Submitted:
20 February 2024
Posted:
21 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
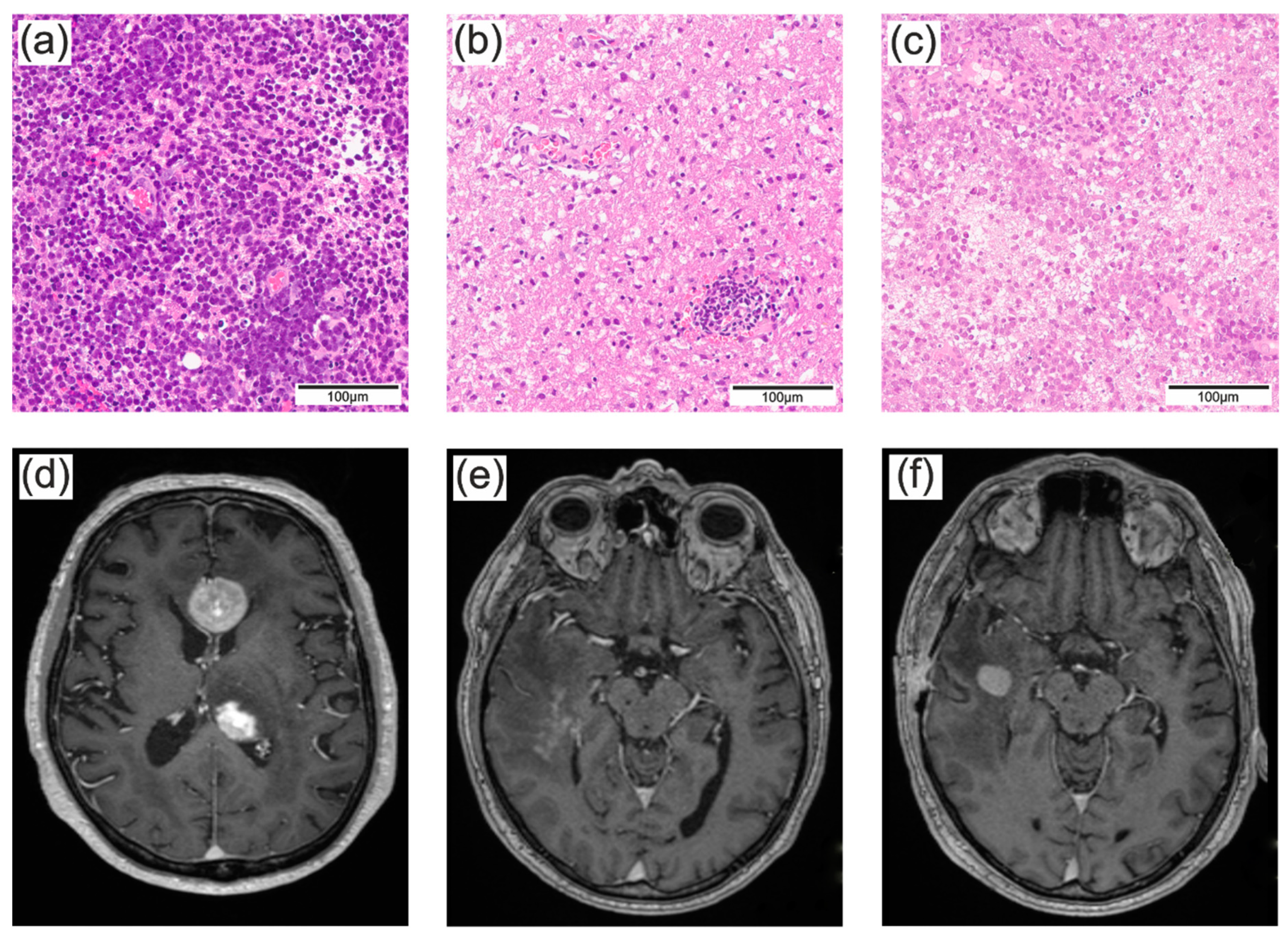
3.1. The majority of PCNSL were diagnosed by stereotactic biopsies
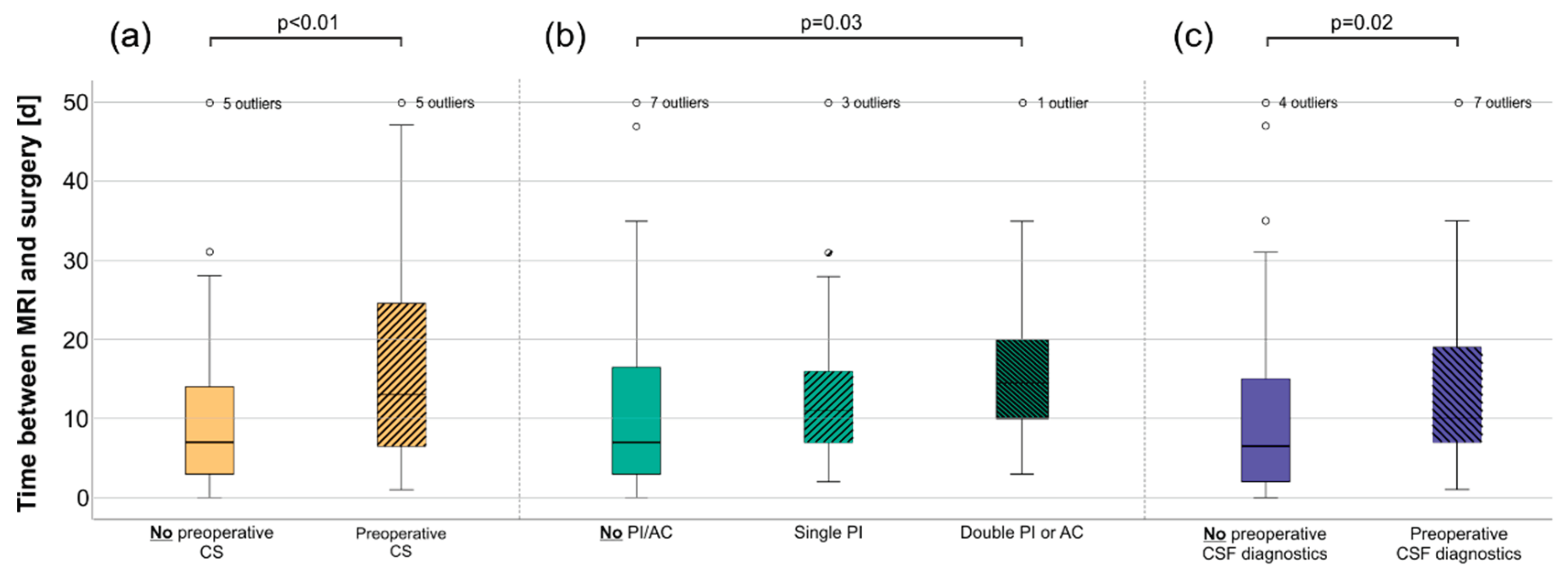
3.2. Patients treated with CS had a slightly higher risk of an unsuccessful first biopsy
3.3. The surgical approach did not influence the accuracy of the histopathologic diagnosis and depended mainly on the suspected diagnosis
3.4. Anticoagulation or platelet inhibition delayed surgery and was associated with the lower success of the biopsy
3.5. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) diagnostics were independent of previous CS treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Batchelor, T.; Loeffler, J.S. Primary CNS lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2006, 24, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Truitt, G.; Boscia, A.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2011-2015. Neuro Oncol 2018, 20, iv1–iv86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang-Xuan, K.; Bessell, E.; Bromberg, J.; Hottinger, A.F.; Preusser, M.; Rudà, R.; Schlegel, U.; Siegal, T.; Soussain, C.; Abacioglu, U.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of primary CNS lymphoma in immunocompetent patients: guidelines from the European Association for Neuro-Oncology. The Lancet Oncology 2015, 16, e322–e332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, E.; Korfel, A.; Martus, P.; Kanz, L.; Griesinger, F.; Rauch, M.; Röth, A.; Hertenstein, B.; von Toll, T.; Hundsberger, T.; et al. High-dose methotrexate with or without whole brain radiotherapy for primary CNS lymphoma (G-PCNSL-SG-1): a phase 3, randomised, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol 2010, 11, 1036–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, M.; Martus, P.; Roth, P.; Thiel, E.; Korfel, A. Surgery for primary CNS lymphoma? Challenging a paradigm. Neuro Oncol 2012, 14, 1481–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, S.; Barasch, J.G.; Young, R.J.; Grommes, C.; Schöder, H. Positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in primary central nervous System lymphoma-a narrative review. Ann Lymphoma 2021, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, M.; van den Bent, M.; Preusser, M.; Le Rhun, E.; Tonn, J.C.; Minniti, G.; Bendszus, M.; Balana, C.; Chinot, O.; Dirven, L.; et al. EANO guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of diffuse gliomas of adulthood. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2021, 18, 170–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abboud, H.; Probasco, J.C.; Irani, S.; Ances, B.; Benavides, D.R.; Bradshaw, M.; Christo, P.P.; Dale, R.C.; Fernandez-Fournier, M.; Flanagan, E.P.; et al. Autoimmune encephalitis: proposed best practice recommendations for diagnosis and acute management. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2021, 92, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.L.; Webb, M.S.; Copik, A.J.; Wang, Y.; Johnson, B.H.; Kumar, R.; Thompson, E.B. p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) is a key mediator in glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis of lymphoid cells: correlation between p38 MAPK activation and site-specific phosphorylation of the human glucocorticoid receptor at serine 211. Mol Endocrinol 2005, 19, 1569–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, P.; Wick, W.; Weller, M. Steroids in neurooncology: actions, indications, side-effects. Curr Opin Neurol 2010, 23, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sionov, R.V.; Spokoini, R.; Kfir-Erenfeld, S.; Cohen, O.; Yefenof, E. Mechanisms regulating the susceptibility of hematopoietic malignancies to glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis. Adv Cancer Res 2008, 101, 127–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrantes-Freer, A.; Engel, A.S.; Rodríguez-Villagra, O.A.; Winkler, A.; Bergmann, M.; Mawrin, C.; Kuempfel, T.; Pellkofer, H.; Metz, I.; Bleckmann, A.; et al. Diagnostic red flags: steroid-treated malignant CNS lymphoma mimicking autoimmune inflammatory demyelination. Brain Pathol 2018, 28, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Neuro Oncol 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheichel, F.; Marhold, F.; Pinggera, D.; Kiesel, B.; Rossmann, T.; Popadic, B.; Woehrer, A.; Weber, M.; Kitzwoegerer, M.; Geissler, K.; et al. Influence of preoperative corticosteroid treatment on rate of diagnostic surgeries in primary central nervous system lymphoma: a multicenter retrospective study. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bataille, B.; Delwail, V.; Menet, E.; Vandermarcq, P.; Ingrand, P.; Wager, M.; Guy, G.; Lapierre, F. Primary intracerebral malignant lymphoma: report of 248 cases. Journal of neurosurgery 2000, 92, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, J.M.; Heffner Jr, R.R.; Dillard, S.H.; Earle, K.M.; Davis, R.L. Primary malignant lymphomas of the central nervous System. Cancer 1974, 34, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeAngelis, L.M.; Yahalom, J.; Heinemann, M.H.; Cirrincione, C.; Thaler, H.T.; Krol, G. Primary CNS lymphoma: combined treatment with chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Neurology 1990, 40, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang-Xuan, K.; Bessell, E.; Bromberg, J.; Hottinger, A.F.; Preusser, M.; Rudà, R.; Schlegel, U.; Siegal, T.; Soussain, C.; Abacioglu, U.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of primary CNS lymphoma in immunocompetent patients: guidelines from the European Association for Neuro-Oncology. Lancet Oncol 2015, 16, e322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rae, A.I.; Mehta, A.; Cloney, M.; Kinslow, C.J.; Wang, T.J.C.; Bhagat, G.; Canoll, P.D.; Zanazzi, G.J.; Sisti, M.B.; Sheth, S.A.; et al. Craniotomy and Survival for Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Neurosurgery 2019, 84, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellekes, N.; Barbotti, A.; Abramov, Y.; Sitt, R.; Di Meco, F.; Ram, Z.; Grossman, R. Resection of primary central nervous system lymphoma: impact of patient selection on overall survival. J Neurosurg 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Hu, F.; Zhao, K.; Jiang, W.; Lei, T.; Shu, K. The role of surgical resection in primary central nervous system lymphoma: a single-center retrospective analysis of 70 patients. BMC Neurol 2021, 21, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houillier, C.; Soussain, C.; Ghesquières, H.; Soubeyran, P.; Chinot, O.; Taillandier, L.; Lamy, T.; Choquet, S.; Ahle, G.; Damaj, G.; et al. Management and outcome of primary CNS lymphoma in the modern era: An LOC network study. Neurology 2020, 94, e1027–e1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, W.A. The safety and efficacy of stereotactic biopsy for intracranial lesions. Cancer 1998, 82, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooman, D.; Belli, A.; Grundy, P.L. Image-guided frameless stereotactic biopsy without intraoperative neuropathological examination. J Neurosurg 2010, 113, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morell, A.A.; Shah, A.H.; Cavallo, C.; Eichberg, D.G.; Sarkiss, C.A.; Benveniste, R.; Ivan, M.E.; Komotar, R.J. Diagnosis of primary central nervous system lymphoma: a systematic review of the utility of CSF screening and the role of early brain biopsy. Neurooncol Pract 2019, 6, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroers, R.; Baraniskin, A.; Heute, C.; Vorgerd, M.; Brunn, A.; Kuhnhenn, J.; Kowoll, A.; Alekseyev, A.; Schmiegel, W.; Schlegel, U.; et al. Diagnosis of leptomeningeal disease in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas of the central nervous System by flow cytometry and cytopathology. Eur J Haematol 2010, 85, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijano, S.; López, A.; Manuel Sancho, J.; Panizo, C.; Debén, G.; Castilla, C.; Antonio García-Vela, J.; Salar, A.; Alonso-Vence, N.; González-Barca, E.; et al. Identification of leptomeningeal disease in aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: improved sensitivity of flow cytometry. J Clin Oncol 2009, 27, 1462–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, U.; Filie, A.; Little, R.F.; Janik, J.E.; Grant, N.; Steinberg, S.M.; Dunleavy, K.; Jaffe, E.S.; Abati, A.; Stetler-Stevenson, M.; et al. High incidence of occult leptomeningeal disease detected by flow cytometry in newly diagnosed aggressive B-cell lymphomas at risk for central nervous system involvement: the role of flow cytometry versus cytology. Blood 2005, 105, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heger, J.M.; Mattlener, J.; Schneider, J.; Gödel, P.; Sieg, N.; Ullrich, F.; Lewis, R.I.; Bucaciuc-Mracica, T.; Schwarz, R.F.; Rueß, D.; et al. Entirely noninvasive outcome prediction in central nervous system lymphomas using circulating tumor DNA. Blood 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brück, W.; Brunn, A.; Klapper, W.; Kuhlmann, T.; Metz, I.; Paulus, W.; Deckert, M. [Differential diagnosis of lymphoid infiltrates in the central nervous System: experience of the Network Lymphomas and Lymphomatoid Lesions in the Nervous System]. Pathologe 2013, 34, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, A.B.; Giannini, C.; Kaufmann, T.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Wu, W.; Decker, P.A.; Atkinson, J.L.D.; O’Neill, B.P. Primary central nervous system lymphoma can be histologically diagnosed after previous corticosteroid use: A pilot study to determine whether corticosteroids prevent the diagnosis of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Annals of Neurology 2008, 63, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullis, C.L.; Maldonado-Perez, A.; Bowden, S.G.; Yaghi, N.; Munger, D.; Wood, M.D.; Barajas, R.F.; Ambady, P.; Neuwelt, E.A.; Han, S.J. Diagnostic impact of preoperative corticosteroids in primary central nervous system lymphoma. J Clin Neurosci 2020, 72, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haldorsen, I.S.; Espeland, A.; Larsen, J.L.; Mella, O. Diagnostic delay in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Acta Oncologica 2005, 44, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoj, N.; Arivazhagan, A.; Mahadevan, A.; Bhat, D.I.; Arvinda, H.R.; Devi, B.I.; Sampath, S.; Chandramouli, B.A. Central nervous system lymphoma: patterns of incidence in Indian population and effect of steroids on stereotactic biopsy yield. Neurol India 2014, 62, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Önder, E.; Arıkök, A.T.; Önder, S.; Han, Ü.; Sorar, M.; Kertmen, H.; Yılmaz, E.D.; Fesli, R.; Alper, M. Corticosteroid pre-treated primary CNS lymphoma: a detailed analysis of stereotactic biopsy findings and consideration of interobserver variability. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015, 8, 7798–7808. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Velasco, R.; Mercadal, S.; Vidal, N.; Alañá, M.; Barceló, M.I.; Ibáñez-Juliá, M.J.; Bobillo, S.; Caldú Agud, R.; García Molina, E.; Martínez, P.; et al. Diagnostic delay and outcome in immunocompetent patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma in Spain: a multicentric study. J Neurooncol 2020, 148, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqua, R.; Balestrini, S.; Perozzi, C.; Cameriere, V.; Renzi, S.; Lagalla, G.; Mancini, G.; Montanari, M.; Leoni, P.; Scerrati, M.; et al. Diagnostic delay and prognosis in primary central nervous system lymphoma compared with glioblastoma multiforme. Neurol Sci 2016, 37, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falanga, A.; Marchetti, M.; Russo, L. Venous thromboembolism in the hematologic malignancies. Curr Opin Oncol 2012, 24, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, K. Thrombosis in Lymphoma Patients and in Myeloma Patients. The Keio Journal of Medicine 2015, 64, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazal, S.; Lebel, E.; Kalish, Y.; Makranz, C.; Gatt, M.E.; Goldschmidt, N.; Nachmias, B. Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis with Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Oncol Res Treat 2021, 44, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstner, E.; Batchelor, T. Primary CNS lymphoma. Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy 2007, 7, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, M. Glucocorticoid treatment of primary CNS lymphoma. J Neurooncol 1999, 43, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.; Iyer, V.; Rooney, N.; Wragg, R.; Waits, P.; Roberts, E.; Haynes, H.R.; Kurian, K.M. Diagnosis of primary cerebral lymphomas: possible value of PCR testing in equivocal cases requiring rebiopsy. Br J Neurosurg 2014, 28, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient | CS paused before 1st surgery [d] | 1st surgery | CS paused before 2nd surgery [d] | 2nd surgery | CS paused before 3rd surgery [d] | 3rd surgery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30 | STB | 88 | STB | ||
| 2 | m.i. | OSB | ≥259 | STB | ||
| 3 | 4 | STB | 71 | Resection | ||
| 4 | 8 | OSB | 19 | OSB | 48 | STB |
| 5 | 1 | STB | 11 | STB | ||
| 6 | 8 | OSB | 21 | Resection | 141 | Resection |
| 7 | 6 | STB | 3 | Resection |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





