Submitted:
28 February 2024
Posted:
29 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
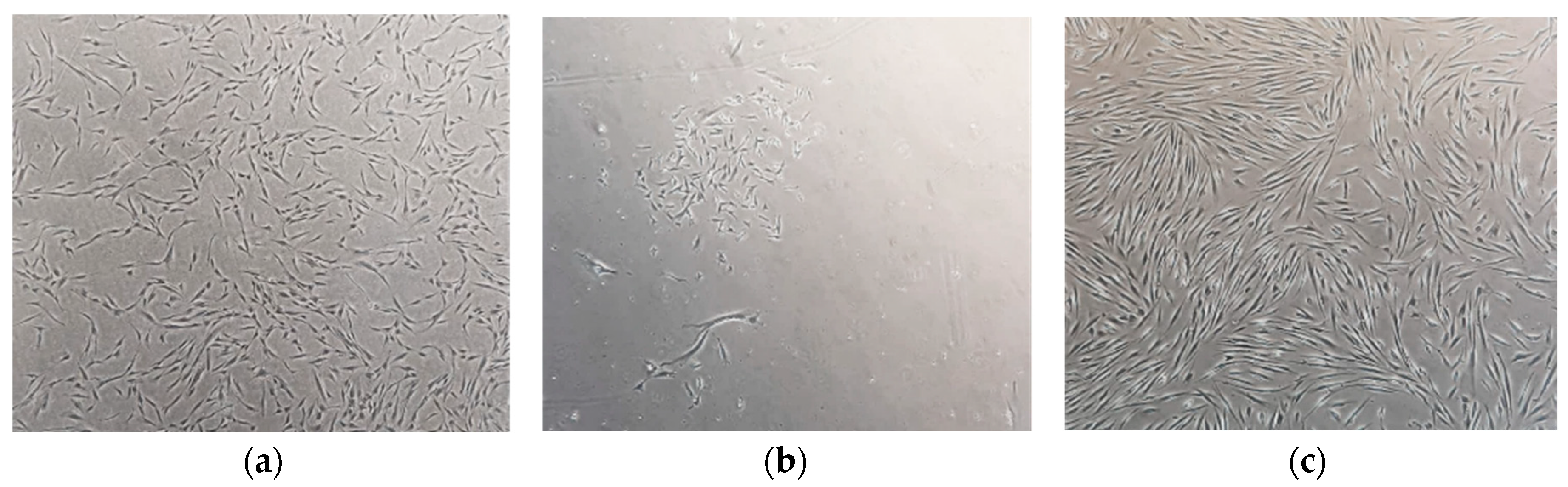
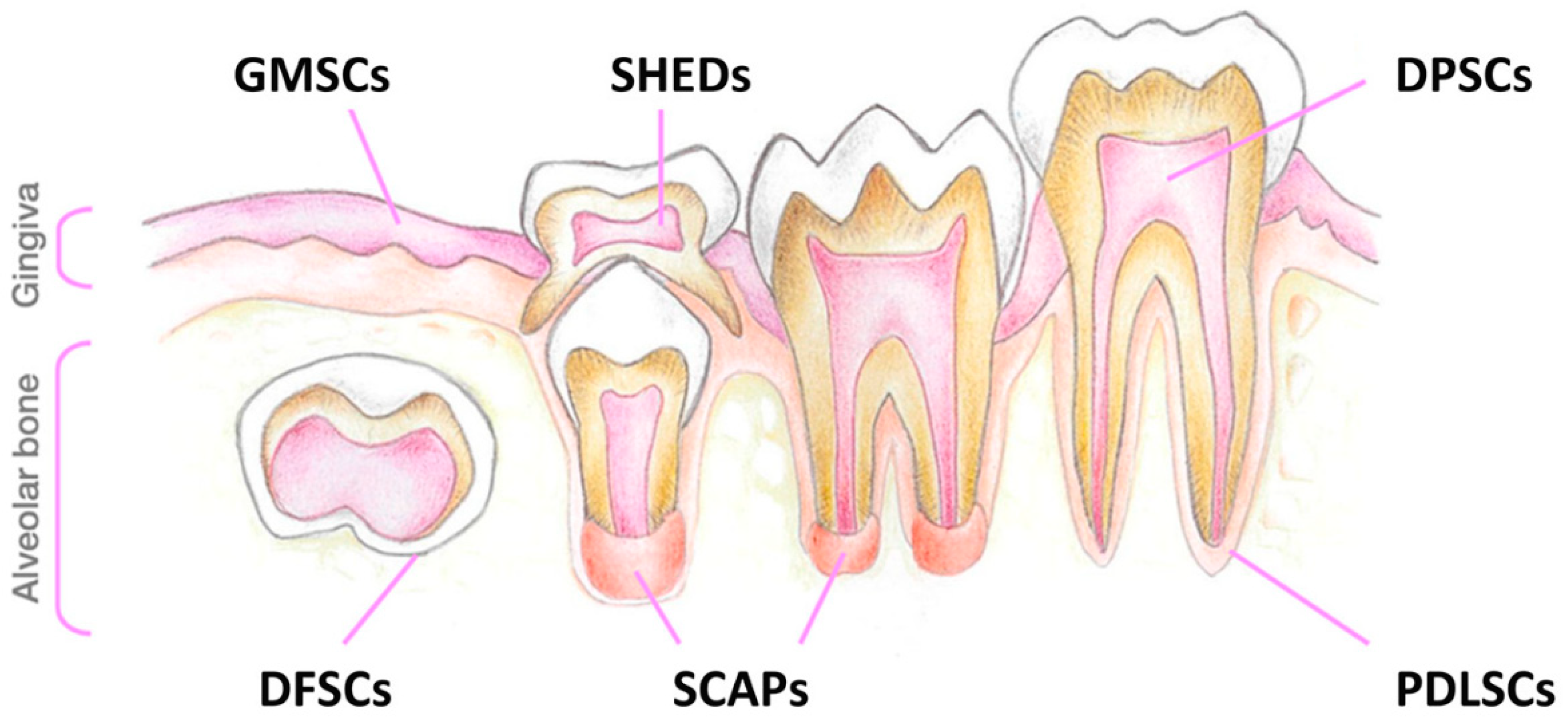
2.1. Establishment of Primary SHED Cell Cultures from Patients and Controls
2.2. The Established SHED Cell Lines Share a MSC Phenotype Identity
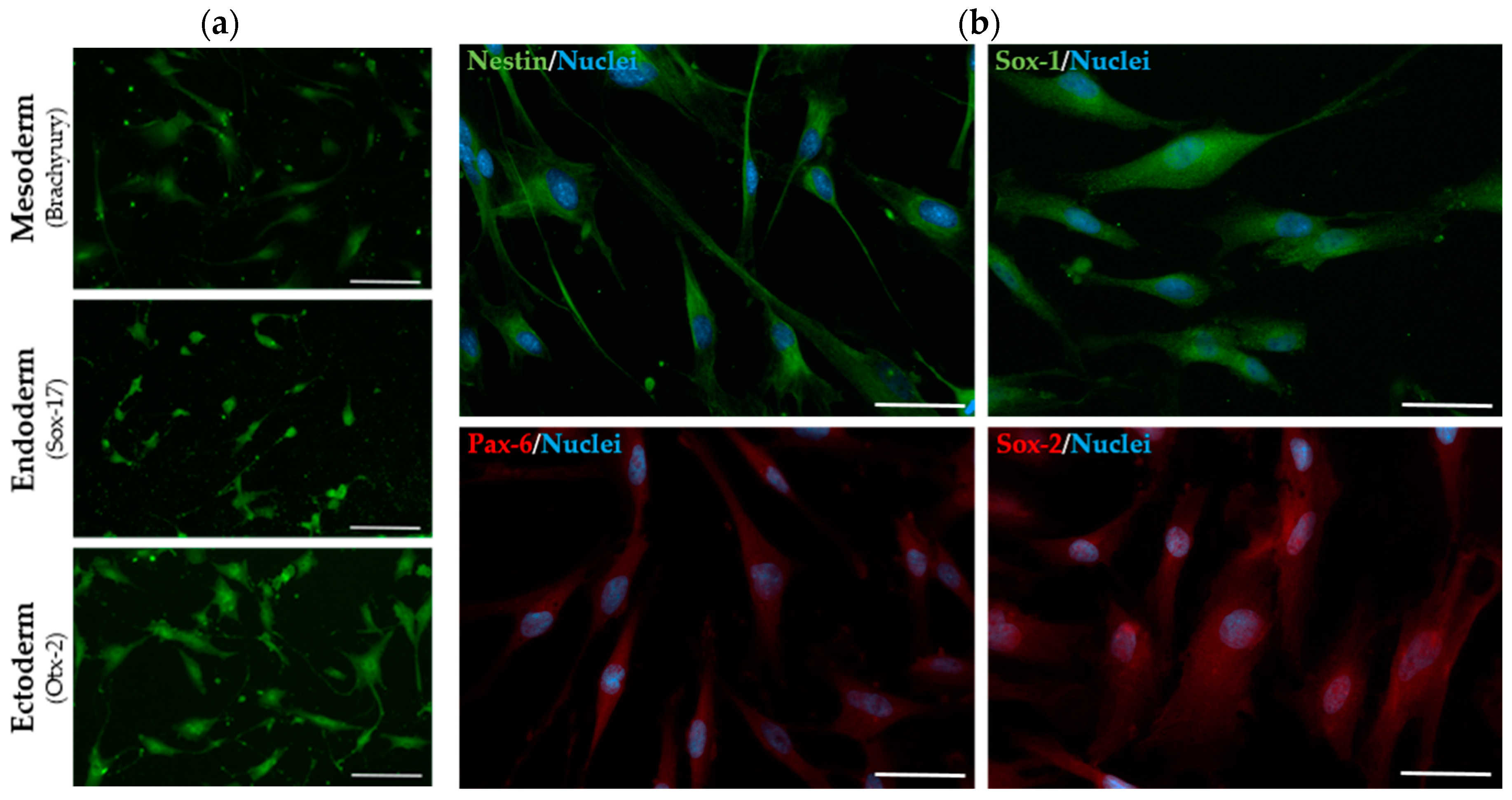
2.3. The Established SHED Cell Lines Express Major NPC Markers
2.4. The Established MPS II-Derived SHED Cell Lines Display the Disease-Related Biochemical and Molecular IDS Defects
2.4.1. The Presence of Pathogenic IDS Variants Was Confirmed in the Established MPS II Patient-Derived SHED Cell Lines
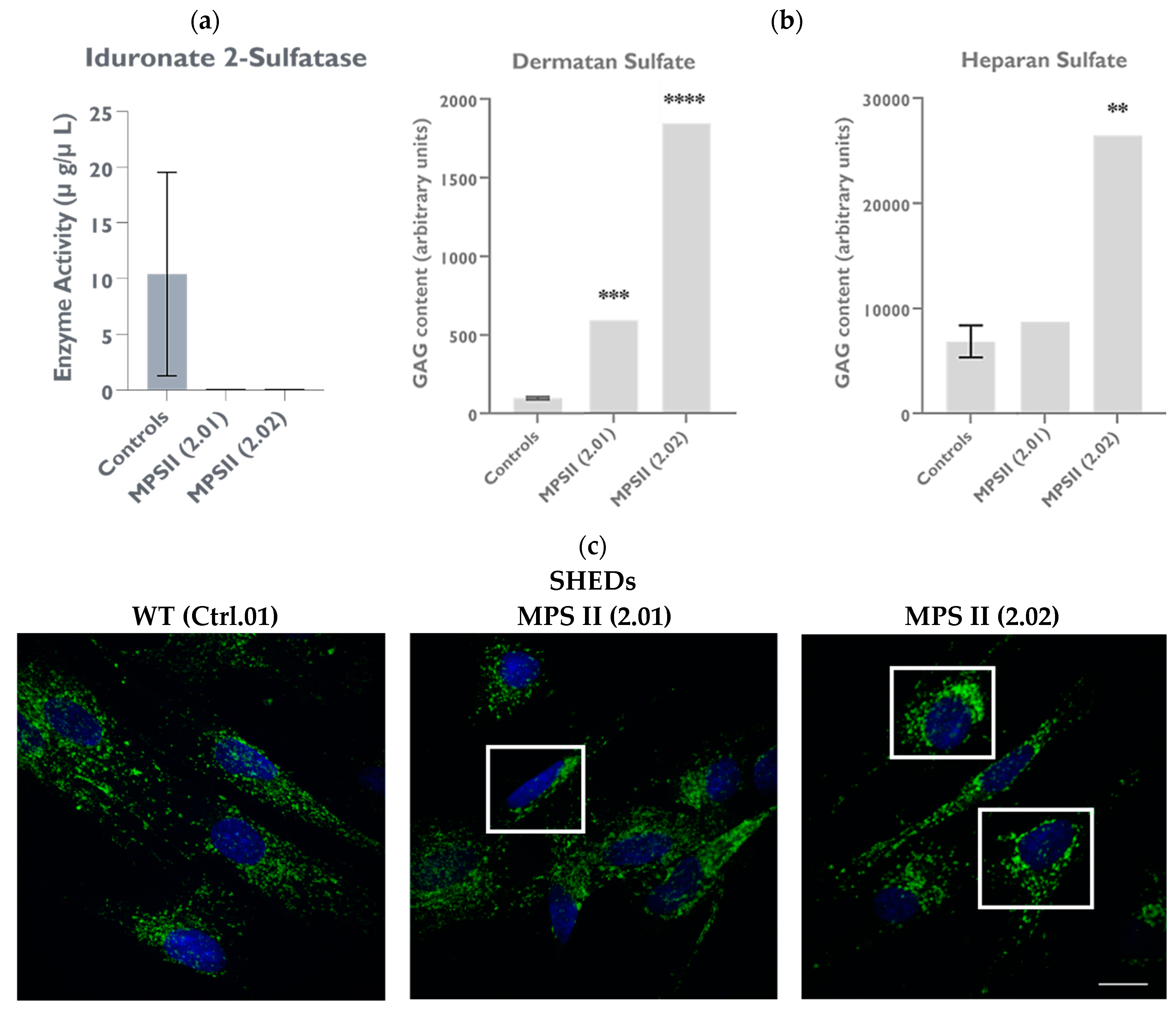
2.4.2. IDS Enzyme Activity Is Significantly Decreased in MPS II Patient-Derived SHED Cells
2.5. MPS II Patient-Derived SHED Cells Exibit a Subcellular LSD Phenotype
2.5.1. GAG Accumulation Is Evident in MPS II Patient-Derived SHED Cells, Despite Their High Proliferation Rate
2.5.2. LAMP1 Staining Is Altered in Patient-Derived SHED Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
| Antibody | Dilution | Company Cat # and RRID | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Antibodies | Germ Layer Markers | Goat Anti-Human Brachyury Polyclonal Antibody, unconjugated (Mesoderm) | 1:10 | R&D Systems Cat# AF2085, RRID:AB_2200235 |
| Goat Anti-Human Sox17 Polyclonal Antibody, unconjugated (Endoderm) | 1:10 | R&D Systems Cat# AF1924, RRID:AB_355060 | ||
| Goat Anti-Human Otx2 Polyclonal Antibody, unconjugated (Ectoderm) | 1:10 | R&D Systems Cat# AF1979, RRID:AB_2157172 | ||
| Neural Stem Cell Markers | Mouse Anti-Human Nestin Monoclonal Antibody | 1:49 | Thermo Fisher Scientific Cat# MA1-110 (A24345) | |
| Rabbit Anti-Human PAX6 | 1:49 | Thermo Fisher Scientific Cat#(A24340) | ||
| Goat Anti-Human SOX1 | 1:49 | Thermo Fisher Scientific Cat#(A24347) | ||
| Rabbit Anti-Human SOX2 | 1:49 | Thermo Fisher Scientific Cat#(A24339) | ||
| LAMP1 Staining | Mouse Anti-Human LAMP-1 Monoclonal Antibody | 1:200 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. Cat# sc-20011 |
|
| Secondary Antibodies | Alexa Fluor 488 Donkey anti-Goat IgG (H + L) Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody | 1:200 | Thermo Fisher Scientific Cat# A-11055, RRID:AB_2534102 | |
| Alexa Fluor™ 488 Donkey Anti-Mouse; for use with anti- Nestin | 1:249 | Thermo Fisher Scientific Cat#(A24350) | ||
| Alexa Fluor™ 488 Donkey Anti-Goat; for use with anti-SOX1 | 1:249 | Thermo Fisher Scientific Cat#(A24349) | ||
| Alexa Fluor™ 555 Donkey Anti-Rabbit; for use with anti-PAX6 or anti-SOX2 | 1:249 | Thermo Fisher Scientific Cat#(A24342) | ||
| Alexa Fluor™ 594 Donkey Anti-Rabbit; for use with anti-PAX6 or anti-SOX2 | 1:249 | Thermo Fisher Scientific Cat#(A24343) |
4.2. Patients and Samples
4.2.1. Patient 1 (Case MPS 2.01)
4.2.2. Patient 2 (Case MPS 2.02)
4.2.3. Biological Samples
4.3. Cell Culture
4.3.1. Establishment of Primary SHED Cell Cultures
4.3.2. Passage, Freezing and Thawing of SHED Cell Cultures
4.4. Molecular Analyses
4.4.1. Genotype Assessment by PCR and Sanger Sequencing
4.4.2. qRT-PCR Analyses
4.5. Biochemical Analyses
4.5.1. Fluorometric IDS Enzyme Assay
4.5.2. Other Enzymatic Assays for Additional Lysosomal Enzymes
4.5.3. Glycosaminoglycans Quantification by LC MS/MS
4.5.4. LAMP1 Immunostaining
4.6. Multi-Lineage Differentiation Protocol
4.7. Data analysis and Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, S.A.; Peracha, H.; Ballhausen, D.; Wiesbauer, A.; Rohrbach, M.; Gautschi, M.; Mason, R.W.; Giugliani, R.; Suzuki, Y.; Orii, K.E.; et al. Epidemiology of Mucopolysaccharidoses. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 121, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dʹavanzo, F.; Rigon, L.; Zanetti, A.; Tomanin, R. Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II: One Hundred Years of Research, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, C. A Rare Disease in Two Brothers. Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1917, 10, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, G.; Eisenberg, F.; Cantz, M.; Neufeld, E.F. The Defect in the Hunter Syndrome: Deficiency of Sulfoiduronate Sulfatase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1973, 70, 2134–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.J.; Meaney, C.A.; Hopwood, J.J.; Morris, C.P. Sequence of the Human Iduronate 2-Sulfatase (IDS) Gene. Genomics 1993, 17, 773–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.J.; Morris, C.P.; Anson, D.S.; Occhiodoro, T.; Bielicki, J.; Clements, P.R.; Hopwood, J.J. Hunter Syndrome: Isolation of an Iduronate-2-Sulfatase CDNA Clone and Analysis of Patient DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1990, 87, 8531–8535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froissart, R.; Da Silva, I.M.; Maire, I. Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II: An Update on Mutation Spectrum. Acta Paediatr. Int. J. Paediatr. 2007, 96, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horgan, C.; Jones, S.A.; Bigger, B.W.; Wynn, R. Current and Future Treatment of Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS) Type II: Is Brain-Targeted Stem Cell Gene Therapy the Solution for This Devastating Disorder? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fesslová, V.; Corti, P.; Sersale, G.; Rovelli, A.; Russo, P.; Mannarino, S.; Butera, G.; Parini, R. The Natural Course and the Impact of Therapies of Cardiac Involvement in the Mucopolysaccharidoses. Cardiol. Young 2009, 19, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.A.; Parini, R.; Harmatz, P.; Giugliani, R.; Fang, J.; Mendelsohn, N.J. The Effect of Idursulfase on Growth in Patients with Hunter Syndrome: Data from the Hunter Outcome Survey (HOS). Mol. Genet. Metab. 2013, 109, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wraith, J.E.; Scarpa, M.; Beck, M.; Bodamer, O.A.; De Meirleir, L.; Guffon, N.; Meldgaard Lund, A.; Malm, G.; Van Der Ploeg, A.T.; Zeman, J. Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II (Hunter Syndrome): A Clinical Review and Recommendations for Treatment in the Era of Enzyme Replacement Therapy. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2008, 167, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomanin, R.; Zanetti, A.; D’Avanzo, F.; Rampazzo, A.; Gasparotto, N.; Parini, R.; Pascarella, A.; Concolino, D.; Procopio, E.; Fiumara, A.; et al. Clinical Efficacy of Enzyme Replacement Therapy in Paediatric Hunter Patients, an Independent Study of 3.5 Years. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, G.A.; Kyosen, S.O.; Patti, C.L.; Martins, A.M.; Tufik, S. Prevalence of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis Types I, II, and VI in a Reference Center. Sleep Breath. 2014, 18, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.; Beck, M.; Eng, C.; Giugliani, R.; Harmatz, P.; Muñoz, V.; Muenzer, J. Recognition and Diagnosis of Mucopolysaccharidosis II (Hunter Syndrome). Pediatrics 2008, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fecarotta, S.; Tarallo, A.; Damiano, C.; Minopoli, N.; Parenti, G. Pathogenesis of Mucopolysaccharidoses, an Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampe, C.; Bosserhoff, A.K.; Burton, B.K.; Giugliani, R.; de Souza, C.F.; Bittar, C.; Muschol, N.; Olson, R.; Mendelsohn, N.J. Long-Term Experience with Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) in MPS II Patients with a Severe Phenotype: An International Case Series. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2014, 37, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muenzer, J.; Botha, J.; Harmatz, P.; Giugliani, R.; Kampmann, C.; Burton, B.K. Evaluation of the Long-Term Treatment Effects of Intravenous Idursulfase in Patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis II (MPS II) Using Statistical Modeling: Data from the Hunter Outcome Survey (HOS). Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parini, R.; Deodato, F. Intravenous Enzyme Replacement Therapy in Mucopolysaccharidoses: Clinical Effectiveness and Limitations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybová, J.; Ledvinová, J.; Sikora, J.; Kuchař, L.; Dobrovolný, R. Neural Cells Generated from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells as a Model of CNS Involvement in Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2018, 41, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobolák, J.; Molnár, K.; Varga, E.; Bock, I.; Jezsó, B.; Téglási, A.; Zhou, S.; Lo Giudice, M.; Hoogeveen-Westerveld, M.; Pijnappel, W.P.; et al. Modelling the Neuropathology of Lysosomal Storage Disorders through Disease-Specific Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 380, 216–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Cheng, Y.S.; Yang, S.; Swaroop, M.; Xu, M.; Beers, J.; Zou, J.; Huang, W.; Marugan, J.J.; Cai, X.; et al. IPS-Derived Neural Stem Cells for Disease Modeling and Evaluation of Therapeutics for Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 412, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, S.; Santos, J.I.; Moreira, L.; Gonçalves, M.; David, H.; Matos, L.; Encarnação, M.; Alves, S.; Coutinho, M.F. Neurological Disease Modeling Using Pluripotent and Multipotent Stem Cells: A Key Step towards Understanding and Treating Mucopolysaccharidoses. Biomedicines 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, M.; Gronthos, S.; Zhao, M.; Lu, B.; Fisher, L.W.; Robey, P.G.; Shi, S. SHED: Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2003, 100, 5807–5812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkis, I.; Kerkis, A.; Dozortsev, D.; Stukart-Parsons, G.C.; Gomes Massironi, S.M.; Pereira, L. V.; Caplan, A.I.; Cerruti, H.F. Isolation and Characterization of a Population of Immature Dental Pulp Stem Cells Expressing OCT-4 and Other Embryonic Stem Cell Markers. Cells Tissues Organs 2006, 184, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.T.J.; Gronthos, S.; Shi, S. Critical Reviews in Oral Biology & Medicine: Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Dental Tissues vs. Those from Other Sources: Their Biology and Role in Regenerative Medicine. J. Dent. Res. 2009, 88, 792–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivoriuunas, A.; Surovas, A.; Borutinskaite, V.; Matuzevicčius, D.; Treigyte, G.; Savickiene, J.; Tunaitis, V.; Aldonyte, R.; Jarmalavicčiuute, A.; Suriakaite, K.; et al. Proteomic Analysis of Stromal Cells Derived from the Dental Pulp of Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth. Stem Cells Dev. 2010, 19, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Lozano, F.J.; Bueno, C.; Insausti, C.L.; Meseguer, L.; Ramírez, M.C.; Blanquer, M.; Marín, N.; Martínez, S.; Moraleda, J.M. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Dental Tissues. Int. Endod. J. 2011, 44, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Tomokiyo, A.; Hasegawa, D.; Hamano, S.; Sugii, H.; Maeda, H. Insight into the Role of Dental Pulp Stem Cells in Regenerative Therapy. Biology (Basel). 2020, 9, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghipour, Z.; Karbalaie, K.; Kiani, A.; Niapour, A.; Bahramian, H.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.H.; Baharvand, H. Transplantation of Undifferentiated and Induced Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth-Derived Stem Cells Promote Functional Recovery of Rat Spinal Cord Contusion Injury Model. Stem Cells Dev. 2012, 21, 1794–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicola, F.; do, C.; Marques, M.R.; Odorcyk, F.; Arcego, D.M.; Petenuzzo, L.; Aristimunha, D.; Vizuete, A.; Sanches, E.F.; Pereira, D.P.; Maurmann, N.; et al. Neuroprotector Effect of Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth Transplanted after Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury Involves Inhibition of Early Neuronal Apoptosis. Brain Res. 2017, 1663, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishii, T.; Osuka, K.; Nishimura, Y.; Ohmichi, Y.; Ohmichi, M.; Suzuki, C.; Nagashima, Y.; Oyama, T.; Abe, T.; Kato, H.; et al. Protective Mechanism of Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth in Treating Spinal Cord Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2024, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, M.; Yamamoto, A.; Kako, E.; Kaneko, N.; Matsubara, K.; Sakai, K.; Sawamoto, K.; Ueda, M. Human Dental Pulp-Derived Stem Cells Protect against Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury in Neonatal Mice. Stroke 2013, 44, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, S.; Liu, D.; Chen, C.; Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Shi, S. Transplantation of SHED Prevents Bone Loss in the Early Phase of Ovariectomy-Induced Osteoporosis. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93, 1124–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaza, T.; Alatas, F.S.; Yuniartha, R.; Yamaza, H.; Fujiyoshi, J.K.; Yanagi, Y.; Yoshimaru, K.; Hayashida, M.; Matsuura, T.; Aijima, R.; et al. In Vivo Hepatogenic Capacity and Therapeutic Potential of Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth in Liver Fibrosis in Mice. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonoda, S.; Yamaza, T. A New Target of Dental Pulp-Derived Stem Cell-Based Therapy on Recipient Bone Marrow Niche in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katahira, Y.; Murakami, F.; Inoue, S.; Miyakawa, S.; Sakamoto, E.; Furusaka, Y.; Watanabe, A.; Sekine, A.; Kuroda, M.; Hasegawa, H.; et al. Protective Effects of Conditioned Media of Immortalized Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth on Pressure Ulcer Formation. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victor, A.K.; Reiter, L.T. Dental Pulp Stem Cells for the Study of Neurogenetic Disorders. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, R166–R171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, S.; Mangas, M.; Prata, M.; Ribeiro, G.; Lopes, L.; Ribeiro, H.; Pinto-Basto, J.; Lima Reis, M.; Lacerda, L. Molecular Characterization of Portuguese Patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II Shows Evidence That the IDS Gene Is Prone to Splicing Mutations. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2006, 29, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagerstedt, K.; Karsten, S.L.; Carlberg, B.M.; Kleijer, W.J.; Tönnesen, T.; Pettersson, U.; Bondeson, M.L. Double-Strand Breaks May Initiate the Inversion Mutation Causing the Hunter Syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1997, 6, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GOORHA, S.; REITER, L.T. Culturing and Neuronal Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2017, 2017, 21.6.1–21.6.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, M.; Schöler, H.R. Oct-4: Gatekeeper in the Beginnings of Mammalian Development OCT-4: THE REGULATOR OF TOTIPOTENCY IN THE. Stem Cells 2001, 19, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsui, K.; Tokuzawa, Y.; Itoh, H.; Segawa, K.; Murakami, M.; Takahashi, K.; Maruyama, M.; Maeda, M.; Yamanaka, S. The Homeoprotein Nanog Is Required for Maintenance of Pluripotency in Mouse Epiblast and ES Cells. Cell 2003, 113, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avilion, A.A.; Nicolis, S.K.; Pevny, L.H.; Perez, L.; Vivian, N.; Lovell-Badge, R. Multipotent Cell Lineages in Early Mouse Development Depend on SOX2 Function. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, A.J.; Ribeiro, D.; Santos, R.; Moreira, L.; Bragança, J.; Amaral, O. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Line (INSAi002-A) from a Fabry Disease Patient Hemizygote for the Rare p.W287X Mutation. Stem Cell Res. 2020, 45, 101794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, J.M.; Sousa, A.C.; Caseiro, A.R.; Pedrosa, S.S.; Pinto, P.O.; Branquinho, M. V.; Amorim, I.; Santos, J.D.; Pereira, T.; Mendonça, C.M.; et al. Dental Pulp Stem Cells and Bonelike® for Bone Regeneration in Ovine Model. Regen. Biomater. 2019, 6, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grau-vorster, M.; Laitinen, A.; Nystedt, J.; Vives, J. HLA-DR Expression in Clinical-Grade Bone Marrow-Derived Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells : A Two-Site Study. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidney, L.E.; Branch, M.J.; Dunphy, S.E.; Dua, H.S.; Hopkinson, A. Concise Review: Evidence for CD34 as a Common Marker for Diverse Progenitors. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.C.; Krause, D.S.; Deans, R.J.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.J.; Horwitz, E.M. Minimal Criteria for Defining Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy Position Statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNiece, I. Subsets of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Cytotherapy 2007, 9, 301–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Jiang, X.; Ito, Y.; Bringas, P.; Han, J.; Rowitch, D.H.; Soriano, P.; Mcmahon, A.P.; Sucov, H.M. Fate of the Mammalian Cranial Neural Crest during Tooth and Mandibular Morphogenesis. 2000, 1679, 1671–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, R. SHED - Basic Structure for Stem Cell Research. J. Clin. Diagnostic Res. 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafiadaki, E.; Cooper, A.; Heptinstall, L.E.; Hatton, C.E.; Thornley, M.; Wraith, J.E. Mutation Analysis in 57 Unrelated Patients with MPS II (Hunter’s Disease). Arch. Dis. Child. 1998, 79, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lualdi, S.; Tappino, B.; Di Duca, M.; Dardis, A.; Anderson, C.J.; Biassoni, R.; Thompson, P.W.; Corsolini, F.; Di Rocco, M.; Bembi, B.; et al. Enigmatic in Vivo Iduronate-2-Sulfatase (IDS) Mutant Transcript Correction to Wild-Type in Hunter Syndrome. Hum. Mutat. 2010, 31, 1261–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filocamo, M.; Bonuccelli, G.; Corsolini, F.; Mazzotti, R.; Cusano, R.; Gatti, R. Molecular Analysis of 40 Italian Patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II: New Mutations in the Iduronate-2-Sulfatase (IDS) Gene. Hum. Mutat. 2001, 18, 164–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forni, G.; Malvagia, S.; Funghini, S.; Scolamiero, E.; Mura, M.; Della Bona, M.; Villanelli, F.; Damiano, R.; la Marca, G. LC-MS/MS Method for Simultaneous Quantification of Heparan Sulfate and Dermatan Sulfate in Urine by Butanolysis Derivatization. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 488, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, H.; Kida, S.; Yoden, E.; Kinoshita, M.; Tanaka, N.; Yamamoto, R.; Koshimura, Y.; Takagi, H.; Takahashi, K.; Hirato, T.; et al. Clearance of Heparan Sulfate in the Brain Prevents Neurodegeneration and Neurocognitive Impairment in MPS II Mice. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 1853–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Cheng, Y.S.; Yang, S.; Swaroop, M.; Xu, M.; Beers, J.; Zou, J.; Huang, W.; Marugan, J.J.; Cai, X.; et al. IPS-Derived Neural Stem Cells for Disease Modeling and Evaluation of Therapeutics for Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 412, 113007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bode, C.J.; Dogterom, E.J.; Rozeboom, A.V.J.; Langendonk, J.J.; Wolvius, E.B.; van der Ploeg, A.T.; Oussoren, E.; Wagenmakers, M.A.E.M. Orofacial Abnormalities in Mucopolysaccharidosis and Mucolipidosis Type II and III : A Systematic Review. JIMD Rep. 2022, 63, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VOZNYI, Y.N.; KEULEMANS, J.L.M.; VAN DIGGELEN, O.P. A Fluorimetric Enzyme Assay for the Diagnosis of MPS II (Hunter Disease). J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2001, 24, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamoles, N.A.; Blanco, M.B.; Gaggioli, D.; Casentini, C. Hurler-like Phenotype: Enzymatic Diagnosis in Dried Blood Spots on Filter Paper. Clin. Chem. 2001, 47, 2098–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civallero, G.; Michelin, K.; de Mari, J.; Viapiana, M.; Burin, M.; Coelho, J.C.; Giugliani, R. Twelve Different Enzyme Assays on Dried-Blood Filter Paper Samples for Detection of Patients with Selected Inherited Lysosomal Storage Diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta 2006, 372, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forni, G.; Malvagia, S.; Funghini, S.; Scolamiero, E.; Mura, M.; Bona, M. Della; Villanelli, F.; Damiano, R.; la Marca, G. Data in Support for the Measurement of Heparan Sulfate and Dermatan Sulfate by LC–MS/MS Analysis. Data Br. 2018, 21, 2398–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encarnação, M.; Coutinho, M.F.; Cho, S.M.; Cardoso, M.T.; Ribeiro, I.; Chaves, P.; Santos, J.I.; Quelhas, D.; Lacerda, L.; Leão Teles, E.; et al. NPC1 Silent Variant Induces Skipping of Exon 11 (p.V562V) and Unfolded Protein Response Was Found in a Specific Niemann-Pick Type C Patient. Mol. Genet. Genomic Med. 2020, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Marker | SHEDs (2.01) | SHEDs (2.02) | iPSCs (INSAi002-A) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD105 | *** | *** | *** |
| CD73 | *** | *** | *** |
| CD90 | *** | *** | *** |
| CD166 | *** | *** | |
| MHC I | *** | *** | |
| Sox-2 | * | * | ** |
| Oct-3/4 | * | * | *** |
| Nanog | * | * | ** |
| CD117 | ** | ** | |
| CD34 | * | * | * |
| MHC II | * | ** | ** |
| Case | Age at Diagnosis (Years) | Symptoms | Age of Starting Treatment (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.01 | 3 | Coarse facies, Stiff Joints, etc. Post-natal macroglossia Mild psychomotor development retardation; Interventricular communication (IVC) and patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)1; Moderate aortic insufficiency and left ventricular hypertrophy; Hydrocele; Chronic nasal obstruction without recurrent otitis or hearing deficit |
|
| 2.02 | 2 | Inguinal Hernias; Claw Hands; Low stature; Hypertrichosis; Hepatomegaly; Cardiac involvement. |
4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





