Submitted:
01 March 2024
Posted:
04 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
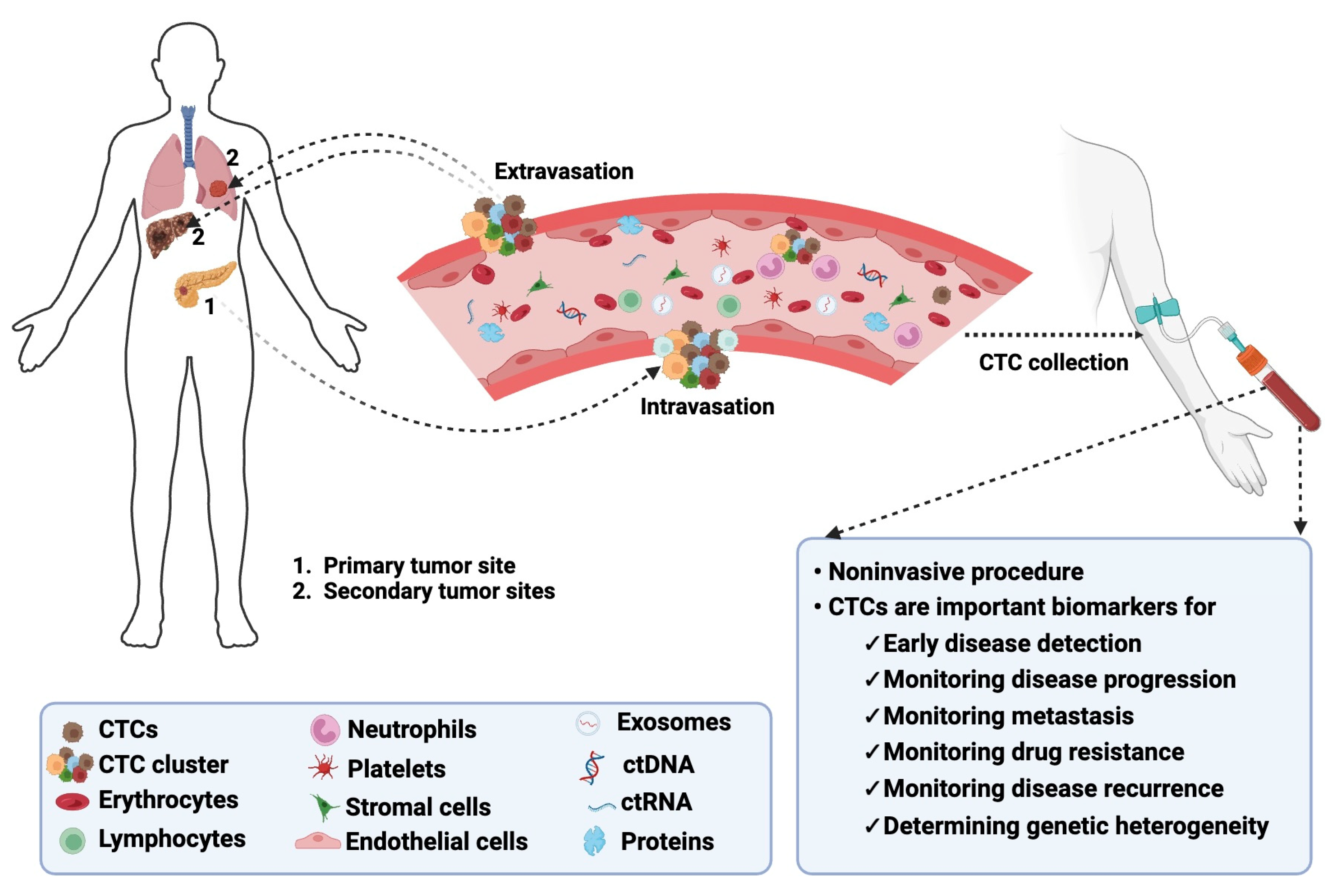
1. Introduction
2. Significance of CTCs in cancer and clinical implications
2.1. Early Cancer Detection
2.2. Prognostic Indicators
2.3. Tumor Heterogeneity
2.4. Metastasis and Disease Progression
2.5. Treatment Response Monitoring
2.6. Minimal Residual Disease Monitoring
2.7. Personalized Medicine
2.8. Clinical Trials and Drug Development
3. Challenges of using CTCs in Research and Clinical Applications
4. Circulating Tumor Cell Detection Strategies- Pros and Cons
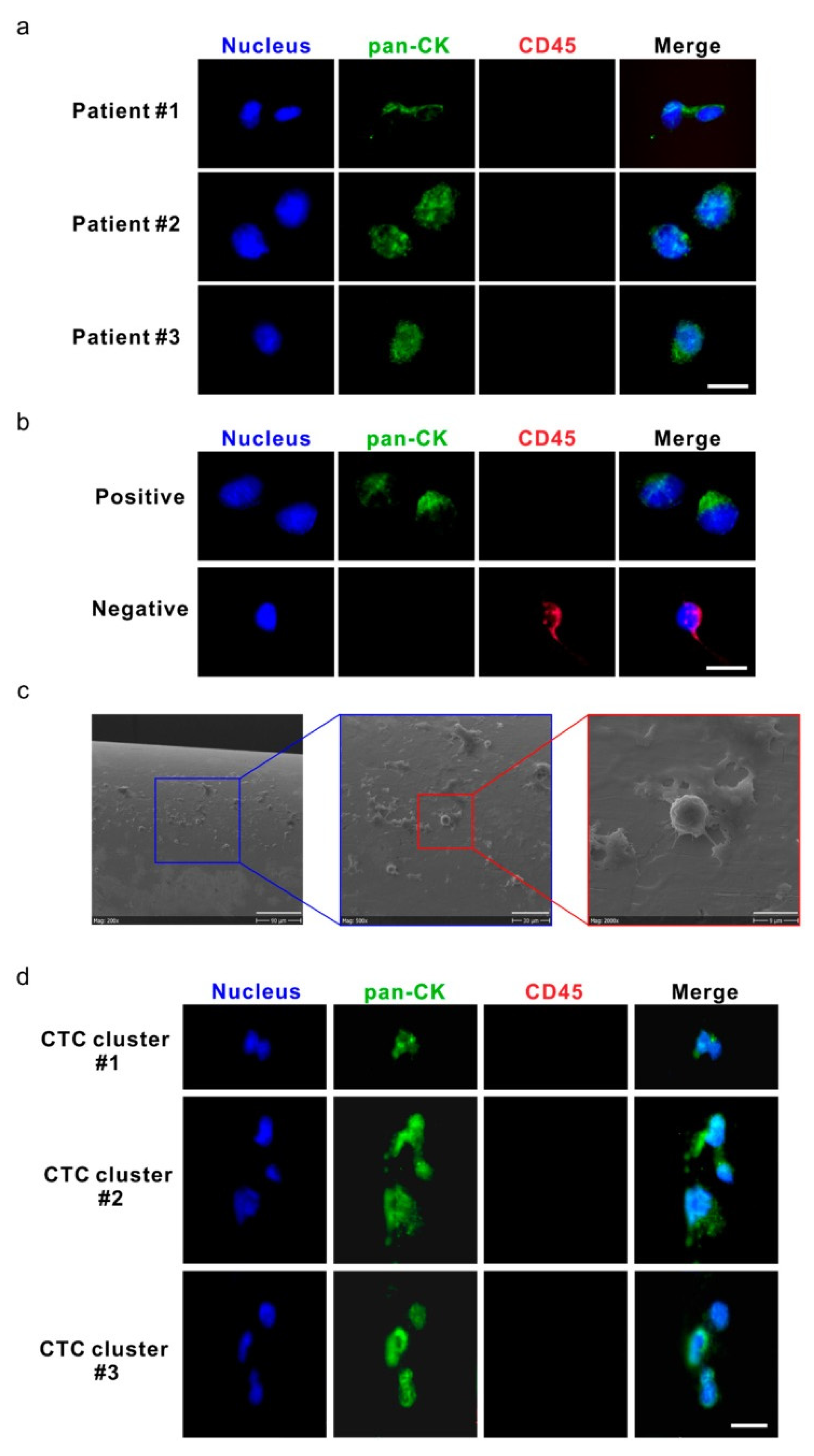
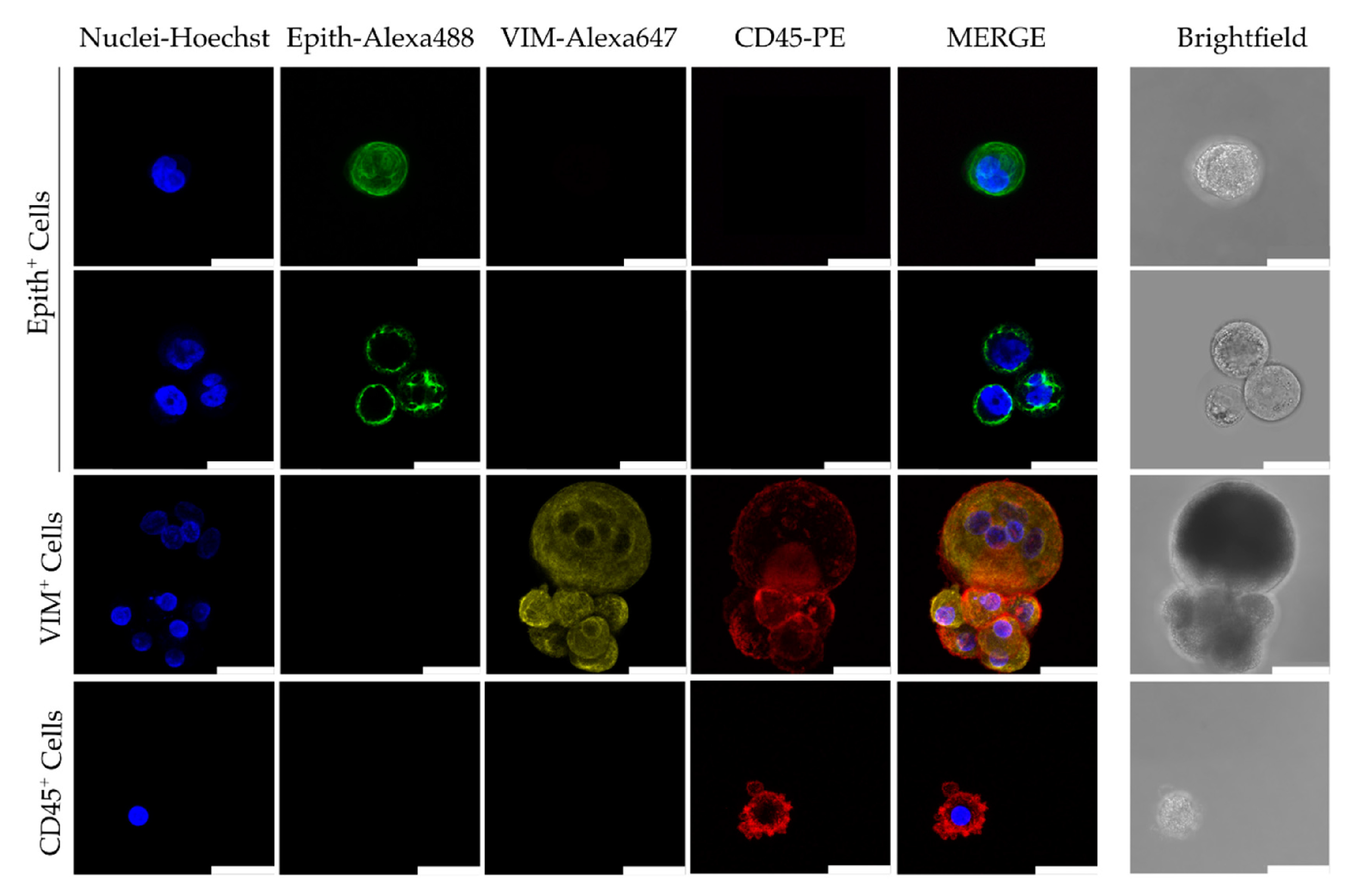
5. Advances in Characterizing CTC Biology and Clinical Implications
5.1. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
5.2. Single-Cell Analysis
5.3. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
5.4. In Situ Analysis
5.5. Functional Assays
6. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasan, N.; Baselga, J.; Hyman, D.M. A view on drug resistance in cancer. Nature 2019, 575, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, J.; Fares, M.Y.; Khachfe, H.H.; Salhab, H.A.; Fares, Y. Molecular principles of metastasis: a hallmark of cancer revisited. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2020, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffman, J.D.; Fisher, P.G.; Gibbs, P. Early detection of cancer: past, present, and future. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book 2015, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connal, S.; Cameron, J.M.; Sala, A.; Brennan, P.M.; Palmer, D.S.; Palmer, J.D.; Perlow, H.; Baker, M.J. Liquid biopsies: the future of cancer early detection. J Transl Med 2023, 21, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ried, K.; Eng, P.; Sali, A. Screening for Circulating Tumour Cells Allows Early Detection of Cancer and Monitoring of Treatment Effectiveness: An Observational Study. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2017, 18, 2275–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvilesh, K.N.; Manjunath, Y.; Pantel, K.; Kaifi, J.T. Preclinical models to study patient-derived circulating tumor cells and metastasis. Trends Cancer 2023, 9, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcuello, M.; Vymetalkova, V.; Neves, R.P.L.; Duran-Sanchon, S.; Vedeld, H.M.; Tham, E.; van Dalum, G.; Flugen, G.; Garcia-Barberan, V.; Fijneman, R.J.; et al. Circulating biomarkers for early detection and clinical management of colorectal cancer. Mol Aspects Med 2019, 69, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Giner, F.; Aceto, N. Tracking cancer progression: from circulating tumor cells to metastasis. Genome Med 2020, 12, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micalizzi, D.S.; Maheswaran, S.; Haber, D.A. A conduit to metastasis: circulating tumor cell biology. Genes Dev 2017, 31, 1827–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Lian, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Du, C.; Xu, Y.; Hu, H.; Rao, H.; Hong, X. Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs): A Unique Model of Cancer Metastases and Non-invasive Biomarkers of Therapeutic Response. Front Genet 2021, 12, 734595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, S.; Chen, C.; Zhang, J.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ji, F.; Wang, L. Detection of circulating tumor cells: opportunities and challenges. Biomark Res 2022, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asante, D.B.; Mohan, G.; Acheampong, E.; Ziman, M.; Calapre, L.; Meniawy, T.M.; Gray, E.S.; Beasley, A.B. Genetic analysis of heterogeneous subsets of circulating tumour cells from high grade serous ovarian carcinoma patients. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, B.M.; Ward, M.P.; Bates, M.; Spillane, C.D.; Kelly, T.; Martin, C.; Gallagher, M.; Heffernan, S.; Norris, L.; Kennedy, J.; et al. Ex vivo expansion of circulating tumour cells (CTCs). Sci Rep 2023, 13, 3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menyailo, M.E.; Tretyakova, M.S.; Denisov, E.V. Heterogeneity of Circulating Tumor Cells in Breast Cancer: Identifying Metastatic Seeds. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edd, J.F.; Mishra, A.; Smith, K.C.; Kapur, R.; Maheswaran, S.; Haber, D.A.; Toner, M. Isolation of circulating tumor cells. iScience 2022, 25, 104696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Li, Z.; Yong, P.; Liang, D.; Xie, D.; Chen, H.; Yang, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, C.; Cheng, Z. Detection and clinical significance of circulating tumor cells in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncol Lett 2019, 18, 2537–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Jin, S.; Han, J.; Li, T.; Shi, J.; Zhong, Q.; Li, W.; Tang, W.; Huang, Q.; Zong, H. Detection and clinical significance of circulating tumor cells in colorectal cancer. Biomark Res 2021, 9, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schochter, F.; Friedl, T.W.P.; deGregorio, A.; Krause, S.; Huober, J.; Rack, B.; Janni, W. Are Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) Ready for Clinical Use in Breast Cancer? An Overview of Completed and Ongoing Trials Using CTCs for Clinical Treatment Decisions. Cells 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchlinska, A.; Smentoch, J.; Zaczek, A.J.; Bednarz-Knoll, N. Detection and Characterization of Circulating Tumor Cells Using Imaging Flow Cytometry-A Perspective Study. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X.; Gan, C.; Yuan, R.; Xiang, Y. Highly specific and sensitive point-of-care detection of rare circulating tumor cells in whole blood via a dual recognition strategy. Biosens Bioelectron 2019, 143, 111604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiele, J.A.; Pitule, P.; Hicks, J.; Kuhn, P. Single-Cell Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells. Methods Mol Biol 2019, 1908, 243–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.Y.; Chou, H.H.; Lim, S.C.; Huang, Y.J.; Lai, K.C.; Guo, C.L.; Tung, C.Y.; Su, C.T.; Wang, J.; Liu, E.; et al. Multiomic characterization and drug testing establish circulating tumor cells as an ex vivo tool for personalized medicine. iScience 2022, 25, 105081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Lin, X.; Hui, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Kong, F. Circulating Tumor Cell Identification Based on Deep Learning. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 843879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Lu, Q.; Lang, J.; Yu, H.; Peng, C.; Bing, P.; Li, S.; Zhou, Q.; Liang, Y.; Tian, G. A New Method for CTC Images Recognition Based on Machine Learning. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2020, 8, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, R.; Watters, M.; Davies, C.R.; Pantel, K.; Lu, Y.J. Circulating tumour cells for early detection of clinically relevant cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2023, 20, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, T.R. A Case of Cancer in Which Cells Similar to Those in the Tumours Were Seen in the Blood after Death. The Medical Journal of Australia 1869, 14, 146–147. [Google Scholar]
- Massague, J.; Obenauf, A.C. Metastatic colonization by circulating tumour cells. Nature 2016, 529, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franses, J.W.; Basar, O.; Kadayifci, A.; Yuksel, O.; Choz, M.; Kulkarni, A.S.; Tai, E.; Vo, K.D.; Arora, K.S.; Desai, N.; et al. Improved Detection of Circulating Epithelial Cells in Patients with Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms. Oncologist 2018, 23, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.H.; Tsai, W.S.; Chang, Y.H.; Chou, T.Y.; Pang, S.T.; Lin, P.H.; Tsai, C.M.; Chang, Y.C. Identifying cancer origin using circulating tumor cells. Cancer Biol Ther 2016, 17, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.S.; You, J.F.; Hung, H.Y.; Hsieh, P.S.; Hsieh, B.; Lenz, H.J.; Idos, G.; Friedland, S.; Yi-Jiun Pan, J.; Shao, H.J.; et al. Novel Circulating Tumor Cell Assay for Detection of Colorectal Adenomas and Cancer. Clin Transl Gastroenterol 2019, 10, e00088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilie, M.; Hofman, V.; Long-Mira, E.; Selva, E.; Vignaud, J.M.; Padovani, B.; Mouroux, J.; Marquette, C.H.; Hofman, P. "Sentinel" circulating tumor cells allow early diagnosis of lung cancer in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. PLoS One 2014, 9, e111597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Mao, X.; Grey, A.; Scandura, G.; Guo, T.; Burke, E.; Marzec, J.; Abdu, S.; Stankiewicz, E.; Davies, C.R.; et al. Noninvasive Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer Using Circulating Tumor Cells. J Urol 2020, 203, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matikas, A.; Kotsakis, A.; Apostolaki, S.; Politaki, H.; Perraki, M.; Kalbakis, K.; Nikolaou, M.; Economopoulou, P.; Hatzidaki, D.; Georgoulias, V. Detection of circulating tumour cells before and following adjuvant chemotherapy and long-term prognosis of early breast cancer. Br J Cancer 2022, 126, 1563–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, N.; Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Cao, W.; Zhang, D.; Feng, C. Circulating tumor cells in blood as a prognostic biomarker in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2022, 134, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Xu, F.; Tian, J.; Gao, K.; Wan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gao, M.; Wang, Z.; Chong, T. The prognostic value of circulating tumour cells (CTCs) and CTC white blood cell clusters in patients with renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murlidhar, V.; Reddy, R.M.; Fouladdel, S.; Zhao, L.; Ishikawa, M.K.; Grabauskiene, S.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, J.; Chang, A.C.; Carrott, P.; et al. Poor Prognosis Indicated by Venous Circulating Tumor Cell Clusters in Early-Stage Lung Cancers. Cancer Res 2017, 77, 5194–5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.N.; Xiang, B.D.; Wu, F.X.; Ye, J.Z.; Zhong, J.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.Y.; Chen, Z.S.; Ma, L.; Chen, J.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells Undergoing EMT Provide a Metric for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res 2018, 78, 4731–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Xu, F.; Tian, J.; Chen, H.; Yang, C.; Huang, S.; Gao, K.; Wan, Z.; Li, M.; He, M.; et al. Pathology of circulating tumor cells and the available capture tools (Review). Oncol Rep 2020, 43, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Pierga, J.Y.; Reuben, J.; Rademaker, A.; Davis, A.A.; Peeters, D.J.; Fehm, T.; Nole, F.; Gisbert-Criado, R.; Mavroudis, D.; et al. The clinical use of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) enumeration for staging of metastatic breast cancer (MBC): International expert consensus paper. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2019, 134, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magbanua, M.J.M.; Savenkov, O.; Asmus, E.J.; Ballman, K.V.; Scott, J.H.; Park, J.W.; Dickler, M.; Partridge, A.; Carey, L.A.; Winer, E.P.; et al. Clinical Significance of Circulating Tumor Cells in Hormone Receptor-positive Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients who Received Letrozole with or Without Bevacizumab. Clin Cancer Res 2020, 26, 4911–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.-P.; Liu, S.-H.; Chen, C.-T.; Lv, L.; Li, D.; Liu, Q.-Y.; Liu, G.-L.; Wu, Y. Circulating tumor cells as a new predictive and prognostic factor in patients with small cell lung cancer. Journal of Cancer 2020, 11, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beasley, A.B.; Isaacs, T.W.; Vermeulen, T.; Freeman, J.; DeSousa, J.L.; Bhikoo, R.; Hennessy, D.; Reid, A.; Chen, F.K.; Bentel, J.; et al. Analysis of Circulating Tumour Cells in Early-Stage Uveal Melanoma: Evaluation of Tumour Marker Expression to Increase Capture. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, A.; Isaacs, T.; Khattak, M.A.; Freeman, J.B.; Allcock, R.; Chen, F.K.; Pereira, M.R.; Yau, K.; Bentel, J.; Vermeulen, T.; et al. Clinical Application of Circulating Tumor Cells and Circulating Tumor DNA in Uveal Melanoma. JCO Precis Oncol 2018, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasantharajan, S.S.; Eccles, M.R.; Rodger, E.J.; Pattison, S.; McCall, J.L.; Gray, E.S.; Calapre, L.; Chatterjee, A. The Epigenetic landscape of Circulating tumour cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 2021, 1875, 188514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freed, I.M.; Kasi, A.; Fateru, O.; Hu, M.; Gonzalez, P.; Weatherington, N.; Pathak, H.; Hyter, S.; Sun, W.; Al-Rajabi, R.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cell Subpopulations Predict Treatment Outcome in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) Patients. Cells 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelletti, V.; Verzoni, E.; Ratta, R.; Vismara, M.; Silvestri, M.; Montone, R.; Miodini, P.; Reduzzi, C.; Claps, M.; Sepe, P.; et al. Analysis of Single Circulating Tumor Cells in Renal Cell Carcinoma Reveals Phenotypic Heterogeneity and Genomic Alterations Related to Progression. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.A.; Gay, C.M.; Xi, Y.; Sivajothi, S.; Sivakamasundari, V.; Fujimoto, J.; Bolisetty, M.; Hartsfield, P.M.; Balasubramaniyan, V.; Chalishazar, M.D.; et al. Single-cell analyses reveal increased intratumoral heterogeneity after the onset of therapy resistance in small-cell lung cancer. Nat Cancer 2020, 1, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, A.; Wagner, J.; Gorges, T.M.; Taenzer, A.; Uzunoglu, F.G.; Driemel, C.; Stoecklein, N.H.; Knoefel, W.T.; Angenendt, S.; Hauch, S.; et al. Characterization of different CTC subpopulations in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 28010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salu, P.; Reindl, K.M. Advancements in Preclinical Models of Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreas 2024, 53, e205–e220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfried, T.N.; Huysentruyt, L.C. On the origin of cancer metastasis. Crit Rev Oncog 2013, 18, 43–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillekas, H.; Rogers, M.S.; Straume, O. Are 90% of deaths from cancer caused by metastases? Cancer Med 2019, 8, 5574–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, Y.; Cain, M.P.; Vanaja, K.; Kurywchak, P.A.; Levchenko, A.; Kalluri, R.; Kshitiz. Systems Biology of Cancer Metastasis. Cell Syst 2019, 9, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, S.; Maldonado, E.B.; Prasad, V. Comparison of Drugs Used for Adjuvant and Metastatic Therapy of Colon, Breast, and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers. JAMA Netw Open 2020, 3, e202488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, K.; Massague, J. Targeting metastatic cancer. Nat Med 2021, 27, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, A.W.; Pattabiraman, D.R.; Weinberg, R.A. Emerging Biological Principles of Metastasis. Cell 2017, 168, 670–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massague, J.; Ganesh, K. Metastasis-Initiating Cells and Ecosystems. Cancer Discov 2021, 11, 971–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyumi, B.; Bharde, A.; Aland, G.; D'Souza, A.; Jayant, S.; Singh, N.; Tripathi, S.; Badave, R.; Kale, N.; Singh, B.; et al. Circulating tumor cells as a predictor for poor prognostic factors and overall survival in treatment naive oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2022, 134, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.W.; Chueh, D.Y.; Chen, P. Real-time in vivo imaging of subpopulations of circulating tumor cells using antibody conjugated quantum dots. J Nanobiotechnology 2019, 17, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkountela, S.; Castro-Giner, F.; Szczerba, B.M.; Vetter, M.; Landin, J.; Scherrer, R.; Krol, I.; Scheidmann, M.C.; Beisel, C.; Stirnimann, C.U.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cell Clustering Shapes DNA Methylation to Enable Metastasis Seeding. Cell 2019, 176, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceto, N.; Bardia, A.; Miyamoto, D.T.; Donaldson, M.C.; Wittner, B.S.; Spencer, J.A.; Yu, M.; Pely, A.; Engstrom, A.; Zhu, H.; et al. Circulating tumor cell clusters are oligoclonal precursors of breast cancer metastasis. Cell 2014, 158, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, S.; Bendahl, P.O.; Larsson, A.M.; Aaltonen, K.E.; Ryden, L. Prognostic impact of circulating tumor cell apoptosis and clusters in serial blood samples from patients with metastatic breast cancer in a prospective observational cohort. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M. Metastasis Stemming from Circulating Tumor Cell Clusters. Trends Cell Biol 2019, 29, 275–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Sun, Q.; Liu, Q.; Wang, C.; Yao, R.; Wang, Y. CTC immune escape mediated by PD-L1. Med Hypotheses 2016, 93, 138–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liao, Q.; Zhao, Y. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) facilitate distant metastasis of malignancies by shielding circulating tumor cells (CTC) from immune surveillance. Med Hypotheses 2016, 87, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, F.; Yao, J.; Mao, C.; Zhu, M.; Qian, M.; Hu, J.; Zhong, H.; Zhou, J.; Shi, X.; et al. Single-cell metabolic fingerprints discover a cluster of circulating tumor cells with distinct metastatic potential. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergers, G.; Fendt, S.M. The metabolism of cancer cells during metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 2021, 21, 162–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, X.X.; Zhang, X.Y.; Xu, C.J. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, circulating tumor cells and cancer metastasis: Mechanisms and clinical applications. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 81558–81571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, A.; Markiewicz, A.; Szade, J.; Majewska, H.; Skokowski, J.; Seroczynska, B.; Welnicka-Jaskiewicz, M.; Zaczek, A. Expression of stem cell and mesenchymal markers in circulating tumor cells is associated with poor prognosis of early breast cancer patients. Annals of Oncology 2017, 28, vii32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, S.; Stenzl, A.; Pantel, K.; Todenhofer, T. Expression of Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition and Cancer Stem Cell Markers in Circulating Tumor Cells. Adv Exp Med Biol 2017, 994, 205–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirahata, T.; Ul Quraish, R.; Quraish, A.U.; Ul Quraish, S.; Naz, M.; Razzaq, M.A. Liquid Biopsy: A Distinctive Approach to the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Cancer. Cancer Inform 2022, 21, 11769351221076062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgkinson, C.L.; Morrow, C.J.; Li, Y.; Metcalf, R.L.; Rothwell, D.G.; Trapani, F.; Polanski, R.; Burt, D.J.; Simpson, K.L.; Morris, K.; et al. Tumorigenicity and genetic profiling of circulating tumor cells in small-cell lung cancer. Nat Med 2014, 20, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, H.; Takahashi, H.; Kawabata-Iwakawa, R.; Nagata, Y.; Uchida, M.; Shino, M.; Ida, S.; Mito, I.; Matsuyama, T.; Chikamatsu, K. Molecular phenotypes of circulating tumor cells and efficacy of nivolumab treatment in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 21573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Xu, K.; Tartarone, A.; Santarpia, M.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, G. Circulating tumor cells can predict the prognosis of patients with non-small cell lung cancer after resection: a retrospective study. Transl Lung Cancer Res 2021, 10, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, H.; Zuo, D.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L.; Shi, Q.; Hua, Y. Detection and surveillance of circulating tumor cells in osteosarcoma for predicting therapy response and prognosis. Cancer Biol Med 2022, 19, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neophytou, C.M.; Kyriakou, T.C.; Papageorgis, P. Mechanisms of Metastatic Tumor Dormancy and Implications for Cancer Therapy. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, K.; Poggiana, C.; Zamarchi, R. The Interplay between Circulating Tumor Cells and the Immune System: From Immune Escape to Cancer Immunotherapy. Diagnostics (Basel) 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.S.; Pandey, P.R.; Butti, R.; Radharani, N.N.V.; Roy, S.; Bhalara, S.R.; Gorain, M.; Kundu, G.C.; Kumar, D. The Biology and Therapeutic Implications of Tumor Dormancy and Reactivation. Front Oncol 2018, 8, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.; Sperduto, J.L.; Farino, C.J.; Slater, J.H. Engineered In Vitro Models of Tumor Dormancy and Reactivation. J Biol Eng 2018, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, C.; Harris, C.R.; Chen, Y.; Ghaddar, B.; Sharma, A.; Shah, M.M.; Roberts, A.I.; Casabianca, A.; Collisson, E.A.; Balachandran, V.P. A novel model of pancreatic cancer dormancy reveals mechanistic insights and a dormancy gene signature with human relevance. BioRxiv 2020. 2020.2004. 2013.037374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Shaw, A.T. Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2018, 15, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboulkheyr Es, H.; Montazeri, L.; Aref, A.R.; Vosough, M.; Baharvand, H. Personalized Cancer Medicine: An Organoid Approach. Trends Biotechnol 2018, 36, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyner, J.W.; Tognon, C.E.; Bottomly, D.; Wilmot, B.; Kurtz, S.E.; Savage, S.L.; Long, N.; Schultz, A.R.; Traer, E.; Abel, M.; et al. Functional genomic landscape of acute myeloid leukaemia. Nature 2018, 562, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; Zheng, H.; Cheung, A.K.; Tang, C.S.; Ko, J.M.; Wong, B.W.; Leong, M.M.; Sham, P.C.; Cheung, F.; Kwong, D.L.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing identifies MST1R as a genetic susceptibility gene in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016, 113, 3317–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Lu, X.; Wang, R.; Li, H.; Yan, B.; Gu, A.; Wang, W.; Huang, A.; et al. Whole-Exome Sequencing on Circulating Tumor Cells Explores Platinum-Drug Resistance Mutations in Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Front Genet 2021, 12, 722078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, B.; Ball, H.; Wuchu, F.; Nagrath, D.; Nagrath, S. Circulating tumor cells in precision medicine: challenges and opportunities. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2022, 43, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidard, F.C.; Jacot, W.; Kiavue, N.; Dureau, S.; Kadi, A.; Brain, E.; Bachelot, T.; Bourgeois, H.; Goncalves, A.; Ladoire, S.; et al. Efficacy of Circulating Tumor Cell Count-Driven vs Clinician-Driven First-line Therapy Choice in Hormone Receptor-Positive, ERBB2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer: The STIC CTC Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol 2021, 7, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerratana, L.; Pierga, J.Y.; Reuben, J.M.; Davis, A.A.; Wehbe, F.H.; Dirix, L.; Fehm, T.; Nole, F.; Gisbert-Criado, R.; Mavroudis, D.; et al. Modeling the Prognostic Impact of Circulating Tumor Cells Enumeration in Metastatic Breast Cancer for Clinical Trial Design Simulation. Oncologist 2022, 27, e561–e570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, A.; Riebensahm, C.; Mohme, M.; Joosse, S.A.; Velthaus, J.L.; Berger, L.A.; Bernreuther, C.; Glatzel, M.; Loges, S.; Lamszus, K.; et al. Frequency of Circulating Tumor Cells (CTC) in Patients with Brain Metastases: Implications as a Risk Assessment Marker in Oligo-Metastatic Disease. Cancers (Basel) 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, K.; Brooks, J.; Batis, N.; Khan, N.; El-Asrag, M.; Nankivell, P.; Mehanna, H.; Taylor, G. Feasibility of mass cytometry proteomic characterisation of circulating tumour cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma for deep phenotyping. Br J Cancer 2023, 129, 1590–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.F.; Wu, L.; Liu, S.P.; Jiang, M.M.; Hu, B.; Zhou, K.Q.; Guo, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Zhou, X.R.; et al. Dissecting spatial heterogeneity and the immune-evasion mechanism of CTCs by single-cell RNA-seq in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, T.; Angeli, D.; Tebaldi, M.; Fici, P.; Rossi, E.; Rocca, A.; Palleschi, M.; Maltoni, R.; Martinelli, G.; Fabbri, F.; et al. Dissecting Molecular Heterogeneity of Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) from Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients through Copy Number Aberration (CNA) and Single Nucleotide Variant (SNV) Single Cell Analysis. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothe, F.; Venet, D.; Peeters, D.; Rouas, G.; Rediti, M.; Smeets, D.; Dupont, F.; Campbell, P.; Lambrechts, D.; Dirix, L.; et al. Interrogating breast cancer heterogeneity using single and pooled circulating tumor cell analysis. NPJ Breast Cancer 2022, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tretyakova, M.S.; Menyailo, M.E.; Schegoleva, A.A.; Bokova, U.A.; Larionova, I.V.; Denisov, E.V. Technologies for Viable Circulating Tumor Cell Isolation. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Otero, N.; Marshall, J.R.; Lash, B.; King, M.R. Chemotherapy-induced release of circulating-tumor cells into the bloodstream in collective migration units with cancer-associated fibroblasts in metastatic cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Lin, E.; Brien, R.; Jung, S.; Chen, Y.T.; Lee, W.; Hao, Z.; Sahoo, S.; Min Kang, H.; et al. Hydro-Seq enables contamination-free high-throughput single-cell RNA-sequencing for circulating tumor cells. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habli, Z.; AlChamaa, W.; Saab, R.; Kadara, H.; Khraiche, M.L. Circulating Tumor Cell Detection Technologies and Clinical Utility: Challenges and Opportunities. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Zhuang, R.; Long, M.; Pavlovic, M.; Kang, Y.; Ilyas, A.; Asghar, W. Circulating tumor cell isolation, culture, and downstream molecular analysis. Biotechnol Adv 2018, 36, 1063–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banko, P.; Lee, S.Y.; Nagygyorgy, V.; Zrinyi, M.; Chae, C.H.; Cho, D.H.; Telekes, A. Technologies for circulating tumor cell separation from whole blood. J Hematol Oncol 2019, 12, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, L.; Engel, K.B.; Greytak, S.R.; Moore, H.M. Understanding preanalytical variables and their effects on clinical biomarkers of oncology and immunotherapy. Semin Cancer Biol 2018, 52, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.Y.; Niu, Z.; Green, M.D.; Zhao, L.; Raupp, S.; Pannecouk, B.; Brenner, D.E.; Nagrath, S.; Ramnath, N. It's not 'just a tube of blood': principles of protocol development, sample collection, staffing and budget considerations for blood-based biomarkers in immunotherapy studies. J Immunother Cancer 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasseur, A.; Kiavue, N.; Bidard, F.C.; Pierga, J.Y.; Cabel, L. Clinical utility of circulating tumor cells: an update. Mol Oncol 2021, 15, 1647–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidaway, P. New data confirm clinical utility of ctDNA. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2023, 20, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrou, G.; Mantikas, K.T.; Allsopp, R.; Yapeter, C.A.; Jahin, M.; Melnick, T.; Ali, S.; Coombes, R.C.; Toumazou, C.; Shaw, J.A.; et al. The Evolution of Affordable Technologies in Liquid Biopsy Diagnostics: The Key to Clinical Implementation. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radfar, P.; Aboulkheyr Es, H.; Salomon, R.; Kulasinghe, A.; Ramalingam, N.; Sarafraz-Yazdi, E.; Thiery, J.P.; Warkiani, M.E. Single-cell analysis of circulating tumour cells: enabling technologies and clinical applications. Trends Biotechnol 2022, 40, 1041–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, K.; Gu, W.; Nie, L.; Wang, G.; Luo, Y. Refining Cancer Management Using Integrated Liquid Biopsy. Theranostics 2020, 10, 2374–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidlarova, M.; Rehulkova, A.; Stejskal, P.; Prokopova, A.; Slavik, H.; Hajduch, M.; Srovnal, J. Recent Advances in Methods for Circulating Tumor Cell Detection. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayrefourcq, L.; De Roeck, A.; Garcia, C.; Stoebner, P.E.; Fichel, F.; Garima, F.; Perriard, F.; Daures, J.P.; Meunier, L.; Alix-Panabieres, C. S100-EPISPOT: A New Tool to Detect Viable Circulating Melanoma Cells. Cells 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danila, D.C.; Samoila, A.; Patel, C.; Schreiber, N.; Herkal, A.; Anand, A.; Bastos, D.; Heller, G.; Fleisher, M.; Scher, H.I. Clinical Validity of Detecting Circulating Tumor Cells by AdnaTest Assay Compared With Direct Detection of Tumor mRNA in Stabilized Whole Blood, as a Biomarker Predicting Overall Survival for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Patients. Cancer J 2016, 22, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorges, T.M.; Stein, A.; Quidde, J.; Hauch, S.; Rock, K.; Riethdorf, S.; Joosse, S.A.; Pantel, K. Improved Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer by the Combination of the CellSearch(R) System and the AdnaTest(R). PLoS One 2016, 11, e0155126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X.; Shen, S.; Pan, Z.; Shi, C. Detection of circulating stage III-IV gastric cancer tumor cells based on isolation by size of epithelial tumor: using the circulating tumor cell biopsy technology. Transl Cancer Res 2019, 8, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hvichia, G.E.; Parveen, Z.; Wagner, C.; Janning, M.; Quidde, J.; Stein, A.; Muller, V.; Loges, S.; Neves, R.P.; Stoecklein, N.H.; et al. A novel microfluidic platform for size and deformability based separation and the subsequent molecular characterization of viable circulating tumor cells. Int J Cancer 2016, 138, 2894–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.I.; Musso, N.; Romano, A.; Caruso, G.; Petralia, S.; Lanzano, L.; Broggi, G.; Camarda, M. The Role of Dielectrophoresis for Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, W.S.; Wan Abas, W.A. Benchtop technologies for circulating tumor cells separation based on biophysical properties. Biomed Res Int 2015, 2015, 239362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Lu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Nan, K.; Zhao, X.; Li, F.; Tian, L.; Dong, H.; et al. CNV Detection from Circulating Tumor DNA in Late Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Genes (Basel) 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslami, S.Z.; Cortes-Hernandez, L.E.; Alix-Panabieres, C. Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule: An Anchor to Isolate Clinically Relevant Circulating Tumor Cells. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozar, T.; Jesenko, T.; Kloboves Prevodnik, V.; Cemazar, M.; Hosta, V.; Jericevic, A.; Nolde, N.; Grasic Kuhar, C. Preclinical and Clinical Evaluation of Magnetic-Activated Cell Separation Technology for CTC Isolation in Breast Cancer. Front Oncol 2020, 10, 554554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, K.A.; Lee, T.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Jung, H.I. Two-stage microfluidic chip for selective isolation of circulating tumor cells (CTCs). Biosens Bioelectron 2015, 67, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Sun, N.; Cao, Y.; Cai, X.; Yuan, F.; Zou, H.; Xing, C.; Pei, R. Antifouling hydrogel-coated magnetic nanoparticles for selective isolation and recovery of circulating tumor cells. J Mater Chem B 2021, 9, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Yang, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Ma, W.; et al. Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) detected by triple-marker EpCAM, CK19, and hMAM RT-PCR and their relation to clinical outcome in metastatic breast cancer patients. Cell Biochem Biophys 2013, 65, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descamps, L.; Le Roy, D.; Deman, A.L. Microfluidic-Based Technologies for CTC Isolation: A Review of 10 Years of Intense Efforts towards Liquid Biopsy. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro-Samy, S.; Oliveira, M.I.; Pereira-Veiga, T.; Muinelo-Romay, L.; Carvalho, S.; Gaspar, J.; Freitas, P.P.; Lopez-Lopez, R.; Costa, C.; Dieguez, L. Fast and efficient microfluidic cell filter for isolation of circulating tumor cells from unprocessed whole blood of colorectal cancer patients. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 8032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Po, J.W.; Roohullah, A.; Lynch, D.; DeFazio, A.; Harrison, M.; Harnett, P.R.; Kennedy, C.; de Souza, P.; Becker, T.M. Improved ovarian cancer EMT-CTC isolation by immunomagnetic targeting of epithelial EpCAM and mesenchymal N-cadherin. J Circ Biomark 2018, 7, 1849454418782617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Medina, R.; Lopez-Tarruella, S.; Del Monte-Millan, M.; Massarrah, T.; Martin, M. Technical Challenges for CTC Implementation in Breast Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, K.; Fan, Z.H. Circulating Tumor Cell Isolation and Analysis. Adv Clin Chem 2016, 75, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofman, V.J.; Ilie, M.I.; Bonnetaud, C.; Selva, E.; Long, E.; Molina, T.; Vignaud, J.M.; Flejou, J.F.; Lantuejoul, S.; Piaton, E.; et al. Cytopathologic detection of circulating tumor cells using the isolation by size of epithelial tumor cell method: promises and pitfalls. Am J Clin Pathol 2011, 135, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolfus, C.; Piton, N.; Toure, E.; Sabourin, J.C. Circulating tumor cell isolation: the assets of filtration methods with polycarbonate track-etched filters. Chin J Cancer Res 2015, 27, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, M.G.; Hou, J.M.; Sloane, R.; Lancashire, L.; Priest, L.; Nonaka, D.; Ward, T.H.; Backen, A.; Clack, G.; Hughes, A.; et al. Analysis of circulating tumor cells in patients with non-small cell lung cancer using epithelial marker-dependent and -independent approaches. J Thorac Oncol 2012, 7, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu-Dinh, H.; Do Quang, L.; Chang, C.C.; Nhu, C.N.; Thanh, H.T.; Bui, T.T.; Duc, T.C.; Jen, C.P. Immunomagnetic separation in a novel cavity-added serpentine microchannel structure for the selective isolation of lung adenocarcinoma cells. Biomed Microdevices 2021, 23, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Hsieh, Y.P.; Ma, S.; Geng, S.; Cao, Z.; Li, L.; Lu, C. Immunomagnetic separation of tumor initiating cells by screening two surface markers. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 40632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamenehfar, A.; Li, P.C. Microfluidic Devices for Circulating Tumor Cells Isolation and Subsequent Analysis. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 2016, 17, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Zhang, W.; Xin, H.; Deng, G. Single Cell Isolation and Analysis. Front Cell Dev Biol 2016, 4, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagwat, N.; Dulmage, K.; Pletcher, C.H., Jr.; Wang, L.; DeMuth, W.; Sen, M.; Balli, D.; Yee, S.S.; Sa, S.; Tong, F.; et al. An integrated flow cytometry-based platform for isolation and molecular characterization of circulating tumor single cells and clusters. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riethdorf, S.; O'Flaherty, L.; Hille, C.; Pantel, K. Clinical applications of the CellSearch platform in cancer patients. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2018, 125, 102–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polzer, B.; Medoro, G.; Pasch, S.; Fontana, F.; Zorzino, L.; Pestka, A.; Andergassen, U.; Meier-Stiegen, F.; Czyz, Z.T.; Alberter, B.; et al. Molecular profiling of single circulating tumor cells with diagnostic intention. EMBO Mol Med 2014, 6, 1371–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Toom, E.E.; Groot, V.P.; Glavaris, S.A.; Gemenetzis, G.; Chalfin, H.J.; Wood, L.D.; Wolfgang, C.L.; de la Rosette, J.; de Reijke, T.M.; Pienta, K.J. Analogous detection of circulating tumor cells using the AccuCyte((R)) -CyteFinder((R)) system and ISET system in patients with locally advanced and metastatic prostate cancer. Prostate 2018, 78, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donato, C.; Kunz, L.; Castro-Giner, F.; Paasinen-Sohns, A.; Strittmatter, K.; Szczerba, B.M.; Scherrer, R.; Di Maggio, N.; Heusermann, W.; Biehlmaier, O.; et al. Hypoxia Triggers the Intravasation of Clustered Circulating Tumor Cells. Cell Rep 2020, 32, 108105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.; Oomens, L.; Broekmaat, J.; Weersink, J.; Abali, F.; Swennenhuis, J.; Tibbe, A. VyCAP's puncher technology for single cell identification, isolation, and analysis. Cytometry A 2018, 93, 1255–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, T.; Tanaka, T.; Nakamura, S.; Negishi, R.; Hosokawa, M.; Matsunaga, T. Manipulation of a Single Circulating Tumor Cell Using Visualization of Hydrogel Encapsulation toward Single-Cell Whole-Genome Amplification. Anal Chem 2016, 88, 7230–7237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negishi, R.; Yamakawa, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Horikawa, M.; Shimoyama, T.; Koizumi, F.; Sawada, T.; Oboki, K.; Omuro, Y.; Funasaka, C.; et al. Transcriptomic profiling of single circulating tumor cells provides insight into human metastatic gastric cancer. Commun Biol 2022, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, A.; Toro, P.V.; Lee, J.; Silberstein, J.L.; Nakazawa, M.; Waters, I.; Cravero, K.; Chu, D.; Cochran, R.L.; Kim, M.; et al. Detection fidelity of AR mutations in plasma derived cell-free DNA. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15651–15662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonarakis, E.S.; Lu, C.; Luber, B.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Silberstein, J.L.; Taylor, M.N.; Maughan, B.L.; Denmeade, S.R.; et al. Clinical Significance of Androgen Receptor Splice Variant-7 mRNA Detection in Circulating Tumor Cells of Men With Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Treated With First- and Second-Line Abiraterone and Enzalutamide. J Clin Oncol 2017, 35, 2149–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, S.R.; Helmijr, J.A.; Gerritsen, M.; Coban, H.; van Dessel, L.F.; Beije, N.; van der Vlugt-Daane, M.; Vigneri, P.; Sieuwerts, A.M.; Dits, N.; et al. Detection of tumor-derived extracellular vesicles in plasma from patients with solid cancer. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciuti, B.; Jones, G.; Severgnini, M.; Alessi, J.V.; Recondo, G.; Lawrence, M.; Forshew, T.; Lydon, C.; Nishino, M.; Cheng, M.; et al. Early plasma circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) changes predict response to first-line pembrolizumab-based therapy in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J Immunother Cancer 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwapisz, D. The first liquid biopsy test approved. Is it a new era of mutation testing for non-small cell lung cancer? Ann Transl Med 2017, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabert, K.; Cojoc, M.; Peitzsch, C.; Kurth, I.; Souchelnytskyi, S.; Dubrovska, A. Cancer biomarker discovery: current status and future perspectives. Int J Radiat Biol 2014, 90, 659–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettegowda, C.; Sausen, M.; Leary, R.J.; Kinde, I.; Wang, Y.; Agrawal, N.; Bartlett, B.R.; Wang, H.; Luber, B.; Alani, R.M.; et al. Detection of circulating tumor DNA in early- and late-stage human malignancies. Sci Transl Med 2014, 6, 224ra224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gezer, U.; Bronkhorst, A.J.; Holdenrieder, S. The Clinical Utility of Droplet Digital PCR for Profiling Circulating Tumor DNA in Breast Cancer Patients. Diagnostics (Basel) 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfitzner, C.; Schroder, I.; Scheungraber, C.; Dogan, A.; Runnebaum, I.B.; Durst, M.; Hafner, N. Digital-Direct-RT-PCR: a sensitive and specific method for quantification of CTC in patients with cervical carcinoma. Sci Rep 2014, 4, 3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, S.; Hendricks, A.; Wittig, A.; Schafmayer, C.; Tepel, J.; Kalthoff, H.; Becker, T.; Roder, C. Detection of circulating tumor cells with CK20 RT-PCR is an independent negative prognostic marker in colon cancer patients - a prospective study. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, T.; Lu, X.; Sun, N.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Liang, M.; Zhou, X.; Fang, Z. Real-time quantitative PCR detection of circulating tumor cells using tag DNA mediated signal amplification strategy. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2018, 158, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.C.; Laperriere, G.; Germain, H. Droplet Digital PCR versus qPCR for gene expression analysis with low abundant targets: from variable nonsense to publication quality data. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedlak, R.H.; Kuypers, J.; Jerome, K.R. A multiplexed droplet digital PCR assay performs better than qPCR on inhibition prone samples. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2014, 80, 285–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.H.; Kim, E.; Yang, S.M.; Kim, D.S.; Suh, S.M.; Lee, G.Y.; Kim, H.Y. Comparison of Real-Time PCR and Droplet Digital PCR for the Quantitative Detection of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum subsp. plantarum. Foods 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Cui, X.; Du, B.; Zhao, H.; Feng, Y.; Cui, J.; Yan, C.; Gan, L.; Fan, Z.; Fu, T.; et al. Detection and Quantification of Klebsiella pneumoniae in Fecal Samples Using Digital Droplet PCR in Comparison with Real-Time PCR. Microbiol Spectr 2023, 11, e0424922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xia, Q.; Yin, Y.; Wang, Z. Comparison of Droplet Digital PCR and Quantitative PCR Assays for Quantitative Detection of Xanthomonas citri Subsp. citri. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0159004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cros, J.; Raffenne, J.; Couvelard, A.; Pote, N. Tumor Heterogeneity in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Pathobiology 2018, 85, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Wang, C.; Xie, M.; Zhu, C.; Shu, Y.; Tang, J.; Guan, X. Heterogeneity of CTC contributes to the organotropism of breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 2021, 137, 111314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, L.; Pantel, K. Unravelling tumour heterogeneity by single-cell profiling of circulating tumour cells. Nat Rev Cancer 2019, 19, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heumos, L.; Schaar, A.C.; Lance, C.; Litinetskaya, A.; Drost, F.; Zappia, L.; Lucken, M.D.; Strobl, D.C.; Henao, J.; Curion, F.; et al. Best practices for single-cell analysis across modalities. Nat Rev Genet 2023, 24, 550–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafemeister, C.; Satija, R. Normalization and variance stabilization of single-cell RNA-seq data using regularized negative binomial regression. Genome Biol 2019, 20, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiau, C.K.; Lu, L.; Kieser, R.; Fukumura, K.; Pan, T.; Lin, H.Y.; Yang, J.; Tong, E.L.; Lee, G.; Yan, Y.; et al. High throughput single cell long-read sequencing analyses of same-cell genotypes and phenotypes in human tumors. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, T.; Butler, A.; Hoffman, P.; Hafemeister, C.; Papalexi, E.; Mauck, W.M., 3rd; Hao, Y.; Stoeckius, M.; Smibert, P.; Satija, R. Comprehensive Integration of Single-Cell Data. Cell 2019, 177, 1888–1902 e1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.X.; Terry, J.M.; Belgrader, P.; Ryvkin, P.; Bent, Z.W.; Wilson, R.; Ziraldo, S.B.; Wheeler, T.D.; McDermott, G.P.; Zhu, J.; et al. Massively parallel digital transcriptional profiling of single cells. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 14049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, D.T.; Zheng, Y.; Wittner, B.S.; Lee, R.J.; Zhu, H.; Broderick, K.T.; Desai, R.; Fox, D.B.; Brannigan, B.W.; Trautwein, J.; et al. RNA-Seq of single prostate CTCs implicates noncanonical Wnt signaling in antiandrogen resistance. Science 2015, 349, 1351–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J. 8-Gene signature related to CD8(+) T cell infiltration by integrating single-cell and bulk RNA-sequencing in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Front Genet 2022, 13, 938611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, L.; Han, L.; Tuo, X.; Ma, S.; Wang, Y.; Feng, X.; Liang, D.; Sun, C.; Wang, Q.; et al. The Discordance of Gene Mutations between Circulating Tumor Cells and Primary/Metastatic Tumor. Mol Ther Oncolytics 2019, 15, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auwal, A.; Hossain, M.M.; Pronoy, T.U.H.; Rashel, K.; Nurujjaman, M.; Lam, A.K.; Islam, F. Clinical significance of genomic sequencing of circulating tumour cells (CTCs) in cancer. The Journal of Liquid Biopsy 2023, 100135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poellmann, M.J.; Bu, J.; Kim, D.; Iida, M.; Hong, H.; Wang, A.Z.; Wheeler, D.L.; Kimple, R.J.; Hong, S. Circulating tumor cell abundance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma decreases with successful chemoradiation and cetuximab treatment. Cancer Lett 2023, 562, 216187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Xu, F.; Wang, Y.; Tian, J.; Wan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chong, T. Identification of key genes and functions of circulating tumor cells in multiple cancers through bioinformatic analysis. BMC Med Genomics 2020, 13, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhang Ghahremani, M.; Seto, K.K.Y.; Cho, W.; Miller, M.C.; Smith, P.; Englert, D.F. Novel method for highly multiplexed gene expression profiling of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) captured from the blood of women with metastatic breast cancer. J Transl Med 2023, 21, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Z.; Helmijr, J.C.A.; Jansen, M.; Boor, P.P.C.; Noordam, L.; Peppelenbosch, M.; Kwekkeboom, J.; Kraan, J.; Sprengers, D. Detection of oncogenic mutations in paired circulating tumor DNA and circulating tumor cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Transl Oncol 2021, 14, 101073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, M.; Miyake, Y.; Inoue, A.; Yokoyama, Y.; Noda, N.; Kouda, S.; Hata, T.; Ogino, T.; Miyoshi, N.; Takahashi, H.; et al. Single-Cell Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells from Patients with Colorectal Cancer Captured with a Dielectrophoresis-Based Micropore System. Biomedicines 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, S.L.; Liu, X.; Suhaimi, N.M.; Koh, K.J.H.; Hu, M.; Lee, D.Y.S.; Cima, I.; Phyo, W.M.; Lee, E.X.W.; Tai, J.A.; et al. Molecular characterization of circulating colorectal tumor cells defines genetic signatures for individualized cancer care. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 68026–68037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.E.; Triboulet, M.; Zia, A.; Vuppalapaty, M.; Kidess-Sigal, E.; Coller, J.; Natu, V.S.; Shokoohi, V.; Che, J.; Renier, C.; et al. Workflow optimization of whole genome amplification and targeted panel sequencing for CTC mutation detection. NPJ Genom Med 2017, 2, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.R. Next-Generation Sequencing in High-Sensitive Detection of Mutations in Tumors: Challenges, Advances, and Applications. J Mol Diagn 2020, 22, 994–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biezuner, T.; Raz, O.; Amir, S.; Milo, L.; Adar, R.; Fried, Y.; Ainbinder, E.; Shapiro, E. Comparison of seven single cell whole genome amplification commercial kits using targeted sequencing. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 17171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saucedo-Zeni, N.; Mewes, S.; Niestroj, R.; Gasiorowski, L.; Murawa, D.; Nowaczyk, P.; Tomasi, T.; Weber, E.; Dworacki, G.; Morgenthaler, N.G.; et al. A novel method for the in vivo isolation of circulating tumor cells from peripheral blood of cancer patients using a functionalized and structured medical wire. Int J Oncol 2012, 41, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Heliebi, A.; Hille, C.; Laxman, N.; Svedlund, J.; Haudum, C.; Ercan, E.; Kroneis, T.; Chen, S.; Smolle, M.; Rossmann, C.; et al. In Situ Detection and Quantification of AR-V7, AR-FL, PSA, and KRAS Point Mutations in Circulating Tumor Cells. Clin Chem 2018, 64, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tauber, G.; Langsenlehner, T.; Schmolzer, L.M.; Potscher, M.; Riethdorf, S.; Kuske, A.; Leitinger, G.; Kashofer, K.; Czyz, Z.T.; et al. In Vivo Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells in High-Risk Non-Metastatic Prostate Cancer Patients Undergoing Radiotherapy. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shreffler, J.; Huecker, M.R. Diagnostic testing accuracy: Sensitivity, specificity, predictive values and likelihood ratios. 2020. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Tang, W.; Cheng, P.; Zhou, Q.; Tian, X.; Wei, X.; He, H. Monitoring circulating tumor cells in vivo by a confocal microscopy system. Cytometry A 2019, 95, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Ule, N.; Gonzalez-Conde, M.; Abuin, C.; Cueva, J.F.; Palacios, P.; Lopez-Lopez, R.; Costa, C.; Davila-Ibanez, A.B. Short-Term Ex Vivo Culture of CTCs from Advance Breast Cancer Patients: Clinical Implications. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.L.; Chiou, J.F.; Wang, P.Y.; Lu, L.S.; Shen, C.N.; Hsu, H.L.; Burnouf, T.; Ting, L.L.; Chou, P.C.; Chung, C.L.; et al. Ex Vivo Expansion and Drug Sensitivity Profiling of Circulating Tumor Cells from Patients with Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapeleris, J.; Kulasinghe, A.; Warkiani, M.E.; Oleary, C.; Vela, I.; Leo, P.; Sternes, P.; O’Byrne, K.; Punyadeera, C. Ex vivo culture of circulating tumour cells derived from non-small cell lung cancer. Translational lung cancer research 2020, 9, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, Y.; Sudo, T.; Akamatsu, S.; Sunada, T.; Myomoto, A.; Okano, K.; Shimizu, K. Cell Lines of Circulating Tumor Cells: What Is Known and What Needs to Be Resolved. J Pers Med 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulasinghe, A.; Perry, C.; Warkiani, M.E.; Blick, T.; Davies, A.; O'Byrne, K.; Thompson, E.W.; Nelson, C.C.; Vela, I.; Punyadeera, C. Short term ex-vivo expansion of circulating head and neck tumour cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 60101–60109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Bardia, A.; Aceto, N.; Bersani, F.; Madden, M.W.; Donaldson, M.C.; Desai, R.; Zhu, H.; Comaills, V.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Cancer therapy. Ex vivo culture of circulating breast tumor cells for individualized testing of drug susceptibility. Science 2014, 345, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, G.; Hochmair, M.; Rath, B.; Klameth, L.; Zeillinger, R. Small cell lung cancer: Circulating tumor cells of extended stage patients express a mesenchymal-epithelial transition phenotype. Cell Adh Migr 2016, 10, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Chu, G.C.Y.; Mrdenovic, S.; Annamalai, A.A.; Hendifar, A.E.; Nissen, N.N.; Tomlinson, J.S.; Lewis, M.; Palanisamy, N.; Tseng, H.R.; et al. Cultured circulating tumor cells and their derived xenografts for personalized oncology. Asian J Urol 2016, 3, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, B.L.; Lee, S.C.; Kumar, P.; Tan, T.Z.; Warkiani, M.E.; Ow, S.G.; Nandi, S.; Lim, C.T.; Thiery, J.P. Short-term expansion of breast circulating cancer cells predicts response to anti-cancer therapy. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 15578–15593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoryeva, E.S.; Tashireva, L.A.; Alifanov, V.V.; Savelieva, O.E.; Vtorushin, S.V.; Zavyalova, M.V.; Cherdyntseva, N.V.; Perelmuter, V.M. The Novel Association of Early Apoptotic Circulating Tumor Cells with Treatment Outcomes in Breast Cancer Patients. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Challenges | Description/ Effects | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Low Frequency in Bloodstream | - Extremely rare compared to other circulating cells (e.g. blood cells) - Ranges from a few to a few hundred CTCs per milliliter of blood - Low frequency makes detection and isolation difficult |
[89,90] |
| Heterogeneity | - Exhibits both genetic and phenotypic variabilities - Reflects cellular diversity within the primary tumor - Heterogeneity complicates efforts to capture a representative sample of CTCs for analysis |
[91,92,93] |
| Cell Viability | - CTCs are fragile and can be damaged during isolation processes - Isolation and analysis of viable CTCs are crucial for meaningful downstream studies - Lack of viable cells may affect subsequent functional assays |
[94] |
| Dynamic Changes in CTC Numbers | - Number of CTCs in the bloodstream vary over time - Number of CTCs is affected by tumor size, treatment effects, and stage of the disease - Variable CTC numbers add complexity to studying CTCs longitudinally |
[14,95] |
| Contamination from Normal Cells | - Isolation of CTCs can be complicated by contamination from normal blood cells such as leukocytes - Presence of other cells reduces the purity of CTC samples - Contaminating cells can interfere with downstream analyses |
[96] |
| Technical Limitations |
- Traditional methods for CTC isolation, such as density gradient centrifugation, do not efficiently capture CTCs due to their similar size and density compared to other blood cells - Newer technologies, like microfluidic devices and immunomagnetic separation, need refinements to achieve high purity and recovery rates |
[97,98] |
| Lack of Standardization |
- Lack of standardized protocols for CTC isolation and characterization - Different isolation methods and technologies may yield varying results - Lack of standardization makes it challenging to compare data across studies, leading to potential discrepancies in the interpretation of findings | [26,99,100] |
| Ethical and Consent Issues | - Obtaining blood samples for CTC analysis requires informed consent - Collecting longitudinal samples to monitor disease progression may have psychological impacts on patients |
[101] |
| Clinical Relevance | - Establishing the clinical relevance of CTCs and their role as prognostic or predictive biomarkers requires large-scale clinical validation - Research findings are not integrated with routine clinical applications |
[102,103] |
| Cost and Accessibility |
- Advanced technologies for CTC isolation and analysis are expensive - The cost associated with isolation and analysis methods limit their widespread implementation and use - Advanced technologies needed are not readily accessible in all healthcare settings |
[104,105] |
| Method | Principle | Pros | Cons | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density Gradient Centrifugation | Differential centrifugation separates blood components based on their density, allowing for the isolation of CTCs |
Simple, cost-effective |
- Limited specificity - Contamination from normal blood cells |
[125] |
| Filtration Techniques |
Filters with defined pore sizes are used to physically separate CTCs from blood cells based on size | Simple, cost-effective |
- Risk of clogging - Loss of smaller CTCs |
[126,127,128] |
| Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule (EpCAM) Enrichment |
EpCAM, a cell surface marker often expressed in epithelial cancers, is targeted for CTC enrichment |
Commonly used, FDA-approved platforms |
- EpCAM-negative CTCs may be missed - Loss of CTC heterogeneity |
[116] |
| Immunomagnetic Separation | Antibodies specific to tumor- associated antigens are used to capture CTCs by attaching to magnetic beads |
High specificity, potential for enrichment of viable CTCs |
- Limited by the availability of specific antigens - Loss of CTC viability |
[129,130] |
| Microfluidic Devices |
Microscale devices use various mechanisms, such as size-based filtration or antibody-coated surfaces, to isolate CTCs from blood |
High throughput, potential for single-cell analysis, and minimal sample processing |
- Requires efficient capture to avoid CTC damage - Requires standardization of devices |
[121,131] |
| Fluorescent- Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) |
Fluorescently tagged cells are separated by flow cytometry |
High specificity and throughput for CTC enrichment | - Requires a high number of input cells |
[132,133] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





