Submitted:
08 March 2024
Posted:
12 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Cultures
2.2. Database Analysis
2.3. Cell Treatments
2.3.1. Photodynamic Treatment
2.3.2. Chemotherapeutic Treatments
2.3.3. H151 (STING Inhibitor) Treatment and PDT
2.4. Cell Viability Assay
2.5. Generation of IFN-1 Pathway Reporter Human Melanoma Cell Line
2.6. Flow Cytometry
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
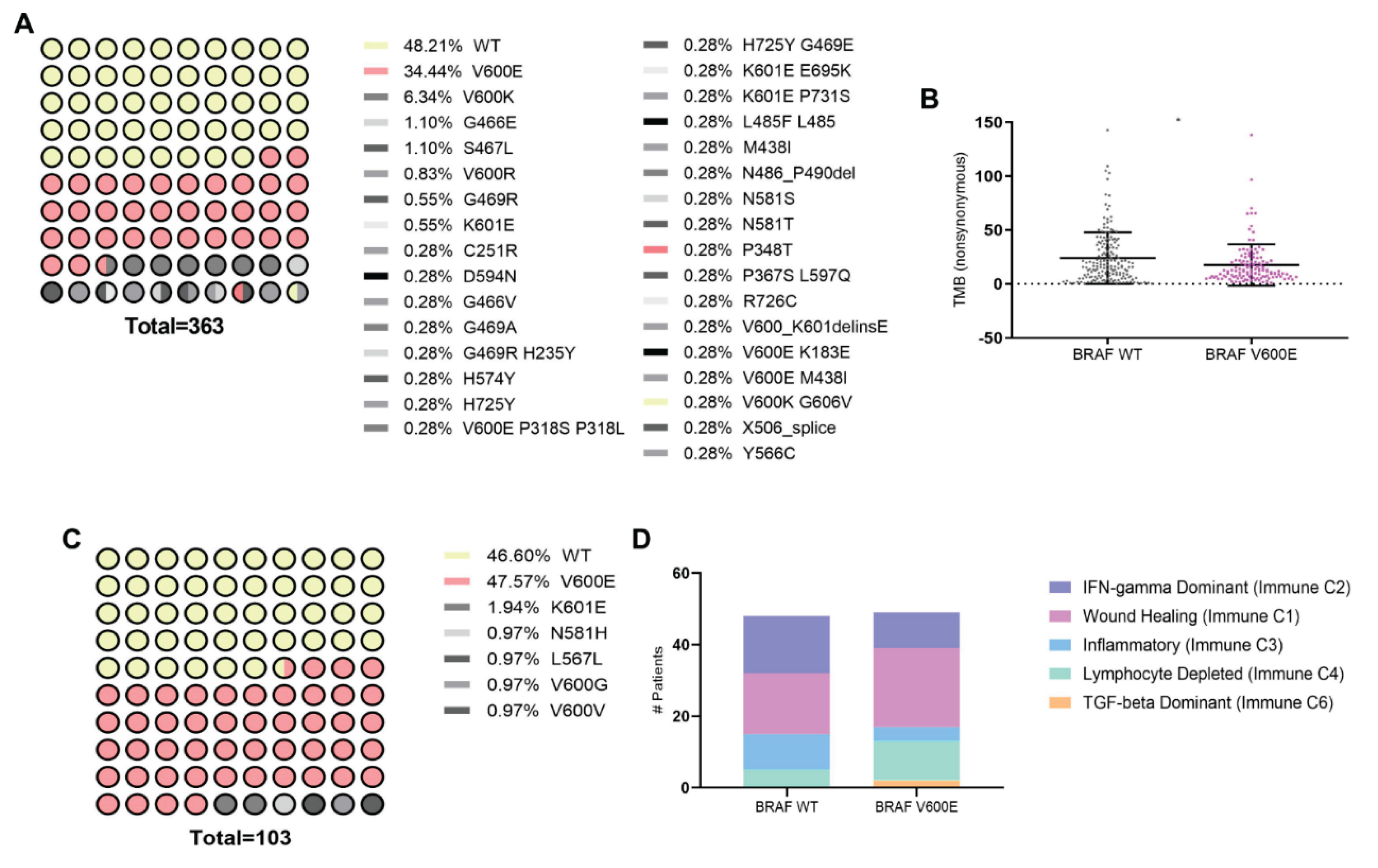
3.1. Association of BRAFV600E Mutation with Genomic and Immune Landscape Alterations in Melanoma Patients
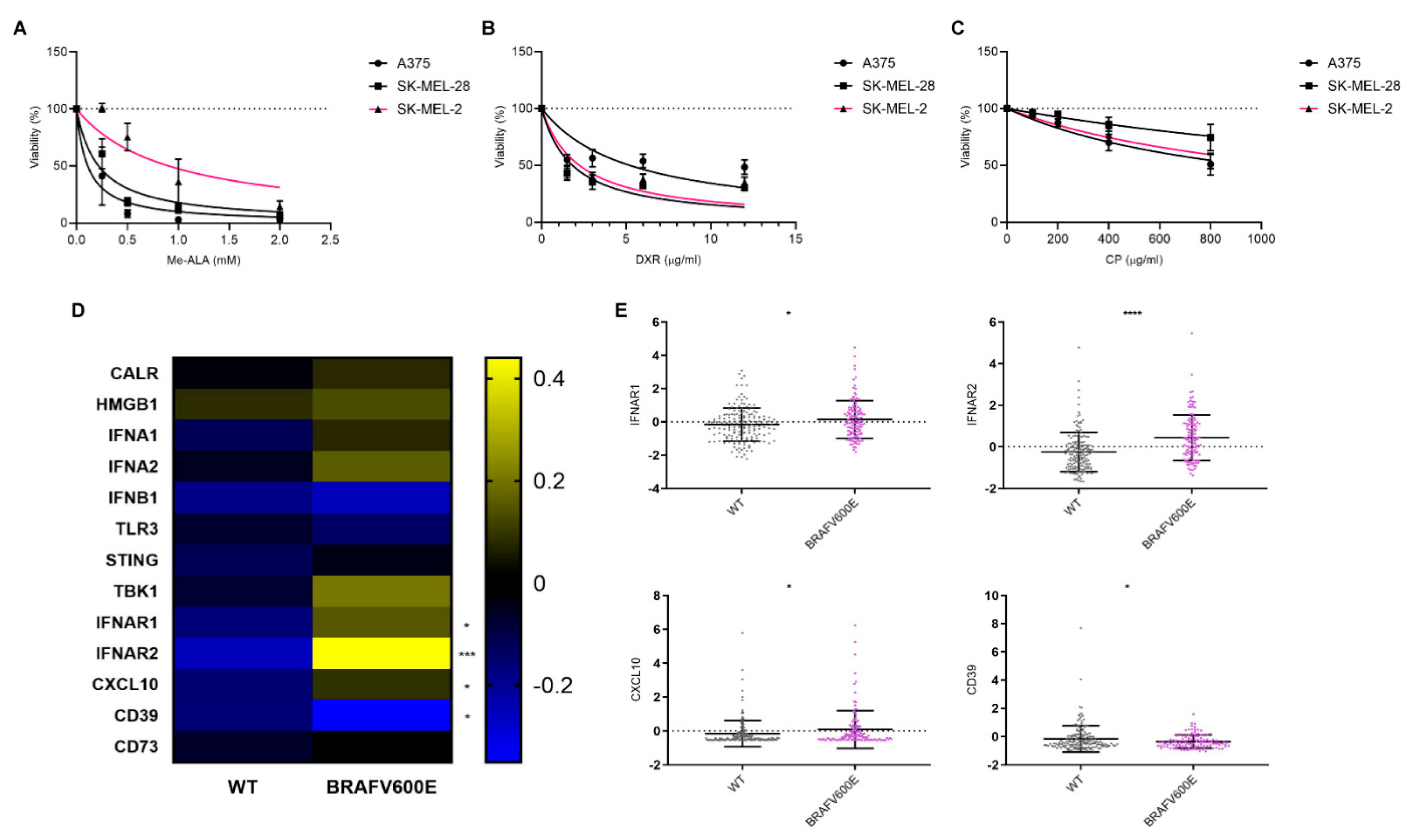
3.2. Impact of BRAFV600E Mutation on Sensitivity to ICD and ICD-Associated Gene Expression Profiles in Melanoma
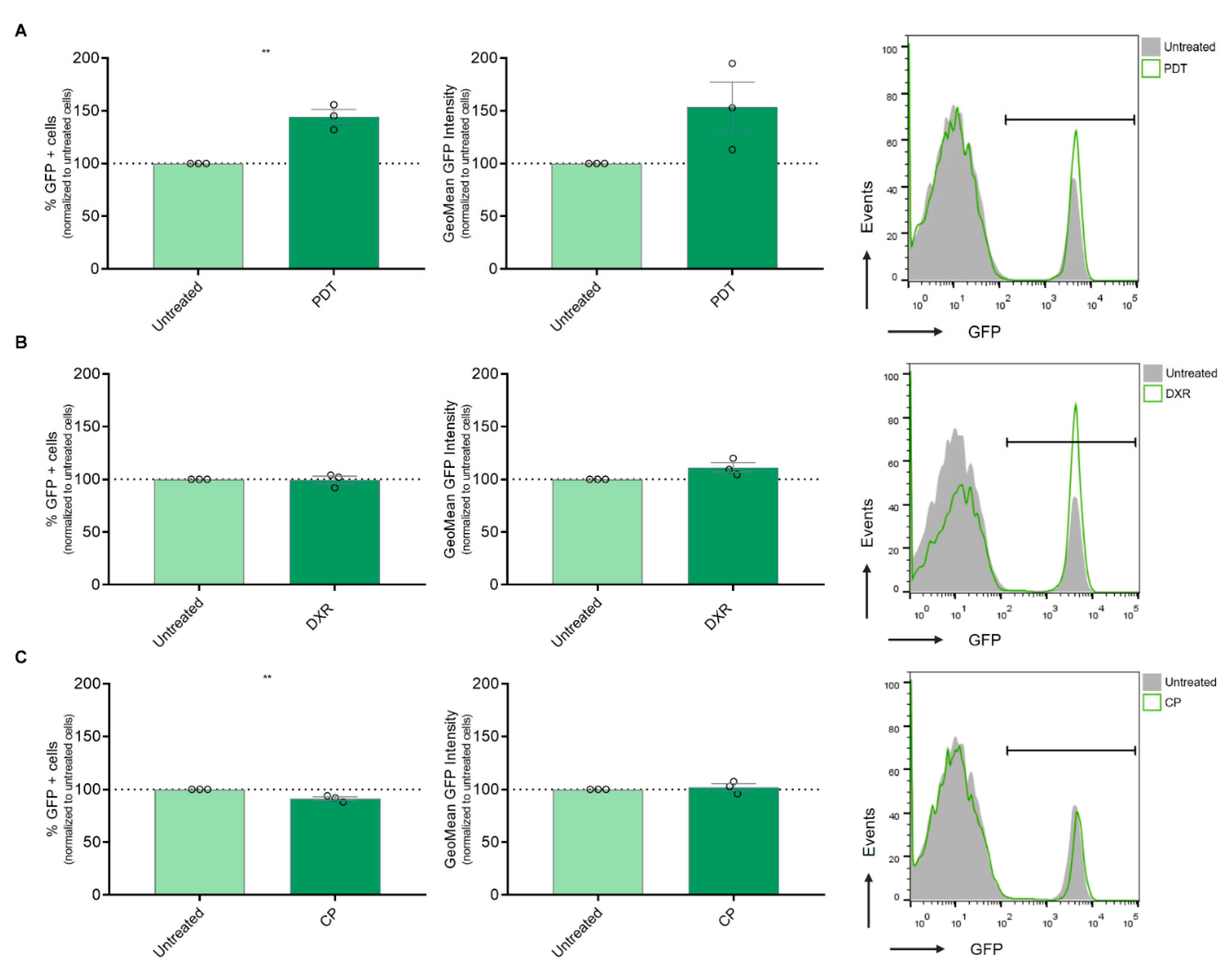
3.3. Modulation of IFN-1 Pathway Activity in Melanoma Cells by PDT-Induced ICD
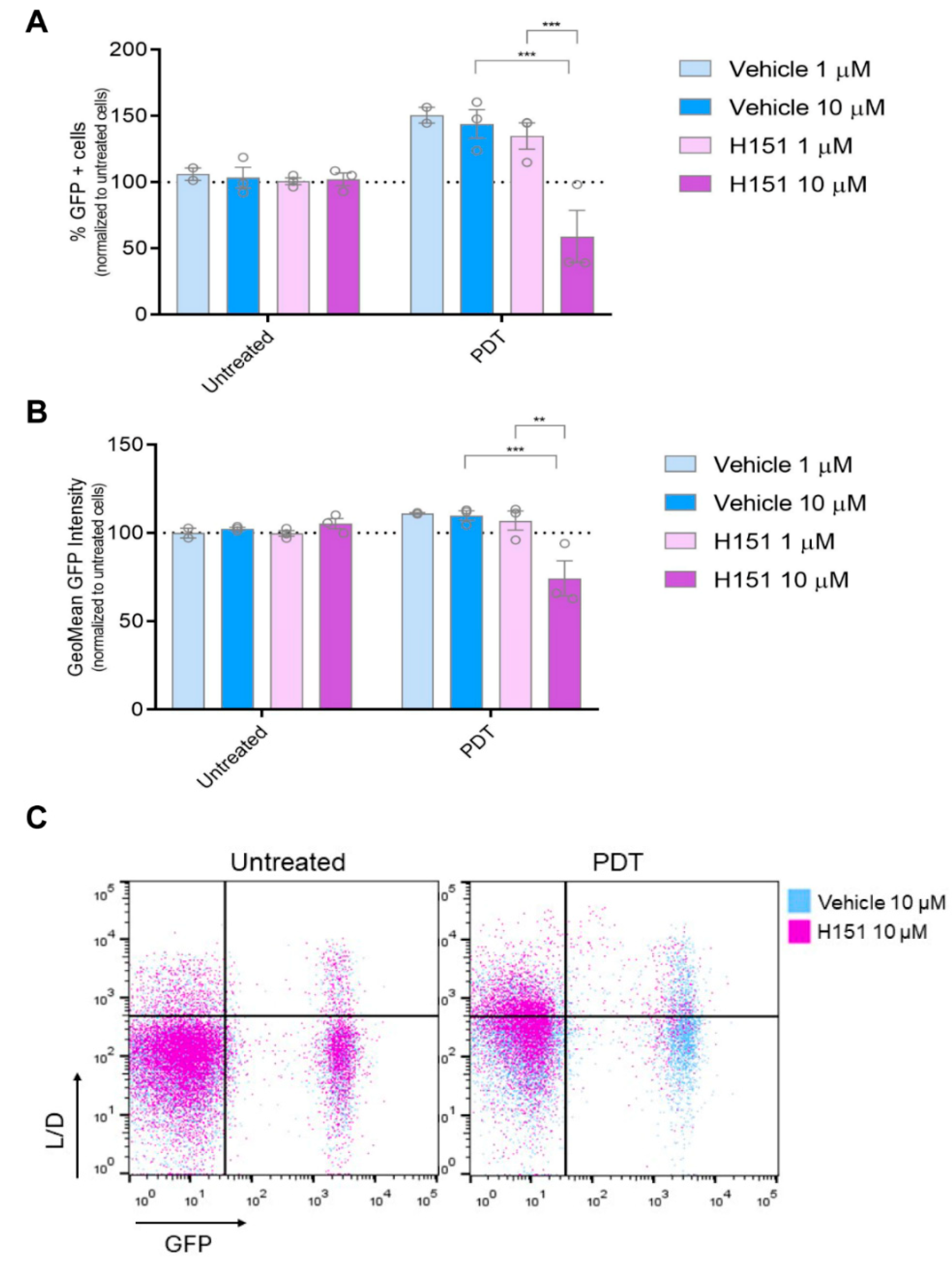
3.4. Inhibition of cGAS-STING Signaling Reverses PDT-Induced Upregulation of IFN-1 Pathway Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Long, G. V.; Swetter, S.M.; Menzies, A.M.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Scolyer, R.A. Cutaneous Melanoma. Lancet 2023, 402, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbani, R.; Akdemir, K.C.; Aksoy, B.A.; Albert, M.; Ally, A.; Amin, S.B.; Arachchi, H.; Arora, A.; Auman, J.T.; Ayala, B.; et al. Genomic Classification of Cutaneous Melanoma. Cell 2015, 161, 1681–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascierto, P.A.; Kirkwood, J.M.; Grob, J.J.; Simeone, E.; Grimaldi, A.M.; Maio, M.; Palmieri, G.; Testori, A.; Marincola, F.M.; Mozzillo, N. The Role of BRAF V600 Mutation in Melanoma. J Transl Med 2012, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Q.; Liu, Z. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Combination Therapies for Advanced Melanoma: A Network Meta-Analysis. BMC Cancer 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, J.; Kartolo, A.; Yeung, C.; Hopman, W.; Baetz, T. Long-Term Toxicities of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor (ICI) in Melanoma Patients. Current Oncology 2022, Vol. 29, Pages 7953-7963 2022, 29, 7953–7963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, F.; Shields, B.; Makhoul, I.; Avaritt, N.; Wong, H.K.; Hutchins, L.F.; Shalin, S.; Tackett, A.J. Immune Surveillance in Melanoma: From Immune Attack to Melanoma Escape and Even Counterattack. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Shklovskaya, E.; Lim, S.Y.; Carlino, M.S.; Menzies, A.M.; Stewart, A.; Pedersen, B.; Irvine, M.; Alavi, S.; Yang, J.Y.H.; et al. Transcriptional Downregulation of MHC Class I and Melanoma De- Differentiation in Resistance to PD-1 Inhibition. Nature Communications 2020 11:1 2020, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiba, S.; Fujimura, T. Significance of Immunosuppressive Cells as a Target for Immunotherapies in Melanoma and Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Failmezger, H.; Muralidhar, S.; Rullan, A.; de Andrea, C.E.; Sahai, E.; Yuan, Y. Topological Tumor Graphs: A Graph-Based Spatial Model to Infer Stromal Recruitment for Immunosuppression in Melanoma Histology a C. Cancer Res 2020, 256, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Agostinis, P.; Vitale, I.; Warren, S.; Adjemian, S.; Coukos, G.; Martinez, A.B.; Chan, T.A.; Edelson, R.L.; Demaria, S.; et al. Consensus Guidelines for the Definition, Detection and Interpretation of Immunogenic Cell Death. J Immunother Cancer 2020, 8:e000337. J Immunother Cancer 2020, 8, e000337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberti, M.; Mentucci, F.; Roselli, E.; Araya, P.; Rivarola, V.; Rumie Vittar, N.; Maccioni, M. Photodynamic Modulation of Type 1 Interferon Pathway on Melanoma Cells Promotes Dendritic Cell Activation. Front Immunol. 2019, 10, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borden, E.C. Interferons α and β in Cancer: Therapeutic Opportunities from New Insights. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2019, 18, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheon, H.J.; Wang, Y.; Wightman, S.M.; Jackson, M.W.; Stark, G.R. How Cancer Cells Make and Respond to Interferon-I. Trends Cancer 2023, 9, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The CBio Cancer Genomics Portal: An Open Platform for Exploring Multidimensional Cancer Genomics Data. Cancer Discov 2012, 2, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, M.J.; Craft, B.; Hastie, M.; Repečka, K.; McDade, F.; Kamath, A.; Banerjee, A.; Luo, Y.; Rogers, D.; Brooks, A.N.; et al. Visualizing and Interpreting Cancer Genomics Data via the Xena Platform. Nat Biotechnol 2020, 38, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgi, M.; Prieto, C.; Oggero, M.; Bollati-Fogolín, M.; Etcheverrigaray, M.; Kratje, R. New Reporter Cell Clones to Determine the Biological Activity of Human Type I Interferons. BMC Proc. 2011, 5, Suppl 8:P4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, E.J.; Johnson, D.B.; Sosman, J.A.; Chandra, S. Melanoma: What Do All the Mutations Mean? Cancer 2018, 124, 3490–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalmers, Z.R.; Connelly, C.F.; Fabrizio, D.; Gay, L.; Ali, S.M.; Ennis, R.; Schrock, A.; Campbell, B.; Shlien, A.; Chmielecki, J.; et al. Analysis of 100,000 Human Cancer Genomes Reveals the Landscape of Tumor Mutational Burden. Genome Med 2017, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsson, V.; Gibbs, D.L.; Brown, S.D.; Wolf, D.; Bortone, D.S.; Ou Yang, T.H.; Porta-Pardo, E.; Gao, G.F.; Plaisier, C.L.; Eddy, J.A.; et al. The Immune Landscape of Cancer. Immunity 2018, 48, 812–830e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.D.; More, S.; Rufo, N.; Mece, O.; Sassano, M.L.; Agostinis, P.; Zitvogel, L.; Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L. Trial Watch: Immunogenic Cell Death Induction by Anticancer Chemotherapeutics. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1386829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberti, M.J.; Montico, B.; Ravo, M.; Nigro, A.; Giurato, G.; Iorio, R.; Tarallo, R.; Weisz, A.; Stellato, C.; Steffan, A.; et al. Integration of MiRNA:MRNA Co-Expression Revealed Crucial Mechanisms Modulated in Immunogenic Cancer Cell Death. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casares, N.; Pequignot, M.O.; Tesniere, A.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Roux, S.; Chaput, N.; Schmitt, E.; Hamai, A.; Hervas-Stubbs, S.; Obeid, M.; et al. Caspase-Dependent Immunogenicity of Doxorubicin-Induced Tumor Cell Death. Journal of Experimental Medicine 2005, 202, 1691–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Li, D.; Du, X.; He, X.; Huang, M.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, J. Carrier-Free Nanoassembly of Doxorubicin Prodrug and SiRNA for Combinationally Inducing Immunogenic Cell Death and Reversing Immunosuppression. Nano Today 2020, 35, 100924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, I.; Kepp, O.; Schlemmer, F.; Adjemian, S.; Tailler, M.; Shen, S.; Michaud, M.; Menger, L.; Gdoura, A.; Tajeddine, N.; et al. Restoration of the Immunogenicity of Cisplatin-Induced Cancer Cell Death by Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Oncogene 2011, 30, 1147–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terenzi, A.; Pirker, C.; Keppler, B.K.; Berger, W. Anticancer Metal Drugs and Immunogenic Cell Death. J Inorg Biochem 2016, 165, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zitvogel, L.; Galluzzi, L.; Kepp, O.; Smyth, M.J.; Kroemer, G. Type I Interferons in Anticancer Immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 2015, 15, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.S.; Chiang, S.F.; Chen, C.Y.; Hong, W.Z.; Chen, T.W.; Chen, W.T.L.; Ke, T.W.; Yang, P.C.; Liang, J.A.; Shiau, A.C.; et al. Targeting CD73 Increases Therapeutic Response to Immunogenic Chemotherapy by Promoting Dendritic Cell Maturation. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2023, 72, 2283–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacchelli, E.; Sistigu, A.; Yamazaki, T.; Vitale, I.; Zitvogel, L.; Kroemer, G. Autocrine Signaling of Type 1 Interferons in Successful Anticancer Chemotherapy. Oncoimmunology 2015, 4, e988042. [Google Scholar]
- Sistigu, A.; Yamazaki, T.; Vacchelli, E.; Chaba, K.; Enot, D.; Adam, J.; Vitale, I.; Goubar, A.; Baracco, E.; Remédios, C.; et al. Cancer Cell-Autonomous Contribution of Type I Interferon Signaling to the Efficacy of Chemotherapy. Nat Med. 2014, 20, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Crowe, W.N.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Petty, W.J.; Habib, A.A.; Zhao, D. An Inhalable Nanoparticulate STING Agonist Synergizes with Radiotherapy to Confer Long-Term Control of Lung Metastases. Nat Commun 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, S.; Bernard Tchounwou, P. Cisplatin in Cancer Therapy: Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Eur J Pharmacol 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Cheng, H.; Yuan, H.; Xu, Q.; Shu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, P.; Tan, J.; Rui, Y.; Li, P.; et al. Antitumor Activity of CGAMP via Stimulation of CGAS-CGAMP-STING-IRF3 Mediated Innate Immune Response. Sci Rep 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Crowe, W.N.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Petty, W.J.; Habib, A.A.; Zhao, D. An Inhalable Nanoparticulate STING Agonist Synergizes with Radiotherapy to Confer Long-Term Control of Lung Metastases. Nat Commun 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Han, C.; Samandi, L.Z.; Dong, C.; Sumer, B.D.; Lea, J.; Fu, Y.X.; Gao, J. Synergistic STING Activation by PC7A Nanovaccine and Ionizing Radiation Improves Cancer Immunotherapy. J Control Release 2019, 300, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, K.; Li, N.; Ye, W.; Gao, H.; Luo, X.; Cheng, B. Activation of Stimulation of Interferon Genes (STING) Signal and Cancer Immunotherapy. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.C.; Zappasodi, R. A Decade of Checkpoint Blockade Immunotherapy in Melanoma: Understanding the Molecular Basis for Immune Sensitivity and Resistance. Nat Immunol 2022, 23, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauschild, A.; Larkin, J.; Ribas, A.; Dréno, B.; Flaherty, K.T.; Ascierto, P.A.; Lewis, K.D.; McKenna, E.; Zhu, Q.; Mun, Y.; et al. Modeled Prognostic Subgroups for Survival and Treatment Outcomes in BRAF V600-Mutated Metastatic Melanoma: Pooled Analysis of 4 Randomized Clinical Trials. JAMA Oncol 2018, 4, 1382–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giugliano, F.; Crimini, E.; Tarantino, P.; Zagami, P.; Uliano, J.; Corti, C.; Trapani, D.; Curigliano, G.; Ascierto, P.A. First Line Treatment of BRAF Mutated Advanced Melanoma: Does One Size Fit All? Cancer Treat Rev 2021, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziogas, D.C.; Theocharopoulos, C.; Lialios, P.P.; Foteinou, D.; Koumprentziotis, I.A.; Xynos, G.; Gogas, H. Beyond CTLA-4 and PD-1 Inhibition: Novel Immune Checkpoint Molecules for Melanoma Treatment. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, N.; Havel, J.J.; Makarov, V.; Desrichard, A.; Urba, W.J.; Sims, J.S.; Hodi, F.S.; Martín-Algarra, S.; Mandal, R.; Sharfman, W.H.; et al. Tumor and Microenvironment Evolution during Immunotherapy with Nivolumab. Cell 2017, 171, 934–949e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugo, W.; Zaretsky, J.M.; Sun, L.; Song, C.; Moreno, B.H.; Hu-Lieskovan, S.; Berent-Maoz, B.; Pang, J.; Chmielowski, B.; Cherry, G.; et al. Genomic and Transcriptomic Features of Response to Anti-PD-1 Therapy in Metastatic Melanoma. Cell 2016, 165, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, N.A.; Hellmann, M.D.; Snyder, A.; Kvistborg, P.; Makarov, V.; Havel, J.J.; Lee, W.; Yuan, J.; Wong, P.; Ho, T.S.; et al. Mutational Landscape Determines Sensitivity to PD-1 Blockade in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Science 2015, 348, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offin, M.; Rizvi, H.; Tenet, M.; Ni, A.; Sanchez-Vega, F.; Li, B.T.; Drilon, A.; Kris, M.G.; Rudin, C.M.; Schultz, N.; et al. Tumor Mutation Burden and Efficacy of EGFR-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Patients with EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancers. Clin Cancer Res 2019, 25, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.T.; Wu, Y.L. Combination Chemotherapy Alone Should Be Used in the Treatment of Patients With Stage IV EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Whose Disease Has Progressed on All Available Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. J Thorac Oncol 2021, 16, 1627–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.R.; Ramkissoon, S.H.; Ross, J.; Weintraub, L. Tumor Mutational Burden and Driver Mutations: Characterizing the Genomic Landscape of Pediatric Brain Tumors. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2020, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckardt, J.; Schroeder, C.; Martus, P.; Armeanu-Ebinger, S.; Kelemen, O.; Gschwind, A.; Bonzheim, I.; Eigentler, T.; Amaral, T.; Ossowski, S.; et al. TMB and BRAF Mutation Status Are Independent Predictive Factors in High-Risk Melanoma Patients with Adjuvant Anti-PD-1 Therapy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2023, 149, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilieva, K.M.; Correa, I.; Josephs, D.H.; Karagiannis, P.; Egbuniwe, I.U.; Cafferkey, M.J.; Spicer, J.F.; Harries, M.; Nestle, F.O.; Lacy, K.E.; et al. Effects of BRAF Mutations and BRAF Inhibition on Immune Responses to Melanoma. Mol Cancer Ther 2014, 13, 2769–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamberti, M.; Nigro, A.; Mentucci, F.; Rumie Vittar, N.; Casolaro, V.; Dal Col, J. Dendritic Cells and Immunogenic Cancer Cell Death: A Combination for Improving Antitumor Immunity. Pharmaceutics 2020, 256, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Kepp, O.; Hett, E.; Kroemer, G.; Marincola, F.M. Immunogenic Cell Death in Cancer: Concept and Therapeutic Implications. J Transl Med 2023, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Buqué, A.; Kepp, O.; Zitvogel, L.; Kroemer, G. Immunogenic Cell Death in Cancer and Infectious Disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2017, 17, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Xiao, J.; Bi, J.; Li, X.Y.; Chen, G.; Lu, L. Review Immune Response of Targeting CD39 in Cancer. Biomark Res 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, G.; Nuñez, N.; Nocera, D.; Dejager, L.; Libert, C.; Giraudo, C.; Maccioni, M. Direct Effect of DsRNA Mimetics on Cancer Cells Induces Endogenous IFN-β Production Capable of Improving Dendritic Cell Function. Eur J Immunol 2013, 43, 1849–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez, N.; Andreani, V.; Crespo, M.; Nocera, D.; Breser, M.; Morón, G.; Dejager, L.; Libert, C.; Rivero, V.; Maccioni, M. IFNβ Produced by TLR4-Activated Tumor Cells Is Involved in Improving the Antitumoral Immune Response. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nocera, D.; Roselli, E.; Araya, P.; Nuñez, N.; Lienenklaus, S.; Jablonska, J.; Weiss, S.; Gatti, G.; Brinkmann, M.; Kröger, A.; et al. In Vivo Visualizing the IFN-β Response Required for Tumor Growth Control in a Therapeutic Model of Polyadenylic-Polyuridylic Acid Administration. J Immunol. 2016 2016, 196, 2860–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernst, M.; Giubellino, A. The Current State of Treatment and Future Directions in Cutaneous Malignant Melanoma. Biomedicines 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatim, N.; Cullen, S.; Albert, M. Dying Cells Actively Regulate Adaptive Immune Responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017, 17, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musella, M.; Manic, G.; De Maria, R.; Vitale, I.; Sistigu, A. Type-I-Interferons in Infection and Cancer: Unanticipated Dynamics with Therapeutic Implications. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1314424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivashkiv, L.; Donlin, L. Regulation of Type I Interferon Responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014, 14, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motwani, M.; Pesiridis, S.; Fitzgerald, K.A. DNA Sensing by the CGAS-STING Pathway in Health and Disease. Nat Rev Genet 2019, 20, 657–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PDT | |||
| SK-MEL-2 | A375 | SK-MEL-28 | |
| SK-MEL-2 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | |
| A375 | 0.0001 | 0.87 | |
| SK-MEL-28 | 0.0001 | 0.87 | |
| DXR | |||
| SK-MEL-2 | A375 | SK-MEL-28 | |
| SK-MEL-2 | 0.0072 | 0.4364 | |
| A375 | 0.0072 | 0.005 | |
| SK-MEL-28 | 0.4364 | 0.005 | |
| CP | |||
| SK-MEL-2 | A375 | SK-MEL-28 | |
| SK-MEL-2 | 0.2866 | 0.003 | |
| A375 | 0.2866 | 0.0004 | |
| SK-MEL-28 | 0.003 | 0.0004 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




