Submitted:
23 February 2024
Posted:
23 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Defining Abundant Community Members
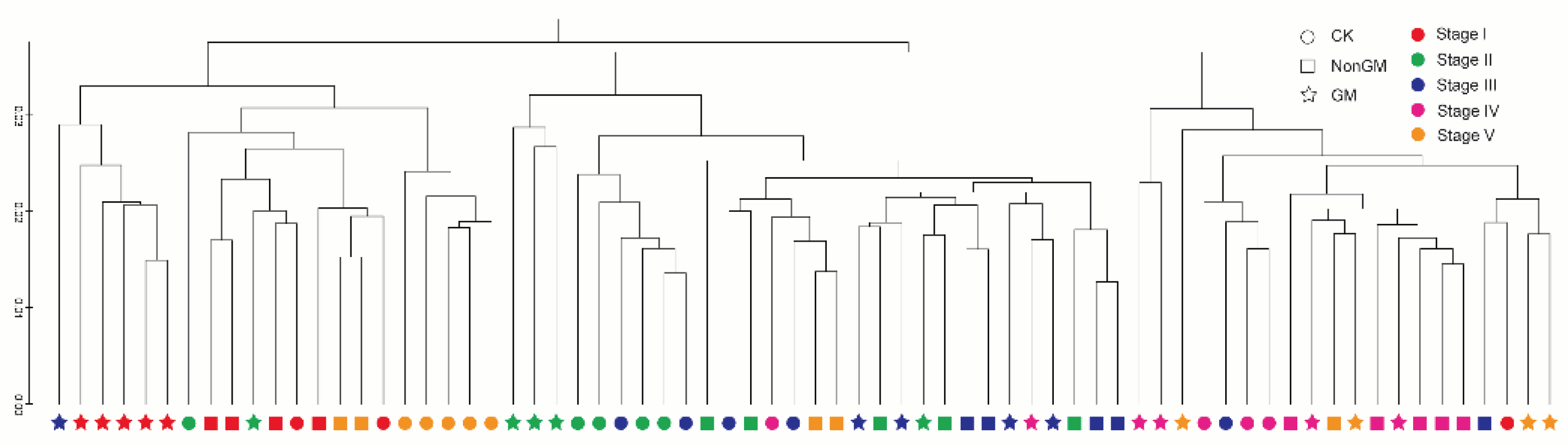
2.2. Community Composition Defined by Different Treatments
2.3. Community Composition Defined by Different Sampling Times
2.4. Identification of the Core Microbiota
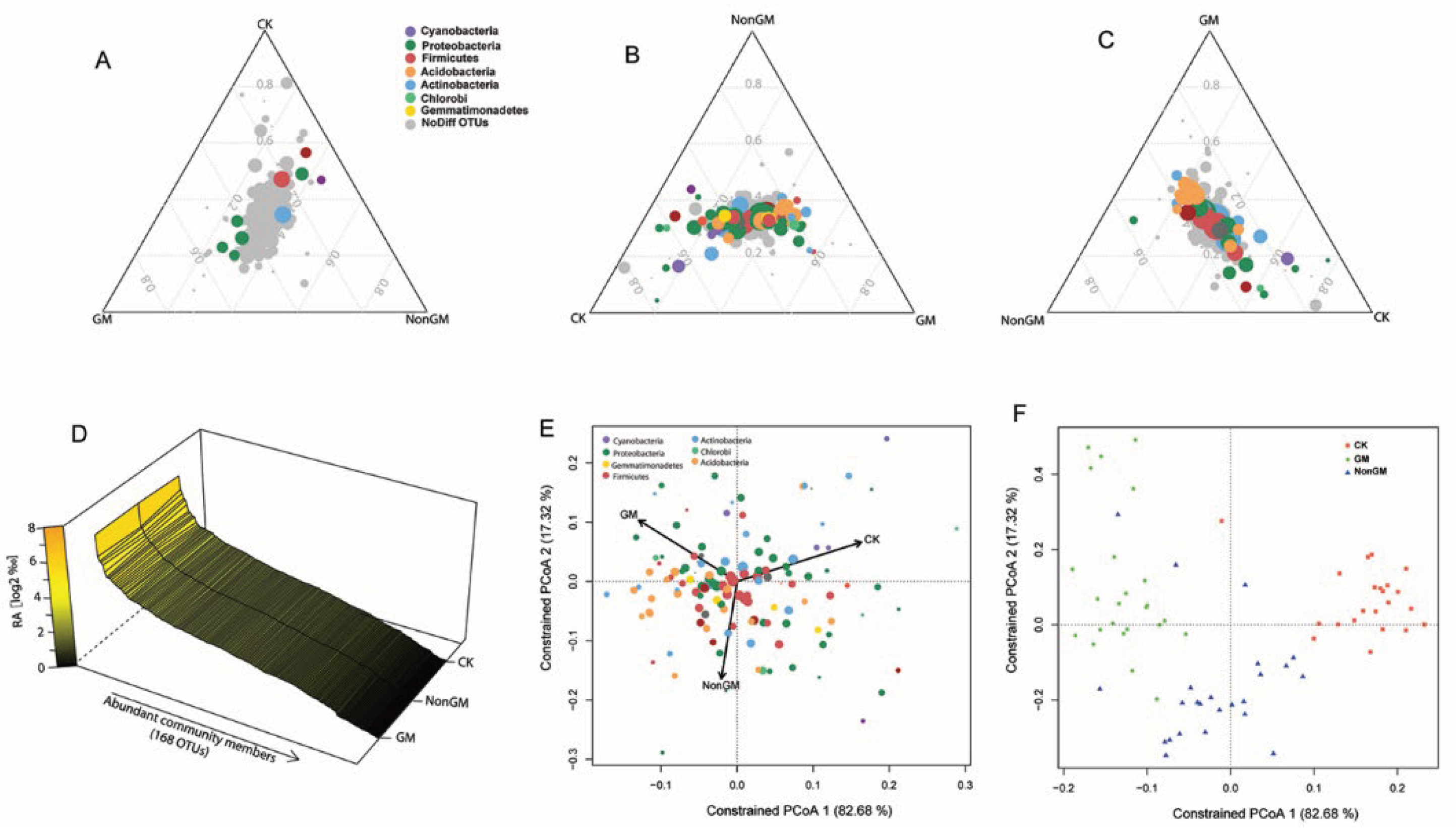
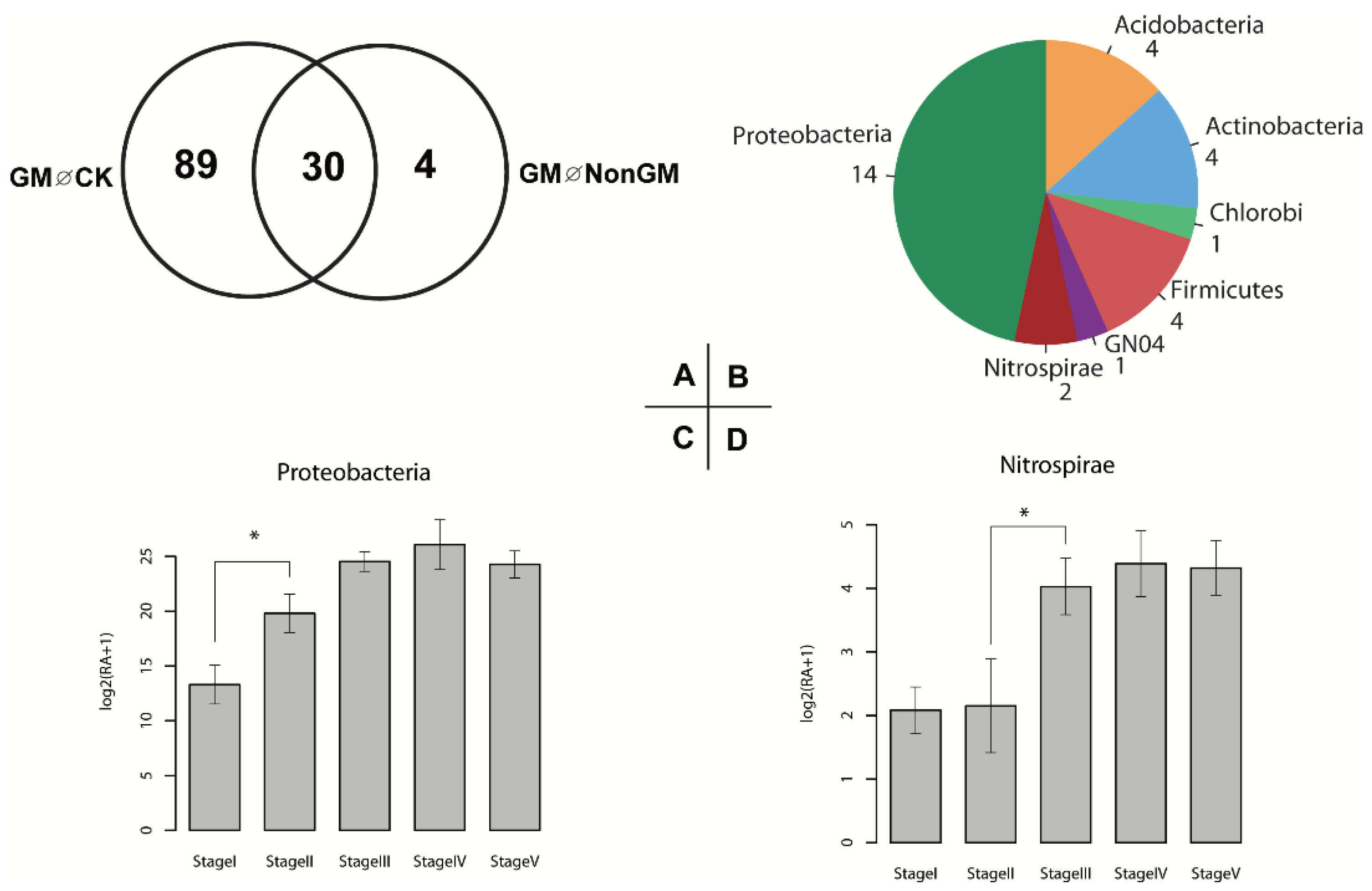
2.5. Identification of the Rice-Enriched Microbiota
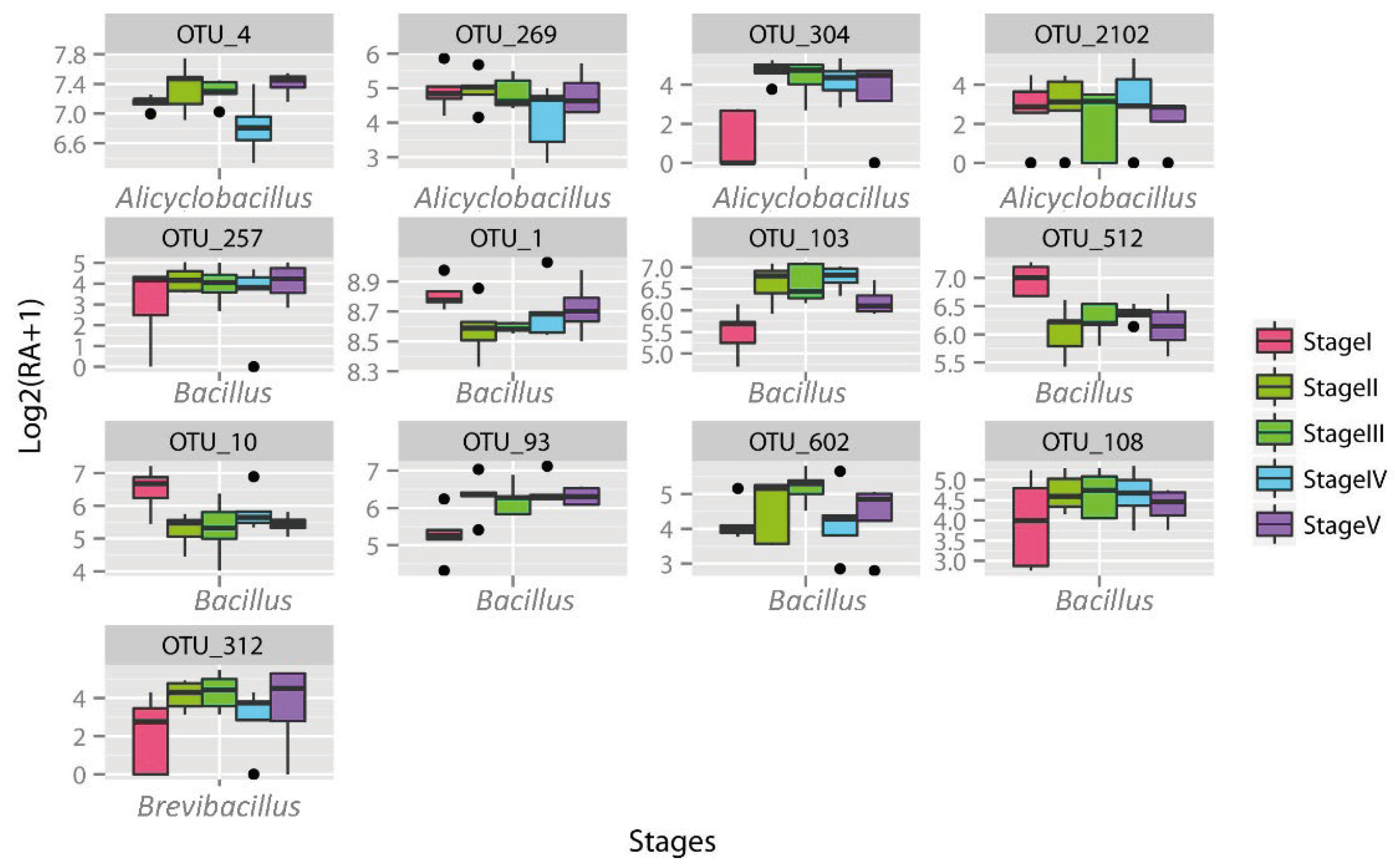
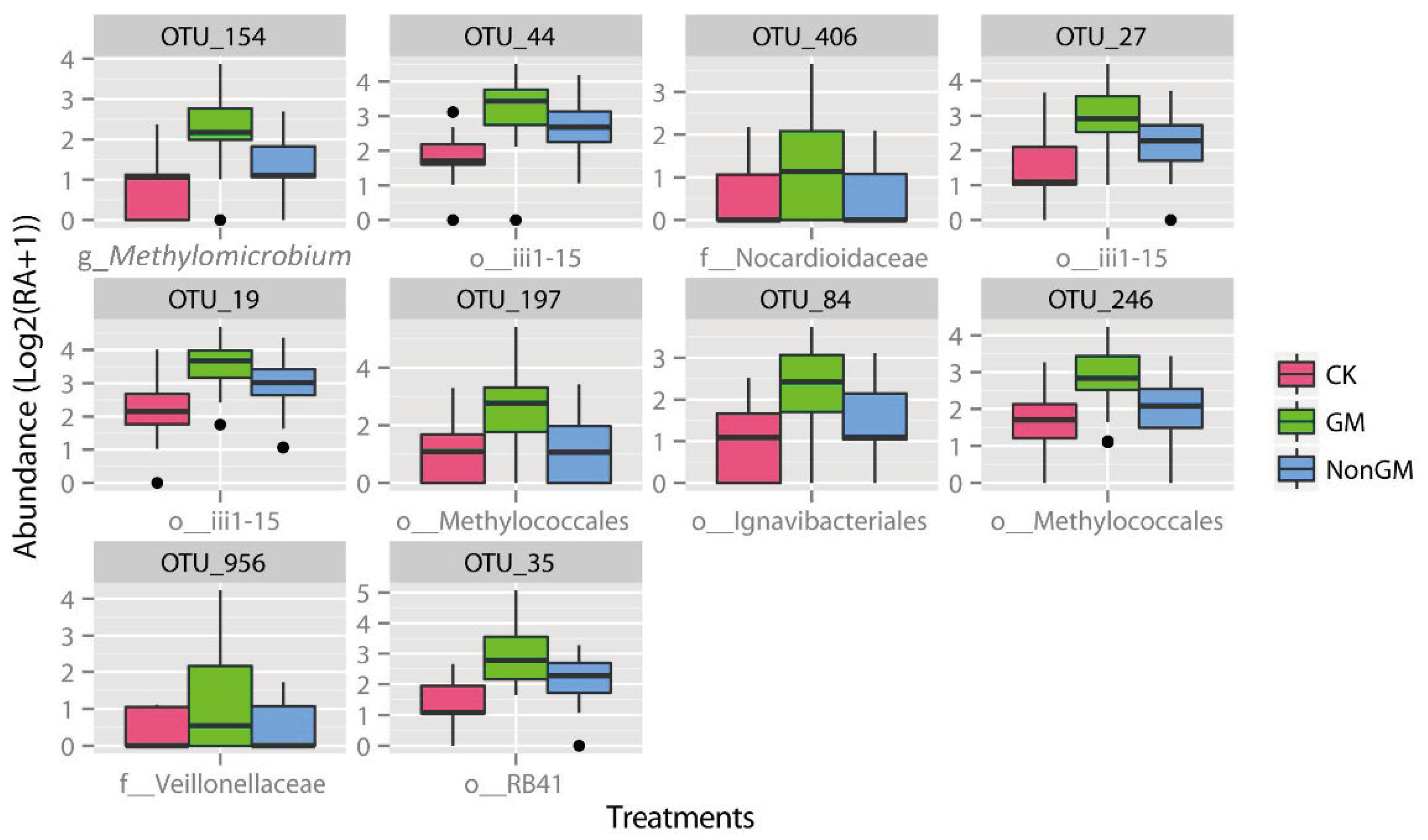
2.6. Defining and Characterizing GM Rice Enriched Microbiota
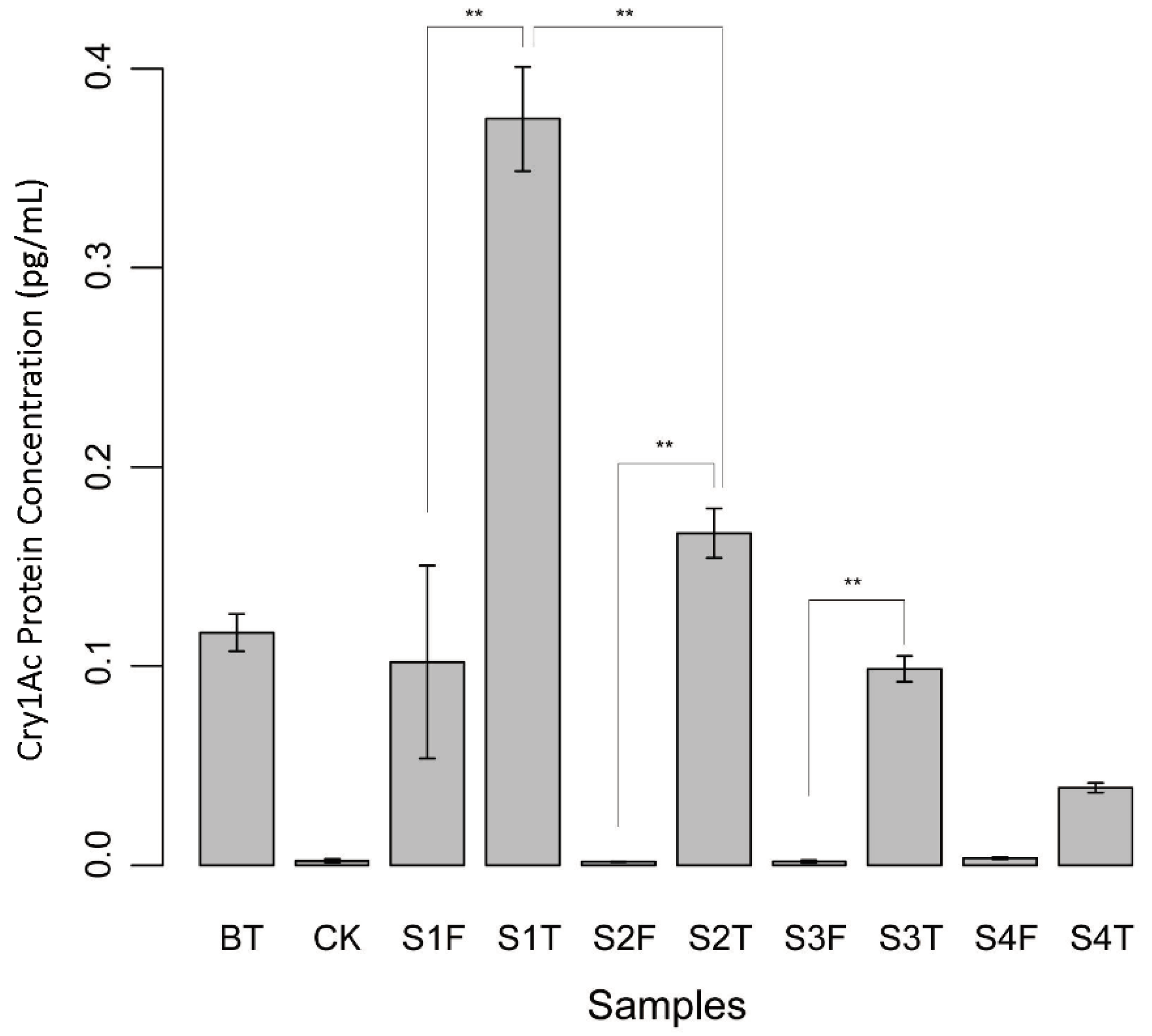
2.7. ELISA Test of cry1Ac Protein Level
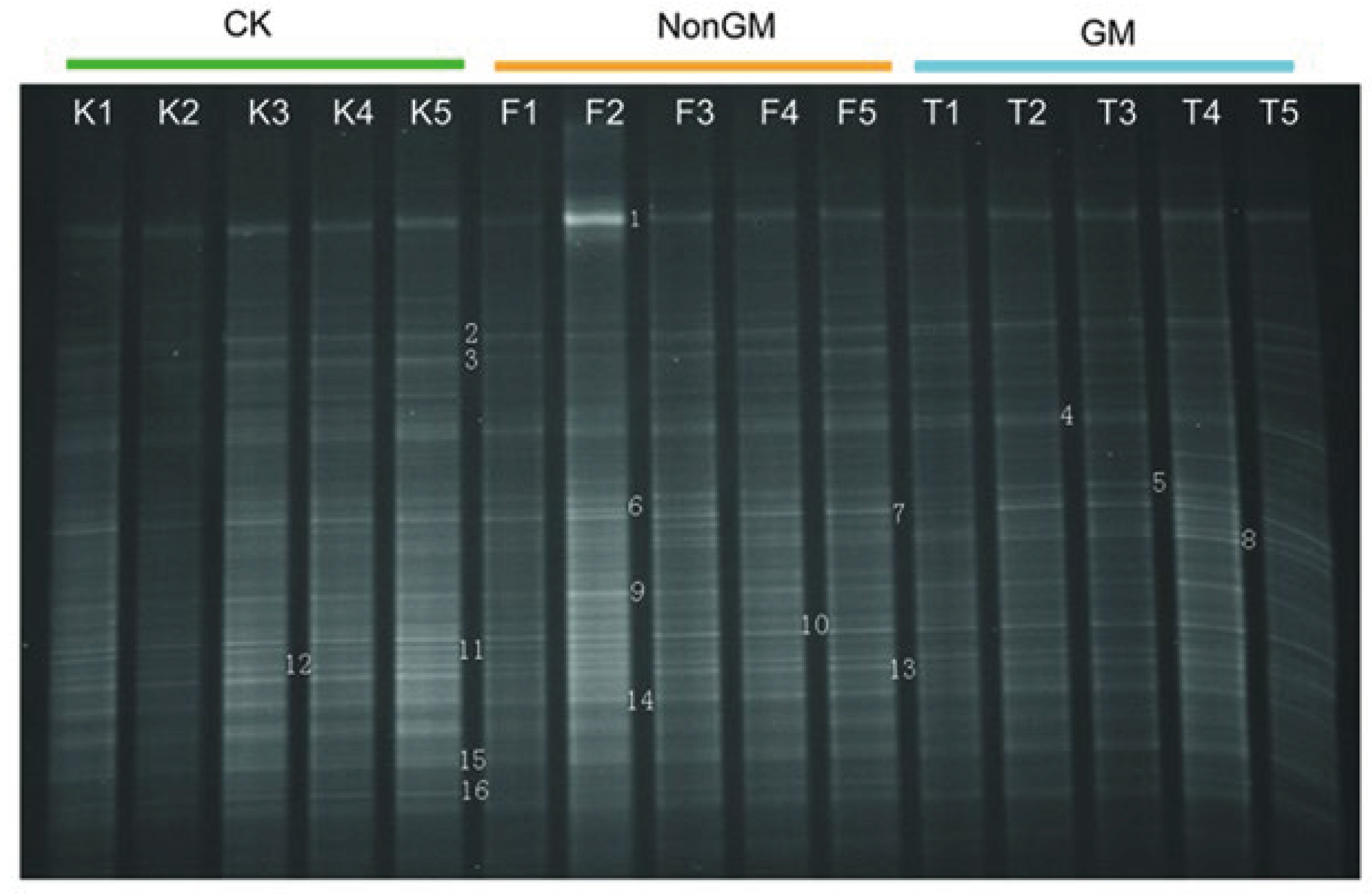
2.8. DDGE Analysis of Bacterial Communities
2.9. Comparison of Soil Properties between GM and NonGM Treatments
3. Discussion
3.1. Rice Planting Tied More Strongly to Rhizospheric Microbiota Communities than Rice Variety
3.2. Transgenic Bt Rice Has a Stronger Impact on Rhizosphere Microbiota Communities, Particularly in the Early Developmental Stages of Rice
3.3. Huahui No. 1 Transgenic Bt Rice Shows a Predominant Short-Term Impact on Bacillaceae Communities in Rice Early Developmental Stages
4. Materials and Methods
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lakshmanan, V.; Selvaraj, G.; Bais, H.P. Functional soil microbiome: belowground solutions to an aboveground problem. Plant Physiology 2014, 166, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloepper, J.W.; Ryu, C.M.; Zhang, S. Induced systemic resistance and promotion of plant growth by Bacillus spp. Phytopathology 2004, 94, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.; Sabri, A.; Ljung, K.; Hasnain, S. Auxin production by plant associated bacteria: impact on endogenous IAA content and growth of Triticum aestivum L. Letters in applied microbiology 2009, 48, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, P.K.; Mishra, S.; Selvakumar, G.; Kundu, S.; Shankar Gupta, H. Enhanced soybean (Glycine max L.) plant growth and nodulation by Bradyrhizobium japonicum-SB1 in presence of Bacillus thuringiensis-KR1. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica Section B-Soil and Plant Science 2009, 59, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Berendsen, R.L.; Pieterse, C.M.; Bakker, P.A. The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends in Plant Science 2012, 17, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaparro, J.M.; Badri, D.V.; Vivanco, J.M. Rhizosphere microbiome assemblage is affected by plant development. The ISME Journal 2014, 8, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiffer, J.A.; Spor, A.; Koren, O.; Jin, Z.; Tringe, S.G.; Dangl, J.L.; Buckler, E.S.; Ley, R.E. Diversity and heritability of the maize rhizosphere microbiome under field conditions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2013, 110, 6548–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armougom, F.; Raoult, D. Exploring microbial diversity using 16S rRNA high-throughput methods. Journal of Computer Science & Systems Biology 2012, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bulgarelli, D.; Rott, M.; Schlaeppi, K.; van Themaat, E.V.L.; Ahmadinejad, N.; Assenza, F.; Rauf, P.; Huettel, B.; Reinhardt, R.; Schmelzer, E. Revealing structure and assembly cues for Arabidopsis root-inhabiting bacterial microbiota. Nature 2012, 488, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, D.S.; Lebeis, S.L.; Paredes, S.H.; Yourstone, S.; Gehring, J.; Malfatti, S.; Tremblay, J.; Engelbrektson, A.; Kunin, V.; Del Rio, T.G. Defining the core Arabidopsis thaliana root microbiome. Nature 2012, 488, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaeppi, K.; Dombrowski, N.; Oter, R.G.; van Themaat, E.V.L.; Schulze-Lefert, P. Quantitative divergence of the bacterial root microbiota in Arabidopsis thaliana relatives. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2014, 111, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, C. Global Status of Commercialized Biotech/GM Crops. ISAAA Brief ISAAA: Ithaca, NY. 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Eizaguirre, M.; Albajes, R.; Lopez, C.; Eras, J.; Lumbierres, B.; Pons, X. Six years after the commercial introduction of Bt maize in Spain: field evaluation, impact and future prospects. Transgenic Research 2006, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- High, S.M.; Cohen, M.B.; Shu, Q.Y.; Altosaar, I. Achieving successful deployment of Bt rice. Trends in Plant Science 2004, 9, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stone, R. China plans $3.5 billion GM crops initiative. Science 2008, 321, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, J.; Ling, F.; You, A. Application and Development of Bt Insect Resistance Genes in Rice Breeding. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C. The first approved transgenic rice in China. GM Crops 2010, 1, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, C.C.; Aguda, R.M.; Cohen, M.B. Effect of rice lines transformed with Bacillus thuringiensis toxin genes on the brown planthopper and its predator Cyrtorhinus lividipennis. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata 2002, 102, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devare, M.; Londoño-R, L.; Thies, J. Neither transgenic Bt maize (MON863) nor tefluthrin insecticide adversely affect soil microbial activity or biomass: a 3-year field analysis. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2007, 39, 2038–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Lu, H.H.; Wu, W.; Wei, Q.K.; Chen, Y.X.; Thies, J.E. Transgenic Bt rice does not affect enzyme activities and microbial composition in the rhizosphere during crop development. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2008, 40, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.X.; Liu, W.; Lu, H.H.; Chen, Y.X.; Devare, M.; Thies, J. Use of 13C labeling to assess carbon partitioning in transgenic and nontransgenic (parental) rice and their rhizosphere soil microbial communities. FEMS microbiology ecology 2009, 67, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wu, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Devare, M.; Thies, J.E. Decomposition of Bt transgenic rice residues and response of soil microbial community in rapeseed-rice cropping system. Plant and Soil 2010, 336, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Xu, T.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, W. Changes in rice allelopathy and rhizosphere microflora by inhibiting rice phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene expression. Journal of Chemical Ecology 2013, 39, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendelsohn, M.; Kough, J.; Vaituzis, Z.; Matthews, K. Are Bt crops safe? Nature Biotechnology 2003, 21, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faith, D.P. Conservation evaluation and phylogenetic diversity. Biological Conservation 1992, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Willis, T.J. Canonical analysis of principal coordinates: a useful method of constrained ordination for ecology. Ecology 2003, 84, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofek, M.; Voronov-Goldman, M.; Hadar, Y.; Minz, D. Host signature effect on plant root-associated microbiomes revealed through analyses of resident vs. active communities. Environmental Microbiology 2014, 16, 2157–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siciliano, S.; Theoret, C.; De Freitas, J.; Hucl, P.; Germida, J. Differences in the microbial communities associated with the roots of different cultivars of canola and wheat. Canadian Journal of Microbiology 1998, 44, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lottmann, J.; Heuer, H.; de Vries, J.; Mahn, A.; Düring, K.; Wackernagel, W.; Smalla, K.; Berg, G. Establishment of introduced antagonistic bacteria in the rhizosphere of transgenic potatoes and their effect on the bacterial community. FEMS microbiology ecology 2000, 33, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nature Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shade, A.; Handelsman, J. Beyond the Venn diagram: the hunt for a core microbiome. Environmental Microbiology 2012, 14, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguiar-Pulido, V.; Huang, W.; Suarez-Ulloa, V.; Cickovski, T.; Mathee, K.; Narasimhan, G. Metagenomics, metatranscriptomics, and metabolomics approaches for microbiome analysis: supplementary issue: bioinformatics methods and applications for big metagenomics data. Evolutionary Bioinformatics 2016, 12, EBO. S36436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




