1. Introduction
The blood, a biofluid circulating within our bodies, serves various purposes, such as carrying oxygen and carbon dioxide and supplying essential nutrients to cells and tissues. Additionally, this circulating blood provides valuable insights into coagulation parameters, hypercoagulability, and changes in fibrinolysis. Blood coagulation is a process in which the circulating blood becomes a solid clot to arrest the bleeding. It is a crucial process initiated in response to an injury, whether internal or external to the body. Nonetheless, disruption to this normal coagulation process, such as hypercoagulation, can cause excessive blood clot formation, which leads to blood vessel blockage, causing stroke [1, 2]. The coagulation status can severely alter and induce severe complications in patients who have cancer, infectious diseases, trauma, diabetes, and retinal vein occlusion [3-12]. Furthermore, patients must take defined doses of anticoagulants to regulate blood clots in some pathological conditions. Therefore, it is critical to monitor blood coagulation to ensure blood is not clotting too rapidly or slowly.
Given the clinical importance of anticoagulant sensing, this review explores the research progress in this area. The working principle of various detection and quantification techniques for blood coagulation has been explained in the literature [13-15]. However, this review focuses on recent advances in coagulation monitoring systems exclusively based on electrochemical methods. In this review, we discussed (i) different steps in the blood clot process, such as platelet activation, initiation of the coagulation cascade to form blood clots and breakdown of blood clots, (ii) an introduction to traditional anticoagulants and the new generation of oral anticoagulants, (iii) clot-based laboratory analysis used for coagulation monitoring, (iv) anticoagulant assays purely based on electrochemical detection methods which use thrombin activity or direct thrombin measurements, (v) electrochemical sensors using direct measurement of anticoagulants depending on redox behaviour of the drug or redox probes utilising electrode modification without the help of coagulant factors such as thrombin or factor Xa.
2. Overview of haemostasis
Haemostasis is a critical physiological function responsible for preserving the blood flow under normal conditions and stopping blood loss after vascular damage [
16]. This process is dependent on both cellular and plasma components. Typical haemostasis involves blocking the damaged blood vessel by platelet adhesion at the site of the injury, forming a fibrin clot to stabilise the blood loss, and finally, clot dissolution [
17]. Moreover, all these processes occur within a flow environment and are managed and governed by factors released from the adjacent endothelium. Therefore, it is essential to understand the different steps involved in haemostasis to design an assay that measures blood coagulation status.
2.1. Platelets
Platelets are essential to circulating blood and play an active role in haemostasis. Platelets are 2-4 µm in diameter and produced by a process called thrombopoiesis in the bone from megakaryocytes. Once formed in human blood, platelets remain circulating for approximately 7-10 days [
18]. In an external stimulus, such as vascular injury to the blood vessels, platelets block the damaged blood vessel to prevent blood loss. This process is achieved by significant changes to the shape of the platelets (platelet activation), attachment to the subendothelial wall and other platelets, and release of intracellular granules [
19]. The initial phase of haemostasis involves the aggregation of platelets at the site of vascular damage under high blood flow conditions [
20]. To accomplish this, platelets cling to collagen and plasma von Willebrand factor (vWf) due to the damaged endothelial cell wall. The interaction of vWf and glycoproteins (GPIb-IX-V) occurs under high shear conditions and is believed to be a predominant receptor-ligand interaction that initiates platelet adhesion [
21]. At the same time, collagen attachment occurs via GPVI and α2β1 integrin complex, further delivering activation signals to platelets. Stable platelet adhesion is achieved through α5β1 to fibronectin or collagen binding at the vessel wall [
20]. After the substantial accumulation of platelets, the delivery of adenosine diphosphate and thromboxane A2 attract more platelets to the site of vascular damage. Such a phenomenon promotes platelet aggregation, causing a secondary accumulation [
18]. Platelets also cause a sequence of enzymatic reactions known as the coagulation cascade [
22]. When platelet activation occurs, the surface membrane becomes charged, and the subsequent exposure of inner leaflets further helps negatively charged phospholipids in the membrane create a conducive platform on which the coagulation cascade can occur when calcium ions are present [
23].
2.2. Coagulation cascade
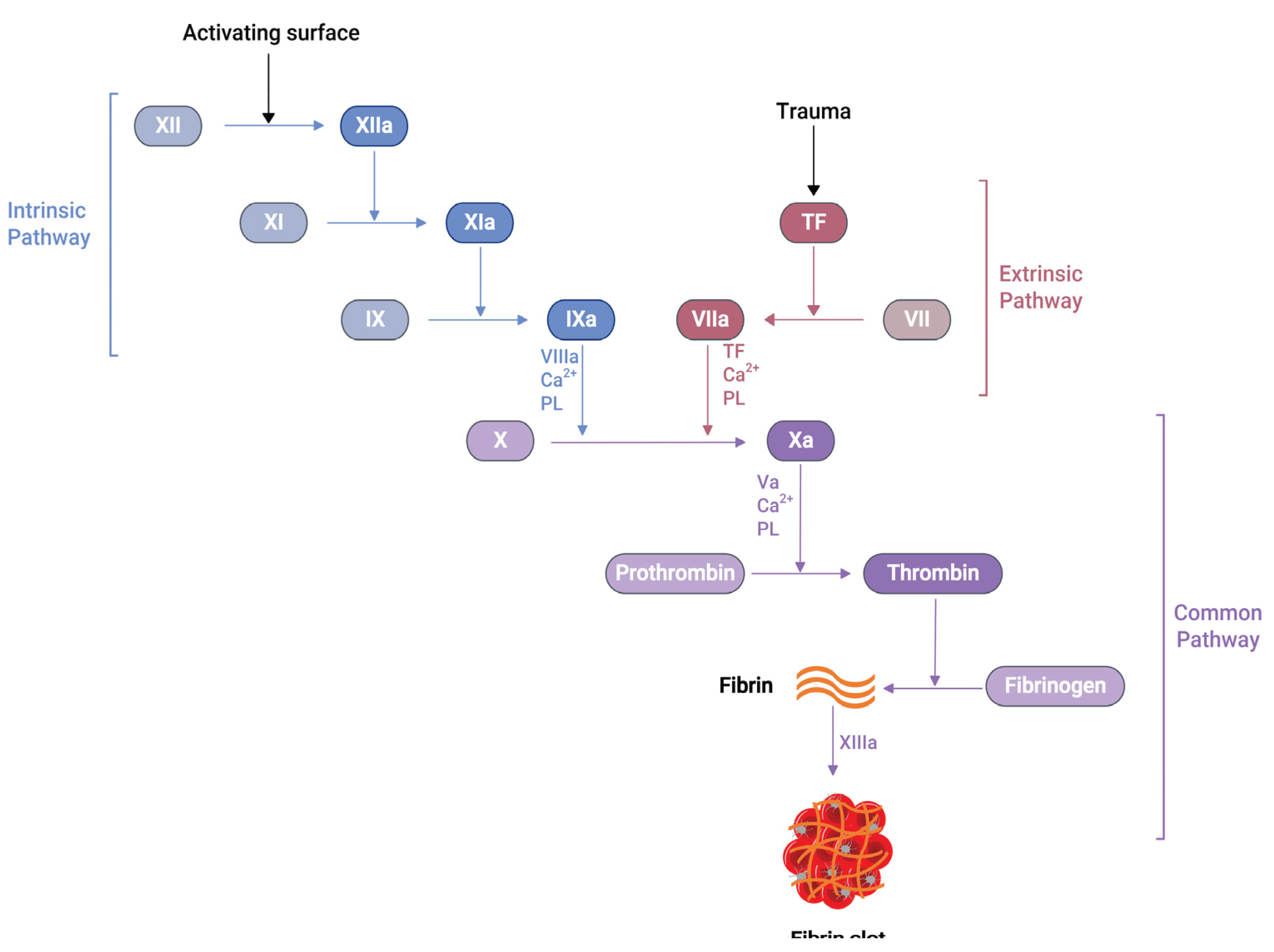
Several soluble proteins in the blood plasma work together in a cascade of enzymatic reactions (
Figure 1), culminating in the production of fibrin polymers and stabilising the blood clot [
24]. When an injury occurs at the blood vessel wall, tissue factor (TF) gets exposed alongside collagen in the subendothelial surfaces. Then, the exposed TF comes into contact with Factor VIIa (FVIIa) in the plasma to produce TF:FVIIa composite, also called extrinsic tenase [
25]. This composite is the initial point in the coagulation cascade, referred to as an extrinsic or tissue factor pathway. This pathway ultimately transforms factor X (FX) to factor Xa (FXa) in vivo [
25].
Similarly, another type of pathway exists in the coagulation cascade, known as the intrinsic or contact pathway (
Figure 1). When damaged cell surfaces are in contact with high molecular weight plasma proteins, such as kininogen and kallikrein, the activation of factor XII (FXII) to factor XIIa (FXIIa) takes place, followed by further downstream conversions of factor XI (FXI) to factor XIa (FXIa), and factor IX (FIX) to factor IXa (FIXa) [
24]. The activated FIXa forms a complex with factor VIIIa (FVIIIa) to produce intrinsic tenase complex FVIIIa:FIXa, which activates FX to FXa [
25]. Independent of the extrinsic or intrinsic pathway, once FXa is released in the coagulation cascade, it forms a 1:1 ratio complex, prothrombinase, with factor Va (FVa), calcium ions and phospholipid. Prothrombinase converts prothrombin to thrombin, resulting in thrombin-mediated cleavage of fibrinogen to fibrin. The prothrombinase production and subsequent thrombin and fibrin creation steps are described as the common pathway in the coagulation cascade (
Figure 1) [
25]. The final product of this common pathway (i.e., fibrin) plays a crucial role in creating a polymer fibrin gel. Then, factor XIIIa (FXIIIa), activated by thrombin, covalently crosslinks loosely bound fibrin gel, forming insoluble fibrin clots with platelets [25, 26].
2.3. Thrombosis
Thrombosis is a phenomenon in which blood clots occur inside the blood vessel walls, caused by the action of the coagulation cascade in response to pathological changes [
24]. This excessive build-up of the blood clot inside the lumen of a blood vessel can trigger acute complications like deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and myocardial infarctions, leading to potentially life-threatening conditions [27, 28]. The process of platelet accumulation and thrombin generation through the coagulation cascade are functions of a healthy person. However, excessive unwanted clots can cause adverse effects. As a result, a down-regulating mechanism controls disproportionate platelet aggregation and thrombin generation, which is in balance with the normal haemostasis process. Naturally occurring anticoagulants, such as antithrombin III, protein C, and heparin cofactor II, are released when coagulation factors are activated [29, 30]. Similarly, prostaglandin-I2 inhibits platelet activation to balance the prothrombic environment in healthy blood vessels [31].
Furthermore, once fibrin clots form at the site of the vessel injury, a counteracting fibrinolytic mechanism also exists to dissolve fibrin clots. When urokinase or tissue-type plasminogen activator interacts with plasminogen, it initiates the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin. This plasmin subsequently dissolves fibrin clots and produces fibrin degradation products known as D-dimer [29, 32].
3. Drugs used in anticoagulation therapy
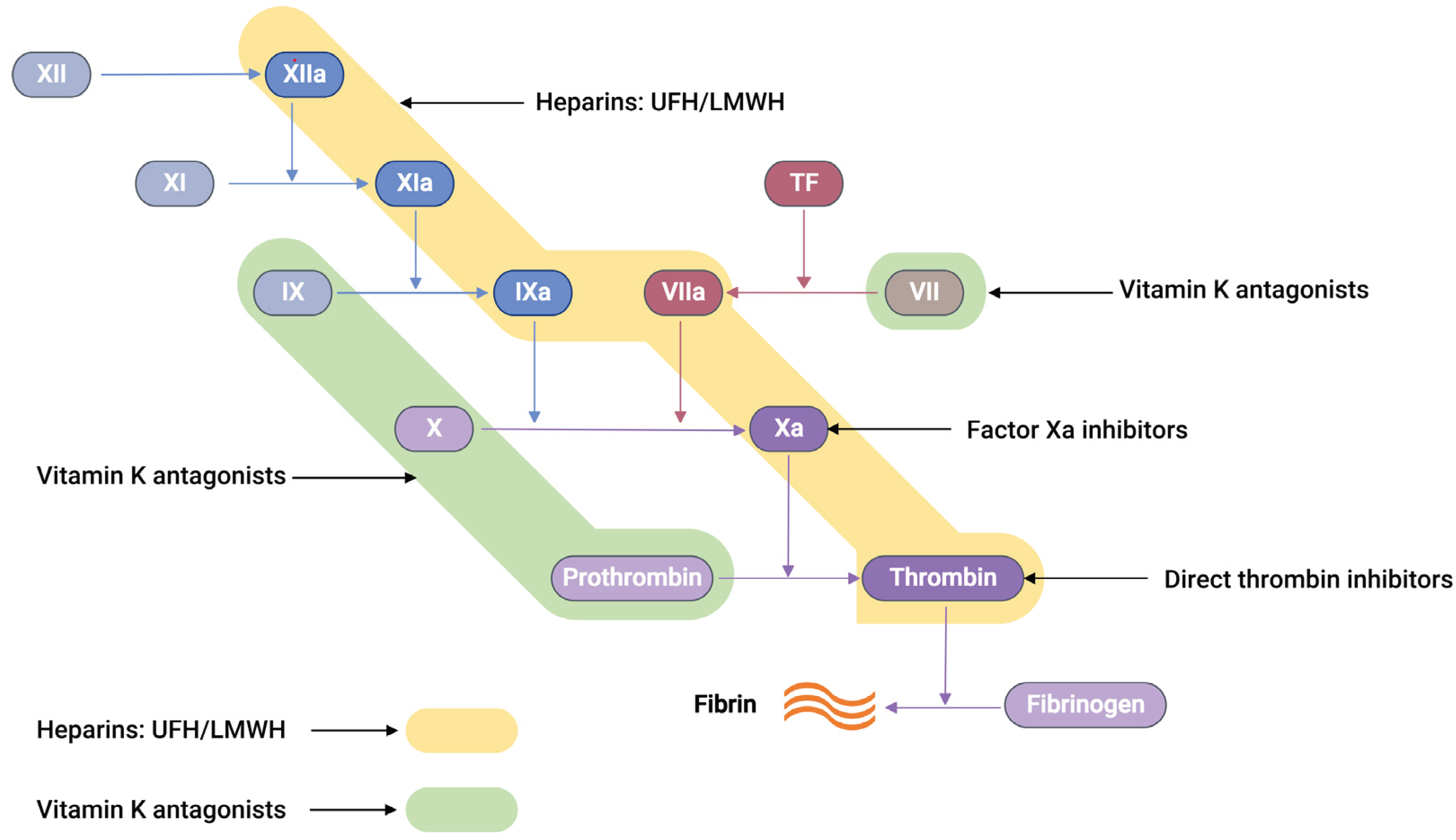
The commercially available anticoagulants work by either directly or indirectly modulating the action of various proteins participating in the coagulation cascade system, thereby controlling blood coagulation (
Figure 2).
Unfractionated heparin, UFH, an anticoagulant drug with an average molecular weight of 15 kDa, is generally extracted and purified from pig intestines [33]. UFH works on antithrombin III (AT-III), a naturally occurring glycoprotein that inhibits several clotting factors such as thrombin, Factor Xa, TF-VIIa, Factor IXa, and Factor XIa to be active. Conformational change at the reactive arginine centre of AT-III induced by heparin interaction converts AT-III from a slow-acting inhibitor to a fast-acting inhibitor [34]. It was observed that the glucosamine unit and the pentasaccharide sequence are responsible for the AT-III binding and subsequent activation. When UFH binds to AT-III, it produces a heparin-AT-III complex capable of inhibiting coagulation factors, preferably thrombin and FXa [34]. In between thrombin and FXa, thrombin has a tenfold greater sensitivity to inhibition than FXa [35]. UFH, thrombin, and AT-III must form a ternary complex for thrombin inhibition to work. However, FXa inhibition only requires UFH and AT-III to create a binary complex.
Low molecular weight heparin (LMWH), a subclass of heparin (MW = 3 – 6.5 kDa), is prepared from the fractionation or chemical depolymerisation of UFH [37]. Consequently, LMWH contains a smaller saccharide chain (typically <18 units), making them predominantly bind to AT-III. This gives the LMWH-AT-III complex greater specificity to FXa inhibition than thrombin inhibition [35].
Vitamin K antagonists (VKAs), such as warfarin, block Vitamin K-epoxide reductase, an enzyme essential to restore vitamin K-epoxide to its active reduced form [38]. This blocking interferes with the activation of coagulation factors such as VII, IX, X, prothrombin, and anti-clotting proteins C and S, effectively producing an anticoagulation effect [38, 39].
Recently, a new class of anticoagulation drugs called direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) have been introduced to replace traditional anticoagulants. These DOACs have several advantages over warfarin. These advantages include a broad therapeutic window, predictable pharmacological effects, minimal interactions with other medications, and prevent the need for regular laboratory monitoring [40, 41]. DOACs are classified into two categories based on their target coagulation factors (
Figure 2). The first category encompasses direct thrombin inhibitors. These inhibitors function by hindering the activity of thrombin, thereby preventing the conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin. The second category comprises FXa inhibitors. These agents specifically inhibit FXa, effectively controlling the conversion of prothrombin into thrombin. Consequently, the intake of DOACs plays a pivotal role in the regulation of clot formation, maintaining the balance within the coagulation cascade.
4. Laboratory testing of coagulation:
The primary aim of laboratory assays in haemostasis is to identify dysfunctions promptly and precisely in the complex coagulation cascade. As a result, a standardised sequence of tests is typically employed for most patients presenting coagulopathies and those under hospital care. Thus, assays involving various coagulation factors are essential for the surveillance of coagulation processes. These tests play a pivotal role in detecting bleeding disorders and in assessing the efficacy of anticoagulant therapies.
The activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT or PTT), Prothrombin time (PT), and activated clotting time (ACT) are some of the clot-based standard techniques for the anticoagulation monitoring of patients. The aPTT assay measures how long it takes for the blood to form a clot. When negatively charged surfaces like kaolin, celite, silica, or ellagic acid meet FXII, they induce changes in protein shape and activate the downstream coagulation cascade [42]. This aPTT assay measures coagulation factors of the intrinsic pathway and proteins of the common pathway (
Figure 1). The PT is another assay that measures the total time to form a clot when the coagulation cascade is initiated through the exogenous addition of TF. Unlike aPTT, this assay measures clotting factors from the extrinsic pathway (FVII) and common pathway proteins such as FX, FV, FII and fibrinogen (
Figure 1). The addition of exogenous TF changes the physiological concentration of coagulation factors in plasma, further activating the TF:FVIIa complex, followed by FX to FXa conversion [42, 43]. When PT results are obtained from different laboratories using various reagents and laboratory techniques, they misrepresent PT values for warfarin therapy. PT results are reported as an international normalised ratio (INR) to solve this issue. This INR is calculated using Eq 1 [44].
where PT
patient is the patient sample clot time, and PT
normal is the geometric mean of PT results obtained from the average population using standard assay method, reagents, and a particular lot of thromboplastins. The supplier provides the international sensitivity index (ISI) for specific reagents. The ISI value measures each thromboplastin reagent’s response against vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors such as FII, FVII, and FX [42].
The ACT test is a whole blood-based assay, generally in a near-patient or point-of-care (POC) setting. ACT proves valuable in situations involving elevated heparin concentrations, such as cardiac catheterisation and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation [43]. In such scenarios, the aPTT test cannot be used. Furthermore, due to its integration into various POC devices, the potential for a quicker turnaround time with the ACT renders it advantageous in operating rooms and cardiac care units. The ACT entails introducing a clotting activator, such as celite, kaolin, or glass beads, to a whole blood sample, and then clotting time is measured [43].
5. Electrochemical sensors for anticoagulants based on coagulation factors
Traditional analytical techniques, such as mass spectrometry, provide clinicians with critical information for anticoagulant testing. Nonetheless, there exist scenarios where hospitals encounter difficulties in swiftly reporting anticoagulant drug concentrations during emergencies, attributable to infrastructural constraints, posing a potential threat to patient safety. An alternative strategy involving POC testing using whole blood samples has been devised in response to this challenge. This approach is designed to support clinicians in managing anticoagulation therapy more effectively. Furthermore, this POC device proves beneficial during emergency procedures, where immediate dosage adjustments are required, and in the ongoing, out-of-hospital monitoring of VKAs, such as warfarin, thereby enhancing patient clinical outcomes [45].
Most testing of anticoagulation drugs depended on the formation of thrombin, which converts fibrinogen to fibrin, leading to the fibrin clot. Naturally, measuring thrombin activity or directly quantifying thrombin can be used to quantify the anticoagulants present in the sample. From the electrochemical detection perspective, the thrombin quantification can be broadly classified into two categories:
1) when a thrombin-specific peptide containing an electroactive group is added to the sample, the hydrolysis of the peptide by thrombin releases an electroactive group, which then can be quantified by applying a respective redox potential
2) the thrombin can be directly quantified with the help of electrode modification by thrombin-specific aptamers; a change in current response is a direct indication of the quantity of thrombin in the sample
5.1. Electrochemical sensors for anticoagulants using thrombin-specific peptides
The Coagucheck XS (manufactured by Roche, Switzerland) is a point-of-care platform readily available for clot-based assay utilising an electrochemical detection method. Blood obtained from a finger puncture is placed onto strips containing thrombin-specific electrogenic substrate, which releases the redox active molecule when thrombin encounters the substrate, which is connected to a portable device that analyses PT/INR values. Several studies utilised a Coagucheck XS coagulation analyser for the INR measurement of warfarin and LMWH [46-49]. Similarly, i-STAT (Abbott Diagnostics) and Xprecia Stride coagulation analyser (Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics) also use a similar electrochemical platform [50-53].
A biosensor system capable of measuring the thrombin generation in a low-volume sample of as little as 10 µL of plasma or whole blood was developed [54]. This amperometric sensor strip contains a palladium working electrode and Ag/AgCl as both a reference and counter electrode, arranged in a co-planar configuration. The test chamber was prepared with a reagent comprising a blood coagulation activator and a thrombin-specific electrogenic substrate, both of which were dried within the chamber. Following the introduction of a blood analyte, thrombin generated in situ cleaves the substrate, consequentially liberating a redox-active group. The quantity of this group released is directly proportional to the thrombin concentration. Comparative analysis of results obtained using diverse activators reveals that this assay system can discern abnormalities in the extrinsic, intrinsic, and common pathways of blood coagulation.
Coagucheck XS pro system was used to analyse DOACs concentration of patient samples and found that rivaroxaban showed an almost linear relationship with PT values [55]. However, this method proved inaccurate in precisely detecting apixaban and dabigatran. It is important to note that tests designed explicitly for traditional coagulation assays, like PT/INR and aPTT, are unsuitable for the sensitive quantification of DOACs.
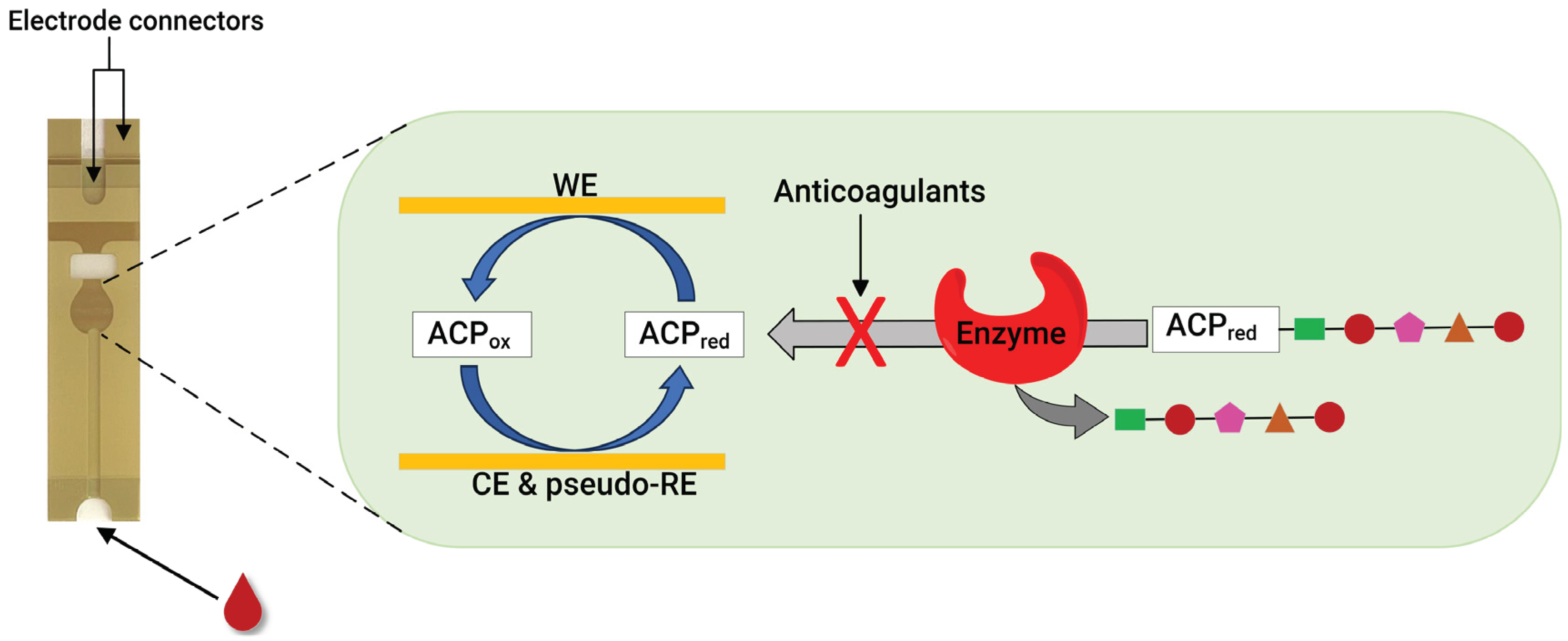
Recently, our group developed an assay for dabigatran using disposable gold co-facing electrodes (
Figure 3), which allows the calibration-free quantification of the electroactive mediator concentration [56, 57]. The working principle of the sensor involves measuring the activity of thrombin using the specific substrate Tos-Gly-Pro-Arg-ACP, which contains the redox active group 4-amino-2-chlorophenol (ACP). Upon the addition of thrombin, the enzyme selectively cleaved the peptide bond between arginine and ACP, thereby releasing ACP. Subsequently, the concentration of ACP was quantified by applying a specific voltage to facilitate its electrochemical oxidation. The resulting amperometric current generated during this process correlates with thrombin activity. This activity is inversely related to the presence of dabigatran. This thrombin activity-based sensor can detect ≥9.6 ng mL
−1 dabigatran and quantify 11.5–140 ng mL
−1 dabigatran when diluted plasma samples are spiked with the drug. The sensor encompassed both the therapeutic range and clinically relevant concentrations, which is significant in emergencies. Concentrations of dabigatran ≤ 30–50 ng mL
−1 are considered safe for emergency surgeries in individuals undergoing dabigatran therapy, underscoring the importance of this sensor [56].
Much research has been dedicated to detecting thrombin as a vital coagulation factor. Aptamer-based detection of thrombin is one such area, and a wide range of sensing mechanisms, including electrochemical systems, are available in the literature [59-61]. Therefore, discussing all the literature on electrochemical aptamer-based thrombin sensors in this review is impossible. As a result, only a few examples where sensors have a linear range of detection in the order of nanomolar concentration of thrombin are discussed. This concentration range is significant because, during a coagulation phase, the quantity of thrombin can vary between 1 nM and greater than 500 nM [62, 63].
A label-free detection of thrombin in blood serum utilising aptamer-based highly specific, selective and reusable electronic sensor has been developed [64]. The detection method employed in this study is based on a conformational change of the aptamer, which occurs selectively upon binding with thrombin. In the absence of the target molecule, the aptamer, tagged with methylene blue and covalently attached to a gold electrode, exhibits high flexibility. This flexibility facilitates a significant degree of electron transfer. Conversely, introducing thrombin leads to the formation of a rigid complex between the aptamer and thrombin. This rigidity hinders the electron transfer between methylene blue and the electrode, altering the electrochemical signal. This change in electron transfer dynamics serves as the basis for detecting thrombin. The sensor described above successfully quantified thrombin concentration in the 6.4 to 768 nM range in a blood sample. Similarly, a thrombin detection electrochemical sensor has been created employing a gold stripping voltammetry assay and DNA aptamer immobilised on the nanostructured surface of the screen-printed and gold nanoparticle electrodes [65]. This sensor measured a linear range of 10 nM to 10 µM of thrombin in a phosphate buffer saline system.
A magnetic force-assisted aptamer-antibody sandwich assay was developed based on an electrochemical detection platform for thrombin detection in serum samples [66]. In this sensor, the washing step was replaced by magnetic fled to remove the unbound conjugate in the sample. The thrombin detection was achieved with the help of an aptamer probe, and the respective electrochemical signal was generated by the cathodic currents of toluidine blue, which were attached to the thrombin antibody-modified magnetic particle. As mentioned earlier, the sensor successfully detected thrombin in the serum sample and quantified it in the 1 to 500 nM range in 7 minutes. On the other hand, a reagentless label-free aptamer-based sensor for thrombin quantification using a capacitive transducer with a face-to-face electrode configuration was developed [67]. The binding of thrombin to a specific aptamer led to a sensitive change in the capacitance values used as a primary sensing mechanism. This sensor showed a linear detection range for thrombin in serum samples between 0.01 and 1000 nM. Zhu and co-workers took advantage of multivalent aptamers, which provide increased binding affinity and selectivity in target identification and developed an electrochemical thrombin sensor [68]. A fourfold increase in binding response was achieved for multivalent aptamers compared to aptamers consisting of a single recognition element. This sensor showed a dynamic range of 50 nM to 1.0 µM thrombin in 50% diluted serum samples. To detect low concentrations of thrombin in serum, an electrochemical sensor utilising hybrid transducers comprised of polypyrrole and palladium nanoparticles, with liposomes containing a redox marker employed as a label, has been developed [69]. This sensor uses aptamer for thrombin recognition in samples; a linear detection range between 0.1 nM to 1 µM was obtained in serum samples.
Similarly to the case of thrombin, monitoring FXa activity is another viable method for quantifying anticoagulants. This was confirmed by our group, where using a disposable gold co-facing recycling electrode system, an FXa enzyme-based point-of-care assay was demonstrated for DOACs involving rivaroxaban, edoxaban and LMWHs, such as enoxaparin and dalteparin [58]. The working principle of this sensor is similar to that described in
Figure 3. The enzymatic reaction releases the ACP in the presence of the FXa-specific substrate Cbz-D-Arg-Gly-Arg-ACP peptide. However, when FXa inhibitors are present, they readily inactivate the FXa enzyme, leading to a proportional decrease in the measured amperometric current. Therefore, the measured amperometric current is related to the activity of FXa, which, in a reciprocal relationship, is influenced by the presence of the FXa inhibitor within the solution. This sensor can detect ≥9.00 ng mL
-1 of rivaroxaban and quantify it within the 11.0 – 140 ng mL
−1 range. In addition, the lower detection limit for edoxaban was 12.9 ng mL
−1, and the quantification range was in the 16.8-140 ng mL
−1 range. Likewise, enoxaparin and dalteparin (two LMWHs) were also quantified using the same sensor. A concentration ≥0.016 IU mL
−1 enoxaparin were detected, showing a quantification range of 0.025–0.75 IU mL
−1. Meanwhile, the dalteparin detection limit was 0.013 IU mL
−1, and the quantification range was 0.019–0.75 IU mL
−1. With a rapid assay completion time of less than 30 seconds, requiring only a minimum sample volume of 7 μL, and the ability to operate at physiological pH without calibration, this sensor is a potentially helpful candidate for POC testing.
5.2. Electrochemical sensors for anticoagulants using modified electrode surfaces
Electrode surfaces can be modified to enable an electrochemical function that is either unfeasible or challenging to achieve with standard electrodes. Specific enhancements tend to improve the electrode surfaces' sensitivity, selectivity, and electrochemical stability. Utilising electrochemical methods for detecting analytes without relying on enzymes offers numerous benefits, such as higher temperature and pH stability, simplicity, reproducibility, and cost-effectiveness [70]. Considerable progress has been achieved in synthetic methodologies, enabling the preparation of diverse materials with precise control over their size, shape, surface charge, and physicochemical attributes for electrochemical sensor applications [71, 72].
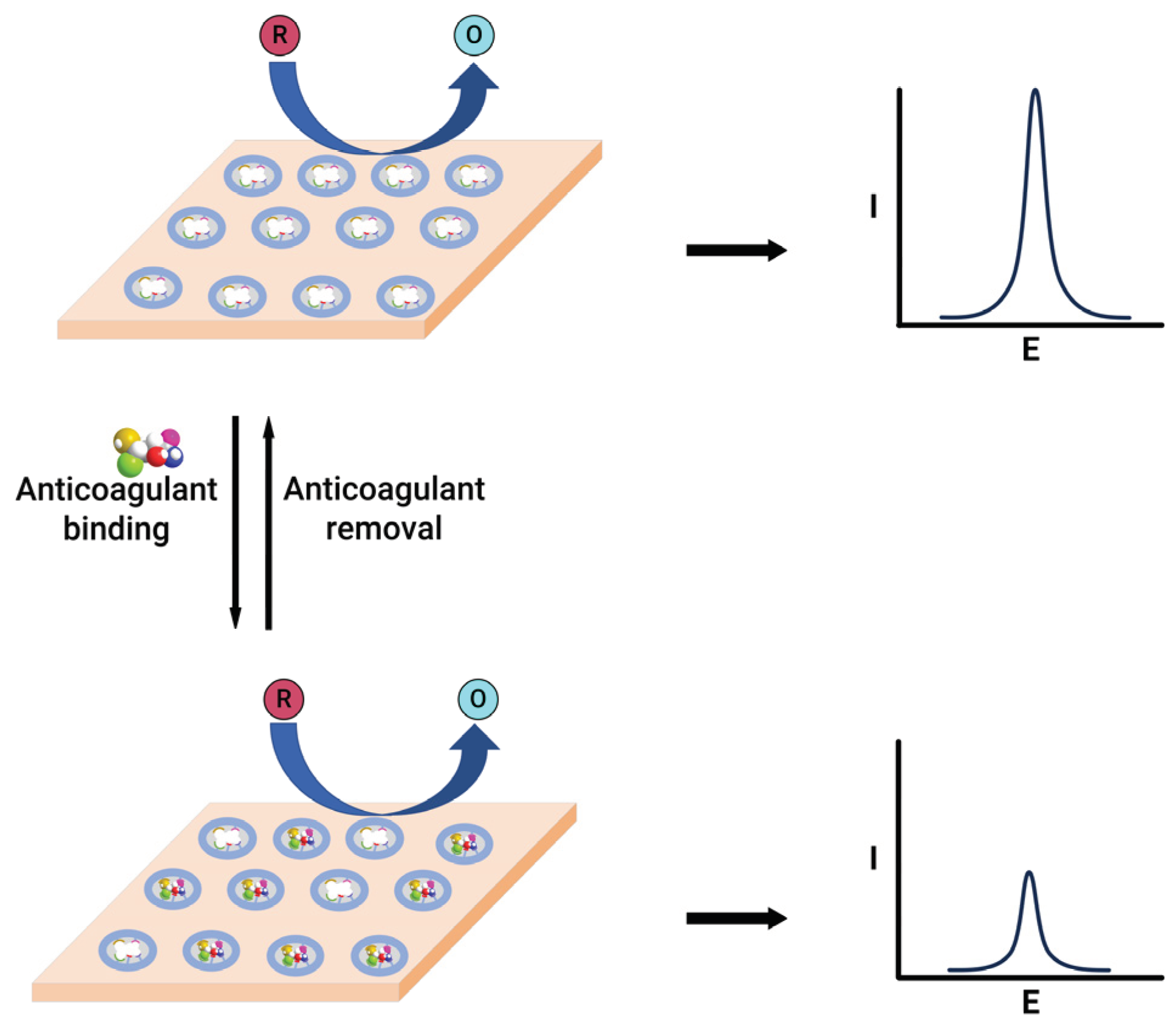
An electrochemical sensor was designed to detect warfarin based on the formation of a molecularly imprinted polymer film within the multi-walled carbon nanotubes and gold nanoparticle double layers [73]. This sensor exploits the high ratio of imprinted sites and the large surface-to-volume ratio associated with carbon nanotubes and gold nanoparticles for achieving higher binding kinetics of the imprinted layer. The modified sensor showed a linear quantification range of 0.101–2.00 nM for warfarin. Similarly, a chip-based sensor containing a gold-silver alloy microwire with a 3D nanoporous surface and the molecularly imprinted polymer are used for warfarin quantification [74]. This system employs two methods for warfarin quantification, based on the electrocatalysis of warfarin and the molecularly imprinted polymer gate effect. The electrochemical catalysis method exhibited linearity within the 5 – 400 µM range, falling short of clinical testing requirements. In contrast, the gate effect, where the alteration in redox peak current of the redox species, observed before and after the binding of the warfarin to the electrode (
Figure 4), demonstrated linearity in the 0.02 – 4 nM range, featuring an exceptionally low detection limit of 8 pM, effectively meeting the demands of clinical assays. A nanoporous gold leaf and molecularly imprinted polymer-modified gold electrode were used to enable highly sensitive and specific determination of warfarin [75]. This sensor utilises a probe ion system such as [Fe(CN)
6]
3-/4-, upon binding the warfarin into the pores of molecularly imprinted polymer leads to decreased access for the electron transfer, which reduces current. This change in current magnitude was employed to quantify warfarin in the 0.04 – 80 nM range.
A cadmium sulphide quantum dots linked to chitosan and multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified glassy carbon electrode was designed and used for warfarin quantification [76]. This sensor detected warfarin within the range of 0.05–80 μM, with a lower detection limit of 8.5 nM warfarin utilising a differential pulse stripping voltammetry technique. The increased electrochemical response for warfarin compared to unmodified glassy carbon electrodes was attributed to the increased active surface area after the modification. Similarly, a nickel-doped ceria nanospheres-modified glassy carbon electrode was employed to quantify warfarin [77]. The presence of nickel-doped ceria nanospheres showed an excellent electrocatalytic capability for warfarin detection with a linear range of 10 nM to 151 µM and a detection limit of 6.3 nM. On the other hand, a carbon paste electrode sensor was also developed for warfarin detection [78]. This sensor works on the principle of direct oxidation of warfarin and uses differential pulse voltammetry to quantify the drug. The warfarin linear quantification range was found to be between 1.05 µM to 3 mM, showing a 0.315 µM limit of detection. Similarly, a flow-injection technique was developed for quantifying warfarin in pharmaceutical formulations [79]. The method relies on the drug's susceptibility to oxidation at the glassy carbon electrode. Applying an electrode potential of +1.5 V vs Ag/AgCl reference electrode achieved a linear calibration curve in the 3.24 –130 µM concentration range, with a minimum detectability of 16.2 nM.
An ion-selective electrode-based detection technique was developed to quantify warfarin in blood samples [80]. The sensing mechanism is elucidated through electrostatic interaction and coordination between warfarin and tetradodecylammonium chloride. This interaction arises from the acid-base reaction involving the acidic enol of warfarin and the ammonium group of tetradodecylammonium chloride at pH 7.4. The sensor showed good sensitivity, with a detection limit of 0.125 and 14 µM warfarin in buffer and blood.
Heparin, an essential anticoagulant, is extensively used in clinical settings to treat thromboembolic conditions. However, patient responses to standardised doses of heparin can vary significantly, potentially leading to severe bleeding complications [95, 96]. This led to the development of sensors whose primary goal is to quantify heparin and help achieve a higher degree of clinical outcomes. In the literature, some reviews discuss heparin sensors based on electrochemical detection methods [97-99]. However, it is necessary to integrate recent advancements and findings in this area to provide a more current and comprehensive understanding. For example, a glassy carbon-modified electrode with a poly(thionine) thin film was developed [81]. The modified electrode displayed distinct redox peaks. These peaks diminished proportionally, without any alteration in the peak potential, upon the introduction of heparin. Utilising the interaction between heparin and poly(thionine), a sensor was constructed. This sensor demonstrated a robust response within the 0.27 – 1.47 µM concentration range, achieving a detection limit of 18.7 nM. Besides, polyethyleneimine was used as a receptor, and surface-confined ferricyanide was used as a redox probe to construct a heparin sensor [82]. The strong attraction of polyethylenimine to heparin facilitates the anionic exchange between the confined ferricyanide and the larger pool of heparin in the test solution. This sensor showed a linear range of 0.133 – 2.67 µM in 0.1 M phosphate buffer saline. However, this work did not use human plasma spiked samples to show the applicability of this sensor for clinical settings.
A simple voltammetric platform was developed for heparin detection [100]. The sensor system consisted of gold nanoparticles and γ-substituted pentamethinium salts modified glassy carbon electrode covered by a plasticised polyvinyl chloride-based membrane. The selectivity was achieved by interacting with positively charged γ-substituted pentamethinium and negatively charged heparin. The suggested voltammetric sensor demonstrated a concentration correlation ranging from 2.23 to 60.0 µM heparin. It was applied to detect heparin in saline buffer and biological samples, achieving a recovery rate between 95.1% and 100.9%. Similarly, the interaction between protamine, a heparin antidote, and heparin was evaluated using a gold-decorated graphene oxide glassy carbon electrode system [83]. This sensor utilises a probe ion system such [Fe(CN)6]3-/4-; upon binding of heparin to protamine, the decrease in peak current was correlated to an increase in heparin concentration. The linear range of heparin quantification was between 1.59 nM and 19 µM with a 0.9 nM low detection limit. A molecularly imprinted polymer grafted onto the graphite paste electrode surface was also presented [101]. The incorporated particles were extensively blended with oil to produce the molecularly imprinted polymer-graphite paste electrode. Standard cyclic voltammetry was conducted using the electrode in saline buffer or bovine whole blood, incorporating 5 mM ferrocyanide, which showed a linear quantification range for heparin from 0 to 10.7 µM. The current intensity rose in tandem with the concentration of heparin, which is attributed to the enlargement of the effective surface area caused by the increased mobility of the oil in the molecularly imprinted polymer-graphite electrode facilitated by heparin.
An aptamer-based sensor for the detection of dabigatran etexilate was also developed [84]. An aptamer with high affinity and specificity was chosen as a sensing probe in addition to the reporting probe [Fe(CN)6]3-/4- redox system. The square wave voltammograms showed a good relationship between dabigatran etexilate concentrations and decreased peak current of [Fe(CN)6]3-/4- redox molecule. The reduction in peak current after the dabigatran binding could be due to the more compact arrangement between aptamer and drug. This hinders the access of the redox molecule to the electrode surface. Even though this work was not carried out in plasma or blood samples, this sensor showed a good response in the 15.9 pM to 1.59 µM range in phosphate buffer saline. On the other hand, an electrocatalytic sensor consisting of graphene and cerium dioxide-modified glassy carbon electrode was prepared to identify and quantify dabigatran etexilate [85]. The square wave voltammograms showed that when dabigatran concentration increased, the cathodic current also increased linearly within the 7.97 nM – 7.97 µM range; this was attributed to the good electrocatalytic activity enhancement of the modified electrode.
An electrochemical sensor for dabigatran etexilate in pharmaceutical and urine samples was designed using a boron-doped diamond electrode (BDDE) and a basal-plane pyrolytic graphite electrode (BPPGE) [86]. This sensor exploited the irreversible oxidation of dabigatran etexilate and obtained a concentration-dependent calibration curve with respect to the oxidation current in a pH 3.0 buffer system. The sensor showed a linear detection range between 0.01–0.7 µM dabigatran using BDDE and 0.07–1.0 µM dabigatran with BPPGE. To test its versatility, analysis of spiked urine and pharmaceutical samples was employed using the standard addition method, which resulted in a good response without any significant interference. In comparison to BPPGE, the BDDE system showed a better performance. Similarly, an ion-selective sensor was developed based on modified carbon paste and pencil graphite electrodes consisting of dabigatran etexilate-phosphotungstate ion pair [87]. These modified electrodes quantified dabigatran etexilate in the 10 µM – 10 mM range for the ion-selective carbon paste electrode and the 1 µM – 10 mM range when the pencil graphite electrode was used.
A new label-free electrochemical aptasensor was created by linking a thiolated aptamer with gold nanoparticles onto the surface of indium tin oxide-polyethylene terephthalate(ITO-PET) [88]. This aptasensor was effectively utilised to quantify rivaroxaban in human plasma and exhaled breath condensate samples, achieving detection limits of 14.08 nM and 6.03 nM, respectively. The square wave voltammetry method assessed the sensor's analytical performance in a [Fe(CN)6]3-/4- redox solution. The electrochemical signal gradually rose with increasing rivaroxaban concentration, establishing a robust linear relationship between the current response signal and rivaroxaban concentration. The calibration curve demonstrated linearity within the 10 – 600 nM concentration range in plasma and exhaled breath condensate samples. A similar approach has been designed using ITO-PET modified by polytoluidine blue, silver nanoparticles, and polyethylene glycol as electrode substrates and aptamers as rivaroxaban-recognising elements [89]. This sensor showed 6.65 nM and 4.13 nM detection limits for plasma and exhaled breath condensate samples.
On the other hand, a potentiometric sensor was developed by modifying a glassy carbon electrode [90]. The sensor required the integration of a molecularly imprinted polymer into polyvinyl chloride with plasticiser and its application as a singular layer on the glassy carbon electrode. Similarly, a voltammetric sensor was crafted through a drop-coating method, sequentially depositing graphene oxide and molecularly imprinted polymer on the untreated glassy carbon electrode. The rivaroxaban potentiometric sensor showed a linear response range between 1.2 nM and 1.0 mM. However, a linear range of 0.054 nM – 3.1 mM was obtained using the voltammetric sensor. Both sensors showed good responses for rivaroxaban in blood and pharmaceutical samples.
An electrochemical sensor for rivaroxaban in pharmaceutical and urine samples was designed using a boron-doped diamond electrode (BDDE) and graphite flake paste electrode (GFPE) [86]. This sensor operated based on the irreversible oxidation of rivaroxaban. As a result, a calibration plot of the increase in anodic current and rivaroxaban concentration was plotted. The calibration range for rivaroxaban was 0.5 – 30.0 µM for BDDE and 1.0 – 10.0 µM for GFPE. To test the sensor performance, analysis of spiked urine and pharmaceutical samples was employed using the standard addition method, which resulted in a good response without any significant interference.
A potentiometric sensor consisting of a glassy carbon electrode coated with an ion-selective membrane and multi-walled carbon nanotubes was developed to measure edoxaban [91]. This modification improved the sensor performance, including an expanded dynamic range from 6.0 µM to 1.0 mM edoxaban and a reduced detection limit of 4.20 µM edoxaban. Moreover, this sensor was also evaluated using a pharmaceutical formulation and edoxaban-spiked human plasma samples. Similarly, a sensor chip based on a carbon paste electrode embedded with molecularly imprinted polymers and p-styrene sulfonate was developed to detect and quantify edoxaban [102]. The interaction of edoxaban through the cavities created inside the grafted layer enhances the oxidation current of ferrocene, used as the redox probe. Besides, p-styrene sulfonate has a greater affinity for edoxaban, improving the sensor’s current response. Nevertheless, the poor sensitivity and selectivity reported prevent the sensor’s practical application in clinical settings.
The surface of the glassy carbon electrode was modified with graphene oxide aerogels and Bi2Fe4O9 semiconductor to design an apixaban sensor [103]. This sensor used [Fe(CN)6]3-/4- redox system as the reporting probe. Upon addition of apixaban to the plasma sample, the redox current of [Fe(CN)6]3-/4- decreased due to apixaban blocking the electrode surface. This correlation of decreasing peak current to increasing apixaban concentration showed a linear range of 10 ng mL-1 to 10 µg mL-1. Besides, a carbon paste electrode modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes was prepared for the voltammetric determination of apixaban in pharmaceutical compounds [94]. At pH 5.0, apixaban showed an oxidation process at 1.21 V vs Ag/AgCl reference system. The peak current vs concentration of apixaban resulted in a linear detection range between 1.99 and 107 µM apixaban. The apixaban-spiked plasma test returned a 100.64 ± 1.22% recovery rate.
6. Common calibration methods:
Most commercially available FXa inhibitor assay depends on measuring FXa activity upon in vitro addition of inhibitor-containing sample. Currently, all the tests that measure FXa inhibitors require individual drug-specific calibration, and no single technique can simultaneously quantify all FXa inhibitors, such as DOACs and LMWHs [104]. This poses a notable challenge, especially for individuals undergoing FXa inhibitor treatment who are admitted to the emergency department due to severe bleeding. It is crucial to ascertain their anticoagulation status before considering any surgical interventions. The complexity escalates further when patients are unconscious and their anticoagulation status remains uncertain. To address this issue, recently, we explored the possibility of replacing individual drug-specific calibrations with a single calibration plot set for DOACs and one for LMWHs, which could quantify inhibitors belonging to the DOACs family (rivaroxaban and edoxaban) and LMWHs family (enoxaparin and dalteparin) respectively [58]. The result suggests that the sensor can detect and quantify rivaroxaban and edoxaban without a calibration plot or a universal calibration plot. Besides, an acceptable small error within the experimental limit is achieved if the inhibitor identity is unknown, where a result of [inhibitor]±3 ng mL-1 is obtained. Similarly, the same idea was extended to LMWHs, and data suggests that the means are not significantly different for the two different LMWHs (P > 0.05), and the universal calibration plot can be used for both inhibitors with a relatively low percentage of error. However, this concept needs further testing with various DOACs and LMWHs of varying molecular sizes to ascertain its suitability for widespread use in point-of-care settings.
7. Conclusions:
This review presented a detailed discussion of the different stages of coagulation and their testing using electrochemical methods. These tests broadly fall into two categories: (a) anticoagulant assays purely based on electrochemical detection methods that use thrombin activity or direct thrombin measurements, and (b) electrochemical sensors using direct measurement of anticoagulants depending on redox behaviour of the drug or redox probes utilising electrode modification without the help of coagulant factors such as thrombin or factor Xa.
To overcome some of the limitations posed by VKAs and heparins, a new class of DOACs with specific anticoagulation behaviour and predictable pharmacokinetics was developed. Initially, experts thought regular coagulation monitoring was unnecessary with the introduction of the first DOACs. Despite this, it would be crucial to know the concentration of DOACs in the blood to achieve better clinical outcomes for patients under coagulation therapy. Even though some research has been done on quantifying DOACs in the literature, the development of POC testing using blood samples is still underway. This could open an excellent opportunity for developing specific, sensitive, quick turnaround time and easy-to-use assays for DOACs, particularly involving complex matrices such as blood and integrating them into electrochemical device platforms.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, A.K.V.M. and A.A.J.T.; methodology, A.K.V.M. and A.A.J.T.; software, A.K.V.M. and A.A.J.T.; validation, A.K.V.M. and A.A.J.T.; formal analysis, A.K.V.M. and A.A.J.T.; investigation, A.K.V.M. and A.A.J.T.; resources, A.K.V.M. and A.A.J.T.; data curation, A.K.V.M. and A.A.J.T.; writing—original draft preparation, A.K.V.M. and A.A.J.T.; writing—review and editing, A.K.V.M. and A.A.J.T.; visualisation, A.K.V.M. and A.A.J.T.; supervision, A.K.V.M. and A.A.J.T.; project administration, A.K.V.M. and A.A.J.T.; funding acquisition, A.K.V.M. and A.A.J.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Levine, S. R. Hypercoagulable states and stroke: a selective review. CNS Spectr 2005, 10, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, M. J. Hypercoagulability as a cause of stroke in adults. (Featured CME Topic: Stroke). Southern Medical Journal 2003, 4, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falanga, A.; Marchetti, M.; Vignoli, A. Coagulation and cancer: biological and clinical aspects. J Thromb Haemost 2013, 11, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijfering, W. M.; Sprenger, H. G.; Georg, R. R.; van der Meulen, P. A.; van der Meer, J. Relationship between progression to AIDS and thrombophilic abnormalities in HIV infection. Clin Chem 2008, 54, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gorp, E. C. M.; Suharti, C.; ten Cate, H.; Dolmans, W. M. V.; van der Meer, J. W. M.; ten Cate, J. W.; Brandjes, D. P. M. Review: Infectious Diseases and Coagulation Disorders. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 1999, 180, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi, M.; Keller, T. T.; van Gorp, E.; ten Cate, H. Infection and inflammation and the coagulation system. Cardiovasc Res 2003, 60, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, W. Z. Coagulation complications following trauma. Mil Med Res 2016, 3, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceriello, A. Coagulation activation in diabetes mellitus: the role of hyperglycaemia and therapeutic prospects. Diabetologia 1993, 36, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzahrani, S. H.; Ajjan, R. A. Coagulation and fibrinolysis in diabetes. Diab Vasc Dis Res 2010, 7, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugeri, L.; Levrat, A.; David, J. S.; Delecroix, E.; Floccard, B.; Gros, A.; Allaouchiche, B.; Negrier, C. Diagnosis of early coagulation abnormalities in trauma patients by rotation thrombelastography. J Thromb Haemost 2007, 5, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhli-Hattenbach, C.; Scharrer, I.; Luchtenberg, M.; Hattenbach, L. O. Coagulation disorders and the risk of retinal vein occlusion. Thromb Haemost 2010, 103, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fegan, C. D. Central retinal vein occlusion and thrombophilia. Eye (Lond) 2002, 16, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganter, M. T.; Hofer, C. K. Coagulation monitoring: current techniques and clinical use of viscoelastic point-of-care coagulation devices. Anesth Analg 2008, 106, 1366–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, L. F.; Castro-López, V.; Killard, A. J. Coagulation monitoring devices: Past, present, and future at the point of care. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2013, 50, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi Aria, M.; Erten, A.; Yalcin, O. Technology Advancements in Blood Coagulation Measurements for Point-of-Care Diagnostic Testing. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2019, 7, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, A.; Green, L. Physiology of haemostasis. Anaesthesia & Intensive Care Medicine 2019, 20, 152–158. [Google Scholar]
- Tynngård, N.; Lindahl, T. L.; Ramström, S. Assays of different aspects of haemostasis – what do they measure? Thrombosis Journal 2015, 13, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Meijden, P. E. J.; Heemskerk, J. W. M. Platelet biology and functions: new concepts and clinical perspectives. Nat Rev Cardiol 2019, 16, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinik, A. I.; Erbas, T.; Park, T. S.; Nolan, R.; Pittenger, G. L. Platelet Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 1476–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Naadiya, C.; Yiming, W.; Reid, C. G.; Alexandra, M.; Heyu, N. Platelets in hemostasis and thrombosis: Novel mechanisms of fibrinogen-independent platelet aggregation and fibronectin mediated protein wave of hemostasis. The Journal of Biomedical Research 2015, 29, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryckaert, M.; Rosa, J. P.; Denis, C. V.; Lenting, P. J. Of von Willebrand factor and platelets. Cell Mol Life Sci 2015, 72, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S. H.; Sim, E. H.; Goh, R. Y.; Park, J. I.; Han, J. Y. Platelet Activation: The Mechanisms and Potential Biomarkers. Biomed Res Int 2016, 2016, 9060143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lentz, B. R. Exposure of platelet membrane phosphatidylserine regulates blood coagulation. Progress in Lipid Research 2003, 42, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S. A.; Travers, R. J.; Morrissey, J. H. How it all starts: Initiation of the clotting cascade. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 2015, 50, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R. L. C.; Bird, R. J. Review article: Coagulation cascade and therapeutics update: Relevance to nephrology. Part 1: Overview of coagulation, thrombophilias and history of anticoagulants. Nephrology 2009, 14, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davie, E. W.; Fujikawa, K.; Kisiel, W. The coagulation cascade: initiation, maintenance, and regulation. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 10363–10370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackman, N. Triggers, targets and treatments for thrombosis. Nature 2008, 451, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oklu, R., Thrombosis. Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy; Vol 7, Supplement 3 (December 21, 2017): Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy (Thrombosis) 2017. 21 December.
- Rosenberg, R. D.; Rosenberg, J. S. Natural anticoagulant mechanisms. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 1984, 74, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollefsen, D. M. Heparin Cofactor II Modulates the Response to Vascular Injury. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 2007, 27, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braune, S.; Küpper, J.-H.; Jung, F. Effect of Prostanoids on Human Platelet Function: An Overview. In International Journal of Molecular Sciences; 2020; Volume 21. [Google Scholar]
- Cesarman-Maus, G.; Hajjar, K. A. Molecular mechanisms of fibrinolysis. British Journal of Haematology 2005, 129, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, L.; Voglmeir, J. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of ultralow and low-molecular weight heparins. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Proteins and Proteomics 2020, 1868, 140301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsh, J. Heparin. New England Journal of Medicine 1991, 324, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumano, O.; Akatsuchi, K.; Amiral, J. Updates on Anticoagulation and Laboratory Tools for Therapy Monitoring of Heparin, Vitamin K Antagonists and Direct Oral Anticoagulants. Biomedicines 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jay, R. M.; Lui, P. How anticoagulants work. Techniques in Regional Anesthesia and Pain Management 2006, 10, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Huang, S.; Luo, C.; Wu, Z.; Liang, B.; Huang, H.; Ci, Z.; Zhang, D.; Han, L.; Lin, J. Pharmacological and clinical application of heparin progress: An essential drug for modern medicine. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2021, 139, 111561. [Google Scholar]
- Schein, J. R.; White, C. M.; Nelson, W. W.; Kluger, J.; Mearns, E. S.; Coleman, C. I. Vitamin K antagonist use: evidence of the difficulty of achieving and maintaining target INR range and subsequent consequences. Thrombosis Journal 2016, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harter, K.; Levine, M.; Henderson, S. O. Anticoagulation drug therapy: a review. West J Emerg Med 2015, 16, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, M.; Birschmann, I.; Peter, A.; Härtig, F.; Spencer, C.; Kuhn, J.; Blumenstock, G.; Zuern, C. S.; Ziemann, U.; Poli, S. Emergency Coagulation Assessment During Treatment With Direct Oral Anticoagulants. Stroke 2017, 48, 2457–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J. D.; Lopez-Espina, C. G.; Ippolito, J.; Hsiao, L. H.; Zaman, F.; Muresan, A. A.; Thomas, S. G.; Walsh, M.; Jones, A. J.; Grisoli, A.; Thurston, B. C.; Artang, R.; Bilden, K. P.; Hartmann, J.; Achneck, H. E. Rapid point-of-care detection and classification of direct-acting oral anticoagulants with the TEG 6s: Implications for trauma and acute care surgery. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery 2019, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, M., Chapter 129 - Laboratory Evaluation of Hemostatic and Thrombotic Disorders. In Hematology (Seventh Edition), Hoffman, R.; Benz, E. J.; Silberstein, L. E.; Heslop, H. E.; Weitz, J. I.; Anastasi, J.; Salama, M. E.; Abutalib, S. A., Eds. Elsevier: 2018; pp 1922-1931.
- Campbell, S., Chapter 26 - Hemostasis. In Contemporary Practice in Clinical Chemistry (Fourth Edition), Clarke, W.; Marzinke, M. A., Eds. Academic Press: 2020; pp 445-467.
- Tripodi, A.; Caldwell, S. H.; Hoffman, M.; Trotter, J. F.; Sanyal, A. J., Review article: the prothrombin time test as a measure of bleeding risk and prognosis in liver disease. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2007, 26, 141–148.
- Perry, D. J.; Fitzmaurice, D. A.; Kitchen, S.; Mackie, I. J.; Mallett, S. Point-of-care testing in haemostasis. British Journal of Haematology 2010, 150, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alserr, A. H. K.; Menshawey, R.; Kotb, A.; Hussein, N.; Kotp, N.; Ashraf-Taha, M.; Anwar, N.; Abdalla, A.; Abdullah, M.; Ela, S. A.; Khairy, H., A Comparison of International Normalized Ratio Results by Point-of-Care Device and Clinical Laboratory Analyzers in a Vascular Surgery Department. Point of Care 2020, 19, (4).
- Bardakci, H.; Altıntaş, G.; Çiçek, O. F.; Kervan, U.; Yilmaz, S.; Kaplan, S.; Birincioglu, C. L. Comparison of the CoaguChek XS Handheld Coagulation Analyzer and Conventional Laboratory Methods Measuring International Normalised Ratio (INR) Values during the Time to Therapeutic Range after Mechanical Valve Surgery. Journal of Cardiac Surgery 2013, 28, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, R. B.; Shane, L. J.; Gregory, M. P.; Ella, C. J.; Katherine, A. M.; David, M. J. Accuracy and clinical utility of the CoaguChek XS portable international normalised ratio monitor in a pilot study of warfarin home-monitoring. Journal of Clinical Pathology 2007, 60, 311. [Google Scholar]
- Wieloch, M.; Hillarp, A.; Strandberg, K.; Nilsson, C.; Svensson, P. J. Comparison and evaluation of a Point-of-care device (CoaguChek XS) to Owren-type prothrombin time assay for monitoring of oral anticoagulant therapy with warfarin. Thrombosis Research 2009, 124, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piacenza, F.; Galeazzi, R.; Cardelli, M.; Moroni, F.; Provinciali, M.; Pierpaoli, E.; Giovagnetti, S.; Appolloni, S.; Marchegiani, F. Precision and accuracy of the new XPrecia Stride mobile coagulometer. Thrombosis Research 2017, 156, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spielmann, N.; Mauch, J. Y.; Madjdpour, C.; Schmugge, M.; Albisetti, M.; Weiss, M.; Haas, T. Comparison of point-of-care testing (POCT): i-STAT® international normalized ratio (INR) vs reference laboratory INR in pediatric patients undergoing major surgery. Pediatric Anesthesia 2011, 21, 1041–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deborah, M.; Andrea, R.; David, A. F. An evaluation of a coagulation system (Xprecia Stride) for utilisation in anticoagulation management. Journal of Clinical Pathology 2018, 71, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Schober, P.; Bossers, S. M.; Koolwijk, J.; Terra, M.; Schwarte, L. A. Prehospital coagulation measurement by a portable blood analyzer in a helicopter emergency medical service (HEMS). The American Journal of Emergency Medicine 2021, 46, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuerlemann, C.; Haeberli, A.; Alberio, L. Monitoring thrombin generation by electrochemistry: development of an amperometric biosensor screening test for plasma and whole blood. Clin Chem 2009, 55, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebner, M.; Peter, A.; Spencer, C.; Härtig, F.; Birschmann, I.; Kuhn, J.; Wolf, M.; Winter, N.; Russo, F.; Zuern, C. S.; Blumenstock, G.; Ziemann, U.; Poli, S. Point-of-Care Testing of Coagulation in Patients Treated With Non–Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants. Stroke 2015, 46, 2741–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ruthunjaya, A. K. V.; Chatelier, R. C.; Torriero, A. A. J., Electrochemical Disposable Biosensor to Monitor Dabigatran in Point-of-Care Anticoagulation Therapy. In Molecules, 2023; Vol. 28.
- Mruthunjaya, A. K. V.; Hodges, A. M.; Chatelier, R. C.; Torriero, A. A. J. Calibration-free disposable electrochemical sensor with co-facing electrodes: Theory and characterisation with fixed and changing mediator concentration. Electrochimica Acta 2023, 460, 142596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mruthunjaya, A. K. V.; Chatelier, R. C.; Torriero, A. A. J. Calibration-free electrochemical sensor to monitor factor-Xa inhibitors at the point-of-care anticoagulation therapy. Talanta 2024, 270, 125593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, B.; Lin, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.-F.; Le, X. C. Aptamer binding assays for proteins: The thrombin example—A review. Analytica Chimica Acta 2014, 837, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Wang, N.; Zhang, L.; Meng, H.; Li, Z. Aptamer-Based Sensors for Thrombin Detection Application. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R.; Saadatidizaji, Z.; Maleki, A.; de la Guardia, M.; Mahdavi, M.; Barzegar, S.; Ahadian, S., Recent Progresses in Development of Biosensors for Thrombin Detection. Biosensors (Basel) 2022, 12, (9).
- Wolberg, A. S.; Campbell, R. A. Thrombin generation, fibrin clot formation and hemostasis. Transfusion and Apheresis Science 2008, 38, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butenas, S.; Mann, K. G.; Butenas, Blood Coagulation. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2002, 67, 3–12.
- Xiao, Y.; Lubin, A. A.; Heeger, A. J.; Plaxco, K. W. Label-Free Electronic Detection of Thrombin in Blood Serum by Using an Aptamer-Based Sensor. Angewandte Chemie 2005, 117, 5592–5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suprun, E.; Shumyantseva, V.; Bulko, T.; Rachmetova, S.; Rad’ko, S.; Bodoev, N.; Archakov, A. Au-nanoparticles as an electrochemical sensing platform for aptamer–thrombin interaction. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2008, 24, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.; Moon, J. M.; Choi, J.; Hwang, H.; Shim, Y. B. Magnetic force assisted electrochemical sensor for the detection of thrombin with aptamer-antibody sandwich formation. Biosens Bioelectron 2018, 117, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H. J.; Chen, R. L. C.; Hsieh, B. C.; Hsiao, H. Y.; Kung, Y.; Hou, Y. T.; Cheng, T. J. Label-free and reagentless capacitive aptasensor for thrombin. Biosens Bioelectron 2019, 131, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Xu, F.; Miao, S.; Xie, C.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Xia, F. Incorporation of a Multi-Valent Aptamer into Electrochemical Biosensors to Achieve an Improved Performance for Thrombin Analysis in Blood Serum. Chempluschem 2022, 87, e202200325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagati, A. K.; Behrent, A.; Tomanek, V.; Chavan, S. G.; Go, A.; Park, S. R.; Jin, Z.; Baeumner, A. J.; Lee, M. H. Polypyrrole-palladium nanocomposite as a high-efficiency transducer for thrombin detection with liposomes as a label. Anal Bioanal Chem 2022, 414, 3205–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhara, K.; Mahapatra, D. R. Recent advances in electrochemical nonenzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensors based on nanomaterials: a review. Journal of Materials Science 2019, 54, 12319–12357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, L.; Qian, K. Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Sensors: Mechanism, Preparation, and Application in Biomedicine. Advanced NanoBiomed Research 2021, 1, 2000104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Chatterjee, S. Nanomaterials based electrochemical sensors for biomedical applications. Chemical Society Reviews 2013, 42, 5425–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, B.; Rahmanian, O.; Ensafi, A. A., An electrochemical sensor based on multiwall carbon nanotubes and molecular imprinting strategy for warfarin recognition and determination. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2014, 196, 539–545.
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, M.; Tian, L.; Sun, S.; Zhao, N.; Zhao, F.; Li, Y. Electrochemical microfluidic chip based on molecular imprinting technique applied for therapeutic drug monitoring. Biosens Bioelectron 2017, 91, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Zhou, S.-F.; Al-Ghanim, K. A.; Mahboob, S.; Ye, B.-C.; Zhang, X. A novel sensitive and selective electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer on a nanoporous gold leaf modified electrode for warfarin sodium determination. RSC Advances 2016, 6, 43724–43731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholivand, M. B.; Mohammadi-Behzad, L., An electrochemical sensor for warfarin determination based on covalent immobilization of quantum dots onto carboxylated multiwalled carbon nanotubes and chitosan composite film modified electrode. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2015, 57, 77–87.
- Maheshwaran, S.; Akilarasan, M.; Chen, S.-M.; Tamilalagan, E.; Keerthiga, E.; Alothman, A. A.; Alqahtani, K. N.; Ganesh, P. S. Synthesis of nickel-doped ceria nanospheres for in situ profiling of Warfarin sodium in biological media. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 146, 108166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, M.; Rahimnejad, M.; Ezoji, H., Facile and sensitive electrochemical sensing device based on carbon paste electrode for warfarin determination. Monatshefte für Chemie - Chemical Monthly 2023.
- Belal, F.; Anderson, J. L. Flow injection analysis of warfarin sodium with amperometric detection. Microchimica Acta 1985, 86, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, I.; Ahmadi, S.; Thompson, M.; Hashemi, P.; Ramezani, Z., Electrochemical Sensor for the Direct Determination of Warfarin in Blood. Chemosensors 2022, 10, (2).
- Huo, H. Y.; Luo, H. Q.; Li, N. B. Electrochemical sensor for heparin based on a poly(thionine) modified glassy carbon electrode. Microchimica Acta 2009, 167, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, Z.; Zhai, J.; Zhang, Z. A facile voltammetric method for detection of heparin in plasma based on the polyethylenimine modified electrode. Analytical Methods 2019, 11, 1324–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 8Rengaraj, A.; Haldorai, Y.; Hwang, S. K.; Lee, E.; Oh, M. H.; Jeon, T. J.; Han, Y. K.; Huh, Y. S. A protamine-conjugated gold decorated graphene oxide composite as an electrochemical platform for heparin detection. Bioelectrochemistry 2019, 128, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljohani, M. M.; Chinnappan, R.; Eissa, S.; Alsager, O. A.; Weber, K.; Cialla-May, D.; Popp, J.; Zourob, M. In Vitro Selection of Specific DNA Aptamers Against the Anti-Coagulant Dabigatran Etexilate. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 13290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Sinha, A. Electrocatalytic quantification of thrombin inhibitor dabigatran etexilate in solubilized system. Ionics 2015, 21, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festinger, N.; Smarzewska, S.; Ciesielski, W. Comparative study of boron-doped diamond, basal-plane pyrolytic graphite, and graphite flake paste electrodes for the voltammetric determination of rivaroxaban and dabigatran etexilate in pharmaceuticals and urine samples. Diamond and Related Materials 2021, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou El-Alamin, M. M.; Mohamed, D. A.; Toubar, S. S. New disposable ion-selective sensors for the determination of dabigatran etexilate: The oral anticoagulant of choice in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation and COVID-19 infection. Measurement 2022, 198, 111406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, R.; Barzegari, A.; Teimuri-Mofrad, R.; Kordasht, H. K.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Khoubnasabjafari, M.; Jouyban-Gharamaleki, V.; Rad, A. A.; Shadjou, N.; Rashidi, M. R.; Afshar Mogaddam, M. R.; Jouyban, A., Selection of Specific Aptamer against Rivaroxaban and Utilization for Label-Free Electrochemical Aptasensing Using Gold Nanoparticles: First Announcement and Application for Clinical Sample Analysis. Biosensors (Basel) 2022, 12, (10).
- Ebrahimi, R.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Rashidi, M.-R.; Jouyban, A. Low fouling aptasensing of rivaroxaban in real samples using poly (toluidine blue) decorated by silver nanoparticle: A new platform for the cardiovascular disease analysis. Microchemical Journal 2023, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, A. B.; Saher, A.; Molouk, A. F. S.; Mortada, W. I.; Khalifa, M. E. Applications of electrochemical techniques for determination of anticoagulant drug (Rivaroxaban) in real samples. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2022, 208, 114213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayish, N. S.; Marzouk, H. M.; El-Zeany, B. A.; Fayed, A. S. A Novel Nanoparticles-based Electrochemical Sensing Platform for Sensitive Detection of Oral Anticoagulant; Edoxaban in Human Plasma. Electroanalysis 2022, 34, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiliç, A.; Aslan, M.; Önal, G.; Levent, A. Firstly electrochemical investigetions and determination of anticoagulant drug edoxaban at single-use pencil graphite electrode: an eco-friendly and cost effective voltammetric method. DARU Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2023, 31, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiliç, A.; Aslan, M.; Levent, A. Investigation of the electrochemical properties of edoxaban using glassy carbon and boron-doped diamond electrodes and development of an eco-friendly and cost effective voltammetric method for its determination. Anal Biochem 2024, 685, 115386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizk, M.; Sultan, M. A.; Taha, E. A.; Attia, A. K.; Abdallah, Y. M. Sensitive validated voltammetric determination of apixaban using a multi-walled carbon nanotube-modified carbon paste electrode: application to a drug product and biological sample. Analytical Methods 2017, 9, 2523–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, M. Heparins: Clinical Use and Laboratory Monitoring. Laboratory Medicine 2010, 41, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsh, J.; Anand, S. S.; Halperin, J. L.; Fuster, V. Guide to Anticoagulant Therapy: Heparin. Circulation 2001, 103, 2994–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromfield, S. M.; Wilde, E.; Smith, D. K. Heparin sensing and binding – taking supramolecular chemistry towards clinical applications. Chemical Society Reviews 2013, 42, 9184–9195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amemiya, S.; Kim, Y.; Ishimatsu, R.; Kabagambe, B. Electrochemical heparin sensing at liquid/liquid interfaces and polymeric membranes. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry 2011, 399, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishenkova, D. A.; Korotkova, E. I. Electrochemical methods for the determination of heparin. Journal of Analytical Chemistry 2017, 72, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishkanova, T. V.; Briza, T.; Rezanka, P.; Kejik, Z.; Jakubek, M., Pentamethinium Salts Nanocomposite for Electrochemical Detection of Heparin. Materials (Basel) 2021, 14, (18).
- Yoshimi, Y.; Yagisawa, Y.; Yamaguchi, R.; Seki, M., Blood heparin sensor made from a paste electrode of graphite particles grafted with molecularly imprinted polymer. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2018, 259, 455–462.
- Yoshimi, Y.; Kani, S. Aaryashree, A disposable edoxaban sensor chip using carbon paste electrode grafted with molecularly imprinted polymer. Journal of Artificial Organs 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Shahbazi-Derakhshi, P.; Abbasi, M.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Hosseinpour, H.; Soleymani, J. A ratiometric electrochemical probe for the quantification of apixaban in unprocessed plasma samples using carbon aerogel/BFO modified glassy carbon electrodes. RSC Advances 2023, 13, 21432–21440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Pelt, L. J.; Lukens, M. V.; Testa, S.; Chatelain, B.; Douxfils, J.; Mullier, F. The DaXa-inhibition assay: A concept for a readily available, universal aXa assay that measures the direct inhibitory effect of all anti-Xa drugs. Thrombosis Research 2018, 168, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).