Submitted:
27 February 2024
Posted:
29 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Basic Considerations
2.1. Cells
2.2. Pre-Synaptic Flux and Learning Rules
2.3. Excitatory/Inhibitory Balance
3. A minimum Free Energy Organizational Unit
3.1. Rationale
3.2. Constraints
3.3. Minimization of Free Energy,
3.4. Minimization of Prediction Error,
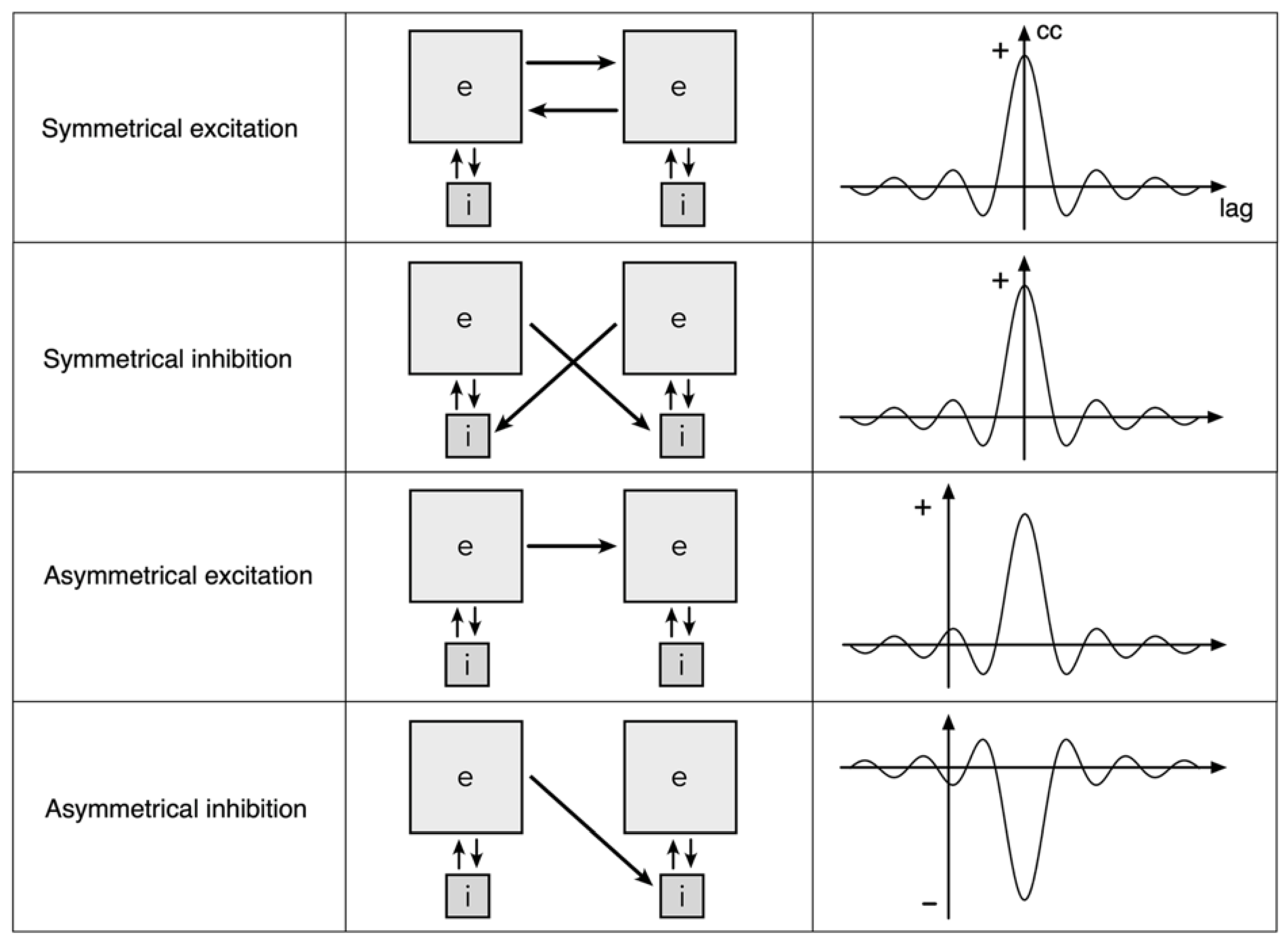
3.5. Excitatory/Inhibitory Balance,
3.6. Interactions within and between Spatial Eigenmodes
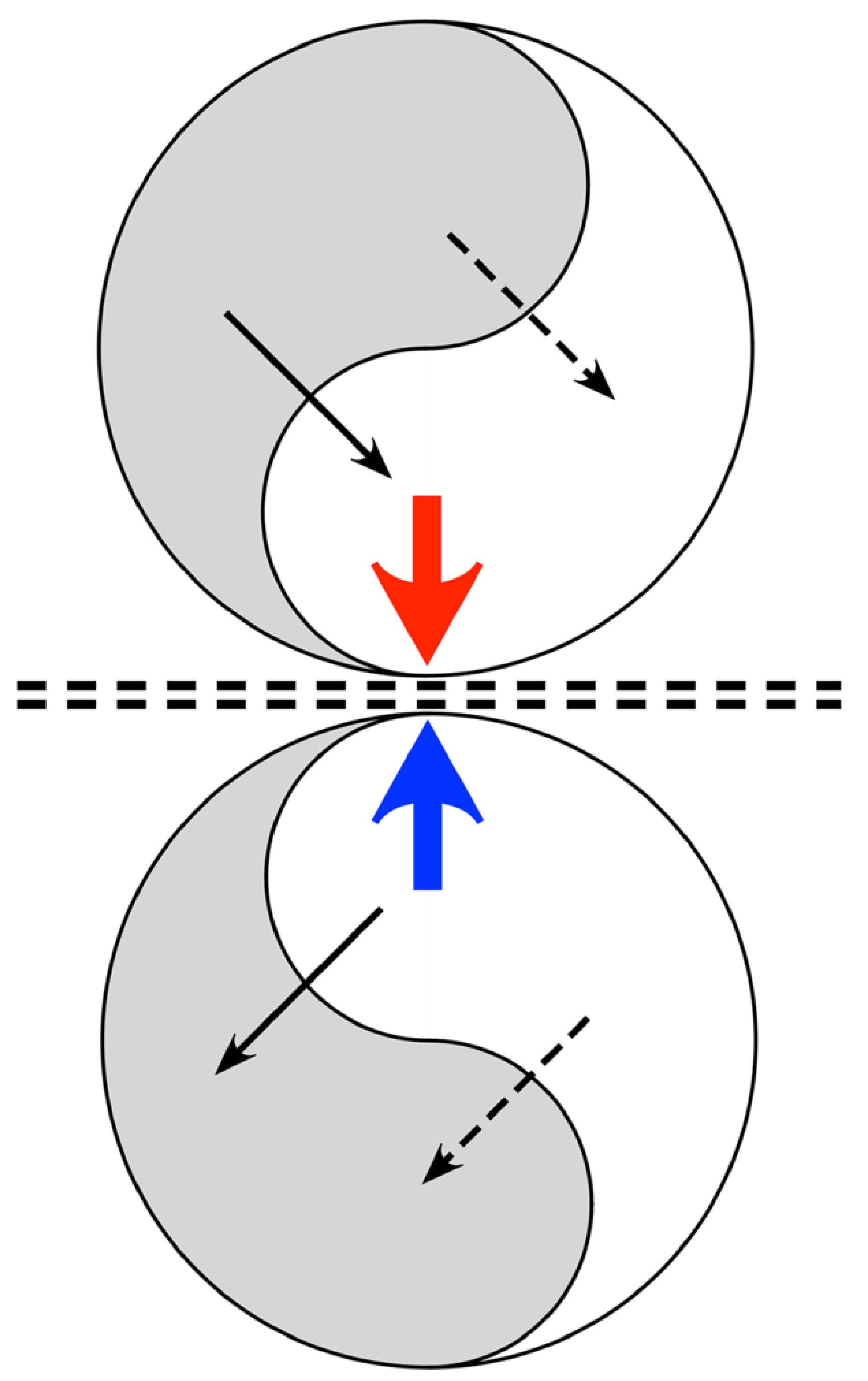
3.7. Mirror Symmetric Fields and Markov Blankets
3.8. Redundancy and Information Storage
4. Emergence of Mirrored Synaptic Maps in Actual Anatomy
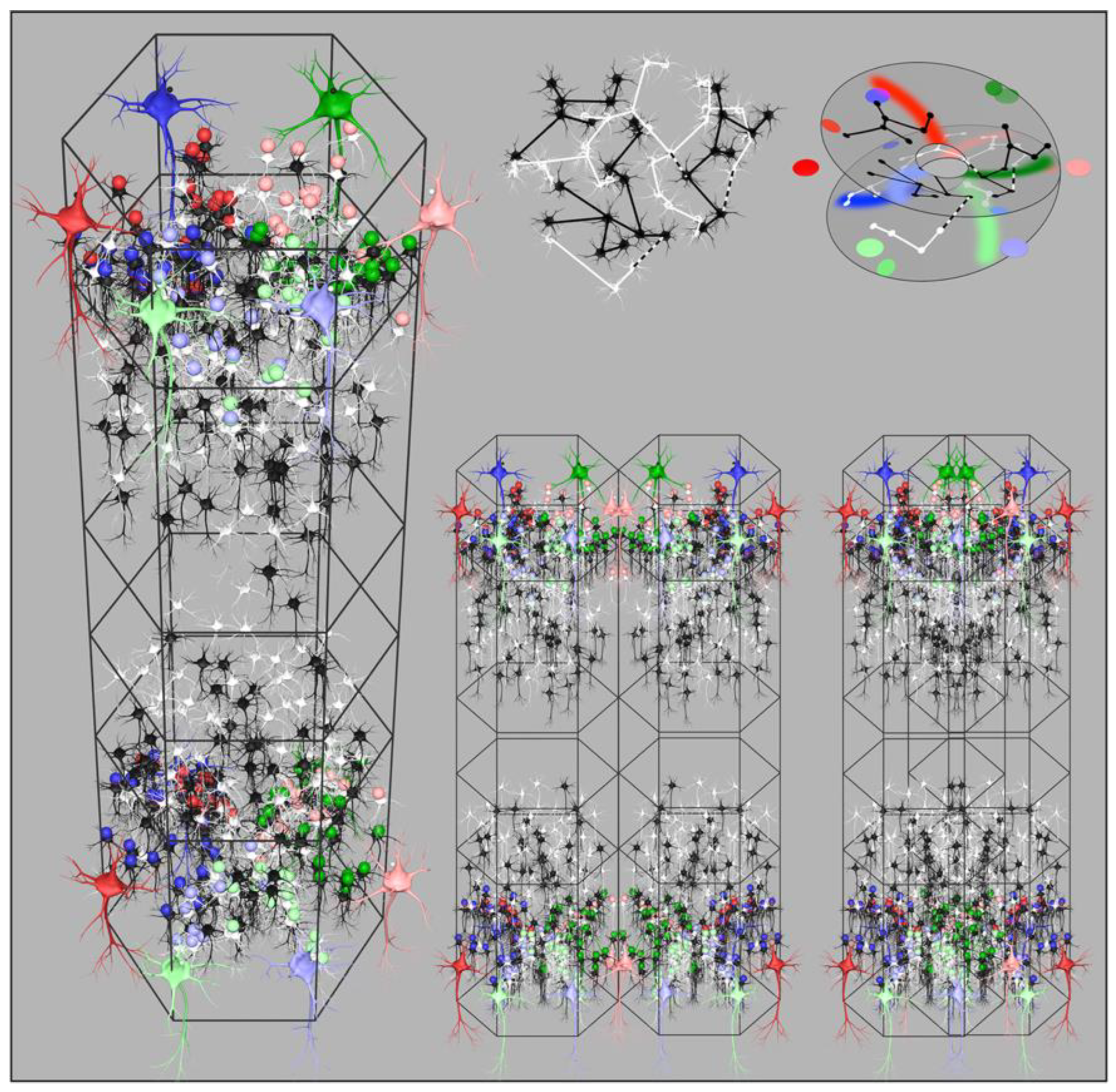
4.1. Columnar versus Noncolumnar Cortex
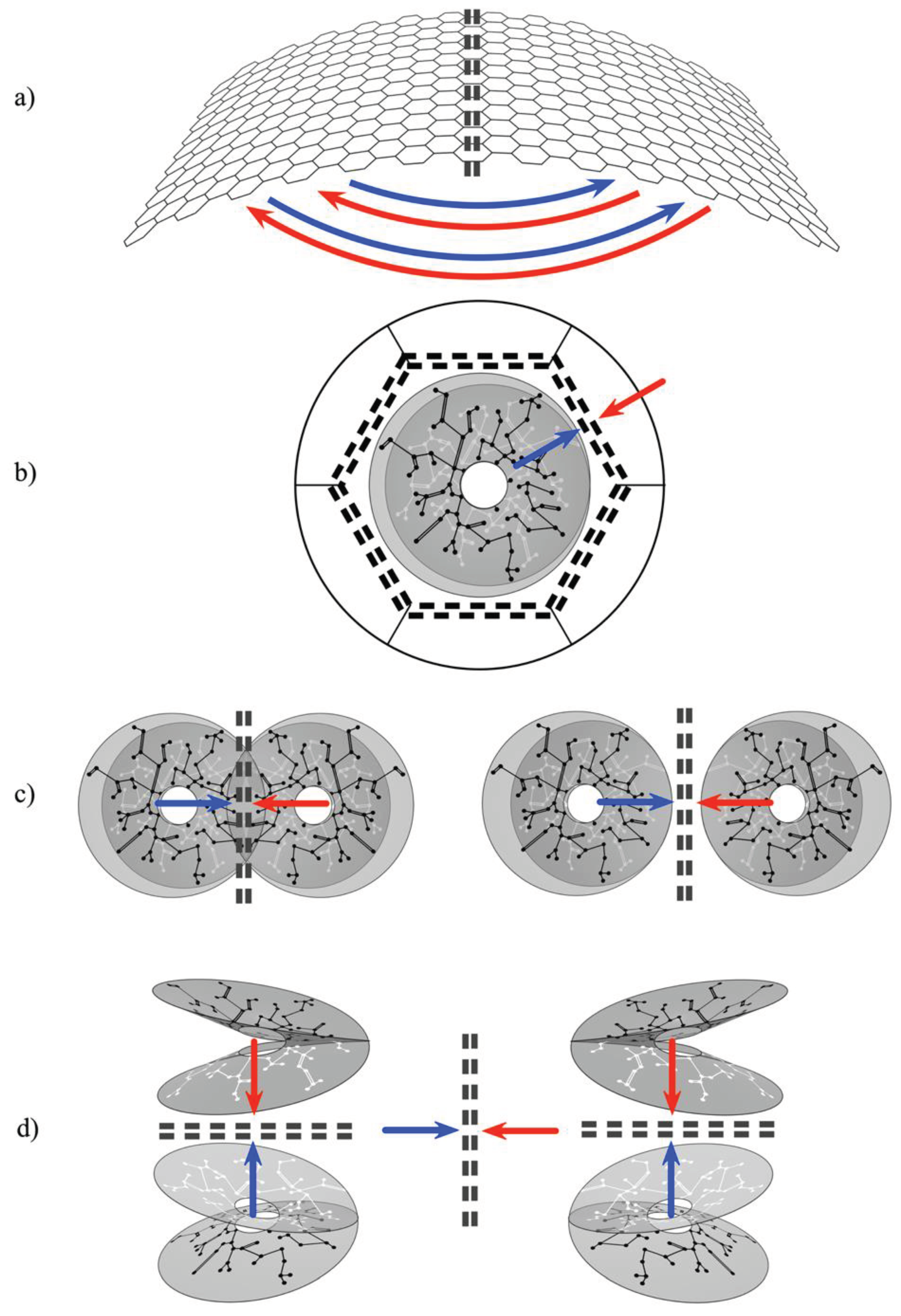
4.2. Early Embryonic Development
- (a).
- Cortico-cortical and Inter-areal connections. Their U-shaped form projects each cortical area to its neighbours with mirror symmetry.
- (b).
- Each local map interacts with the global map with (topological) mirror symmetry, as the local short-axon neurons exchange flux with the surrounding cortex via the patch cell system.
- (c).
- Local cell groups interact with adjacent groups of opposite chirality - whether the groups interpenetrate, abut, or are further separated.
- (d).
- Within every column mirror symmetry is generated between layers, while also able to interact laterally with other mirrored systems.
4.3. Later Embryonic and Early Antenatal Development
4.4. Spatiotemporal Images
4.5. Coupled Spatial Eigenmodes, Spatial and Temporal Frequency Preferences
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbas H. Pattern in the laminar origin of cortico-cortical connections J Comp Neurol 1986 252 415-422. [CrossRef]
- Barbas H, Rempel-Clower N. Cortical structure predicts the pattern of cortico-cortical connections. Cerebral Cortex 1997 7 635-646. [CrossRef]
- Barbas H General cortical and special prefrontal connections: principles from structure to function. Annual Rev Neuroscience 2015 38 269-289. [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cabezas MA, Zikopoulos B, Barbas H. The structural model: a theory linking connections, plasticity, pathology, development and evolution of the cerebral cortex. Brain Struct. Function 2019 224 985-1008. [CrossRef]
- Tucker DM, Luu, P. Adaptive control of functional connectivity: dorsal and ventral limbic divisions regulate the dorsal and ventral neocortical networks. Cerebral Cortex 2023 33 7870-7895. [CrossRef]
- Luu P, Tucker DM Continuity and change in neural plasticity through embryonic morphogenesis, fetal activity-dependent synaptogenesis and infant memory consolidation. Developmental Psychobiology 2023 65(8):e22439. [CrossRef]
- Markov NT et al. Weight consistency specifies regularities of macaque cortical networks. Cerebral Cortex 2011 21 1254-1272. [CrossRef]
- Vezoli J et al. Cortical hierarchy, dual counterstream architecture and the importance of top-down generative networks. Neuroimage 2021 225 117479. [CrossRef]
- Aparicio-Rodriguez G, Garcia-Cabezas MA Comparison of the predictive power of two models of cortico-cortical connections in primates: the distance rule model and the structural model. Cerebral Cortex 2023 33 8131-8149. [CrossRef]
- Campbell K Cortical neuron specification: it has its time and place. Neuron 2005 46 373-376. [CrossRef]
- Muir DR et al. Embedding of cortical representations by the superficial patch system. Cerebral Cortex 2011 21 2244-2260. [CrossRef]
- Muir DR, Douglas RJ From neural arbours to daisies. Cerebral Cortex 2011 21 1118-1133. [CrossRef]
- Martin KAC, Roth S, Rusch ES. Superficial layer pyramidal cells communicate heterogeneously between multiple functional domains of cat primary visual cortex Nature Communication 2014 55252. [CrossRef]
- Molnar Z. Cortical columns. In: In: Rubenstein JLR. and Rakic P. (ed.) Comprehensive Developmental Neuroscience: Neural Circuit Development and Function in the Brain, volume 3, pp. 109-129 Amsterdam: Elsevier. [CrossRef]
- Bosking WH, Zhang Y, Schofield B, Fitzpatrick D. Orientation selectivity and the arrangement of horizontal connections in tree shrew striate cortex. J Neurosci, 1997 17 2112-2127. [CrossRef]
- Rockland KS, Lund JS. Intrinsic laminar lattice connections in primate visual cortex. J Comp Neurol, 1983 216 303-318. [CrossRef]
- Issa NP, Trepel C, Stryker MP. (2000). Spatial frequency maps in cat visual cortex. J. Neurosci. 2000 20 8504–8514. [CrossRef]
- Girman SV, Sauve Y, Lund RD. Receptive field properties of single neurons in rat primary visual cortex J Neurophysiol. 1999 82 301-311. [CrossRef]
- Wiesel TN, Hubel DH. Ordered arrangement of orientation columns in monkeys lacking visual experience. J. Comput. Neurol. 1974 158 307–318. [CrossRef]
- Blakemore C, Van Sluyters RC. Reversal of the physiological effects of monocular deprivation in kittens: Further evidence for a sensitive period. J. Physiol. 1974 237, 195–216. [CrossRef]
- Obermayer K, Blasdel GG. Geometry of orientation and ocular dominance columns in monkey striate cortex. J. Neurosci. 1993 13 4114–4129. [CrossRef]
- Takahata T et al. Identification of ocular dominance domains in new world owl monkeys by immediate-early gene expression. PNAS 2014 111 4297-4302. [CrossRef]
- Horton JC, Adams DL The cortical column: a structure without a function. Philosophical Trans Royal Soc. 2005 360 837-862. [CrossRef]
- Friston K. (2002). Functional integration and inference in the brain. Prog. Neurobiol. 68, 113–143. [CrossRef]
- Friston K. A theory of cortical responses. Philos. Trans. R Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005 360, 815–836. [CrossRef]
- Friston K. The free energy principle: a unified brain theory? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010a 11, 127–138. [CrossRef]
- Friston K. Is the free-energy principle neurocentric? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010b 11, 605. [CrossRef]
- Friston K. Maps and territories, smoke and mirrors. Behav. Brain Sci. 2022 45, e195. [CrossRef]
- Friston K, Ao P. Free energy, value, and attractors. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2012, 937860. [CrossRef]
- Friston K, Levin M, Sengupta B, Pezzulo G. Knowing one’s place: a free-energy approach to pattern regulation. J. R. Soc. Interface. 2015 12, 1383. [CrossRef]
- Friston, K., Thornton, C., Clark, A. Free energy minimization and the dark room problem. Front. Psychol. 2012 3, 130. [CrossRef]
- Friston, K, Parr T, Yufik Y, Sajid N, Price CJ., Holmes E. Generative models, linguistic communication and active inference. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020 118, 42–64. [CrossRef]
- Buckley CL., Kim CS., McGregor S, Seth AK. The free energy principle for action and perception: a mathematical review. J. Math. Psychol. 2017 81, 55–79. [CrossRef]
- Constant A. The free energy principle: it’s not about what it takes, it’s about what took you there. Biol. Philos. 2021 36, 10. [CrossRef]
- Ramstead MJD. et al. (2022). On Bayesian Mechanics: A Physics of and by Beliefs. Interf. Focus. 2022 13, 20220029. [CrossRef]
- beim Graben P, Pinotsis D, Saddy D, Potthas R. Language processing by dynamic fields. Cognitive Neurodynamics 2008 2 79-88. [CrossRef]
- Kirchhoff M, Parr T, Palacious E, Friston K, Kiverstein J. The Markov blankets of life: autonomy, active inference and the free energy principle. Journal of the Royal Society Interface 2018. [CrossRef]
- Luu P, Tucker DM, Friston K. From active affordance to active inference: vertical integration of cognition in the cerebral cortex through dual subcortical control systems. Cerebral Cortex 2024 34 bhad458. [CrossRef]
- Bastos AM et al. Canonical microcircuits for predictive coding Neuron 2012 76 695-711. [CrossRef]
- Vergara RC et al. The energy homeostasis principle: neuronal energy regulation drives local network dynamics generating behavior. Front. Comp. Neurosci. 2019 10 49. [CrossRef]
- Perin R, Berger TK, Markram H. A synaptic organizing principle for cortical neuronal groups Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011 108 5419-5424. [CrossRef]
- Song S et al. Highly non-random features of synaptic connectivity in local cortical circuits PLoS Biol. 2005 3 e350. [CrossRef]
- 43. Izhikevich EM, Desai NS. Relating STDP to BCM. Neural. Comput. 2003 15, 1511–1523. [CrossRef]
- Keck T et al. Integrating Hebbian and homeostatic plasticity: the current state of the field and future research directions. Philosoph. Trans. Royal Society B. 2017 327 1715. [CrossRef]
- Chapman CL, Wright JJ, Bourke PD. Spatial eigenmodes and synchronous oscillation: coincidence detection in simulated cerebral cortex. J. Math. Biol. 2002 45 57-78. [CrossRef]
- Downes JH, et al. Emergence of a small-world functional network in cultured neurons. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012 8:e1002522. [CrossRef]
- Hollville E, Romero SE, Deshmukh M. Apoptotic cell death regulation in neurons. FEBS J. 2019 286 3276-3298. [CrossRef]
- Heck N, et al. Activity dependent regulation of neuronal apoptosis in neonatal mouse cerebral cortex. Cereb. Cortex 2008 18, 1335–1349. [CrossRef]
- Sang I, et al. (2021). Optogenetically controlled activity pattern determines survival rate of developing neocortical neurons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:6575. [CrossRef]
- Bassett DS, Bullmore, E. Small-world brain networks. Neuroscientist 2006 12 512-513. [CrossRef]
- Wright JJ, Bourke PD. Further work on the shaping of cortical development and function by synchrony and metabolic competition. Front. Comp. Neurosci. 2016 10. [CrossRef]
- Cohen R, Havlin S. Scale-free networks are ultra-small. Phys Rev Lett, 2003 90 058701. [CrossRef]
- Wright JJ, Bourke PD. On the dynamics of cortical development: synchrony and synaptic self-organization. Front. Comp. Neurosci. 2003 7. [CrossRef]
- Basole A, White LE, Fitzpatrick D. Mapping of multiple features in the population response of visual cortex. Nature 2003 423, 986–990. [CrossRef]
- Sereno MI et al. Borders of multiple visual areas in humans revealed in functional magnetic resonance imaging. Science 1995 12 889-893. [CrossRef]
- Konkle T. Emergent organization of multiple visuotopic maps without a feature hierarchy.2021. [CrossRef]
- 57. Espinosa JS, Stryker MP. Development and plasticity of the primary visual cortex. Neuron 2012 75, 230–249. [CrossRef]
- Sheth BR, Young R. Two visual pathways in primates based on sampling of space: exploitation and exploration of visual information. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2016 10. [CrossRef]
- Wright JJ, Bourke PD. Unification of free energy minimization, spatio-temporal energy, and dimension reduction models of V1 organization:postnatal learning on an antenatal scaffold. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2022 16. [CrossRef]
- Issa NP, Rosenberg A, Hussson TR. (2008). Models and measurements of functional maps in V1. J. Neurophysiol. 2008 99 2754–2754. [CrossRef]
- Issa NP, Trepel C, Stryker MP. Spatial frequency maps in cat visual cortex. J. Neurosci. 2000 20, 8504–8514. [CrossRef]
- Baker CL. Spatial- and temporal-frequency selectivity as a basis for velocity preference in cat striate cortex neurons. Vis. Neurosci. 1990 4 101–113. [CrossRef]
- Wright JJ, Bourke PD. The mesoanatomy of the cortex, minimization of free energy, and generative cognition. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2023 12. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




