1. Introduction
Marine algae are important sources of compounds with health-enhancing biological properties [
1], including anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and immune enhancing functionalities [
2,
3,
4,
5]. Also, algal metabolites such as sulphated polysaccharide and polyphenols have demonstrated multistep antiviral capability and provided new paths for forming new therapeutics methods for treating COVID-19 and other viral diseases [
6].
Codium fragile, a green algae, is a traditional Asian food ingredient [
7]. Main components of green algae are sulphated structural polysaccharides, such as ulvans and sulfated galactans, xylans and mannans. These polymers are composed mainly of rhamnose, xylose, glucose, glucuronic acid, and sulphates, follow by mannose, arabinose, and galactose in smaller amounts [
8,
9]. These polysaccharides are not fully fermented by human gut microbiota [
10,
11,
12]. In addition, sulfated polysaccharides purified from
C.
fragile polysaccharide have various biological effects, including anti-viral, immune-stimulatory, and anti-cancer effects [
13,
14]. These findings provide a rationale for the potential application of
C.
fragile polysaccharide as a prebiotic.
The gut microbiota are microorganisms or microbiotas living in the gastrointestinal tract of a host. Human health is widely affected by the composition and metabolic effect of these microbiota [
15]. Microbiota of the human gastrointestinal tract have been studied extensively owing to their role both in pathogenesis and gut health maintanence. An important function of large intestinal microbiota is to break down substrates such as resistant starch and dietary fiber, which are not completely hydrolyzed by host enzymes in the small intestine [
16,
17,
18,
19]. Thus, health improvement via regulation of the gut microbiota has become an interesting research field.
Akkermansia muciniphila is a strictly anaerobic bacterium recently isolated from human feces, it uses the mucin as the sole sources of carbon and nitrogen elements [
20]. Ottman
et al. reported that
A. muciniphila can utilize the mucin-derived monosaccharides fucose, galactose and
N-acetylglucosamin[
21,
22].These additional mucin-derived components might be needed for its optimal growth. The presence of
A. muciniphila in feces has been associated with a healthy intestine, and its abundance has been inversely correlated to several disease states. In patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, the abundance of
A. muciniphila was found to be decreased [
23,
24]. However, as
A. muciniphila is a strict anaerobe with highly limited growth conditions, there are currently no
A. muciniphila- containing products in the world. Therefore, consuming prebiotics that can selectively promote
A. muciniphila in the intestine is necessary.
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs), ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease (CD) are chronic intestinal disorders of unknown etiology [
25,
26]. Recent developments in understanding the pathogenesis of IBD have created opportunities for developing novel therapeutic approaches focused on therapeutic targets and involving safe and efficient natural compounds that can normalize the intestinal microflora, maintain clinical remission, and speed up the healing of intestinal mucus layer [
27,
28,
29]. Marine algae serves as a significant bioresource of natural compounds with beneficial activities. Algal polysaccharides are excellent therapeutic agents for treating intestinal inflammatory diseases such as IBD due to their resistance to the action of the gastric juice and enzymes of the host and their ability to serve as a fermentation substrate to beneficial intestinal microbes [
30,
31].
In this study, we hypothesized that Codium fragile extract (CFE) is a fermentation substrates for gut microbial population that is an excellent therapeutic agents for treating intestinal inflammatory diseases. Until now, few reports have been published on the protective effects of CFE in mice with DSS-induced colitis. So, the present study was conducted to evaluate protective effect of CFE against dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) colitis along with the proliferation of specific beneficial bacteria associated with a healthy intestine.
2. Materials and Methods
In this section, Methods for the effects of CFE on potential prebiotics and intestinal diseases are presented.
Section 2.2 presents methods for evaluating prebiotics to grow specific beneficial bacteria important for maintaining intestine health. In
Section 2.3, methods for evaluating improvement in intestinal diseases are presented.
2.1. Preparation of CFE
CFE was prepared according to a previously described method [
32].
C. fragile was collected from a seaweed farm in Wando, Jellanamdo, South Korea in September 2023.
C. fragile was repeatedly washed with tap water for 10 min in order to remove salt and then air-dried at 47.5 ± 2.5 °C for 6h. The dried
C. fragile was grinded into powder. After sieving 20-mesh, extraction was performed at 100 °C for 3 h using 20 times the amount of fresh water. The resultant CFE was concentrated using a vacuum rotary evaporator. CFE was freeze-dried and stored at -20 °C.
2.2. Potential Prebiotics for Improving Intestinal Diseases
2.2.1. Animal Model
Seven-week-old BALB/c male mice (15-20 g) were purchased from KOSA BIO Inc. (Seongnam, Korea) and housed in an air-conditioned room with a 12h light/dark cycle at 22 ± 2 ℃ with 50 ± 5% of humidity. All mice were fed a AIN-93 diet (Research Diets, Inc., New Brunswick, NJ, USA) (
Table 1) and sterilized water
ad libitium for a week in an adaptation period. The mice were then divided into four groups (n = 5 per group): (1) CTRL group, fed a normal diet; (2) LCFE group, fed 75 mg of CFE per kg of body weight; (3) MCFE group, fed 150 mg of CFE per kg of body weight; (4) HCFE group, fed 300 mg of CFE per kg of body weight. All procedures for this experiment were conducted in accordance with Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) for the care and use of laboratory animals of the Berry & Biofood Research Institute (BBRI-IACUC-21001).
2.2.2. Real-Time PCR Quantification
Fecal samples were collected from individual mice in autoclaved tubes and stored -80 ℃. Genomic DNA was extracted using a QIAamp DNA Stool Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), according to the manufacturer’s instruction.
The primers used to detect A. muciniphila and S. aureus were based on 16S rRNA gene sequences retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information databases using the Entrez program (Wheeler et al.,2006). All bacterium sequences were aligned with sequences from closely related species using ClustalW. Forward primers and reverse primers were designed using the Primer Express 2.0 software (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) (Table. 2)
PCR amplification was carried out in a total volume of 25 ml containing 1 x TaqMan Universal PCR Master Mix (Applied Biosystems), both primers (10 pmol each), 50 ng purified target DNA, and BSA at the final concentration of 0.1 mg/ml (New England Biolabs). Amplification (2 min at 50 °C, 10 min at 95 °C, followed by 40 cycles of 15 s at 95 °C and 1 min at 60 °C) and detection were carried out on an StepOne Plus Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems). The amount of genomic DNA extracted was determined by an ultraviolet spectrophotometer at 260 nm. In our PCR assay, we compared different quantities of bacterial DNA extracted from fecal samples to overcome the bias due to the presence of inhibitory compounds, such as bile salts. Each assay was performed in duplicate in the same run. The cycle threshold (CT) was calculated as the cycle number at which the reaction became exponential. The cycle threshold of each sample was then compared to a standard curve made by diluting genomic DNA (10-fold serial dilution) from cultures of target bacterium.
Table 2.
16S rRNA gene-targeted bacteria-specific primers used in this study.
Table 2.
16S rRNA gene-targeted bacteria-specific primers used in this study.
| Target |
Primer |
Primer sequence (5’-3’) |
| Probiotics |
Bifidobacterium
spp. |
Forward
Reverse |
CTCCTGGAAACGGGTGG
GGTGTTCTTCCCGATATCTAC |
Akkermansia
muciniphila
|
Forward
Reverse |
CAGCACGTGAAGGTGGGGAC
CCTTGCGGTTGGCTTCAGAT |
| Pathogens |
Staphylococcus
aureus
|
Forward
Reverse |
GCCCCTTAGTGCTGCAGCTA
AGTTTCAACCTTGCGGTCGTA |
Clostridium
spp. |
Forward
Reverse |
TTGAGCGATTTACTTCGGT
CCATCCTGTACTGGCTCAC |
2.2.3. Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs) Analysis
To determine SCFAs concentration, cecum contents were collected and stored at -70 °C until further processing. Acetic acid and butyric acid concentration were determined by flame ionization detection on an Agilent 7890A GC-MS equipped with a DB-FATWAX Ultra Inert column 30 m × 530 mm × 0.25 μm (Agilent Technologies).
2.2.4. β-Glucuronidase Activity Analysis
Fecal activities of β-glucuronidase was analyzed through a method described by Goldin et al [
33]. Fecal samples were incubated to 37 °C in the wells of a microtiter plate, and then 10 mL of sample was added in duplicate. Next, 100 μL of substrate solution was added, and the mixture was incubated at 37 °C for 60 min. The reaction was stopped by adding 500 μL of 0.5 N NaOH. Enzymatic activity was quantified by measuring the absorbance at 405 nm. Triplicate assays for each effector were performed, and the mean values and standard deviations were reported. The concentration of 4-nitrophenol was determined using a standard curve of 4-nitrophenol in sodium phosphate buffer.
2.3. Potential Prebiotics for Improving Intestinal Diseases
2.3.1. Animal Model
Male C57BL/6J mice (9 weeks, 18 ± 2g) were purchased from Orient Bio (Korea). The mice were adapted to a specific pathogen-free condition (12 h light/dark cycle, 22 ± 2 °C) for 7 days before the experiments, with free access to drinking water and a commercial diet. The colitis induced by orally administering 3% (w/v) DSS drinking water for 5 days, followed by 3 days without DSS (molecular weight 36–50 kDa; MP Biomedicals, Irvine, CA, USA). During the whole experimental period for 8 days, CFE and sulfasalazine (St. Louis, MO, USA) were orally daily administrated to mice. The mice were randomly divided into six groups (n = 5 per groups): (1) the normal group fed water (N group), (2) negative control group fed DSS (NC group), (3) positive control group fed DSS + sulfasalazine (150mg/kg) (PC group), (4) DSS+LCFE group, fed DSS + 75 mg of CFE per kg of body weight, (5) DSS+MCFE group, fed DSS + 150 mg of CFE per kg of body weight, (6) DSS+HCFE group, fed DSS + 300 mg of CFE per kg of body weight. All animal experiments were approved by the Animal and Ethics Review Committee of Woojung Bio Inc. (Suwon, Korea) and performed in accordance with the guidelines established by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. The approval ID for using the animals was IACUC2303–041 at the Animal Facility of Woojung Bio.
2.3.2. Assessment of Severity of Colitis
The length of the colon was measured from the ileocecal junction to the anal verge [
34]. The disease activity index (DAI) was calculated by average scores for changes in body weight loss, stool condition, and fecal bleeding, according to the DAI scoring system [
35]. Briefly, loss in body weight was scored as follows: (i) weight loss: 0, no weight loss; 1, 1–5% loss; 2, 5–10% loss; 3, 10–20% loss; 4, more than 20% loss, (ii) stool consistency: 0, normal; 1, loose stools; 2, watery diarrhea; 3, slimy diarrhea; 4, severe watery diarrhea, and (iii) fecal bleeding: 0, no blood; 2, slight bleeding, 4, visible bleeding.
2.3.3. Quantification of Enzymatic Activity
β-glucuronidase activity was detected using modified protocols [
36,
37]. In brief, the reaction mixture, containing 50 μL fecalase, 100 μL potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.4, 0.01 M), and 100 μL 4-nitrophenyl-β-D-glucopyranoside (1 mM, in buffer; Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO; CAS no. 2492-87-7) for β-glucuronidase, was incubated at 37 °C for 15 min, or 20 min for human fecalase samples due to the darker color of human fecal pellets. After incubation, 250 μL, sodium hydroxide (NaOH) (0.5 N) was added to stop the reaction, and the absorbance was measured at 405 nm (UV-vis spectrophotometer).
The Pierce BCA protein assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific; CAS no. 23225) was used, following the manufacturer’s protocol, to measure the total protein concentration in the fecalase samples. Enzyme activity was calculated after correction for controls (to account for the background fecalase absorbance), from a standard curve of 4-nitrophenol (Sigma Aldrich; CAS no. 100-02-7). The unit of activity, normalized to fecalase protein, was expressed as the amount required to catalyze the formation of 1 mol of p-nitrophenol per minute under the standard assay conditions (i.e., U/mg protein).
2.3.4. Myeloperoxidase (MPO) Activity
MPO activity of serum and colonic tissue was determined with MPO assay kit (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, China). Concisely, colon tissues were homogenized in the stocking buffer from manufacturer. Homogenate or serum was mixed and incubated at 37 °C for 30 min in the reaction solution. The mixture was subsequently kept for 10 min at 60 °C, followed by adding hydrogen peroxide (50 μL). A multimode microplate reader (BioTek Instruments, VT, USA) was used to measure the absorbance of mixture at 460 nm. One unit of MPO activity was designated as the quantity of enzyme capable of degrading 1 μM hydrogen peroxide at 37 °C. The results were determined as units per liter serum or per gram colon tissue.
2.3.6. Statistical Analysis
Data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). Data were analyzed with SPSS 22.0 software by t-test and one-way ANOVA analysis for comparison of two or more groups, followed by the post hoc Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
3. Results
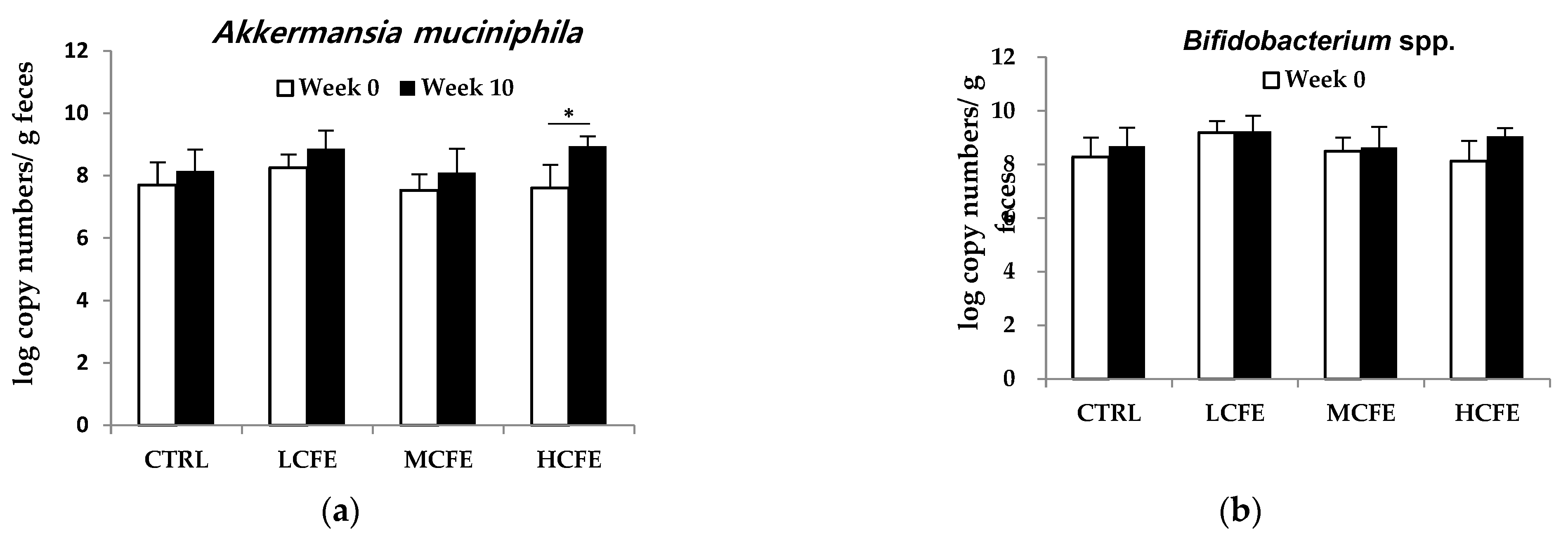
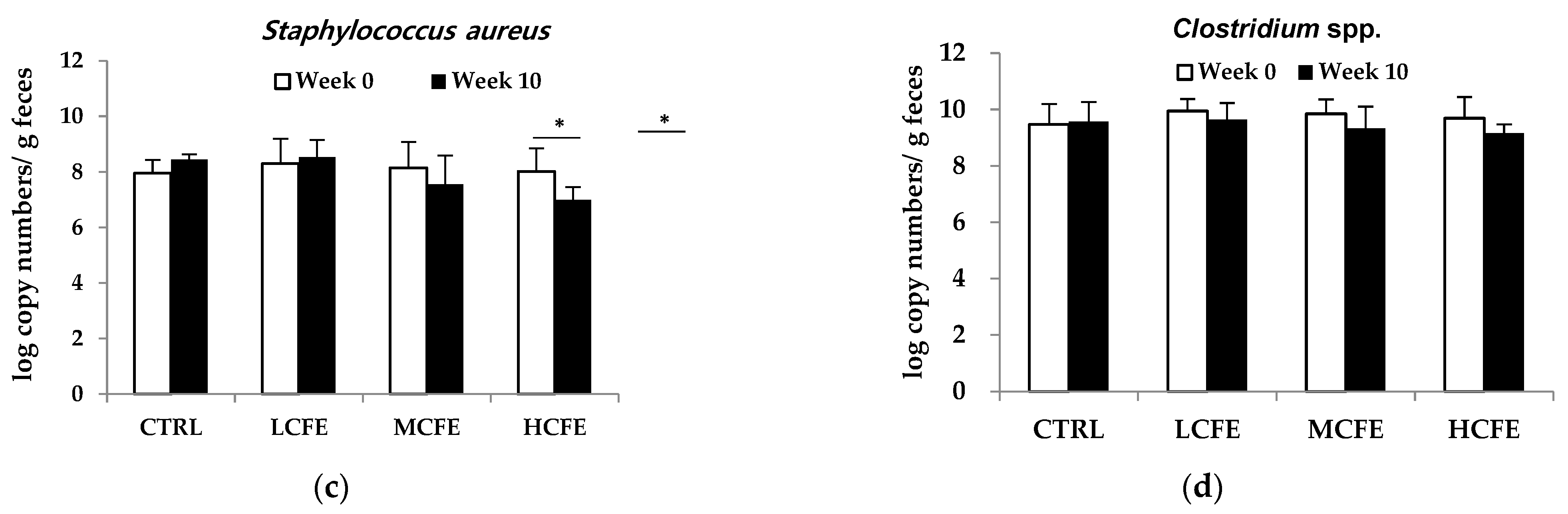
3.1. Effect of CFE on the Growth of Individual Bacteria
After feeding CFE for 10 weeks, changes in DNA log copy number of bacteria in mouse feces were determined (Figure 1). During CFE intake (10 weeks), a increase in beneficial bacteria,
A. muciniphila and
Bifidobacterium spp., was observed, while the pathogenic bacteria,
S. aureus and
Clostridium spp., decreased. Moreover, in the HCEF group,
A. muciniphila significantly increased and
S. aureus significantly decreased (
Figure 2a,c).
3.2. Effect of CFE on Cecum SCFA Production
As shown in
Table 3, the main metabolite in mouse cecum contents was acetic acid, followed by butyric acid, which was present in a small amount. The content of SCFAs in CFE-fed groups were higher than those in the CTRL group in a CFE concentration-dependent manner. The content of acetic acid in LCFE group (
p<0.05), MCFE and HCFE group (
p<0.001) and butyric acid in MCFE and HCFE group (
p<0.05) were higher than those in CTRL group.
Table 3.
SCFA analysis of mouse cecum contents.
Table 3.
SCFA analysis of mouse cecum contents.
| Groups |
SCFAs (μmol/g) |
| Acetic acid |
Butyric acid |
| CTRL |
9.05 ± 2.03 |
2.54 ± 0.48 |
| LCFE |
13.83 ± 1.12**
|
3.27 ± 0.98 |
| MCFE |
18.91 ± 2.70***
|
3.70 ± 0.53*
|
| HCFE |
20.24 ± 1.60***
|
3.94 ± 0.69*
|
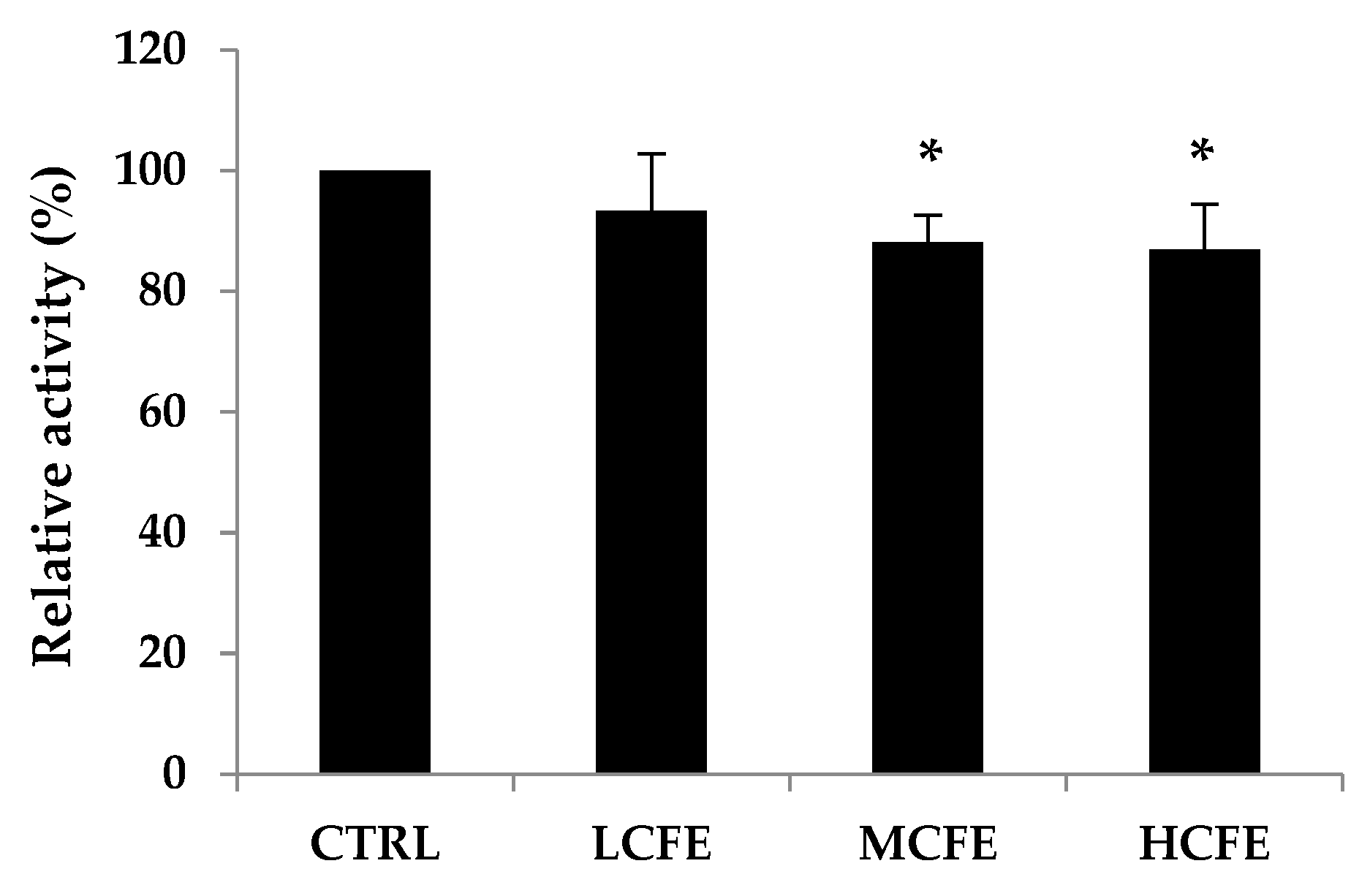
3.3. Effect of CFE on Fecal β-Glucuronidase Activities
β-Glucuronidase activities in mouse feces were measured at week 10 of CFE feeding (
Figure 3). In particular, a marked decrease was observed for β-glucuronidase activity in MCFE and HCFE group (
p<0.05), as compared with the CTRL group, being 88% and 87%, respectively.
3.4. Effect of CFE on Mouse Colitis
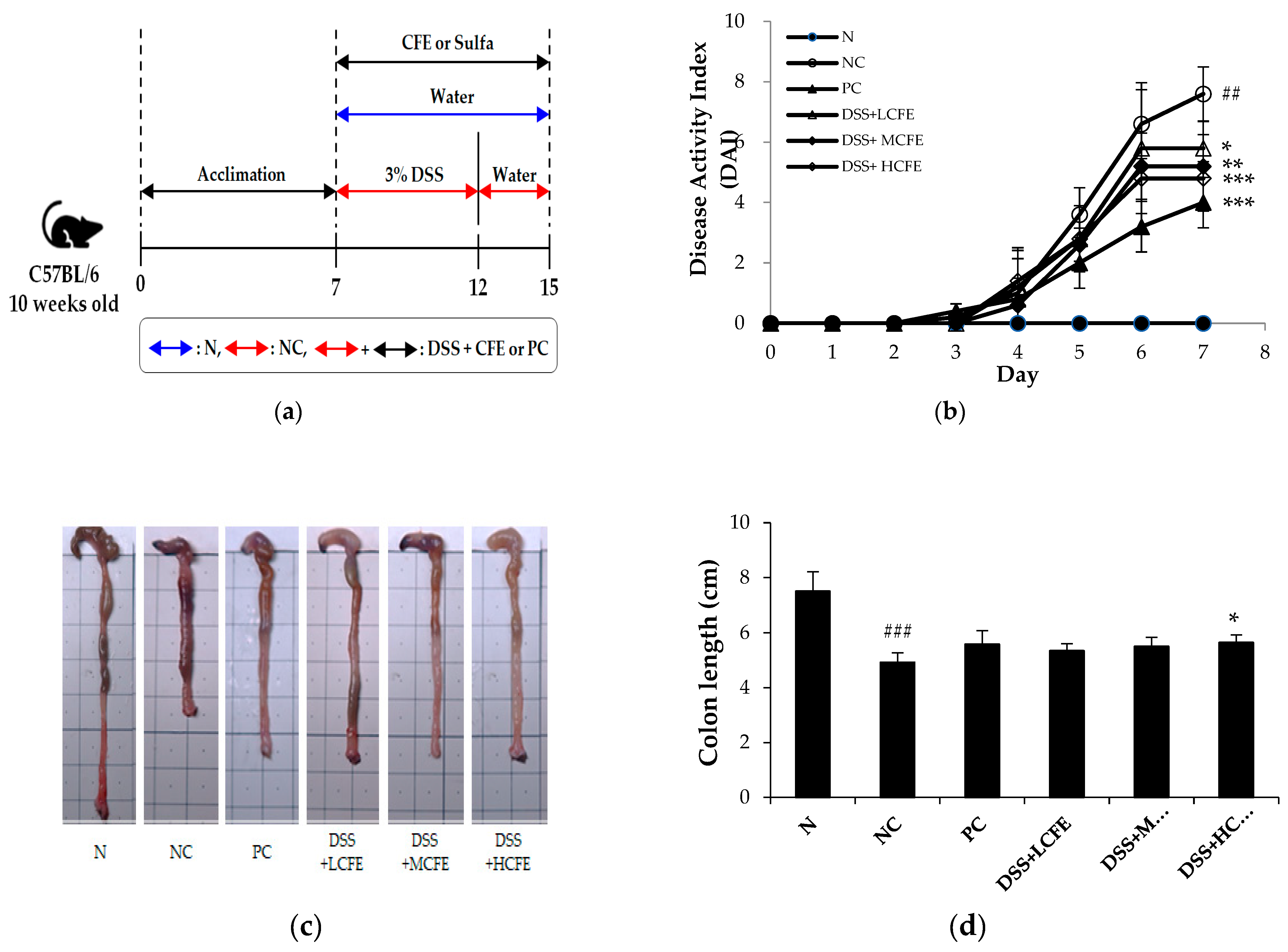
To evaluate the anti-colitis effects of CFE, C57BL/6 mice were administrated with 3% DSS, sulfasalazine (150 mg/kg), and CFE (75 mg/kg, 150 mg/kg, 300 mg/kg) separately or combined for 8 days (
Figure 3a). The DAI score and colon length reflect the severity of ulcerative colitis (UC) in animal models directly and are commonly utilized to assess the severity of colitis preliminarily. The DAI scores of each mice group during days 0 – 7 are presented in
Figure 3b. The DAI scores were also significantly reduced in the CFE-fed group compared with that of the NC group. Another indicator reflecting the severity of intestinal inflammation is colon length, which is restored with improvement in inflammatory [
38,
39]. The colon length of mice in the DSS + HCFE group (
p<0.05) was significantly longer than that of the NC group and similar to that of the PC group (
Figure 3c,
3d).
3.5. Effect of CFE on the Histological Injury of Colonic Epithelium Caused by DSS
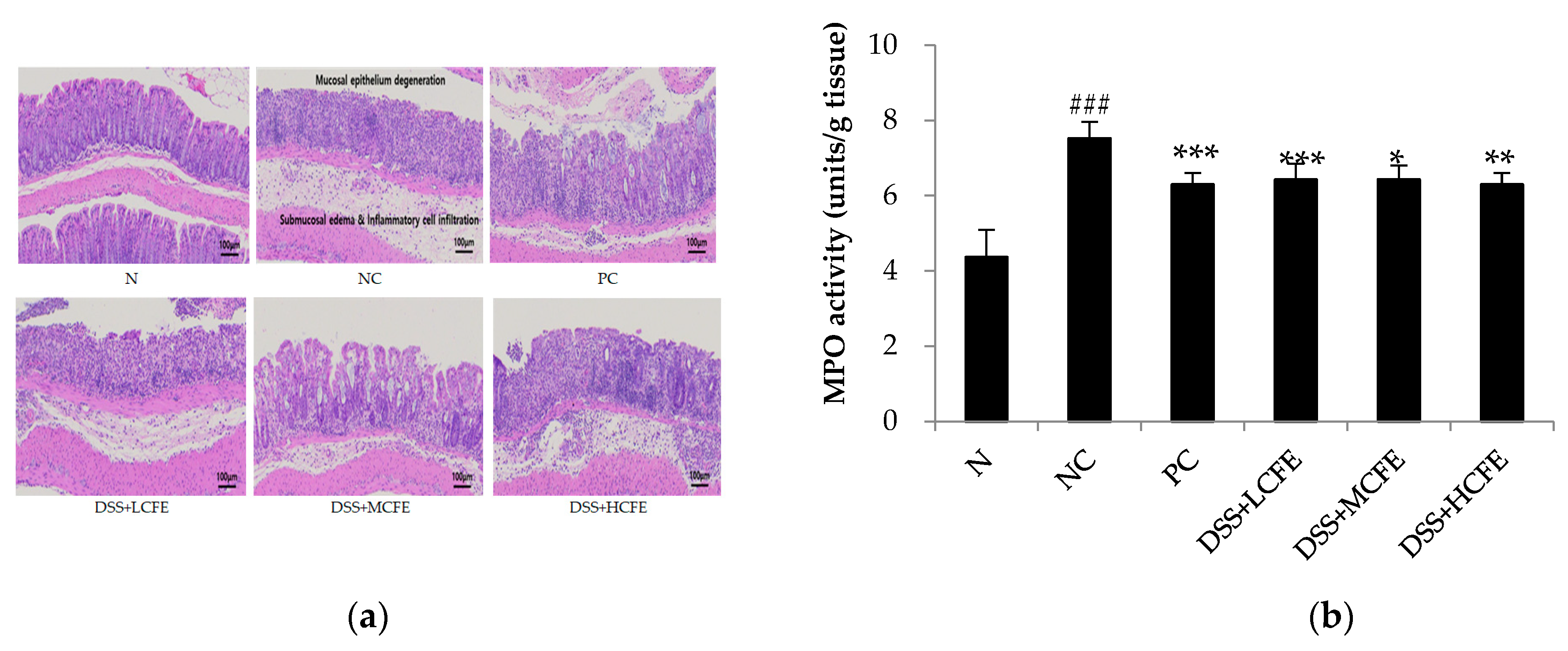
To investigate mucosal inflammation, we performed H/E staining. Colons in the N group exhibited normal crypt morphology, abundant goblet cells, no signs of mucosal thickening, and complete absence of ulceration. Compared with the N group, pathological section of colon tissue of mice in the NC group showed intestinal wall edema and thickening, with a considerable number of inflammatory cells infiltration, severely deformed crypt structure, and destroyed or even disappeared goblet cells (
Figure 4a). On the contrary, microscopic damage was lower in DSS + HCHE (CFE-fed) or PC group than in the NC group. Test results exhibited that MPO activity in the colon was significantly reduced in the CFE-fed and PC groups compared with that of the NC group (
Figure 4b).
4. Discussion
Marine algae polysaccharides can be used as prebiotics for gut microbiota, which partially degrade them into other bioactive compounds, such as oligosaccharides and short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) acting as food sources for these organisms and allowing them to proliferate [
40,
41,
42,
43,
44]. In the present study, we elucidated the ability of CFE to promote the growth of
A. muciniphila. The presence of
A. muciniphila in feces has been associated with a healthy intestine, and its abundance has been inversely correlated to several disease states. Further analysis confirmed that
A. muciniphila can degrade mucin and exert competitive inhibition on other pathogenic bacteria that degrade the mucin [
45]. Therefore, present study aimed to investigate efficacy and underlying mechanisms of CFE in alleviating DSS-induced colitis in mice.
The proliferation of bacteria was determined by quantitative PCR during 10 weeks of CFE feeding. As the administration of CFE increased, the proliferation of A. muciniphila increased, whereas the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria decreased. A. muciniphila is abundant in the gut microbiota of healthy individuals, and it is beneficial in the prevention and treatment of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and other metabolic dysfunctions [213,46-49]. Therefore, CFE can be used as a prebiotic that specifically promotes A. muciniphila growth for the treatment metabolic diseases.
After CFE administration for 10 weeks, acetic acid was revealed as the major metabolite in mouse cecum. A similar result was also reported by Li et al. [
50], who found acetic acid as a major metabolite produced by
A. muciniphila under static and dynamic culture. Li et al. [
50], reported that acetic acid increased lipolysis and decreases lipid synthesis in BRL-3A cells, thus reducing hepatic fat accumulation in BRL-3A cells. Therefore, CFE was thought to reduce lipid synthesis, as it led to the production of acetic acid by promoting the growth of
A. muciniphila.
β-Glucuronidase activity is a prime factor in the etiology of colon cancer [
51]. β-Glucuronidase hydrolyze β-D-glucuronides to glucuronic acid and aglycone that may have the form of an alcohol, rest of oranic acid, amine, imine or a thiol compound. The formation of glucuronides is catalyzed by UDP-glucuronylotransferase. From the liver, where their synthesis take place, they are partially removed with bile to the large intestine. There, under the influence of bacterial β-glucuronidase, they are subject to hydrolysis to aglycones. In patients with diagnosed tumors of the large intestine high activity of β-glucuronidase was observed, which suggests that this enzyme plays as important role in promoting large intestine tumors [
52]. During the adaptation period, all mice were fed the AIN-93 diet for 1 week, but the enzymatic activity of each group at week 0 was not the same because the large intestine of all mice forms a complex microbial ecosystem. A marked decrease was observed for enzymatic activity in MCFE and HCFE group as compared with the CTRL group, being 88% and 87%, respectively. These results suggest that β-glucuronidase activity is decreased under feeding with CFE at more than 150 mg per body weight.
Dextran sulfate sodium (DDS)–induced colitis is commonly used to evaluate the efficacy of new drugs for inflammatory bowel disease. Our results showed that CFE significantly alleviates the acute intestinal injury induced by DSS administration, including DAI scores and colon length. MPO activity is a marker of neutrophil infiltration and is proportional to the number of neutrophils in the inflamed tissue [
53]. In our study, MPO activity in the colon was significantly reduced in the CFE-fed group compared with that of the NC group, which indicated that CFE could inhibit neutrophils infiltration and inflammation in mice.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, a protective effect of CFE against DSS colitis suggests its clinical use for IBD patients. Further detailed studies would be needed to deepen A. muciniphila activity in relation to microecological interventions for IBD.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.W.O., B.J.A., S.K.K. and S.H.Y.; methodology, S.W.O., B.J.A., S.K.L. and S.H.Y.; software, S.W.O. and S.K.L.; validation, S.W.O. and S.H.Y.; formal analysis, S.W.O., B.J.A., and S.H.Y.; investigation, S.W.O., S.K.K., B.J.A., and S.H.Y.; resources, S.W.O., S.K.K., B.J.A., and S.H.Y.; data curation, S.W.O., S.K.L., B.J.A., and S.H.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, S.W.O.; writing—review and editing, S.W.O., S.K.L., B.J.A., S.K.K. and S.H.Y.; visualization, S.W.O.; supervision, S.H.Y.; project administration, S.W.O., S.K.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Ministry of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises(SMEs) and Startups(MSS), Korea, under the “Regional Specialized Industry Development Plus Program(R&D, S3365918)” supervised by the Korea Technology and Information Promotion Agency(TIPA) for SMEs.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Animal experiments were approved and performed in accordance with the guidelines of the Berry & Biofood Research Institute (BBRI-IACUC-21001) and Woojung Bio, Inc. (IACUC2303–041).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Woojung Bio, Inc. and Berry & Biofood Research Institute for helping with technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
Not applicable.
References
- Pérez, M.J.; Falqué, E.; Domínguez, H. Antimicrobial Action of Compounds from Marine Seaweed. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 52. [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Guo, K.; Huang, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L.; Li, D.; Pang, K.-L.; Wang, G.; Chen, L.; et al. Fucoxanthin, a Marine Xanthophyll Isolated From Conticribra weissflogii ND-8: Preventive Anti-Inflammatory Effect in a Mouse Model of Sepsis. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 906. [CrossRef]
- Yayeh, T.; Im, E.J.; Kwon, T.-H.; Roh, S.-S.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, S.-B.; Cho, J.Y.; Park, N.-H.; Rhee, M.H. Hemeoxygenase 1 partly mediates the anti-inflammatory effect of dieckol in lipopolysaccharide stimulated murine macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 22, 51–58. [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, S.A.M.; Elias, N.; Farag, M.A.; Chen, L.; Saeed, A.; Hegazy, M.-E.F.; Moustafa, M.S.; El-Wahed, A.A.; Al-Mousawi, S.M.; Musharraf, S.G.; et al. Marine Natural Products: A Source of Novel Anticancer Drugs. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 491. [CrossRef]
- Monmai, C.; Rod-In, W.; Jang, A.-Y.; Lee, S.-M.; Jung, S.-K.; You, S.; Park, W.J. Immune-enhancing effects of anionic macromolecules extracted from Codium fragile coupled with arachidonic acid in RAW264.7 cells. PLOS ONE 2020, 15, e0239422. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, R.P.; Kumar, I.; Yadav, P.; Singh, S.K.; Kaushalendra; Singh, P.K.; Gupta, R.K.; Singh, S.M.; Kesawat, M.S.; et al. Algal Metabolites Can Be an Immune Booster against COVID-19 Pandemic. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 452. [CrossRef]
- Ohta, Y.; Lee, J.-B.; Hayashi, K.; Hayashi, T. Isolation of Sulfated Galactan from Codium fragile and Its Antiviral Effect. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 892–898. [CrossRef]
- Wells, M.L.; Potin, P.; Craigie, J.S.; Raven, J.A.; Merchant, S.S.; Helliwell, K.E.; Smith, A.G.; Camire, M.E.; Brawley, S.H. Algae as nutritional and functional food sources: revisiting our understanding. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 949–982. [CrossRef]
- Cherry, P.; Yadav, S.; Strain, C.R.; Allsopp, P.J.; McSorley, E.M.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. Prebiotics from seaweeds: An ocean of opportunity? Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 327.
- Wan-Loy, C.; Siew-Moi, P. Marine Algae as a Potential Source for Anti-Obesity Agents. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 222. [CrossRef]
- O’ Sullivan, L.; Murphy, B.; McLoughlin, P.; Duggan, P.; Lawlor, P.G.; Hughes, H.; Gardiner, G.E. Prebiotics from marine macroalgae for human and animal health applications. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2038–2064.
- Jiao, G.; Yu, G.; Zhang, J.; Ewart, H.S. Chemical Structures and Bioactivities of Sulfated Polysaccharides from Marine Algae. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 196–223. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Park, J.; You, S.G.; Hong, S. Immuno-stimulatory effects of sulfated polysaccharides isolated from Codium fragile in olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 87, 609–614. [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, J.L.; Jeong, S.; Kim, B.R.; Na, Y.J.; Jo, M.J.; Yun, H.K.; Jeong, Y.A.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, B.G.; et al. Codium fragile F2 sensitize colorectal cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis via c-FLIP ubiquitination. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 508, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Carmody, R.N.; Gerber, G.K.; Luevano, J.M., Jr.; Gatti, D.M.; Somes, L.; Svenson, K.L.; Turnbaugh, P.J. Diet Dominates Host Genotype in Shaping the Murine Gut Microbiota. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 72–84. [CrossRef]
- de Vos, W.M.; de Vos, E.A. Role of the intestinal microbiome in health and disease: from correlation to causation. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, S45–S56.
- Bird, A.R.; Brown, I.L.; Topping, D.L. Starches, resistant starches, the gut ant starches, the gut microflora and human health. Curr. Issues Intest. Microbiol. 2000, 1, 25–37.
- Louis, P.; Scott, K.P.; Duncan, S.H.; Flint, H.J. Understanding the effects of diet on bacterial metabolism in the large intestine. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 1197–1208. [CrossRef]
- Topping, D.L.; Clifton, P.M. Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Human Colonic Function: Roles of Resistant Starch and Nonstarch Polysaccharides. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 1031–1064. [CrossRef]
- Derrien, M.; Vaughan, E.E.; Plugge, C.M.; de Vos, W.M. Akkermansia muciniphila gen. nov., sp. nov., a human intestinal mucin-degrading bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1469–1476. [CrossRef]
- Ottman, N.; Reunanen, J.; Meijerink, M.; Pietilä, T.E.; Kainulainen, V.; Klievink, J.; Huuskonen, L.; Aalvink, S.; Skurnik, M.; Boeren, S.; et al. Pili-like proteins of Akkermansia muciniphila modulate host immune responses and gut barrier function. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0173004. [CrossRef]
- Ottman, N.; Davids, M.; Suarez-Diez, M.; Boeren, S.; Schaap, P.J.; dos Santos, V.A.P.M.; Smidt, H.; Belzer, C.; de Vos, W.M. Genome-Scale Model and Omics Analysis of Metabolic Capacities of Akkermansia muciniphila Reveal a Preferential Mucin-Degrading Lifestyle. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83. [CrossRef]
- Png, C.W.; Lindén, S.K.; Gilshenan, K.S.; Zoetendal, E.G.; McSweeney, C.S.; I Sly, L.; A McGuckin, M.; Florin, T.H.J. Mucolytic Bacteria With Increased Prevalence in IBD Mucosa Augment In Vitro Utilization of Mucin by Other Bacteria. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 2420–2428. [CrossRef]
- Rajilić-Stojanović, M.; Shanahan, F.; Guarner, F.; de Vos, W.M. Phylogenetic Analysis of Dysbiosis in Ulcerative Colitis During Remission. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 481–488. [CrossRef]
- Laura, R.G.; Adam, S.C.; Lauren, F. Ulcerative colitis in adults. JAMA 2020, 324 (12), 1205–1206.
- Bergemalm, D.; Andersson, E.; Hultdin, J.; Eriksson, C.; Rush, S.T.; Kalla, R.; Adams, A.T.; Keita, .V.; D’amato, M.; Gomollon, F.; et al. Systemic Inflammation in Preclinical Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 1526–1539.e9. [CrossRef]
- Catalan-Serra, I.; Brenna, . Immunotherapy in inflammatory bowel disease: Novel and emerging treatments. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2018, 14, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Dulai, P.S.; Siegel, C.A. The Risk of Malignancy Associated with the Use of Biological Agents in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 2014, 43, 525–541. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.S.; Passos, C.P.; Madureira, P.; Vilanova, M.; Coimbra, M.A. Structure–function relationships of immunostimulatory polysaccharides: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 132, 378–396. [CrossRef]
- Okolie, C.L.; CK Rajendran, S.R.; Udenigwe, C.C.; Aryee, A.N.; Mason, B. Prospects of brown seaweed polysaccharides (BSP) as prebiotics and potential immunomodulators. J. Food Biochem. 2017, 41, e12392.
- Xie, S.-Z.; Liu, B.; Ye, H.-Y.; Li, Q.-M.; Pan, L.-H.; Zha, X.-Q.; Liu, J.; Duan, J.; Luo, J.-P. Dendrobium huoshanense polysaccharide regionally regulates intestinal mucosal barrier function and intestinal microbiota in mice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 206, 149–162. [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Kim, S.; Jung, K.; Pham, T.N.A.; Yang, S.; Ahn, B. Potential Prebiotic and Anti-Obesity Effects of Codium fragile Extract. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 959. [CrossRef]
- Goldin, B.R.; Swenson, L.; Dwyer, J.; Sexton, M.; Gorbach, S.L. Effect of Diet and Lactobacillus acidophilus Supplements on Human Fecal Bacterial Enzymes23. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1980, 64, 255–261. [CrossRef]
- Zong, S.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Ye, M. Protective effect of Lachnum polysaccharide on dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 846–859. [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.-D.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-M.; Kim, D.-K. Puerarin inhibits inflammation and oxidative stress in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis mice model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 124, 109847. [CrossRef]
- Lee D-S.; Kim Y-S.; Ko C-N.; Cho K-H.; Bae H-S.; Lee K-S.; Kim J-J.; Park E-K.; Kim D-H. Fecal metabolic activities of herbal components to bioactive compounds. Arch Pharm Res. 2002, 25, 165–169.
- Yoo, D.H.; Kim IS, Van Le TK, Jung IH, Yoo HH, Kim DH. Gut microbiota-mediated drug interactions between lovastatin and antibiotics. Drug Metab Dispos, 2014, 42, 1508 –1513.
- Qiu, X.; Li, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wang, N.; Wu, N.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y. Fungal–bacterial interactions in mice with dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced acute and chronic colitis. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 65995–66006. [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-G.; Lee, M.-R.; Yoo, J.-M.; Park, K.-I.; Ma, J.-Y. Fermented herbal formula KIOM-MA-128 protects against acute colitis induced by dextran sodium sulfate in mice. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.J.; Keshavarzian, A.; Patterson, J.A.; Venkatachalam, M.; Gillevet, P.; Hamaker, B.R. Starch-entrapped microspheres extend in vitro fecal fermentation, increase butyrate production, and influence microbiota pattern. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, S121–S130.
- Timm, D.A.; Stewart, M.L.; Hospattankar, A.; Slavin, J.L. Wheat Dextrin, Psyllium, and Inulin Produce Distinct Fermentation Patterns, Gas Volumes, and Short-Chain Fatty Acid ProfilesIn Vitro. J. Med. Food 2010, 13, 961–966. [CrossRef]
- Belenguer, A.; Duncan, S.H.; Calder, a G.; Holtrop, G.; Louis, P.; Lobley, G.E.; Flint, H.J. Two routes of metabolic cross-feeding between Bifidobacterium adolescentis and butyrate-producing anaerobes from the human gut. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 3593–3599. [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, G.T.; Macfarlane, S. Bacteria, colonic fermentation, and gastrointestinal health. J. AOAC Int. 2012, 95, 50–60.
- Ríos-Covián, D.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Margolles, A.; Gueimonde, M.; De Los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; Salazar, N. Intestinal Short Chain Fatty Acids and their Link with Diet and Human Health. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 185. [CrossRef]
- Belzer, C.; de Vos, W.M. Microbes inside–from diversity to function: the case of Akkermansia. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1449-1458.
- Karlsson, C.L.J.; Önnerfält, J.; Xu, J.; Molin, G.; Ahrné, S.; Thorngren-Jerneck, K. The Microbiota of the Gut in Preschool Children With Normal and Excessive Body Weight. Obesity 2012, 20, 2257–2261. [CrossRef]
- Santacruz, A.; Collado, M.C.; García-Valdés, L.; Segura, M.T.; Martín-Lagos, J.A.; Anjos, T.; Martí-Romero, M.; Lopez, R.M.; Florido, J.; Campoy, C.; et al. Gut microbiota composition is associated with body weight, weight gain and biochemical parameters in pregnant women. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 83–92. [CrossRef]
- Everard, A.; Belzer, C.; Geurts, L.; Ouwerkerk, J.P.; Druart, C.; Bindels, L.B.; Guiot, Y.; Derrien, M.; Muccioli, G.G.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Cross-talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9066–9071. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, D.; Fang, Z.; Jie, Z.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Y.; Ji, L. Human Gut Microbiota Changes Reveal the Progression of Glucose Intolerance. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e71108. [CrossRef]
- Zhitao, L.; Guoao, H.; Li, Z.; Zhenglong, S.; Yun, J.; Min-jie, G.; Xiaobei, Z. Study of growth, metabolism, and morphology of Akkermansia muciniphila with an in vitro advanced bionic intestinal reactor. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 61.
- Ouwerkerk, J.P.; van der Ark, K.C.H.; Davids, M.; Claassens, N.J.; Finestra, T.R.; de Vos, W.M.; Belzer, C. Adaptation of Akkermansia muciniphila to the Oxic-Anoxic Interface of the Mucus Layer. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 6983–6993. [CrossRef]
- Kim, D. H.; Jin, Y. H. Intestinal bacterial beta-glucuronidase activity of patients with colon cancer. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2021, 24, 564-567.
- Wei, W.C.; Ding, M.L.; Zhou, K.; Xie, H.F.; Zhang, M.A.; Zhang, C.F. Protective effects of widelolactone on dextran sodium sulfate induced murine colitis partly through inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome activation via AMPK signaling. Biomed Pharmacother 2017, 94, 27–36.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).