Submitted:
22 November 2023
Posted:
23 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
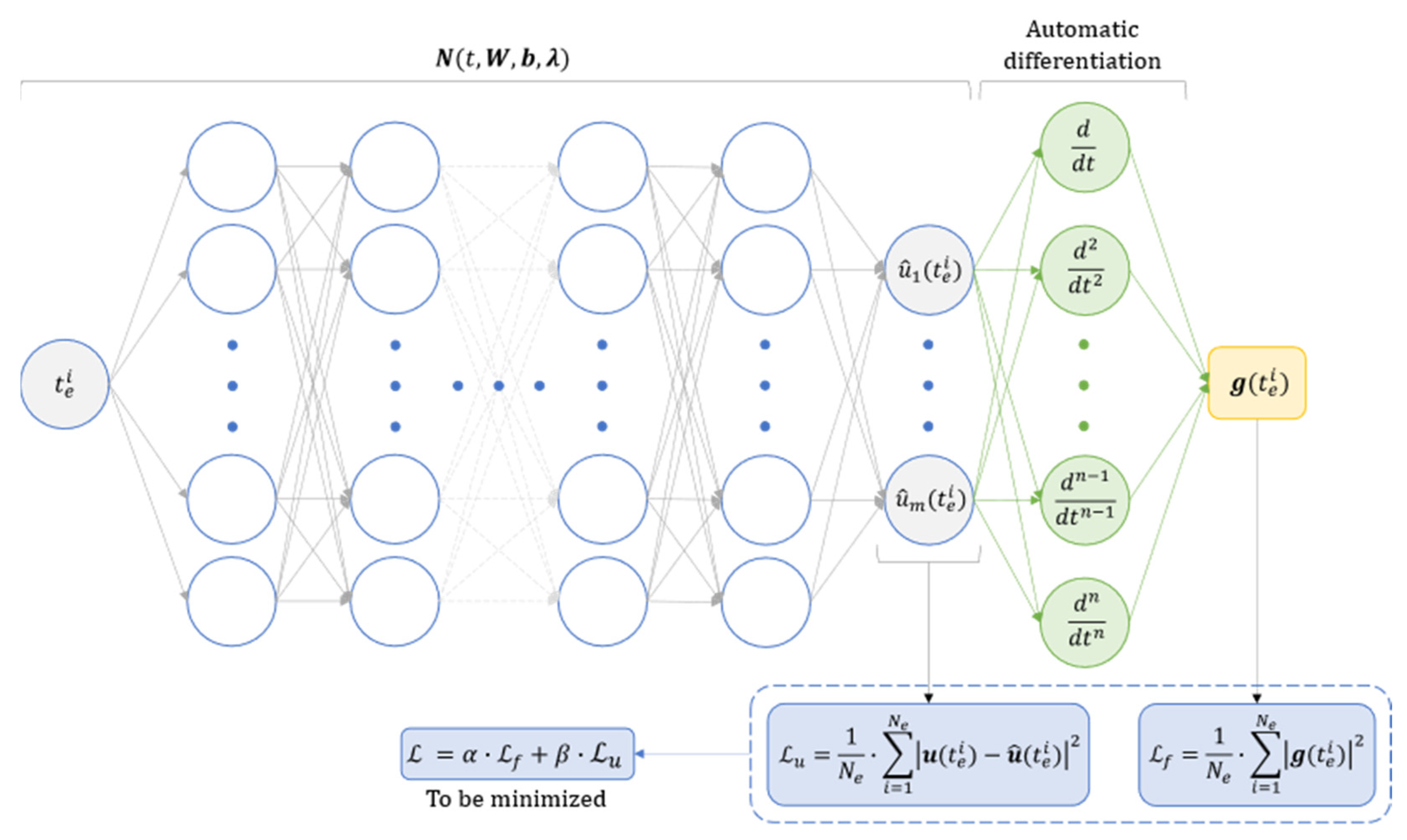
2. Methodology
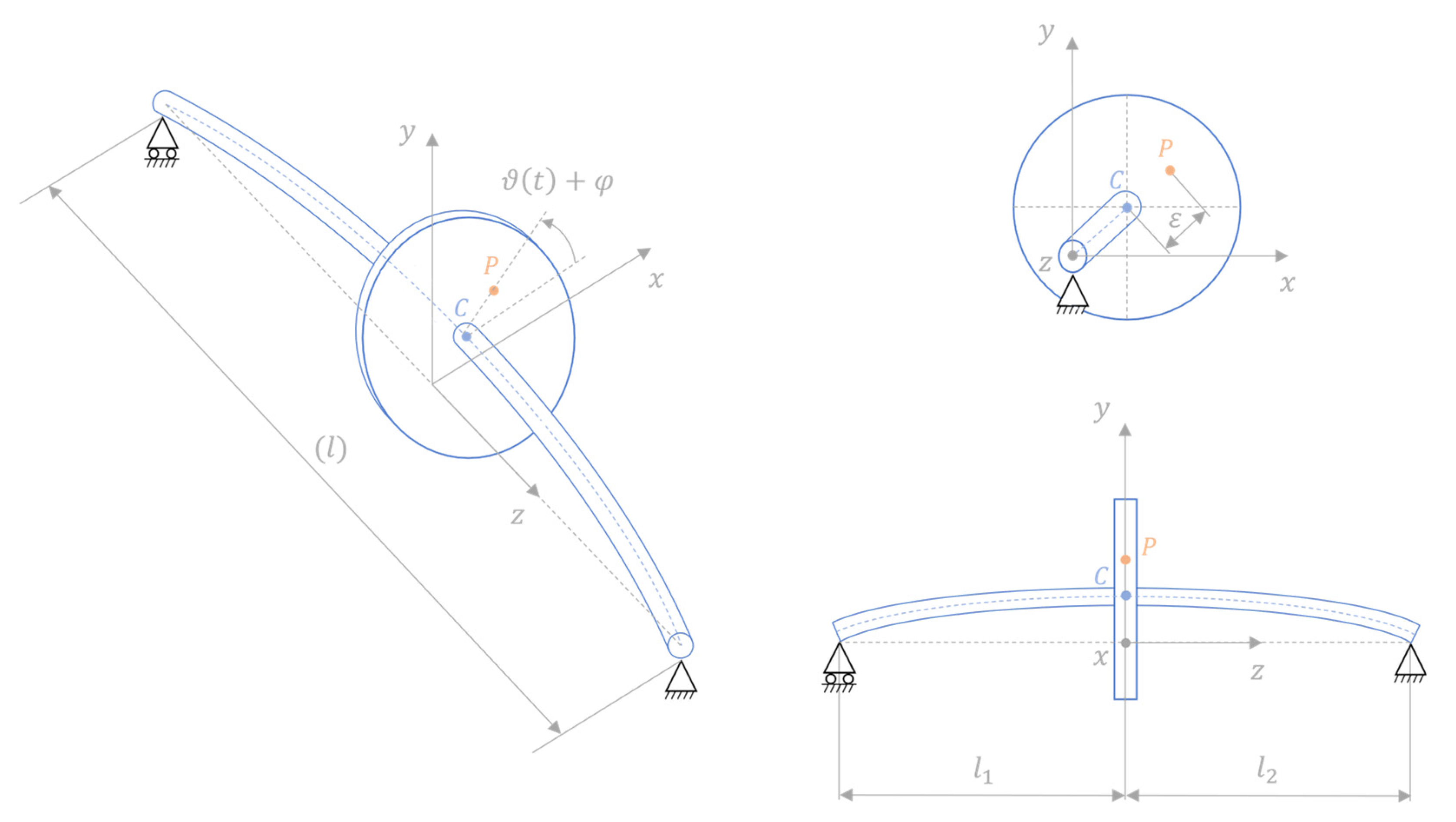
3. Case study
3.1. Extended Jeffcott rotor with unknown system parameters
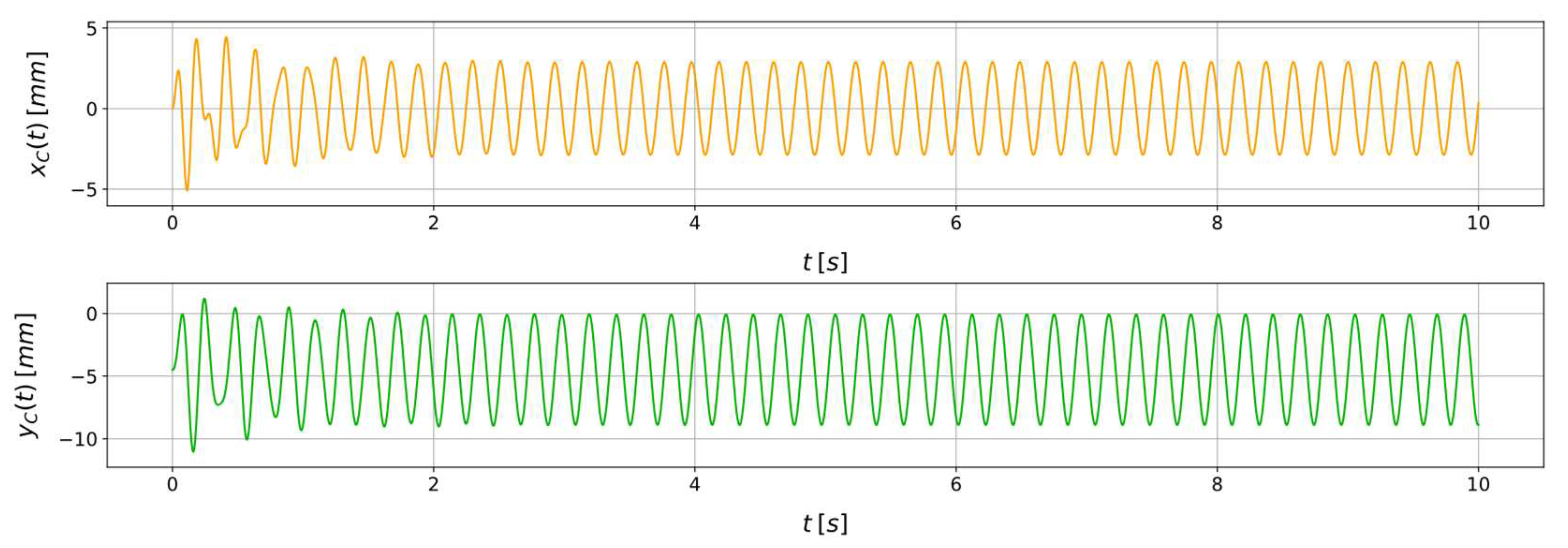
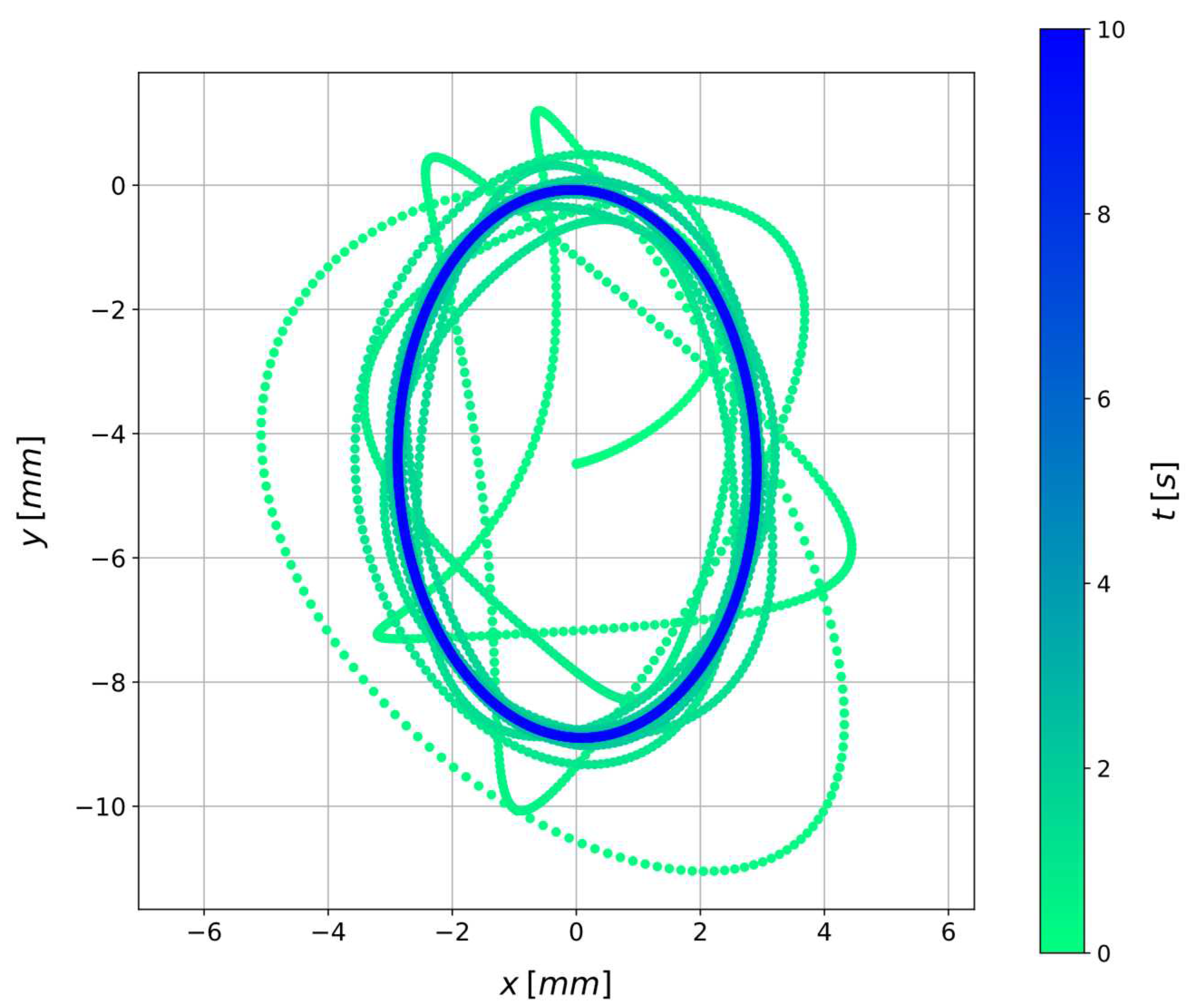
3.2. System state characterization through physics-informed neural networks
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tandon, N.; Parey, A. Condition Monitoring of Rotary Machines. 2006, 109–136. [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Park, S.; Woo, S.; Lee, S. Rotating Machinery Diagnostics Using Deep Learning on Orbit Plot Images. Procedia Manuf. 2016, 5, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiboni, M.; Remino, C.; Bussola, R.; Amici, C. A Review on Vibration-Based Condition Monitoring of Rotating Machinery. Appl. Sci. 2022, Vol. 12, Page 972 2022, 12, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.; Mendes, J.C.; Pereira, A.B.; Gégot, F.; Alves, L.N. Measuring Torque and Temperature in a Rotating Shaft Using Commercial SAW Sensors. Sensors 2017, Vol. 17, Page 1547 2017, 17, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, S.; Toliyat, H.A.; Li, X. Condition Monitoring and Fault Diagnosis of Electrical Motors - A Review. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2005, 20, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, C.R.; Worden, K. An Introduction to Structural Health Monitoring. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2006, 365, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, Z.; Hong, Y.S.; Cho, Y.M.; Ahn, S.H.; Song, C.K. Condition Monitoring and Fault Detection of Wind Turbines and Related Algorithms: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Huang, X.; Wen, G.; Lei, Z.; Dong, S.; Zhang, P.; Chen, X. Construction of Health Indicators for Condition Monitoring of Rotating Machinery: A Review of the Research. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 203, 117297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogue, R. Sensors for Condition Monitoring: A Review of Technologies and Applications. Sens. Rev. 2013, 33, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, H. Effects of Environmental and Operational Variability on Structural Health Monitoring. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2006, 365, 539–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parziale, M.; Lomazzi, L.; Giglio, M.; Cadini, F. Vibration-Based Structural Health Monitoring Exploiting a Combination of Convolutional Neural Networks and Autoencoders for Temperature Effects Neutralization. Struct. Control Heal. Monit. 2022, 29, e3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Yan, R.; Chen, Z.; Mao, K.; Wang, P.; Gao, R.X. Deep Learning and Its Applications to Machine Health Monitoring. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 115, 213–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Chu, J.; Guo, P.; Chen, Z. Condition Monitoring of Wind Turbine Gearbox Bearing Based on Deep Learning Model. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 57078–57087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, K.; Nash, R. An Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2015, 10, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.M. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): A Gentle Introduction and Overview. 2019.
- Souza, R.M.; Nascimento, E.G.S.; Miranda, U.A.; Silva, W.J.D.; Lepikson, H.A. Deep Learning for Diagnosis and Classification of Faults in Industrial Rotating Machinery. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 153, 107060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisal, M.; Oh, K.Y. A New Deep Learning Framework for Imbalance Detection of a Rotating Shaft. Sensors 2023, Vol. 23, Page 7141 2023, 23, 7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition 2016, 770–778.
- Dosilovic, F.K.; Brcic, M.; Hlupic, N. Explainable Artificial Intelligence: A Survey. 2018 41st Int. Conv. Inf. Commun. Technol. Electron. Microelectron. MIPRO 2018 - Proc. 2018, 210–215. [CrossRef]
- Lomazzi, L.; Fabiano, S.; Parziale, M.; Giglio, M.; Cadini, F. On the Explainability of Convolutional Neural Networks Processing Ultrasonic Guided Waves for Damage Diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 183, 109642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parziale, M.; Lomazzi, L.; Giglio, M.; Cadini, F. Transmissibility Functions-Based Structural Damage Assessment with the Use of Explainable Convolutional Neural Networks. 2023, 540–549. [CrossRef]
- Parziale, M.; Henrique Silva, P.; Giglio, M.; Cadini, F. Explainability of Convolutional Neural Networks for Damage Diagnosis Using Transmissibility Functions. [CrossRef]
- Raissi, M.; Perdikaris, P.; Karniadakis, G.E. Physics-Informed Neural Networks: A Deep Learning Framework for Solving Forward and Inverse Problems Involving Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations. J. Comput. Phys. 2019, 378, 686–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raissi, M.; Perdikaris, P.; Karniadakis, G.E. Physics Informed Deep Learning (Part I): Data-Driven Solutions of Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations. 2017.
- Haghighat, E.; Raissi, M.; Moure, A.; Gomez, H.; Juanes, R. A Physics-Informed Deep Learning Framework for Inversion and Surrogate Modeling in Solid Mechanics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2021, 379, 113741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Lu, H.; Sadoughi, M.; Hu, C.; Nemani, V.; Thelen, A.; Webster, K.; Darr, M.; Sidon, J.; Kenny, S. A Physics-Informed Deep Learning Approach for Bearing Fault Detection. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 103, 104295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garpelli, L.N.; Alves, D.S.; Cavalca, K.L.; de Castro, H.F. Physics-Guided Neural Networks Applied in Rotor Unbalance Problems. https://doi.org/10.1177/14759217231163081 2023. [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Nguyen, K.T.P.; Medjaher, K.; Gogu, C.; Morio, J. Rotor Dynamics Informed Deep Learning for Detection, Identification, and Localization of Shaft Crack and Unbalance Defects. Adv. Eng. Informatics 2023, 58, 102128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cybenko, G. Approximation by Superpositions of a Sigmoidal Function. Math. Control. Signals, Syst. 1989, 2, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-C. Artificial Neural Network. Interdiscip. Comput. Java Program. 2003, 81–100. [CrossRef]
- Margossian, C.C.; Charles Margossian, C.C. A Review of Automatic Differentiation and Its Efficient Implementation. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2019, 9, e1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Seyab, R.K.; Cao, Y. Nonlinear System Identification for Predictive Control Using Continuous Time Recurrent Neural Networks and Automatic Differentiation. J. Process Control 2008, 18, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genta, G.; Keith, R.H. Vibration Dynamics and Control. Noise Control Eng. J. 2009, 57, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrada, M.; Sánchez, R.V.; Li, C.; Pacheco, F.; Cabrera, D.; Valente de Oliveira, J.; Vásquez, R.E. A Review on Data-Driven Fault Severity Assessment in Rolling Bearings. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 99, 169–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogacki, P.; Shampine, L.F. An Efficient Runge-Kutta (4,5) Pair. Comput. Math. with Appl. 1996, 32, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning Representations by Back-Propagating Errors. Nat. 1986 3236088 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.C.; Nocedal, J. On the Limited Memory BFGS Method for Large Scale Optimization. Math. Program. 1989, 45, 503–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
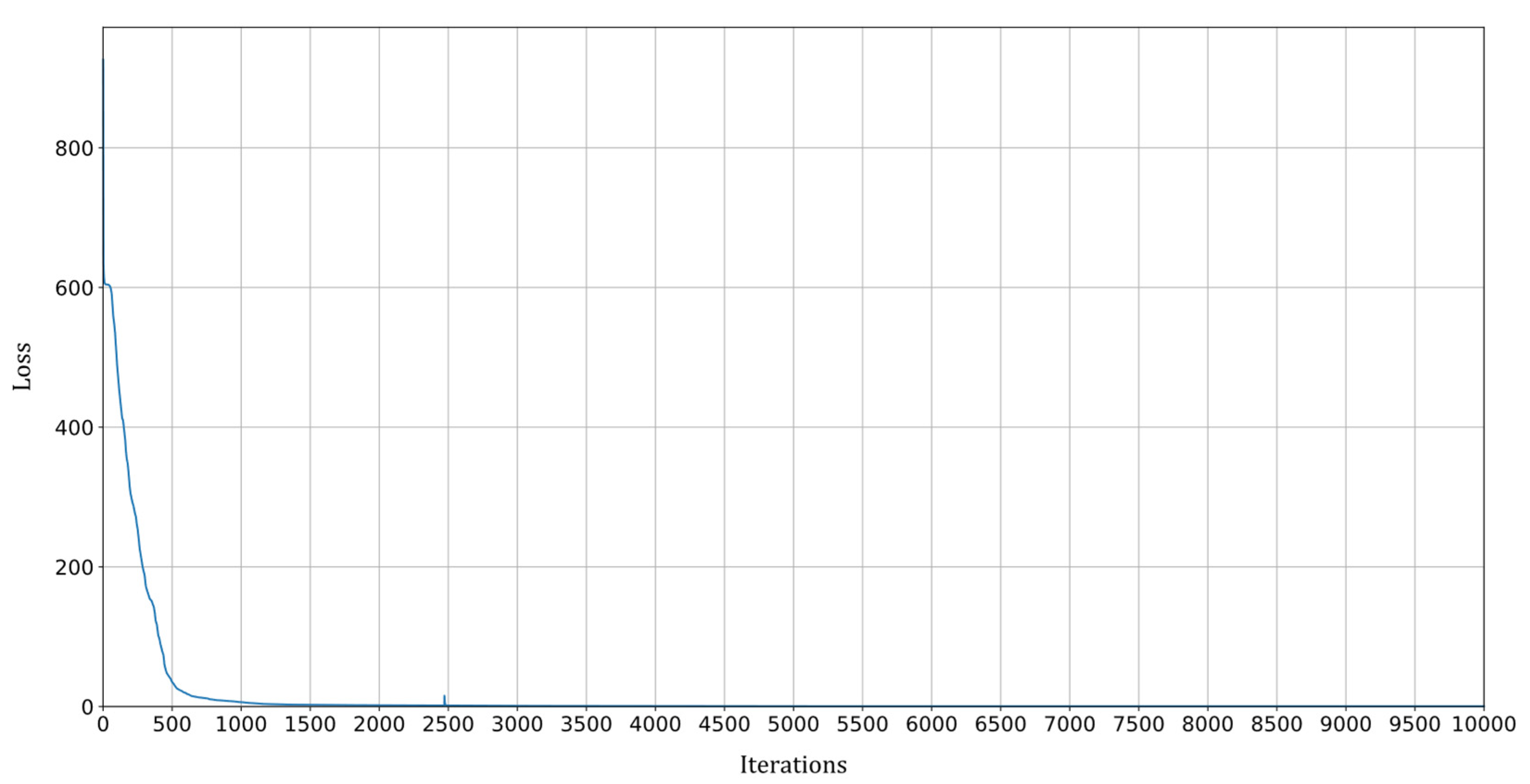
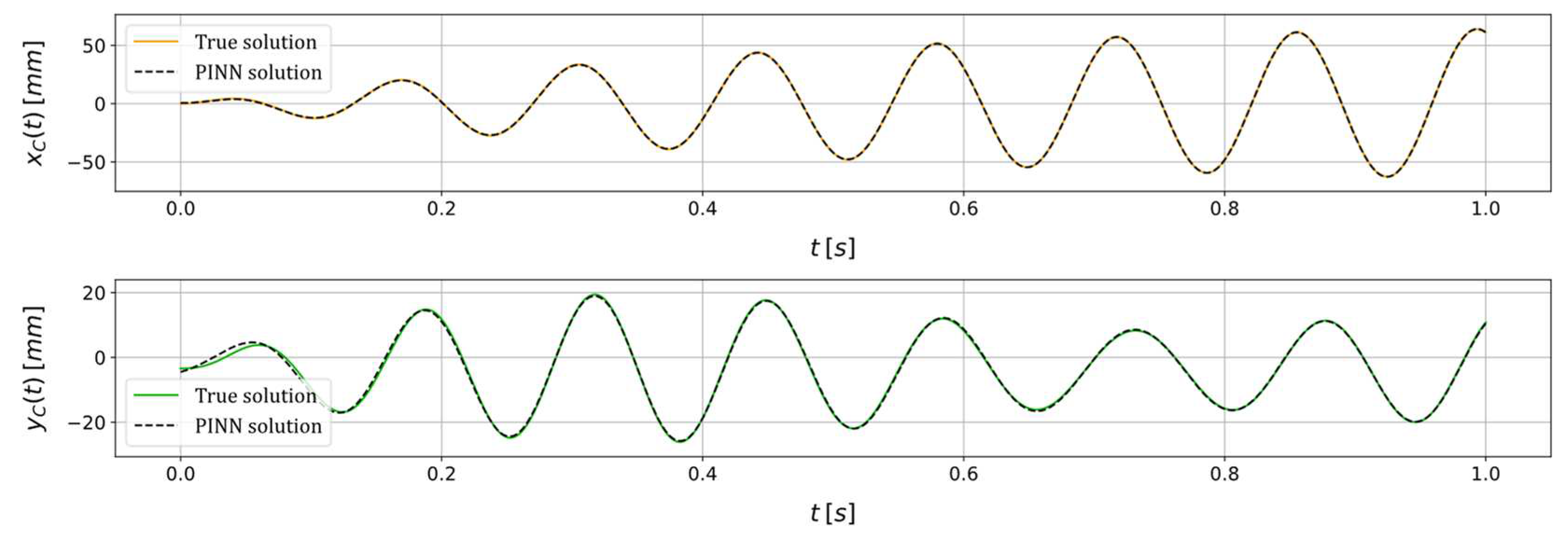
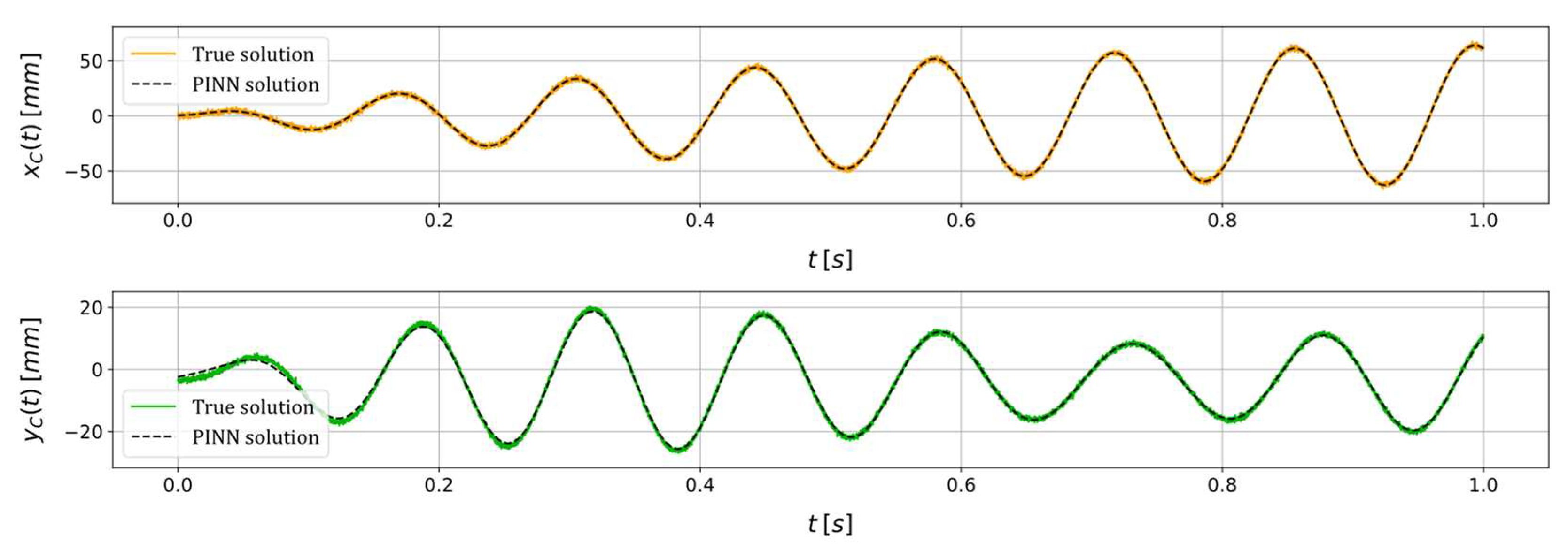
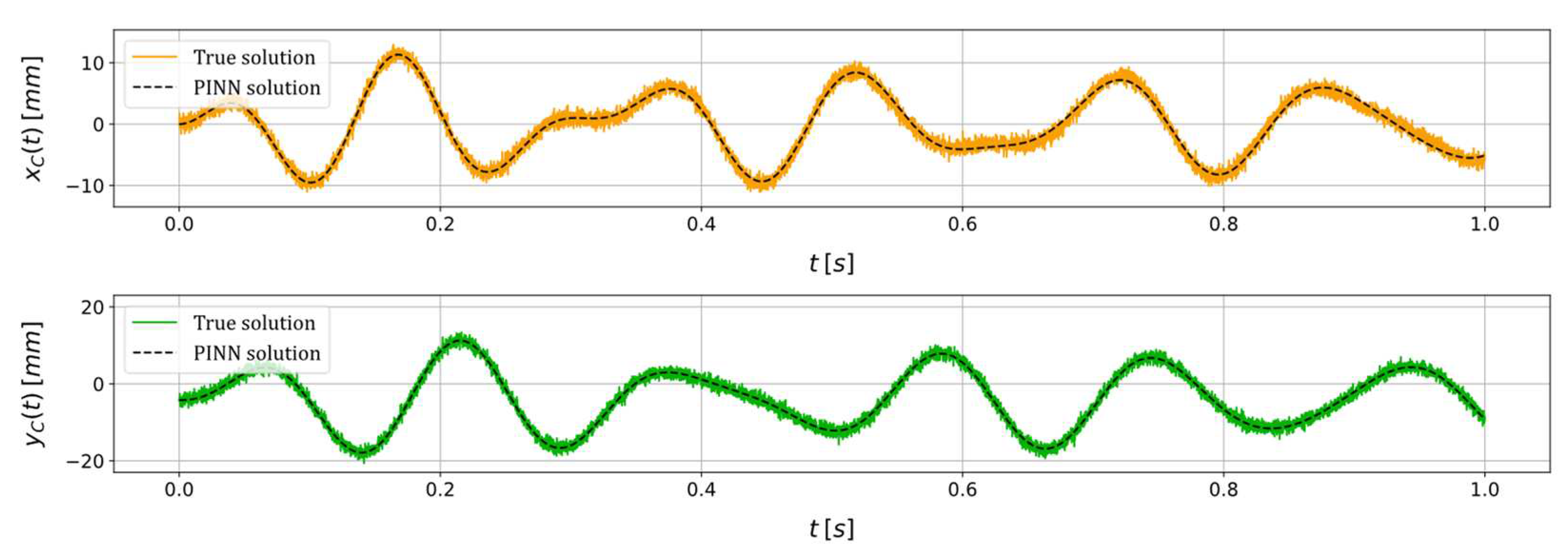
| Unknown parameter | True value | PINN estimation | Relative error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unknown parameter | True value | PINN estimation | Relative error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unknown parameter | True value | PINN estimation | Relative error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





