Submitted:
03 March 2024
Posted:
05 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Structures, Antimicrobial Activities, and Common Properties of Insect AMPs
2.1. Structures and Antimicrobial Activities of Insect AMPs
2.1.1. α-Helical Insect AMPs
2.1.2. β-Sheet Cysteine-Rich Insect AMPs
2.1.3. Proline-Rich Insect AMPs
2.1.4. Glycine-Rich Insect AMPs
2.2. Common Properties of Insect AMPs
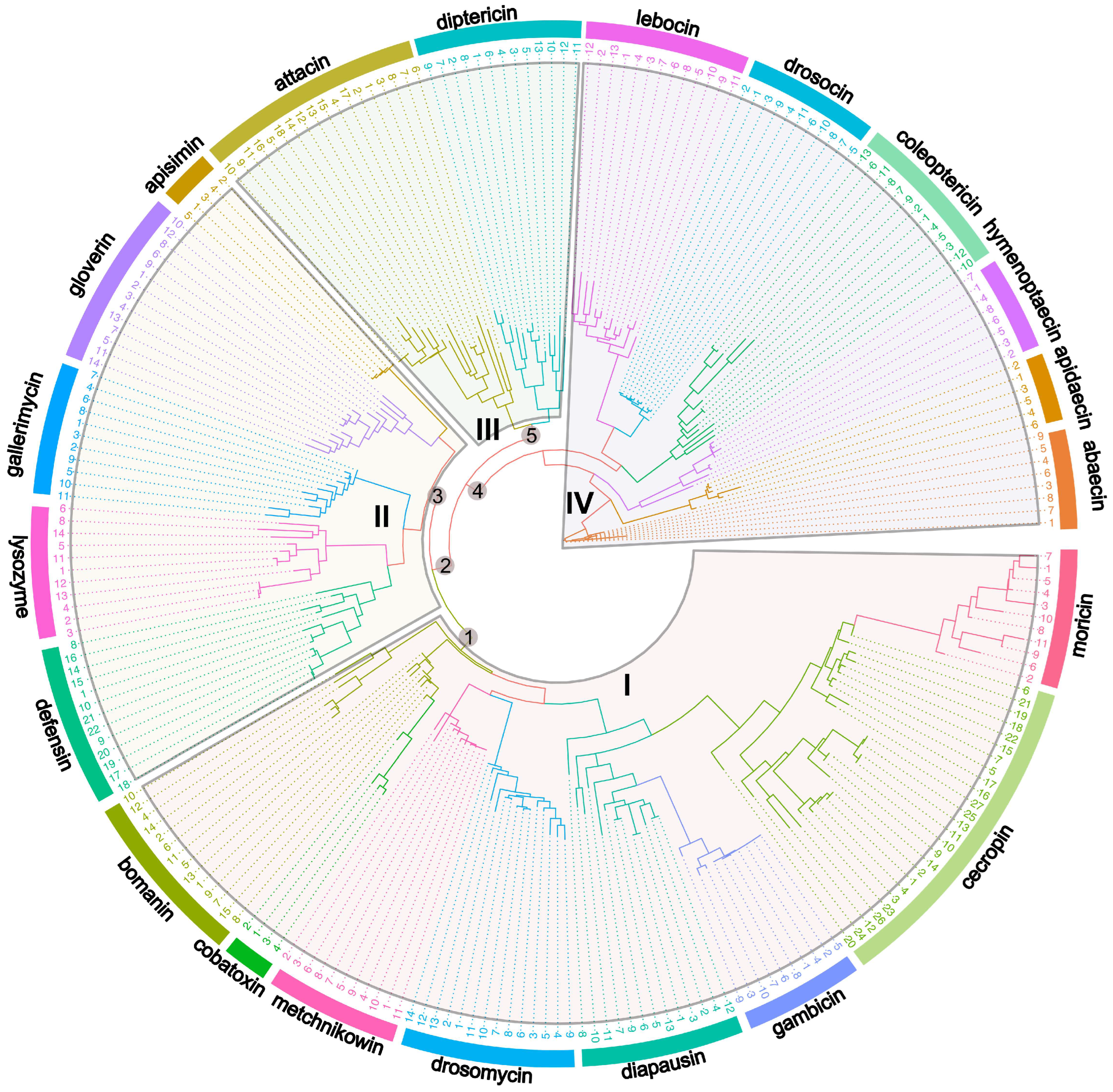
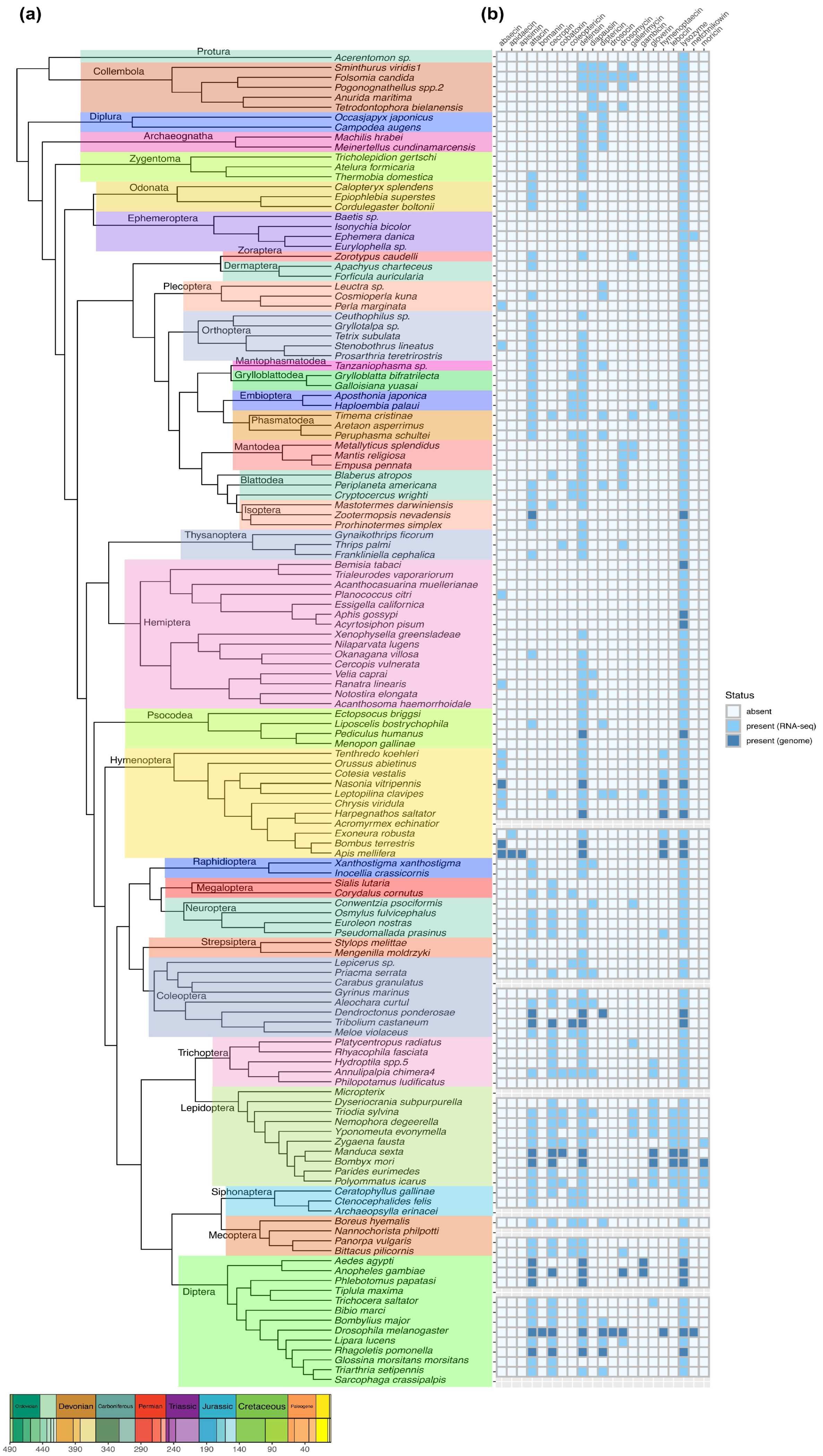
3. Evolution of Insect AMPs
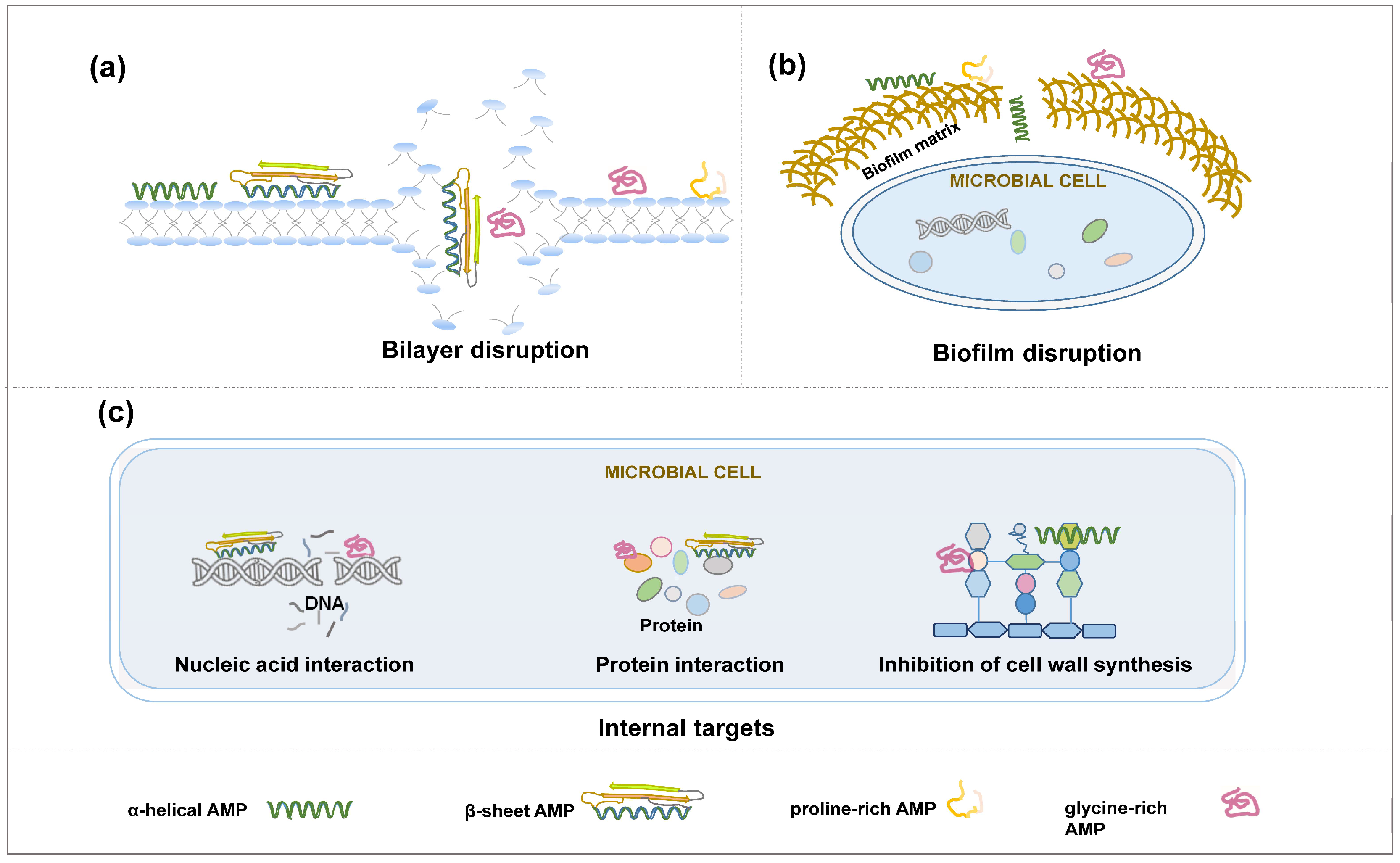
4. Action Mechanisms of AMPs
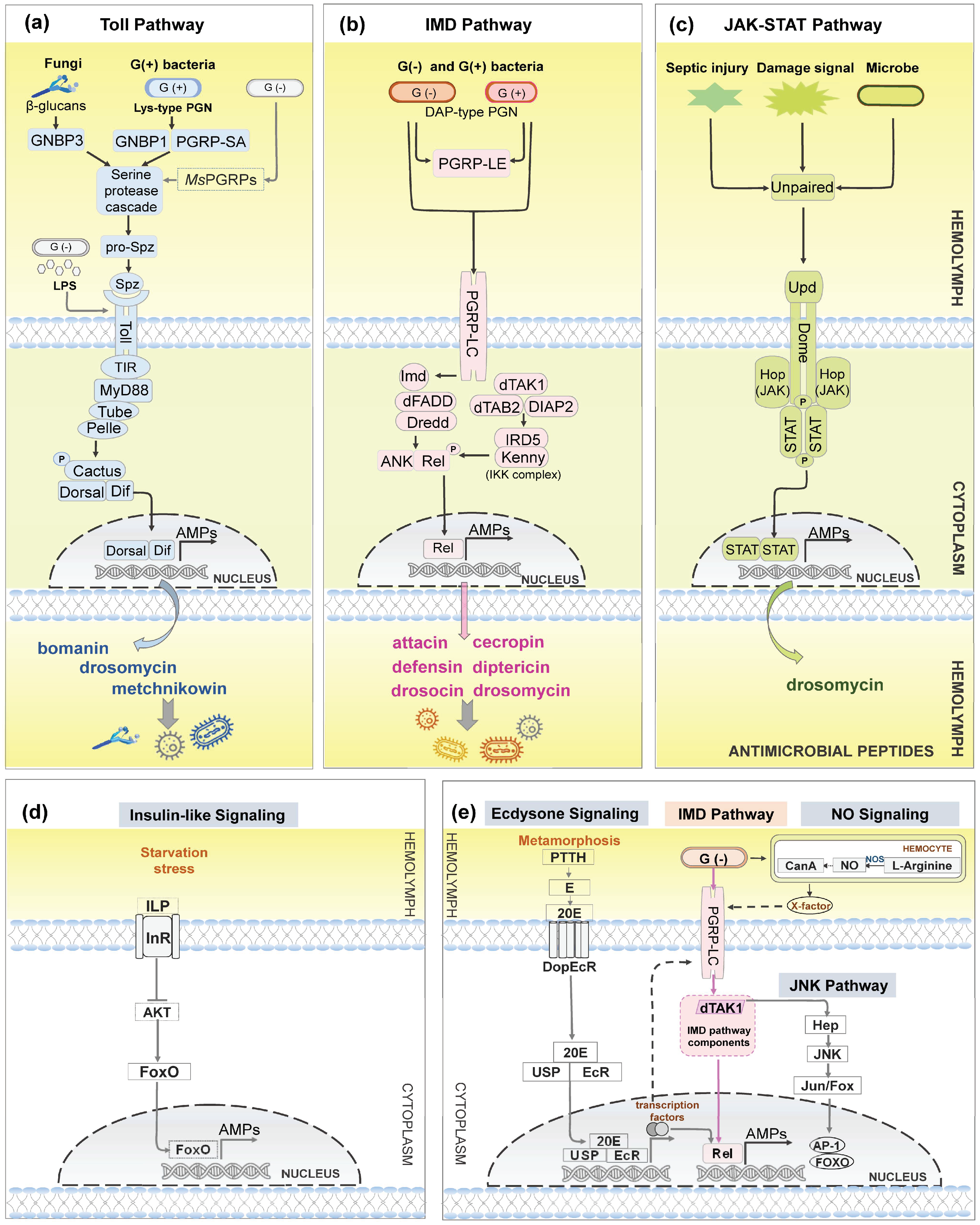
5. Transcriptional Regulation of AMPs
5.1. Insect AMPs Regulated by Toll Pathway
5.2. Insect AMPs Regulated by IMD Pathway
5.3. Insect AMPs Regulated by Intestinal IMD-NF-κB Pathway
5.4. Insect AMPs Regulated by JAK-STAT Pathway
5.5. Insect AMPs Regulated by Other Signaling Pathways
6. Potential Applications of Insect AMPs
7. Future Perspective
8. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoffmann, J.A. Innate immunity of insects. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1995, 7, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hultmark, D. Immune reactions in Drosophila and other insects: a model for innate immunity. Trends Genet. TIG 1993, 9, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Lu, Z. Immune responses to bacterial and fungal infections in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 83, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Tettamanti, G.; Bassal, T.; Heryanto, C.; Eleftherianos, I.; Mohamed, A. Regulators and signalling in insect antimicrobial innate immunity: Functional molecules and cellular pathways. Cellular Signal. 2021, 83, 110003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, U.; Vogel, P.; Alber, G.; Schaub, G.A. The innate immune system of mammals and insects. Contrib. Microbiol. 2008, 15, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-j.; Gallo, R.L. Antimicrobial peptides. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R14–R19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, G.; Beckloff, N.; Weinberg, A.; Kisich, K.O. The roles of antimicrobial peptides in innate host defense. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 2377–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zasloff, M. Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature 2002, 415, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stączek, S.; Cytryńska, M.; Zdybicka-Barabas, A. Unraveling the role of antimicrobial peptides in insects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczepanik, K.; Świątkiewicz, M. Hermetia illucens as a source of antimicrobial peptides-a review of in vitro and in vivo studies. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2024, 24, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanjal, D.S., Chopra, C., Bhardwaj, S., Sharma, P., Nepovimova, E., Singh, R., Kuca, K. Insect peptides with antimicrobial effects. In Antimicrobial Peptides. 2023.pp. 117-138. Academic Press.
- Bulet, P.; Stöcklin, R.; Menin, L. Anti-microbial peptides: from invertebrates to vertebrates. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 198, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, R.E.; Diamond, G. The role of cationic antimicrobial peptides in innate host defences. Trends Microbiol. 2000, 8, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ageitos, J.M.; Sánchez-Pérez, A.; Calo-Mata, P.; Villa, T.G. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs): Ancient compounds that represent novel weapons in the fight against bacteria. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 133, 117–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubos, R.J. Studies on a bactericidal agent extracted from a soil bacillus: II. Protective effect of the bactericidalagent against experimental pneumococcus infections in mice. J. Exp. Med. 1939, 70, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubos, R.J. Studies on a bactericidal agent extracted from a soil bacillus: I. Preparation of the agent. Its activity in virto. J. Exp. Med. 1939, 70, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balls, A.K.; Hale, W.S.; Harris, T.H. A crystalline protein obtained from a lipoprotein of wheat flour. Cereal Chem. 1942, 19, 279–288. [Google Scholar]
- Kiss, G.; Michl, H. Uber das Giftsekret der Gelbbauchunke, Bombina variegata L. Toxicon 1962, 1, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultmark, D.; Steiner, H.; Rasmuson, T.; Boman, H.G. Insect immunity. Purification and properties of three inducible bactericidal proteins from hemolymph of immunized pupae of Hyalophora cecropia. Eur. J. Biochem. 1980, 106, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, H.; Hultmark, D.; Engström, A.; Bennich, H.; Boman, H.G. Sequence and specificity of two antibacterial proteins involved in insect immunity. Nature 1981, 292, 246–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchon, N.; Silverman, N.; Cherry, S. Immunity in Drosophila melanogaster - from microbial recognition to whole-organism physiology. Nature Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 796–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, M.A.; Lemaitre, B. New insights on Drosophila antimicrobial peptide function in host defense and beyond. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2020, 62, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleftherianos, I.; Zhang, W.; Heryanto, C.; Mohamed, A.; Contreras, G.; Tettamanti, G.; Wink, M.; Bassal, T. Diversity of insect antimicrobial peptides and proteins - A functional perspective: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 191, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mylonakis, E.; Podsiadlowski, L.; Muhammed, M.; Vilcinskas, A., Diversity, evolution and medical applications of insect antimicrobial peptides. Philos. T. R. Soc. B 2016, 371, (1695). [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.Y.; Chowdhury, M.; Huang, Y.D.; Yu, X.Q. Insect antimicrobial peptides and their applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 5807–5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, D.; Grapputo, A.; Romoli, O.; Sandrelli, F. Insect Cecropins, Antimicrobial Peptides with Potential Therapeutic Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmi, H.; Ishibashi, J.; Hara, S.; Yamakawa, M. Solution structure of moricin, an antibacterial peptide, isolated from the silkworm Bombyx mori. FEBS Lett. 2002, 518, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, M.-A.; Separovic, F. How membrane-active peptides get into lipid membranes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pöppel, A.K.; Vogel, H.; Wiesner, J.; Vilcinskas, A. Antimicrobial peptides expressed in medicinal maggots of the blow fly Lucilia sericata show combinatorial activity against bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 2015, 59, 2508–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carboni, A.L.; Hanson, M.A.; Lindsay, S.A.; Wasserman, S.A.; Lemaitre, B.; Andrew, D., Cecropins contribute to Drosophila host defense against a subset of fungal and Gram-negative bacterial infection. Genetics 2022, 220, (1). [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; He, H.J.; Zhao, X.F.; Wang, J.X. Immune responses of Helicoverpa armigera to different kinds of pathogens. BMC Immunol. 2010, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Cheng, T.; Ye, M.; Deng, X.; Yi, H.; Huang, Y.; Tan, X.; Han, D.; Wang, B.; Xiang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Xia, Q. Functional divergence among silkworm antimicrobial peptide paralogs by the activities of recombinant proteins and the induced expression profiles. PLoS One 2011, 6, e18109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Rayaprolu, S.; Gong, Y.; Huang, R.; Prakash, O.; Jiang, H. Solution structure, antibacterial activity, and expression profile of Manduca sexta moricin. J. Pept. Sci. 2008, 14, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imler, J.L.; Bulet, P. Antimicrobial peptides in Drosophila: structures, activities and gene regulation. Chem. Immunol. Allergy 2005, 86, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonk, M.; Knorr, E.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Valdés, J.J.; Kollewe, C.; Vilcinskas, A. Tribolium castaneum defensins are primarily active against Gram-positive bacteria. J. Inverteb. Pathol. 2015, 132, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altincicek, B.; Vilcinskas, A. Analysis of the immune-inducible transcriptome from microbial stress resistant, rat-tailed maggots of the drone fly Eristalis tenax. BMC Genomics 2007, 8, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.A.; Hetru, C. Insect defensins: inducible antibacterial peptides. Immunol. Today 1992, 13, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, H.; Altincicek, B.; Glöckner, G.; Vilcinskas, A. A comprehensive transcriptome and immune-gene repertoire of the lepidopteran model host Galleria mellonella. BMC Genomics 2011, 12, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchon, N.; Broderick, N.A.; Poidevin, M.; Pradervand, S.; Lemaitre, B. Drosophila Intestinal Response to Bacterial Infection: Activation of Host Defense and Stem Cell Proliferation. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 5, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, S.; Imai, J.; Fujiwara, M.; Yaeshima, T.; Kawashima, T.; Kobayashi, K. A potent antibacterial protein in royal jelly. Purification and determination of the primary structure of royalisin. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 11333–11337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilikova, K.; Wu, G.; Simuth, J. Isolation of a peptide fraction from honeybee royal jelly as a potential antifoulbrood factor. Apidologie 2001, 32, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langen, G.; Imani, J.; Altincicek, B.; Kieseritzky, G.; Kogel, K.H.; Vilcinskas, A. Transgenic expression of gallerimycin, a novel antifungal insect defensin from the greater wax moth Galleria mellonella, confers resistance to pathogenic fungi in tobacco. Biol. Chem. 2006, 387, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Ishibashi, J.; Iwasaki, T.; Yamakawa, M. Gene expression of a novel defensin antimicrobial peptide in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 2353–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehlbaum, P.; Bulet, P.; Michaut, L.; Lagueux, M.; Broekaert, W.F.; Hetru, C.; Hoffmann, J.A. Insect immunity. Septic injury of Drosophila induces the synthesis of a potent antifungal peptide with sequence homology to plant antifungal peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 33159–33163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.T.; Zhu, S.Y. Drosomycin, an essential component of antifungal defence in Drosophila. Insect Mol. Biol. 2009, 18, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lele, D.S.; Talat, S.; Kumari, S.; Srivastava, N.; Kaur, K.J. Understanding the importance of glycosylated threonine and stereospecific action of Drosocin, a Proline rich antimicrobial peptide. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 92, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, A.M.; Otvos, L., Jr.; Hoffmann, R.; Craik, D.J. Conformational studies by NMR of the antimicrobial peptide, drosocin, and its non-glycosylated derivative: effects of glycosylation on solution conformation. Biochem. 1999, 38, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casteels, P.; Ampe, C.; Riviere, L.; Van Damme, J.; Elicone, C.; Fleming, M.; Jacobs, F.; Tempst, P. Isolation and characterization of abaecin, a major antibacterial response peptide in the honeybee (Apis mellifera). Eur. J. Biochem. 1990, 187, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, X.-J.; Xu, X.-X.; Yu, X.-Q. Functional analysis of two lebocin-related proteins from Manduca sexta. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 42, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayaprolu, S.; Wang, Y.; Kanost, M.R.; Hartson, S.; Jiang, H. Functional analysis of four processing products from multiple precursors encoded by a lebocin-related gene from Manduca sexta. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.L.; Zhan, M.Y.; Zhuo, Y.L.; Dang, X.L.; Li, M.Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, X.H.; Yu, X.Q.; Rao, X.J. Characterization of the active fragments of Spodoptera litura Lebocin-1. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 103, e21626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulet, P.; Urge, L.; Ohresser, S.; Hetru, C.; Otvos, L., Jr. Enlarged scale chemical synthesis and range of activity of drosocin, an O-glycosylated antibacterial peptide of Drosophila. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 238, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulet, P.; Hetru, C.; Dimarcq, J.L.; Hoffmann, D. Antimicrobial peptides in insects; structure and function. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1999, 23, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casteels, P.; Ampe, C.; Jacobs, F.; Vaeck, M.; Tempst, P. Apidaecins: antibacterial peptides from honeybees. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 2387–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilcinskas, A.; Mukherjee, K.; Vogel, H. Expansion of the antimicrobial peptide repertoire in the invasive ladybird Harmonia axyridis. Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 2013, 280, 20122113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, M.; Wada, S.; Ueda, K.; Saito, A.; Koizumi, N.; Iwahana, H.; Sato, R. Multipeptide precursor structure of acaloleptin A isoforms, antibacterial peptides from the Udo longicorn beetle, Acalolepta luxuriosa. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2009, 33, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilcinskas, A. Anti-infective therapeutics from the Lepidopteran model host Galleria mellonella. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedengren, M.; Borge, K.; Hultmark, D. Expression and Evolution of the Drosophila Attacin/Diptericin Gene Family. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 279, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.C.; Lindström, I.; Lee, J.Y.; Faye, I. Structure and expression of the attacin genes in Hyalophora cecropia. Eur. J. Biochem. 1991, 196, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hultmark, D.; Engström, A.; Andersson, K.; Steiner, H.; Bennich, H.; Boman, H.G. Insect immunity. Attacins, a family of antibacterial proteins from Hyalophora cecropia. EMBO J. 1983, 2, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, K.; Park, S.; Yoo, J.Y.; Cho, S. Characterization and expression of attacin, an antibacterial protein-encoding gene, from the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua (Hübner) (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 39, 5151–5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.M.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, Y.I.; Kang, Y.J.; Lee, I.H.; Jin, B.R.; Han, Y.S.; Cheon, H.M.; Ha, N.G.; Seo, S.J. Comparative analysis of two attacin genes from Hyphantria cunea. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B: Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 151, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesa, J.; Sadat, A.; Buccini, D.F.; Kati, A.; Mandal, A.K.; Franco, O.L. Antimicrobial peptides from Bombyx mori: a splendid immune defense response in silkworms. RSC Adv. 2019, 10, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-X.; Zhong, X.; Yi, H.-Y.; Yu, X.-Q. Manduca sexta gloverin binds microbial components and is active against bacteria and fungi. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 38, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axén, A.; Carlsson, A.; Engström, A.; Bennich, H. Gloverin, an antibacterial protein from the immune hemolymph of Hyalophora pupae. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 247, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaoka, S.; Katsuma, S.; Daimon, T.; Isono, R.; Omuro, N.; Mita, K.; Shimada, T. Functional analysis of fourGloverin-like genes in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2008, 67, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrinal, N.; Nagaraju, J. Intron loss is associated with gain of function in the evolution of the gloverin family of antibacterial genes in Bombyx mori. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 23376–23387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.; Kim, Y. RNA interference of an antimicrobial peptide, gloverin, of the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua, enhances susceptibility to Bacillus thuringiensis. J. Inverteb. Pathol. 2011, 108, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudic, M.; Bulet, P.; Hoffmann, R.; Craik, D.J.; Otvos, L., Jr. Chemical synthesis, antibacterial activity and conformation of diptericin, an 82-mer peptide originally isolated from insects. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 266, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimarcq, J.L.; Keppi, E.; Dunbar, B.; Lambert, J.; Reichhart, J.M.; Hoffmann, D.; Rankine, S.M.; Fothergill, J.E.; Hoffmann, J.A. Insect immunity. Purification and characterization of a family of novel inducible antibacterial proteins from immunized larvae of the dipteran Phormia terranovae and complete amino-acid sequence of the predominant member, diptericin A. Eur. J. Biochem. 1988, 171, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Kubo, T.; Natori, S. Purification and characterization of a diptericin homologue from Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly). Biochem. J. 1992, (Pt 2) Pt 2, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichhart, J.M.; Meister, M.; Dimarcq, J.L.; Zachary, D.; Hoffmann, D.; Ruiz, C.; Richards, G.; Hoffmann, J.A. Insect immunity: developmental and inducible activity of the Drosophila diptericin promoter. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 1469–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnon, M.-C.; Strandberg, E.; Grau-Campistany, A.; Wadhwani, P.; Reichert, J.; Bürck, J.; Rabanal, F.; Auger, M.; Paquin, J.-F.; Ulrich, A.S. Influence of the length and charge on the activity of α-helical amphipathic antimicrobial peptides. Biochem. 2017, 56, 1680–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dathe, M.; Nikolenko, H.; Meyer, J.; Beyermann, M.; Bienert, M. Optimization of the antimicrobial activity of magainin peptides by modification of charge. FEBS Lett. 2001, 501, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Guarnieri, M.T.; Vasil, A.I.; Vasil, M.L.; Mant, C.T.; Hodges, R.S. Role of peptide hydrophobicity in the mechanism of action of alpha-helical antimicrobial peptides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2007, 51, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kizhakkedathu, J.; Straus, S. Antimicrobial Peptides: Diversity, mechanism of action and strategies to improve the activity and biocompatibility in vivo. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeaman, M.R.; Yount, N.Y. Mechanisms of antimicrobial peptide action and resistance. Pharmacol. Rev. 2003, 55, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misof, B.; Liu, S.; Meusemann, K.; Peters, R.S.; Donath, A.; Mayer, C.; Frandsen, P.B.; Ware, J.; Flouri, T.; Beutel, R.G.; Niehuis, O.; Petersen, M.; Izquierdo-Carrasco, F.; Wappler, T.; Rust, J.; Aberer, A.J.; Aspöck, U.; Aspöck, H.; Bartel, D.; Blanke, A.; Berger, S.; Böhm, A.; Buckley, T.R.; Calcott, B.; Chen, J.; Friedrich, F.; Fukui, M.; Fujita, M.; Greve, C.; Grobe, P.; Gu, S.; Huang, Y.; Jermiin, L.S.; Kawahara, A.Y.; Krogmann, L.; Kubiak, M.; Lanfear, R.; Letsch, H.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Lu, H.; Machida, R.; Mashimo, Y.; Kapli, P.; McKenna, D.D.; Meng, G.; Nakagaki, Y.; Navarrete-Heredia, J.L.; Ott, M.; Ou, Y.; Pass, G.; Podsiadlowski, L.; Pohl, H.; von Reumont, B.M.; Schütte, K.; Sekiya, K.; Shimizu, S.; Slipinski, A.; Stamatakis, A.; Song, W.; Su, X.; Szucsich, N.U.; Tan, M.; Tan, X.; Tang, M.; Tang, J.; Timelthaler, G.; Tomizuka, S.; Trautwein, M.; Tong, X.; Uchifune, T.; Walzl, M.G.; Wiegmann, B.M.; Wilbrandt, J.; Wipfler, B.; Wong, T.K.F.; Wu, Q.; Wu, G.; Xie, Y.; Yang, S.; Yang, Q.; Yeates, D.K.; Yoshizawa, K.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, L.; Ziesmann, T.; Zou, S.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Kjer, K.M.; Zhou, X. Phylogenomics resolves the timing and pattern of insect evolution. Science 2014, 346, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Liu, S.; Lu, P.; Yan, X.; Hao, C.; Wang, H.; Wei, J.; Qie, X.; Lu, Z. The IMD pathway in Hemipteran: A comparative analysis and discussion. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2022, 136, 104513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventola, C.L. The antibiotic resistance crisis: part 2: management strategies and new agents. P. T. 2015, 40, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhu, C.; Ren, B.; Yin, X.; Shim, S.H.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, P.; Liu, C.; Yu, R.; Xia, X.; Zhang, L. Two optimized antimicrobial peptides with therapeutic potential for clinical antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 183, 111686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benfield, A.H.; Henriques, S.T. Mode-of-Action of Antimicrobial Peptides: Membrane Disruption vs. Intracellular Mechanisms. Front. Med. Technol. 2020, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, N.; Kahne, D.; Silhavy, T.J. Advances in understanding bacterial outer-membrane biogenesis. Nature Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikaido, H. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability revisited. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2003, 67, 593–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhao, X.; Yang, L.; Su, P.; Fu, P.; Peng, J.; Yang, N.; Guo, G. Antimicrobial peptide AMP-17 Affects Candida albicans by disrupting its cell wall and cell membrane integrity. Infect. Drug. Resist. 2020, 13, 2509–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Koh, J.-J.; Liu, S.; Lakshminarayanan, R.; Verma, C.S.; Beuerman, R.W. Membrane Active Antimicrobial Peptides: Translating Mechanistic Insights to Design. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroueh, S.O.; Bencze, K.Z.; Hesek, D.; Lee, M.; Fisher, J.F.; Stemmler, T.L.; Mobashery, S. Three-dimensional structure of the bacterial cell wall peptidoglycan. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2006, 103, 4404–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogden, K.A. Antimicrobial peptides: pore formers or metabolic inhibitors in bacteria? Nature Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.-F.; Fang, C.-M.; Sekaran, S.D., Intracellular targeting mechanisms by antimicrobial peptides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, (4). [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, D.; Leontiadou, H.; Mark, A.E.; Marrink, S.-J. Toroidal pores formed by antimicrobial peptides show significant disorder. Biophys. Acta. 2008, 1778, 2308–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, J.D.; Hancock, R.E. Alternative mechanisms of action of cationic antimicrobial peptides on bacteria. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2007, 5, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazit, E.; Boman, A.; Boman, H.G.; Shai, Y. Interaction of the mammalian antibacterial peptide cecropin P1 with phospholipid vesicles. Biochem. 1995, 34, 11479–11488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Harroun, T.A.; Weiss, T.M.; Ding, L.; Huang, H.W. Barrel-stave model or toroidal model? A case study on melittin pores. Biophys. J. 2001, 81, 1475–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.P.; Appelberg, R.; Gama, F.M. Antimicrobial peptides as novel anti-tuberculosis therapeutics. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 924–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolintineanu, D.; Hazrati, E.; Davis, H.T.; Lehrer, R.I.; Kaznessis, Y.N. Antimicrobial mechanism of pore-forming protegrin peptides: 100 pores to kill E. coli. Peptides 2010, 31, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Hsiao, F.S.; Ho, Y.H.; Chen, C.S. The proteome targets of intracellular targeting antimicrobial peptides. Proteomics 2016, 16, 1225–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardirossian, M.; Grzela, R.; Giglione, C.; Meinnel, T.; Gennaro, R.; Mergaert, P.; Scocchi, M. The host antimicrobial peptide bac71-35 binds to bacterial ribosomal proteins and inhibits protein synthesis. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesnokova, L.S.; Slepenkov, S.V.; Witt, S.N. The insect antimicrobial peptide, l-pyrrhocoricin, binds to and stimulates the ATPase activity of both wild-type and lidless DnaK. FEBS Lett. 2004, 565, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.-F.; Ma, G.-X.; Zhou, X.-X. Apidaecin-type peptides: Biodiversity, structure-function relationships and mode of action. Peptides 2006, 27, 2350–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donlan, R.M.; Costerton, J.W. Biofilms: Survival Mechanisms of Clinically Relevant Microorganisms. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 167–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batoni, G.; Maisetta, G.; Esin, S. Antimicrobial peptides and their interaction with biofilms of medically relevant bacteria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2016, 1858, 1044–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Kamesh, A.C.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, V.; Hayes, M.; Daniell, H.; Koo, H. Topical delivery of low-cost protein drug candidates made in chloroplasts for biofilm disruption and uptake by oral epithelial cells. Biomaterials 2016, 105, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewenza, S. Extracellular DNA-induced antimicrobial peptide resistance mechanisms in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duperthuy, M.; Sjöström, A.E.; Sabharwal, D.; Damghani, F.; Uhlin, B.E.; Wai, S.N. Role of the Vibrio cholerae matrix protein Bap1 in cross-resistance to antimicrobial peptides. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imler, J.-L. Overview of Drosophila immunity: A historical perspective. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 42, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.G. Developmental and comparative perspectives on mosquito immunity. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 103, 103458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaitre, B.; Hoffmann, J. The host defense of Drosophila melanogaster. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 697–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Cao, X.; Li, K.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Y.R.; Blissard, G.; Kanost, M.R.; Jiang, H. A genome-wide analysis of antimicrobial effector genes and their transcription patterns in Manduca sexta. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 62, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Luo, F.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, L.H. Drosophila innate immunity involves multiple signaling pathways and coordinated communication between different tissues. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valanne, S.; Wang, J.-H.; Rämet, M. The Drosophila Toll signaling pathway. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valanne, S.; Vesala, L.; Maasdorp, M.K.; Salminen, T.S.; Rämet, M. The Drosophila Toll pathway in innate immunity: from the core pathway toward effector functions. J. Immunol. (Baltimore, Md. 1950) 2022, 209, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kariyawasam, U.; Gulati, M.; Wang, Y.; Bao, H.; Shan, T.; Li, X.; Cao, X.; Sumathipala, N.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Boons, G.-J.; Jiang, H. Preferential binding of DAP-PGs by major peptidoglycan recognition proteins found in cell-free hemolymph of Manduca sexta. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2022, 148, 103827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myllymäki, H.; Valanne, S.; Rämet, M. The Drosophila IMD signaling pathway. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 3455–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liehl, P.; Blight, M.; Vodovar, N.; Boccard, F.; Lemaitre, B. Prevalence of local immune response against oral infection in a Drosophila/Pseudomonas infection model. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzou, P.; Ohresser, S.; Ferrandon, D.; Capovilla, M.; Reichhart, J.M.; Lemaitre, B.; Hoffmann, J.A.; Imler, J.L. Tissue-specific inducible expression of antimicrobial peptide genes in Drosophila surface epithelia. Immunity 2000, 13, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco-Drayon, V.; Poidevin, M.; Boneca, Ivo G.; Narbonne-Reveau, K.; Royet, J.; Charroux, B. Peptidoglycan sensing by the receptor PGRP-LE in the Drosophila gut induces immune responses to infectious bacteria and tolerance to microbiota. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchon, N.; Broderick, N.A.; Lemaitre, B. Gut homeostasis in a microbial world: insights from Drosophila melanogaster. Nature Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyen, C.; Poidevin, M.; Roussel, A.; Lemaitre, B. Tissue- and ligand-specific sensing of gram-negative infection in drosophila by PGRP-LC isoforms and PGRP-LE. J. Immunol. (Baltimore, Md. 1950) 2012, 189, 1886–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, A.; Hanson, M.A.; Kondo, S.; Erkosar, B.; Lemaitre, B. Drosophila antimicrobial peptides and lysozymes regulate gut microbiota composition and abundance. mBio 2021, 12, e0082421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarvari, M.; Mikani, A.; Mehrabadi, M. The innate immune gene Relish and Caudal jointly contribute to the gut immune homeostasis by regulating antimicrobial peptides in Galleria mellonella. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 110, 103732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, C.S.; Figueiredo, M.B.; Moraes, C. d. S.; Pereira, S.B.; Dyson, P.; Mello, C.B.; Castro, D.P.; Azambuja, P. Azadirachtin interferes with basal immunity and microbial homeostasis in the Rhodnius prolixus midgut. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2021, 114, 103864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Z.; Boquete, J.-P.; Lemaitre, B. Cell-specific IMD-NF-κB responses enable simultaneous antibacterial immunity and intestinal epithelial cell shedding upon bacterial infection. Immunity 2018, 48, 897–910.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.H.; Ha, E.M.; Oh, C.T.; Seol, J.H.; Brey, P.T.; Jin, I.; Lee, D.G.; Kim, J.; Lee, D.; Lee, W.J. An essential complementary role of NF-kappaB pathway to microbicidal oxidants in Drosophila gut immunity. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 3693–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Karpac, J.; Tran, Susan L.; Jasper, H., PGRP-SC2 promotes gut immune homeostasis to limit commensal dysbiosis and extend lifespan, Cell 2014, 156, (1-2), 109-122. [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Cai, Z.; Ma, Q.; Bai, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Guo, Q.; Gu, J.; Lemaitre, B.; Zhang, H. Compartmentalized PGRP expression along the dipteran Bactrocera dorsalis gut forms a zone of protection for symbiotic bacteria. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerardo, N.M.; Altincicek, B.; Anselme, C.; Atamian, H.; Barribeau, S.M.; de Vos, M.; Duncan, E.J.; Evans, J.D.; Gabaldón, T.; Ghanim, M.; Heddi, A.; Kaloshian, I.; Latorre, A.; Moya, A.; Nakabachi, A.; Parker, B.J.; Pérez-Brocal, V.; Pignatelli, M.; Rahbé, Y.; Ramsey, J.S.; Spragg, C.J.; Tamames, J.; Tamarit, D.; Tamborindeguy, C.; Vincent-Monegat, C.; Vilcinskas, A. Immunity and other defenses in pea aphids, Acyrthosiphon pisum. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumaya-Estrada, F.A.; Martínez-Barnetche, J.; Lavore, A.; Rivera-Pomar, R.; Rodríguez, M.H., Comparative genomics analysis of triatomines reveals common first line and inducible immunity-related genes and the absence of Imd canonical components among hemimetabolous arthropods. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, (1). [CrossRef]
- French, S.S.; DeNardo, D.F.; Moore, M.C. Trade-offs between the reproductive and immune systems: facultative responses to resources or obligate responses to reproduction? Am. Nat. 2007, 170, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łukasik, P.; van Asch, M.; Guo, H.; Ferrari, J.; Charles, J.; Godfray, H.; van der Putten, W. Unrelated facultative endosymbionts protect aphids against a fungal pathogen. Ecology Lett. 2013, 16, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchida, T.; Koga, R.; Meng, X.Y.; Matsumoto, T.; Fukatsu, T. Characterization of a facultative endosymbiotic bacterium of the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 49, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorburger, C.; Gehrer, L.; Rodriguez, P. A strain of the bacterial symbiont Regiella insecticola protects aphids against parasitoids. Biology Lett. 2010, 6, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, I.S. JAK/STAT signaling in insect innate immunity. Entomol. Res. 2019, 49, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, D.A. The JAK/STAT pathway. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a011205–a011205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agaisse, H.; Petersen, U.-M.; Boutros, M.; Mathey-Prevot, B.; Perrimon, N. Signaling role of hemocytes in Drosophila JAK/STAT-dependent response to septic injury, Dev. Cell 2003, 5, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Morton, J.C.; Ramirez, J.L.; Souza-Neto, J.A.; Dimopoulos, G. The entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana activate toll and JAK-STAT pathway-controlled effector genes and anti-dengue activity in Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 42, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, V.M.; Vogt, K.L.; Smythe, E.; Zeidler, M.P. Differential activities of the Drosophila JAK/STAT pathway ligands Upd, Upd2 and Upd3. Cell Signal. 2011, 23, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myllymäki, H.; Rämet, M. JAK/STAT pathway in Drosophila immunity. Scand. J. Immunol. 2014, 79, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadekuzzaman, M.; Kim, Y. Nitric oxide mediates antimicrobial peptide gene expression by activating eicosanoid signaling. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0193282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijkers, P.F.; O’Farrell, P.H. Drosophila calcineurin promotes induction of innate immune responses. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 2087–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Wang, X.; Wei, X.; Chen, J.; Wei, Y.; Jiang, H.; Lu, Z.; Feng, C. Nitric oxide-induced calcineurin a mediates antimicrobial peptide production through the IMD pathway. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 905419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallio, J.; Leinonen, A.; Ulvila, J.; Valanne, S.; Ezekowitz, R.A.; Rämet, M. Functional analysis of immune response genes in Drosophila identifies JNK pathway as a regulator of antimicrobial peptide gene expression in S2 cells. Microbes Infect. 2005, 7, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaney, J.R.; Stöven, S.; Uvell, H.; Anderson, K.V.; Engström, Y.; Mlodzik, M. Cooperative control of Drosophila immune responses by the JNK and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 3068–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, C.; Sucena, É.; Koyama, T. Endocrine regulation of immunity in insects. The FEBS J. 2020, 288, 3928–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regan, J.C.; Brandão, A.S.; Leitão, A.B.; Mantas Dias, A.R.; Sucena, E.; Jacinto, A.; Zaidman-Rémy, A. Steroid hormone signaling is essential to regulate innate immune cells and fight bacterial infection in Drosophila. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbuzov, A.; Tatar, M. Hormonal regulation of Drosophila microRNA let-7 and miR-125 that target innate immunity. Fly 2014, 4, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rus, F.; Flatt, T.; Tong, M.; Aggarwal, K.; Okuda, K.; Kleino, A.; Yates, E.; Tatar, M.; Silverman, N. Ecdysone triggered PGRP-LC expression controls Drosophila innate immunity. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 1626–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.P.; Kurthkoti, K.; Chang, K.Y.; Li, J.L.; Ren, X.; Ni, J.Q.; Rana, T.M.; Zhou, R. miR-34 modulates innate immunity and ecdysone signaling in Drosophila. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1006034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.-M.; Wang, Y.-H.; Yang, Q.-T.; Wang, X.-L.; Wang, M.; Raikhel, A.S.; Zou, Z. Regulation of antimicrobial peptides by juvenile hormone and its receptor, Methoprene-tolerant, in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 128, 103509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, W.; Xu, J.; Yang, W.; Li, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Cao, Y.; Yu, X.-Q.; Deng, X. Regulation of antimicrobial peptide genes via insulin-like signaling pathway in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 103, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, T.; Loch, G.; Beyer, M.; Zinke, I.; Aschenbrenner, A.C.; Carrera, P.; Inhester, T.; Schultze, J.L.; Hoch, M. FOXO-dependent regulation of innate immune homeostasis. Nature 2010, 463, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nässel, D.R.; Liu, Y.; Luo, J. Insulin/IGF signaling and its regulation in Drosophila. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2015, 221, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Tang, T.; Song, Q.; Wang, Z.; He, K.; Liu, X.; Song, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Feng, C. Transcription analysis of the stress and immune response genes to temperature stress in Ostrinia furnacalis. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Shi, Y.; Zhai, P.; Le, G. Inhibition of foodborne pathogens by Hf-1, a novel antibacterial peptide from the larvae of the housefly (Musca domestica) in medium and orange juice. Food Control 2007, 18, 1350–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Pandit, R.; Gaikwad, S.; Kövics, G. Antimicrobial peptides as natural bio-preservative to enhance the shelf-life of food. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 3381–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sameen, D.E.; Ahmed, S.; Dai, J.; Qin, W. Antimicrobial peptides and their application in food packaging. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Zhao, X.; Tan, Y.; Wu, J.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X. A systematical review on antimicrobial peptides and their food applications. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 155, 213684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patyra, E.; Kwiatek, K. Insect meals and insect antimicrobial peptides as an alternative for antibiotics and growth promoters in livestock production. Pathogens 2023, 12, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibinga, N.A., M.T. Lee, N. Buchon, E.L. Johnson, V. Selvaraj, H. Marquis., Do antimicrobial peptide levels alter performance of insect-based aquaculture feeds-a study using genetic models of insect immune activation. J. Insects Food Feed 2023, 9, 919-934. [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, F.; Huang, Z.; Liu, H.; Xie, C.; Zhang, J.; Thacker, P.A.; Qiao, S. Effects of the antimicrobial peptide cecropin AD on performance and intestinal health in weaned piglets challenged with Escherichia coli. Peptides 2012, 35, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, P.-S.; Huang, H.-Y.; Chen, H.-M. Expression of a synthesized gene encoding cationic peptide cecropin B in transgenic tomato plants protects against bacterial diseases. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2010, 76, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnamaeian, M.; Vilcinskas, A. Defense gene expression is potentiated in transgenic barley expressing antifungal peptide metchnikowin throughout powdery mildew challenge. J. Plant Res. 2011, 125, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilchie, A.L.; Hoskin, D.W.; Power Coombs, M.R. Anticancer activities of natural and synthetic peptides. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1117, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Mei, H.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Zeng, A.-h.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X.; Chu, F.; Wu, Q.; Zhu, J. Apoptosis-inducing activity of the antimicrobial peptide cecropin of Musca domestica in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line BEL-7402 and the possible mechanism. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2010, 42, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvy, J.P.; Yu, Y.; Dostalova, A.; Kondo, S.; Kurjan, A.; Bulet, P.; Lemaître, B.; Vidal, M.; Cordero, J.B. The antimicrobial peptide defensin cooperates with tumour necrosis factor to drive tumour cell death in Drosophila. Elife 2019, 8, e45061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswaro, L.S.; da Costa Sousa, M.G.; Rezende, T.M.B.; Dias, S.C.; Franco, O.L. Antimicrobial peptides and nanotechnology, recent advances and challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, M.A.; Dostálová, A.; Ceroni, C.; Poidevin, M.; Kondo, S.; Lemaitre, B. Synergy and remarkable specificity of antimicrobial peptides in vivo using a systematic knockout approach. eLife 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unckless, Robert L.; Howick, Virginia M.; Lazzaro, Brian P., Convergent balancing selection on an antimicrobial peptide in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 257-262. [CrossRef]
- Krams, I.; Daukšte, J.; Kivleniece, I.; Kaasik, A.; Krama, T.; Freeberg, T.M.; Rantala, M.J. Trade-off between cellular immunity and life span in mealworm beetles Tenebrio molitor. Curr. Zool. 2013, 59, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedick, J.C.; Tunaz, H.; Nor Aliza, A.R.; Putnam, S.M.; Ellis, M.D.; Stanley, D.W. Eicosanoids act in nodulation reactions to bacterial infections in newly emerged adult honey bees, Apis mellifera, but not in older foragers. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C 2001, 130, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Koo, H.; Richman, A.M.; Seeley, D.; Vizioli, J.; Klocko, A.D.; O’Brochta, D.A. Ectopic expression of a cecropin transgene in the human malaria vector mosquito Anopheles gambiae (Diptera: Culicidae): effects on susceptibility to Plasmodium. J. Med. Entomol. 2004, 41, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokoza, V.; Ahmed, A.; Woon Shin, S.; Okafor, N.; Zou, Z.; Raikhel, A.S. Blocking of Plasmodium transmission by cooperative action of Cecropin A and Defensin A in transgenic Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2010, 107, 8111–8116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.; Fei, S.; Xia, J.; Labropoulou, V.; Swevers, L.; Sun, J. Antimicrobial peptides as potential antiviral factors in insect antiviral immune response. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malheiros, P. da. S.; Daroit, D.J.; Brandelli, A. Food applications of liposome-encapsulated antimicrobial peptides. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretta, A.; Salvia, R.; Scieuzo, C.; Di Somma, A.; Vogel, H.; Pucci, P.; Sgambato, A.; Wolff, M.; Falabella, P. A bioinformatic study of antimicrobial peptides identified in the Black Soldier Fly (BSF) Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christophides, G.K.; Zdobnov, E.; Barillas-Mury, C.; Birney, E.; Blandin, S.; Blass, C.; Brey, P.T.; Collins, F.H.; Danielli, A.; Dimopoulos, G.; Hetru, C.; Hoa,; Hoffmann, J.A.; Kanzok, S.M.; Letunic, I.; Levashina, E.A.; Loukeris, T.G.; Lycett, G.; Meister, S.; Michel, K.; Moita, L.F.; Müller, H.M.; Osta, M.A.; Paskewitz, S.M.; Reichhart, J.M.; Rzhetsky, A.; Troxler, L.; Vernick, K.D.; Vlachou, D.; Volz, J.; von Mering, C.; Xu, J.; Zheng, L.; Bork, P.; Kafatos, F.C., Immunity-related genes and gene families in Anopheles gambiae. Science 2002, 298, 159-165. [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.D.; Aronstein, K.; Chen, Y.P.; Hetru, C.; Imler, J.L.; Jiang, H.; Kanost, M.; Thompson, G.J.; Zou, Z.; Hultmark, D. Immune pathways and defence mechanisms in honey bees Apis mellifera. Insect Mol. Biol. 2006, 15, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Ishibashi, J.; Fujita, K.; Nakajima, Y.; Sagisaka, A.; Tomimoto, K.; Suzuki, N.; Yoshiyama, M.; Kaneko, Y.; Iwasaki, T.; Sunagawa, T.; Yamaji, K.; Asaoka, A.; Mita, K.; Yamakawa, M. A genome-wide analysis of genes and gene families involved in innate immunity of Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 1087–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.H.; Xing, L.S.; Lin, Z.; Saha, T.T.; Wang, C.; Jiang, H.; Zou, Z. High throughput profiling of the cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera immunotranscriptome during the fungal and bacterial infections. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Evans, J.D.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, P.; Williams, M.; Sumathipala, N.; Hetru, C.; Hultmark, D.; Jiang, H. Comparative genomic analysis of the Tribolium immune system. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Kanost, M.R. Manduca sexta serpin-5 regulates prophenoloxidase activation and the Toll signaling pathway by inhibiting hemolymph proteinase HP6. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, X.J.; Yu, X.Q. Lipoteichoic acid and lipopolysaccharide can activate antimicrobial peptide expression in the tobacco hornworm Manduca sexta. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemmons, A.W.; Lindsay, S.A.; Wasserman, S.A. An effector peptide family required for Drosophila toll-mediated immunity. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, S.M.; Cavenaugh, A.; Journigan, V.; Pokorny, A.; Almeida, P.F. A quantitative model for the all-or-none permeabilization of phospholipid vesicles by the antimicrobial peptide cecropin A. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 1667–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.L.; Zheng, A.L. Genomic organization and regulation of three cecropin genes in Anopheles gambiae. Insect Mol. Biol. 2002, 11, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, A.P.; Florecki, M.M.; Simões, Z.L.P.; Evans, J.D. Silencing of Apis mellifera dorsal genes reveals their role in expression of the antimicrobial peptide defensin-1. Insect Mol. Biol. 2018, 27, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Souhail, Q.; Hiromasa, Y.; Rahnamaeian, M.; Giraldo, M.C.; Takahashi, D.; Valent, B.; Vilcinskas, A.; Kanost, M.R. Characterization and regulation of expression of an antifungal peptide from hemolymph of an insect, Manduca sexta. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 61, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizioli, J.; Bulet, P.; Hoffmann, J.A.; Kafatos, F.C.; Müller, H.M.; Dimopoulos, G. Gambicin: a novel immune responsive antimicrobial peptide from the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2001, 98, 12630–12635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlüns, H.; Crozier, R.H. Relish regulates expression of antimicrobial peptide genes in the honeybee, Apis mellifera, shown by RNA interference. Insect Mol. Biol. 2007, 16, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levashina, E.A.; Ohresser, S.; Bulet, P.; Reichhart, J.M.; Hetru, C.; Hoffmann, J.A. Metchnikowin, a novel immune-inducible proline-rich peptide from Drosophila with antibacterial and antifungal properties. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 233, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, A. AliView: a fast and lightweight alignment viewer and editor for large datasets. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3276–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junier, T.; Zdobnov, E.M. The Newick utilities: high-throughput phylogenetic tree processing in the UNIX shell. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1669–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Smith, D.K.; Zhu, H.; Guan, Y.; Lam, T.T.-Y. ggtree: an r package for visualization and annotation of phylogenetic trees with their covariates and other associated data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durbin, R.; Eddy, S.R.; Krogh, A.; Mitchison, G., Biological sequence analysis: probabilistic models of proteins and nucleic acids, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1998.
- Krogh, A.; Brown, M.; Mian, I.S.; Sjolander, K.; Haussler, D. Hidden Markov models in computational biology. Applications to protein modeling. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 235, 1501–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Le, S.; Li, Y.; Hu, F. SeqKit: A cross-platform and ultrafast toolkit for FASTA/Q file manipulation. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0163962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| AMP genes | Dm | Ms | Bm | Ha | Tc | Ag | Am |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| abaecin | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| apidaecin | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 |
| apisimin | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| attacin | 4 | 11 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | - |
| bomanin | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| cecropin | 4 | 15 | 13 | 5 | 3 | 4 | - |
| cobatoxin | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - |
| coleoptericin | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - |
| defensin | 1 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| diapausin | - | 14 | - | - | - | - | - |
| diptericin | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| drosocin | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| drosomycin | 7 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| gambicin | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| gloverin | - | 1 | 4 | 3 | - | - | - |
| hymenoptaecin | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| lebocin | - | 4 | 1 | 1 | - | - | - |
| metchnikowin | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| moricin | - | 6 | 9 | 4 | - | - | - |
| AMP family | Species | Accession number |
Gene name | Main activity |
Immune pathway |
References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| abaecin | Apis mellifera | NP_001011617.1 | abaecin | G+, G— | Imd | [48] |
| apidaecin | Apis mellifera | NP_001011642.1 | apidaecin I | G— | nd | [54] |
| apidaecin | Apis mellifera | NP_001011613.1 | apidaecin II | G— | nd | [54] |
| attacin | Drosophila melanogaster | NP_523745.1 | attA | G— | Imd | [39] |
| attacin | Drosophila melanogaster | NP_523746.1 | attB | G— | Imd | [39] |
| attacin | Drosophila melanogaster | NP_523729.3 | attC | G— | Imd | [39] |
| attacin | Drosophila melanogaster | NP_524391.2 | attD | G— | Imd | [39,58] |
| attacin | Bombyx mori | ADB08384.1 | attacin | G+, G— | nd | [63] |
| attacin | Helicoverpa armigera | ADR51155.1 | Haatt | G+, F | nd | [31] |
| attacin | Tribolium castaneum | XP_001809637.1 | Tc-attacin 2 | G+, G— | nd | [179] |
| attacin | Manduca sexta | AAY82587.1 | attacin-1 | G+, | nd | [180] |
| attacin | Manduca sexta | CAL25130.1 | attacin-2 | G+, G— | nd | [181] |
| bomanin | Drosophila melanogaster | NP_611319.1 | IM1-type | G+, F | Toll | [182] |
| bomanin | Drosophila melanogaster | NP_001262823.1 | CG5778-type | G+, F | Toll | [182] |
| bomanin | Drosophila melanogaster | NP_611318.2 | IM23-type | G+, F | Toll | [182] |
| cecropin | Drosophila melanogaster | NP_524588.1 | cecA1 | G— | Imd | [30,39] |
| cecropin | Drosophila melanogaster | NP_524589.1 | cecA2 | G— | Imd | [30,39] |
| cecropin | Drosophila melanogaster | NP_524590.1 | cecB | G— | Imd | [30,39] |
| cecropin | Drosophila melanogaster | NP_524591.1 | cecC | G— | Imd | [30,39] |
| cecropin | Bombyx mori | NP_001037462.1 | Bmcec A1 | G+, G— | nd | [183] |
| cecropin | Bombyx mori | NP_001037460.1 | BmcecB6 | G+, G— | nd | [32] |
| cecropin | Bombyx mori | BAL70382.1 | BmcecD | G+, G— | nd | [32] |
| cecropin | Bombyx mori | NP_001037392.1 | BmcecE | G— | nd | [32] |
| cecropin | Helicoverpa armigera | ADR51154.1 | cecropin-1 | F | nd | [31] |
| cecropin | Helicoverpa armigera | ADR51147.1 | cecropin-2 | G+, G— | nd | [31] |
| cecropin | Helicoverpa armigera | ADR51148.1 | cecropin-3 | F | nd | [31] |
| cecropin | Anopheles gambiae | AAF22649.1 | cecropin A | G+, G— | nd | [184] |
| cecropin | Anopheles gambiae | XP_040173530.1 | cecropin B | G+, G— | nd | [184] |
| cecropin | Manduca sexta | AAO74638.1 | cecropin-6 | G+ | nd | [180] |
| cobatoxin | Helicoverpa armigera | ADR51150.1 | Hacob | G+, G—,F | nd | [31] |
| defensin | Drosophila melanogaster | NP_523672.1 | def | G+, G— | Imd | [39] |
| defensin | Apis mellifera | NP_001011616.1 | Royalisin | G+, F | Toll | [185] |
| defensin | Bombyx mori | NP_001037370.1 | Bmdef | G+, G—,F | Toll,Imd | [43] |
| defensin | Tribolium castaneum | XP_973575.3 | Tcdefensin1 | G+, G—,F | nd | [179] |
| defensin | Tribolium castaneum | XP_968237.2 | Tcdefensin2 | G+, G—,F | nd | [179] |
| diapausin | Manduca sexta | ALP00204.1 | diapausin-1 | F | nd | [186] |
| diptericin | Drosophila melanogaster | NP_476808.1 | dptA | G— | Imd | [39,69] |
| diptericin | Drosophila melanogaster | NP_523787.2 | dptB | G— | Imd | [39,69] |
| drosocin | Drosophila melanogaster | NP_523744.1 | dro | G— | Imd | [52] |
| drosomycin | Drosophila melanogaster | NP_523901.1 | drs | G—, F | Toll, Imd | [44],[45] |
| drosomycin | Drosophila melanogaster | NP_728872.1 | drs-like1 | G— | JAK-STAT | [39] |
| drosomycin | Drosophila melanogaster | AAF47756.2 | drs-like2 | G— | JAK-STAT | [39] |
| drosomycin | Drosophila melanogaster | NP_728861.1 | drs-like3 | G— | JAK-STAT | [39] |
| drosomycin | Drosophila melanogaster | NP_728862.1 | drs-like4 | G— | JAK-STAT | [39] |
| drosomycin | Drosophila melanogaster | AAF47757.1 | drs-like5 | G— | JAK-STAT | [39] |
| drosomycin | Drosophila melanogaster | AAF47765.1 | drs-like6 | G— | JAK-STAT | [39] |
| gambicin | Anopheles gambiae | ACA05604.1 | gambicin | G+, G— | nd | [187] |
| gloverin | Manduca sexta | CAL25129.1 | Msglv | G+, G—,F | nd | [64] |
| gloverin | Bombyx mori | NP_001036930.1 | Bmglv1 | G+, G— | nd | [32],[69] |
| gloverin | Bombyx mori | NP_001037683.1 | Bmglv2 | G+, G— | nd | [32],[69] |
| gloverin | Bombyx mori | NP_001093312.1 | Bmglv3 | G+, G— | nd | [32] |
| gloverin | Bombyx mori | NP_001093312.1 | Bmglv4 | G+, G— | nd | [32] |
| gloverin | Helicoverpa armigera | ADR51146.1 | Haglo | G+, G—,F | nd | [31] |
| hymenoptaecin | Apis mellifera | NP_001011615.1 |
hymenoptaecin | G+, G— | Imd | [188] |
| lebocin | Manduca sexta | ADE20197.1 | lebocin B | G+, G—,F | nd | [49] |
| lebocin | Manduca sexta | XP_030038912.2 | lebocin C | G+, G—,F | nd | [49] |
| lebocin | Bombyx mori | sp|P54684.1| | lebocin 1/2 | G+, G— | nd | [51] |
| lebocin | Bombyx mori | NP_001119732.2 | lebocin 3 | G+, G— | nd | [51] |
| moricin | Manduca sexta | sp|Q86MA1.1| | moricin 1 | G+, G— | nd | [32,33] |
| moricin | Bombyx mori | NP_001036829.2 | Bmmor | G+, G— | nd | [32] |
| moricin | Bombyx mori | pdb|1KV4| | morLA1 | G+, G— | nd | [32] |
| moricin | Helicoverpa armigera | ADR51149.1 | Hamor | G+, G—,F | nd | [31] |
| metchnkowin | Drosophila melanogaster | NP_523752.1 | mtk | G+, G—,F | Toll, Imd | [39,189] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





