Submitted:
18 February 2024
Posted:
20 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Analysis of the results of PNF transformation by T. flavus
2.2. The total saponins of PNF were transformed by crude extracellular enzymes from T. flavus
2.3. Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. HPLC procedure and methodology
3.3. Transformation of P. notoginseng saponins by T. flavus
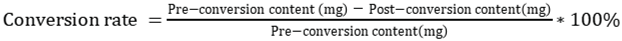
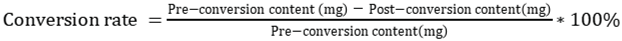
3.4. Transformation of PNF by crude extracellular enzymes
4. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
References
- Mohanan, P.; Yang, T.J.; Song, Y.H. Genes and regulatory mechanisms for ginsenoside biosynthesis. J. Plant Biol. 2023, 66, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, N.; Yan, X.; Yuan, Y.; Luo, F.; Jiang, Z.; Zhou, Y.F. Ginsenoside Re impacts on biotransformation products of ginsenoside Rb1 by cellulosimicrobium cellulans sp. 21 and its mechanisms. Process Biochem. 2019, 77, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cong, X.; Hao, M. Effect of anti-skin disorders of ginsenosides-A Systematic Review. J. Ginseng Res. 2023, 47, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Zhang, S.Q.; Lu, W.X.; Shen, S.Z.; Wei, L. Preparation of Panax notoginseng flower saponins enteric-coated sustained-release pellets and its pharmacokinetics and in vitro-in vivo correlation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Tec. 2021, 62, 102321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, C.; Lu, W.; Wei, L. Phytochemistry, pharmacology, and clinical use of Panax notoginseng flowers buds. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 2155–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.P.; Chen, M.Y.; Shao, L.; Zhang, W.; Rao, T.; Zhou, H.H.; Huang, W.H. Quantification of Panax notoginseng saponins metabolites in rat plasma with in vivo gut microbiota-mediated biotransformation by HPLC-MS/MS. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2019, 17, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, M.; Ai, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y. Highly regioselective hydrolysis of the glycosidic bonds in ginsenosides catalyzed by snailase. Process Biochem. 2021, 103, 910–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Huang, L.; Song, Y.; Liu, Z.X.; Liang, L.S.; Wang, L.M.; Wang, T.Y. Preparation and pharmacological effects of minor ginsenoside nanoparticles: a review. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 974274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.F.; Ling, X.F.; Zhao, S.J.; Xu, L.L.; Wang, R.F. Diversity and isolation of Endophytic Fungi in Panax japonicus and biotransformation activity on saponins. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, R.; Hou, G.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, F.; Liu, Z.; Meng, Q. Stereoscopic differences in the identification, bioactivity, and metabolism of C-20 and C-24 epimeric ginseng saponins. Mini. Rev. Med. Chem, 2023, 23, 804–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Hu, Z.Y.; Li, A.; Zhu, Z.Z.; Yang, N.; Ying, Z.X.; He, J.; Wang, C.T.; Yin, S.; Cheng, S.Y. Recent advances in biotransformation of saponins. Molecules 2019, 24, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, Y.F.; Dai, Z.P.; Liang, Y.; Zhu, C.Y.; Su, C.; Song, L.S.; Wang, K.P.; Li, J.; Wei, X.Y. Gypenoside biotransformation into ginsenoside F2 by endophytic Aspergillus niger from Gynostemma pentaphyllum. Nat. Prod. Res 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Wu, Z.S.; Cao, S.S.; Tao, Z.D.; Fan, D.D.; Liu, X.C. Simultaneous transformation of ginsenoside Rb1 into rare ginsenoside F2 and Compound K by the extracellular enzyme from Aspergillus Niger Wu-16. Bioresource Technol. Rep. 2023, 22, 101419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.Y.; Li, W.N.; Fan, D.D. Biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1 to ginsenoside CK by Strain XD101: a safe bioconversion strategy. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 193, 2110–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.Y.; Zhou, R.X.; Sun, C.K.; Jin, Y.H.; Yu, H.S.; Zhang, T.Y.; Xu, L.Q.; Jin, F.X. Preparation of minor ginsenosides C-Mc, C-Y, F2, and C-K from American ginseng PPD-ginsenoside using special ginsenosidase type-I from Aspergillus niger g.848. J. Ginseng Res. 2015, 39, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.K.; Liu, C.Y.; Im, W.T.; Chen, S.; Zuo, K.Z.; Yu, H.S.; Song, J.G.; Xu, L.Q.; Yi, T.H.; Jin, F.X. Dynamic changes of multi-notoginseng stem-leaf ginsenosides in reaction with ginsenosidase type-I. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.S.; Liu, Q.M.; Zhang, C.Z.; Lu, M.C.; Fu, Y.Y.; Im, W.T.; Lee, S.T.; Jin, F.X. A new ginsenosidase from Aspergillus strain hydrolyzing 20-O-multi-glycoside of PPD ginsenoside. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 772–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.F.; Yu, H.S.; Wang, D.M.; Liu, T.Q.; Liu, C.Y.; An, D.S.; Im, W.t.; Kim, S.G.; Jin, F.X. Kinetics of a cloned special ginsenosidase hydrolyzing 3-O-glucoside of multi-protopanaxadiol-type ginsenosides, named ginsenosidase type III. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 22, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.M.; Yu, H.S.; Song, J.G.; Xu, Y.F.; Liu, C.Y.; Jin, F.X. A novel ginsenosidase from an Aspergillus strain hydrolyzing 6-O-multi-glycosides of protopanaxatriol-type ginsenosides, named ginsenosidase type IV. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 21, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.M.; Yu, H.S.; Song, J.G.; Xu, Y.F.; Jin, F.X. Enzyme kinetics of ginsenosidase type IV hydrolyzing 6-O-multi-glycosides of protopanaxatriol type ginsenosides. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.Z.; Guo, M.; Li, Y.F.; Shao, L.J.; Cui, X.M.; Yang, X.Y. Highly regioselective biotransformation of protopanaxadiol-type and protopanaxatriol-type ginsenosides in the underground parts of Panax notoginseng to 18 minor ginsenosides by Talaromyces flavus. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 14910–14919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhou, Y.K.; Xu, M.H.; Yu, S.S. Production of gypenoside XVII from ginsenoside Rb1 by enzymatic transformation and their anti-inflammatory activity in Vitro and in Vivo. Molecules 2023, 28, 7001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Liang, Y.Z.; Cui, X.M.; Shao, L.J.; Lou, D.J.; Yang, X.Y. Production of minor ginsenosides from Panax notoginseng flowers by Cladosporium xylophilum. Molecules 2022, 27, 6615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Lee, W.J.; Gebru, Y.A.; Upadhyaya, J.; Ko, S.R.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, M.K. Production of minor ginsenosides C-K and C-Y from naturally occurring major ginsenosides using crude β-glucosidase preparation from submerged culture of Fomitella fraxinea. Molecules 2021, 26, 4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Q.M.; Sung, B.H.; An, D.H.; Lee, H.G.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, S.C.; Lee, S.T.; Im, W.T. Bioconversion of ginsenosides Rb1, Rb2, Rc and Rd by novel β-glucosidase hydrolyzing outer 3-O glycoside from Sphingomonas sp. 2F2: cloning, expression, and enzyme characterization. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 156, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.C.; Kim, T.H.; Choi, J.H.; Oh, D.K. Complete biotransformation of protopanaxadiol-type ginsenosides to 20- O-β-glucopyranosyl-20(S)-protopanaxadiol using a novel and thermostable β-glucosidase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 2822–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Zuo, K.Z.; Yu, H.S.; Sun, C.K.; Zhang, T.Y.; Xu, L.Q.; Jin, Y.H.; Im, W.T.; Jin, F.X. Preparation of minor ginsenosides C-Mx and C-K from notoginseng leaf ginsenosides by a special ginsenosidase type-I. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 2158–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.H.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, M.R.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Suh, H.J. Changes of ginsenoside content by mushroom mycelial fermentation in red ginseng extract. J. Ginseng Res. 2011, 35, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, M.; Min, J.W.; Yang, D.U.; Jung, S.K.; Kim, S.Y.; Yang, D.C. Ethanolic fermentation from red ginseng extract using Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 20, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.L.; Wu, H.; Piao, X.C.; Yin, Z.H.; Yin, C.R. Microbial transformation of ginsenosides extracted from Panax ginseng adventitious roots in an airlift bioreactor. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Nguyen, T.T.; Lim, T.Y.; Lim, J.; Park, B.; Lee, S.; Mok, I.K.; Pal, K.; Lim, S.; Kim, D. Fermented wild ginseng by Rhizopus oligosporus improved l-Carnitine and ginsenoside contents. Molecules 2020, 25, 2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.H.; Zhou, J.L.; Harindintwali, J.D.; Yu, X.B. Production of minor ginsenosides by combining Stereum hirsutum and cellulase. PLoS One. 2021, 16, e0255899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Substrates | Products | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Types | transformation rate (%) | Types | yield of products (%) |
| Rb1 | 44.16 | Gyp-ⅩⅦ | 0.18 |
| Rc | 55.22 | C-Mc1 | 0.05 |
| Rb2 | 48.63 | C-Mx1 | 0.14 |
| Rb3 | 47.25 | F2 | 0.07 |
| Rg3 | 3.24 | ||
| 20(R)-Rg3 | 2.10 | ||
| Rk1 | 0.58 | ||
| Rg5 | 0.80 | ||
| Substrates | Products | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Types | transformation rate (%) | Types | yield of products (%) |
| Rb1 | 36.21 | Gyp-ⅩⅦ | 0.006 |
| Rc | 21.13 | C-Mc1 | 0.036 |
| Rb2 | 19.92 | C-Mx1 | 0.070 |
| Rb3 | 20.15 | F2 | 0.008 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




