1. Introduction
Garlic, as a globally significant economic crop and vegetable, is widely cultivated worldwide. With the growth of the global population and changes in dietary patterns, the cultivation area and production of garlic have been continually increasing. In the cultivation process of this crop, there is a significant demand for fertilizers and pesticides. In recent years, with the global emphasis on ecological conservation and sustainable development, there has been a call for remote sensing identification to facilitate industry adjustments and precise management in garlic cultivation. However, the above-ground part of garlic is similar to other vegetation, making it challenging to directly extract its information from optical data. This poses a challenge for achieving high-precision identification of garlic.
Currently, remote sensing technology has been extensively utilized in the identification of crop growth, monitoring of growth status, and other processes related to crop development. Based on series of remote sensing images such as MODIS, Landsat, GF, Sentinel, etc., it is possible to efficiently and intelligently support agricultural development as well as crop identification [
1,
2], This includes scholars collaborating through the use of multi-source high-resolution data, leveraging temporal information for crop classification among different crop types [
3]. Zhao et al. [
4] utilized Landsat imagery combined with multi-temporal data to create the first 30-meter spatial resolution bamboo distribution maps for Uganda, Ethiopia, and Kenya. In the NDVI time series, some scholars generated the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) through temporal analysis of Sentinel-2 satellite imagery, They proposed a composite hybrid evolution algorithm and a temporal similarity threshold to extract winter wheat in the study area. The research achieved significant breakthroughs, with an overall accuracy reaching 99% [
5]. Alternatively, researchers achieved high-precision classification of rice by combining phenological features to form a time series curve [
6]. In classification, both pixel-based and object-oriented classification methods are commonly employed, which to some extent enhance classification accuracy. For instance, Chen [
7] developed a POK-based method that integrates pixel and object-oriented approaches with knowledge, achieving favorable results in feasibility validation for the selected area. Using both pixel-based and object-oriented methods, Wessel [
8] successfully conducted effective classification of deciduous trees, oak trees, and others. Mathieu [
9], by creating maps for multiple tree species, verified that object-oriented classification methods exhibit high accuracy in classification. The above methods are all based on local computer analysis, which poses issues such as low efficiency, long processing times, and no guarantee of identification accuracy.
As the volume of data increases, traditional computing models gradually struggle to handle large-scale, high-resolution storage, leading to issues like lag, data loss, etc. The emergence of remote sensing cloud computing platforms has successfully addressed these problems, enabling the processing and analysis of large-scale, extensive calculations. Currently, the most mature remote sensing cloud computing platform is Google Earth Engine (GEE), widely utilized both domestically and internationally [
10]. Apart from classifying and extracting information on major crops such as rice, wheat, and maize, remote sensing can also be used for the identification of other crops like palm trees [
11], tea plantations [
12], significantly enhancing the classification effectiveness and accuracy while further refining the remote sensing detection system for crop cultivation. Therefore, the crop remote sensing extraction models supported by the GEE platform are crucial for achieving high-precision planting monitoring.
This study focuses on the Erhai Lake Basin in Yunnan Province. It utilizes the GEE platform to perform feature selection on Landsat data and employs the RF remote sensing extraction model for garlic identification. The study incorporates the kNDVI index feature into the spectral characteristics and combines texture features and terrain features, aiming to construct optimal multidimensional feature sets for crop classification suitable for GEE to extract the garlic crops, It is also to identify garlic in the Erhai Lake Basin and conduct spatiotemporal analysis of garlic cultivation from 1999 to 2023.
2. Materials and Methods
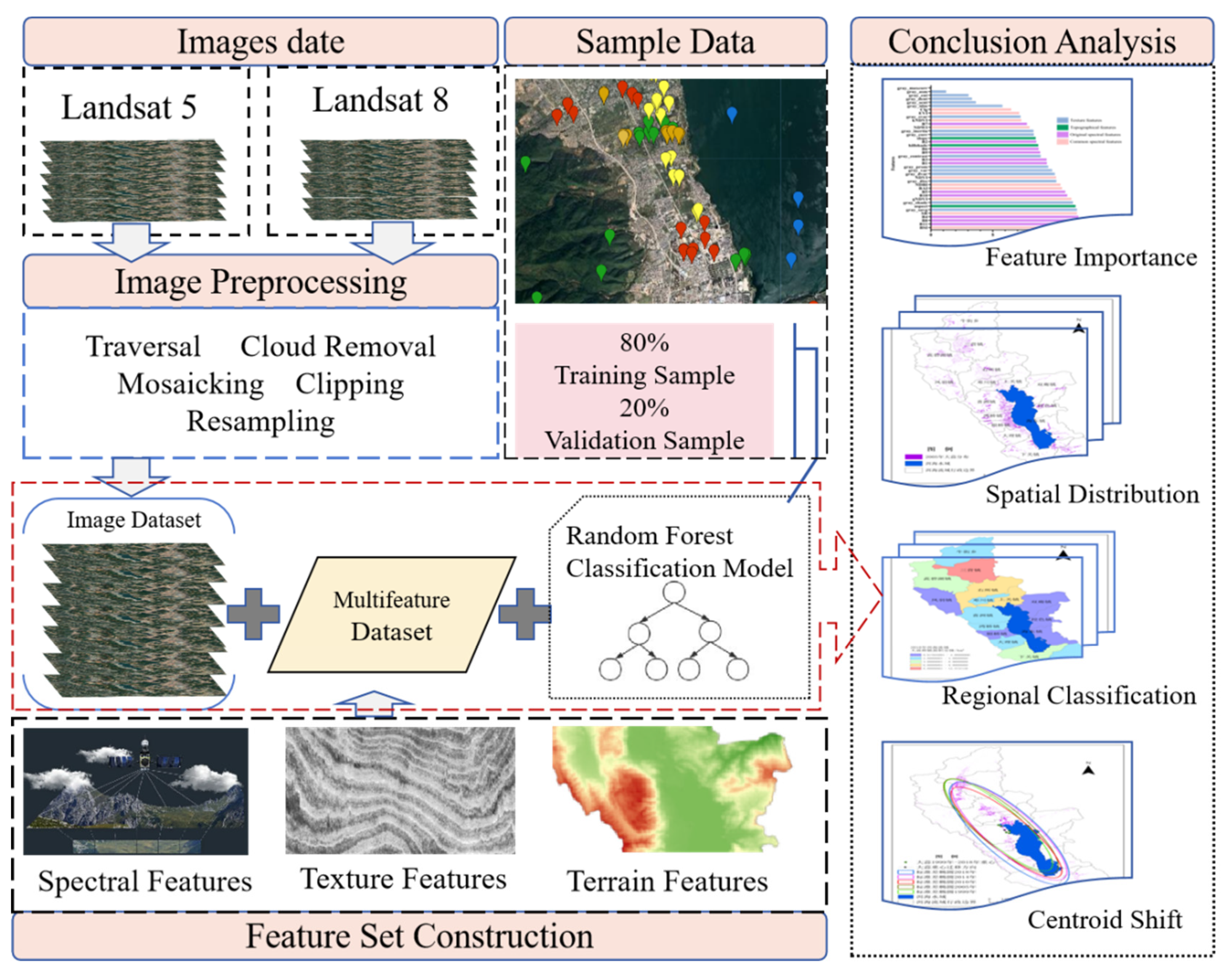
This study aims to identify garlic in the Erhai Lake Basin. Initially, the image data is synthesized with the minimum cloud coverage, cropped, and resampled to the same resolution. Subsequently, terrain features and texture features are extracted by combining DEM data with the gray-level co-occurrence matrix algorithm. Finally, band synthesis is conducted to form a new remote sensing image.
Next, the study analyzes the importance of spectral, texture, and terrain features in crop identification. Multi-dimensional features were conducted, optimal features are selected, and the random forest algorithm was used to classify crops from 1999 to 2023. Then, Classification accuracy was evaluated using verification samples and statistical data, and the spatiotemporal changes in the garlic crops were analyzed. As shown in
Figure 1.
2.1. Study Area
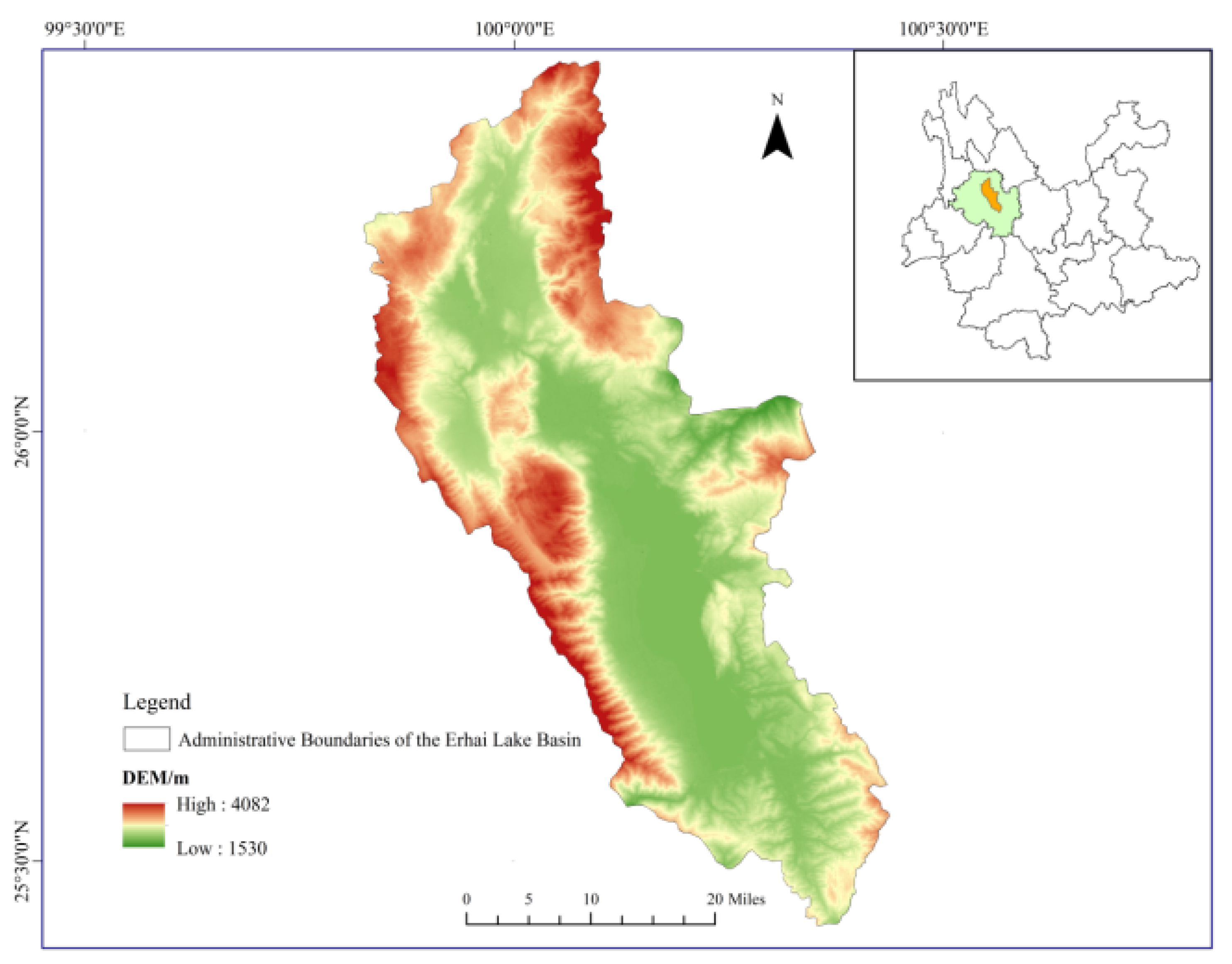
Erhai Lake is the seventh-largest freshwater lake in China, situated on the Yunnan Plateau in the southwestern part of the country. It belongs to the southern end of the Hengduan Mountains, spanning from approximately 100°05′ to 100°17′ east longitude and 25°36′ to 25°58′ north latitude. The total area of the lake is 2565 km². The Erhai Lake Basin falls under a subtropical plateau monsoon climate, characterized by mild temperatures and distinct seasons resembling spring throughout the year. The annual average temperature is 15.5°C, and the average annual precipitation is 1000 mm.
Figure 2.
The geographic location of the study area.
Figure 2.
The geographic location of the study area.
2.2. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
2.2.1. Image Data
This study is based on the Landsat 5 and Landsat 8 satellite image datasets provided by Google Earth Engine (GEE). Image collections are created based on the planting and maturity time of garlic, selecting images for the time periods of 1999, 2005, 2010, 2014, 2018, and January to February 2023. First, atmospheric correction and radiometric calibration are applied to the data. Images with a cloud coverage of no more than 30% are selected, followed by cropping and cloud removal operations. These steps aim to provide high-quality and accurate surface reflectance and radiance information for garlic identification. The dataset consists of a total of 11 spectral bands. Bands B1 to B9 are provided by the OLI sensor with a resolution of 30m, where the panchromatic band (Band 8) has a resolution of 15m and a swath width of 185km. Bands B10 and B11 are provided by the TIRS sensor with a resolution of 100m. To enhance the accuracy and coherence of the data, all bands are resampled to a resolution of 30m.
2.2.2. DEM Data
The SRTM DEM (Shuttle Radar Topography Mission Digital Elevation Model) is a DEM dataset jointly measured by the NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administra-tion) and the NGA (National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency), with a spatial resolution of 30 m. It is used to generate terrain parameters, including elevation, slope, aspect, hill shade, elevation profile, and others.
2.2.3. Sample Data
To identify the primary land cover types of garlic during the maturity period in January to February in the Erhai Lake Basin, on-site investigations were conducted. Sample collection work was carried out using the Google Earth Engine (GEE) cloud platform. The Erhai Lake Basin, characterized by Cangshan Mountain and Erhai Lake, classifies land cover types into seven major categories: construction land, garlic cultivation areas, greenhouses, non-garlic areas, water, forests, and grasslands. Among them, built-up areas include 110 samples of houses, roads, factories, and mines. Non-garlic areas encompass 110 samples of cultivated land, succulent planting, flower planting, etc., excluding garlic and greenhouses. Additionally, there are 310 garlic samples, 100 water body samples, 145 forest samples, 100 greenhouse samples, and 45 grassland samples, totaling 920 sample points. To ensure an adequate number of validation samples for assessing the model’s performance and addressing overfitting issues, the training and validation ratio is set at 8:2.
2.3. Feature Extraction
2.3.1. Feature Set Construction
According to the vegetation cover types, terrain characteristics, and vegetation maturity period in the study area, Using Landsat 8 imagery as an example, calculations were performed to obtain a total of 40 features, including spectral indices, terrain characteristics, and texture features, for the purpose of garlic identification. The selected features have all appeared in previous feature selection for land use classification [
13]. The details of these features are provided in
Table 1. apart from the original spectral features(B1-B11), These features include Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), Normalized Water Index (NDWI), Normalized Built-up Index (NDBI), Bare Soil Index (BSI), Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI), and Spectral Ratio (SR). Different from sensors like Sentinel, the dataset from Landsat 8 does not include the red-edge band and related vegetation indices mentioned by YOU [
14] during feature selection. When extracting texture features from the images, we use the gray-level co-occurrence matrix to compute the following 16 features: entropy (ENT), inverse difference moment (IDM), angular second moment (ASM), variance (VAR), contrast (CONTRAST), correlation (CORR), dissimilarity (DISS), sum average (SAVG), shade (SHADE), difference variance (DVAR), profile (PROM), inertia (INTERTIA), sum variance (SVAR), spectral entropy (SENT), direction entropy (DENT), and maximum correlation (MAXCORR). In the terrain features, to prevent overfitting and computational redundancy, only three terrain features are selected: slope (Slope), aspect (Aspect), and hillshade (Hill Shade).
2.3.2. Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) Algorithm
Gray-Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) is a statistical tool used to describe the texture features of digital images. It finds wide applications in various fields such as image processing, computer vision, and remote sensing image analysis. The Gray-Level Co-occurrence Matrix is based on the spatial relationships of grayscale values in an image, capturing the statistical relationships between pixel grayscale values in the image texture. In this study, the “glcm Texture()” function is utilized in GEE for calculating texture features. The parameter “size” for the co-occurrence matrix’s neighborhood size is set to 1, and the “kernel” for calculating the offset of the center pixel is set to the default neighborhood kernel. Afterwards, through the operation “gray.unitScale(0, 0.30)”, the pixel values of the grayscale image are normalized, bringing the pixel values within the range of 0 to 0.30. Following this, the operation “multiply” is applied to multiply the pixel values by 100, scaling the values to be within the range of 0 to 30. Finally, the operation “toInt()” is used to convert the pixel values to integer type.
In the calculation of the grayscale image, the original color composite image is created by linearly combining the red (Red band, R), green (Green, G), and near-infrared (Near Infrared, NIR) bands of the composite image with specific weights. The weights used are 0.3, 0.59, and 0.11, respectively [
15]. This linear combination is commonly used for extracting texture features after converting a color image to a grayscale image. The formula is as follows:
where
is the Near Infrared, and
is the Infrared, and
is the Green light.
2.3.3. Random Forest Algorithm and Feature Selection
Leo Breiman first introduced the Random Forest algorithm in his 2001 paper, “Random Forests” [
16]. It is an ensemble learning algorithm consisting of multiple decision trees. Multiple decision trees are created by performing random, with-replacement sampling on the training data (bootstrap sampling). Additionally, random feature selection is applied to each decision tree, enhancing the model’s diversity and generalization capability. Randomly selecting a subset of features at each node of every decision tree ensures that each tree is distinct, thereby enhancing the diversity of the Random Forest. This contributes to preventing certain features from dominating the model’s predictions. This article applies the Random Forest algorithm for the classification of Landsat 5 and Landsat 8 images. In Google Earth Engine (GEE), the advanced Random Forest classifiers can be constructed using the “ee.Classifier.randomForest()” and “ee.Classifier.smileRandomForest()” functions. These functions train and predict models by configuring hyperparameters such as the number of decision trees, the method of feature selection, the maximum depth of decision trees, and other relevant parameters. Combining multiple experiments, this study sets the number of decision trees to 50.
Relevant studies have found that the classification performance may deteriorate after adding a certain number of feature variables [
17,
18]. To address issues such as overfitting due to excessive variables and poor classification performance caused by computational complexity, the Random Forest algorithm automatically leverages out-of-bag (OOB) data. It utilizes internal functions to perform importance ranking and selects the top-ranked features for classification, thereby achieving optimal classification performance.
2.3.4. Accuracy assessment
In Google Earth Engine (GEE), the sample points are integrated into a test set named “Test” to compute the confusion matrix of the classifier. Subsequently, relevant metrics related to classification performance are outputted. The confusion matrix is employed to assess the performance of the classifier, illustrating the correct and incorrect classifications on the test set to validate classification accuracy. To assess the performance of the classifier, various evaluation metrics such as Consumer’s Accuracy (CA), Producer’s Accuracy (PA), Overall Accuracy (OA), and Kappa coefficient are computed. Consumer’s Accuracy (CA) represents the proportion of correctly classified samples by the classifier among all true samples, Producer’s Accuracy (PA) represents the proportion of samples that actually belong to a certain class among all samples predicted by the classifier to be of that class, Overall Accuracy (OA) represents the proportion of correctly classified samples over the entire test set. It is a crucial metric for assessing the overall performance of the classifier, Kappa coefficient is a measure of consistency between the classifier and random classification. It accurately assesses the performance of the classifier in handling class imbalances and random predictions.
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Feature Selection Analysis
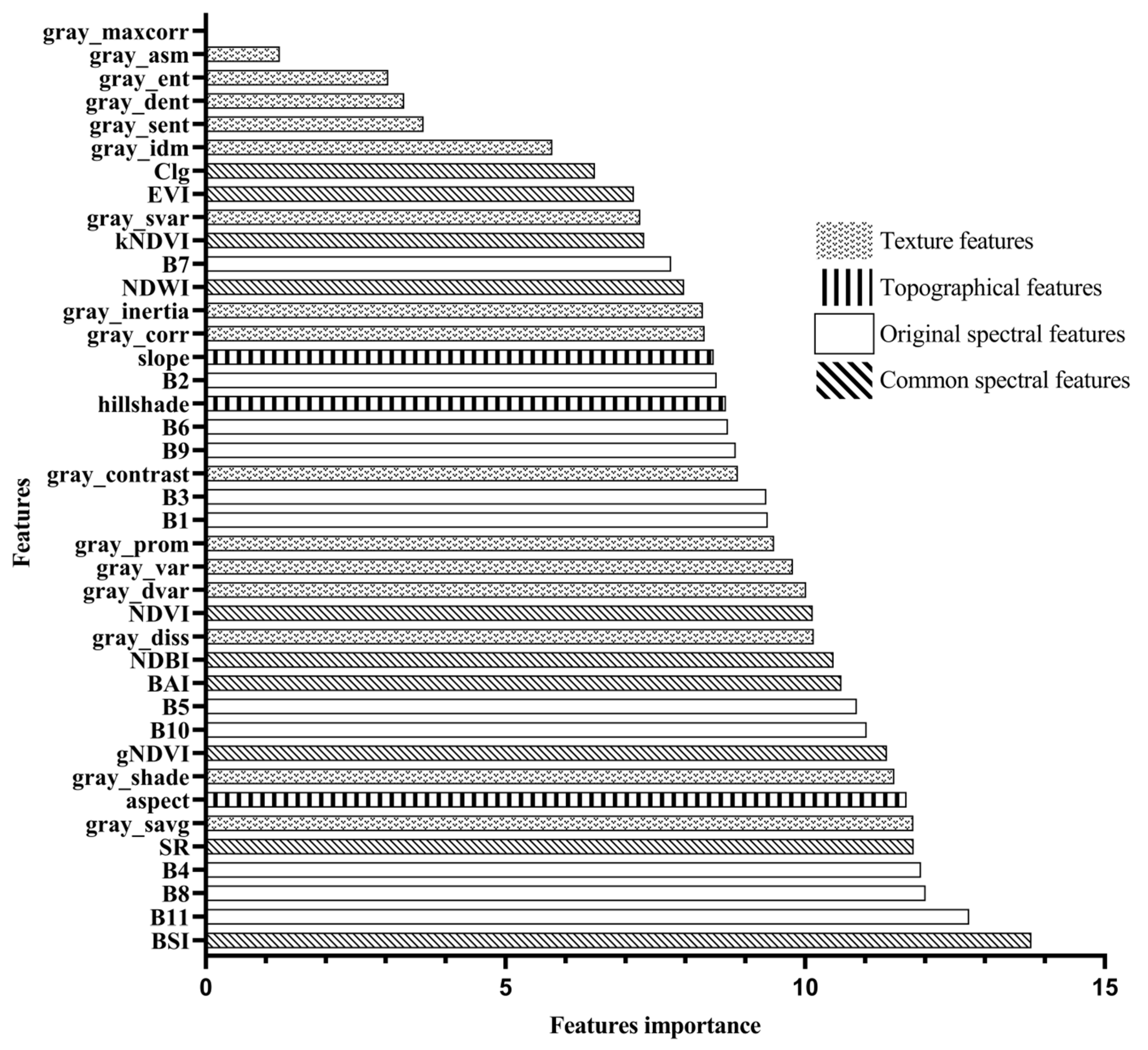
Based on remote sensing imagery of the Erhai Lake Basin in 2018, this study selected a total of 40 feature variables. The Random Forest algorithm was then applied to rank the importance of these feature variables, and the results are presented in
Figure 3.
Figure 3 visually indicates that the importance of each feature variable is concentrated between 0% and 14%. Ordinary spectral features and raw spectral features are among the most important for land-use classification.
In the texture features, the gray_savg band has the highest importance, reaching up to 11.81%. On the other hand, Second-order moments of angles (gray_amxcorr) do not play a role in land use classification. In the ordinary spectral indices, the BSI (Bare Soil Index) contributes the most, reaching up to 13.75%. Among the terrain features, the aspect contributes the most, reaching up to 11.69%. Among the texture features, gray_maxcorr, gray_sent, gray_dent, gray_ent, and gray_asm have the least impact on the classification. Out of the 40 feature variables, 16 features have an importance of 10% or higher in the classification.
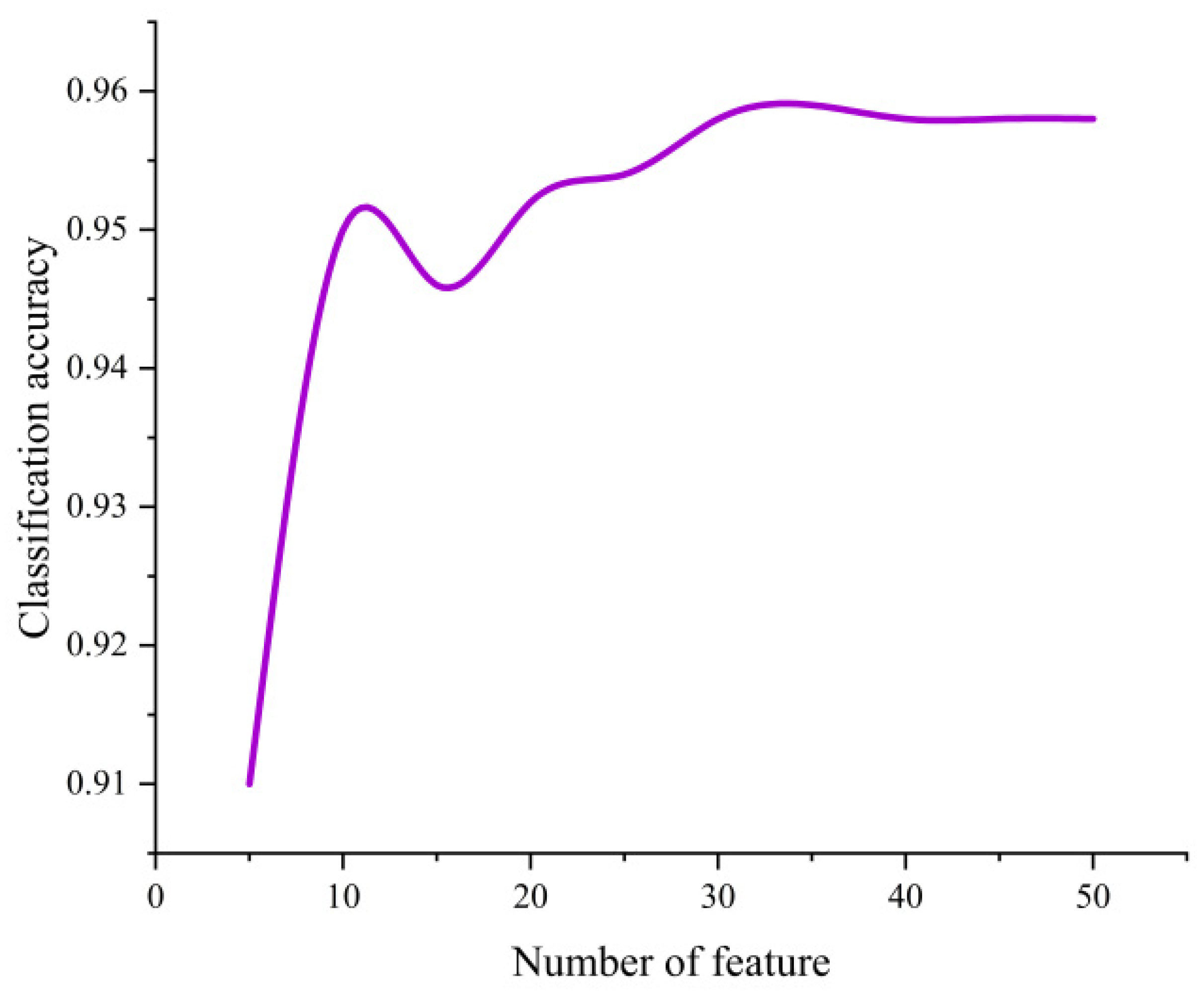
According to the relationship between the number of classification features and classification accuracy, as shown in
Figure 4. With the increase in the number of features, the classification accuracy initially rises, then decreases, followed by another increase before gradually leveling off. The stability of classification accuracy exhibits fluctuations with the number of features in the range of 10-30. As the number of features increased from 5 to 10, the classification accuracy increased from 0.910 to 0.950, However, after the number of features reached 35, the classification accuracy did not show a consistent increase but fluctuated with the increasing number of features. When the number of features reaches 35, the classification accuracy peaks at 0.959. As the number of classification features exceeds 45, the accuracy gradually levels off and stabilizes at 0.958. Considering that the increase in the number of features could reduce the computational efficiency, the top 35 features of importance were used. This includes 11 original spectral features (B11, B8, B4, B10, B5, B1, B3, B9, B6, B2, B7), 10 spectral index features (BSI, SR, gNDVI, BAI, NDBI, NDVI, NDWI, kNDVI, EVI, Clg), 11 texture features (gray_savg, gray_shade, gray_diss, gray_dvar, gray_var, gray_prom, gray_corr, gray_intertia, gray_svar, gray_idm, gray_contrast), and 3 terrain features (aspect, hillshade, slope).
3.2. Accuracy Analysis
Based on the 2018 classified data with feature selection, the confusion matrix is presented in
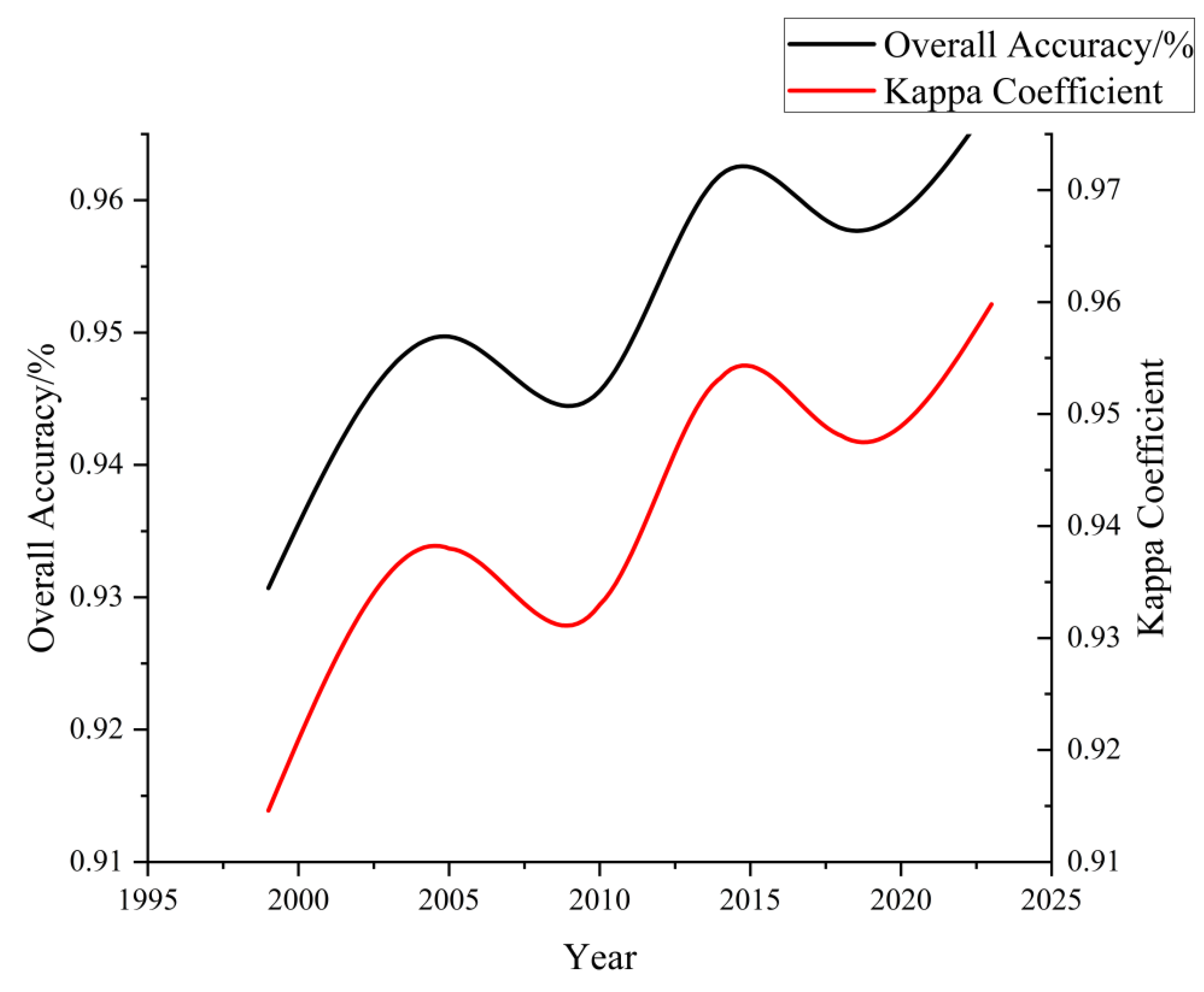
Table 2. The overall accuracy achieved is 95.79%, and the Kappa coefficient is 0.9481. The user’s accuracy for each land class classification is consistently above 90%. In terms of producer’s accuracy, garlic, water bodies, built-up areas, forests, greenhouses, and grassland exhibit accuracies exceeding 90%. However, the producer’s accuracy for the non-garlic land class is relatively lower at 89.25%. The lower accuracy for the non-garlic land class is mainly attributed to the inclusion of cultivated land other than garlic and greenhouses, areas with succulent plants, flower cultivation, etc. During the collection of sample points, accurate classification for these specific land uses might not have been conducted. The spectral similarity reflected in the remote sensing imagery leads to mutual confusion, resulting in comparatively lower accuracy for this category. The land classes that exhibit better classification results are mainly garlic, water bodies, and forests. Specifically, the mapping accuracy and user’s accuracy for garlic are 99.16% and 96.71%, respectively, meeting high classification standards. Over the past five years, both the overall accuracy and Kappa coefficient have consistently remained above 90%, demonstrating a stable and satisfactory classification level. This indicates a good model performance and effective training, as depicted in
Figure 5.
3.3. Classification Results Analysis
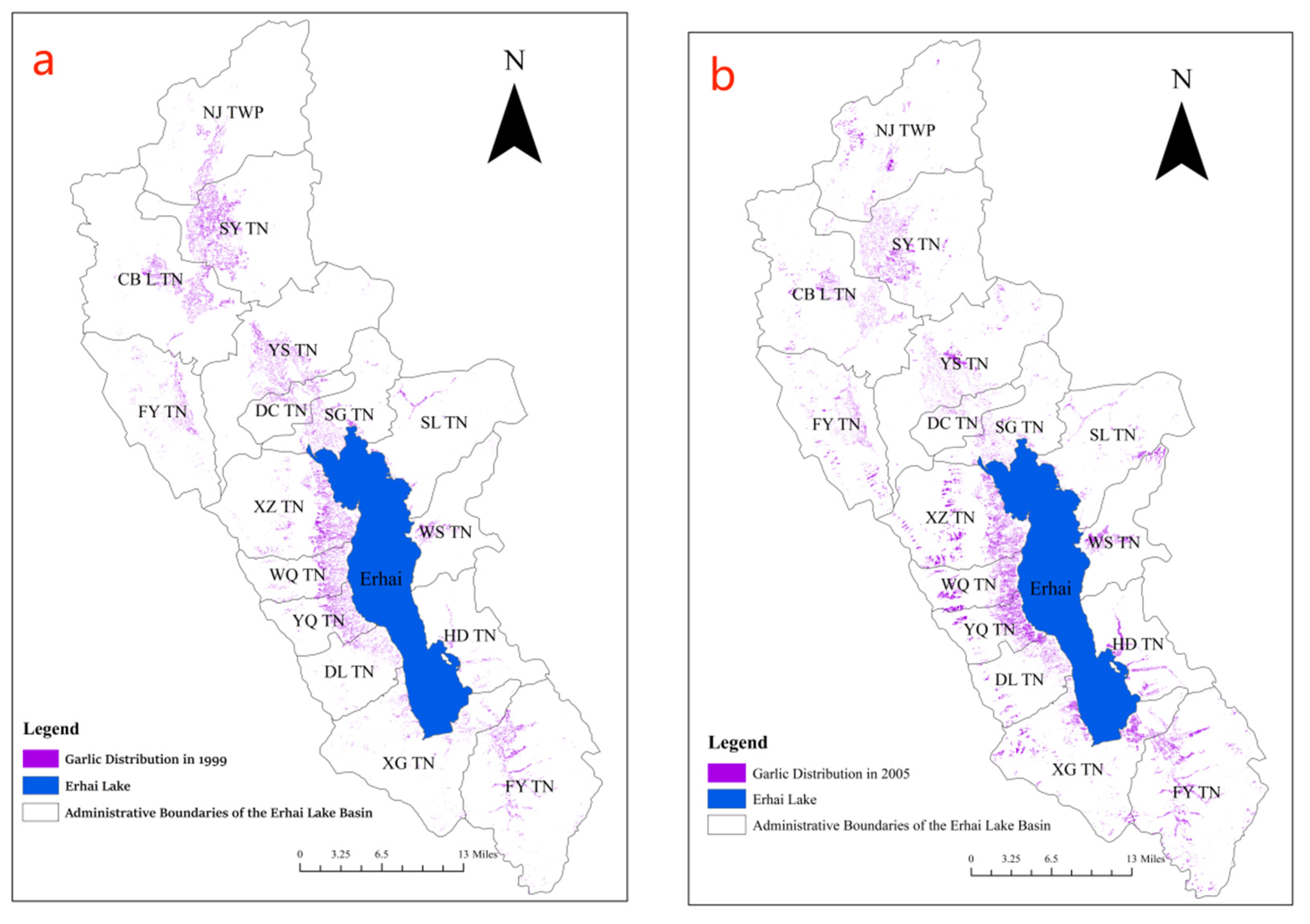
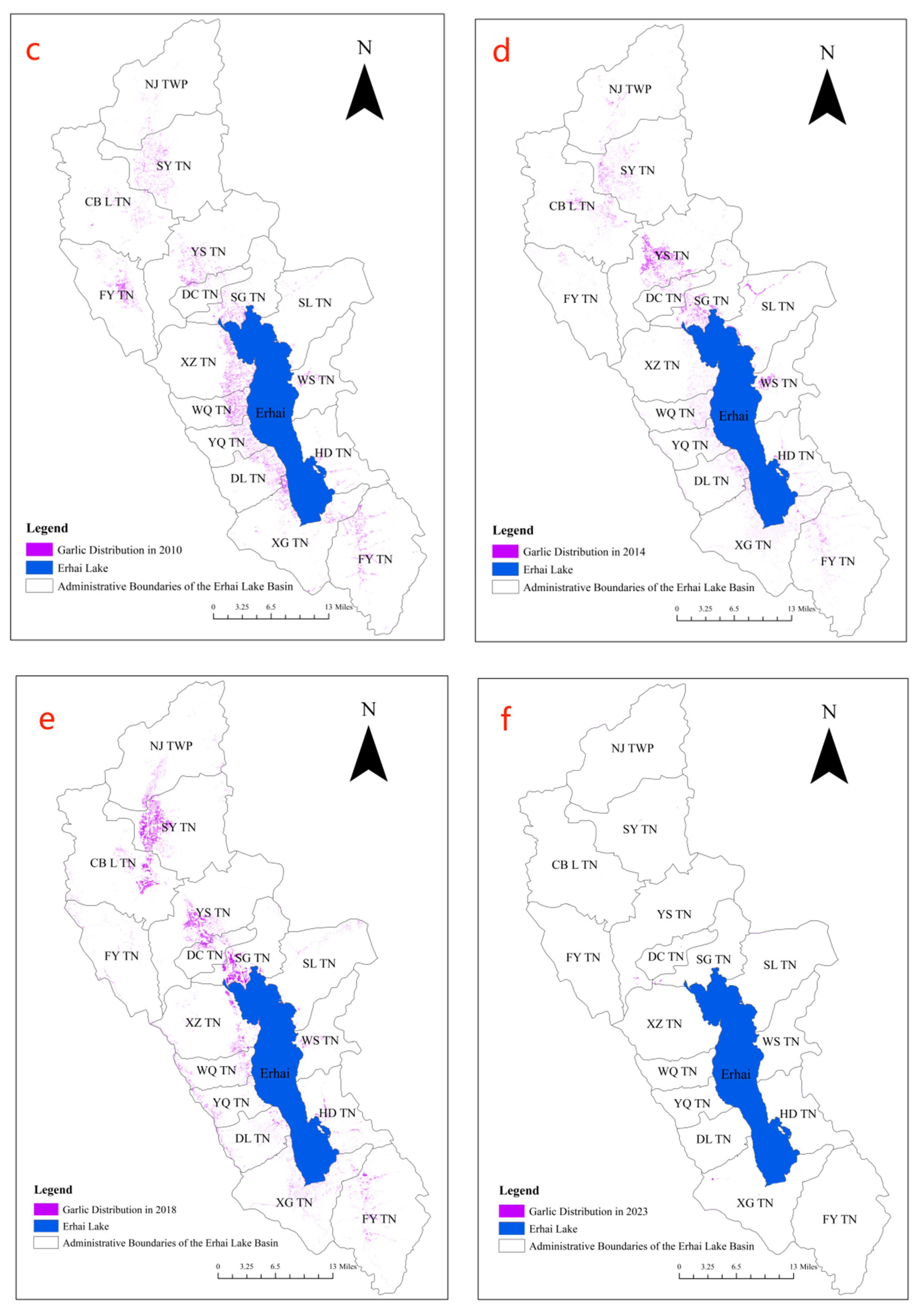
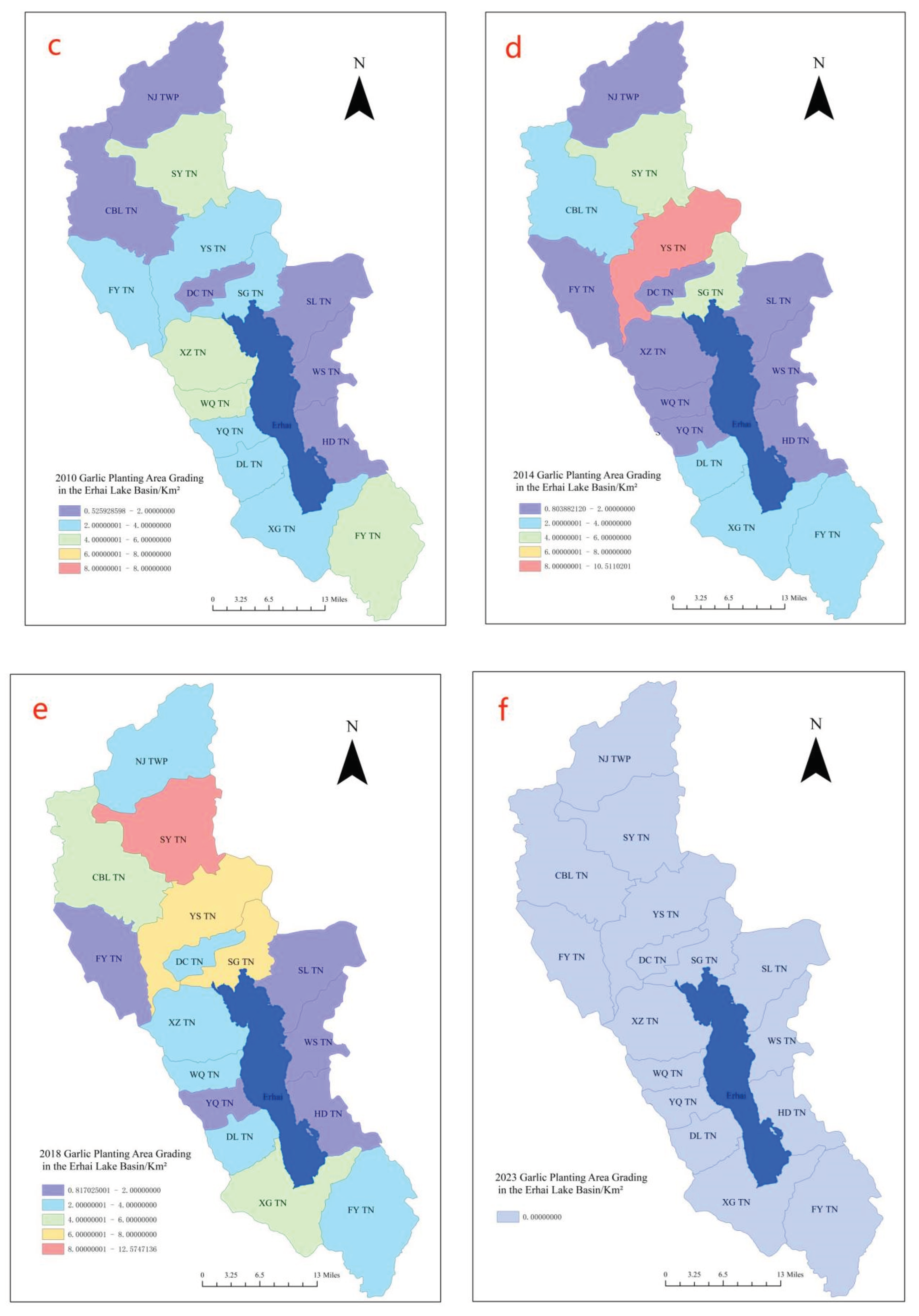
Following the above steps, conducting feature selection analysis, and sequentially processing remote sensing imagery data from 1999, 2005, 2010, 2014, 2018, and 2023, the garlic planting distribution in the Erhai Lake Basin over the past 20 years has been obtained, as illustrated in
Figure 6. From the figure, it can be observed that from 1999 to 2005, the main garlic planting areas were in the upstream of the Erhai Lake Basin and the western region. By 2010, with a decline in garlic prices, the planting area significantly decreased, mainly concentrated in the western and northwest areas of the Erhai Lake Basin. By 2014, influenced by policies, the garlic planting area shifted towards the northern part of the Erhai Lake Basin. This trend continued until 2018, forming a minor cultivation area in the western region. The primary concentration of garlic cultivation was observed in the northern part of the Erhai Lake Basin across five townships. By 2023, there is no longer any garlic cultivation within the Erhai Lake Basin. In terms of image recognition, the garlic cultivation area in 2023 is nearly zero, aligning with the actual scenario and achieving a satisfactory classification result.
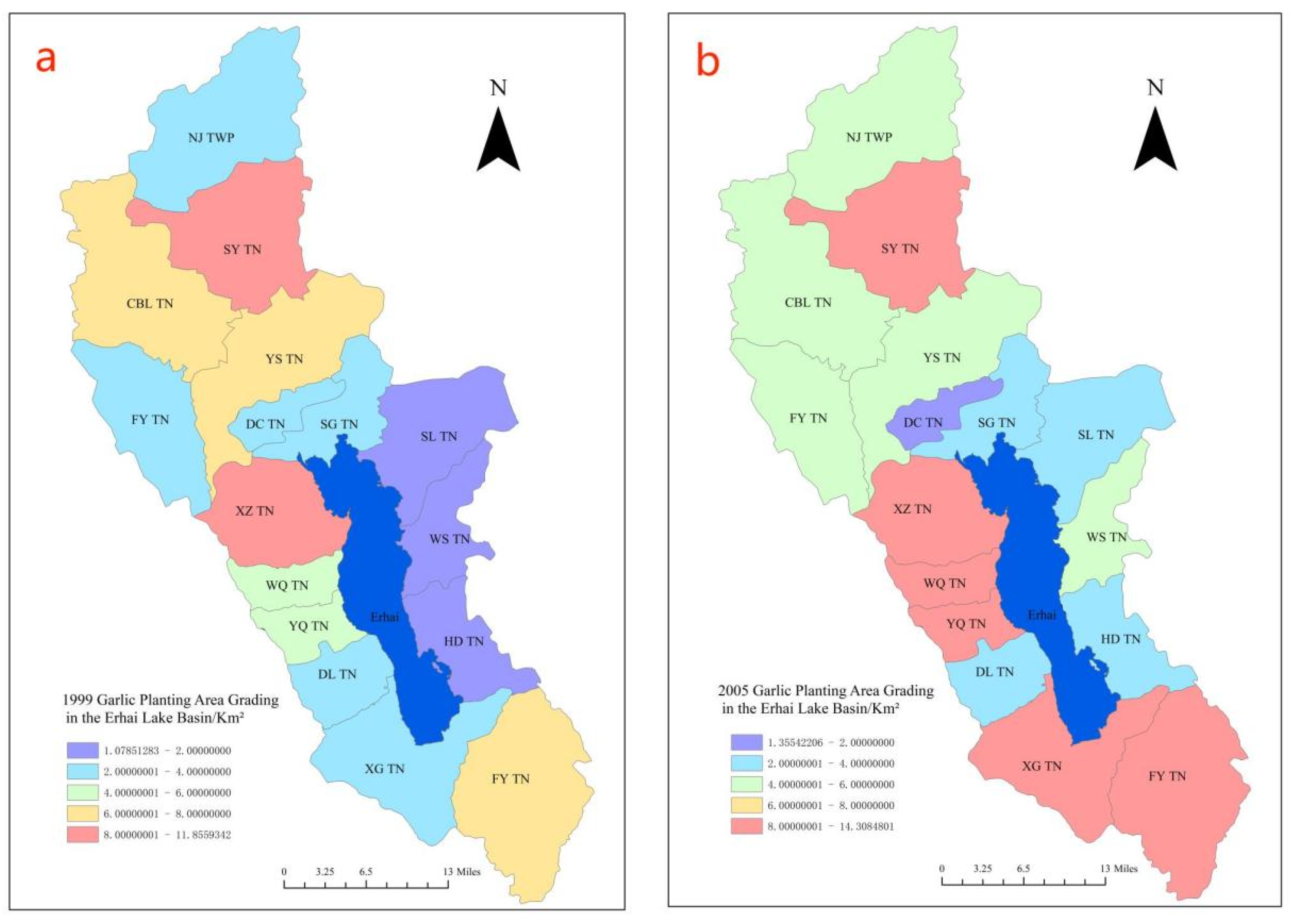
To better illustrate the garlic cultivation area in various townships within the Erhai Lake Basin, a classification map based on remote sensing image recognition was generated to show the statistical distribution of garlic cultivation areas. Please refer to
Figure 7 for the garlic cultivation area classification map. Considering the development history of garlic cultivation in the Erhai Lake Basin, in 1999, garlic planting was primarily concentrated in the northern and western parts of the basin, encompassing several townships. By 2005, the garlic cultivation area gradually expanded. Townships with garlic cultivation areas exceeding 8 km
2 accounted for 3/8 of the total number of townships in the Erhai Lake Basin. By 2010, inflation led to a decline in garlic prices, resulting in a decrease in garlic cultivation areas across various townships in the Erhai Lake Basin, with none exceeding 6 km
2. In 2014, garlic cultivation gradually rebounded, and the planting distribution gradually shifted towards the northern part of the Erhai Lake basin, with an increasing planting area. By 2018, garlic cultivation was predominantly concentrated in the northern part of the Erhai Lake Basin. Looking at the overall picture, garlic cultivation in the Erhai Lake Basin began in the western region, spreading towards the upstream areas of the Erhai Lake Basin. Comparatively, the eastern part of Erhai had the least garlic cultivation area. From a geographical perspective, Garlic is a crop that requires a significant amount of water and fertilizer consumption., and it is primarily cultivated in the areas surrounding Erhai Lake where water resources are abundant.
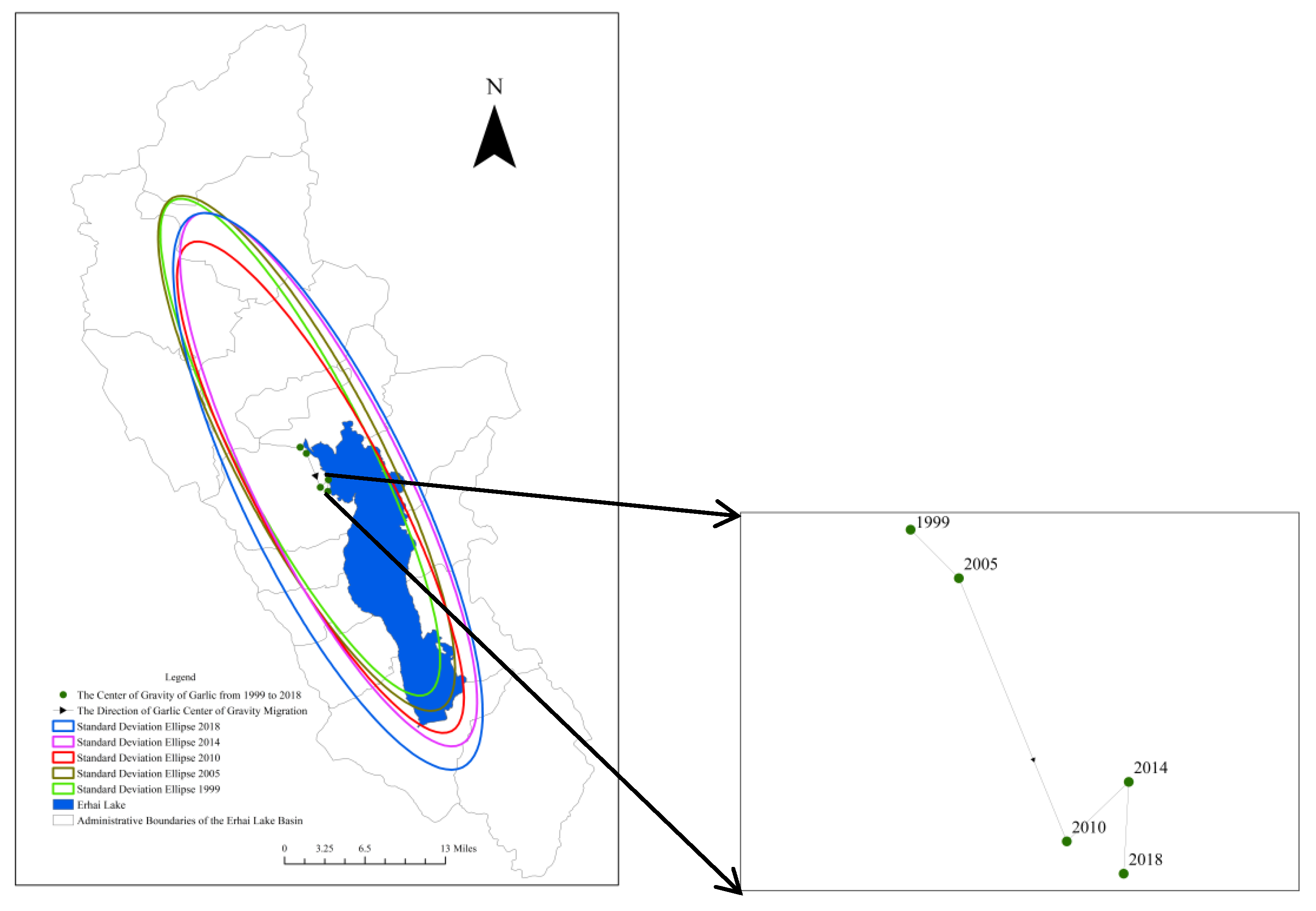
As there is no longer garlic cultivation in 2023, the center of gravity analysis method [
19] and standard deviation ellipse theory [
20] were employed to calculate the center of gravity and standard deviation ellipse of garlic cultivation in the Erhai Lake Basin from 1999 to 2018. Refer to
Figure 8 and
Table 3. In the center of gravity analysis, from 1999 to 2010, garlic cultivation in the Erhai Lake Basin expanded towards the southeast. From 2010 to 2014, the center of gravity shifted towards the northeast. Between 2014 and 2018, the direction of the garlic cultivation center of gravity was southwest. The eastward speed of the garlic cultivation center of gravity in the Erhai Lake Basin slowed down from 2010 to 2018, and a change in direction occurred in 2014. In the standard deviation ellipse theory, the major axis represents the directional distribution, the minor axis represents the range of distribution, and the ratio of the major to minor axis indicates the directionality of expansion. If this ratio is close to 1, it suggests no clear directionality. During the period from 1999 to 2018, the ratio of the major to minor axis consistently exceeds 2, indicating a pronounced directionality. From 1999 to 2010, the ratio of the major to minor axis decreased from 4.3 to 4, then increased to 4.2. This indicates that the directional expansion of garlic cultivation strengthened initially and then weakened during this period. By 2018, the ratio of the major to minor axis further decreased to 3.64, indicating a continued weakening of the directional expansion. Furthermore, it was observed that the minor axis of the standard deviation ellipse elongated during the period from 2005 to 2018, indicating an increase in the distribution range of garlic cultivation.
4. Discussion
In agricultural remote sensing research, most scholars primarily focus on the identification of cereal crops, while there is relatively less research by scholars both domestically and internationally on remote sensing identification of economic crops such as tobacco, rubber, tea, and garlic. Currently, the research on garlic extraction primarily combines phenological periods with machine learning algorithms. For example, Wu Shuang and others obtained Sentinel-2 remote sensing images covering the entire growth cycle of garlic. They made progress in garlic extraction by utilizing different combinations of multiple temporal phases [
21]. Additionally, experts and scholars have utilized convolutional neural networks to create garlic land classification models based on growth stages. Through the use of high-resolution images and deep learning, they were able to detect garlic yield throughout the entire growth stage [
22].
In terms of classification methods, Indonesian scholars chose the k-nearest neighbors and maximum likelihood classification methods and compared them with the pixel-based and image-based garlic classification results from previous studies, finding that The k-nearest neighbors classification method has been found to yield better classification results compared to support vector machine classification and maximum likelihood classification [
23]. Ma Zhanlin and colleagues based on the random forest algorithm and the object-oriented approach, added index features and utilized Simple Non-Iterative Clustering (SINC) to select the optimal segmentation scale for garlic extraction. The overall accuracy and Kappa coefficient reached 94.54% and 0.93, respectively. This achievement is consistent with the good classification results obtained by Tian Haifeng and others in the identification of garlic and winter wheat using active and passive remote sensing [
24,
25]. However, research on garlic is mainly concentrated in the northeastern part of China, such as in Shandong, and there is almost no research on the identification of garlic in Yunnan. This study utilized Landsat satellite imagery on the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform for garlic identification in the Erhai Lake Basin. This approach significantly reduces data acquisition and preprocessing efforts. The classification performance has been improved compared to previous studies. The overall accuracy has improved by approximately 1.3%, and the Kappa coefficient has increased by around 2%. In addition to supplementing the literature references related to garlic in the Erhai Lake Basin, this study validates the applicability of feature selection combined with a random forest classification model based on the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform for garlic extraction.
In most articles related to feature selection, spectral features and vegetation index features play a dominant role. Spectral indices such as B8 and B11 hold higher positions in the feature importance ranking, followed by texture features, and lastly, red edge spectral indices [
26,
27,
28,
29]. There are fewer articles in the literature that simultaneously incorporate texture features and terrain features in feature selection studies using Landsat imagery. However, related studies indicate that texture features, along with terrain features, play an important role in land use classification [
30]. The response to texture features becomes more pronounced as land use types become more complex [
31]. In this study, it was observed that four terrain features exhibited high correlation, which could impact the classification results. Therefore, only a subset of terrain features was included in the analysis. Considering interference from noise and other factors, a combination of median filtering and Gaussian filtering was employed for elimination. Additionally, the kNDVI index, which is better at handling noise, enhancing saturation, and reducing “background effects” (such as soil, sparse vegetation, and water) [
32], was added. This approach effectively addresses the saturation mixing pixel issue encountered by traditional indices. The kNDVI plays a role in improving the quantification and understanding of photosynthesis on a global scale. It goes beyond the scope of vegetation monitoring, including applications in change and anomaly detection, phenology, and greening studies, among others. The study also found that kNDVI exhibits stronger stability and robustness under various environmental conditions, such as dense forests, grasslands, and mixed forests, compared to traditional NDVI and NIRv indices [
33,
34]. In the classification conducted in this study, kNDVI played a significant role, with a feature importance of 7.314%. However, its importance is relatively lower compared to NDVI.
5. Conclusions
This study, leveraging the powerful data processing and computational capabilities of Google Earth Engine (GEE), utilized Landsat 5 and Landsat 8 satellite imagery as remote sensing data. By employing feature selection and the Random Forest (RF) algorithm, this study achieved the extraction of spatial distribution information for garlic in the Erhai Lake Basin. Subsequently, the center of gravity analysis and standard deviation ellipse theory were utilized to analyze the spatiotemporal evolution patterns of garlic. The main conclusions are as follows:
(1) In the land use classification of the Erhai Lake Basin, the Random Forest algorithm selected feature bands with the importance ranking as follows: spectral features > vegetation features > texture features > terrain features. Through feature selection analysis, the number of features was reduced from 40 to 35. Having too many features can burden the model, making it prone to overfitting and resulting in a decrease in accuracy [
35].
(2) The Random Forest method based on feature selection achieved high classification accuracy in land use classification in the Erhai Lake Basin, Yunnan Province. The overall classification accuracy reached 95.79%, with a Kappa coefficient of 0.9481. Specifically, the garlic mapping accuracy reached 99.16%, and the user accuracy reached 96.71%. The land use classification accuracy from 1999 to 2018 consistently exceeded 93%, meeting a good classification standard.
(3) The expansion directionality of garlic cultivation in the Erhai Lake Basin increased first and then decreased from 1999 to 2018. From 2005 to 2018, garlic cultivation showed a saturation trend in the longitudinal direction, slowly exhibiting a trend of lateral development. Over the past 20 years, the center of garlic cultivation has gradually shifted in the southeast direction. Over the past 20 years, garlic cultivation in various towns in the Erhai Lake Basin has gradually shifted from a relatively even distribution to a concentration in the upstream region of the Erhai Lake Basin.
Considering the interference that may occur when applying pixel-based methods for crop extraction and classification, resulting in phenomena such as “salt-and-pepper artifacts” and “salt-and-pepper noise,” In the study, a combination of Median Filtering and Gaussian Filtering was employed to eliminate interference, aiming to enhance classification accuracy. Additionally, the incorporation of the kNDVI feature index was introduced to better handle noise and reduce the impact of interference on classification results, thereby improving accuracy to a certain extent.
Author Contributions
Methodology, formal analysis, W.L.; visualization, software, writing-original draft, validation, data curation, investigation, J.P.; supervision, writing—review and editing, funding acquisition, C.L.; resources, project administration, W.P. and Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Yunnan International Joint Laboratory for Crop Smart Production.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Weiss, M.; Jacob, F.; Duveiller, G. Remote sensing for agricultural applications: A meta-review. Remote Sensing of Environment 2020, 236, 111402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Chen, Z.; Ren, J.; Li, H.; Wu, S. Modeling winter wheat leaf area index and canopy water content with three different approaches using Sentinel-2 multispectral instrument data. IEEE J-Stars 2018, 12, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Ren, T.W.; et al. Identification of seed maize fields with high spatial resolution and multiple spectral remote sensing using random forest classifier. Remote Sensing 2020, 12, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Feng, D.L.; Jayaraman, D.; et al. Bamboo mapping of Ethiopia, Kenya and Uganda for the year 2016 using multi-temporal Landsat imagery. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 2018, 66, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ren, J.; Wu, S.; et al. Effects of NDVI time series similarity on the mapping accuracy controlled by the total planting area of winter wheat. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE) 2021, 37, 127–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Li, W.; Tang, Z.; Chen, C.; Qi, W. Mapping paddy rice areas based on vegetation phenology and surface moisture conditions. Ecol Indic 2015, 56, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Liao, A.P.; et al. Global land cover map-ping at 30 m resolution: A POK-based operational approach. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2015, 103, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, M.; Brandmeier, M.; Tiede, D. Evaluation of different machine learning algorithms for scalable classification of tree types and tree species based on Sentinel-2 Data. Remote Sensing 2018, 10, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varin, M.; Chalghaf, B.; Joanisse, G. Object-based approach using very high spatial resolution 16-band Worldview-3 and LIDAR data for tree species classification in a broadleaf forest in Quebec, Canada. Remote Sensing 2020, 12, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Menarguez, M.A.; Zhang, G.; Qin, Y.; Thau, D.; Biradar, C.; Moore, I.I.I.B. Mapping paddy rice planting area in northeastern Asia with Landsat 8 images, phenology-based algorithm and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens Environ 2016, 185, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, Y.; Yu, L.; Cracknell, A.P.; et al. Oil palm mapping using Landsat and PALSAR: A case study in Malaysia. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2016, 37, 5431–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.Y.; Sun, R.; Jin, Z.F. Extracting tea plantations based on ZY- 3 satellite data. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering 2016, 32 (Suppl. S1), 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Xue, H.; Liu, C.; et al. Identification of garlic based on active and passive remote sensing data and object-oriented technology. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE) 2022, 38, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.T.; Huang, Y.W.; Qin, Z.G.; et al. Forest Tree Species Classification based on Sentinel-2 images and auxiliary data. Forests 2022, 13, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassi, A.; Vizzari, M. Object-orientied LULC classification in Google earth engine combining SNIC, GLCM, and machine learning algorithms. Remote Sensing 2020, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Machine Learning 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stromann, O.; Nascetti, A.; Yousif, O.; et al. Di-mensionality reduction and feature selection for object-based land cover classification based on Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 time series using Google Earth Engine. Romote Sensing 2019, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitzer, M.; Atzberger, C.; Koukal, T. Treespecies classification with random forest using very high spatial resolution 8—Band World View—2 satellite data. Remote Sensing 2012, 4, 2661–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Liu, Y.S. The changes of grain output center of gravity and its driving forces in China since 1990 to 2005. Resources Science 2009, 31, 1188–1194. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, X.; Zhu, X. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Urban Land Expansion in Chinese Urban Agglomerations. Acta Geographica Sinica 2020, 75, 571–588. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Lu, H.; Guan, H.; et al. Optimal bands combination selection for extracting garlic planting area with multi-temporal sentinel-2 imagery. Sensors 2021, 21, 5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhibah, D.; Imas, S.S. Classification of Garlic Land Based on Growth Phase using Convolutional Neural Network. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitanggang, I.S.; Rahmani, I.A.; Caesarendra, W.; et al. Garlic Field Classification Using Machine Learning and Statistic Approaches. AgriEngineering 2023, 5, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Xue, H.; Liu, C.; et al. Identification of garlic based on active and passive remote sensing data and object-oriented technology. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE) 2022, 38, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Pei, J.; Huang, J.; et al. Garlic and winter wheat identification based on active and passive satellite imagery and the google earth engine in northern china. Remote Sensing 2020, 12, 3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, D.; Yang, W. An algorithm for early rice area mapping from satellite remote sensing data in southwestern Guangdong in China based on feature optimization and random Forest. Ecological Informatics 2022, 72, 101853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Huang, C.; Li, H.; et al. Land- cover classification of random forest based on Sentinel- 2A image feature optimization. Resources Science 2019, 41, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Ren, H.R. Remote sensing extraction of paddy rice in Northeast China from GF-6 images by combining feature optimization and random forest. National Remote Sensing Bulletin 2023, 27, 2153–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immitzer, M.; Atzberger, C.; Koukal, T. Tree spacies classification with random forest using very high spatial resolution 8-band WorldView-2 satellite date. Remote Sensing 2012, 4, 2661–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.L.; Chen, Y.L.; Lu, D.S.; et al. Classification of land cover, forest, and tree species classes with ZiYuan-3 multispectral and stereo data. Remote Sensing 2019, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.X.; Wang, Y.J.; Shang, J.L.; et al. Investigating the impact of classification features and classifiers on crop mapping performance in heterogeneous agricultural landscapes. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geo-information 2021, 102, 102388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps-Valls, G.; Campos-Taberner, M.; Moreno-Martínez, Á.; et al. A unified vegetation index for quantifying the terrestrial biosphere. Science Advances 2021, 7, eabc7447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Biederman, J.A.; Knowles, J.F.; et al. Satellite solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence and near-infrared reflectance capture complementary aspects of dry-land vegetation productivity dynamics. Remote sensing of environment 2022, 270, 112858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Moreno-Martínez, Á.; Muñoz-Marí, J.; et al. Estimation of vegetation traits with kernel NDVI. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2023, 195, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Xue, H.; Liu, C.; et al. Identification of garlic based on active and passive remote sensing data and object-oriented technology. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE) 2022, 38, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).