1. Introduction
Chronic skin wounds, a prevalent medical concern, significantly deteriorate patient quality of life and impose substantial socioeconomic burdens. The physiological response to skin injury involves the generation of an endogenous electric field (EEF), a critical factor in wound closure processes1, 2. However, in chronic wounds, this natural EEF is often impaired or absent, necessitating alternative therapeutic interventions.Electrical Stimulation Therapy (EST) has emerged as a promising approach to facilitate wound healing. It aids in simulating the natural EEF, thus playing a pivotal role in mitigating bacterial proliferation, fostering cell migration, and stimulating the proliferation of fibroblasts. These processes are crucial in accelerating wound repair and compensating for the dysfunctional EEF inherent in chronic wounds3-6.
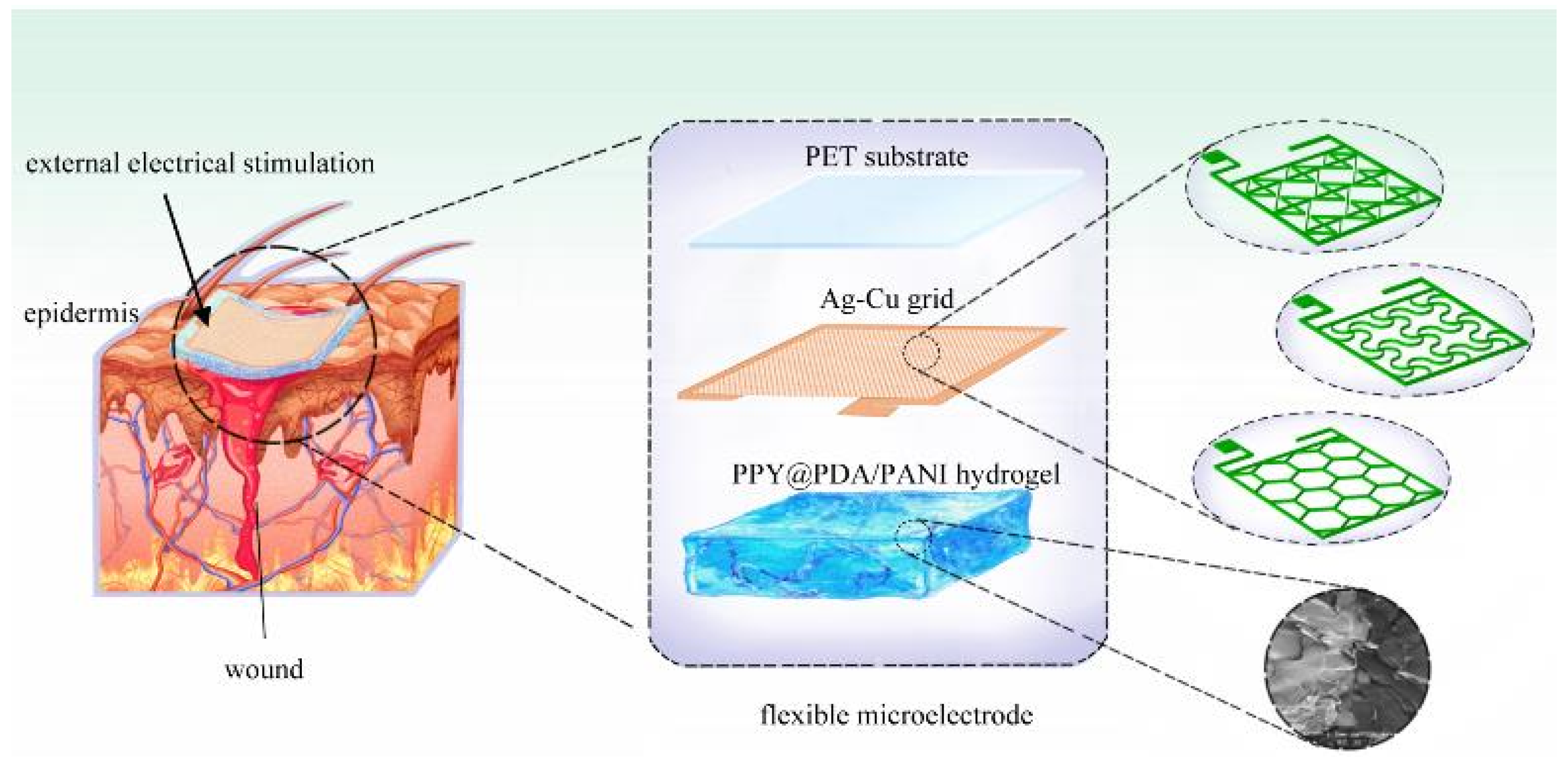
In the realm of biomedical engineering, particularly in the development of devices for EST, flexible microelectrodes (FMs) have garnered considerable attention. Their diverse structures and functionalities make them highly suitable for such applications. Attributes such as reduced weight, smaller dimensions, and enhanced adaptability to the contours of the human body render these devices particularly advantageous[
8,
9]. The design of FMs is intricately linked to their flexibility and the distribution of stimulation, factors that can significantly impact the effectiveness of EST. Moreover, the safety of these devices is a paramount consideration, especially concerning the thermal effects associated with continuous current stimulation in wound therapy. In particular, DC stimulation poses a risk of thermal injury to the skin, underscoring the need for careful design and material selection in electrode construction
6, 7.
Our research delves into the development and application of three distinct types of FMs, each featuring Ag-Cu coverings (ACCs) and adopting unique geometric configurations: hexagonal, cross-shaped, and serpentine. These designs were integrated with hydrogel technology, a novel approach in EST. This integration aimed to investigate the influence of electrode structure on key cellular processes such as proliferation and migration, factors essential for effective wound healing. In addition, our study extends to the safety aspects of these electrode designs, a critical consideration in their clinical application. Employing a combination of experimental methods and computational simulations, we offer a comprehensive analysis of how different FM structures contribute to the efficacy and safety of EST in chronic wound management4.
This introduction sets the stage for a detailed exploration of the intersection between advanced MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) technology in electrode design and its application in medical therapy, particularly in the domain of wound healing. Our investigation aims to bridge the gap between engineering innovation and clinical application, offering insights that could transform the landscape of chronic wound management.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication of FMs
The fabrication process of the flexible microelectrodes (FMs) commenced with the application of UV photoresist onto a glass substrate using a doctor’s blade. This initial step was critical for ensuring a uniform coating. Subsequently, photolithography techniques were employed to intricately shape the UV photoresist film. This film served as a precise mask for the creation of a nickel master mold. The next phase involved patterning the poly (ethylene terephthalate) (PET) substrate. For this, the nickel master was accurately imprinted onto the UV glue previously coated on the PET substrate, which had a thickness of 120 μm. This process resulted in a mask-shaped pattern with a fine thickness of 3μm on the substrate grid. Following this, silver nano ink was meticulously filled into the formed grooves and then subjected to a sintering process at 150°C for 15 minutes. This step was essential for ensuring the structural integrity and conductivity of the silver grid. The subsequent electroplating phase involved the application of a 2A current, facilitating the deposition of a dense copper layer over the silver grid. This copper covering, electroplated for approximately 5 minutes, was crucial to prevent any further oxidation of the electrodes. The final step in the fabrication process entailed the smoothing of the film’s surface. This was achieved by employing an aqueous solution containing fine silica particles, which helped in creating a more uniform and refined surface finish. Illustrations of this intricate process are provided for clarity:
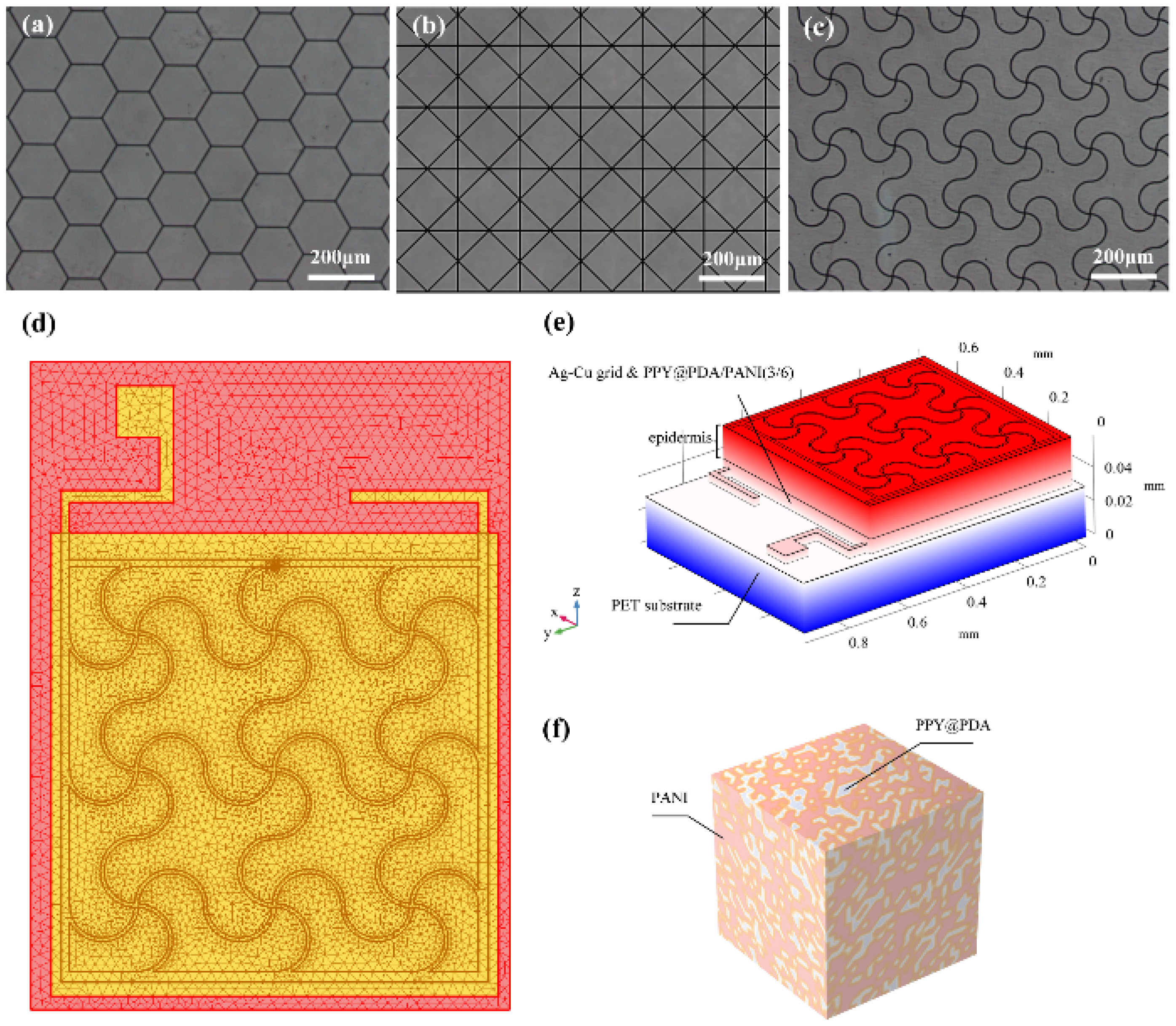
Figure 1 depicts the structured design of the FMs, while
Figure 2a-c showcase the detailed images of the three types of flexible electrodes under an optical microscope, highlighting their distinct geometrical configurations
8.
2.2. Modeling and simulation of FMs-hydrogel-epidermis system (FHES)
For the modeling and analysis of the flexible microelectrodes (FMs) within the Flexible Microelectrodes-Hydrogel-Epidermis System (FHES), a finite element analysis (FEA) approach was employed. The detailed meshing of the serpentine FM, a crucial step in ensuring accurate simulation results, is depicted in
Figure 2d. The FEA methodology allowed for a thorough investigation of the complex interactions within the multi-layered structure of the FHES. The constructed model of the FHES, as shown in
Figure 2e, consists of four distinct layers: the PET substrate, Ag-Cu coverings (ACCs), hydrogel, and epidermis. Each layer’s unique properties were taken into account to develop a comprehensive representation of the system. While the model parameters for the three electrode types were consistent, variations were introduced in the shapes of the ACCs to assess their impact on the system’s performance. Underpinning this model are fundamental principles from electrical, mechanical, and energy conversion theories. These principles were meticulously integrated to ensure a holistic and scientifically robust simulation environment, as detailed in Notes S1 and S2. A critical aspect of the model is the representation of the hydrogel layer. Hydrogels in this study were formulated as a non-uniformly doped mixture, incorporating components such as PPY@PDA and PANI. The doping and mixing of these components followed a specific ratio of 1:2, as shown in
Figure 2f. This approach to hydrogel composition is pivotal as it leads to a dispersed distribution of internal conductivity, a factor crucial in simulating realistic interactions within the FHES. By incorporating these varied conductivity patterns, the model more accurately reflects the complex electrical behavior of the hydrogel layer, which is essential for understanding the overall efficacy of the FMs in EST applications
3, 9.
2.3. Animal experiment
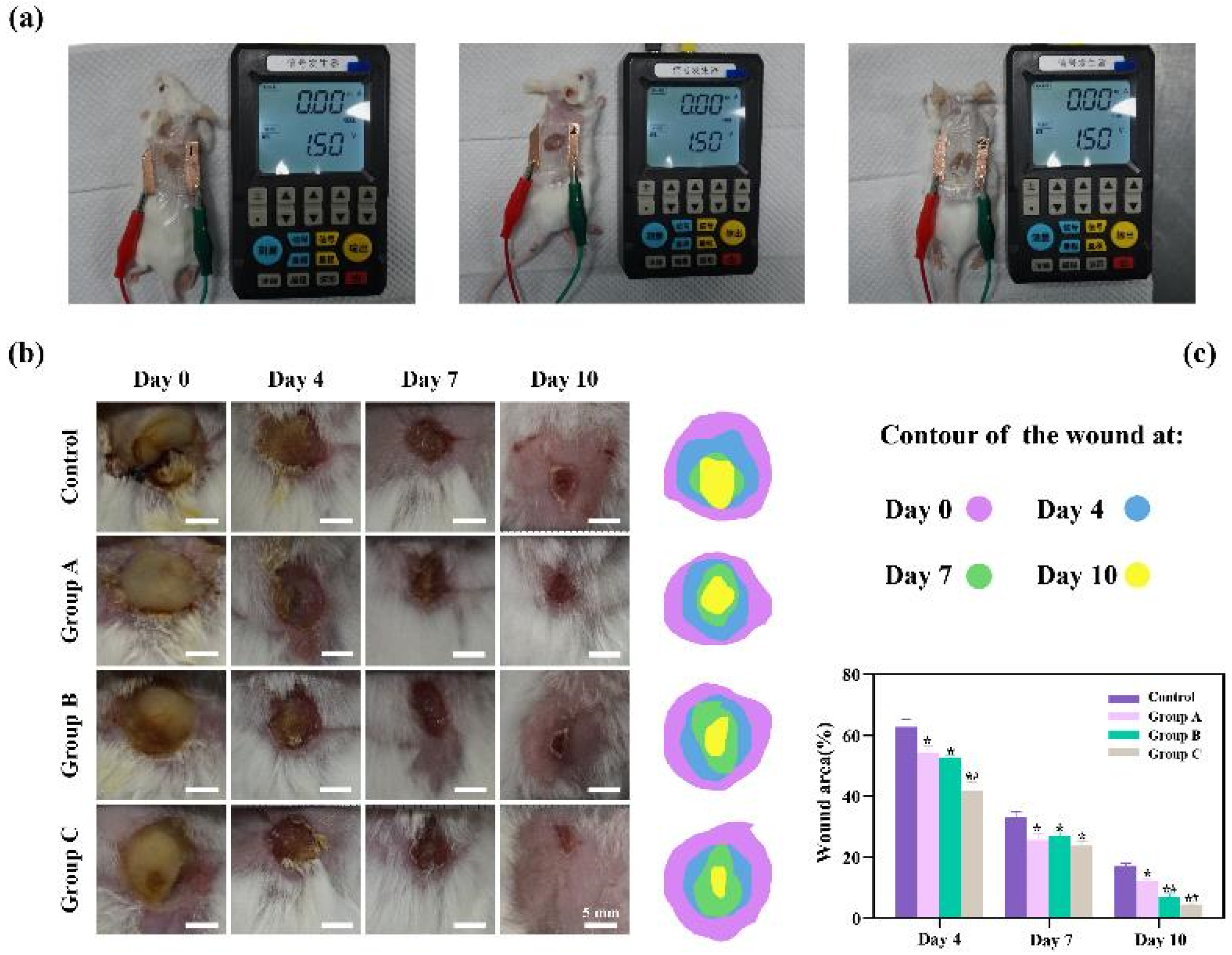
To rigorously assess the therapeutic efficacy of the three distinct types of flexible microelectrodes (FMs) with Ag-Cu coverings, a controlled animal study was meticulously designed, as detailed in
Figure 3a. The experimental setup included a control group, wherein the subjects’ wounds were treated using Tegaderm film dressings, a standard wound care approach, without the application of any electrical stimulation. In contrast, the experimental groups, each corresponding to one of the three FM types (hexagonal, cross-shaped, and serpentine), underwent Electrical Stimulation Therapy (EST) under uniform conditions, facilitating a direct comparison of the effectiveness of each electrode type. The progression of wound healing was meticulously documented through serial photography at predetermined intervals. This visual record provided an empirical basis for evaluating the rate and extent of wound healing across the different groups. In addition to qualitative observations, a quantitative analysis was conducted to objectively measure and compare the healing outcomes. This dual approach, encompassing both visual and quantitative data, allowed for a comprehensive assessment of the therapeutic potential of each FM variant in the context of chronic wound management.
3. Discussion
In the cell culture experiments, the electrical parameters settings ensured that biological response was induced. The results of animal experiments demonstrated that all three electrons accelerated wound healing. On day 10, the wounds of the rats treated with the serpentine FM achieved a high closure ratio of 91%, while the wound in the control group remained largely unhealed (less than 95%) (
Figure 3c). In addition, the wounds treated with the hexagonal and cross-shaped electrode achieved the closure ratio of 85% and 90%, respectively
10-12. As shown by
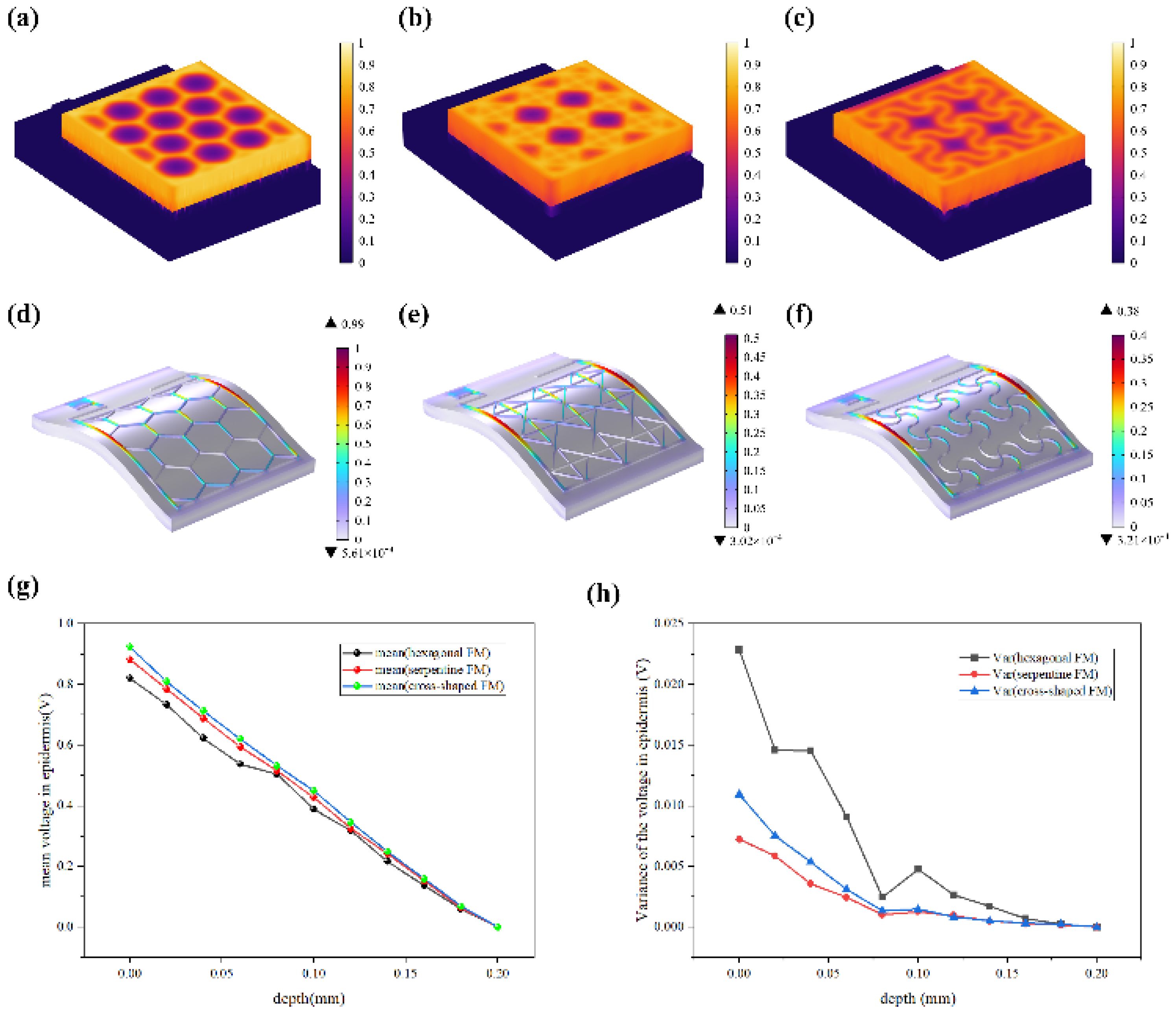
Figure 3b, there is a pronounced yellow purulent discharge in the control group in the early stages of wound healing. By contrast, the other three groups are relatively mild. These findings confirmed that FMs with Ag-Cu coverings can significantly increase the healing rate of chronic wound and the serpentine electrode showed a clear advantage compared with other two types in terms of healing speed. To clearly compare the physical properties distribution of the epidermis, a 0.6 mm×0.65 mm part of the cell structure was selected in the simulation, and the simulation results were normalized
13.
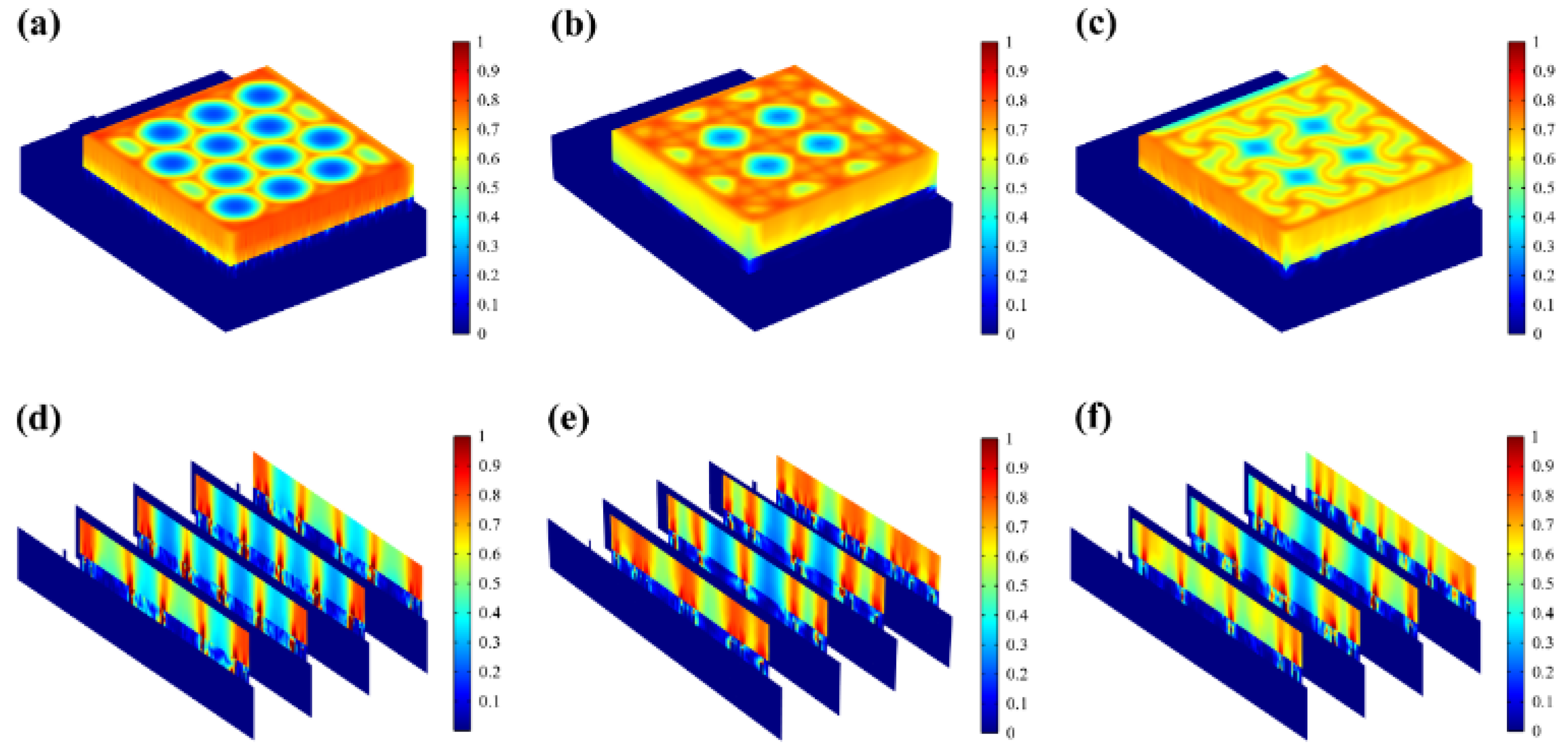
Most of the energy transferred to the epidermis from electrical stimulation is converted to heat. The resistive loss distribution (
Figure 4a-c) is highly correlated with the heat accumulation rate (
Figure 5a-c). As far as safety is concerned, the high impedance of the epidermis leads to thermal accumulation, which may cause risks of burns. Normalized results showed that the epidermis accumulated heat faster when hexagonal and cross-shaped FMs were applied, especially at the cross point, indicating risks of burns (
Figure 5a-b). While for serpentine FM, heat accumulation displayed a more balanced distribution (
Figure 5c), which was well validated and explained higher survival rates in cell culture experiments.
Figure 5d-f revealed that the stress of ACC is larger compared with that of PET. Therefore, the structure of ACC is the dominant factor affecting the flexibility of FMs. The maximum stress of serpentine FM (
Figure 5f) is lower, which is 39% of hexagonal FM (
Figure 5d) and 85% of cross-shaped FM (
Figure 5e), denoting its optimal flexibility. Consequently, the serpentine FM fits more closely with the skin surface, thus, the air resistive loss caused by the loose fitting is less and the external electrical stimulation can be better transmitted to the skin surface. Besides, the air impedance is high; if the contact between FMs and the skin surface is not tight enough, the heat accumulation caused by high-impedance air will aggravate the possibility and severity of skin burns. Therefore, the high flexibility of the serpentine structure also contributes to the safety of EST
14-16.
Figure 5g demonstrates that EST compensates well for the loss of endogenous electric potential when working with the highly-conductive hydrogel. The electric potential distribution of serpentine FM is more uniform, with a normalized variance 32% of hexagonal one and 66% of cross-shaped one (
Figure 5h,
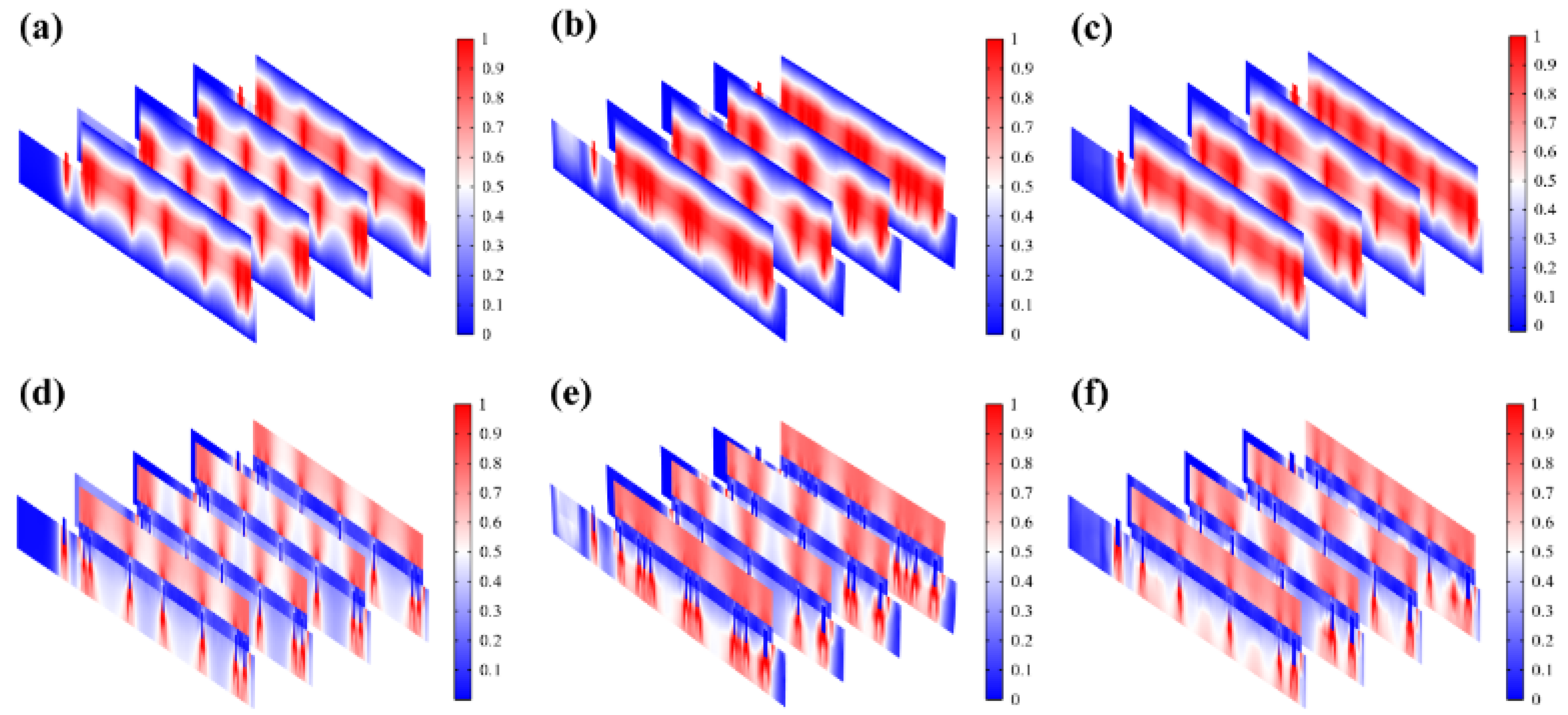
Figure 6a-c). Also, the electric field (
Figure 6d-f) maintains its intensity inside the skin, playing a key role in compensating for the endogenous electric field. It was observed from
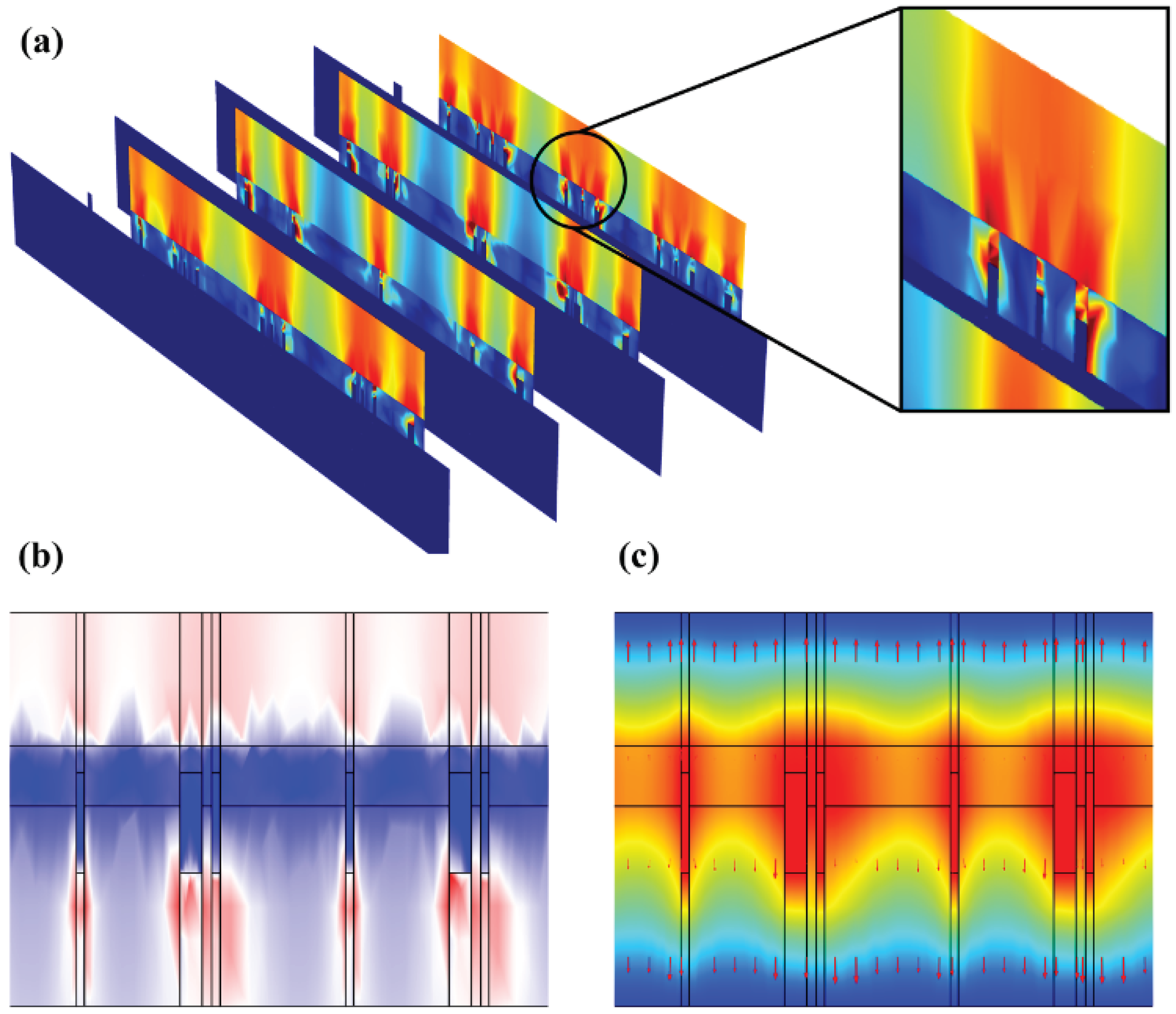
Figure 7a-b that hydrogel showed a dispersed resistive loss distribution and electric field distribution due to the random doping, which also had an impact on the distribution in the epidermis. However, the voltage distribution didn’t show an obviously dispersed distribution in hydrogel and epidermis (
Figure 7c), because the voltage is an integral of the potential and the discrete type is greatly reduced. Therefore, the voltage is minimally affected by non-uniform doping, which may offer guidance for EST when working with hydrogel dressings that composition and structure of hydrogels affect the epidermal electrical stimulation. Less than 3% of the substrate is covered with the ACCs, causing low optical losses, which indicates that FMs designed have great potential for optoelectronic self-power
1, 17.
4. Conclusion
In conclusion, this study decisively establishes that the geometry of Flexible Microelectrodes (FMs) is crucial in optimizing the efficacy of Electrical Stimulation Therapy (EST) for chronic wound healing. Our comparative analysis of hexagonal, cross-shaped, and serpentine FMs indicates that the serpentine design is superior, demonstrating enhanced wound healing efficiency, primarily due to its more effective promotion of cell proliferation and migration. This is attributed to its ability to more uniformly distribute electrical stimulation across the wound surface, thereby compensating for the deficient endogenous electric field in chronic wounds. Notably, the serpentine FM also exhibits a lower thermal accumulation rate, significantly reducing burn risks, a critical safety consideration in EST. Furthermore, its mechanical properties, with a markedly lower stress level compared to the other designs, ensure better adaptability to skin contours, enhancing treatment effectiveness and patient comfort. Additionally, the study highlights the impact of hydrogel non-uniformity on the electrical properties of skin, suggesting the need for careful consideration of hydrogel composition in EST applications. The minimal coverage of the substrate by Ag-Cu coverings (less than 3%) in the serpentine FM design also hints at its potential for optoelectronic self-powering capabilities, opening new avenues for self-sustaining therapeutic devices. Collectively, these findings underscore the significance of FM design in advancing the field of bioelectronic medicine, particularly in the context of chronic wound management.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Lihong Qi. and ; methodology, Lihong Qi; software, Lihong Qi, Mujie Liu, Kai Yao; validation, Lihong Qi, Zeru Tao; formal analysis, Yuheng Wang; investigation, Yuheng Wang; resources, Yuheng Wang; data curation, Yuheng Wang; writing—original draft preparation, Lihong Qi, Ying Yu; writing—review and editing, Yuheng Wang; visualization, Yuheng Wang; supervision, Yuheng Wang; project administration, Yuheng Wang; funding acquisition, Yuheng Wang and Yongwei Jiang.
Funding
Please add: This research was funded by Logistics Science and Technology Planning Project of PLA, grant number “BJZ15J001XXX” and Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangzhou, China, grant number “20190301001”. Zhejiang Medical Health Science and Technology Project (Grant Nos. 2023RC044)
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Experimental Animal Ethics Committee of Ningbo University, (code NBU20220063) on 2022.3.1.
Data Availability Statement
Access to all data may be made on reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank the Department of Basic Medicine School of the Air Force Military Medical University and the State Key Laboratory for Manufacturing System Engineering for their scientific research instrument support.
Conflicts of Interest
All the authors state that this research was carried out without any commercial or financial relationships that might be interpreted as a possible conflict of interest.
References
- Long, Y.; Wei, H.; Li, J.; Yao, G.; Yu, B.; Ni, D.; Gibson, A. L.; Lan, X.; Jiang, Y.; Cai, W. Effective wound healing enabled by discrete alternative electric fields from wearable nanogenerators. ACS nano 2018, 12(12), 12533–12540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.; Dai, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z. Accelerated skin wound healing by electrical stimulation. Advanced healthcare materials 2021, 10(16), 2100557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoogerwerf, A. C.; Wise, K. D. A three-dimensional microelectrode array for chronic neural recording. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 1994, 41(12), 1136–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadi, M. R.; Torkaman, G. Bacterial inhibition by electrical stimulation. Advances in wound care 2014, 3(2), 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karba, R.; Šemrov, D.; Vodovnik, L.; Benko, H.; Savrin, R. DC electrical stimulation for chronic wound healing enhancement Part 1. Clinical study and determination of electrical field distribution in the numerical wound model. Bioelectrochemistry and Bioenergetics 1997, 43(2), 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Huang, J.; Zhangji, A.; Tong, X.; Yu, K.; Chen, K.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ali Memon, W. Accelerated skin wound healing using flexible photovoltaic-bioelectrode electrical stimulation. Micromachines 2022, 13(4), 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wang, X.; Rajagopalan, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhan, S.; Huang, S.; Li, W.; Zeng, X.; Ye, Q.; Liu, Y. Toward controlled electrical stimulation for wound healing based on a precision layered skin model. ACS Applied Bio Materials 2020, 3(12), 8901–8910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awolusi, I.; Marks, E.; Hallowell, M. Wearable technology for personalized construction safety monitoring and trending: Review of applicable devices. Automation in construction 2018, 85, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Huang, L.; Nie, S.; Xu, W.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, S.; Pei, F.; Yu, K.; Su, W. Highly Conductive Omnidirectionally Stretchable 2D Transparent Copper Mesh Electrodes and Applications in Optoelectronic Devices. Advanced Materials Technologies 2023, 2201406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Hu, Y.; Shi, S.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, K. Hydrogel Bioelectronics for Health Monitoring. Biosensors 2023, 13(8), 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Wang, S.; Xu, L.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, B. Z. AIEgen-based smart system for fungal-infected wound monitoring and on-demand photodynamic therapy. Matter 2023, 6(10), 3449–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y. W.; Wang, Y. H.; Yang, F.; Liu, D. X.; Lu, G. H.; Li, S. T.; Wei, Z. X.; Shen, X.; Jiang, Z. D.; Zhao, Y. F. Flexible Organic Photovoltaic-Powered Hydrogel Bioelectronic Dressing With Biomimetic Electrical Stimulation for Healing Infected Diabetic Wounds. Advanced Science 2023, 2307746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.; Xu, N.; Wu, X.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, Q. Enhanced heterogeneous interface to construct intelligent conductive hydrogel gas sensor for individualized treatment of infected wounds. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2024, 258, 128520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Luo, G.; Ji, Z.; Bo, R.; Xue, Z.; Yan, D.; Zhang, F.; Bai, K.; Liu, J.; Cheng, X. Highly-integrated, miniaturized, stretchable electronic systems based on stacked multilayer network materials. Science Advances 2022, 8(11), eabm3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Lin, Q.; Yao, K.; Wang, Y.; Han, F. Flexible pressure sensors with ultrahigh stress tolerance enabled by periodic microslits. Microsystems & Nanoengineering 2024, 10(1), 24. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, G.; Zhang, Y.; Sheng, L. Simulation and verification electrical properties of liquid metal flexible bioelectrodes. Microsystem Technologies 2021, 27, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Jing, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, F.; Yu, K. Superior performances via designed multiple embossments within interfaces for flexible pressure sensors. Chemical Engineering Journal 2023, 454, 139990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).