1. Introduction
Medicinal plants, used in traditional medicine or traditional medical practices as medicines, are one of the most useful natural resources in the world, as they play an important role in health care in many ancient and modern cultures [
1,
2]. Therefore, natural products and traditional medicines derived from plant species have incomparable advantages, such as rich clinical experience and unique diversity of chemical structures and biological activities, which can be used in drug development and discovery [
3].
Saussurea DC. - a large, predominantly East Asian genus belonging to the family
Asteraceae, which includes about 465 species found in the Arctic and temperate zones of the Eurasian and North American continents. Many representatives of the genus are also used in pharmaceuticals, cosmetology, official and traditional medicine [
4,
5]. The genus
Saussurea DC is well known for its rich chemical composition and wide range of biological activity, and therefore it is necessary to resolve issues related to the conservation of the biological diversity of species of the genus
Saussurea, which require a preliminary in-depth study of the composition, morphology and geography of the species [
6]. At the moment, the scope and boundaries of the genus, as well as the family relationships between its constituent substances and pharmacological activities remain as the subject of debate and continue to be revised [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13].
Medicinal properties of the genus
Saussurea DC. are gaining popularity in modern traditional medicine systems, including Chinese and Tibetan traditional medicine. According to the literature, the following pharmacological activities of the genus
Saussurea DC were determined: Anticancer/antitumor effect; Hepatoprotective effect; Immunostimulant effect; Anti-angiogenesis effect; Antidiabetic effect; Antimicrobial effect; Anti-inflammatory effect; Activity against coronavirus (COVID-19); Antibacterial and antifungal effect; Antioxidant effect; Antihyperlipidemic and antihyperglycemic effect. See
Table 1.
There are 41 species of
Saussurea DC growing on the territory of Kazakhstan [
14,
15]. The objects of this study are S. sordida, S. alpina, which has a identified as quercetin 5-O-β-D-glucopyranoside. Similarly, flavonoids 6, 7 and 10 were characterized as kaempferol 5-O-glucoside, kaempferol 7-O-glucoside and isorhamnetin 5-O-glucoside. Flavone and flavonol 5-O-glucosides are comparatively rare in the plant kingdom [
16].
Figure 1.
Saussurea species growing in Kazakhstan.
Figure 1.
Saussurea species growing in Kazakhstan.
Based on the results of these studies, species of this plant family were found to exhibit multiple types of activity in terms of pharmacological action. It becomes clear that in terms of phytochemical composition, the medicinal plants S. sordida, S. alpina are closer (similar or identical) to other species of the genus Saussurea. Thus, the present work was carried out with the aim of studying the phytochemical composition, as well as biochemical and histological studies of these species of medicinal plants (S. sordida, S. alpina) growing in the South Kazakhstan.
2. Results
Aerial parts of S.alpina and S. sordida were grinded by an analytical mill and packed in polyethylene bags. The grinded mass with 50 g of S.alpina and S. sordida from the aerial parts was extracted with 70% ethanol.
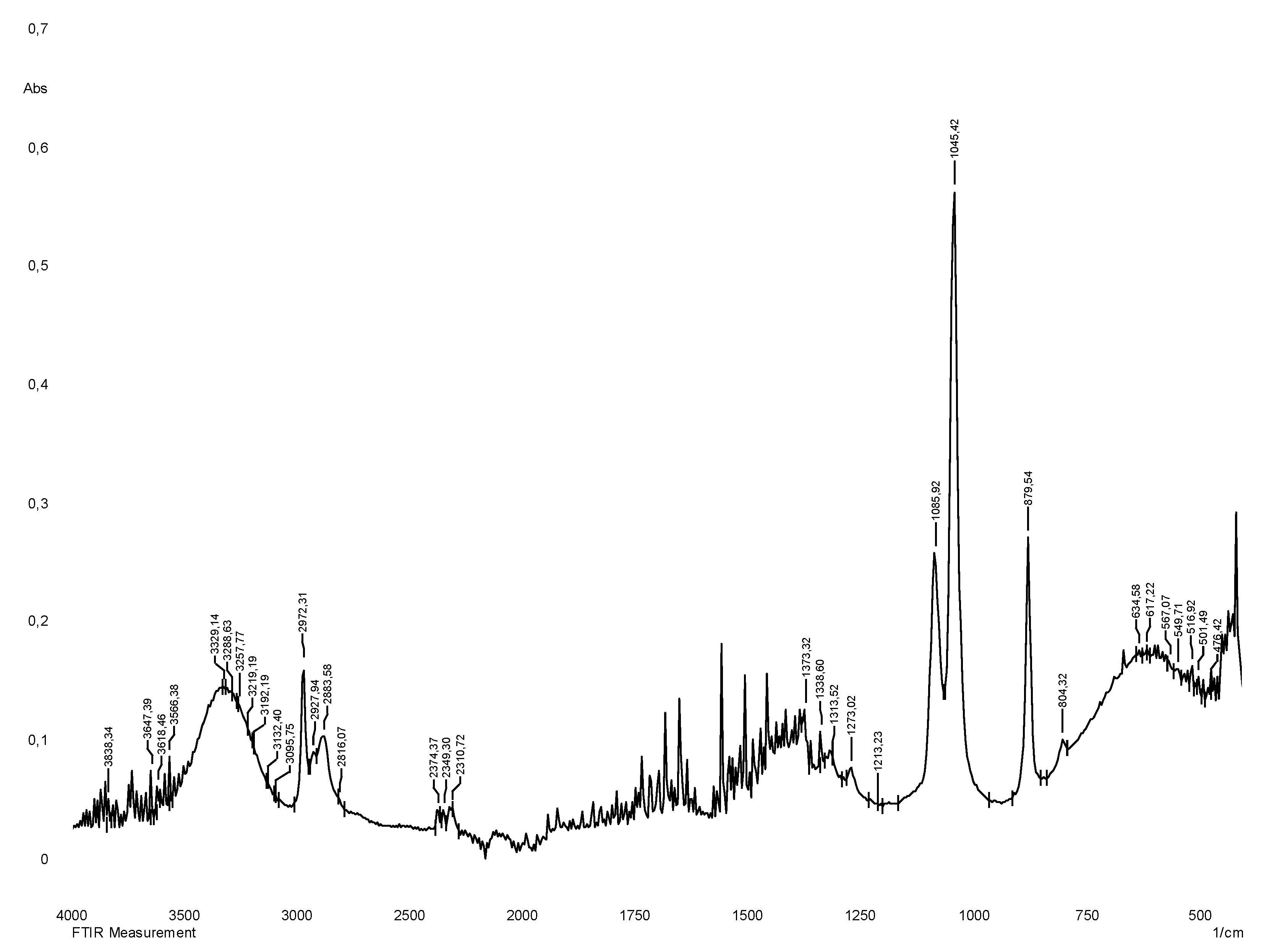
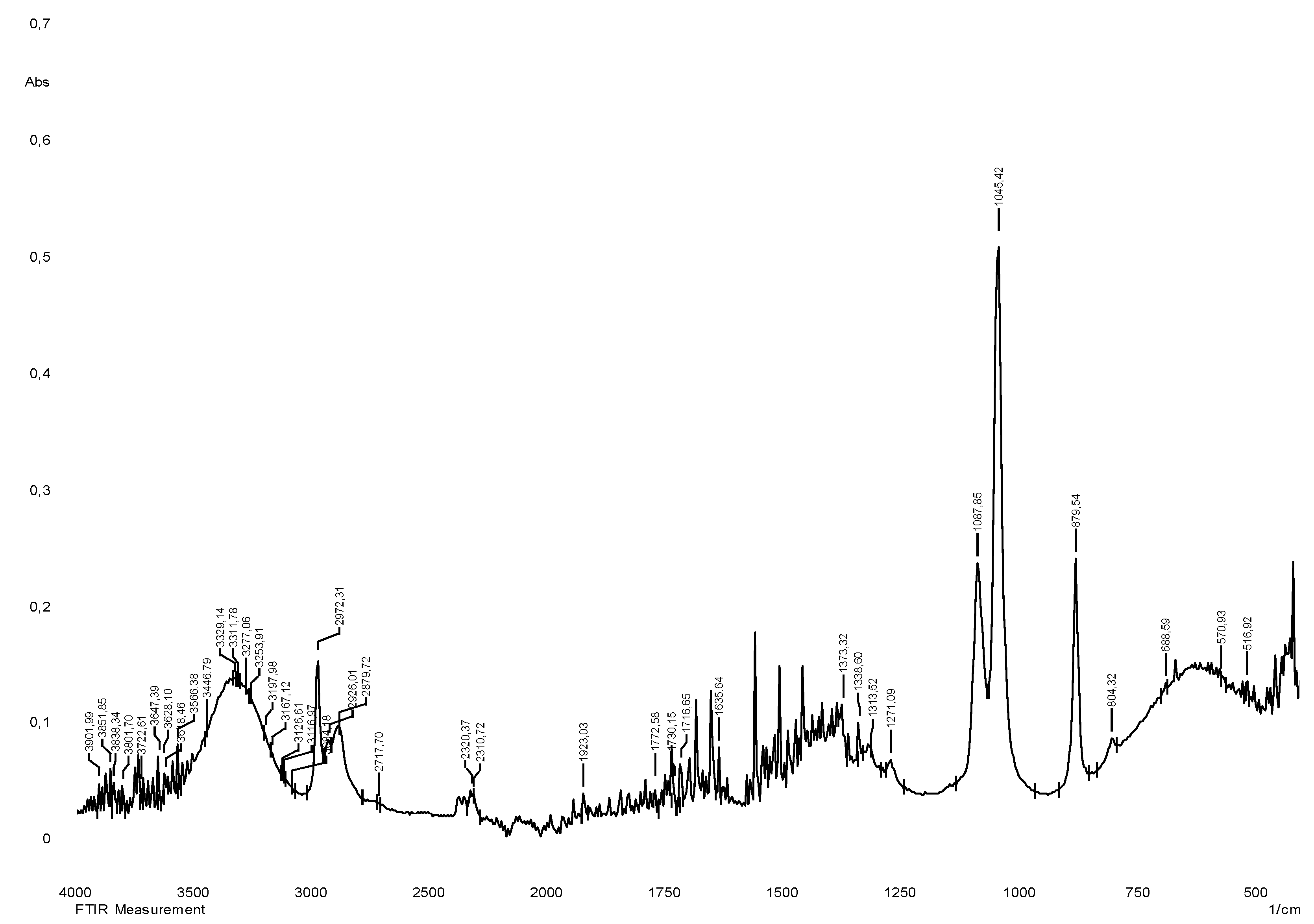
The vibrational spectrum of a chemical molecule is considered to be a unique physical property. Absorption spectra of dried herbal extracts obtained in the range 4000–400 cm−1 are shown in
Figure 3. The main vibrational range of the molecules, called "mid-infrared", lies between wave numbers from 4000 to 400 cm
-1. All the spectra of the studied samples (70% ethanol extracts from
S.
sordida and
S.
alpine) absorption bands reflecting the general chemical composition were detected. In the IR spectra of the studied medicinal plant extracts, characteristic absorption bands of the aromatic part of flavonoids can be identified: The region of 3385 - 2850 cm−1 indicates a symmetric (sym) and asymmetric (asym) stretching of polymeric hydroxyl group (O–H), H-bonded stretching, which is characteristic of phenolic compounds (
Table 2), 1680-1615 cm
-1 (carbonyl group of γ-pyrone), The stretching of the C–H and C=C–C aromatic bond appears in the region of 1620-1470 cm
−1 (skeletal vibrations of aromatic rings), 2950-2880 cm
-1. There are absorption bands due to valence vibrations of free groups with phenolic compounds (frequencies 3750-3700 cm-1), intermolecular hydrogen bonds in dimers and polymers (frequencies 3400-3200 cm
-1) characteristic peaks are observed from 2000 to 1380 cm-1 [
17,
18]. The results of the obtained spectra are shown in
Figure 2 and
Figure 3.
2.1. Determination of Functional Groups in Medicinal Herbal Raw Materials
Furthermore, the 70% ethyl alcohol extract
S.alpina and
S. sordida extracts from South Kazakhstan. The peaks same at 3329, 2927, 1373, 1273, 1045, 879 and 634 cm−1 were identical in two extracts (
Figure 2 and
Figure 3). These peaks attributed to phenolic and organic compounds. The most prominent signals for the two 70% ethyl alcohol extracts were the major absorption band (
Figure 2 and
Figure 3) around 3300 cm−1, which can be associated with O–H stretching and C–H stretching vibrations. The peaks between 700 and 1800 cm−1, the fingerprint zone, could be attributed to C=C–C aromatic ring stretching (1580–1615 cm−1, 1450–1510 cm−1) and several aromatic out-of-plane C–H (670–900 cm−1) and in-plane (950–1225 cm−1) bending14–16. In addition, peaks for water were observed in the range 1640 cm−1 and 3300 cm−1 on the basis of functional group H and OH (
Table 2 and
Table 3).
S.alpina extract have two different peaks 1772 and 1635 cm-1. This band could be due to stretching vibration of C=C groups, due to aromatic ring deformations, due to flavonoids. Besides the bands previously described, there were other bands encountered. A band at 1772 cm-1, probably related to: stretching vibration of carboxyl groups, stretching of C = O of flavonoids and lipids. A band at 1635 cm-1, related to aromatic ring deformations and to flavonoids and aromatic rings (stretching of aromatic C=C) [
19,
20,
21]. This study can lead to the production of new herbal medicines from various diseases employing and to creation of new medications.
2.2. Subacute Toxicity Studies
According to the testing procedure outlined in this manual, the experiment was performed in 2 stages. The first stage was a "maximum permissible dose" test. The study subjects were administered Per Os through a gastric atraumatic tube at a dose of 2000 mg/kg. Calculation of the administered dose and preparation of the oral solution were done individually for each animal. Survival and behavioral responses of mice were monitored for 48 hours. If 5 consecutive animals did not die, the experiment was stopped and the LD50 value was taken to be greater than or equal to 2000 mg/kg (LD50 ≥ 2000 mg/kg). Otherwise, the main test was performed.
In the "maximum permissible dose" test, the administration of the studied 70% ethanol extracts from S. sordida and S. alpine, showed no death and no significant deviations in the behavior, sensorimotor activity of animals and their general condition were observed. Thus, we did not proceed to the second stage of acute toxicity assessment of the studied extracts. For further studies, the value of LD50 was taken as 2000 mg/kg.
The research showed that the studied extracts do not have a systemic toxic effect in the acute experiment.
2.3. Results of Assessing the Influence of the Studied Compounds on Changes in Biochemical Parameters of Blood Serum
The studied objects were extracts under the codes ET-1 and ET-2. ET-1 - extract (70% alcohol extract) of the above-ground part of S. alpine; ET-2 - extract (70% alcohol extract) of the above-ground part of S. sordida.
Changes in the activity of hepatic enzymes in blood serum against the background of administration of the studied pyrimidine derivatives to animals are presented in
Table 4 and
Table 5.
As a result, evaluating the changes in the activity of hepatic enzymes in animals against the background of administration of the studied objects, statistically significant differences between the control group of rats and animals receiving the studied objects in the activity of AlAt (alanine aminotransferase), AsAt (aspartate aminotransferase) and ALP (alkaline phosphatase) were not found, which may be evidence of the absence of hepatotoxic effect.
Changes in the concentration of total protein and its fractions against the background of chronic administration of pyrimidine derivatives are presented in
Table 6 and
Table 7.
Thus, it was found that during the application of the studied objects, no changes in protein metabolism in rats were found.
Changes in the state of nitrogenous metabolism in animals are presented in
Table 8 and
Table 9.
Based on the obtained data it is possible to assume the absence of toxic effect of the studied objects on changes in nitrogen metabolism in rats of both sexes at chronic administration.
The effect of the studied objects on the change of lipid metabolism is presented in
Table 10 and
Table 11.
Thus, it was established that there was no negative effect of the analyzed extracts on lipid metabolism in rats of both sexes.
2.4. Results of Assessing the Influence of the Studied Substances on the Change in the Mass Coefficient of Organs in Animals
The results of necropsy of animals receiving the studied objects for 30 days are presented in
Table 12 and
Table 13. As a result, it was found that there was no significant effect of the studied substances on the change in the mass coefficient of organs in animals upon chronic administration.
2.5. Histological Study of S. sordida Exctract
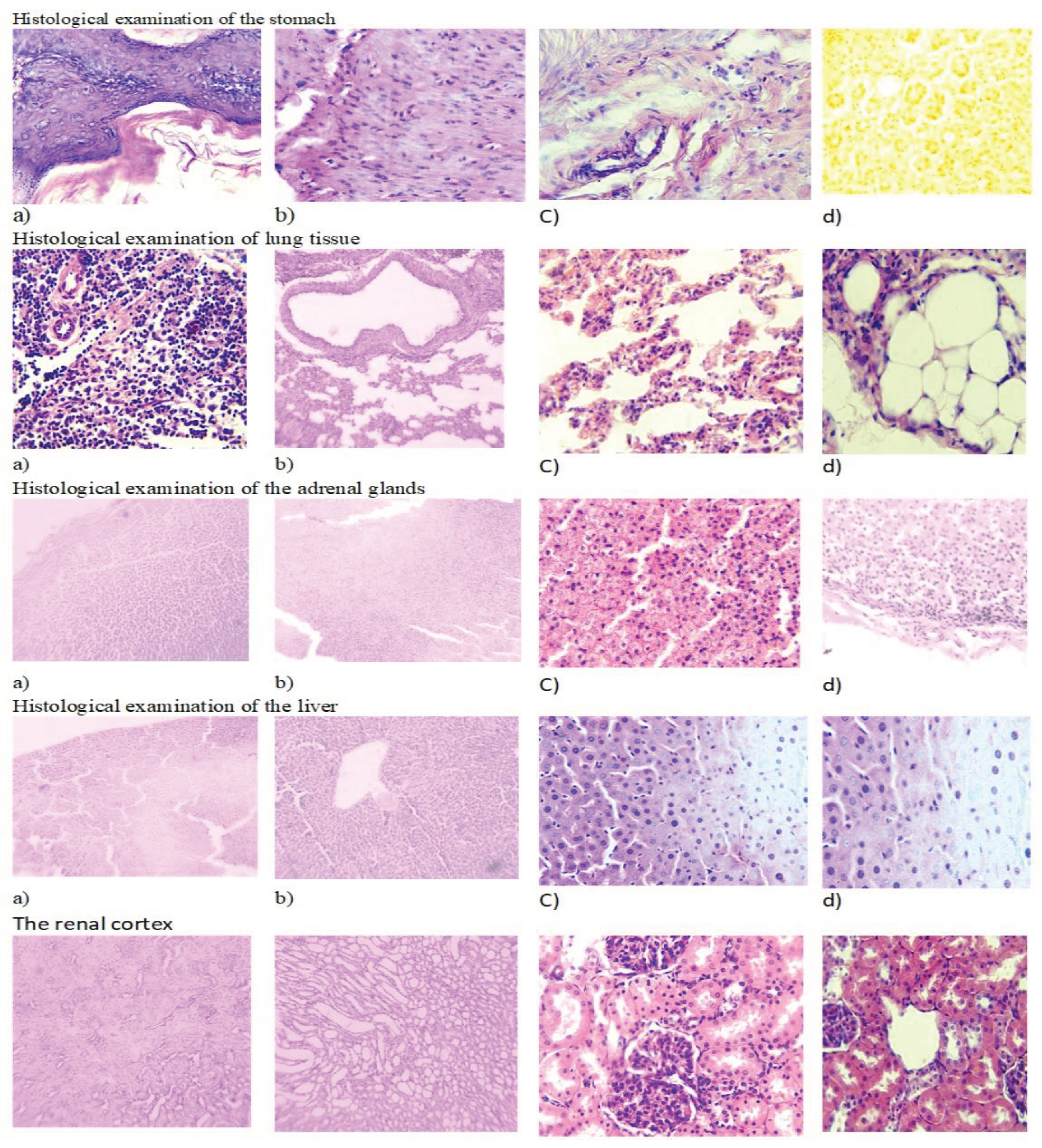
Histological examination of the stomach revealed the presence of intact single-layer prismatic epithelium over the entire surface of the mucosa, including the pits (
Figure 4). The lamina propria was represented by the tubular glands of the stomach, between which lay thin layers of connective loose fibrous tissue. The secretory parts of the glands and excretory ducts with a narrow lumen, free from contents, were clearly visible.
The cells of the body and bottom of the glands were stained basophilically more intensely than the excretory ducts. The gland cells are located in the form of continuous straight cords, fit tightly to each other and had granular cytoplasm. The nuclei had a round shape and were located centrally.
In a histological study of sections of the lungs, the lumens of the respiratory bronchioles are mostly free of contents; some contain a moderate amount of mucus. The single-layer cubic epithelium of the bronchioles is arranged in a uniform layer, the basophilic nuclei are well and uniformly stained. The lumen of the alveoli gapes and is free of contents in all fields examined. The interalveolar septa are thin and uniform in thickness. The blood vessels of the lungs contain a small amount of red blood cells. In sections of this group, the adrenal glands are clearly divided into two structurally and functionally different zones: the cortex and the medulla. The cortex consists of several areas. The subcapsular zone is formed by small undifferentiated corticocytes. The subcapsular zone is formed by small undifferentiated corticocytes. The zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex is composed of small corticocytes that form the glomeruli. The zona fasciculata is formed by large-sized oxyphilic corticocytes, forming cords and bundles (
Figure 4). Between the bundles, sinusoidal capillaries lie in thin layers of loose fibrous connective tissue. On sections, two types of tufted corticocytes can be distinguished: dark and light. The reticular zone consists of small cells that lie in a network. The medulla is separated from the cortex by a thin capsule of loose fibrous connective tissue. The medulla contains large light cells and small dark cells containing a large number of dense granules.
The general plan of the architectonics of the hepatic lobules has been preserved. The structure of the hepatic beams is preserved, the hepatocytes in them are arranged in rows with smooth tortuosity, in the direction from the central vein to the periphery of the lobule, the cells in the beams fit tightly to each other. Sinusoids of regular sizes. The interlobular septa are not strengthened and are represented by barely visible thin connective tissue formations.
The central veins of the lobules are oval in shape and contain a small amount of red blood cells. Both in the center of the lobules and along their periphery in hepatocytes, the cytoplasm is homogeneous. Signs of karyorrhexis and karyolysis are observed in individual hepatocytes. There is a slight lymphocytic infiltration in the periportal areas. There are no signs of degenerative changes (vacuolization, fatty and other pathological inclusions).
On sections of kidneys the surface is smooth and even. In the cortical layer, glomeruli and nephron capsules located in homogeneously colored cortical tissue are clearly visible. The convoluted tubules of the cortex gape, their lumen is free of contents. The epithelial cells of the tubules fit tightly to the wall of the tubules over the entire surface and are represented by one layer of cells, uniformly stained with a central location of the nuclei.
There are a small number of red blood cells in the vessels of the cortex. The round glomeruli of nephrons are located closer to one pole of the capsule, which is crescent-shaped. The lumen of the capsule is free of content. The capsule epithelium is unchanged. The medulla of the pyramid is evenly colored, the lumens of numerous tubules are free of content. The epithelium is unchanged, located in a continuous single-cell layer with a central arrangement of nuclei and homogeneous cytoplasm.
On histological sections of the spleen, all anatomical and morphological structures are clearly visible.
The spleen is covered with a capsule that tightly adheres to the surface of the parenchyma of the organ. Trabeculae extend inward from it in various directions. The sinusoids of the red pulp were collapsed, as the spleen was not specially stretched during the preparation and fixation of the preparation. The sinusoids of the red pulp were collapsed, as the spleen was not specially stretched during the preparation and fixation of the preparation.
In histological sections of the heart of this group, cardiomyocytes are arranged in longitudinal parallel layers. There were numerous anastomoses between the fibers of the cardiomyocytes. The cell cytoplasm is homogeneously stained. The nuclei of cardiomyocytes had an oval shape, were oriented along the longitudinal axis of the fibers and occupied a central position, the surface of the nuclei was smooth, the color was homogeneous. Between the muscle fibers and parallel to them there were layers of loose connective tissue, spindle-shaped in sections.
2.6. Histological Study of S. alpina Exctract
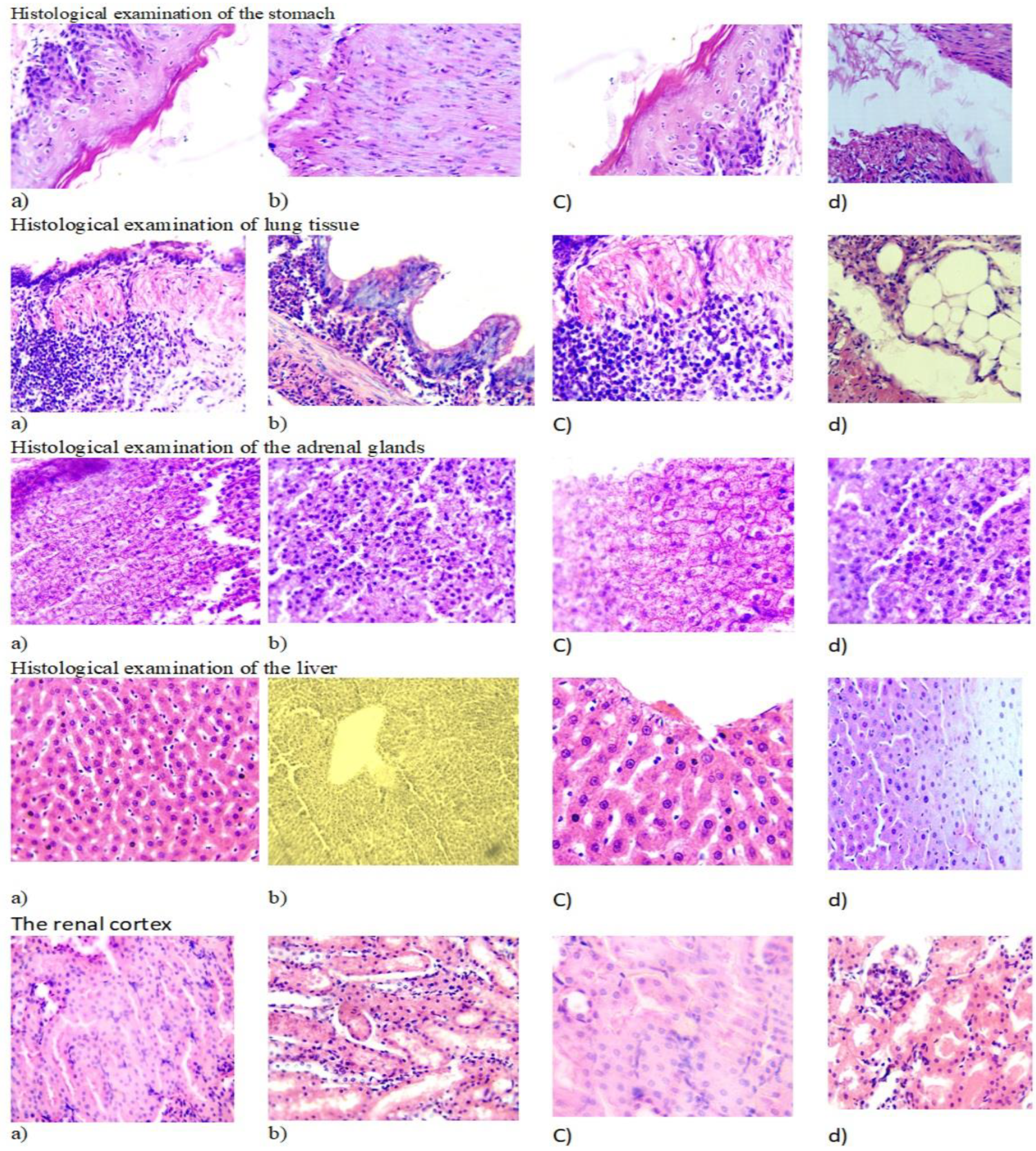
The surface of the gastric mucosa is covered with single-layer prismatic epithelium over the entire surface, including the pits. The lamina propria of the mucosa is represented by the tubular glands of the stomach, between which lay thin layers of connective loose fibrous tissue. The secretory sections of the glands and excretory ducts with a narrow lumen, free of contents, were clearly visible. The cells of the body and bottom of the glands were stained basophilically more intensely than the excretory ducts. The gland cells were located in the form of continuous straight cords, tightly adjacent to each other, and had granular cytoplasm (
Figure 5).
The location of nuclei in cells is central. The kernels are round in shape with a smooth surface. Loose fibrous connective tissue was detected in the layer proper.
Histological examination of the lung tissue remained airy with the presence of rounded alveoli, the wall of which had a normal structure with the presence of epithelial cells and an abundance of capillaries forming an air-blood barrier (
Figure 5). The presence of alveolar macrophages and single lymphocytes was noted, which were located per bronchially, which is a physiological norm. The bronchi were free of mucus and lined with single-layer cubic epithelium. The vessels of the lungs are moderately filled with blood.
Histological examination of the adrenal glands preserved the zonation of the tissue with division into the cortex and medulla. The cortex consists of several areas. The subcapsular zone is formed by small, poorly differentiated corticocytes. The zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex is formed by small corticocytes that form glomeruli. The zona fasciculata is formed by large oxyphilic corticocytes that form cords and bundles. Between the bundles in thin layers of loose fibrous connective tissue lie sinusoidal capillaries. In sections, two types of tufted corticocytes are distinguished: dark and light. The reticular zone consists of small cells that lie in the form of a network. The medulla is separated from the cortex by a thin capsule of loose fibrous connective tissue. The medulla contains large light cells and dark small ones containing a large number of dense granules.
Hepatocytes with light pinkish cytoplasm (light hepatocytes) were located centrilobularly. Closer to the portal tracts in liver cells, the cytoplasm is darker - “dark hepatocytes.” Closer to the portal tracts in liver cells, the cytoplasm is darker - “dark hepatocytes”. In centrilobular hepatocytes, single cells are visible with perinuclear clearing of the cytoplasm. The liver cell nuclei were round in shape with clearly verifiable chromatin. The liver lobules had a beam structure. The vessels of the triads of the portal tracts had moderate blood filling. In the interstation, within the border plate, single mononuclear cells such as macrophages and lymphocytes were encountered.
During histological examination of the kidney tissue, the capsule, cortical and medulla layers were clearly distinguishable. In the cortical layer, numerous glomeruli of nephrons were clearly visible, having a spherical shape with a slightly uneven surface. The leaves of the Shumlyansky-Bowman capsule were thin, the volume of the urinary space was unchanged. The vascular loops were moderately filled with blood; mesangiocytes had rounded nuclei and evenly stained cytoplasm.
The proximal and distal tubules were lined with cuboidal epithelium lying on the basement membrane, a centrally located nucleus, and homogeneous cytoplasm with slight granularity, which corresponded to a normal histological structure. The stroma was represented by thin fibers of connective tissue, the microvasculature vessels were moderately filled with blood.
The white pulp of the spleen was composed of lymphoid follicles with a reactive center around the central vein. It contained macrophages, lymphocytes, and single plasma cells. Clusters of lymphocytes with an admixture of macrophages were also detected near the trabecular arteries. The red pulp is composed of plethoric sinuses and cords of cells containing macrophages, granulocytes, plasma cells and granulocytes. The trabecular vessels of the red pulp are full of blood. In the white pulp, lymphoid follicles are clearly demarcated. No signs of plasmatization or hyperplasia were detected in the reactive centers, in the thymus-dependent and thymus-independent zones.
Myocardial cells are spindle-shaped. The staining of the cytoplasm of myocardiocytes is homogeneous. The kernels are located in a central axial position, not displaced, oval in shape, with a smooth surface. Arterioles and capillaries are not dilated and contain red blood cells. No pathological inclusions are detected in the cytoplasm of myocardiocytes. The ratio of muscle and connective tissue is within the physiological norm.
3. Discussion
Some frequencies are absorbed when infrared radiation passes through a sample of an organic compound; however, some frequencies are transmitted through the sample without any absorption. Absorption of infrared radiation is associated with vibrational changes occurring within the molecule caused by infrared radiation. Therefore, infrared spectroscopy can be characterized as vibrational spectroscopy. Different bonds (C–C, C=C, C–C, C–O, C=O, O–H, and N–H) have different vibrational frequencies. If such bonds are present in an organic molecule, they can be detected by determining the characteristic frequency absorption band in the infrared spectrum [
22]. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) is a high-resolution analytical tool for detecting chemical components and detecting structural compounds. FTIR offers rapid and non-destructive testing of herbal extracts or powders [
23,
24].
The methanolic extracts from S.sordida and S. alpina was shown to have several bioactive components that were confirmed by FTIR spectroscopy, including alcohol, carboxylic acid, phenolic acids, and aromatic compounds. the functional groups identified from the methanolic extract are shown in
Table 2 and
Table 3 and
Figure 2 and
Figure 3. The powerful instance peak is located at peak number 3329, which assigns the NH stretch.
The principal aim of evaluating the safety of any medicinal plant is to identify the nature and significance of adverse effect and to establish the exposure level at which this effect is observed [
25]. The results of the acute toxicity study indicate that the 70% ethanol extracts from S.sordida and S. alpina administered through oral route to animal 2000 mg/kg using the up and down method of acute toxicity testing did not produce any sign of toxicity and death in the animals.
When studying “acute” toxicity, the oral route of administration was used. To remove ethanol, extracts were concentrated under reduced pressure on a rotary evaporator to obtain a dry residue. The studied objects were administered per os through a gastric atraumatic tube in the form of a suspension.
According to the testing procedure outlined in this manual, the experiment was carried out in 2 stages. The first stage was a "maximum permissible dose" test. The objects under study were administered per os through a gastric atraumatic tube at a dose of 2000 mg/kg. The calculation of the administered dose and the preparation of a solution for oral administration were carried out individually for each animal. Survival and behavioral responses of mice were monitored for 48 hours. If 5 consecutive animals did not die, the experiment was stopped and the LD50 value was taken to be greater than or equal to 2000 mg/kg (LD50 ≥ 2000 mg/kg). Otherwise, main testing was performed.
In the “maximum permissible dose” test, with the introduction of the studied 70% ethanol extracts from S.sordida and S. alpina, the absence of death and significant deviations in behavior, sensorimotor activity of animals and their general condition were noted. Thus, the second stage of assessing the acute toxicity of the studied extracts was not started. For further studies, the LD50 value was taken to be 2000 mg/kg.
The study showed that the extracts studied do not have a systemic toxic effect in an acute experiment.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
Above-ground parts of medicinal plant raw material S. sordida, collected in the South Kazakhstan during the flowering period in the spring-summer months of 2021 in Tolebi district, as well as above-ground parts of medicinal plant raw material S. alpina collected from the height of 3050 m of Sayram peak in Tolebi district. Drying of herbs was carried out in South Kazakhstan Medical Academy in a drying oven at room temperature 25±2°C.
4.1. FT-IR Spectroscopic Analysis
All plant material was collected in South Kazakhstan (Saussurea sordida, Saussurea alpina ) 2021 and was identified by Dr. Issayeva E. specimens are kept in the herbarium of the Laboratory of Pharmacognosy, South Kazakhstan Medical Academy, Kazakhstan. Botanical name, taxonomic authority, plant part, voucher specimen number, place and date of collection of each plant.
4.2. Acute Toxicity Studies
Acute toxicity was evaluated on 10 Balb/c mice weighing 18-20 grams. The animals were obtained from the laboratory animal nursery "Rappolovo". Before the immediate experiment the animals were placed in a quarantine compartment for 14 days. During the study, the animals were kept in controlled conditions of the vivarium at air temperature 22±2 0C, relative humidity 60±5% and 12-hour daily cycle in macrolon cages of 5 animals each. Access to food and water was not restricted. Biomethodology and animal care complied with international ethical standards for the treatment of laboratory animals (Directive 2010/63 / EU of the European Parliament and of the council on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes, September 22, 2010). According to the OECD recommendations No. 425, the range of administered doses of the studied compounds in the main test was: 1.75; 5.5; 17.5; 55; 175; 550; 1750; 5000 mg/kg with dose progression coefficient. The study compounds were administered fractionally with 1 hour time intervals until the required dose was achieved according to the following scheme: the first animal received the studied object at a dose of 1.75 mg/kg; if the animal survived, the administration of the compound is continued in increasing order of doses until the 1st case of lethal outcome was reached.
All the experiments were approved by the Local Ethics Committee of South Kazakhstan Medical Academy (Protocol No o44-65/, 22.02.2012).
4.3. Studying the Effect of the Analyzed Objects on Some Biochemical Parameters of Blood Serum and Urine.
After 14 days, urine was collected from rats. The groups were euthanized by decapitation with blood collection and biochemical, hematological and pathomorphological studies were performed to assess the effect of these drugs on metabolic, detoxification, excretory functions of the animal organism.
Serum was obtained from blood by centrifugation, in which the following biochemical parameters were determined: Glucose content, total protein and its fractions, urea, creatinine, uric acid, total bilirubin and its fractions, cholesterol, triglycerides (TRG), activity of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), alanine aminotransferase (AlAt), aspartate aminotransferase (AsAt), alkaline phosphatase (ALP). All parameters are determined on an automatic biochemical analyzer BS-120 (Mindray).
4.4. Histological Study
The organs were fixed in 10% neutral formalin and embedded in paraffin. Then slices were prepared, stained with hematoxylin-eosin and viewed under a microscope, describing the histological picture. Sections of organs and tissues were made on a sledge microtome. Microphotographic images were made on a BIOMED microscope combined with a Levenhuk M1000 Plus digital camera and a personal computer.
Figure 2.
IR spectrum of liquid extract of S. sordida plant obtained with 70% ethyl alcohol.
Figure 2.
IR spectrum of liquid extract of S. sordida plant obtained with 70% ethyl alcohol.
Figure 3.
IR spectrum of liquid extract of S.alpina plant obtained with 70% ethyl alcohol.
Figure 3.
IR spectrum of liquid extract of S.alpina plant obtained with 70% ethyl alcohol.
Figure 4.
Histological study of S. sordida exctract (a) Env. hematoxylin and eosin. H&E x10; (b) Intact animal. Env. hematoxylin and eosin. H&E x10; (c) Env. hematoxylin and eosin. H&E x40; (d) Intact animal. Env. hematoxylin and eosin. H&E x40.
Figure 4.
Histological study of S. sordida exctract (a) Env. hematoxylin and eosin. H&E x10; (b) Intact animal. Env. hematoxylin and eosin. H&E x10; (c) Env. hematoxylin and eosin. H&E x40; (d) Intact animal. Env. hematoxylin and eosin. H&E x40.
Figure 5.
Histological study of S. alpina exctrac: (a) Env. hematoxylin and eosin. H&E x10; (b) Intact animal. Env. hematoxylin and eosin. H&E x10; (c) Env. hematoxylin and eosin. H&E x40; (d) Intact animal. Env. hematoxylin and eosin. H&E x40.
Figure 5.
Histological study of S. alpina exctrac: (a) Env. hematoxylin and eosin. H&E x10; (b) Intact animal. Env. hematoxylin and eosin. H&E x10; (c) Env. hematoxylin and eosin. H&E x40; (d) Intact animal. Env. hematoxylin and eosin. H&E x40.
Table 1.
Pharmacological activity of plants of the genus Saussurea according to the results of studies presented in different literature reviews.
Table 1.
Pharmacological activity of plants of the genus Saussurea according to the results of studies presented in different literature reviews.
| Authors |
Type of plant |
Therapeutic effects of Saussurea herbs on the human body |
|
Jehan S Al-Brahim, et al 2023 |
S.costus |
The antimicrobial properties of IONPs were evaluated on nine pathogenic microbes, which showed that the nanoparticles have antimicrobial activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Shigella sp., Staphylococcus sp. and Aspergillus niger, with potential applications in therapeutic and biomedical fields. |
|
Hajo Idriss, et al 2023 |
S.costus |
The acetic acid extract of Saussurea costus has been shown to possess phytochemical profile, molecular additivity, anti-candida and antiviral activities. Was found to have active properties indicating inhibition of SARS-CoV-2. The extract showed significant antimicrobial activity (in vitro) against Candida albicans. |
| Min Liu, et al 2021 |
S.involucrata |
A new auronic glycoside was isolated from the extract of the above-ground parts of Saussurea involucrata. All the identified compounds showed in vitro inhibitory activity against α-glucosidase. Among them, compounds 1 and 6 showed significant inhibitory activity against α-glucosidase with IC50 values of 47.1 and 57.7 μM, respectively. |
|
Yang Wang, et al 2020 |
S.lappa |
Pharmacological studies included extracts, essential oils and monomeric components represented by dehydrocostal lactone. It has antitumor, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects on the digestive system. |
| Gasha S. Ahmed, et al 2023 |
S.costus |
The antibacterial and antifungal activities of essential oil, hexane-chloroform, methanol and aqueous extracts of Saussurea costus root was evaluated against Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus epidermalis, Enterobacter cloacae, Enterococcus faecalis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Escherichia coli and Candida albicans. |
| Sana Naseer, et al 2022 |
S.lappa |
Antioxidant potential refers to the ability of a plant to absorb reactive oxygen species (ROS), which increases the therapeutic potential of the plant. |
| Sana Naseer, et al 2022 |
S.lappa |
S. lappa extracts have antibacterial potential against six ATCC and three multidrug resistant (MLD) strains were evaluated by agar well method. The research showed antibacterial effect. |
Table 2.
FT-IR spectra analysis of dried medical plant extracts.
Table 2.
FT-IR spectra analysis of dried medical plant extracts.
| Herbs |
Absorption spectrum, wave number (cm−1) |
| 3385 - 2850 |
2950-2880 |
1785–1640 |
1680-1615 |
1600–1300 |
1450–1050 |
1080–620 |
935–710 |
| S. sordida |
3329 |
2927 |
- |
- |
1373 |
1273 |
1045 |
879 |
| S.alpina |
3329 |
2927 |
1772 |
1635 |
1373 |
1271 |
1045 |
879 |
Table 3.
Fundamental IR vibrations of phytochemicals present in fractions of S. Sordida and S.alpina.
Table 3.
Fundamental IR vibrations of phytochemicals present in fractions of S. Sordida and S.alpina.
| S. sordida |
Functional Group |
S.alpina |
Functional Group |
| 3329 |
Imino compounds,
NH stretch |
3329 |
Imino compounds,
NH stretch |
| 2927 |
Ac-H carbonyl |
2927 |
Ac-H carbonyl |
| - |
|
1772 |
C=C–C aromatic ring stretching |
| - |
|
1635 |
Alkenyl C=C stretch |
| 1373 |
Phenol or tertiary alcohol, OH
bend |
1373 |
Phenol or tertiary alcohol, OH
bend |
| 1273 |
Primary or secondary, OH
in-plane bend |
1271 |
Primary or secondary, OH
in-plane bend |
| 1045 |
Primary alcohol, C |
1045 |
Primary alcohol, C |
| 879 |
Alkenyl C=C stretch |
879 |
Alkenyl C=C stretch |
Table 4.
Effect of the studied objects on changes in the activity of hepatic enzymes in blood serum in male rats.
Table 4.
Effect of the studied objects on changes in the activity of hepatic enzymes in blood serum in male rats.
| Group |
AlAt (IU/L) |
AsAt (IU/L) |
ALP (IU/L) |
| EТ-1 |
54,5±10,816 |
154,6±13,991 |
494,5±12,284 |
| EТ-2 |
54,6±14,204 |
149,3±18,299 |
477,8±13,461 |
| Control |
42,3±18,792 |
140,1±11,089 |
498,1±13,397 |
Table 5.
Effect of the studied objects on the change in the activity of hepatic enzymes in serum in female rats.
Table 5.
Effect of the studied objects on the change in the activity of hepatic enzymes in serum in female rats.
| Group |
AlAt (IU/L) |
AsAt (IU/L) |
ALP (IU/L) |
| EТ-1 |
56,9±19,473 |
153,6±12,662 |
486,3±11,965 |
| EТ-2 |
56,5±18,093 |
152,9±13,487 |
476,6±16,054 |
| Control |
45,8±13,124 |
158,1±12,732 |
460,7±14,615 |
Table 6.
Effect of the studied objects on changes in the concentration of protein and its fractions in blood serum in male rats.
Table 6.
Effect of the studied objects on changes in the concentration of protein and its fractions in blood serum in male rats.
| Group |
Total protein, g/l |
Albumin, g/l |
Globulins, g/l |
| EТ-1 |
49,3±10,677 |
28,8±8,819 |
36,3±10,005 |
| EТ-2 |
44,4±9,506 |
25,4±7,259 |
38,9±10,269 |
| Control |
47,2±5,282 |
24,6±6,155 |
26,1±11,492 |
Table 7.
Effect of the studied compounds on the change in the concentration of protein and its fractions in blood serum in female rats.
Table 7.
Effect of the studied compounds on the change in the concentration of protein and its fractions in blood serum in female rats.
| Group |
Total protein, g/l |
Albumin, g/l |
Globulins, g/l |
| EТ-1 |
43±10,923 |
34,5±6,22 |
26,1±8,468 |
| EТ-2 |
52,2±6,46 |
28,9±10,851 |
24±10,47 |
| Control |
51,1±11,762 |
26,2±5,23 |
34,7±11,898 |
Table 8.
Effect of the studied objects on the change of nitrogen metabolism in blood serum in male rats.
Table 8.
Effect of the studied objects on the change of nitrogen metabolism in blood serum in male rats.
| Group |
Urea (mmol/L) |
Creatinine (μmol/L) |
Uric acid (μmol/L) |
| FIH-12 |
6,5±0,632 |
69,7±9,771 |
46,2±11,279 |
| EТ-1 |
6±0,735 |
65,2±8,94 |
50,1±8,043 |
| EТ-2 |
6,1±1,141 |
57,5±9,468 |
45,6±8,877 |
| Control |
5,1±1,099 |
63±10,598 |
48,5±10,649 |
Table 9.
Effect of the studied objects on the change of nitrogen metabolism in blood serum in female rats.
Table 9.
Effect of the studied objects on the change of nitrogen metabolism in blood serum in female rats.
| Group |
Urea (mmol/L) |
Creatinine (μmol/L) |
Uric acid (μmol/L) |
| EТ-1 |
6,8±1,254 |
59,5±10,495 |
54,2±9,122 |
| EТ-2 |
5,4±0,737 |
68,4±8,394 |
52±11,366 |
| Control |
6,4±1,132 |
58,4±10,088 |
48,3±8,781 |
Table 10.
Effect of the studied objects on changes in serum lipid metabolism in male rats.
Table 10.
Effect of the studied objects on changes in serum lipid metabolism in male rats.
| Group |
Cholesterol, mmol/L |
Triglycerides, mmol/L |
| EТ-1 |
0,93±0,5 |
1,11±0,828 |
| EТ-2 |
1,03±0,944 |
1,19±0,366 |
| Control |
1,04±0,847 |
0,97±0,779 |
Table 11.
Effect of the studied objects on the change of lipid metabolism in blood serum in female rats.
Table 11.
Effect of the studied objects on the change of lipid metabolism in blood serum in female rats.
| Group |
Cholesterol, mmol/L |
Triglycerides, mmol/L |
| EТ-1 |
0,92±0,982 |
1,04±0,272 |
| EТ-2 |
1,02±0,407 |
1,08±0,733 |
| Control |
1,12±0,556 |
0,98±0,672 |
Table 12.
The influence of the studied objects on the change in the mass coefficient of organs in male rats.
Table 12.
The influence of the studied objects on the change in the mass coefficient of organs in male rats.
| Group |
Liver |
Heart |
Lungs |
Left kidney |
Right kidney |
Left Adrenal Gland |
Right Adrenal Gland |
Spleen |
Stomach |
| EТ-1 |
3,34±0,887 |
4,45±0,451 |
5,63±0,264 |
5,83±0,081 |
6,06±0,696 |
1,31±0,061 |
1,71±0,838 |
6,18±0,627 |
6,87±0,432 |
| EТ-2 |
3,14±0,222 |
3,93±0,884 |
6,03±0,825 |
6,51±0,995 |
5,54±0,658 |
1,29±0,136 |
1,27±0,219 |
5,58±0,281 |
5,06±0,416 |
| Control |
3,3±0,655 |
3,85±0,18 |
5,18±0,912 |
6,86±0,656 |
6,31±0,971 |
1,35±0,716 |
1,73±0,703 |
6,77±0,177 |
5,4±0,781 |
Table 13.
The influence of the studied objects on the change in the mass coefficient of organs in female rats.
Table 13.
The influence of the studied objects on the change in the mass coefficient of organs in female rats.
| Group |
Liver |
Heart |
Lungs |
Left kidney |
Right kidney |
Left Adrenal Gland |
Right Adrenal Gland |
Spleen |
Stomach |
| EТ-1 |
3,77±0,559 |
3,1±0,403 |
5,08±0,21 |
6,71±0,157 |
5,58±0,416 |
1,43±0,462 |
1,74±0,128 |
5,02±0,477 |
6,99±0,107 |
| EТ-2 |
4,39±0,563 |
4,39±0,365 |
5,71±0,176 |
6,15±0,31 |
5,39±0,738 |
1,38±0,942 |
1,8±0,376 |
5,55±0,414 |
5,99±0,12 |
| Control |
3,85±0,437 |
2,64±0,508 |
6,92±0,979 |
5,59±0,904 |
5,93±0,836 |
1,69±0,659 |
1,28±0,879 |
6,22±0,518 |
5,31±0,389 |