Submitted:
04 March 2024
Posted:
05 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Establish the physical and mathematical model to derive the Jeffcott rotor model and identify the model parameters, including imbalance and shaft-bow characteristics.
- After parameter identification, the physical model can be used to generate sufficient sets of simulated data for ANN-supervised training, which helps to produce a more reliable model. A trained ANN can be integrated into a Jeffcott rotor monitoring system for online diagnosis of imbalance and shaft-bow fault components using simulated and experimental data from Jeffcott rotor experiments.
2. Physical Model of Jeffcott Rotor with Simultaneous Imbalance and Shaft-Bow
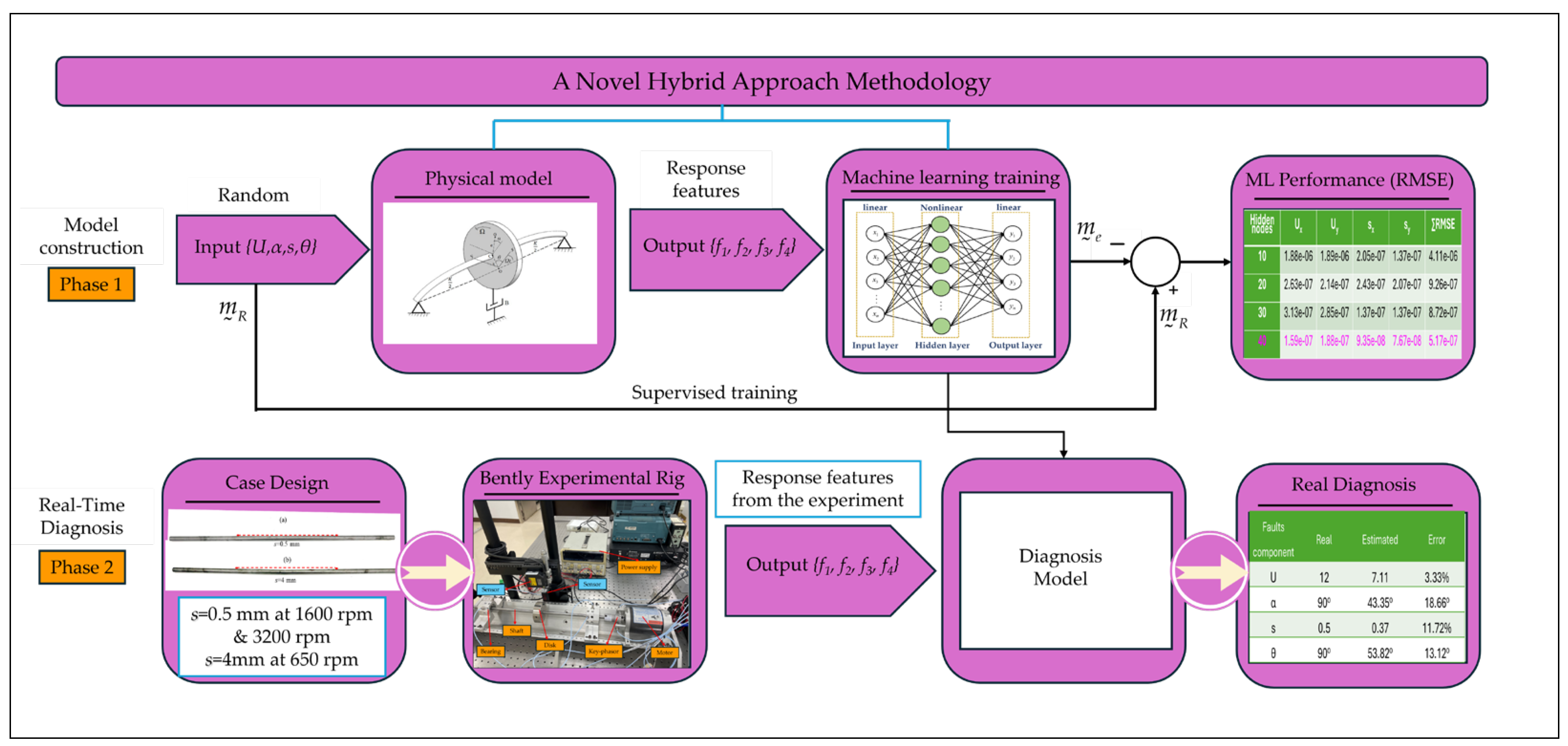
3. Hybrid Methodology
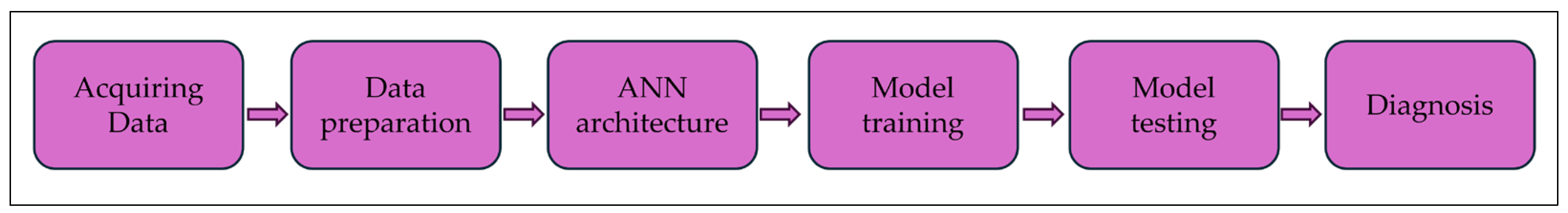
- Acquiring data: The physical model is used to generate the datasets randomly. Nevertheless, the training set can be generated from measured data as much as one need. It is notable that these imbalance and shaft-bow components, mT= {U, α, s, θ}, are randomly inputs to the physical model, and the response features components at the disk centre after forwarding calculation, are the output, i.e., Equation (24).
- Data preparation: The generated datasets will be considered raw data for further processing by supervised training. The simulated inputs/outputs are reversed during the network training. The response components, fT, i.e., 4 parameters are used for input to the ANN, and the 4 parameters i.e., mT are used for the target.
- ANN architecture: An appropriate model needs to be selected and configured for the problem at hand. Typically, a feedforward neural network (FNN) with one or more hidden layers is used. There are several parameters in each model that were varied to arrive at the best model parameter for each case. The proposed framework is modeled in MATLAB software.
- Model Training: In the present study, the FNN is trained with a single hidden layer architecture with a varying number of nodes by using 10,000 datasets, which are randomly generated from a physical model. The first 70 percent of the datasets are utilized for training, the second 15 percent are used for validation, and the final 15 percent are used for testing.
- Model Testing: To rigorously evaluate the FNN model’s performance, we employed root mean squared error (RMSE) to evaluate the closer alignment between the randomly generated (so-called real data) and the estimated values. A lower RMSE value signifies better accuracy and model performance. The formula of RMSE is:where denotes the real value for the ith point, denotes the estimated value, and n denotes the number of data points.
- Diagnosis: The trained FNN is tested using simulated and real data acquired from the experimental setup of the Jeffcott rotor to diagnose the multi-fault components, i.e., U, α, s, and θ. Based on the output of the FNN, the machine operator can monitor the growth of imbalances and shaft-bow to take necessary actions.
4. Numerical analysis and Experimental Verification
4.1. Numerical Analysis Using Simulated Data
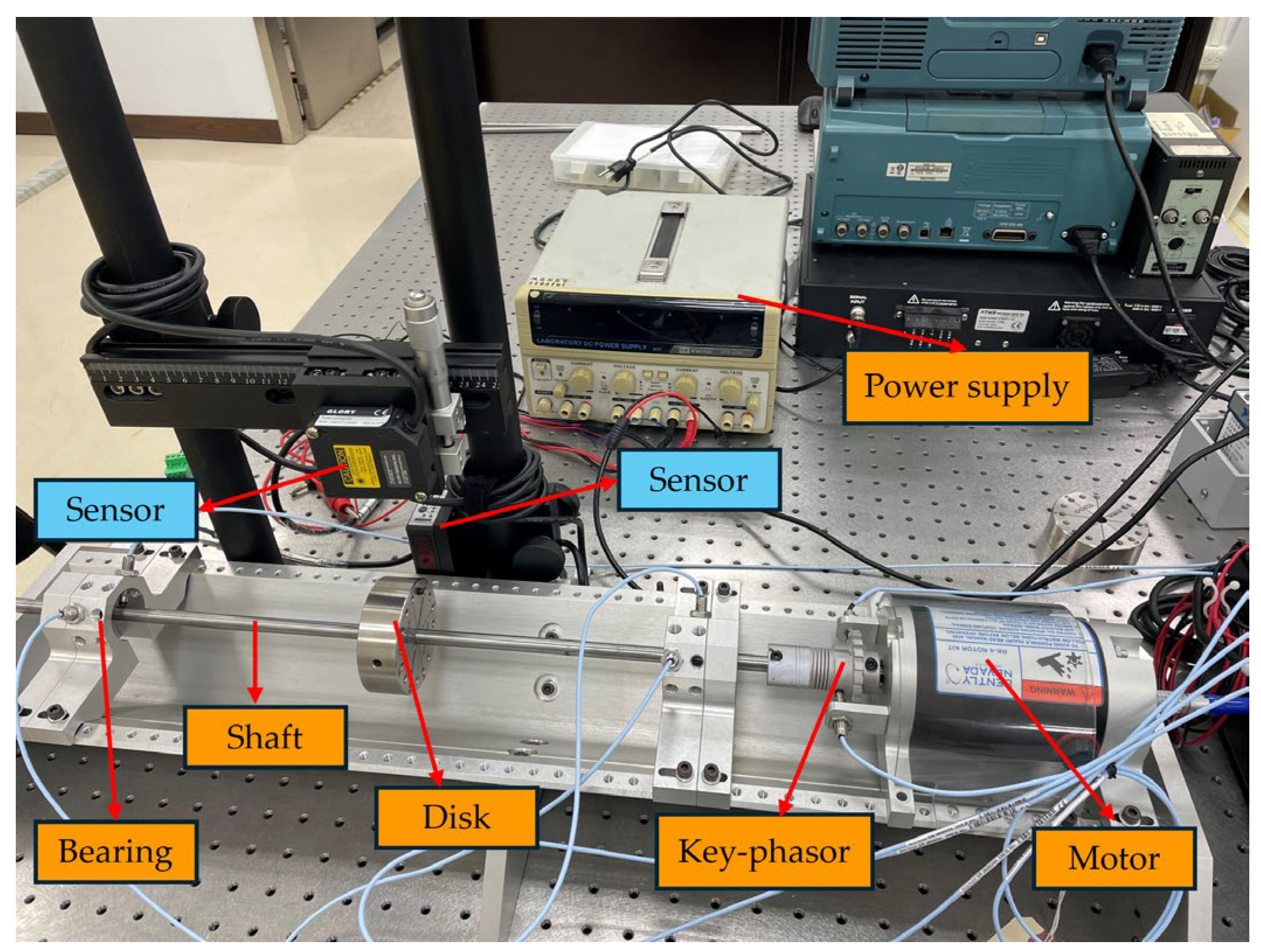
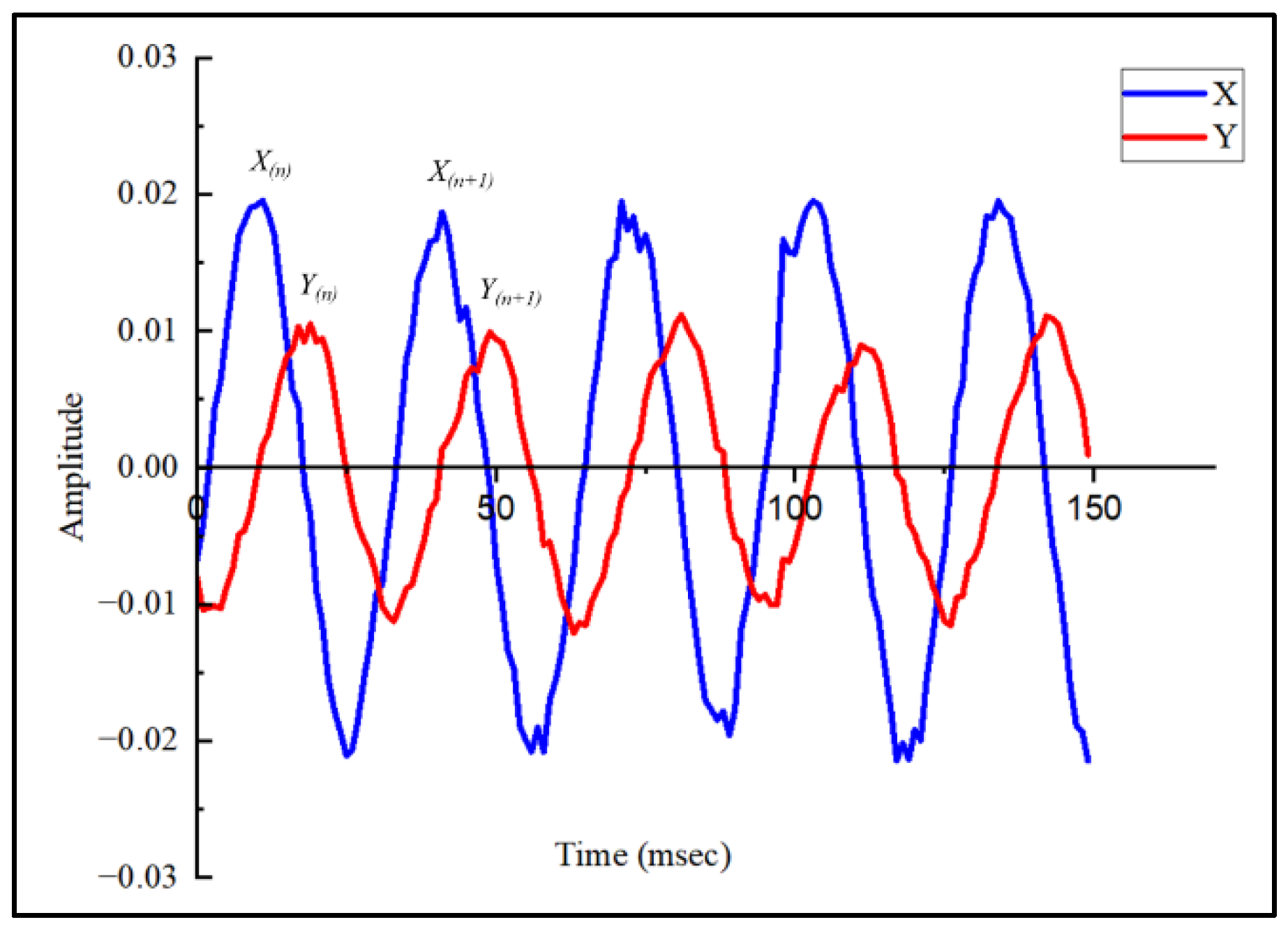
4.2. Experimental Verification and Real-time Diagnosis
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Misbah, I.; Lee, C.; Keung, K. Fault Diagnosis in Rotating Machines Based on Transfer Learning: literature review. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2023: p. 111158. [CrossRef]
- Lees, A.; Sinha, J.; Friswell, M. Model-based identification of rotating machines. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2009. 23(6): p. 1884-1893. [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.; Perinpanayagam, S.; Jennions, I.K. Rotordynamic faults: recent advances in diagnosis and prognosis. International Journal of Rotating Machinery, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X. Data-driven fault detection, isolation and identification of rotating machinery: With applications to pumps and gearboxes. 2012. [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Chung, Y. Misalignment diagnosis of rotating machinery through vibration analysis via the hybrid EEMD and EMD approach. Smart Materials and Structures, 2009. 18(9): p. 095004. [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Chu, F. HHT-based AE characteristics of natural fatigue cracks in rotating shafts. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2012. 26: p. 181-189. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Junsheng, C. A roller bearing fault diagnosis method based on EMD energy entropy and ANN. Journal of sound and vibration, 2006. 294(1-2): p. 269-277. [CrossRef]
- Al-Badour, F.; Sunar, M.; Cheded, L. Vibration analysis of rotating machinery using time–frequency analysis and wavelet techniques. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2011. 25(6): p. 2083-2101. [CrossRef]
- Ocak, H.; Loparo, K.A.; Discenzo, F.M. Online tracking of bearing wear using wavelet packet decomposition and probabilistic modeling: A method for bearing prognostics. Journal of sound and vibration, 2007. 302(4-5): p. 951-961. [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Chen, J.; Pu, Y. Wavelet time-frequency analysis of torsional vibrations in rotor system with a transverse crack. Computers & structures, 2004. 82(15-16): p. 1181-1187. [CrossRef]
- Walker, R. et al., Unbalance localization through machine nonlinearities using an artificial neural network approach. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2014. 75: p. 54-66. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, K.A.-H.; Hassaan, G.A.; Hegazy, A.A.-H. Artificial neural network based intelligent fault identification of rotating machinery. Technology, 2016. 2(2): p. 26-39. [CrossRef]
- Liu, R. et al., Artificial intelligence for fault diagnosis of rotating machinery: A review. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018. 108: p. 33-47. [CrossRef]
- Nath, A.G.; Udmale, S.S.; Singh, S.K. Role of artificial intelligence in rotor fault diagnosis: A comprehensive review. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2021. 54(4): p. 2609-2668. [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Howard, I. Torsional vibration signal analysis as a diagnostic tool for planetary gear fault detection. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018. 100: p. 706-728. [CrossRef]
- Edwards, S.; Lees, A.; Friswell, M. Estimating rotor unbalance from a single run-down, in IMeche Conference Transactions. 2000, Professional Engineering Publishing;. p. 323-334.
- Bachschmid, N.; Pennacchi, P. Accuracy of fault detection in real rotating machinery using model based diagnostic techniques. JSME International Journal Series C Mechanical Systems, Machine Elements and Manufacturing, 2003. 46(3): p. 1026-1034. [CrossRef]
- Bachschmid, N. et al., Identification and simulation of faults in rotor systems: experimental results. Euro Diname, 1999. 99: p. 3-11.
- Audebert, S., et al., Identification of transverse cracks in rotors systems, in Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Transport Phenomena and Dynamics of Rotating Machinery (ISROMAC-8). 2000. p. 1065-1072.
- Bachschmid, N.; Pennacchi, P.; Audebert, S. Some results in model-based transverse crack identification in rotor systems. CIT Informacion Tecnologica, 2001. 12(5): p. 25-32.
- Sekhar, A. Identification of unbalance and crack acting simultaneously in a rotor system: Modal expansion versus reduced basis dynamic expansion. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2005. 11(9): p. 1125-1145. [CrossRef]
- Jain, J.; Kundra, T. Model based online diagnosis of unbalance and transverse fatigue crack in rotor systems. Mechanics Research Communications, 2004. 31(5): p. 557-568. [CrossRef]
- Sinha, J.K.; Lees, A.; Friswell, M. Estimating unbalance and misalignment of a flexible rotating machine from a single run-down. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2004. 272(3-5): p. 967-989. [CrossRef]
- Jalan, A.K.; Mohanty, A. Model based fault diagnosis of a rotor–bearing system for misalignment and unbalance under steady-state condition. Journal of sound and vibration, 2009. 327(3-5): p. 604-622. [CrossRef]
- Pennacchi, P.; Vania, A. Diagnosis and model based identification of a coupling misalignment. Shock and Vibration, 2005. 12(4): p. 293-308. [CrossRef]
- Bachschmid, N.; Pennacchi, P.; Vania, A. Identification of multiple faults in rotor systems. Journal of sound and vibration, 2002. 254(2): p. 327-366. [CrossRef]
- Pennacchi, P. et al., Use of modal representation for the supporting structure in model-based fault identification of large rotating machinery: part 1—theoretical remarks. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2006. 20(3): p. 662-681. [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-L. et al., A novel model-based unbalance monitoring and prognostics for rotor-bearing systems. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2023. 15(1): p. 16878132221148019. [CrossRef]
- Bently, D.E.; Hatch’Charles, T. Fundamentals of rotating machinery diagnostics. Mechanical Engineering-CIME, 2003. 125(12): p. 53-54.
- Gavalas, I. et al. On the quality of stability and bifurcation sets in rotors with permanent shaft bow on nonlinear supports. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 2023: p. 104563. [CrossRef]
- Diouf, P.; Herbert, W. Understanding rotor balance for electric motors. Conference Record of 2014 Annual Pulp and Paper Industry Technical Conference, 2014: p. 7-17.
- Zhang, J.H. et al., Dynamic analysis of flexible rotor-ball bearings system with unbalance-misalignment-rubbing coupling faults, in Applied Mechanics and Materials. 2012, Trans Tech Publ. p. 448-453. [CrossRef]
- Ganeriwala, S.N.; Schwarz, B.; Richardson, M.H. Operating deflection shapes detect unbalance in rotating equipment. Sound and Vibration, 2009. 43(5): p. 11-13. Available online: http://www.sandv.com/downloads/0905gane.pdf.
- Edwards, S.; Lees, A.W.; Friswell, M.I. Fault diagnosis of rotating machinery. Shock and vibration digest, 1998. 30(1): p. 4-13. [CrossRef]
- Randall, R.B. State of the art in monitoring rotating machinery-part 1. Sound and vibration, 2004. 38(3): p. 14-21.
- Walker, R.; Perinpanayagam, S.; Jennions, I.K. Physics-based simulation for health management of rotating machinery. 2011. Available online: http://dspace.lib.cranfield.ac.uk/handle/1826/8453.
- Mogal, S.; Lalwani, D. Fault diagnosis of bent shaft in rotor bearing system. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2017. 31(1): p. 1-4. [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, J.; Gunter, E.; Allaire, P. Effect of residual shaft bow on unbalance response and balancing of a single mass flexible rotor—Part I: Unbalance response. 1976. [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, J.; Gunter, E.; Allaire, P. Effect of residual shaft bow on unbalance response and balancing of a single mass flexible rotor—Part II: balancing. 1976. [CrossRef]
- Flack, R.; Rooke, J. A theoretical-experimental comparison of the synchronous response of a bowed rotor in five different sets of fluid film bearings. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1980. 73(4): p. 505-517. [CrossRef]
- Shiau, T.N.; Lee, E.K. The residual shaft bow effect on dynamic response of a simply supported rotor with disk skew and mass unbalances. 1989. [CrossRef]
- Ehrich, F.F. Handbook of rotordynamics. (No Title), 1992.
- Rao, J. A note on Jeffcott warped rotor. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2001. 36(5): p. 563-575. [CrossRef]
- Kang, C. et al., Dynamic analysis of gear-rotor system with viscoelastic supports under residual shaft bow effect. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2011. 46(3): p. 264-275. [CrossRef]
- Pennacchi, P.; Vania, A. Accuracy in the identification of a generator thermal bow. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2004. 274(1-2): p. 273-295. [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Jia, J.; Zhao, M. Nonlinear analysis of a rub-impact rotor-bearing system with initial permanent rotor bow. Archive of Applied Mechanics, 2008. 78: p. 225-240. [CrossRef]
- Darpe, A.; Gupta, K.; Chawla, A. Dynamics of a bowed rotor with a transverse surface crack. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2006. 296(4-5): p. 888-907. [CrossRef]
- Song, G. et al., Theoretical–experimental study on a rotor with a residual shaft bow. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2013. 63: p. 50-58. [CrossRef]
- Rossner, M.;Thuemmel, T.; Ulbrich, H. Inclusion of unsteady bow in a model-based monitoring system for rotors. in Proceedings of the 9th IFToMM International Conference on Rotor Dynamics. 2015. Springer.
- Tong, X.; Palazzolo, A.; Suh, J. A Review of the Rotordynamic Thermally Induced Synchronous Instability (Morton) Effect. Applied Mechanics Reviews, 2017. 69(6). [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, H.; Srinivasan, K.; Umesh, K. Application of artificial neural network and wavelet transform for vibration analysis of combined faults of unbalances and shaft bow. Adv. Theor. Appl. Mech, 2010. 3(4): p. 159-176.
- Rezazadeh, N. et al. Classification of Unbalanced and Bowed Rotors under Uncertainty Using Wavelet Time Scattering, LSTM, and SVM. Applied Sciences, 2023. 13(12): p. 6861. [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-C.; Lin, C.-L.; Najibullah, M. Identification of A Turbine Rotor Unbalance Using A Hybrid Approach International Congress on Sound and Vibration 2022.
- Huang, S.-C.N.M. Unbalance Monitoring of an Overhung Rotor Using a Physics-Based and Machine Learning Approach, in 29th International Congress on Sound and Vibration. 2023.
- Djeziri, M.A.; Benmoussa, S.; Sanchez, R. Hybrid method for remaining useful life prediction in wind turbine systems. Renewable Energy, 2018. 116: p. 173-187. [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, Y. et al., Overview on hybrid approaches to fault detection and diagnosis: Combining data-driven, physics-based and knowledge-based models. Procedia Cirp, 2021. 99: p. 278-283. [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Puig, V.; Zhang, S. Fault diagnosis and prognosis using a hybrid approach combining structural analysis and data-driven techniques, in 2021 5th International Conference on Control and Fault-Tolerant Systems (SysTol). 2021, IEEE. p. 145-150. [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.S. Mechanical vibrations fifth edition. 2011.
- Razavi, S.; Tolson, B.A. A new formulation for feedforward neural networks. IEEE Transactions on neural networks, 2011. 22(10): p. 1588-1598. [CrossRef]
- Najibullah, M.; Lin, C.-L.; Huang, S.-C. Effect of Different Training Algorithms in Artificial Neural Networks on the Rotor Unbalance Diagnosis, in 2022 IET International Conference on Engineering Technologies and Applications (IET-ICETA). 2022. p. 1-2. [CrossRef]
- Alsaleh, A.; Sedighi, H.M.; Ouakad, H.M. Experimental and theoretical investigations of the lateral vibrations of an unbalanced Jeffcott rotor. Frontiers of Structural and Civil Engineering, 2020. 14: p. 1024-1032. [CrossRef]
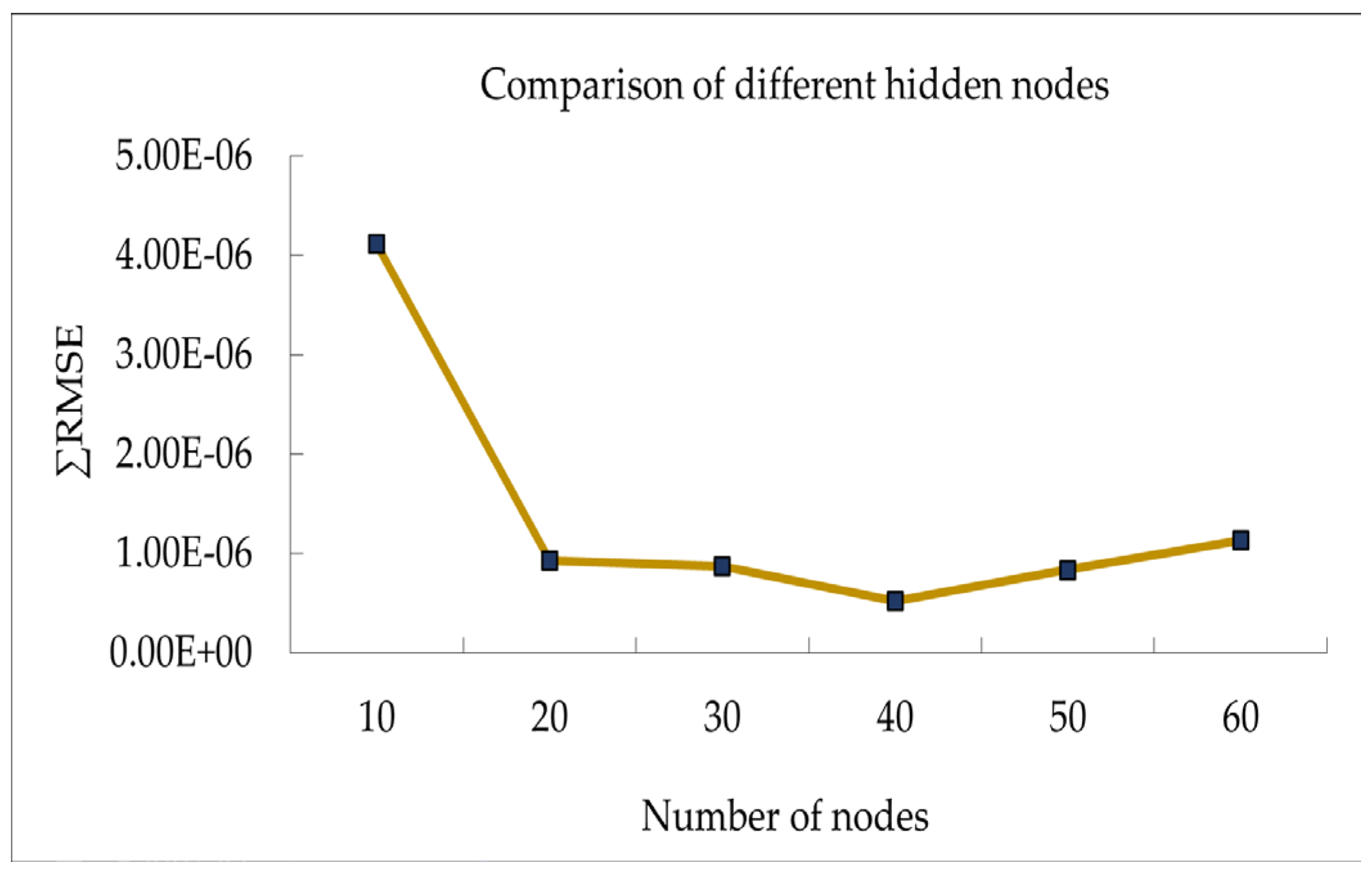
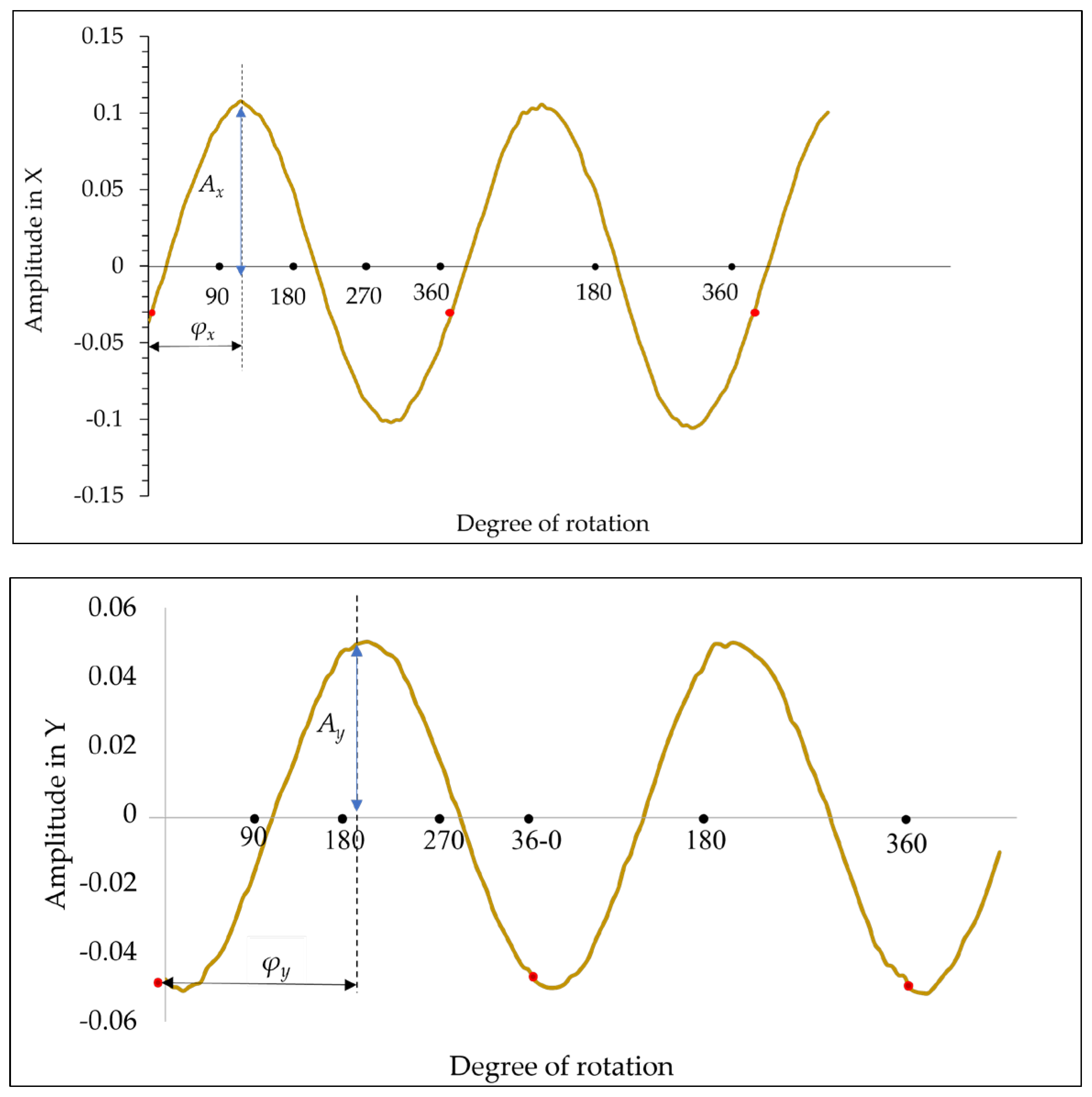
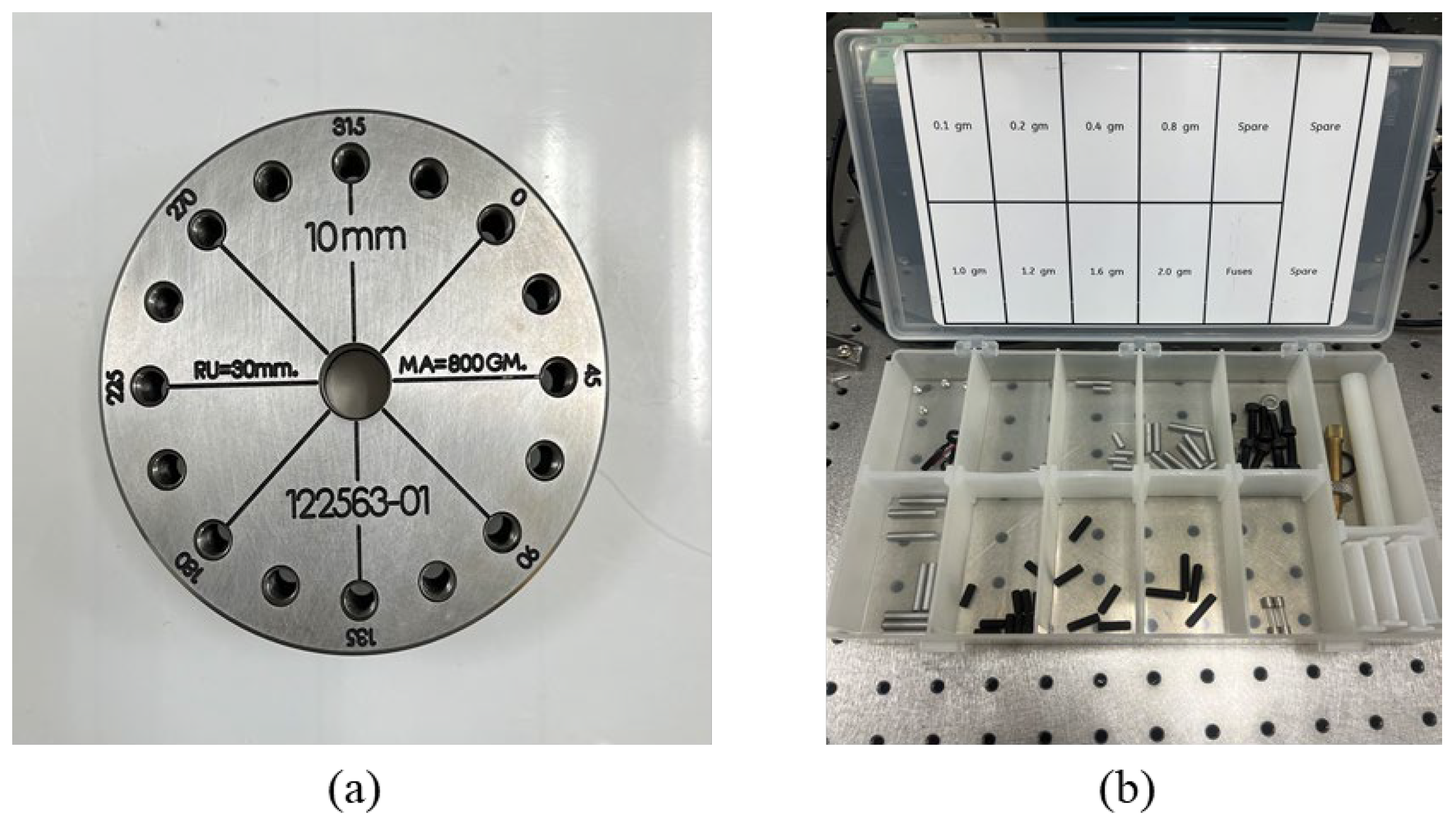
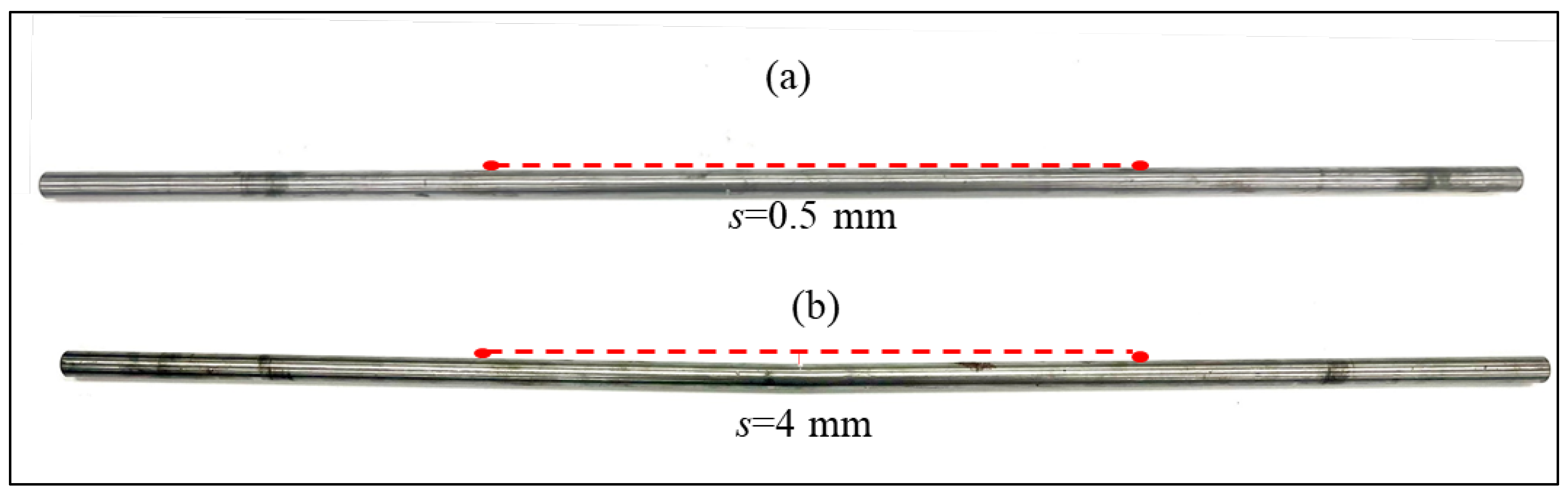
| Hidden nodes | Ux | Uy | sx | sy | ∑RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 1.88e-06 | 1.89e-06 | 2.05e-07 | 1.37e-07 | 4.11e-06 |
| 20 | 2.63e-07 | 2.14e-07 | 2.43e-07 | 2.07e-07 | 9.26e-07 |
| 30 | 3.13e-07 | 2.85e-07 | 1.37e-07 | 1.37e-07 | 8.72e-07 |
| 40 | 1.59e-07 | 1.88e-07 | 9.35e-08 | 7.67e-08 | 5.17e-07 |
| 50 | 2.18e-07 | 2.73e-07 | 1.57e-07 | 1.87e-07 | 8.34e-07 |
| 60 | 4.59e-07 | 4.34e-07 | 1.17e-07 | 1.18e-07 | 1.13e-06 |
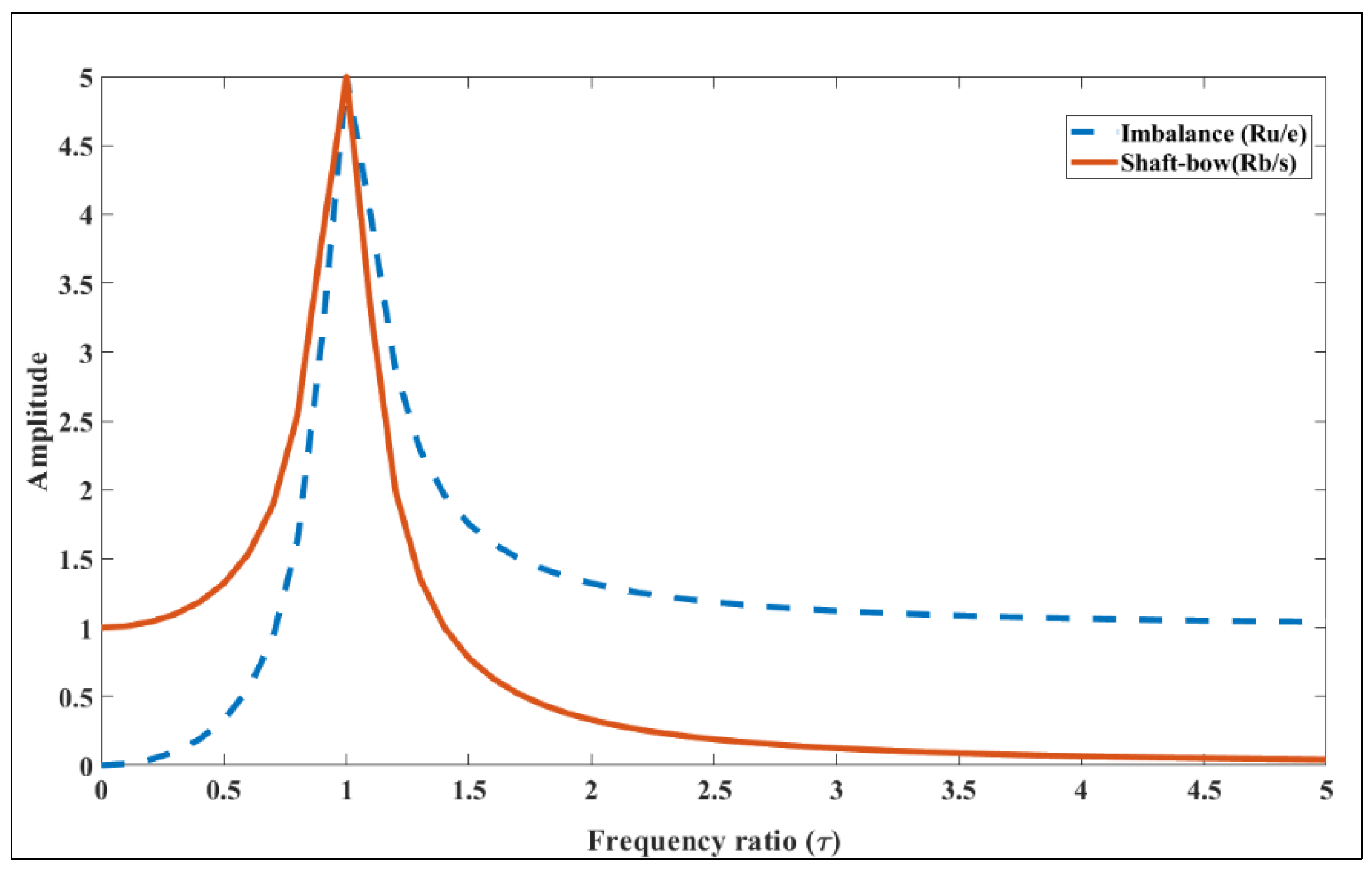
| Fault components | Imbalance dominant | Shaft-bow dominant | Equal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| τ < 1 | ||||
| Ux | 0.0323 | 0.3101 | 4.69e-05 | |
| Uy | 0.0581 | 0.3140 | 6.01e-05 | |
| sx | 0.2924 | 0.0147 | 1.37e-05 | |
| sy | 0.3398 | 0.0215 | 1.66e-05 | |
| τ ≈ 1 | ||||
| Ux | 0.0200 | 0.2937 | 3.96e-06 | |
| Uy | 0.0200 | 0.3295 | 6.87e-06 | |
| sx | 0.3031 | 0.0238 | 3.31e-05 | |
| sy | 0.2727 | 0.0146 | 6.67e-05 | |
| τ > 1 | ||||
| Ux | 0.0288 | 0.3557 | 6.59e-06 | |
| Uy | 0.0315 | 0.3008 | 3.11e-06 | |
| sx | 0.3459 | 0.0105 | 4.07e-05 | |
| sy | 0.2873 | 0.0221 | 6.99e-05 | |
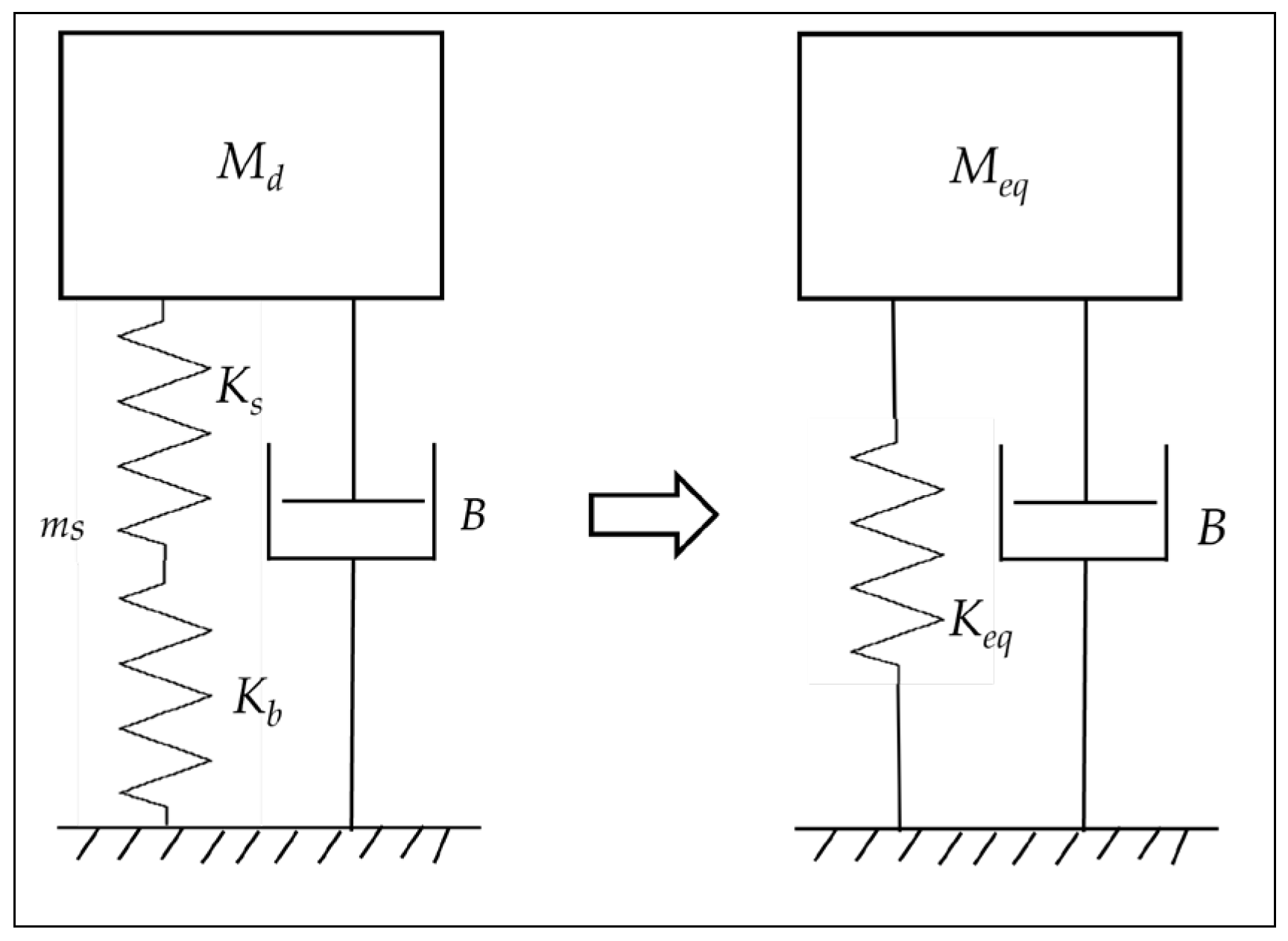
| C | Meq (kg) | ζ | Ks (kN/m) | Kb (kN/m) | Keq (kN/m) | ωn (rad/s) |
| Y | 0.96 | 0.47% | 96.908 | 108.92 | 51.282 | 230.1 |
| X | 0.96 | 0.5% | 96.908 | 135.72 | 56.538 | 241.6 |
| Case | Faults | Real | Diagnosed | Error | Comp | Error% |
| 1 (same quadrant) | U | 6 | 7.03 | 17.2% | ΔU// | 17.0 |
| α | 45o | 48.80o | 3.08o | ΔU⊥ | 6.3 | |
| s | 0.5 | 0.36 | 28.0% | Δs// | -28.4 | |
| θ | 60o | 53.95o | 6.05o | Δs⊥ | -7.6 | |
| 2 (in-phase) | U | 12 | 12.29 | 2.4% | ΔU// | -0.6 |
| α | 90o | 76.14o | 13.86o | ΔU⊥ | -24.5 | |
| s | 0.5 | 0.58 | 16.0% | Δs// | 14.6 | |
| θ | 90o | 81.16o | 8.84o | Δs⊥ | -17.8 | |
| 3 (anti-phase) | U | 24 | 21.28 | 11.3% | ΔU// | -13.1 |
| α | 225o | 213.63o | 11.37o | ΔU⊥ | -17.5 | |
| s | 0.5 | 0.39 | 22.0% | Δs// | -22.3 | |
| θ | 30o | 35.28o | 5.28o | Δs⊥ | 7.2 | |
| 4 (perpendicular) | U | 30 | 38.24 | 27.5% | ΔU// | 22.9 |
| α | 67.5o | 82.88o | 15.38o | ΔU⊥ | 33.8 | |
| s | 0.5 | 0.35 | 30.0% | Δs// | -30.0 | |
| θ | 150o | 147.87o | 2.13o | Δs⊥ | -2.6 |
| Number | Faults | Real | Diagnosed | Error | Comp | Error% |
| 1 (same quadrant) | U | 6 | 4.4 | 26.7% | ΔU// | -27.7 |
| α | 45o | 35.24o | 9.76o | ΔU⊥ | 12.4 | |
| s | 0.5 | 0.69 | 38.0% | Δs// | 36.5 | |
| θ | 60o | 54.41o | 8.59o | Δs⊥ | 20.6 | |
| 2 (in-phase) | U | 12 | 13..34 | 11.2% | ΔU// | 10.3 |
| α | 90o | 97.24o | 7.24 o | ΔU⊥ | 14.0 | |
| s | 0.5 | 0.31 | 38.0% | Δs// | -38.4 | |
| θ | 90o | 96.18o | 6.18.o | Δs⊥ | 6.7 | |
| 3 (anti-phase) | U | 24 | 26.72 | 11.3% | ΔU// | 2.8 |
| α | 225o | 202.39o | 22.61o | ΔU⊥ | 42.8 | |
| s | 0.5 | 0.54 | 8.0% | Δs// | 5.9 | |
| θ | 30o | 18.68o | 11.32o | Δs⊥ | 21.2 | |
| 4 (perpendicular) | U | 30 | 28.41 | 5.3% | ΔU// | -7.0 |
| α | 67.5o | 56.53o | 10.97o | ΔU⊥ | 18.0 | |
| s | 0.5 | 0.31 | 38.0% | Δs// | -39.0 | |
| θ | 150o | 139.88o | 10.12o | Δs⊥ | 10.9 |
| Number | Faults | Real | Diagnosed | Error | Comp | Error% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (same quadrant) | U | 6 | 5.12 | 14.7% | ΔU// | -15.9 |
| α | 45o | 54.71o | 9.71o | ΔU⊥ | 14.4 | |
| s | 4.0 | 4.17 | 4.2% | Δs// | 0.8 | |
| θ | 60o | 74.84o | 14.84o | Δs⊥ | 26.7 | |
| 2 (in-phase) | U | 12 | 14.86 | 23.8% | ΔU// | 11.7 |
| α | 90o | 64.39o | 25.61o | ΔU⊥ | 53.5 | |
| s | 4.0 | 4.27 | 6.8% | Δs// | -4.7 | |
| θ | 90o | 116.83o | 26.83o | Δs⊥ | 48.2 | |
| 3 (anti-phase) | U | 24 | 30.28 | 26.0% | ΔU// | 24.3 |
| α | 225o | 215.06o | 9.94o | ΔU⊥ | 21.8 | |
| s | 4.0 | 3.72 | 7.0% | Δs// | -7.1 | |
| θ | 30o | 32.71o | 2.71o | Δs⊥ | 4.4 | |
| 4 (perpendicular) | U | 30 | 32.16 | 7.2% | ΔU// | -5.2 |
| α | 67.5o | 39.63o | 27.87o | ΔU⊥ | 50.1 | |
| s | 4.0 | 3.0 | 25.0% | Δs// | -29.7 | |
| θ | 150o | 169.19o | 19.9o | Δs⊥ | 25.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





