1. Introduction
The adoption of alternative fuels that reduce the carbon footprint of internal combustion engines represents a pivotal advancement in sustainability of transportation [
1] and power generation [
2]. The compatibility of new fuels with existing engines and distribution infrastructure is fundamental to ensure a seamless transition [
3]. Engines that harness the benefits of alternative fuels without necessitating extensive modifications provide a pragmatic pathway toward sustainable power for vehicles and industry [
4,
5]. This adaptability contributes to the feasibility and scalability of alternative fuel adoption, across different automotive and industrial platforms. Thus, the adoption of alternative and green fuels stands as a progressive strategy to substantially reduce the environmental impact of engine operation. In some engineering fields, such as lubrication and fluid power [
6], alternative fluids are being tested to progressively reduce and to replace fossil materials. This transition towards green sources not only aligns with environmental goals but also signifies a fundamental step in fostering a more sustainable and resilient transportation [
7] and industrial ecosystem.
Diesel engines inherently exhibit superior efficiency due to their high compression ratios [
8]. This efficiency translates into better fuel economy and reduced carbon emissions per unit of produced energy. Hence, combining diesel technology and the adoption of renewable fuels is regarded as a convenient choice to minimize the environmental footprint of internal combustion engines. (Carbon footprint and pollutant emissions).
The common rail high-pressure injection system plays a fundamental role in advanced diesel engines, chasing optimal combustion and effective control of pollutant formation. On one end, research efforts are devoted to improving the injector behavior [
9], with particular attention on advanced nozzle layouts operating under real-like conditions [
10]. On the other end, the high-pressure pumps require a substantial demand on engine power for their operation, making their overall efficiency a critical parameter in determining energy loss during fuel injection. This power requirement must be accurately considered when configuring injection strategies, seeking to strike the necessary trade-off between engine fuel efficiency and precise combustion control. The overall efficiency of the high-pressure pump is dependent on its operating conditions such as injection pressure level, pump shaft speed, and fuel properties. It is conveniently represented by the product of volumetric efficiency and torque efficiency. Investigating these factors is essential to optimize the injection strategy taking the pump efficiency into account. According to [
11], the fuel type has a significant influence on the performance of the high-pressure pump. It has been observed that the pump behavior reflects the mechanical characteristics of fuels (viscosity and bulk modulus) and that certain diesel-biodiesel blends can lead to significant increases in pump efficiency [
12].
Beside the diesel-biodiesel blends, fossil-free fuels have been recently introduced to the market. These fuels are known as Hydrotreated Vegetable Oils (HVOs), obtained by vegetable oils through a hydrotreatment process [
13,
14]. Biodiesel, typically produced through transesterification, utilizes vegetable oils or animal fats. However, it may have higher oxidation susceptibility and storage instability. On the other hand, HVO involves the reaction of oils or fats with hydrogen, resulting in a fuel with enhanced stability and lower susceptibility to oxidation. HVO boasts a lower freezing point, enhancing its suitability across a diverse spectrum of environmental conditions. Both fuels play a relevant role in curbing greenhouse gas emissions, providing renewable alternatives to traditional diesel. The selection between them is in general dependent on precise application requirements, as well as compliance with environmental considerations and regulations. Thus, specific experimental investigations would provide precious information about their influence on pump behavior.
As reported in [
15], the real-time pressure measurements within the piston working chamber provide the means to discern the suction, compression-expansion, and delivery phases of the fluid. The fuel properties affect distinctly the pumping phases, enabling straightforward comparative analyses, highlighting the behavior of cylinder-piston pair, valve throttling, leakages, and other non-idealities that influence pump operation. The current investigation aims at integrating the in-depth analysis of the pump operation cycle with the experimental characterization of the pump volumetric efficiency.
As thoroughly reported in the next section, after completing the analysis of a single-piston common rail pump with a reference diesel fuel, the attention is directed towards alternative fuels (pure biodiesel and two HVO fuels), illustrating how fluids impact pump operation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pump operation cycle
The influence of the fuels on pump operation is investigated through the work cycle analysis. The work cycle is built in terms of pressure-volume diagrams. The pressure in the piston working chamber is measured and related to the piston stroke, that is dependent on pump shaft angular position. As reported in the next paragraph, the high-pressure pump under investigation is a single-piston unit, driven by a roller-cam pair, with two strokes per shaft revolution. The angular position of the pump shaft is monitored with an incremental quadrature encoder (1800 pulses per revolution). As a first investigation step, the piston kinematics as a function of the pump shaft angular position is measured. At each pulse of the encoder, the cam profile is measured through a digital comparator with 1µm resolution. The signals coming from encoder and comparator are reported to the DAQ system, driving the pump shaft at very low speed (1 RPM). Once the volume of the working chamber is related to the pump shaft position, the pressure measurement is achieved through a piezoresistive pressure transducer that reaches the working chamber. Such a transducer undergoes a wide range of pressure variations, from the boost level (4 bar), up to the maximum level (1800 bar). Another, narrow range, piezoresistive pressure transducer is put immediately upstream the pump inlet valve. A third transducer reads the pressure in the delivery ambient (rail). All pressure signals are acquired simultaneously and referred to a certain angular position of the pump shaft, that is provided by a dedicated encoder output channel.
Alongside the operating cycle of the pump, the pump volumetric efficiency is measured Equation (1).
is the volumetric flow rate to the rail volume at each shaft revolution, whereas
is the theoretical flow rate, defined as
.
is here computed trough Equation (2), where
and
are the measured flow rates at pump inlet and at pump return lines, respectively.
2.2. Experimental Set-Up
The experimental set up is implemented at the Fluid Power Laboratory (Industrial, Electronic and Mechanical Engineering Department, Roma TRE University). The pump model here investigated is the Bosch CP4.1 [
16], typically adopted for light- and medium-duty diesel engines.
Table 1 reports the relevant pump specification.
Figure 1 illustrates the mechanical-hydraulic configuration of the system. Pump shaft speed is imposed regardless the rail pressure conditions by the electric drive (e-DRV). In the rail tube (Rail), pressure regulation is based on PID control of the Pressure Control Valve (PCV). The Boost Pump supplies the High-Pressure Pump. The Pressure Relief Valve (PRV), situated in the HP pump body, governs the fuel pressure upstream the Flow Control Valve (FMV). The tested fuel is delivered by a parallel-flow fluid handling system that provides thermal regulation and filtration within the reservoir. Flow rates are measured trough volumetric flow meters on pump inlet line (VFM1) and on pump return line (VFM2). A rotary encoder (ENC) is used to measure the speed and the angular position of the pump shaft. The pressure transducers detect the piston working chamber pressure (PT1), the inlet pressure (PT2), the boost pressure (PT3), and the rail pressure (PT4).
All the instrumentation signals are sent to a multi-channel DAQ system. The data acquisition of all the signal lines is simultaneous, and each signal is synchronized to the reference angular position given by the rotary encoder (ENC). Pump operating cycles are built by averaging 64 cycles.
Table 2 reports the relevant specifications of DAQ system and instrumentation.
2.2. Tested Fluids
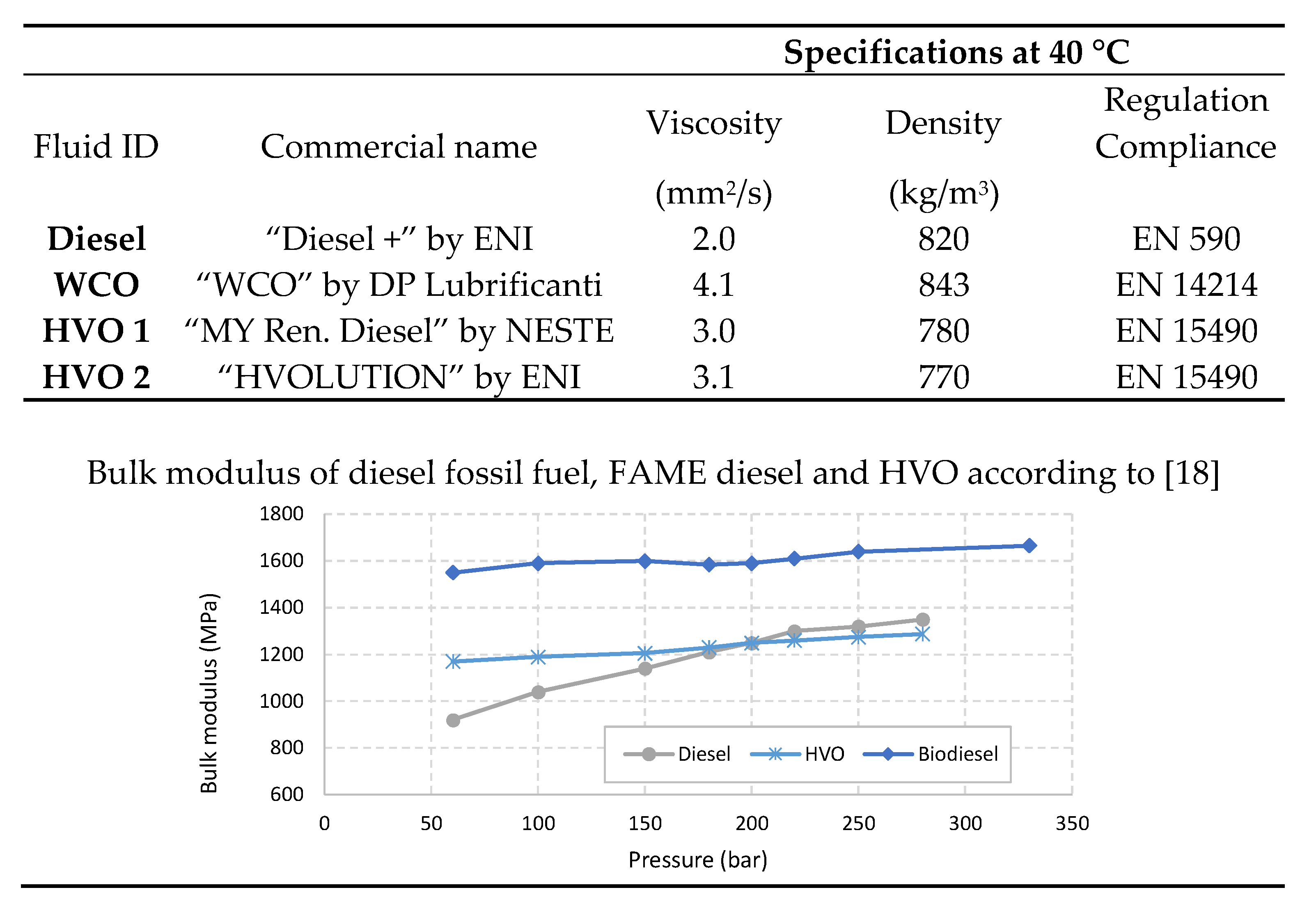
As mentioned in the introduction, the commercial diesel fuel “ENI Diesel+” is here considered as the reference fluid. The alternative tested fluids are represented by three fully renewable fuels. The first one belong to the FAME category, and it is obtained through the transesterification of used cooking oils and animal fats from industry waste. The other two fuels belong to the HVO category. They are obtained by hydrotreating renewable raw vegetal materials.
Figure 2 resumes their features. Information about density and viscosity are derived by the producers’ datasheets, whereas bulk modulus is found in the literature [
17,
18,
19].
2.3. Test Cases
The influence of fuel type is investigated at low (L), medium (M), and high (H) pressure in the most two significant speed conditions, one belonging to the range of the maximum torque of the engine (1500 RPM), the other typically meaningful at medium/high engine power (3000 RPM).
Table 3 reports the test conditions, namely 6 operation points for each fuel type, 24 in total.
3. Results and Discussion
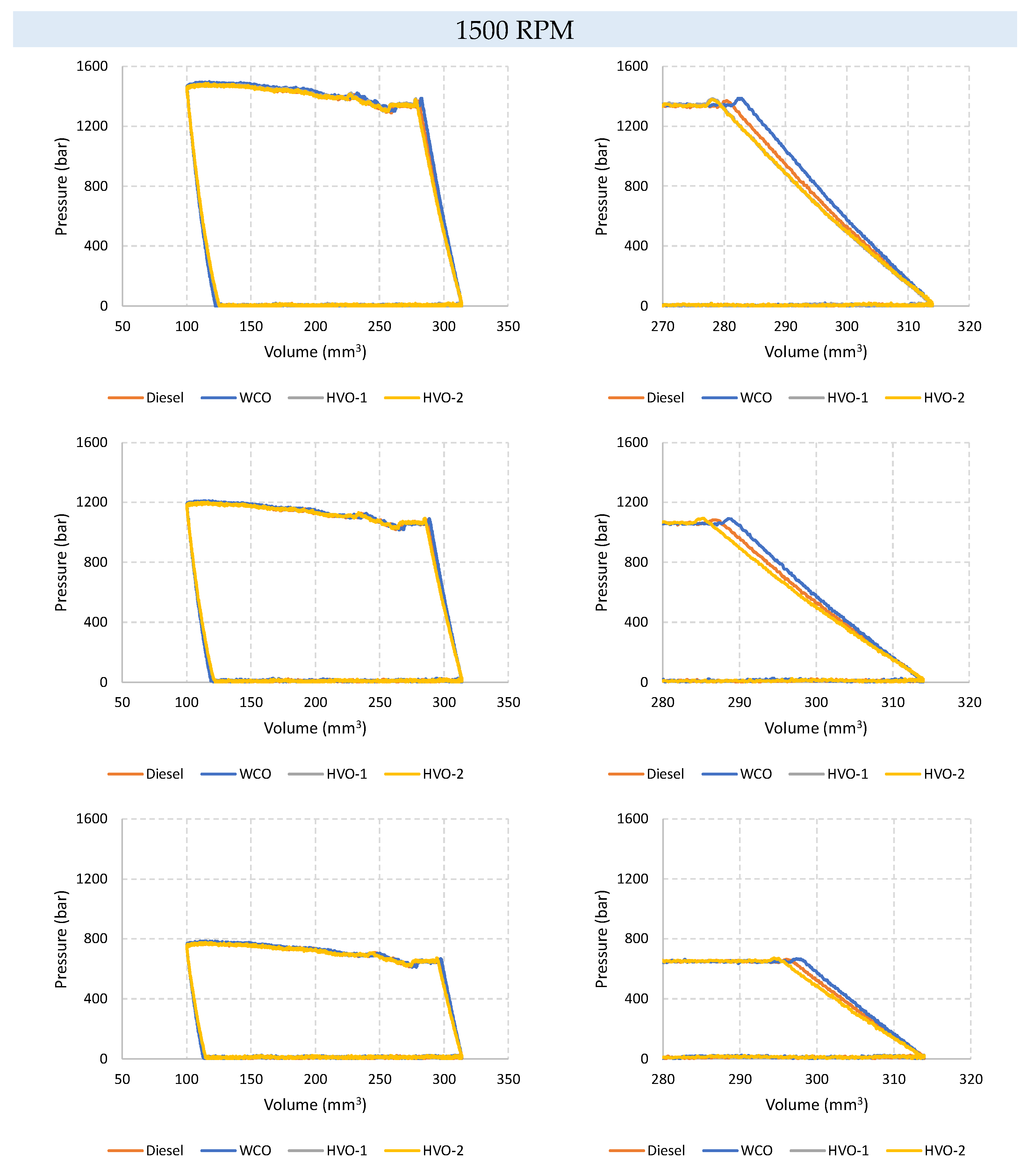
Figure 3 presents diagrams of the pump internal pressure at 1500 RPM. The internal pressure is plotted against the piston working chamber volume for the three pressure levels (L, M, and H) and the four considered fuels. The results are organized in the figure by displaying the complete pump operation cycles in the left column, while cycle details or subphases are shown on the right. Pressure-Volume (p-V) diagrams highlight the pump behavior throughout its operating cycle, depending on the fuel. Each fuel type and pressure level produce its own distinctive curve, reflecting how the pump's internal pressure varies with changes in the piston working chamber volume. The left column of the Figure reports the complete cycle diagrams. The right column provides more detailed information about specific phases or subphases within each cycle, highlighting key events or transitions.
The pump sensitivity to different fluids is primarily evident in the compression and expansion phases. Fluids with higher compressibility modulus enable the pump to initiate the delivery phase earlier, thereby enhancing its fluid transfer capability. Additionally, the graphs illustrate that both hydrogenated fuels under consideration (HVO 1 and HVO 2) induce very similar operational modes in the pump. Specifically, hydrogenated fuels lead to a moderate yet noteworthy extension of the compression phase, resulting in a reduction in the amplitude of the delivery phase. The fluid that achieves the shortest compression phase is WCO, indicated by the steepest trace of the compression phase. Diesel fuel exhibits an intermediate behavior between HVO and WCO. In all cases, the concavity of both the compression and expansion phases is evident, aligning with the increasing function of the compressibility modulus of liquids with pressure [
19]. The characteristics of the delivery phase remain consistently similar across different fluids.
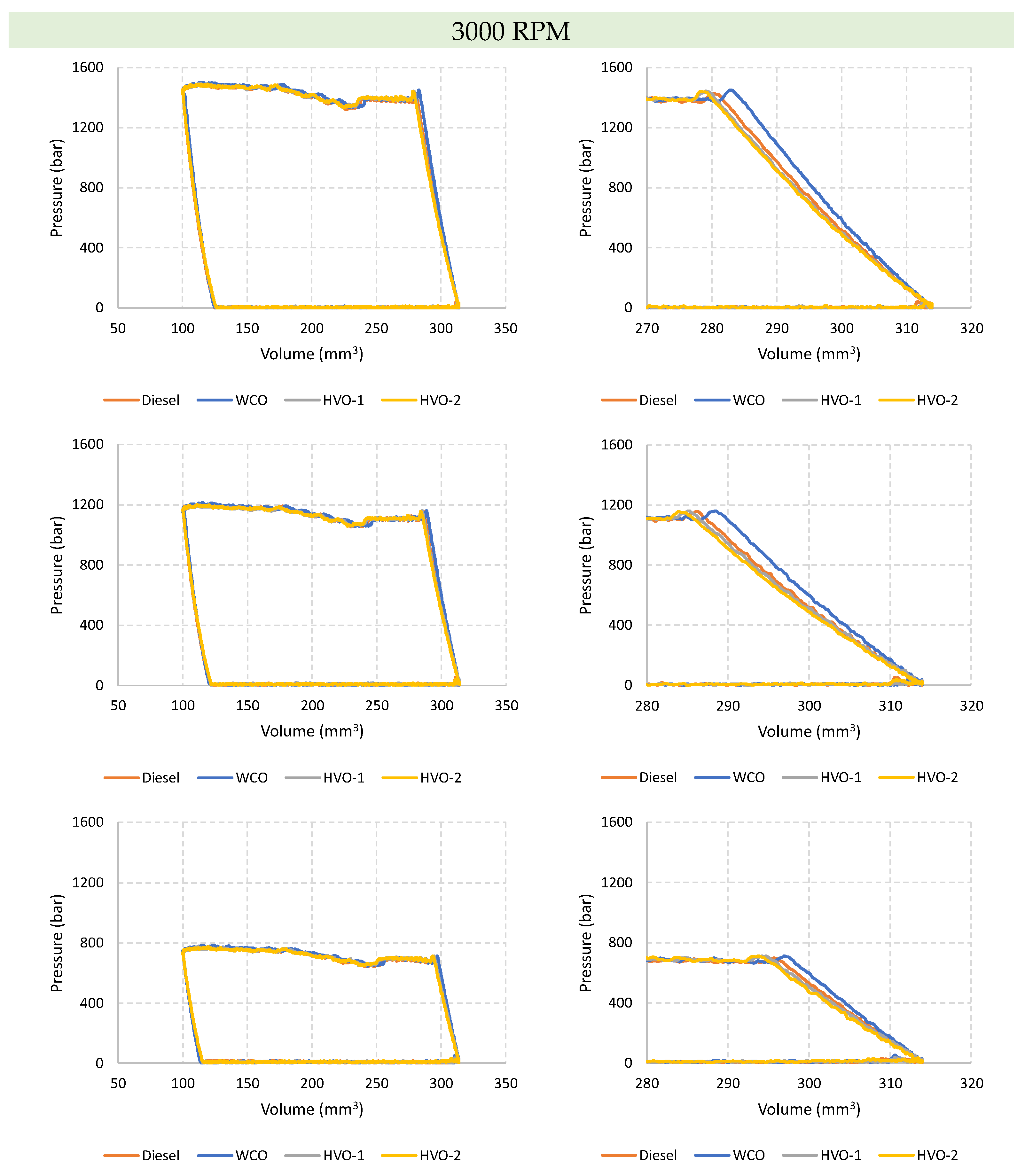
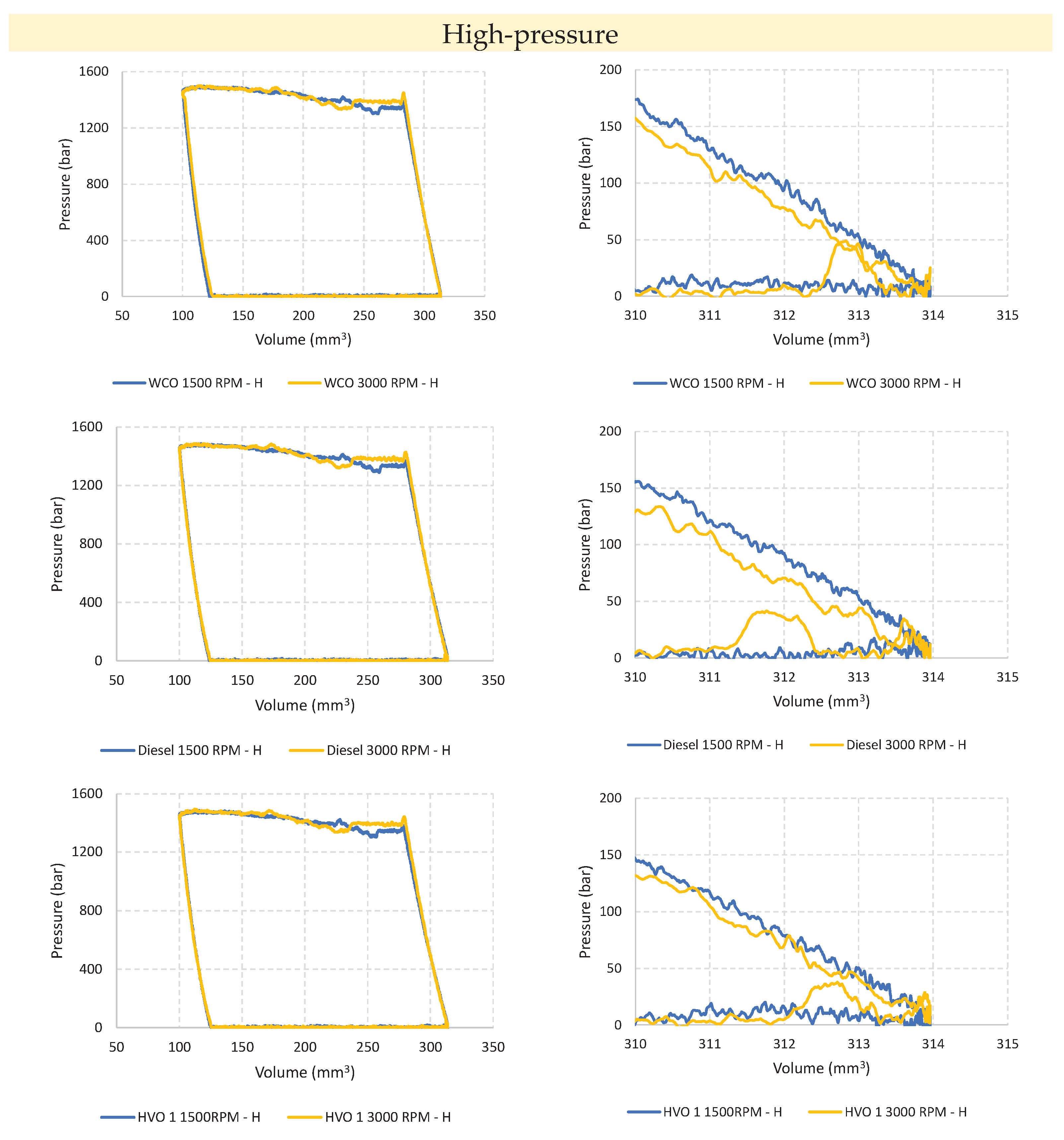
Figure 4 shows the working diagrams of the pump at 3000 RPM. The impact of fluids on the pump behavior resembles that observed at 1500 RPM, with the diagrams of the two HVO fuels superimposed, and the Diesel diagram positioned between HVO and WCO. However, it is noteworthy that at 3000 RPM, the pump exhibits some irregularities towards the end of the intake phase. Upon closer inspection of the end of the suction phase (
Figure 5), significant deviations in pressure trends are observed compared to the set admission pressure of 4 bar. The pressure peaks highlighted in
Figure 5-right occur during the final stages of intake, when the volume of the working chamber is still increasing. In such instances, it is conceivable that these pressure peaks stem from communication with the delivery environment, possibly due to imperfect sealing of the delivery valve or its oscillation/vibrations. This phenomenon is present across all three pressure levels and never appears at low speed.
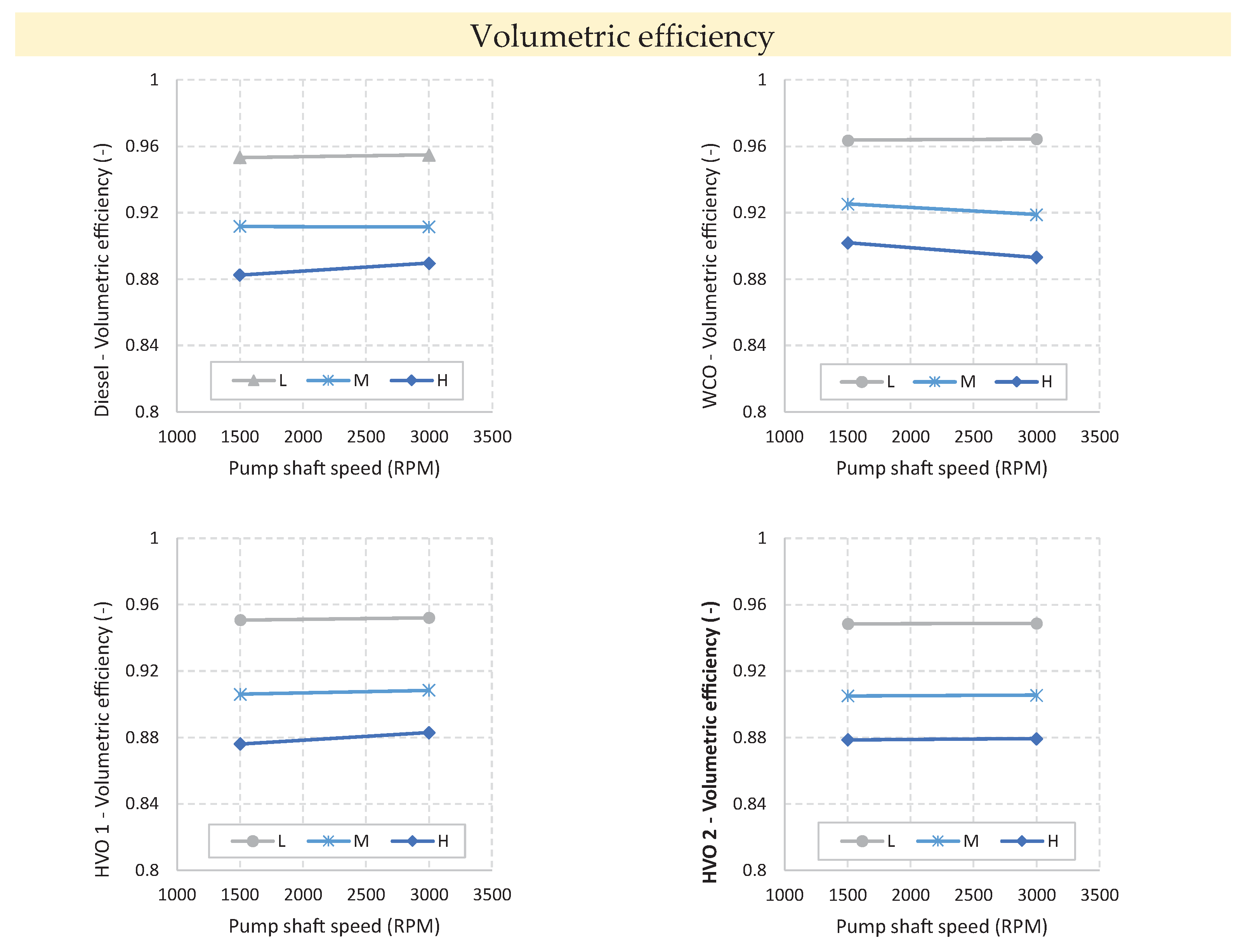
Figure 6 illustrates the trends in volumetric efficiency measured at each investigated operation point. Notably, as pressure increases, there is a significant decrease in efficiency. These findings align with the pressure-volume diagrams previously presented, underscoring that the pump fluid transfer capability primarily hinges on the compressibility modulus of the fluid. While speed dependence is of secondary importance, it remains perceptible. Specifically, at high pressures, the volumetric efficiency of the pump operating with fluids characterized by lower viscosity (such as Diesel, HVO 1, and HVO 2) tends to increase with speed. Conversely, when operating with WCO fluid, the pump tends to be penalized at high speeds, despite WCO consistently yielding the highest volumetric efficiency under all conditions. This observation suggests that when pump speed increases, it doesn't necessarily result in a higher volumetric efficiency due to leakage reduction. Using fluids with relatively high viscosity, such as WCO, the increased speed leads to increased losses that affect fluid transfer process.
5. Conclusions
The behavior of the high-pressure pump is analyzed combining pressure-volume diagrams to volumetric efficiency measurements. It is found that the pump's performance is notably influenced by the type of fuel being processed. Through investigations of each fluid, the effects of the pump's two primary operating parameters—rotation speed and delivery pressure—are elucidated. The analysis reveals that speed dependence is moderate. This conclusion is drawn from the combined examination of pressure trends within the pump's working chamber and volumetric efficiency values, indicating that rotation speed has little influence on fluid transfer. In contrast, the dependence on delivery pressure is much more pronounced. While the fluids under consideration vary in viscosity and compressibility modulus, it's the compressibility modulus that predominantly affects the pump's fluid transfer ability. Diesel (fossil) fluid exhibits intermediate characteristics compared to hydrogenated fossil diesel fluids and FAME biodiesel. Notably, hydrogenated carbon-neutral fluids allow for performance levels that do not significantly hinder the pump's flow rate transfer capability.
References
- Hua, Y. Research progress of higher alcohols as alternative fuels for compression ignition engines. Fuel 2024, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, J.; Deppenkemper, K.; Pischinger, S. Impact of renewable fuels on heavy-duty engine performance and emissions. Energy Reports 2023, 9, 1977–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betgeri, V.; Bhardwaj, O.P.; Pischinger, S. Investigation of the drop-in capabilities of a renewable 1-Octanol based E-fuel for heavy-duty engine applications. Energy 2023, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.A.; Khan, H.A.; Ravi, S.S.; Turner, J.W.; Aziz, M. Potential of clean liquid fuels in decarbonizing transportation – An overlooked net- zero pathway? Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2023, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiatti, G.; Chiavola, O.; Recco, E.; Palmieri, F. Soot Particles Experimental Characterization during Cold Start of a Micro Car Engine. Proceedings of the Energy Procedia 2016, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochi, D.; Fanigliulo, R.; Grilli, R.; Fornaciari, L.; Bisaglia, C.; Cutini, M.; Brambilla, M.; Sagliano, A.; Capuzzi, L.; Palmieri, F.; et al. Design and Assessment of a Test Rig for Hydrodynamic Tests on Hydraulic Fluids. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering 2020, 67, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonthalia, A.; Kumar, N. Hydroprocessed vegetable oil as a fuel for transportation sector: A review. Journal of the Energy Institute 2019, 92, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, R.B.R.; Coronado, C.J.R.; Hernández, J.J.; Malaquias, A.C.T.; Flores, L.F.V.; de Carvalho, J.A. Experimental assessment of power generation using a compression ignition engine fueled by farnesane – A renewable diesel from sugarcane. Energy 2021, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavola, O.; Palmieri, F. On a Modified VCO Nozzle Layout for Diesel Common Rail Injectors under Actual Needle Displacement. Proceedings of the Energy Procedia 2017, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Wang, C.; Moro, A.; Roell, A.; Wu, X.; Luo, F. The influence of needle eccentric motion on injection and spray characteristics of a two-layered eight-hole diesel injector. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, D.M.; Chiavola, O.; Frattini, E.; Palmieri, F. On the Modeling of Single-Piston CR Pump. In Proceedings of the SAE Technical Papers; 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cavallo, M.; Frattini, E.; Palmieri, F. Fuel Influence on Single-Piston Common Rail Pump Performance. In Proceedings of the SAE Technical Papers; 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Trzaska, J.; Hernández, J.J.; Boehman, A.L. The effect of 1-octanol blending on the multi-stage autoignition of conventional diesel and HVO fuels. Fuel 2023, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuß, J.; Munch, K.; Denbratt, I. Performance and emissions of renewable blends with OME3-5 and HVO in heavy duty and light duty compression ignition engines. Fuel 2021, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavola, O.; Frattini, E.; Lancione, S.; Palmieri, F. Operation Cycle of Diesel CR Injection Pump via Pressure Measurement in Piston Working Chamber. Energies 2021, 14, 5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, R. Automotive Handbook, 10th ed.; Wiley, Ed.; 2019; p. 1750. [Google Scholar]
- Payri, R.; Salvador, F.J.; Gimeno, J.; Bracho, G. The effect of temperature and pressure on thermodynamic properties of diesel and biodiesel fuels. Fuel 2011, 90, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapuerta, M.; Agudelo, J.R.; Prorok, M.; Boehman, A.L. Bulk modulus of compressibility of diesel/biodiesel/HVO blends. Energy and Fuels 2012, 26, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Boehman, A.L. Experimental Measurement of the Isothermal Bulk Modulus of Compressibility and Speed of Sound of Conventional and Alternative Jet Fuels. Energy and Fuels 2021, 35, 13813–13829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).