262535.1 and MH262542.1), and
T. curvipenis in ROK (NCBI accession no. OQ121363.1). The nucleotide of
C. lactis mite isolated from Korean honeybee colonies exhibited a high nucleotide similarity of 80.2% with
Tyrophagus mites.
3.3. Prevalence of Carpoglyphus lactis Mite in Korean Honeybee Colonies
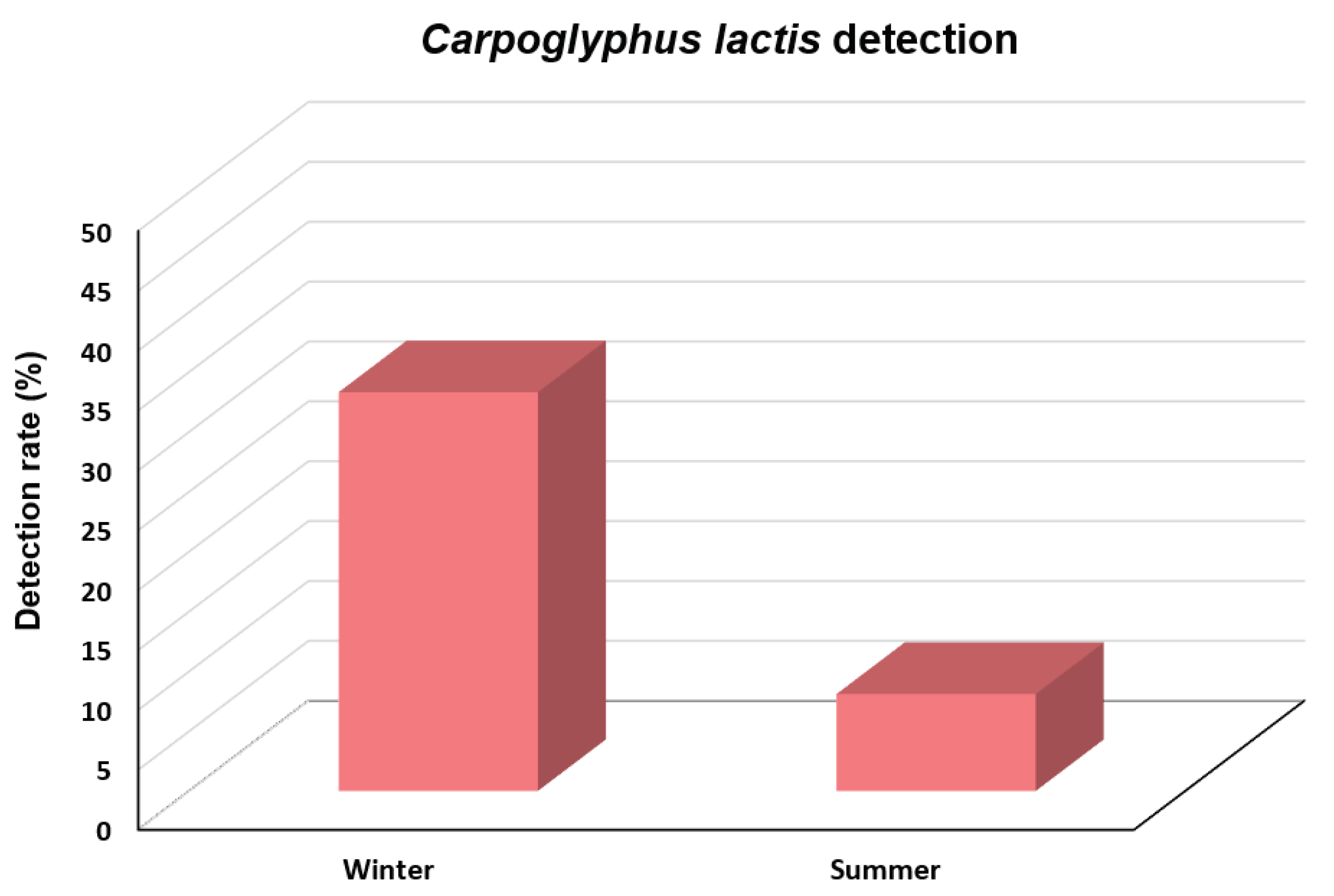
We investigated
C. lactis mite in honeybee colonies collected during winter and summer in ROK in 2023 (
Figure 5). The results indicated a significantly higher detection rate of this mite during winter compared to summer (χ2 = 62.713,
df = 1,
p < 0.001). The detection rate of
C. lactis in 267 colonies from 66 apiaries collected during winter was 33.3%, whereas this rate during summer was only 8.1% in 348 colonies from 58 apiaries. The highest detection rate was observed in March, with the prevalence rate of 74.7% among the 75 honeybee colonies collected from 23 apiaries.
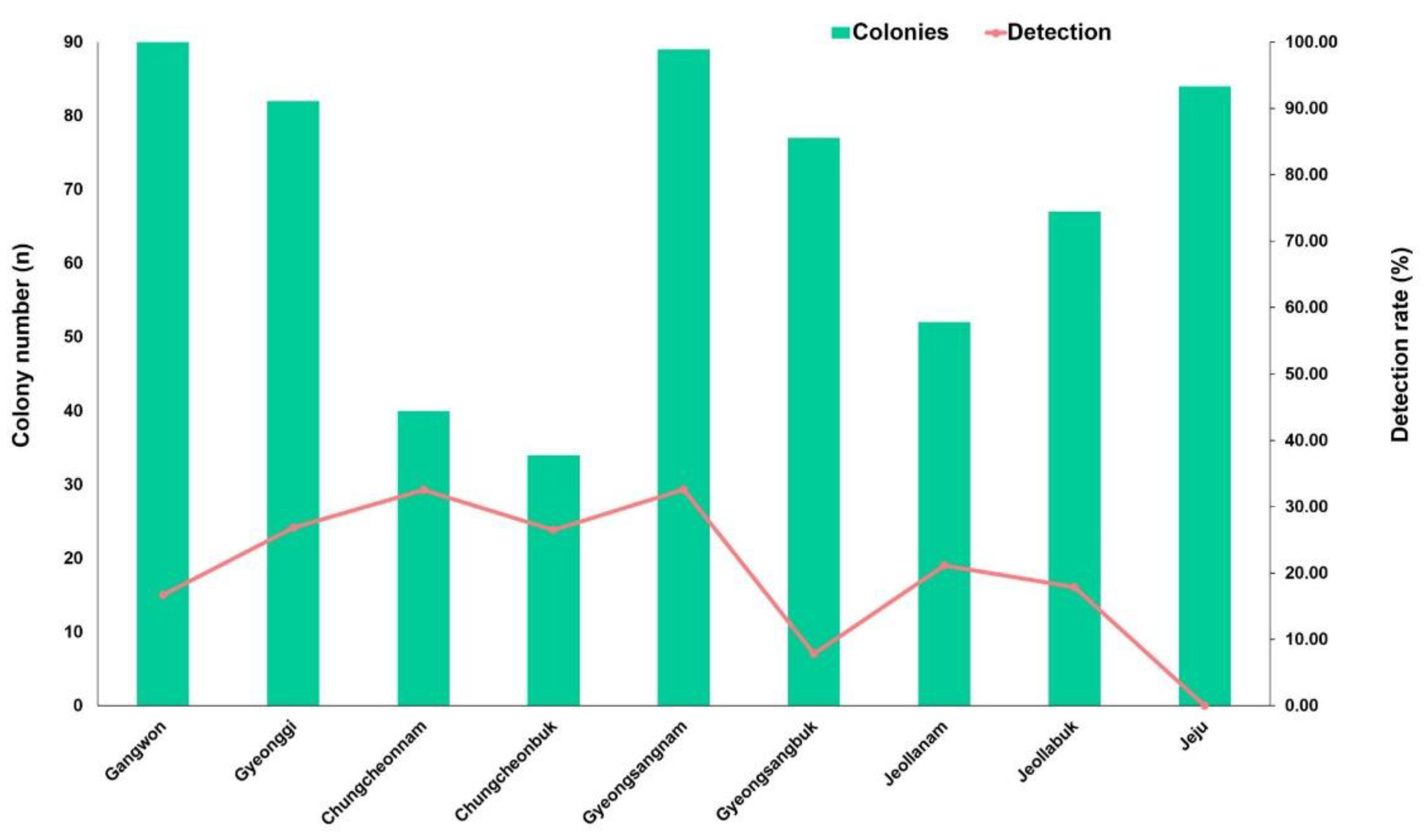
As shown in
Figure 6,
C. lactis mites were found in 8 out of 9 provinces. This mite was not detected in any of the surveyed apiaries in the Jeju province. The detection rates of
C. lactis in different provinces were as follows: Gangwon at 16.7% (15/90), Gyeonggi at 26.8% (22/82), Chungcheongbuk at 26.5% (9/34), Chungcheongnam at 32.5% (13/40), Gyeongsangbuk at 7.8% (6/77), Gyeongsangnam at 32.6% (29/89), Jeollabuk at 17.9% (12/67), and Jeollanam at 21.2% (11/52). The highest infection rate was observed in the provinces of Chungcheonnam and Gyeongsangnam.
4. Discussion
This study investigated the molecular detection and prevalence of C. lactis mites in honeybee colonies in the ROK. This finding provides valuable insight into the occurrence, prevalence, and phylogenetic position of C. lactis mites in the ROK, highlighting their significance as a potential pest in honeybee colonies.
We employed molecular techniques to identify
C. lactis mites in honeybee colonies. To achieve this, we designed specific primers targeting the
COI gene of
C. lactis mites, with an amplicon size of 1,242 bp, to minimize non-specific binding of PCR (
Table 1). Successful amplification of the targeted
COI gene segment confirmed the presence of
C. lactis mites in the tested colonies. The subsequent sequencing and comparative analysis of these gene segments with reference sequences in GenBank database revealed a substantial nucleotide similarity with previously isolated
C. lactis strains from China and the UK, further supporting the accurate identification of the mite species.
Honeybee mites constitute one of the major factors causing harm to honey bee colonies globally. They parasitize bees and act as disease vectors within the population. Consequently, they adversely impact the health and alter the healthy behaviour of honeybees. As the life cycle of the mite occurs within the beehive, the dense population of these parasites can lead to contaminated honeybee products, reduced food resources, and compromised honeybee health. Recently,
T. curvipenis mite was reported in Korean honeybee apiaries [
12].
C. lactis and
Tyrophagus mites have been found in beehives that primarily feed on stored pollen and other organic materials [
22,
27,
31]. In this study, we detected the new
C. lactis mite in the Korean honeybee in 8 of 9 provinces in the ROK. The nucleotide of
COI gene of
C. lactis mite is similar to that of
Tyrophagus mite as 80.2%. Building on prior research by Dabert et al. [
32], our analysis using the
COI gene further supports the close relationship between
C. lactis and
Tyrophagus mites within the suborder Astigmata. Notably, Dabert et al. [
32] also found these two species to cluster together in their phylogenetic tree of Arachnid mites, constructed using the 18S rDNA gene. In 2023, Bowman reported that
C. lactis and
Tyrophagus mites can co-occur in UK beehives [
15]. The spread of diseases within bee populations infested with these parasites is increasing; hence, effective control measures are challenging. Therefore, investigating the types of parasitic mites and assessing their prevalence is crucial to sustain honeybee health and prevent severe propagation of harmful parasites.
The prevalence analysis provided valuable insights into the occurrence and distribution of
C. lactis mites in honeybee colonies in the ROK. Our survey was conducted in 2023, with samples collected during winter and summer across 9 provinces nationwide. Survey results indicated the presence of this mite species in 8 of 9 provinces, with temporal variations in the infection rate potentially influenced by factors such as environmental conditions and fluctuations in the honeybee population. Our study also revealed a higher infection rate during winter. The initial detection of
C. lactis in overwintering honeybee colonies was first reported in Germany [
27], suggesting a robust development of
C. lactis mite at lower temperature, particularly within the beehive, making it an ideal habitat for this mite species. This is a significant factor contributing to honeybee colony damage during winter.
Furthermore, we found its significant presence in a considerable portion of the sampled honeybee population in the ROK. The C. lactis mites were not detected in honeybee apiaries only in Jeju province among the surveillance areas. In addition, identifying C. lactis in both honeybee and beeswax samples indicates that C. lactis mites may have a substantial impact on the honeybee health environmentally as well as individually. A more profound investigation into the life cycle of C. lactis mites in honeybee colonies is necessary to better understand the effects of mite infestation on honeybee populations and overall hive health. This knowledge will inform timely strategies and protective measures for the sustainability of beekeeping in the ROK.
Although our study successfully identified C. lactis mites in Korean honeybee colonies, some limitations warrant consideration. Identifying C. lactis mites were not our initial objective, leading to delayed sampling for morphological confirmation during late winter season. Winter sampling focused solely on bees, and excluding mite examination in comb or beehive, thus precluding direct morphological confirmation of C. lactis. Summer sampling across different bee stages and materials also yielded no detections, possibly due to low prevalence in summer or dead mite presence. Further investigation using alternative methods are ongoing. The detected C. lactis mites using PCR solely confirms its presence and doesn’t necessarily reflect active infection. Further research is need to assess the impact of different infection levels and potential harm to bee health and honey production. Despite these limitations, our study provides valuable initial insights into the presence of C. lactis in Korean apiaries. Further research addressing these limitations will be crucial for understanding its potential impact on honeybee health and developing effective management strategies.
5. Conclusions
This study provides the first report of C. lactis mites in honeybee colonies within the ROK. Employing molecular detection techniques, we revealed a widespread distribution of C. lactis across eight out of nine provinces surveyed. Furthermore, our results demonstrated a seasonal variation in prevalence, with higher detection rates observed during winter. Phylogenetic analysis confirmed the distinct identity of C. lactis within the suborder Astigmata and its near relationship with Tyrophagus mites. These findings highlight the potential threat posed by C. lactis to Korean honeybee health and emphasize the need for further research. Future investigations should focus on elucidating the impact of C. lactis infestation on bee colony health and productivity, particularly during winter.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Figure S1: Multiple alignments of the differing nucleotide positions in the COI gene of Carpoglyphus lactis. A comparison was conducted between the COI sequence (1,137 nucleotides) of C. lactis mite isolated from the ROK in this study and the published sequence in GenBank. The highlighted blue frame signified shared nucleotide differences between the isolated strains and those from China (NCBI accession nos.: NC_048990.1, MN073839.1) and the UK (NCBI accession no. KY922482.1).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T-T.N., M-S.Y. and Y.S.C.; methodology, T-T.N. and Y.S.C.; software, T-T.N.; Collected honeybee samples and isolated nucleic acids, H-S.L., S.Y.Y., S-J.L. and S-K.S.; writing—original draft preparation, T-T.N.; writing—review and editing, M-S.Y., J.K. and Y.S.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency, the Republic of Korea (Project No. N-1543081-2021-25-03).
Data Availability Statement
All data are provided in the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
Our heartfelt thanks go out to the beekeepers who facilitated our sampling process. We extend our appreciation to all the members of our laboratories for their unwavering dedication and diligent efforts.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Truong, A-T.; Yoo, M-S.; Seo S.K.; Hwang, T.J.; Yoon, S-S.; Cho, Y.S. Prevalence of honey bee pathogens and parasites in South Korea: A five-year surveillance study from 2017 to 2021. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13494. [CrossRef]
- Klein, A-M.; Vaissière, B.E.; Cane JH, Steffan-Dewenter I, Cunningham SA, Kremen C, et al. Importance of pollinators in changing landscapes for world crops. Proc. R. Soc. B 2007, 274, 303–313. [CrossRef]
- Mutinelli, F.; Pinto, A.; Barzon, L.; Toson, M. Some Considerations about Winter Colony Losses in Italy According to the Coloss Questionnaire. Insects 2022, 13, 1059. [CrossRef]
- Johannesen, J.; Wöhl, S.; Berg, S.; Otten, C. (2022). Annual fluctuations in winter colony losses of Apis mellifera L. are predicted by honey flow dynamics of the preceding year. Insects 2022, 13, 829.
- Gray, A.; Adjlane, N.; Arab, A.; Ballis, A.; Brusbardis, V.; Bugeja Douglas, A.; Cadahia, L.; Charriere, J.D.; Chlebo, R.; Coffey, M.F.; et al. Honey bee colony loss rate in 37 countries using the COLOSS survey for winter 2019-2020: the combined effects of operation size, migration and queen replacement. J. Api. Res. 2023, 62, 204-210.
- Chantawannakul, P.; de Guzman, L.I.; Li, J.; Williams, G.R. Parasites, pathogens, and pests of honeybees in Asia. Apidologie 2016, 47, 301–324. [CrossRef]
- Chantawannakul, P.; Ramsey, S.; Khongphinitbunjong, K.; Phokasem, P. Tropilaelaps mite: an emerging threat to European honey bee. Curr. Opin. Insect. Sci. 2018, 26, 69–75. [CrossRef]
- Denmark, H.A.; Cromroy, H.L.; Sanford, M.T. Honey bee tracheal mite, Acarapis woodi (Rennie) (Arachnida: Acari: Tarsonemidae). University of Florida, IFAS Extension. 2000. [CrossRef]
- Sammataro, D.; Gerson, U.; Needham, G. Parasitic mites of honey bees: life history, implications, and impact. Annu. Rev. Ento. 2000, 45, 519–548. [CrossRef]
- Emmanouel, N.G.; Pelekassis, C.D.; Santas, L.A. Harmful mesostigmatic mites ectoparasitic to honey bees. Entomol. Hell. 1983, 1, 17–23. [CrossRef]
- Truong, A-T.; Yoo, M-S.; Yun, B-R.; Kang, J.E.; Noh, J.; Hwang, T.J.; Seo, S.K.; Yoon, S-S.; Cho, Y.S. Prevalence and pathogen detection of Varroa and Tropilaelaps mites in Apis mellifera (Hymenoptera, Apidae) apiaries in South Korea. J. Apicul. Res. 2023, 62, 804–812.
- Nguyen, T-T.; Yoo, M-S.; Truong, A-T.; Lee, J.H.; Youn, S.Y.; Lee, S-J.; Kim, D-H.; Yoon, S-S.; Cho, Y.S. First identification of Tyrophagus curvipenis (Acari: Acaridae) and pathogen detection in Apis mellifera colonies in the Republic of Korea. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9469. [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.; Lee, M.L. Beekeeping in Korea: Past, present, and future challenges. In: Chantawannakul P, Williams G, Neumann P, editors. Asian Beekeeping in the 21st Century. Singapore: Springer; 2018. p. 175–197.
- Ahn, A.J.; Ahn, K.S.; Noh, J.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Yoo, M.S.; Kang, S.W.; Yo, D.H.; Shin, S.S. Molecular prevalence of Acarapis mite infestations in honey bees in Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 2015, 53, 315–320. [CrossRef]
- Bowman, C. Variation in the trophic morphology of Astigmatid mites common in UK beehives. Acarologia 2023, 63, Suppl:4–16. [CrossRef]
- Hubert, J.; Nesvorna, M.; Kopecký, J.; Ságová-Marečková, M.; Poltronieri, P. Carpoglyphus lactis (Acari: Astigmata) from various dried fruits differed in associated micro-organisms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 118, 470–484. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z. A new species of Carpoglyphidae from China (Acarina: Acaroidea). J. Jiang. Univ. 1991, 15, 82–86.
- Chmielewski, W. Morphological and bio-ecological characteristics of Carpoglyphus lactis found in natural honey, warehouses and beehives. Pszczelnicze Zeszyty Naukowe. 1970, 14, 109–127.
- Clark, J.M. A new species of Carpoglyphus (Astigmatina: Carpoglyphidae) from the bark of black beech (Nothofagus) honeydew in New Zealand. Int. J. Acarol. 2010, 36, 453–459. [CrossRef]
- Haragsim, O.; Samšiňák, K.; Vobrázková, E. The mites inhabiting the beehives in ČSR. Z. Angew. Entomol. 1978, 87, 52–67.
- Vijayakumar, K.; Muthuraman, M.; Jayaraj, R. Infestation of Carpoglyphus lactis (Linnaeus)(Acari: Carpoglyphidae) on Trigona iridipennis (Apidae: Meliponinae) from India. Sch. J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 3, 25–28.
- Baker, E.; Delfinado, M. Notes on the driedfruit mite Carpoglyphus lactis (Acarina: Carpoglyphidae) infesting honeybee combs. J. Apicul. Res. 1978, 17, 52–54. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z-Q. New Zealand records of Carpoglyphus lactis (Acari: Carpoglyphidae). Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2012, 17, 239–240. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z-Q. The dried fruit mite Carpoglyphus lactis (Acari: Carpoglyphidae) is a suitable alternative prey for Amblyseius herbicolus (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2021, 26, 2167–2176. [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.M. The mites of stored food and houses her majesty's stationery office. 2nd ed.; London, UK, 1976.
- Chmielewski, W. Bionomics of Carpoglyphus lactis (Acari: Carpoglyphidae) on honey. In Ecology and Evolution of the Acari, 3rd ed.; Bruin, J., van der Geest, L.P.S., Sabelis, M.W., Eds.; Spinger: Dordrecht, Netherlands, 1999; pp. 423–424.
- Zander, E. Handbook of beekeeping in individual representations. Diseases and pests of adult bees. Stuttgart: Verlag Eugen Ulmer, 1947.
- Yang, B.; Cai, J.; Cheng, X. Identification of astigmatid mites using ITS2 and COI regions. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 108, 497–503. [CrossRef]
- Hall, T. BioEdit version 7.0.0. 2004. Distributed by the Author, website. Available online: www.mbio.ncsu.edu/BioEdit/bioedit.html.
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [CrossRef]
- Chmielewski, W. Stored products mites (Acaroidea) in Polish bee hives. In Modern acarology, proceedings of the 8 International Congress of Acarology, held in Ceske Budejovice, Czechoslovakia, 6-11 August 1990; Dusbabek, F., Bukva, V., Eds; SPB Academic Publishing bv: The Hague, Netherlands. 1991; 615–619.
- Dabert, M.; Witalinski, W.; Kazmierski, A.; Olszanowski, Z.; Dabert, J. Molecular phylogeny of acariform mites (Acari, Arachnida): Strong conflict between phylogenetic signal and long-branch attraction artifacts. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010, 56, 222–241. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).