Submitted:
26 February 2024
Posted:
27 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factors
2.1. Cag A and Vac A
2.2. H. pylori Outer Membrane Proteins
2.2.1. Hop B and Hop C
2.2.2. Hop H, a Phase-Variable Protein
2.2.3. Hop P
2.2.4. Hop Q
2.2.5. Hop S, Hop T and Hop U
2.2.6. Hop Z
2.2.7. Hop V, Hop W and Other OMPs
3. H. pylori Survival Strategies
3.1. Genetic Characteristics of H. pylori OMPs Contribute to Its Ability to Survive
3.2. H. pylori Biofilm, an Alternative Strategy for Survival
4. H. pylori and Host Responses
5. Advancements and Challenges in Therapeutic Strategies Targeting H. pylori
| Vaccine | Type | Status | Reference | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imevax/IMX101 | Multicomponent | I | [223] | Ongoing |
| VacA, CagA, NAP (NCT00736476) | Recombinant | I/II | [224] | 2018 |
| HpaA expression by Vibrio cholera | Recombinant | Preclinical | [225] | 2017 |
| Cholera toxin B and H. pylori Lpp20 | Epitope | Preclinical | [226] | 2016 |
| H. pylori vaccine | Oral recombinant | III | [227] | 2015 |
| CTB-UreI-UreB (BIB) | Recombinant multi-epitope | Preclinical | [228] | 2014 |
| HelicoVax | Multi-epitope | Preclinical | [229] | 2011 |
| OMP | Also known as | Receptor | PU | GC | GA | DU | MALT | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cag A | Cytotoxicity in associated gene | Epithelial cell | ✓ | ✓ | EPIYAD/C | - | ✓ | [54] |
| Cag L | ||||||||
| Vac A | Vacuolating cytotoxin | RPTP-α | VacAs1m1VacAs2m2 | VacAs1m1 | VacAs1m1 | - | - | [43,54] |
| RPTP-β | ||||||||
| Lipids | ||||||||
| Heparin sulphate | ||||||||
| Sphingomyelin | ||||||||
| Fibronectin | ||||||||
| Β2- integrin | ||||||||
| EGFR | ||||||||
| Hop B/C | Alp A/B | Laminin | - | - | - | - | - | [230,231] |
| Collagen IV | ||||||||
| Hop H | Oip A | Not known | ✓ | ✓ | - | ✓ | [54,87,90] | |
| Hop P | Sab A | sLex | - | - | - | - | ✓ | [58] |
| sLea | ||||||||
| Hop S | Bab A | sLeb | Bab A2 | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | [54] |
| A, B, O blood group | ||||||||
| Hop Q | - | CEACAMs | - | ✓ | - | - | - | [121] |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamaoka, Y.; Orito, E.; Mizokami, M.; Gutierrez, O.; Saitou, N.; Kodama, T.; Osato, M.S.; Kim, J.G.; Ramirez, F.C.; Mahachai, V.; et al. Helicobacter pylori in North and South America before Columbus. FEBS Lett. 2002, 517, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, G. Nobel prize is awarded to doctors who discovered H. pylori. BMJ 2005, 331, 795–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hocker, M.; Hohenberger, P. Helicobacter pylori virulence factors — one part of a big picture. Lancet 2003, 362, 1231–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, W.; Mohamed, S.O.; Ogbomo, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Quan, Z. Are Helicobacter pylori and other Helicobacter species infection associated with human biliary lithiasis? A meta-analysis. PloS ONE 2011, 6, e27390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonezawa, H.; Osaki, T.; Woo, T.; Kurata, S.; Zaman, C.; Hojo, F.; Hanawa, T.; Kato, S.; Kamiya, S. Analysis of outer membrane vesicle protein involved in biofilm formation of Helicobacter pylori. Anaerobe 2011, 17, 388–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravina, A.G.; Zagari, R.M.; De Musis, C.; Romano, L.; Loguercio, C.; Romano, M. Helicobacter pylori and extragastric diseases: A review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3204–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capurso, G.; Lahner, E.; Marcheggiano, A.; Caruana, P.; Carnuccio, A.; Bordi, C.; Delle Fave, G.; Annibale, B. Involvement of the corporal mucosa and related changes in gastric acid secretion characterize patients with iron deficiency anaemia associated with Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 15, 1753–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellicano, R.; Franceschi, F.; Saracco, G.; Fagoonee, S.; Roccarina, D.; Gasbarrini, A. Helicobacters and extragastric diseases. Helicobacter 2009, 14 Suppl 1, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, D.M.; Bernotas, A.; Nazi, I.; Stasi, R.; Kuwana, M.; Liu, Y.; Kelton, J.G.; Crowther, M.A. Platelet count response to H. pylori treatment in patients with immune thrombocytopenic purpura with and without H. pylori infection: a systematic review. Haematologica 2009, 94, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirouz, T.; Zounubi, L.; Keivani, H.; Rakhshani, N.; Hormazdi, M. Detection of Helicobacter pylori in paraffin-embedded specimens from patients with chronic liver diseases, using the amplification method. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2009, 54, 1456–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.; Wu, J.; Zhang, G. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2013, 99, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.W.; Kwon, H.T.; Kang, J.M.; Park, J.H.; Choi, H.C.; Park, M.S.; Park, S.M.; Son, K.Y.; Cho, B. Association between metabolic syndrome and Helicobacter pylori infection diagnosed by histologic status and serological status. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 46, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayvergiya, R.; Vadivelu, R. Role of Helicobacter pylori infection in pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. World J. Cardiol. 2015, 7, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osawa, H.; Kawakami, M.; Fujii, M.; Kubo, N.; Iwanaka, H.; Yamamoto, W.; Saitoh, M.; Yaginuma, T.; Sugano, K. Helicobacter pylori infection and coronary heart disease in Japanese patients. Cardiology 2001, 95, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.Z.; Chen, D. Helicobacter pylori and hepatocellular carcinoma: Correlated or uncorrelated? J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 21, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooi, J.K.Y.; Lai, W.Y.; Ng, W.K.; Suen, M.M.Y.; Underwood, F.E.; Tanyingoh, D.; Malfertheiner, P.; Graham, D.Y.; Wong, V.W.S.; Wu, J.C.Y.; et al. Global prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, B.E.; Cohen, H.; Blaser, M.J. Helicobacter pylori . Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1997, 10, 720–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.-L.; Chan, W.-K.; Shiota, S.; Yamaoka, Y. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection and public health implications. Helicobacter 2011, 16 Suppl 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, D.M.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Pisani, P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA: A Cancer J. Clin. 2005, 55, 74–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.-H.; Wang, H.; Chai, S.-G.; Liu, L.-M. Research progress on Helicobacter pylori outer membrane protein. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 3011–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, A.P. The role of lipopolysaccharide in Helicobacter pylori pathogenesis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1996, 10 Suppl 1, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H. Role of flagella in the pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori. Curr. Microbiol. 2017, 74, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, H.L. The role of Helicobacter pylori urease in the pathogenesis of gastritis and peptic ulceration. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1996, 10 Suppl 1, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentschel, E.; Brandstatter, G.; Dragosics, B.; Hirschl, A.M.; Nemec, H.; Schutze, K.; Taufer, M.; Wurzer, H. Effect of ranitidine and amoxicillin plus metronidazole on the eradication of Helicobacter pylori and the recurrence of duodenal ulcer. New Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibony, M.; Jones, N.L. Recent advances in Helicobacter pylori pathogenesis. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 28, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, Y. Roles of the plasticity regions of Helicobacter pylori in gastroduodenal pathogenesis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Lee, H.; Nakayama, J.; Fukuda, M. Roles of gastric mucin-type O-glycans in the pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection. Glycobiology 2009, 19, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuna, L.; Jakab, J.; Smolic, R.; Raguz-Lucic, N.; Vcev, A.; Smolic, M. Peptic ulcer disease: a brief review of conventional therapy and herbal treatment options. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauren, P. The two histological main types of gastric carcinona: diffuse and so-called intestinal type carcinoma: an attempt at a histo-clinical classification. Acta Pathol. Et Microbiol. Scand. 1965, 64, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forman, D.; Burley, V.J. Gastric cancer: global pattern of the disease and an overview of environmental risk factors. Best Pract. Research. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2006, 20, 633–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, D.M. The global health burden of infection-associated cancers in the year 2002. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 3030–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Shin, H.R.; Bray, F.; Forman, D.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2893–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papastergiou, V.; Georgopoulos, S.D.; Karatapanis, S. Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: meeting the challenge of antimicrobial resistance. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 9898–9911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, K.J.; Joyce, S.L.; Ismond, K.P. Extragastric diseases associated with Helicobacter pylori infection. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2006, 8, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guruge, J.L.; Falk, P.G.; Lorenz, R.G.; Dans, M.; Wirth, H.P.; Blaser, M.J.; Berg, D.E.; Gordon, J.I. Epithelial attachment alters the outcome of Helicobacter pylori infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3925–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomb, J.F.; White, O.; Kerlavage, A.R.; Clayton, R.A.; Sutton, G.G.; Fleischmann, R.D.; Ketchum, K.A.; Klenk, H.P.; Gill, S.; Dougherty, B.A.; et al. The complete genome sequence of the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature 1997, 388, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alm, R.A.; Bina, J.; Andrews, B.M.; Doig, P.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Trust, T.J. Comparative genomics of Helicobacter pylori: Analysis of the outer membrane protein families. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 4155–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covacci, A.; Censini, S.; Bugnoli, M.; Petracca, R.; Burroni, D.; Macchia, G.; Massone, A.; Papini, E.; Xiang, Z.; Figura, N. Molecular characterization of the 128-kDa immunodominant antigen of Helicobacter pylori associated with cytotoxicity and duodenal ulcer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 5791–5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cover, T.L.; Blanke, S.R. Helicobacter pylori VacA, a paradigm for toxin multifunctionality. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieder, G.; Fischer, W.; Haas, R. Interaction of Helicobacter pylori with host cells: function of secreted and translocated molecules. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2005, 8, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leunk, R.D.; Johnson, P.T.; David, B.C.; Kraft, W.G.; Morgan, D.R. Cytotoxic activity in broth-culture filtrates of Campylobacter pylori. J. Med. Microbiol. 1988, 26, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bernard, M.; Papini, E.; de Filippis, V.; Gottardi, E.; Telford, J.; Manetti, R.; Fontana, A.; Rappuoli, R.; Montecucco, C. Low pH activates the vacuolating toxin of Helicobacter pylori, which becomes acid and pepsin resistant. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 23937–23940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backert, S.; Tegtmeyer, N. the versatility of the Helicobacter pylori vacuolating cytotoxin vacA in signal transduction and molecular crosstalk. Toxins 2010, 2, 69–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Censini, S.; Lange, C.; Xiang, Z.; Crabtree, J.E.; Ghiara, P.; Borodovsky, M.; Rappuoli, R.; Covacci, A. cag, a pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori, encodes type I-specific and disease-associated virulence factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 14648–14653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atherton, J.C.; Cao, P.; Peek, R.M., Jr.; Tummuru, M.K.; Blaser, M.J.; Cover, T.L. Mosaicism in vacuolating cytotoxin alleles of Helicobacter pylori. Association of specific vacA types with cytotoxin production and peptic ulceration. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 17771–17777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyfoo, D.M.; Doomah, Y.H.; Xu, D.; Zhang, C.; Sang, H.-M.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Zhang, G.-X.; Jiang, J.-X.; Xu, S.-F. New genotypes of Helicobacter pylori VacA d-region identified from global strains. BMC Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 4–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
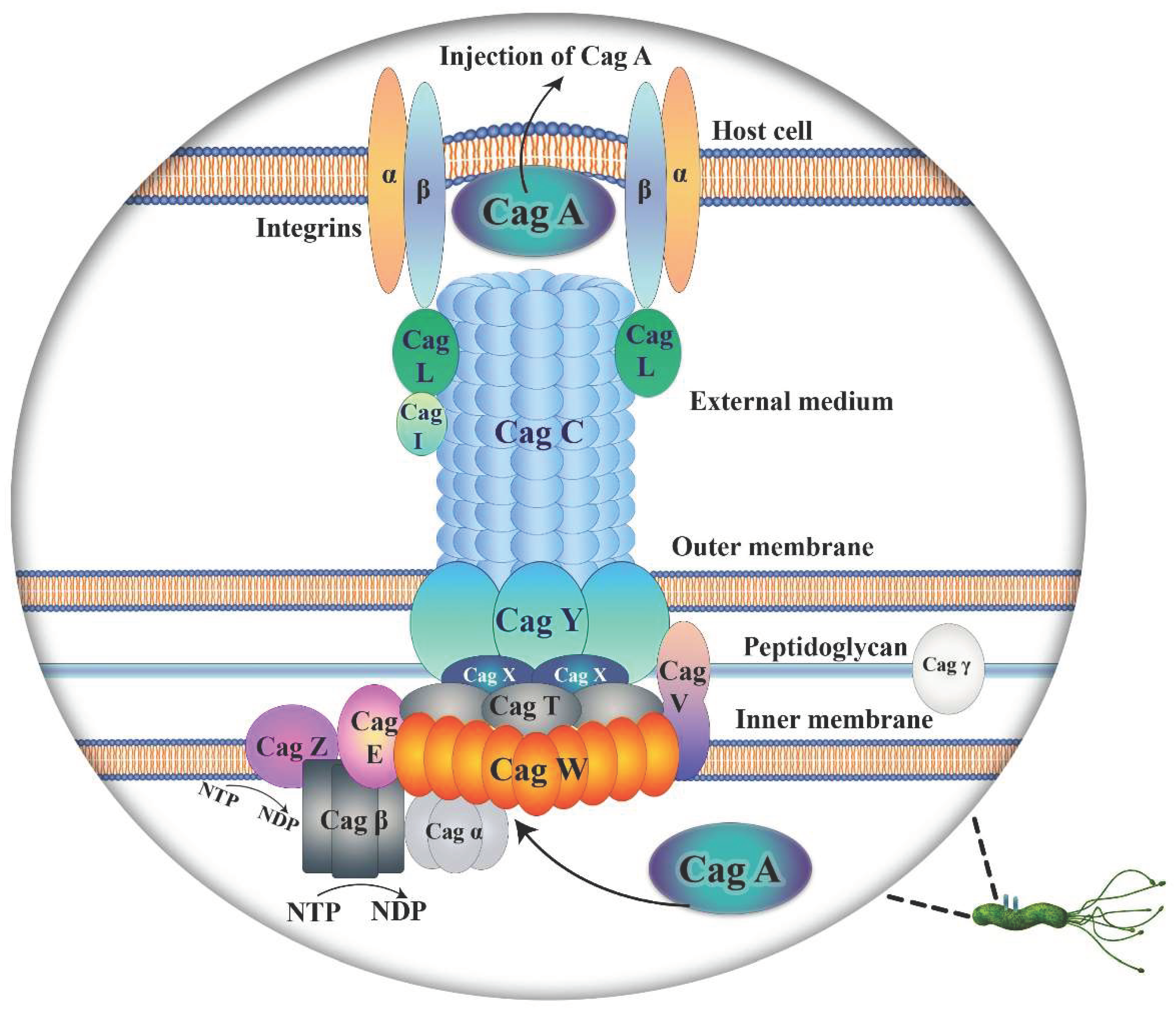
- Backert, S.; Selbach, M. Role of type IV secretion in Helicobacter pylori. Cell. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backert, S.; Meyer, T.F. Type IV secretion systems and their effectors in bacterial pathogenesis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waksman, G. From conjugation to T4S systems in Gram-negative bacteria: a mechanistic biology perspective. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grohmann, E.; Christie, P.J.; Waksman, G.; Backert, S. Type IV secretion in Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 2018, 107, 455–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi-Kanemitsu, A.; Knight, C.T.; Hatakeyama, M. Molecular anatomy and pathogenic actions of Helicobacter pylori CagA that underpin gastric carcinogenesis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimuro, H.; Suzuki, T.; Tanaka, J.; Asahi, M.; Haas, R.; Sasakawa, C. Grb2 is a key mediator of Helicobacter pylori CagA protein activities. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick-Cheng, A.E.; Pyburn, T.M.; Voss, B.J.; McDonald, W.H.; Ohi, M.D.; Cover, T.L. Molecular and structural analysis of the Helicobacter pylori cag type IV secretionsystem core complex. mBio 2016, 7, e02001–e02015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.L.; Yeh, Y.C.; Sheu, B.S. The impacts of H. pylori virulence factors on the development of gastroduodenal diseases. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Censini, S.; Bayeli, P.F.; Telford, J.L.; Figura, N.; Rappuoli, R.; Covacci, A. Analysis of expression of CagA and VacA virulence factors in 43 strains of Helicobacter pylori reveals that clinical isolates can be divided into two major types and that CagA is not necessary for expression of the vacuolating cytotoxin. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odenbreit, S.; Puls, J.; Sedlmaier, B.; Gerland, E.; Fischer, W.; Haas, R. Translocation of Helicobacter pylori CagA into gastric epithelial cells by type IV secretion. Science 2000, 287, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikenoue, T.; Maeda, S.; Ogura, K.; Akanuma, M.; Mitsuno, Y.; Imai, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Shiratori, Y.; Omata, M. Determination of Helicobacter pylori virulence by simple gene analysis of the cag pathogenicity island. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2001, 8, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehours, P.; Menard, A.; Dupouy, S.; Bergey, B.; Richy, F.; Zerbib, F.; Ruskone-Fourmestraux, A.; Delchier, J.C.; Megraud, F. Evaluation of the association of nine Helicobacter pylori virulence factors with strains involved in low-grade gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, Y.; Kodama, T.; Gutierrez, O.; Kim, J.G.; Kashima, K.; Graham, D.Y. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori iceA, cagA, and vacA status and clinical outcome: studies in four different countries. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 2274–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, W.; Hu, J.-L.; Xiao, B.; Wu, K.-C.; Peng, D.-R.; Atherton, J.C.; Xue, H. cagA and vacA genotype of Helicobacter pylori associated with gastric diseases in Xi'an area. World J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 9, 1762–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsonnet, J.; Friedman, G.; Orentreich, N.; Vogelman, H. Risk for gastric cancer in people with CagA positive or CagA negative Helicobacter pylori infection. Gut 1997, 40, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Taleb, A.M.F.; Abdelattef, R.S.; Abdel-Hady, A.A.; Omran, F.H.; El-Korashi, L.A.; Abdel-Aziz El-Hady, H.; El-Gebaly, A.M. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori cagA and iceA genes and their association with gastrointestinal diseases. Int. J. Microbiol. 2018, 2018, 4809093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamogawa-Schifter, Y.; Yamaoka, Y.; Uchida, T.; Beer, A.; Tribl, B.; Schöniger-Hekele, M.; Trauner, M.; Dolak, W. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori and its CagA subtypes in gastric cancer and duodenal ulcer at an Austrian tertiary referral center over 25 years. PloS One 2018, 13, e0197695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erzin, Y.; Koksal, V.; Altun, S.; Dobrucali, A.; Aslan, M.; Erdamar, S.; Dirican, A.; Kocazeybek, B. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori vacA, cagA, cagE, iceA, babA2 genotypes and correlation with clinical outcome in Turkish patients with dyspepsia. Helicobacter 2006, 11, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, Y.H.; Kim, P.S.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Shin, Y.W.; Hwang, T.S.; Kim, H.J.; Song, S.U.; Choi, M.S. Diverse vacA allelic types of Helicobacter pylori in Korea and clinical correlation. Yonsei Med. J. 2002, 43, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, F.; Kaklikkaya, N.; Ozgur, O.; Cubukcu, K.; Kilic, A.O.; Tosun, I.; Erturk, M. Distribution of vacA alleles and cagA status of Helicobacter pylori in peptic ulcer disease and non-ulcer dyspepsia. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2004, 10, 1102–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Ha, J.H.; Shin, J.I.; Kim, K.M.; Choi, J.G.; Park, S.; Park, J.S.; Seo, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Shin, M.K.; et al. Increased risk of severe gastric symptoms by virulence factors vacAs1c, alpA, babA2, and hopZ in Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikaido, H.; Vaara, M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol. Rev. 1985, 49, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, B.; Ortkamp, M.; Diehl, K.D.; Hundt, E.; Knapp, B. Conservation, localization and expression of HopZ, a protein involved in adhesion of Helicobacter pylori. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 3325–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsor, D.A.; Sundberg, E.J. Roles of adhesion to epithelial cells in gastric colonization by Helicobacter pylori. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1149, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindén, S.K.; Wickström, C.; Lindell, G.; Gilshenan, K.; Carlstedt, I. Four modes of adhesion are used during Helicobacter pylori binding to human mucins in the oral and gastric niches. Helicobacter 2008, 13, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheu, B.S.; Yang, H.B.; Yeh, Y.C.; Wu, J.J. Helicobacter pylori colonization of the human gastric epithelium: a bug's first step is a novel target for us. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 25, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, C.A.; David, L.; Nielsen, P.A.; Clausen, H.; Mirgorodskaya, K.; Roepstorff, P.; Sobrinho-Simões, M. Immunohistochemical study of MUC5AC expression in human gastric carcinomas using a novel monoclonal antibody. Int. J. Cancer 1997, 74, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, C.A.; David, L.; Carvalho, F.; Mandel, U.; de Bolós, C.; Mirgorodskaya, E.; Clausen, H.; Sobrinho-Simões, M. Immunohistochemical study of the expression of MUC6 mucin and co-expression of other secreted mucins (MUC5AC and MUC2) in human gastric carcinomas. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2000, 48, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bolos, C.; Real, F.X.; Lopez-Ferrer, A. Regulation of mucin and glycoconjugate expression: from normal epithelium to gastric tumors. Front. Biosci. 2001, 6, D1256–D1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odenbreit, S.; Faller, G.; Haas, R. Role of the alpAB proteins and lipopolysaccharide in adhesion of Helicobacter pylori to human gastric tissue. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. : IJMM 2002, 292, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odenbreit, S.; Till, M.; Haas, R. Optimized BlaM-transposon shuttle mutagenesis of Helicobacter pylori allows the identification of novel genetic loci involved in bacterial virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 1996, 20, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loke, M.F.; Lui, S.Y.; Ng, B.L.; Gong, M.; Ho, B. Antiadhesive property of microalgal polysaccharide extract on the binding of Helicobacter pylori to gastric mucin. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 50, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odenbreit, S.; Swoboda, K.; Barwig, I.; Ruhl, S.; Borén, T.; Koletzko, S.; Haas, R. Outer membrane protein expression profile in Helicobacter pylori clinical isolates. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 3782–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wu, J.Y.; Beswick, E.J.; Ohno, T.; Odenbreit, S.; Haas, R.; Reyes, V.E.; Kita, M.; Graham, D.Y.; Yamaoka, Y. Functional and intracellular signaling differences associated with the Helicobacter pylori AlpAB adhesin from Western and East Asian strains. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 6242–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jonge, R.; Durrani, Z.; Rijpkema, S.G.; Kuipers, E.J.; van Vliet, A.H.; Kusters, J.G. Role of the Helicobacter pylori outer-membrane proteins AlpA and AlpB in colonization of the guinea pig stomach. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonezawa, H.; Osaki, T.; Fukutomi, T.; Hanawa, T.; Kurata, S.; Zaman, C.; Hojo, F.; Kamiya, S. Diversification of the AlpB outer membrane protein of Helicobacter pylori affects biofilm formation and cellular adhesion. J. Bacteriol. 2017, 199, e00729–e00716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymournejad, O.; Mobarez, A.M.; Hassan, Z.M.; Talebi Bezmin Abadi, A. Binding of the Helicobacter pylori OipA causes apoptosis of host cells via modulation of Bax/Bcl-2 levels. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzi, N.; Yadegar, A.; Aghdaei, H.A.; Yamaoka, Y.; Zali, M.R. Genetic diversity and functional analysis of oipA gene in association with other virulence factors among Helicobacter pylori isolates from Iranian patients with different gastric diseases. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 60, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horridge, D.N.; Begley, A.A.; Kim, J.; Aravindan, N.; Fan, K.; Forsyth, M.H. Outer inflammatory protein a (OipA) of Helicobacter pylori is regulated by host cell contact and mediates CagA translocation and interleukin-8 response only in the presence of a functional cag pathogenicity island type IV secretion system. Pathog. Dis. 2017, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, Y.; Kwon, D.H.; Graham, D.Y. A M(r) 34,000 proinflammatory outer membrane protein (oipA) of Helicobacter pylori. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 7533–7538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, Y.; Kikuchi, S.; el-Zimaity, H.M.; Gutierrez, O.; Osato, M.S.; Graham, D.Y. Importance of Helicobacter pylori oipA in clinical presentation, gastric inflammation, and mucosal interleukin 8 production. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, T.; Peek, R.M.; Pride, D.; Levine, S.M.; Takata, T.; Lee, Y.C.; Kusugami, K.; van der Ende, A.; Kuipers, E.J.; Kusters, J.G.; et al. Polymorphisms of Helicobacter pylori HP0638 reflect geographic origin and correlate with cagA status. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peek, R.M., Jr.; Blaser, M.J. Helicobacter pylori and gastrointestinal tract adenocarcinomas. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhard, M.; Lehn, N.; Neumayer, N.; Boren, T.; Rad, R.; Schepp, W.; Miehlke, S.; Classen, M.; Prinz, C. Clinical relevance of the Helicobacter pylori gene for blood-group antigen-binding adhesin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 12778–12783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiroga, A.J.; Cittelly, D.M.; Bravo, M.M. BabA2, oipA and cagE Helicobacter pylori genotypes in Colombian patients with gastroduodenal diseases. Biomedica 2005, 25, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartpho, T.S.; Wattanawongdon, W.; Tongtawee, T.; Paoin, C.; Kangwantas, K.; Dechsukhum, C. Precancerous gastric lesions with Helicobacter pylori acA+/babA2+/oipA+genotype increase the risk of gastric cancer. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 7243029–7243029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabiri, H.; Jafari, F.; Baghaei, K.; Shokrzadeh, L.; Abdi, S.; Pourhoseingholi, M.A.; Mohammadzadeh, A. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori vacA, cagA, cagE, oipA, iceA, babA2 and babB genotypes in Iranian dyspeptic patients. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 105, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossumbekova, A.; Prinz, C.; Mages, J.; Lang, R.; Kusters, J.G.; Van Vliet, A.H.; Reindl, W.; Backert, S.; Saur, D.; Schmid, R.M.; et al. Helicobacter pylori HopH (OipA) and bacterial pathogenicity: genetic and functional genomic analysis of hopH gene polymorphisms. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 194, 1346–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, B.A.; Abasiyanik, M.F.; Ahmed, N. A preliminary study on the genetic profile of cag pathogenicity-island and other virulent gene loci of Helicobacter pylori strains from Turkey. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2007, 7, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspinall, G.O.; Monteiro, M.A.; Pang, H.; Walsh, E.J.; Moran, A.P. Lipopolysaccharide of the Helicobacter pylori type strain NCTC 11637 (ATCC 43504): structure of the O antigen chain and core oligosaccharide regions. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 2489–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherburne, R.; Taylor, D.E. Helicobacter pylori expresses a complex surface carbohydrate, Lewis X. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 4564–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdavi, J.; Sonden, B.; Hurtig, M.; Olfat, F.O.; Forsberg, L.; Roche, N.; Angstrom, J.; Larsson, T.; Teneberg, S.; Karlsson, K.A.; et al. Helicobacter pylori SabA adhesin in persistent infection and chronic inflammation. Science 2002, 297, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alper, J. Searching for medicine's sweet spot. Science 2001, 291, 2338–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid, J.F.; Ballesta, J.; Castells, M.T.; Hernández, F. Glycoconjugate distribution in the human fundic mucosa revealed by lectin- and glycoprotein-gold cytochemistry. Histochemistry 1990, 95, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walz, A.; Odenbreit, S.; Mahdavi, J.; Boren, T.; Ruhl, S. Identification and characterization of binding properties of Helicobacter pylori by glycoconjugate arrays. Glycobiology 2005, 15, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, N.; Angstrom, J.; Hurtig, M.; Larsson, T.; Boren, T.; Teneberg, S. Helicobacter pylori and complex gangliosides. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, S.; Konradt, M.; Groll, C.; Scheid, P.; Hanauer, G.; Werling, H.-O.; Josenhans, C.; Suerbaum, S. The spatial orientation of Helicobacter pylori in the gastric mucus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5024–5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspholm, M.; Olfat, F.O.; Norden, J.; Sonden, B.; Lundberg, C.; Sjostrom, R.; Altraja, S.; Odenbreit, S.; Haas, R.; Wadstrom, T.; et al. SabA is the H. pylori hemagglutinin and is polymorphic in binding to sialylated glycans. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorkholm, B.; Salama, N.R. Genomics of Helicobacter 2003. Helicobacter 2003, 8 Suppl 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, N.J.; Peden, J.F.; Hood, D.W.; Moxon, E.R. Simple sequence repeats in the Helicobacter pylori genome. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 27, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talarico, S.; Whitefield, S.E.; Fero, J.; Haas, R.; Salama, N.R. Regulation of Helicobacter pylori adherence by gene conversion. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 84, 1050–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sáenz, J.B.; Vargas, N.; Mills, J.C. Tropism for spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia allows Helicobacter pylori to expand its intragastric niche. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusters, J.G.; van Vliet, A.H.M.; Kuipers, E.J. Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 449–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, Y. Increasing evidence of the role of Helicobacter pylori SabA in the pathogenesis of gastroduodenal disease. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2008, 2, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, Y.; Ojo, O.; Fujimoto, S.; Odenbreit, S.; Haas, R.; Gutierrez, O.; El-Zimaity, H.M.; Reddy, R.; Arnqvist, A.; Graham, D.Y. Helicobacter pylori outer membrane proteins and gastroduodenal disease. Gut 2006, 55, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, B.S.; Odenbreit, S.; Hung, K.H.; Liu, C.P.; Sheu, S.M.; Yang, H.B.; Wu, J.J. Interaction between host gastric Sialyl-Lewis X and H. pylori SabA enhances H. pylori Density Patients Lacking Gastric Lewis B Antigen. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonge, R.; Pot, R.; Loffeld, R.; van Vliet, A.; Kuipers, E.; Kusters, J. The functional status of the Helicobacter pylori sabB adhesin gene as a putative marker for disease outcome. Helicobacter 2004, 9, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein, G.; Hanieh, R.; Mitra, R.; Afsoon, T. Determination of the status of Helicobacter pylori sabA gene in relation to clinical findings. J. Med. Bacteriol. 2012, 1, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, J.; Orcini, W.; Peruquetti, R.; Cardoso Smith, M.; Payão, S.; Rasmussen, L. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori cag A and sab A genotypes in patients with gastric disease. Adv. Microbiol. 2019, 09, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alm, R.A.; Ling, L.S.; Moir, D.T.; King, B.L.; Brown, E.D.; Doig, P.C.; Smith, D.R.; Noonan, B.; Guild, B.C.; deJonge, B.L.; et al. Genomic-sequence comparison of two unrelated isolates of the human gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature 1999, 397, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, P.; Lee, K.J.; Blaser, M.J.; Cover, T.L. Analysis of hopQ alleles in East Asian and Western strains of Helicobacter pylori. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 251, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Cover, T.L. Two different families of hopQ alleles in Helicobacter pylori. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 4504–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicinschi, L.A.; Correa, P.; Bravo, L.E.; Peek, R.M., Jr.; Wilson, K.T.; Loh, J.T.; Yepez, M.C.; Gold, B.D.; Thompson, D.T.; Cover, T.L.; et al. Non-invasive genotyping of Helicobacter pylori cagA, vacA, and hopQ from asymptomatic children. Helicobacter 2012, 17, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gur, C.; Maalouf, N.; Gerhard, M.; Singer, B.B.; Emgård, J.; Temper, V.; Neuman, T.; Mandelboim, O.; Bachrach, G. The Helicobacter pylori HopQ outer membrane protein inhibits immune cell activities. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1553487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Königer, V.; Holsten, L.; Harrison, U.; Busch, B.; Loell, E.; Zhao, Q.; Bonsor, D.A.; Roth, A.; Kengmo-Tchoupa, A.; Smith, S.I.; et al. Helicobacter pylori exploits human CEACAMs via HopQ for adherence and translocation of CagA. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 2, 16188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuespert, K.; Pils, S.; Hauck, C.R. CEACAMs: their role in physiology and pathophysiology. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2006, 18, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javaheri, A.; Kruse, T.; Moonens, K.; Mejías-Luque, R.; Debraekeleer, A.; Asche, C.I.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Kalali, B.; Bach, N.C.; Sieber, S.A.; et al. Helicobacter pylori adhesin HopQ engages in a virulence-enhancing interaction with human CEACAMs. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 2, 16189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, J.T.; Torres, V.J.; Algood, H.M.; McClain, M.S.; Cover, T.L. Helicobacter pylori HopQ outer membrane protein attenuates bacterial adherence to gastric epithelial cells. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 289, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, R.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Jia, Q. Pathogenic interactions between Helicobacter pylori adhesion protein HopQ and human cell surface adhesion molecules CEACAMs in gastric epithelial cells. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2019, 22, 710–715. [Google Scholar]
- Hamway, Y.; Taxauer, K.; Moonens, K.; Neumeyer, V.; Fischer, W.; Schmitt, V.; Singer, B.B.; Remaut, H.; Gerhard, M.; Mejías-Luque, R. Cysteine residues in Helicobacter pylori adhesin HopQ are required for CEACAM-HopQ interaction and subsequent CagA translocation. Microorganisms 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, I.K.; Busch, B.; Ishikawa-Ankerhold, H.; Palamides, P.; Shively, J.E.; Stanners, C.; Chan, C.; Leung, N.; Gray-Owen, S.; Haas, R. The HopQ-CEACAM interaction controls CagA translocation, phosphorylation, and phagocytosis of Helicobacter pylori in neutrophils. mBio 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi Bezmin Abadi, A.; Mohabbati Mobarez, A. High prevalence of Helicobacter pylori hopQ II genotype isolated from Iranian patients with gastroduodenal disorders. J. Pathog. 2014, 2014, 842469–842469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakoob, J.; Abbas, Z.; Khan, R.; Salim, S.A.; Awan, S.; Abrar, A.; Jafri, W. Helicobacter pylori outer membrane protein Q allele distribution is associated with distinct pathologies in Pakistan. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 37, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, T.; Sugimoto, M.; Nagashima, A.; Ogiwara, H.; Vilaichone, R.K.; Mahachai, V.; Graham, D.Y.; Yamaoka, Y. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori hopQ genotype and clinical outcome in Asian and Western populations. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 24, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dara, M.; Khashei, R.; Dehghani, B. High frequency of hopQ genotypes among Iranian Helicobacter pylori clinical isolates. Le Infez. Med. 2017, 25, 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Sedarat, Z.; Khashei, R.; Shirzad, H.; Bagheri, N.; Sadeghiani, M.; Shahi, H.; Zamanzad, B. Frequency of Helicobacter pylori hopQI, hopQII and sabA genes among Iranian patients with gastroduodenal diseases. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2018, 11, e56017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Yoon, S.J.; Choi, S.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, S.H.; Min, J.K.; Son, M.Y.; Ryu, C.M.; et al. Bacterial type III effector protein HopQ inhibits melanoma motility through autophagic degradation of vimentin. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilver, D.; Arnqvist, A.; Ogren, J.; Frick, I.M.; Kersulyte, D.; Incecik, E.T.; Berg, D.E.; Covacci, A.; Engstrand, L.; Boren, T. Helicobacter pylori adhesin binding fucosylated histo-blood group antigens revealed by retagging. Science 1998, 279, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, S.; Olaniyi Ojo, O.; Arnqvist, A.; Wu, J.Y.; Odenbreit, S.; Haas, R.; Graham, D.Y.; Yamaoka, Y. Helicobacter pylori BabA expression, gastric mucosal injury, and clinical outcome. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 5, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pride, D.T.; Meinersmann, R.J.; Blaser, M.J. Allelic Variation within Helicobacter pylori babA and babB. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 1160–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, C.; Barone, A.; Boren, T.; Teneberg, S. Helicobacter pylori-binding nonacid glycosphingolipids in the human stomach. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 17248–17266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boren, T.; Falk, P.; Roth, K.A.; Larson, G.; Normark, S. Attachment of Helicobacter pylori to human gastric epithelium mediated by blood group antigens. Science 1993, 262, 1892–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspholm-Hurtig, M.; Dailide, G.; Lahmann, M.; Kalia, A.; Ilver, D.; Roche, N.; Vikstrom, S.; Sjostrom, R.; Linden, S.; Backstrom, A.; et al. Functional adaptation of BabA, the H. pylori ABO blood group antigen binding adhesin. Science 2004, 305, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugaytsova, J.A.; Björnham, O.; Chernov, Y.A.; Gideonsson, P.; Henriksson, S.; Mendez, M.; Sjöström, R.; Mahdavi, J.; Shevtsova, A.; Ilver, D.; et al. Helicobacter pylori adapts to chronic infection and gastric disease via pH-responsive BabA-mediated adherence. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 21, 376–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.M.; Gideonsson, P.; Canfield, D.R.; Borén, T.; Solnick, J.V. Dynamic expression of the BabA adhesin and its BabB paralog during Helicobacter pylori infection in rhesus macaques. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e00094–00017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheu, S.M.; Sheu, B.S.; Chiang, W.C.; Kao, C.Y.; Wu, H.M.; Yang, H.B.; Wu, J.J. H. H. pylori clinical isolates have diverse babAB genotype distributions over different topographic sites of stomach with correlation to clinical disease outcomes. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colbeck, J.C.; Hansen, L.M.; Fong, J.M.; Solnick, J.V. Genotypic profile of the outer membrane proteins BabA and BabB in clinical isolates of Helicobacter pylori. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 4375–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solnick, J.V.; Hansen, L.M.; Salama, N.R.; Boonjakuakul, J.K.; Syvanen, M. Modification of Helicobacter pylori outer membrane protein expression during experimental infection of rhesus macaques. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2106–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Yamaoka, Y. Helicobacter pylori BabA in adaptation for gastric colonization. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 4158–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishijima, N.; Suzuki, M.; Ashida, H.; Ichikawa, Y.; Kanegae, Y.; Saito, I.; Borén, T.; Haas, R.; Sasakawa, C.; Mimuro, H. BabA-mediated adherence is a potentiator of the Helicobacter pylori type IV secretion system activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 25256–25264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kable, M.E.; Hansen, L.M.; Styer, C.M.; Deck, S.L.; Rakhimova, O.; Shevtsova, A.; Eaton, K.A.; Martin, M.E.; Gideonsson, P.; Borén, T.; et al. Host determinants of expression of the Helicobacter pylori BabA adhesin. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asl, S.F.; Pourvahedi, M.; Mojtahedi, A.; Shenagari, M. Analysis of babA, cagE and cagA genes in Helicobacter pylori from upper gastric patients in the north of Iran. Infect. Disordorders Drug Targets 2019, 19, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, S.; Schmidt, A.; Eybpoosh, S.; Esmaili, M.; Talebkhan, Y.; Mohajerani, N.; Oghalaie, A.; Eshagh Hosseini, M.; Mohagheghi, M.A.; Bugaytova, J.; et al. Helicobacter pylori strains from duodenal ulcer patients exhibit mixed babA/B genotypes with low levels of BabA adhesin and Lewis b binding. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 2868–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoreson, A.C.; Hamlet, A.; Celik, J.; Bystrom, M.; Nystrom, S.; Olbe, L.; Svennerholm, A.M. Differences in surface-exposed antigen expression between Helicobacter pylori strains isolated from duodenal ulcer patients and from asymptomatic subjects. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 3436–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Chen, Y.; Jin, J.-F.; Zhang, Z.-S.; Zhou, D.-Y. Cloning and expression and immunogenicity of Helicobacter pylori BabA2 gene. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 2560–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Leung, W.K.; Go, M.Y.Y.; Chan, M.C.W.; To, K.F.; Ng, E.K.W.; Chan, F.K.L.; Ling, T.K.W.; Chung, S.C.S.; Sung, J.J.Y. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori babA2 status with gastric epithelial cell turnover and premalignant gastric lesions. Gut 2002, 51, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomvarin, C.; Namwat, W.; Chaicumpar, K.; Mairiang, P.; Sangchan, A.; Sripa, B.; Tor-Udom, S.; Vilaichone, R.K. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori vacA, cagA, cagE, iceA and babA2 genotypes in Thai dyspeptic patients. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 12, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, A.G.; Santos, A.; Guerra, J.B.; Rocha, G.A.; Rocha, A.M.C.; Oliveira, C.A.; Cabral, M.M.D.A.; Nogueira, A.M.M.F.; Queiroz, D.M.M. babA2- and cagA-positive Helicobacter pylori strains are associated with duodenal ulcer and gastric carcinoma in Brazil. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 3964–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kpoghomou, M.-A.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Jin, G. Association of Helicobacter pylori babA2 gene and gastric cancer risk: a meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 465–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennemann, L.; Brenneke, B.; Andres, S.; Engstrand, L.; Meyer, T.F.; Aebischer, T.; Josenhans, C.; Suerbaum, S. In vivo sequence variation in HopZ, a phase-variable outer membrane protein of Helicobacter pylori. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 4364–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennemann, L.; Didelot, X.; Aebischer, T.; Kuhn, S.; Drescher, B.; Droege, M.; Reinhardt, R.; Correa, P.; Meyer, T.F.; Josenhans, C.; et al. Helicobacter pylori genome evolution during human infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5033–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannakis, M.; Backhed, H.K.; Chen, S.L.; Faith, J.J.; Wu, M.; Guruge, J.L.; Engstrand, L.; Gordon, J.I. Response of gastric epithelial progenitors to Helicobacter pylori isolates obtained from Swedish patients with chronic atrophic gastritis. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 30383–30394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lienlaf, M.; Morales, J.P.; Díaz, M.I.; Díaz, R.; Bruce, E.; Siegel, F.; León, G.; Harris, P.R.; Venegas, A. Helicobacter pylori HopE and HopV porins present scarce expression among clinical isolates. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bina, J.; Bains, M.; Hancock, R.E. Functional expression in Escherichia coli and membrane topology of porin HopE, a member of a large family of conserved proteins in Helicobacter pylori. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 2370–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, B.; Ortkamp, M.; Nau, U.; Niederweis, M.; Hundt, E.; Knapp, B. Characterization of four members of a multigene family encoding outer membrane proteins of Helicobacter pylori and their potential for vaccination. Microbes Infect. 2001, 3, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Y.; Lu, X.; Han, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Shao, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Tang, W.; Sun, Y.; et al. Helicobacter pylori outer membrane protein 18 (Hp1125) is involved in persistent colonization by evading interferon-gamma signaling. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 571280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamrakar, A.; Singh, R.; Kumar, A.; Makde, R.D.; Ashish; Kodgire, P. Biophysical characterization of the homodimers of HomA and HomB, outer membrane proteins of Helicobacter pylori. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24471–24471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oleastro, M.; Cordeiro, R.; Ferrand, J.; Nunes, B.; Lehours, P.; Carvalho-Oliveira, I.; Mendes, A.I.; Penque, D.; Monteiro, L.; Mégraud, F.; et al. Evaluation of the clinical significance of homB, a novel candidate marker of Helicobacter pylori strains associated with peptic ulcer disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 198, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleastro, M.; Cordeiro, R.; Ménard, A.; Yamaoka, Y.; Queiroz, D.; Mégraud, F.; Monteiro, L. Allelic diversity and phylogeny of homB, a novel co-virulence marker of Helicobacter pylori. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 248–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Mirko, R.; Sara, L.; Medea, P.; Caroline, B.; Eva, B.; Myrthe, J.; Bram, F.; Wim, V.D.; Richard, D.; et al. The Helicobacter heilmannii hofE and hofF genes are essential for colonization of the gastric mucosa and play a role in IL-1beta-induced gastric MUC13 expression. Helicobacter 2016, 21, 504–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suerbaum, S.; Smith, J.M.; Bapumia, K.; Morelli, G.; Smith, N.H.; Kunstmann, E.; Dyrek, I.; Achtman, M. Free recombination within Helicobacter pylori. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 12619–12624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallström, A.; Lundberg, C.; Kersulyte, D.; Berg, D.; Borén, T.; Arnqvist, A. Metastability of Helicobacter pylori bab adhesin genes and dynamics in Lewis b antigen binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16923–16928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odenbreit, S.; Haas, R. Helicobacter pylori: impact of gene transfer and the role of the cag pathogenicity island for host adaptation and virulence. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 264, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Suerbaum, S.; Josenhans, C. Helicobacter pylori evolution and phenotypic diversification in a changing host. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, M.P.; Prete, G.; Kooyk, Y.; Appelmelk, B. Helicobacter pylori phase variation, immune modulation and gastric autoimmunity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonciarz, W.; Walencka, M.; Moran, A.P.; Hinc, K.; Obuchowski, M.; Chmiela, M. Upregulation of MUC5AC production and deposition of Lewis determinants by Helicobacter pylori facilitate gastric tissue colonization and the maintenance of infection. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 23–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, Y.; Kita, M.; Kodama, T.; Imamura, S.; Ohno, T.; Sawai, N.; Ishimaru, A.; Imanishi, J.; Graham, D.Y. Helicobacter pylori infection in mice: role of outer membrane proteins in colonization and inflammation. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 1992–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peek, R.M., Jr.; Thompson, S.A.; Donahue, J.P.; Tham, K.T.; Atherton, J.C.; Blaser, M.J.; Miller, G.G. Adherence to gastric epithelial cells induces expression of a Helicobacter pylori gene, iceA, that is associated with clinical outcome. Proc. Assoc. Am. Physicians 1998, 110, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ashour, A.A.; Collares, G.B.; Mendes, E.N.; de Gusmão, V.R.; Queiroz, D.M.; Magalhães, P.P.; de Carvalho, A.S.; de Oliveira, C.A.; Nogueira, A.M.; Rocha, G.A.; et al. iceA genotypes of Helicobacter pylori strains isolated from Brazilian children and adults. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 1746–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.H.; Xie, Y.; Li, B.M.; Liu, D.S.; Wan, S.H.; Luo, L.J.; Xiao, Z.J.; Li, H.; Yi, L.J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori cagA, vacA, and iceA genotypes in children with gastroduodenal diseases]. Chin. J. Contemp. Pediatr. 2016, 18, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Hsu, P.-I.; Graham, D.Y.; Yamaoka, Y. Duodenal ulcer promoting gene of Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 833–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, L.I.; Rocha, G.A.; Rocha, A.M.; Soares, T.F.; Oliveira, C.A.; Bittencourt, P.F.; Queiroz, D.M. Lack of association between Helicobacter pylori infection with dupA-positive strains and gastroduodenal diseases in Brazilian patients. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. IJMM 2008, 298, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souod, N.; Sarshar, M.; Dabiri, H.; Momtaz, H.; Kargar, M.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Abdi, S. The study of the oipA and dupA genes in Helicobacter pylori strains and their relationship with different gastroduodenal diseases. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2015, 8, S47–S53. [Google Scholar]
- Cammarota, G.; Sanguinetti, M.; Gallo, A.; Posteraro, B. Biofilm formation by Helicobacter pylori as a target for eradication of resistant infection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 36, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronci, M.; Del Prete, S.; Puca, V.; Carradori, S.; Carginale, V.; Muraro, R.; Mincione, G.; Aceto, A.; Sisto, F.; Supuran, C.T.; et al. Identification and characterization of the α-CA in the outer membrane vesicles produced by Helicobacter pylori. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Feng, J.; Scott, D.R.; Marcus, E.A.; Sachs, G. The HP0165-HP0166 two-component system (ArsRS) regulates acid-induced expression of HP1186 alpha-carbonic anhydrase in Helicobacter pylori by activating the pH-dependent promoter. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 2426–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, G.; Kraut, J.A.; Wen, Y.; Feng, J.; Scott, D.R. Urea transport in bacteria: acid acclimation by gastric Helicobacter spp. J. Membr. Biol. 2006, 212, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grande, R.; Di Giulio, M.; Bessa, L.J.; Di Campli, E.; Baffoni, M.; Guarnieri, S.; Cellini, L. Extracellular DNA in Helicobacter pylori biofilm: a backstairs rumour. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 110, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulp, A.; Kuehn, M.J. Biological functions and biogenesis of secreted bacterial outer membrane vesicles. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 64, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prashar, A.; Capurro, M.I.; Jones, N.L. Under the radar: Strategies used by Helicobacter pylori to evade host responses. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2022, 84, 485–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachathundikandi, S.K.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Backert, S. Signal transduction of Helicobacter pylori during interaction with host cell protein receptors of epithelial and immune cells. Gut Microbes 2013, 4, 454–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, S.; Ooki, T.; Murata-Kamiya, N.; Komura, D.; Tahmina, K.; Wu, W.; Takahashi-Kanemitsu, A.; Knight, C.T.; Kunita, A.; Suzuki, N.; et al. Helicobacter pylori CagA elicits BRCAness to induce genome instability that may underlie bacterial gastric carcinogenesis. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 941–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheok, Y.Y.; Lee, C.Y.Q.; Cheong, H.C.; Vadivelu, J.; Looi, C.Y.; Abdullah, S.; Wong, W.F. An overview of Helicobacter pylori survival tactics in the hostile human stomach environment. Microorganisms 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, N.; Tsujimoto, H.; Ueno, H.; Xie, Q.; Shinomiya, N. Helicobacter pylori-mediated immunity and signaling transduction in gastric cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudnicka, K.; Matusiak, A.; Miszczyk, E.; Rudnicka, W.; Tenderenda, M.; Chmiela, M. Immunophenotype of peripheral blood natural killer cells and IL-10 serum levels in relation to Helicobacter pylori status. APMIS 2013, 121, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnicka, K.; Miszczyk, E.; Matusiak, A.; Walencka, M.; Moran, A.P.; Rudnicka, W.; Chmiela, M. Helicobacter pylori-driven modulation of NK cell expansion, intracellular cytokine expression and cytotoxic activity. Innate Immun. 2015, 21, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Kong, X.; Li, X.; Yan, S.; Yuan, C.; Hu, W.; Yang, Q. Metadherin mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. PloS ONE 2011, 6, e29363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yuan, B.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, Z. MicroRNA-146a-5p attenuates irradiation-induced and LPS-induced hepatic stellate cell activation and hepatocyte apoptosis through inhibition of TLR4 pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathroubi, S.; Zerebinski, J.; Ottemann, K.M. Helicobacter pylori biofilm involves a multigene stress-biased response, including a structural role for flagella. mBio 2018, 9, e01973–01918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debowski, A.W.; Walton, S.M.; Chua, E.G.; Tay, A.C.; Liao, T.; Lamichhane, B.; Himbeck, R.; Stubbs, K.A.; Marshall, B.J.; Fulurija, A.; et al. Helicobacter pylori gene silencing in vivo demonstrates urease is essential for chronic infection. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mégraud, F.; Neman-Simha, V.; Brügmann, D. Further evidence of the toxic effect of ammonia produced by Helicobacter pylori urease on human epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 1858–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera-Severo, D.; Uberti, A.F.; Marques, M.S.; Pinto, M.T.; Gomez-Lazaro, M.; Figueiredo, C.; Leite, M.; Carlini, C.R. A new role for Helicobacter pylori urease: contributions to angiogenesis. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uberti, A.F.; Olivera-Severo, D.; Wassermann, G.E.; Scopel-Guerra, A.; Moraes, J.A.; Barcellos-de-Souza, P.; Barja-Fidalgo, C.; Carlini, C.R. Pro-inflammatory properties and neutrophil activation by Helicobacter pylori urease. Toxicon 2013, 69, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, C.; Tan, S.; Nakajima, M.; Skoog, E.C.; Camarillo-Guerrero, L.F.; Klein, J.A.; Lawley, T.D.; Solnick, J.V.; Fukami, T.; Amieva, M.R. High-resolution mapping reveals that microniches in the gastric glands control Helicobacter pylori colonization of the stomach. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lina, T.T.; Alzahrani, S.; Gonzalez, J.; Pinchuk, I.V.; Beswick, E.J.; Reyes, V.E. Immune evasion strategies used by Helicobacter pylori. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 12753–12766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debraekeleer, A.; Remaut, H. Future perspective for potential Helicobacter pylori eradication therapies. Future Microbiol. 2018, 13, 671–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilleringmann, M.; Pansegrau, W.; Doyle, M.; Kaufman, S.; MacKichan, M.L.; Gianfaldoni, C.; Ruggiero, P.; Covacci, A. Inhibitors of Helicobacter pylori ATPase Cagalpha block CagA transport and cag virulence. Microbiology 2006, 152, 2919–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, D.P.; Asim, M.; Leiman, D.A.; de Sablet, T.; Singh, K.; Casero, R.A., Jr.; Chaturvedi, R.; Wilson, K.T. Difluoromethylornithine is a novel inhibitor of Helicobacter pylori growth, CagA translocation, and interleukin-8 induction. PloS ONE 2011, 6, e17510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, J.R.; Walldén, K.; Pesnot, T.; Campbell, F.; Gane, P.J.; Simone, M.; Koss, H.; Buelens, F.; Boyle, T.P.; Selwood, D.L.; et al. 2- and 3-substituted imidazo[1,2-a]pyrazines as inhibitors of bacterial type IV secretion. Bioorgic Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 6459–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doua, F.; Boa, F.Y.; Schechter, P.J.; Miézan, T.W.; Diai, D.; Sanon, S.R.; De Raadt, P.; Haegele, K.D.; Sjoerdsma, A.; Konian, K. Treatment of human late stage gambiense trypanosomiasis with alpha-difluoromethylornithine (eflornithine): efficacy and tolerance in 14 cases in Côte d'Ivoire. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1987, 37, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broutet, N.; Marais, A.; Lamouliatte, H.; de Mascarel, A.; Samoyeau, R.; Salamon, R.; Mégraud, F. cagA status and eradication treatment outcome of anti-Helicobacter pylori triple therapies in patients with nonulcer dyspepsia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 1319–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, V.; Gimenez, S.; Haensler, J.; Geoffroy, C.; Rokbi, B.; Seguin, D.; Lissolo, L.; Harris, B.; Rizvi, F.; Kleanthous, H.; et al. Formulations of single or multiple H. pylori antigens with DC Chol adjuvant induce protection by the systemic route in mice Optimal prophylactic combinations are different from therapeutic ones. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 30, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Bai, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.-D.; Zhang, Z.-S.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Zhou, D.-Y. Expression of Helicobacter pylori AlpA protein and its immunogenicity. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 2260–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahboubi, M.; Falsafi, T.; Sadeghizadeh, M.; Mahjoub, F. The role of outer inflammatory protein A (OipA) in vaccination of theC57BL/6 mouse model infected by Helicobacter pylori. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 47, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, N.; She, F. Helicobacter pylori outer inflammatory protein DNA vaccine-loaded bacterial ghost enhances immune protective efficacy in C57BL/6 mice. Vaccine 2014, 32, 6054–6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soudi, H.; Falsafi, T.; Mahboubi, M.; Gharavi, S. Evaluation of Helicobacter pylori OipA protein as a vaccine candidate and propolis as an adjuvant in C57BL/6 mice. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2021, 24, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, A.; Hultberg, A.; Sjöström, R.; Kacskovics, I.; Breimer, M.E.; Borén, T.; Hammarström, L.; Holgersson, J. Carbohydrate-dependent inhibition of Helicobacter pylori colonization using porcine milk. Glycobiology 2006, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naz, A.; Awan, F.M.; Obaid, A.; Muhammad, S.A.; Paracha, R.Z.; Ahmad, J.; Ali, A. Identification of putative vaccine candidates against Helicobacter pylori exploiting exoproteome and secretome: a reverse vaccinology based approach. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 32, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keikha, M.; Eslami, M.; Yousefi, B.; Ghasemian, A.; Karbalaei, M. Potential antigen candidates for subunit vaccine development against Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 21460–21470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urrutia-Baca, V.H.; Gomez-Flores, R.; De La Garza-Ramos, M.A.; Tamez-Guerra, P.; Lucio-Sauceda, D.G.; Rodríguez-Padilla, M.C. Immunoinformatics approach to design a novel epitope-based oral vaccine against Helicobacter pylori. J. Comput. Biol. 2019, 26, 1177–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doohan, D.; Rezkitha, Y.A.A.; Waskito, L.A.; Yamaoka, Y.; Miftahussurur, M. Helicobacter pylori BabA-SabA key roles in the adherence phase: the synergic mechanism for successful colonization and disease development. Toxins 2021, 13, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benktander, J.; Barone, A.; Johansson, M.M.; Teneberg, S. Helicobacter pylori SabA binding gangliosides of human stomach. Virulence 2018, 9, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakoob, J.; Abbas, Z.; Mehmood, M.H.; Tariq, K.; Saleem, S.A.; Awan, S.; Malik, A.; Hamid, S.; Khan, R.; Jafri, W. Helicobacter pylori outer membrane protein Q genotypes and their susceptibility to anti-adhesive phytotherapeutic agents. J. Integr. Med. 2017, 15, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsor, D.A.; Zhao, Q.; Schmidinger, B.; Weiss, E.; Wang, J.; Deredge, D.; Beadenkopf, R.; Dow, B.; Fischer, W.; Beckett, D.; et al. The Helicobacter pylori adhesin protein HopQ exploits the dimer interface of human CEACAMs to facilitate translocation of the oncoprotein CagA. EMBO J. 2018, 37, e98664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesmann, M.; Paraskevopoulou, V.; Mohammed, A.; Falcone, F.H.; Hensel, A. BabA and LPS inhibitors against Helicobacter pylori: pectins and pectin-like rhamnogalacturonans as adhesion blockers. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurbuz, A.K.; Ozel, A.M.; Ozturk, R.; Yildirim, S.; Yazgan, Y.; Demirturk, L. Effect of N-acetyl cysteine on Helicobacter pylori. South. Med. J. 2005, 98, 1095–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Phase 1a/b study on safety of IMX101 in H. pylori-negative and H. pylori-infected healthy volunteers. 2019. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03270800.
- Malfertheiner, P.; Selgrad, M.; Wex, T.; Romi, B.; Borgogni, E.; Spensieri, F.; Zedda, L.; Ruggiero, P.; Pancotto, L.; Censini, S.; et al. Efficacy, immunogenicity, and safety of a parenteral vaccine against Helicobacter pylori in healthy volunteers challenged with a Cag-positive strain: a randomised, placebo-controlled phase 1/2 study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, J.; Lebens, M.; Wai, S.N.; Holmgren, J.; Svennerholm, A.M. Surface expression of Helicobacter pylori HpaA adhesion antigen on Vibrio cholerae, enhanced by co-expressed enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli fimbrial antigens. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 105, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ye, J.; Ning, L.; Luo, J.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Xi, Y.; Ning, Y. Antibody production and Th1-biased response induced by an epitope vaccine composed of cholera toxin B unit and Helicobacter pylori Lpp20 epitopes. Helicobacter 2016, 21, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, M.; Mao, X.H.; Li, J.X.; Tong, W.D.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.J.; Guo, G.; Zhao, Z.J.; Li, L.; Wu, D.L.; et al. Efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of an oral recombinant Helicobacter pylori vaccine in children in China: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2015, 386, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Pan, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yang, J.; Li, W. Immunological response of recombinant H. pylori multi-epitope vaccine with different vaccination strategies. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 6559–6566. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moss, S.F.; Moise, L.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, W.; Zhang, S.; Lee, J.; Rogers, A.B.; Martin, W.; De Groot, A.S. HelicoVax: epitope-based therapeutic Helicobacter pylori vaccination in a mouse model. Vaccine 2011, 29, 2085–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkovich, O.A.; Yin, J.; Ekshyyan, V.; Conant, C.; Traylor, J.; Adegboyega, P.; McGee, D.J.; Rhoads, R.E.; Slepenkov, S.; Testerman, T.L. Helicobacter pylori AlpA and AlpB bind host laminin and influence gastric inflammation in gerbils. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 3106–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, Y.; Kido, Y.; Yamaoka, Y. Helicobacter pylori outer membrane protein-related pathogenesis. Toxins 2017, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsonnet, J.; Friedman, G.D.; Vandersteen, D.P.; Chang, Y.; Vogelman, J.H.; Orentreich, N.; Sibley, R.K. Helicobacter pylori infection and the risk of gastric carcinoma. New Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talley, N.J.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Weaver, A.; DiMagno, E.P.; Carpenter, H.A.; Perez-Perez, G.I.; Blaser, M.J. Gastric adenocarcinoma and Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1991, 83, 1734–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, M.; Suzuki, H.; Suzuki, M.; Kai, A.; Miura, S.; Ishii, H. Catalase and superoxide dismutase secreted from Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter 1997, 2, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela-Valderrama, M.; Cerda-Opazo, P.; Backert, S.; González, M.F.; Carrasco-Véliz, N.; Jorquera-Cordero, C.; Wehinger, S.; Canales, J.; Bravo, D.; Quest, A.F.G. The Helicobacter pylori urease virulence factor is required for the induction of hypoxia-induced factor-1α in gastric cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa, P. Is gastric cancer preventable? Gut 2004, 53, 1217–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugge, M.; Busatto, G.; Cassaro, M.; Shiao, Y.H.; Russo, V.; Leandro, G.; Avellini, C.; Fabiano, A.; Sidoni, A.; Covacci, A. Patients younger than 40 years with gastric carcinoma: Helicobacter pylori genotype and associated gastritis phenotype. Cancer 1999, 85, 2506–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleastro, M.; Ménard, A. The role of Helicobacter pylori outer membrane proteins in adherence and pathogenesis. Biology 2013, 2, 1110–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.L.; Huang, H.L.; Huang, B.S.; Chen, P.C.; Chen, C.S.; Wang, H.L.; Lin, P.H.; Chieh, M.S.; Wu, J.J.; Yang, J.C.; et al. Combination of OipA, BabA, and SabA as candidate biomarkers for predicting Helicobacter pylori-related gastric cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, M.; Khashei, R.; Alizadeh, M.; Asl, M.H.; Nejati, M.A.; Dara, M.; Bazargani, A. Low rate of babA2 genotype among Iranian Helicobacter pylori clinical isolates. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, Dc32–Dc36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honarmand-Jahromy, S.; Siavoshi, F.; Malekzadeh, R.; Nejad Sattari, T.; Latifi-Navid, S. Reciprocal impact of host factors and Helicobacter pylori genotypes on gastric diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 9317–9327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safaralizadeh, R.; Dastmalchi, N.; Hosseinpourfeizi, M.; Latifi-Navid, S. Helicobacter pylori virulence factors in relation to gastrointestinal diseases in Iran. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 105, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Protein family | Number of sub-family | Sub-family genes |
|---|---|---|
| Hop | 22 |
hopZ, hopD, hopM, hopA, hopF, hopG, hopJ, hopH, hopE, hopO, hopP, hopC, hopB, hopK, hopI, hopL, hopQ, hopQ, hopN, hopU babA, babB |
| Hor | 12 | horA, horB, horC, horD, horE, horF, horG, horH, horI, horJ, horK, horL |
| Hof | 8 | hofA, hofB, hofC, hofD, hofE, hofF, hofG, hofH |
| Hom | 4 | homA, homB, homC, homD |
| FecA-like | 3 | fecA-1, fecA-2, fecA-3 |
| FrpB-like | 3 | frpB-1, frpB-2, frpB-3 |
| Efflux pump | 6 |
hefA, hefD, hefG flgH palA lpp20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





