Submitted:
06 March 2024
Posted:
07 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
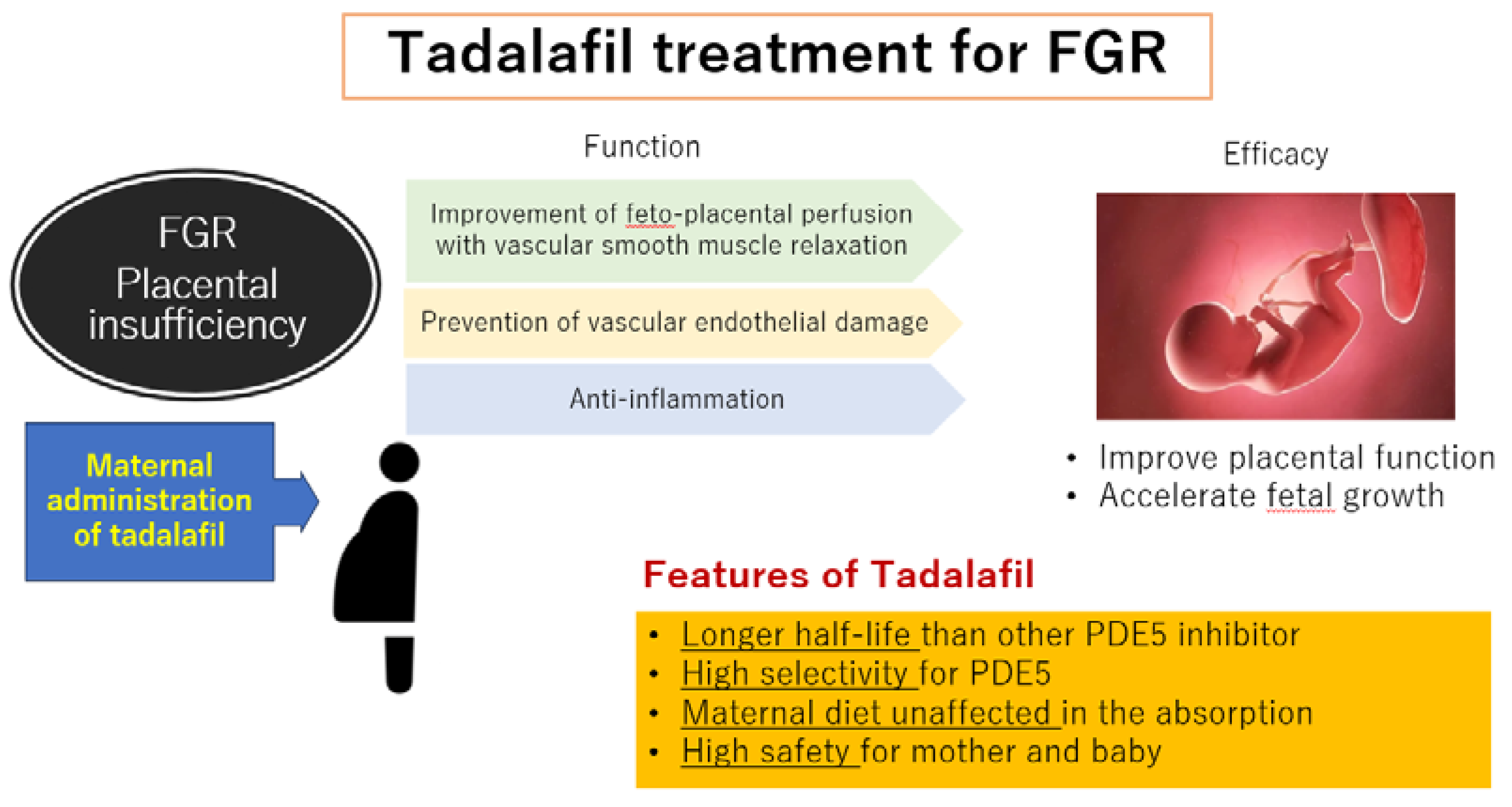
2. Why Did We Select to Study Tadalafil as an Agent for the Treatment of FGR?
2.1. PDE5 Inhibitors
2.2. Sildenafil
2.3. The Characteristics of Tadalafil
2.4. Case Report
2.5. Case-Control Study
2.6. Phase I Trial
2.7. Phase II Trial
2.8. Basic Research
2.9. Developmental Prognosis of Children Treated with Tadalafil
2.10. TADAFER IIb
3. Conclusions and Future Aspects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Temming, L.A.; Dicke, J.M.; Stout, M.J.; Rampersad, R.M.; Macones, G.A.; Tuuli, M.G.; Cahill, A.G. Early second-trimester fetal growth restriction and adverse perinatal outcomes. Obstet Gynecol 2017, 130, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lees, C.; Marlow, N.; Arabin, B.; Bilardo, C.M.; Brezinka, C.; Derks, J.B.; Duvekot, J.; Frusca, T.; Diemert, A.; Ferrazzi, E.; et al. Perinatal morbidity and mortality in early-onset fetal growth restriction: cohort outcomes of the trial of randomized umbilical and fetal flow in Europe (TRUFFLE). Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013, 42, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, T.A.; Grunau, R.E.; McAuliffe, F.M.; Pinnamaneni, R.; Foran, A.; Alderdice, F.A. Early childhood neurodevelopment after intrauterine growth restriction: a systematic review. Pediatrics 2015, 135, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, L.; Challis, D. Diagnosis and management of fetal growth restriction: the role of fetal therapy. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 2008, 22, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeyama, K.; Morioka, I.; Iwatani, S.; Fukushima, S.; Kurokawa, D.; Yamana, K.; Nishida, K.; Ohyama, S.; Fujioka, K.; Awano, H.; et al. Gestational age-dependency of height and body mass index trajectories during the first 3 years in Japanese small-for-gestational age children. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 38659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baschat, A.A. Neurodevelopment after fetal growth restriction. Fetal Diagn Ther 2014, 36, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluckman, P.D.; Hanson, M.A. Living with the past: evolution, development, and patterns of disease. Science 2004, 305, 1733–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flenady, V.; Koopmans, L.; Middleton, P.; Frøen, J.F.; Smith, G.C.; Gibbons, K.; Coory, M.; Gordon, A.; Ellwood, D.; McIntyre, H.D.; et al. Major risk factors for stillbirth in high-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2011, 377, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliodromiti, S.; Mackay, D.F.; Smith, G.C.; Pell, J.P.; Sattar, N.; Lawlor, D.A.; Nelson, S.M. Customised and noncustomised birth weight centiles and prediction of stillbirth and infant mortality and morbidity: a cohort study of 979,912 term singleton pregnancies in Scotland. PLOS Med 2017, 14, e1002228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redman, C.W.; Sargent, I.L. Latest advances in understanding preeclampsia. Science 2005, 308, 1592–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; McDougall, A.R.A.; Goldstein, M.; Tuttle, A.; Hastie, R.; Tong, S.; Ammerdorffer, A.; Rushwan, S.; Ricci, C.; Gülmezoglu, A.M.; et al. Analysis of a maternal health medicines pipeline database 2000–2021: new candidates for the prevention and treatment of fetal growth restriction. BJOG 2023, 130, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, C.; Nunes, A.K.; Luna, R.L.; Araújo, S.M.; da Cruz-Höfling, M.A.; Peixoto, C.A. Sildenafil (Viagra) protective effects on neuroinflammation: the role of iNOS/NO system in an inflammatory demyelination model. Mediators Inflamm 2013, 2013, 321460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, G.; Liu, A.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, W.; Xu, Y.; Wang, C. Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor sildenafil prevents neuroinflammation, lowers beta-amyloid levels and improves cognitive performance in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Behav Brain Res 2013, 250, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdan, S.; Seferian, A.; Totoescu, A.; Dumitrache-Rujinski, S.; Ceausu, M.; Coman, C.; Ardelean, C.M.; Dorobantu, M.; Bogdan, M. Sildenafil reduces inflammation and prevents pulmonary arterial remodeling of the monocrotaline - induced disease in the Wistar rats. Maedica (Bucur) 2012, 7, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.B.; Nakashima, A.; Huber, W.J.; Davis, S.; Banerjee, S.; Huang, Z.; Saito, S.; Sadovsky, Y.; Sharma, S. Pyroptosis is a critical inflammatory pathway in the placenta from early onset preeclampsia and in human trophoblasts exposed to hypoxia and endoplasmic reticulum stressors. Cell Death Dis 2019, 10, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravipati, G.; McClung, J.A.; Aronow, W.S.; Peterson, S.J.; Frishman, W.H. Type 5 phosphodiesterase inhibitors in the treatment of erectile dysfunction and cardiovascular disease. Cardiol Rev 2007, 15, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaodhiar, L.; Veves, A. Acute and prolonged effects of sildenafil on brachial artery flow-mediated dilatation in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 962–963, author reply 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halcox, J.P.; Nour, K.R.; Zalos, G.; Mincemoyer, R.A.; Waclawiw, M.; Rivera, C.E.; Willie, G.; Ellahham, S.; Quyyumi, A.A. The effect of sildenafil on human vascular function, platelet activation, and myocardial ischemia. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002, 40, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, H.C.; Chang, G.; Klugherz, B.D.; Mahoney, P.D. Hemodynamic effects of sildenafil in men with severe coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 2000, 342, 1622–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, S.D.; Balidemaj, K.; Homma, S.; Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Maybaum, S. Acute type 5 phosphodiesterase inhibition with sildenafil enhances flow-mediated vasodilation in patients with chronic heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 2000, 36, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, A.; Hennessy, M.; Feely, J. Effect of sildenafil on blood pressure and arterial wave reflection in treated hypertensive men. J Hum Hypertens 2001, 15, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schofield, R.S.; Edwards, D.G.; Schuler, B.T.; Estrada, J.; Aranda, J.M.; Pauly, D.F.; Hill, J.A.; Aggarwal, R.; Nichols, W.W. Vascular effects of sildenafil in hypertensive cardiac transplant recipients. Am J Hypertens 2003, 16, 874–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoma, W.D.; Baker, R.S.; Clark, K.E. Effects of combined use of sildenafil citrate (Viagra) and 17beta-estradiol on ovine coronary and uterine hemodynamics. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004, 190, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, J.L.; Andersson, I.J.; Poudel, R.; Rueda-Clausen, C.F.; Sibley, C.P.; Davidge, S.T.; Baker, P.N. Sildenafil citrate rescues fetal growth in the catechol-O-methyl transferase knockout mouse model. Hypertension 2012, 59, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wareing, M.; Myers, J.E.; O’Hara, M.; Baker, P.N. Sildenafil citrate (Viagra) enhances vasodilatation in fetal growth restriction. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005, 90, 2550–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraiz, S.; Pellicer, B.; Serra, V.; Cauli, O.; Cortijo, J.; Felipo, V.; Pellicer, A. Sildenafil citrate improves perinatal outcome in fetuses from pre-eclamptic rats. BJOG 2012, 119, 1394–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharaj, C.H.; O’Toole, D.; Lynch, T.; Carney, J.; Jarman, J.; Higgins, B.D.; Morrison, J.J.; Laffey, J.G. Effects and mechanisms of action of sildenafil citrate in human chorionic arteries. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 2009, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.N.; Hamoud, H.; Warren, A.; Wong, L.F.; Arulkumaran, S. Relaxant action of sildenafil citrate (Viagra) on human myometrium of pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004, 191, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méhats, C.; Schmitz, T.; Breuiller-Fouché, M.; Leroy, M.J.; Cabrol, D. Should phosphodiesterase 5 selective inhibitors be used for uterine relaxation? Am J Obstet Gynecol 2006, 195, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.H.; Su, Y.N.; Shih, J.C.; Hsu, H.C.; Lee, C.N. Resolution of high uterine artery pulsatility index and notching following sildenafil citrate treatment in a growth-restricted pregnancy. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2012, 40, 609–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samangaya, R.A.; Mires, G.; Shennan, A.; Skillern, L.; Howe, D.; McLeod, A.; Baker, P.N. A randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study of the phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor sildenafil for the treatment of preeclampsia. Hypertens Pregnancy 2009, 28, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Dadelszen, P.; Dwinnell, S.; Magee, L.A.; Carleton, B.C.; Gruslin, A.; Lee, B.; Lim, K.I.; Liston, R.M.; Miller, S.P.; Rurak, D.; et al. Sildenafil citrate therapy for severe early-onset intrauterine growth restriction. BJOG 2011, 118, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganzevoort, W.; Alfirevic, Z.; von Dadelszen, P.; Kenny, L.; Papageorghiou, A.; van Wassenaer-Leemhuis, A.; Gluud, C.; Mol, B.W.; Baker, P.N. STRIDER: sildenafil Therapy in Dismal prognosis Early-onset intrauterine growth restriction--a protocol for a systematic review with individual participant data and aggregate data meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Syst Rev 2014, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, A.; Cornforth, C.; Jackson, R.; Harrold, J.; Turner, M.A.; Kenny, L.C.; Baker, P.N.; Johnstone, E.D.; Khalil, A.; von Dadelszen, P.; et al. Maternal sildenafil for severe fetal growth restriction (STRIDER): a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. Lancet Child Adolesc Health 2018, 2, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groom, K.M.; McCowan, L.M.; Mackay, L.K.; Lee, A.C.; Gardener, G.; Unterscheider, J.; Sekar, R.; Dickinson, J.E.; Muller, P.; Reid, R.A.; et al. STRIDER NZAus: a multicentre randomised controlled trial of sildenafil therapy in early-onset fetal growth restriction. BJOG 2019, 126, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pels, A.; Derks, J.; Elvan-Taspinar, A.; van Drongelen, J.; de Boer, M.; Duvekot, H.; van Laar, J.; van Eyck, J.; Al-Nasiry, S.; Sueters, M.; et al. Maternal sildenafil vs placebo in pregnant women with severe early-onset fetal growth restriction: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open 2020, 3, e205323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, A.; Jackson, R.; Cornforth, C.; Harrold, J.; Turner, M.A.; Kenny, L.; Baker, P.N.; Johnstone, E.D.; Khalil, A.; von Dadelszen, P.; et al. A prediction model for short-term neonatal outcomes in severe early-onset fetal growth restriction. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2019, 241, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.; Sharp, A.; Cornforth, C.; Jackson, R.; Mousa, H.; Stock, S.; Harrold, J.; Turner, M.A.; Kenny, L.C.; Baker, P.N.; et al. Effect of sildenafil on maternal hemodynamics in pregnancies complicated by severe early-onset fetal growth restriction: planned subgroup analysis from a multicenter randomized placebo-controlled double-blind trial. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2020, 55, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terstappen, F.; Richter, A.E.; Lely, A.T.; Hoebeek, F.E.; Elvan-Taspinar, A.; Bos, A.F.; Ganzevoort, W.; Pels, A.; Lemmers, P.M.; Kooi, E.M.W. Prenatal use of sildenafil in fetal growth restriction and its effect on neonatal tissue oxygenation-A retrospective analysis of hemodynamic data from participants of the Dutch STRIDER trial. Front Pediatr 2020, 8, 595693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groom, K.M.; Ganzevoort, W.; Alfirevic, Z.; Lim, K.; Papageorghiou, A.T.; STRIDER Consortium. Clinicians should stop prescribing sildenafil for fetal growth restriction (FGR): comment from the STRIDER Consortium. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2018, 52, 295–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keogh, A.M.; Jabbour, A.; Hayward, C.S.; Macdonald, P.S. Clinical deterioration after sildenafil cessation in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Vasc Health Risk Manag 2008, 4, 1111–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, I.R.; Aronson, J.K. Adverse drug reactions: definitions, diagnosis, and management. Lancet 2000, 356, 1255–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacci, M.; Andersson, K.E.; Chapple, C.; Maggi, M.; Mirone, V.; Oelke, M.; Porst, H.; Roehrborn, C.; Stief, C.; Giuliano, F. Latest evidence on the use of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur Urol 2016, 70, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiè, N.; Humbert, M.; Vachiery, J.L.; Gibbs, S.; Lang, I.; Torbicki, A.; Simonneau, G.; Peacock, A.; Vonk Noordegraaf, A.; Beghetti, M.; et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Heart J 2016, 37, 67–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aversa, A.; Fittipaldi, S.; Francomano, D.; Bimonte, V.M.; Greco, E.A.; Crescioli, C.; Di Luigi, L.; Lenzi, A.; Migliaccio, S. Tadalafil improves lean mass and endothelial function in nonobese men with mild ED/LUTS: in vivo and in vitro characterization. Endocrine 2017, 56, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenório, M.B.; Ferreira, R.C.; Moura, F.A.; Bueno, N.B.; de Oliveira, A.C.M.; Goulart, M.O.F. Cross-talk between oxidative stress and inflammation in preeclampsia. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019, 2019, 8238727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lip, S.V.; Boekschoten, M.V.; Hooiveld, G.J.; van Pampus, M.G.; Scherjon, S.A.; Plösch, T.; Faas, M.M. Early-onset preeclampsia, plasma microRNAs, and endothelial cell function. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2020, 222, 497.e1–497.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotella, D.P. Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors: current status and potential applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2002, 1, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forgue, S.T.; Patterson, B.E.; Bedding, A.W.; Payne, C.D.; Phillips, D.L.; Wrishko, R.E.; Mitchell, M.I. Tadalafil pharmacokinetics in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2006, 61, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. Scientific Discussion. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-discussion/viagra-epar-scientific-discussion_en.pdf (accessed on 13 October 2023).
- European Medicines Agency. Annex I: Summary of Product Characteristics: ADCIRCA. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/adcirca-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 13 October 2023).
- Coppage, K.H.; Sun, X.; Baker, R.S.; Clark, K.E. Expression of phosphodiesterase 5 in maternal and fetal sheep. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005, 193, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nii, M.; Enomoto, N.; Ishida, M.; Magawa, S.; Takakura, S.; Maki, S.; Tanaka, K.; Toriyabe, K.; Tanaka, H.; Kondo, E.; et al. Two-dimensional phase-contrast MRI reveals changes in uterine arterial blood flow in pregnant women administered tadalafil for fetal growth restriction. Placenta 2024, 146, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuragi, S.; Yamanaka, K.; Neki, R.; Kamiya, C.; Sasaki, Y.; Osato, K.; Miyoshi, T.; Kawasaki, K.; Horiuchi, C.; Kobayashi, Y.; et al. Maternal outcome in pregnancy complicated with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circ J 2012, 76, 2249–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daimon, A.; Kamiya, C.A.; Iwanaga, N.; Ikeda, T.; Nakanishi, N.; Yoshimatsu, J. Management of pulmonary vasodilator therapy in three pregnancies with pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2017, 43, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walton, R.B.; Reed, L.C.; Estrada, S.M.; Schmiedecke, S.S.; Villazana-Kretzer, D.L.; Napolitano, P.G.; Ieronimakis, N. Evaluation of sildenafil and tadalafil for reversing constriction of fetal arteries in a human placenta perfusion model. Hypertension 2018, 72, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, K.; Umekawa, T.; Maki, S.; Kubo, M.; Nii, M.; Tanaka, K.; Tanaka, H.; Osato, K.; Kamimoto, Y.; Kondo, E.; et al. Tadalafil improves L-NG-nitroarginine methyl ester-induced preeclampsia with fetal growth restriction-like symptoms in pregnant mice. Am J Hypertens 2017, 31, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Ishii, M.; Tanaka, H.; Noguchi, S.; Ikeda, T.; Tomi, M. Breast cancer resistance protein limits fetal transfer of tadalafil in mice. J Pharm Sci 2024, 113, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, K.; Tanaka, K.; Tanaka, H.; Maki, S.; Enomoto, N.; Takakura, S.; Nii, M.; Toriyabe, K.; Katsuragi, S.; Ikeda, T. Tadalafil treatment ameliorates hypoxia and alters placental expression of proteins downstream of mTOR signaling in fetal growth restriction. Medicina (Kaunas) 2020, 56, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, M.; Osato, K.; Kubo, M.; Nii, M.; Tanaka, H.; Murabayashi, N.; Umekawa, T.; Kamimoto, Y.; Ikeda, T. Early-onset fetal growth restriction treated with the long-acting phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor tadalafil: a case report. J Med Case Rep 2016, 10, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, M.; Umekawa, T.; Maekawa, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Nii, M.; Murabayashi, N.; Osato, K.; Kamimoto, Y.; Ikeda, T. Retrospective study of tadalafil for fetal growth restriction: impact on maternal and perinatal outcomes. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2017, 43, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakami, H.; Maeda, T.; Fujii, T.; Hamada, H.; Iitsuka, Y.; Itakura, A.; Itoh, H.; Iwashita, M.; Kanagawa, T.; Kanai, M.; et al. Guidelines for obstetrical practice in Japan: Japan Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology (JSOG) and Japan Association of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (JAOG) 2014 edition. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2014, 40, 1469–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, M.; Tanaka, H.; Maki, S.; Nii, M.; Murabayashi, N.; Osato, K.; Kamimoto, Y.; Umekawa, T.; Kondo, E.; Ikeda, T. Safety and dose-finding trial of tadalafil administered for fetal growth restriction: a phase-1 clinical study. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2017, 43, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCI Division of Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis. Common terminology criteria for adverse events v4.0. Available online: https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/ctc.htm#ctc_40 (accessed on 14 June 2014).
- Maki, S.; Tanaka, H.; Tsuji, M.; Furuhashi, F.; Magawa, S.; Kaneda, M.K.; Nii, M.; Tanaka, K.; Kondo, E.; Tamaru, S.; et al. Safety evaluation of tadalafil treatment for fetuses with early-onset growth restriction (TADAFER): results from the Phase II trial. J Clin Med 2019, 8, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapani, A.; Gonçalves, L.F.; Trapani, T.F.; Vieira, S.; Pires, M.; Pires, M.M.S. Perinatal and hemodynamic evaluation of sildenafil citrate for preeclampsia treatment: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2016, 128, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Das, A.; Md Nowroz, H. Sildenafil citrate in fetal growth restriction. J Reprod Infertil 2014, 15, 168–169. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yang, N.; Wang, B.; Niu, X.; Cai, W.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, S. Effect and mechanism of prophylactic use of tadalafil during pregnancy on l-NAME-induced preeclampsia-like rats. Placenta 2020, 99, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.A.; Carlisle, M.A.; Lam, A.; Aggarwal, S.; Doran, S.; Ren, C.; Bradley, W.E.; Dell’Italia, L.; Ambalavanan, N.; Ford, D.A.; et al. Mechanisms and treatment of halogen inhalation-induced pulmonary and systemic injuries in pregnant mice. Hypertension 2017, 70, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laxmi, V.; Gupta, R.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Ray, A.; Gulati, K. Inhibitory effects of sildenafil and tadalafil on inflammation, oxidative stress and nitrosative stress in animal model of bronchial asthma. Pharmacol Rep 2019, 71, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachibana, R.; Umekawa, T.; Yoshikawa, K.; Owa, T.; Magawa, S.; Furuhashi, F.; Tsuji, M.; Maki, S.; Shimada, K.; Kaneda, M.K.; et al. Tadalafil treatment in mice for preeclampsia with fetal growth restriction has neuro-benefic effects in offspring through modulating prenatal hypoxic conditions. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkalainen, N.; Räsänen, J.; Kaukola, T.; Kallankari, H.; Hallman, M.; Mäkikallio, K. Fetal hemodynamics and adverse outcome in primary school-aged children with fetal growth restriction: a prospective longitudinal study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2017, 96, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fushima, T.; Sekimoto, A.; Minato, T.; Ito, T.; Oe, Y.; Kisu, K.; Sato, E.; Funamoto, K.; Hayase, T.; Kimura, Y.; et al. Reduced uterine perfusion pressure (RUPP) model of preeclampsia in mice. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0155426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekimoto, A.; Tanaka, K.; Hashizume, Y.; Sato, E.; Sato, H.; Ikeda, T.; Takahashi, N. Tadalafil alleviates preeclampsia and fetal growth restriction in RUPP model of preeclampsia in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2020, 521, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, M.; Maki, S.; Enomoto, N.; Okamoto, K.; Kitamura, A.; Magawa, S.; Takakura, S.; Nii, M.; Tanaka, K.; Yodoya, N.; et al. Fetal biometric assessment and infant developmental prognosis of the tadalafil treatment for fetal growth restriction. Medicina (Kaunas) 2023, 59, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maki, S.; Tanaka, H.; Takakura, S.; Nii, M.; Tanaka, K.; Ogura, T.; Kotera, M.; Nishimura, Y.; Tamaru, S.; Ushida, T.; et al. Tadalafil treatment for fetuses with early-onset growth restriction: a protocol for a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind phase II trial (TADAFER IIb). BMJ (Open) 2022, 12, e054925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Japan Society of Ultrasound in Medicine. Ultrasound fetal measurement standardization and Japanese standard. J Med Ultrason 2003, 30, 416–440. [Google Scholar]
- Japan Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Sanfujinka Shinryou Gaidorain-Sankahen 2017; Japan society of Obstetrics and Gynecology: Tokyo, Japan, 2017. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, H.; Maki, S.; Magawa, S.; Nii, M.; Tanaka, K.; Ikemura, K.; Toriyabe, K.; Ikeda, T. Maternal blood concentration of tadalafil and uterine blood flow in pregnancy. Medicina (Kaunas) 2019, 55, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.M.; Russo, F.; Deprest, J.; Mol, B.W.; Kumar, S. Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors in pregnancy: systematic review and meta-analysis of maternal and perinatal safety and clinical outcomes. BJOG 2022, 129, 1817–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pels, A.; Ganzevoort, W.; Kenny, L.C.; Baker, P.N.; von Dadelszen, P.; Gluud, C.; Kariya, C.T.; Leemhuis, A.G.; Groom, K.M.; Sharp, A.N.; et al. Interventions affecting the nitric oxide pathway versus placebo or no therapy for fetal growth restriction in pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2023, 7, CD014498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
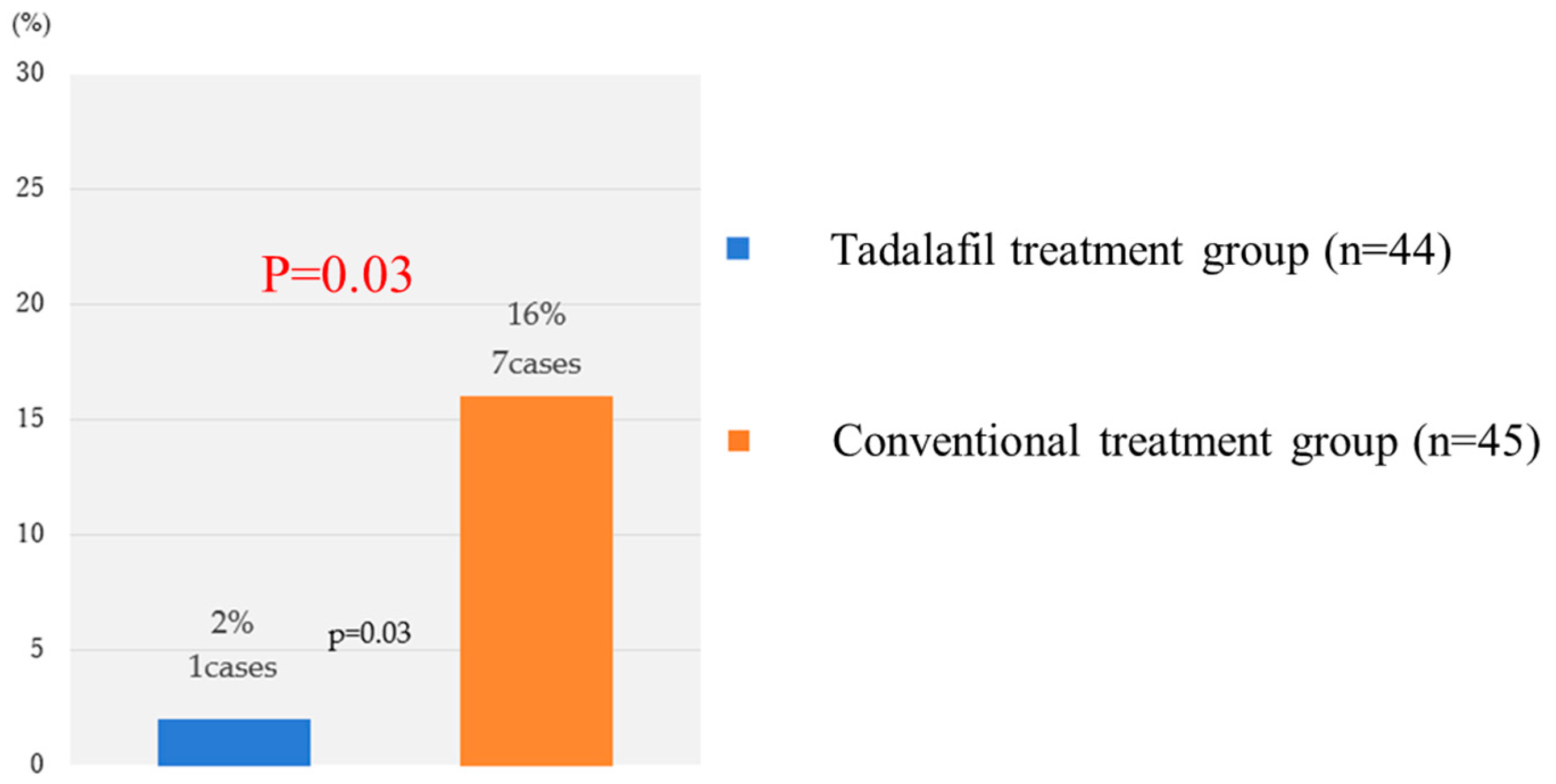
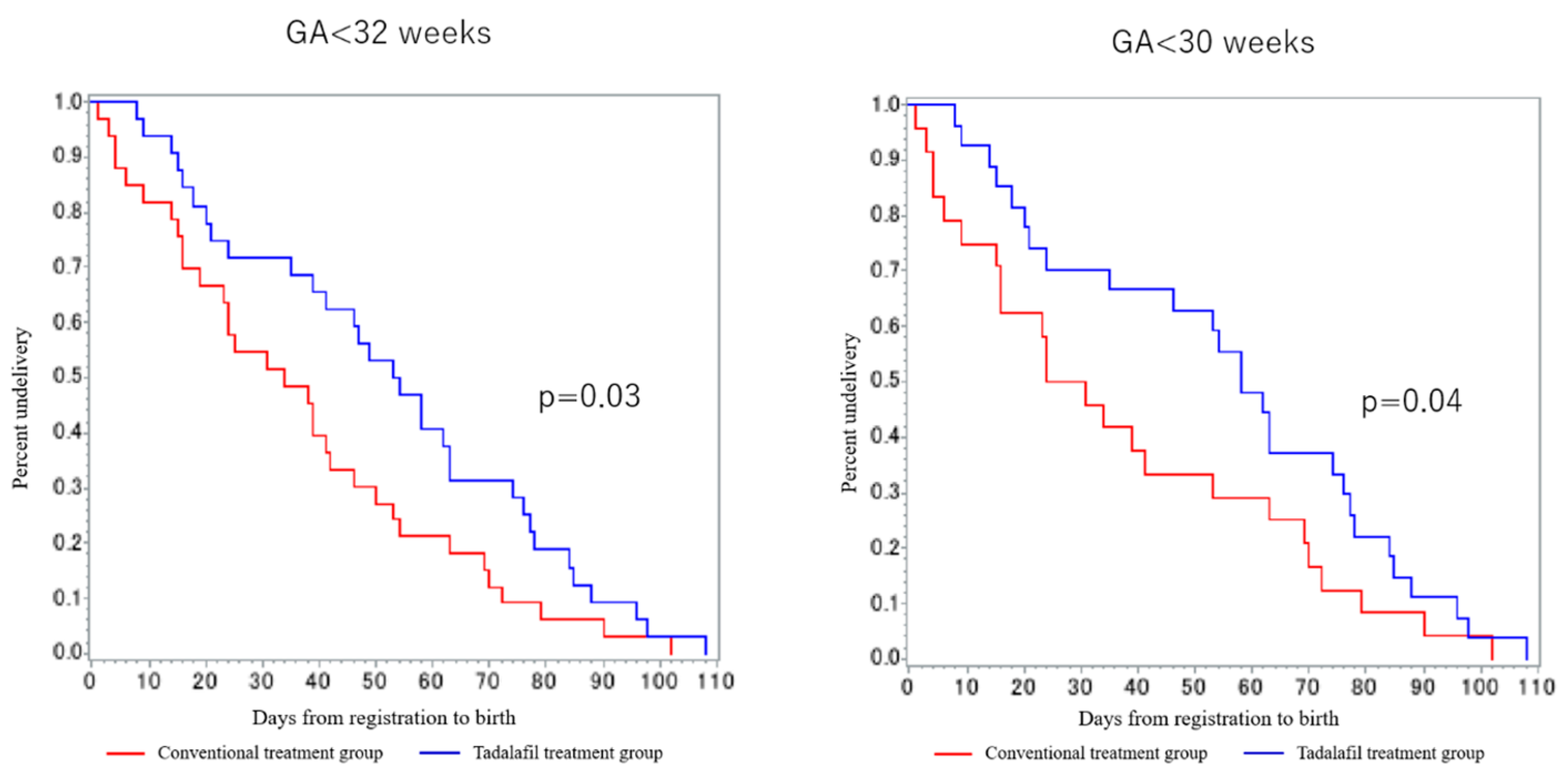
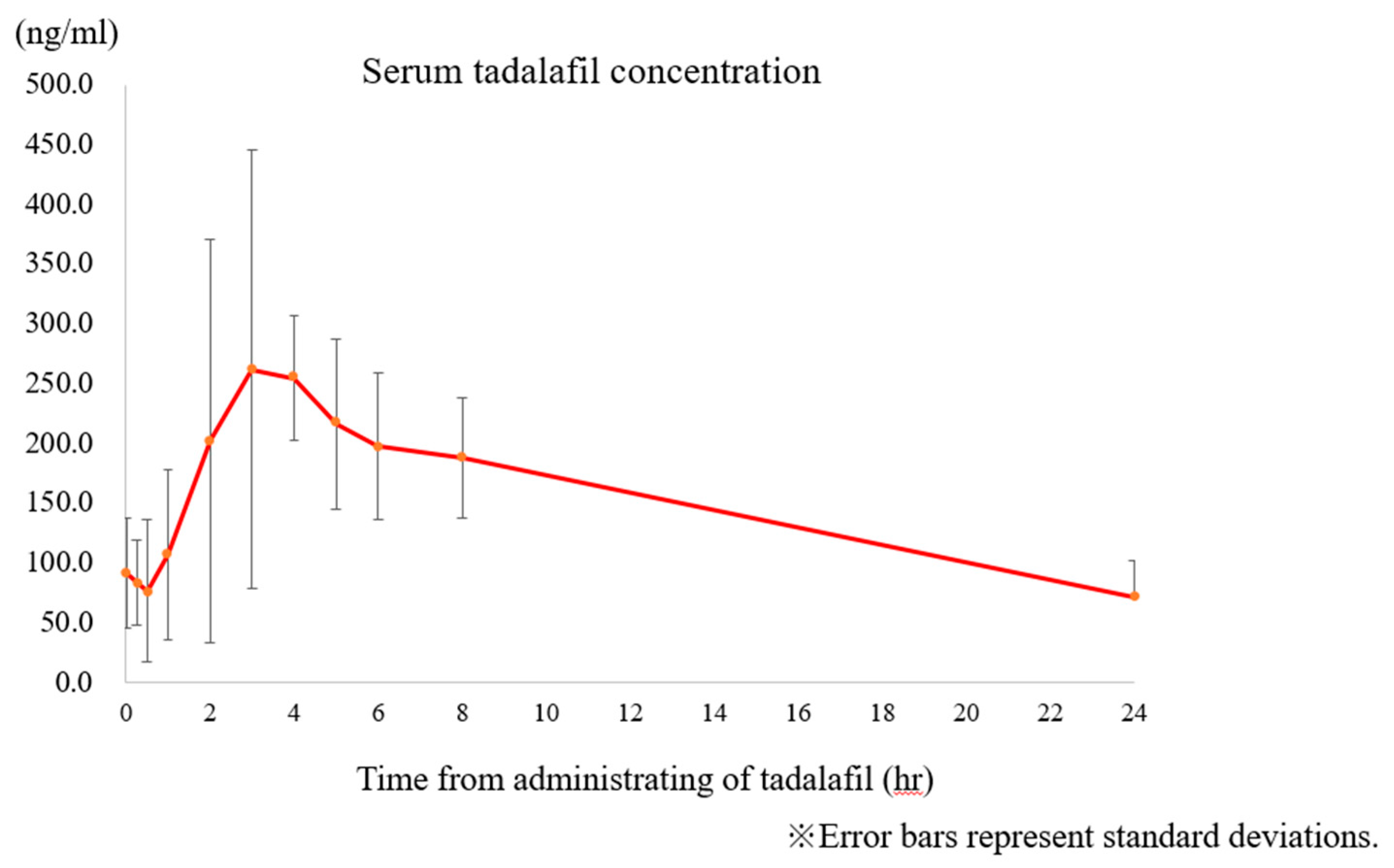
| Case | Allocation | GW at registration (week) | BW (g) | UA REDV or AEDV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fetal death | Conventional treatment group | 23 | 328 | + | |
| Fetal death | Conventional treatment group | 20 | <300 | + | |
| Fetal death | Conventional treatment group | 25 | 440 | + | |
| Fetal death | Conventional treatment group | 21 | 484 | − | |
| Neonatal death | Tadalafil treatment group | 21 | 317 | − | |
| Neonatal death | Conventional treatment group | 24 | 440 | − | |
| Infant death | Conventional treatment group | 27 | 704 | − | |
| Infant death | Conventional treatment group | 28 | 730 | − |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





