3.4. Antidiabetic Effect of Extract Fractions in Yeast Cell
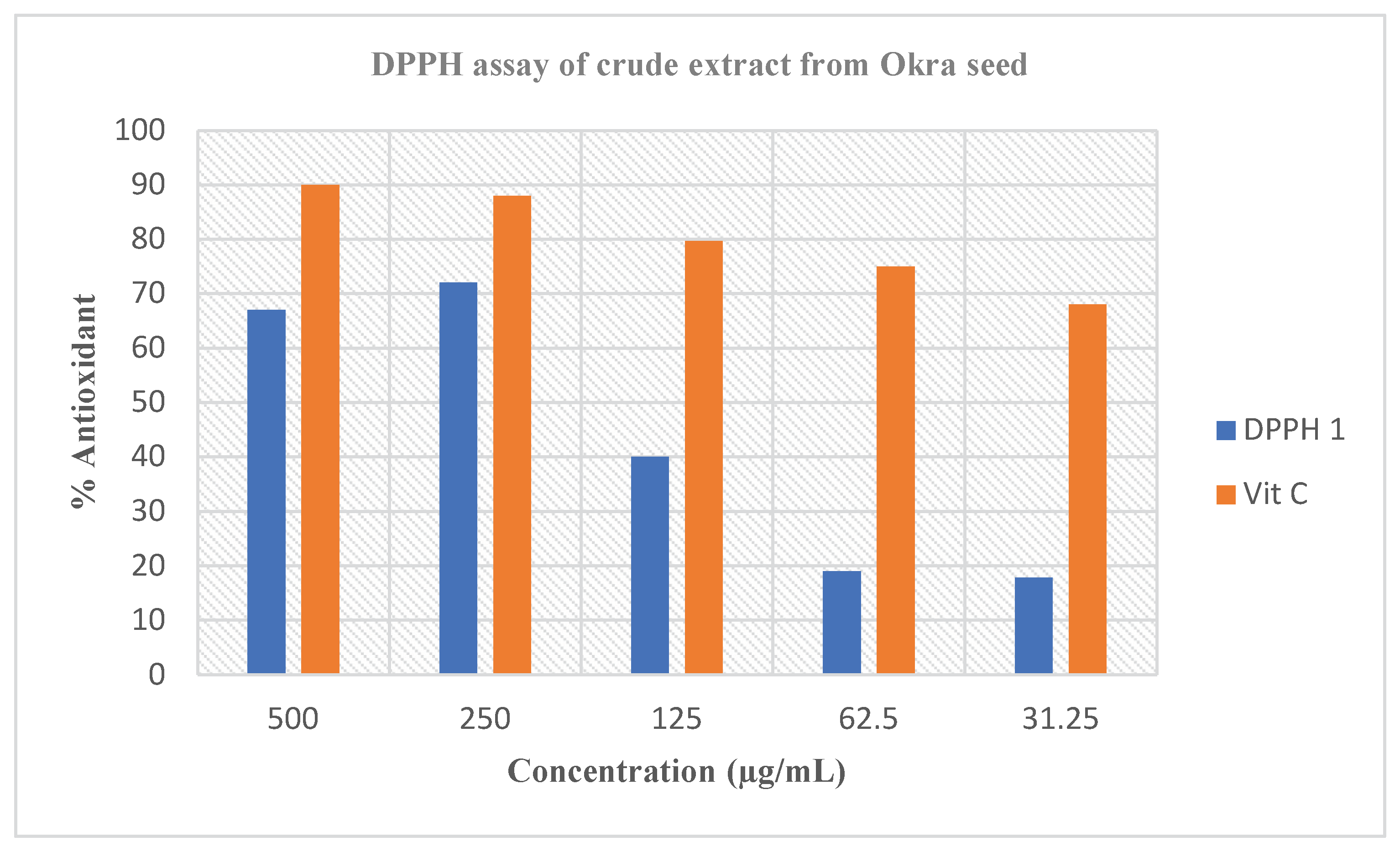
DPPH is the appropriate free radical compound typically utilized for analyzing free-radical scavenging actions of numerous forms of samples. The DPPH radical scavenging analysis generally relies on the ability of a compound to give hydrogen atoms; therefore, steadying the free radicals which in turn discontinue oxidation chemical mixtures well-known in lively organisms [
27]. However, the DPPH radical prevents imitation of any biological combinations (and therefore has a comparatively slight significance in lively organisms), though, DPPH test is typically replicated as an indicator of the ability of plant extracts to quench free radicals, as well as their hydrogen atom or electron giving capacity, in the nonappearance of any enzymatic exploit [
28]. The greatest beneficial purpose for the utilization of DPPH in evaluating in vitro antioxidant actions of medications and extracts from plant due to its greater strength than hydroxyl and superoxide radicals [
29]. Therefore, the antioxidant actions showed by the extracts via DPPH scavenging capabilities
Figure 1 could be said to be largely owing to their hydrogen atom or electron contribution capacity. The hydrogen-contributing ability, likewise, may be link to the existence of phenolic mixtures in the extracts as these lesser products have been proven to retain antioxidant activities [
30]. Hence, it is rational to deduce that the higher activity of the crude extract of
Abelmoschus esculentus L. extract could be as a consequence of greater concentrations of phenolics in the crude extract. The electron-contributing capacity of antioxidants in the crude extracts is usually replicated by the capacity of that particular antioxidants to decrease iron (Fe) in the oxidation form of iron 3+ (Fe
3+) to iron 2+ (Fe
2+). Thus, the greater the action of the antioxidants shows the greater electron-contributing capacity (decreasing capacity) [
31]. Thus, the important actions of the extracts propose that they remained capable to decrease iron 3+ (Fe3
+) to iron 2+ (Fe2+), demonstrating their electron-contributing capacity, which evitable proposes the prospect of consuming the extracts in preventing oxidation of chemical mixtures proven in lively cells. The results gotten for the
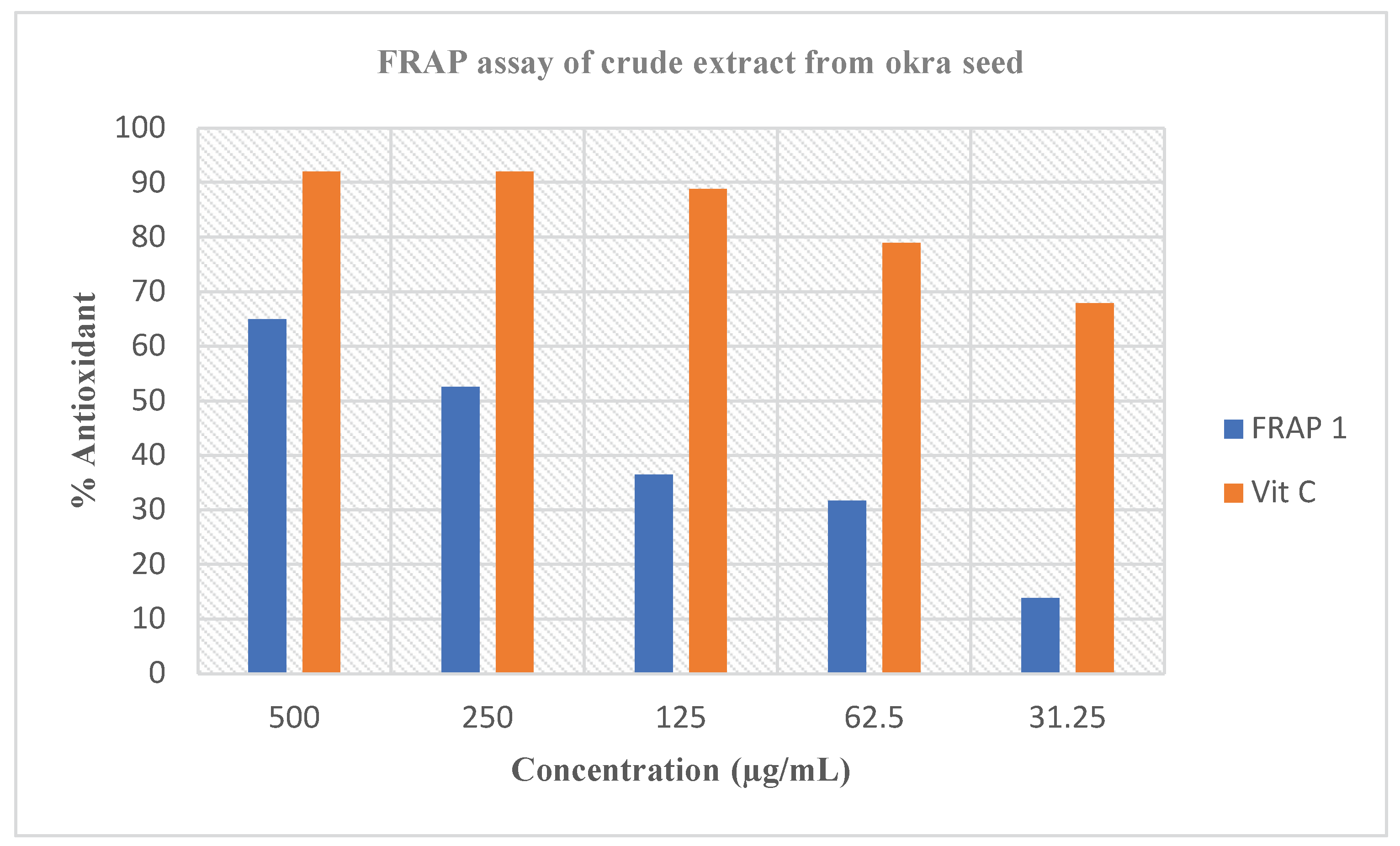
Abelmoschus esculentus L. extract and the percentage (%) inhibition gotten in
Figure 3 remained greater. The similar aims stated in the DPPH radical scavenging assay could likewise be liable for the changes in this assay. Though,
Abelmoschus esculentus L. extract offered important ferric decreasing power
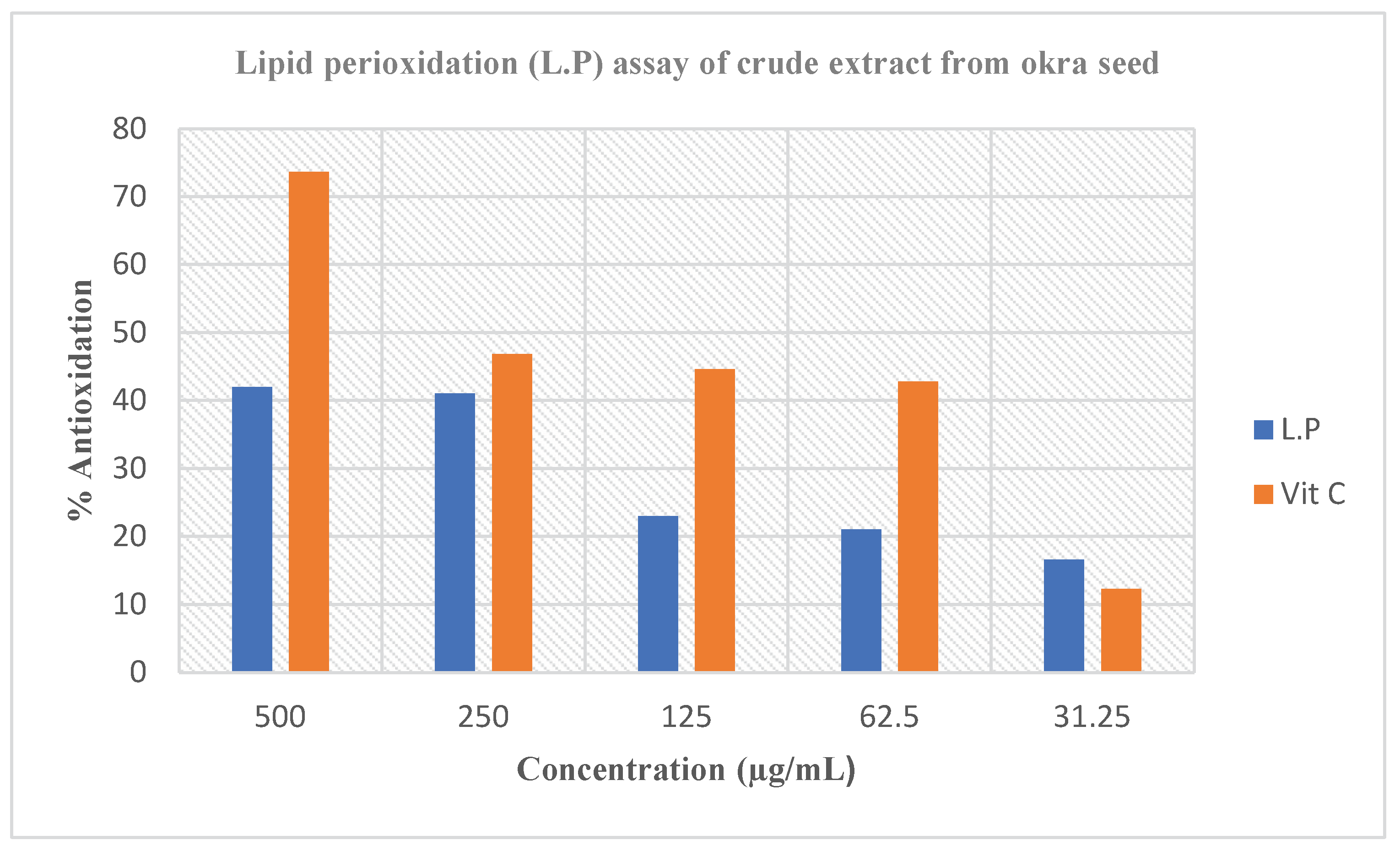
Figure 2. Lipid peroxidation has remained defined as an oxidative analysis of lipids, a procedure in which free radical’s theoretical electrons from cell membrane lipids (this typically touches polyunsaturated fatty acids owing to the existence of dual bonds). The method of lipid peroxidation has been suggested to take place via a free radical chain response, which has been associated with the destruction of cell by a system of opening membrane that separate the cell from external settings [
32]. The destruction initiated has been recognized to impact the ailment disorders of several persons, such ailments as cardiovascular ailments, cancer, and diabetes [
33]. Thus, the capacity of the extracts to significantly prevent lipid peroxidation of the egg homogenate proposes that they remained capable to quench the activities of the free radicals by preventing the idea of the electrons from cell membrane lipids by the free radicals and thus could do the work of protecting individuals from protracted ailments and other oxidative stress-related ailments.
The results obtained in this study suggest that the crude extracts Abelmoschus esculentus L., possess antioxidant activities and may therefore be used in the treatments and management of oxidative stress-related diseases.
The percentage scavenging antioxidant activity (also referred to as DPPH) of the extract fractions
Table 2 showed decreased scavenging antioxidant ability with decreased extract fraction concentration. The extract fraction OE (59.19%) revealed higher antioxidant percentage activity compared to other fractions partitioned. All of the higher activity was exhibited at the concentration of 500µg/mL; The percentage ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) of the extract fractions
Table 3 shows a decreased FRAP percentage capacity with a decreased extract fraction concentration. Extract fraction OE (93.62%) produced higher FRAP percentage capacity compared to other fractions. Though, the other fractions were also very high at concentrations of 500µg/mL and 250µg/mL respectively.
Also, the percentage inhibitory activity of antioxidants (also referred to as lipid peroxidation) for all extract fraction
Table 4 also showed decreased inhibitory activity with decreased extract fraction concentration. Extract fractions OE (84.59%) and OH (70.54%) gave higher inhibitory ability than other extract fractions. The standard antioxidant was higher than the extract fractions in all concentrations of the antioxidant assays (i.e., DPPH, FRAP, and lipid peroxidation).
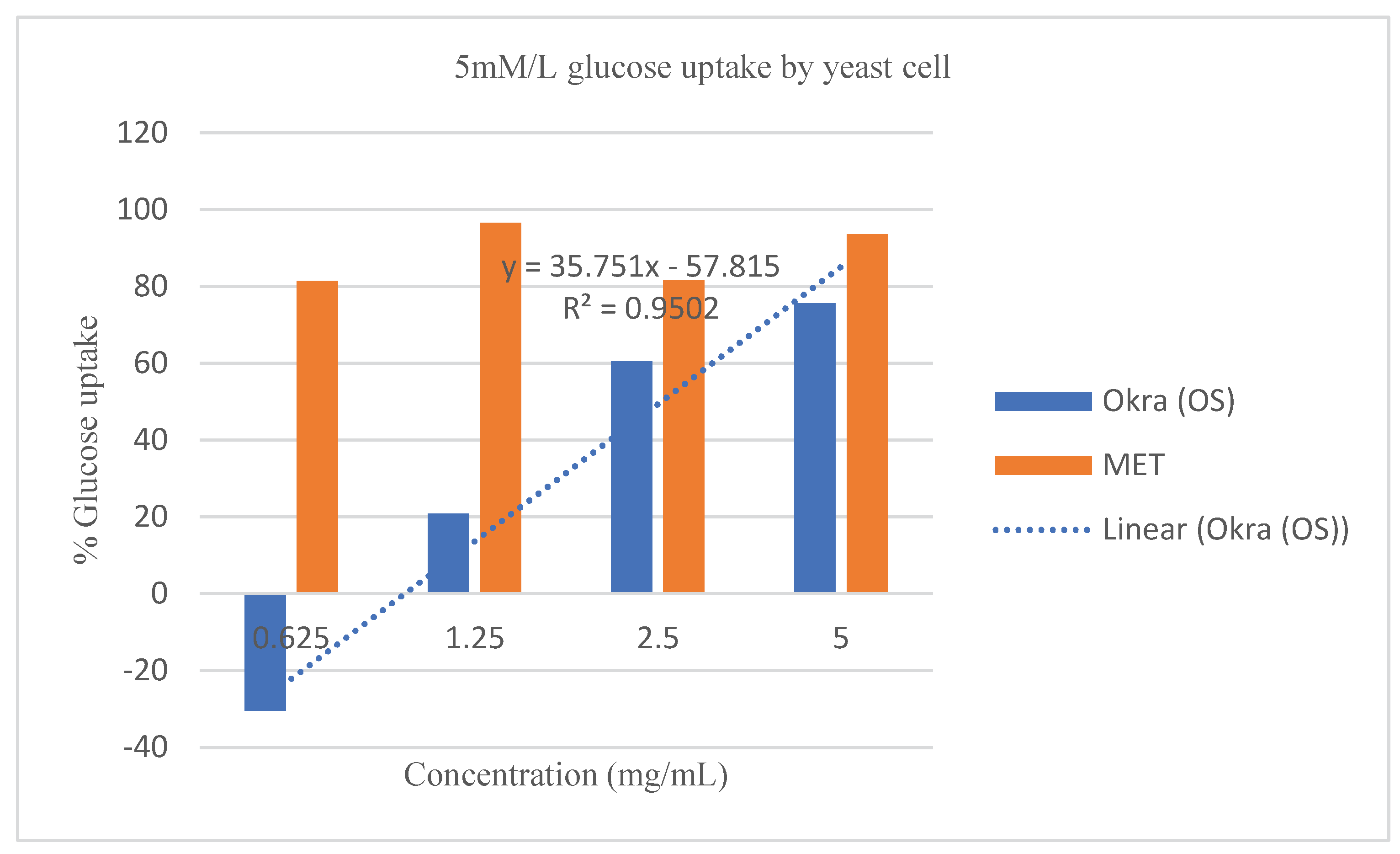
Effect of crude extract of
Abelmoschus esculentus L. on glucose uptake ability by yeast cell. The crude extract of
Abelmoschus esculentus L. stimulated the uptake of glucose through the partially but not entirely permeable membrane of yeast cells
Figure 4,
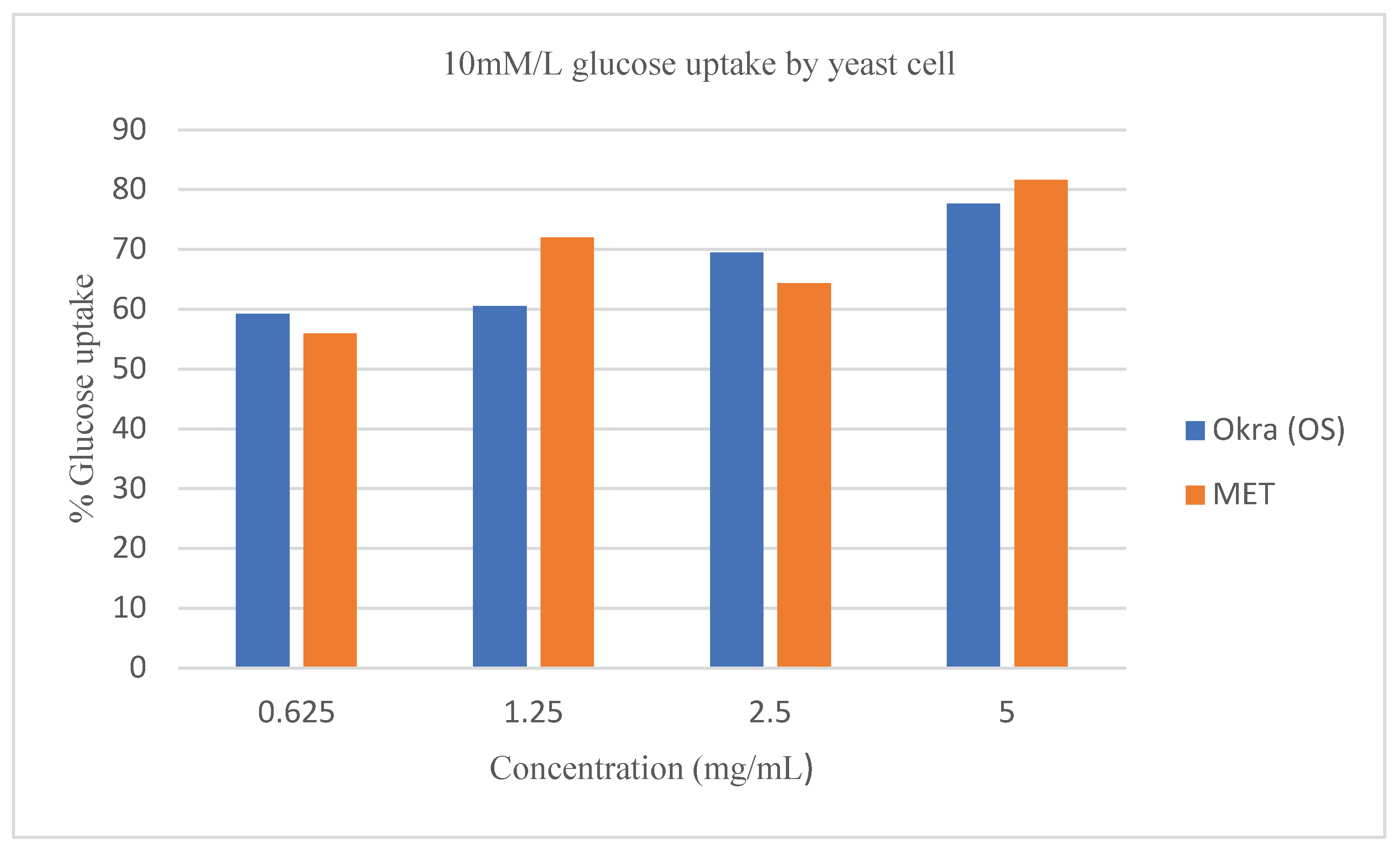
Figure 5, and
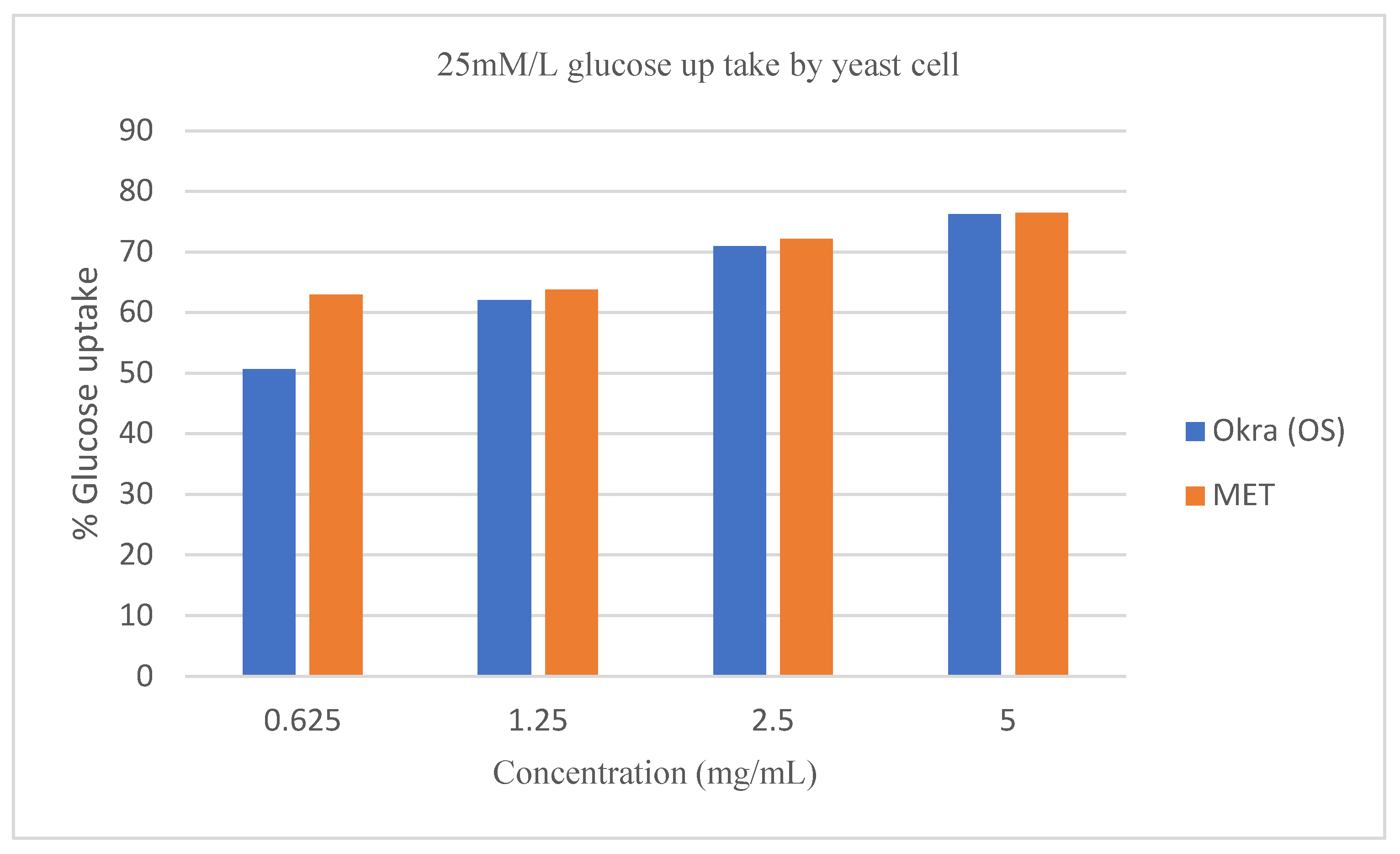
Figure 6 respectively. The glucose uptake at an initial concentration of 5mM/L and 10mM/L by the crude extract of
Abelmoschus esculentus L. was consistent to that of the known standard drug (
Figure 4 and
Figure 5). However, the effect of Metronidazole on glucose uptake by the yeast cell at 25mM/L glucose concentration was at par with the crude extract of
Abelmoschus esculentus L (
Figure 6).
Moreover, at 0.625 mg/mL the linear equations, and R
2 shows that the extract was higher in dose predictability than the standard drug as shown by the equation; y = 35.751x - 57.815, and R² = 0.9502 (95%) for
Abelmoschus esculentus L., while y = 2.1324x + 82.881, and R² = 0.1213 (12.1%) for Metronidazole when 5 mg/mL of crude extract of
Abelmoschus esculentus L was used (
Figure 4). This suggests that increasing the concentration of crude extract of
Abelmoschus esculentus L., increased the potential of yeast cells to take up more glucose from the environment; however, the standard drug; although it showed high glucose uptake capacity, but had a very low drug-dose predictability compared to the extracts as confirmed by the very low R
2 value of 12.1% against the crude extract R
2 value of 92.3% respectively. On the other hand,
Figure 5 and
Figure 6 showed a linear increase in the uptake of glucose by yeast cells with a gradual increase in the concentration of the crude extract. However, an inverse correlation to the molar concentration of glucose was observed, when glucose uptake by yeast cells was compared among 5mM/L, 10mM/L, and 25mM/L for the similar amount of crude extract of
Abelmoschus esculentus L., (
Figure 4,
Figure 5, and
Figure 6).
Remarkably, the fraction OE was higher than the standard drug at a lower extract fraction concentrations of 125µg/mL (79.55 %), 62.5µg/mL (81.58%), 31.25µg/mL (81.65 %) which showed a different trend of increase in percentage glucose uptake with a decrease in extract fraction concentration.