Submitted:
23 July 2024
Posted:
25 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Rationale for Usage
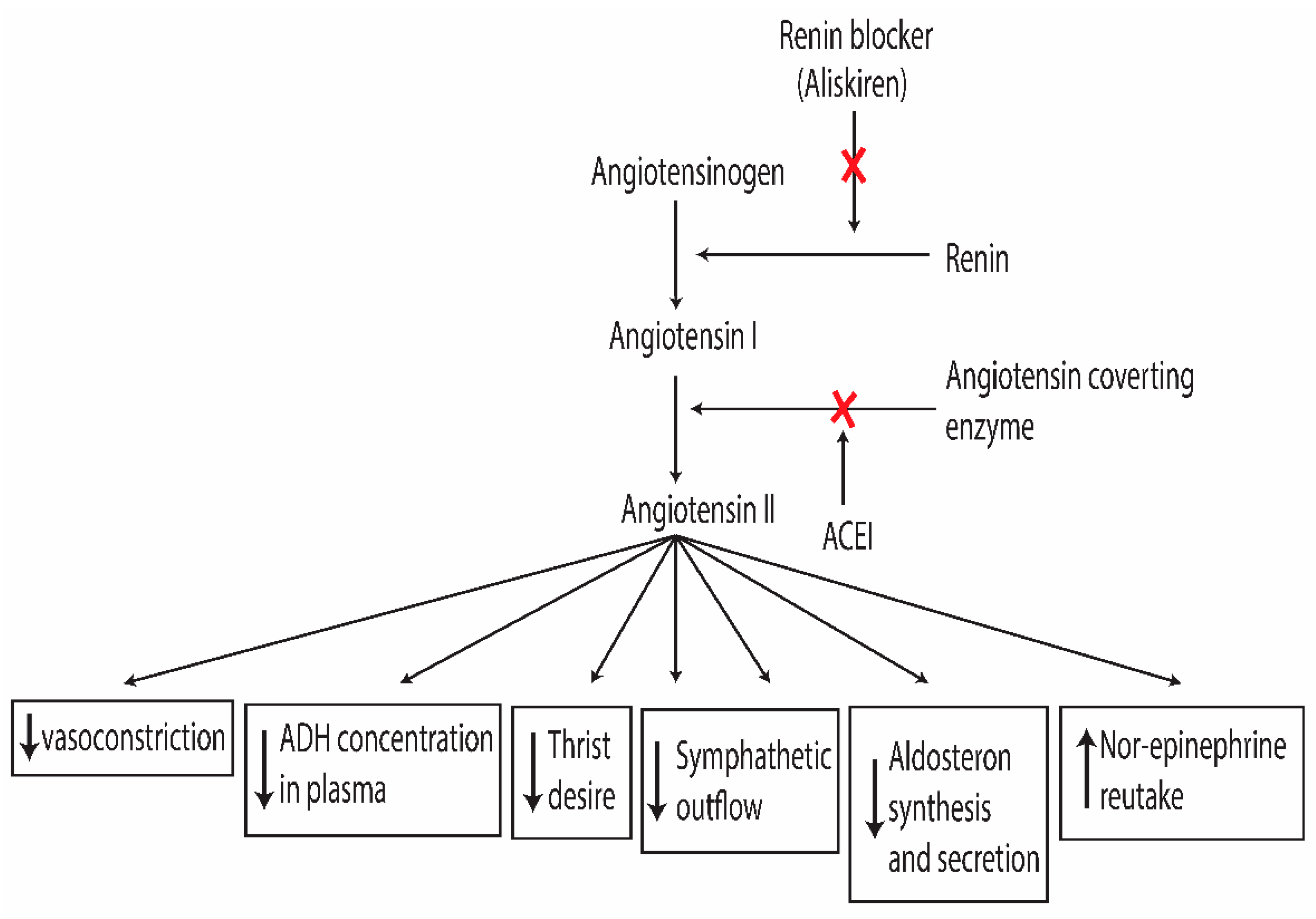
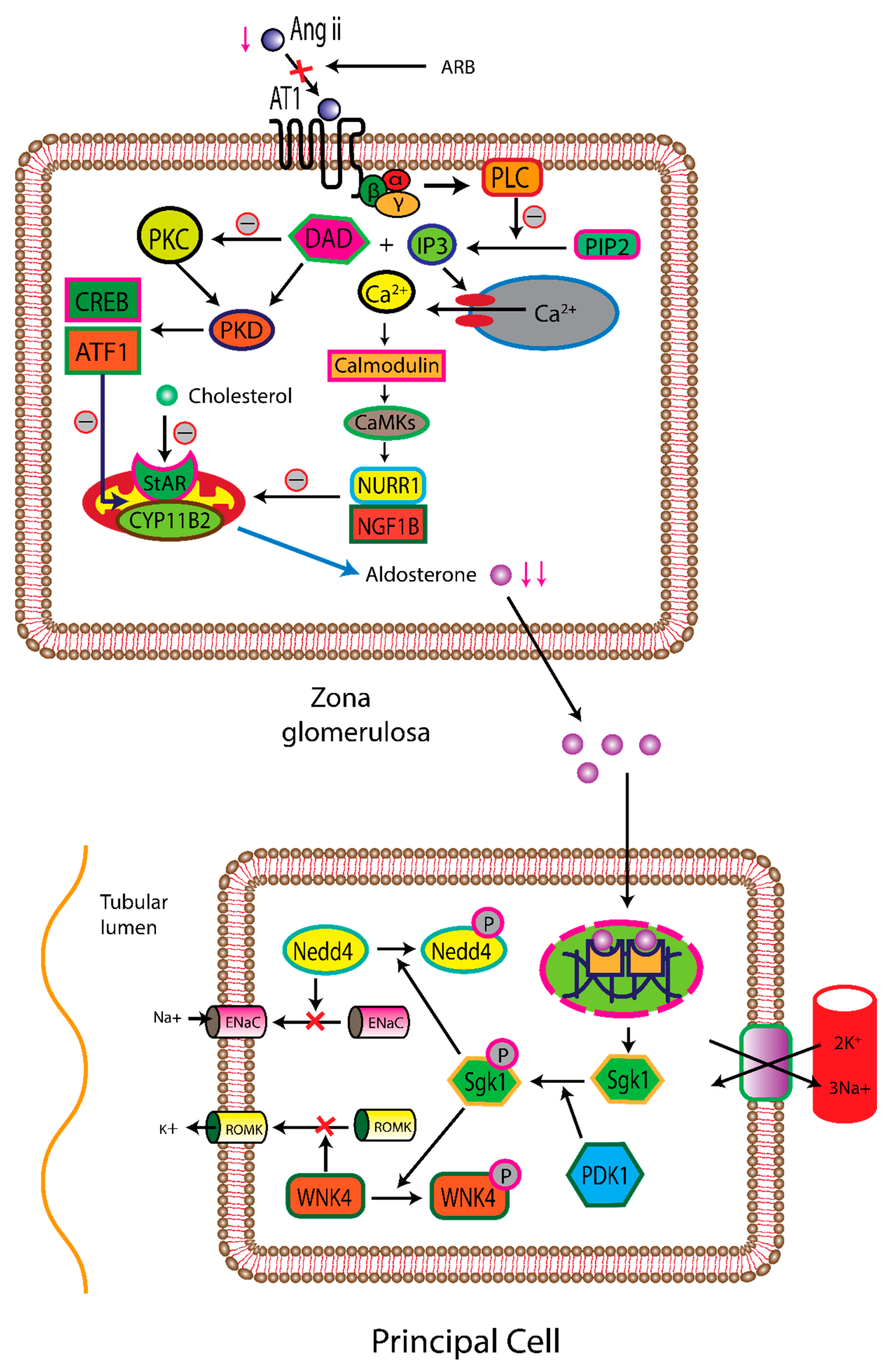
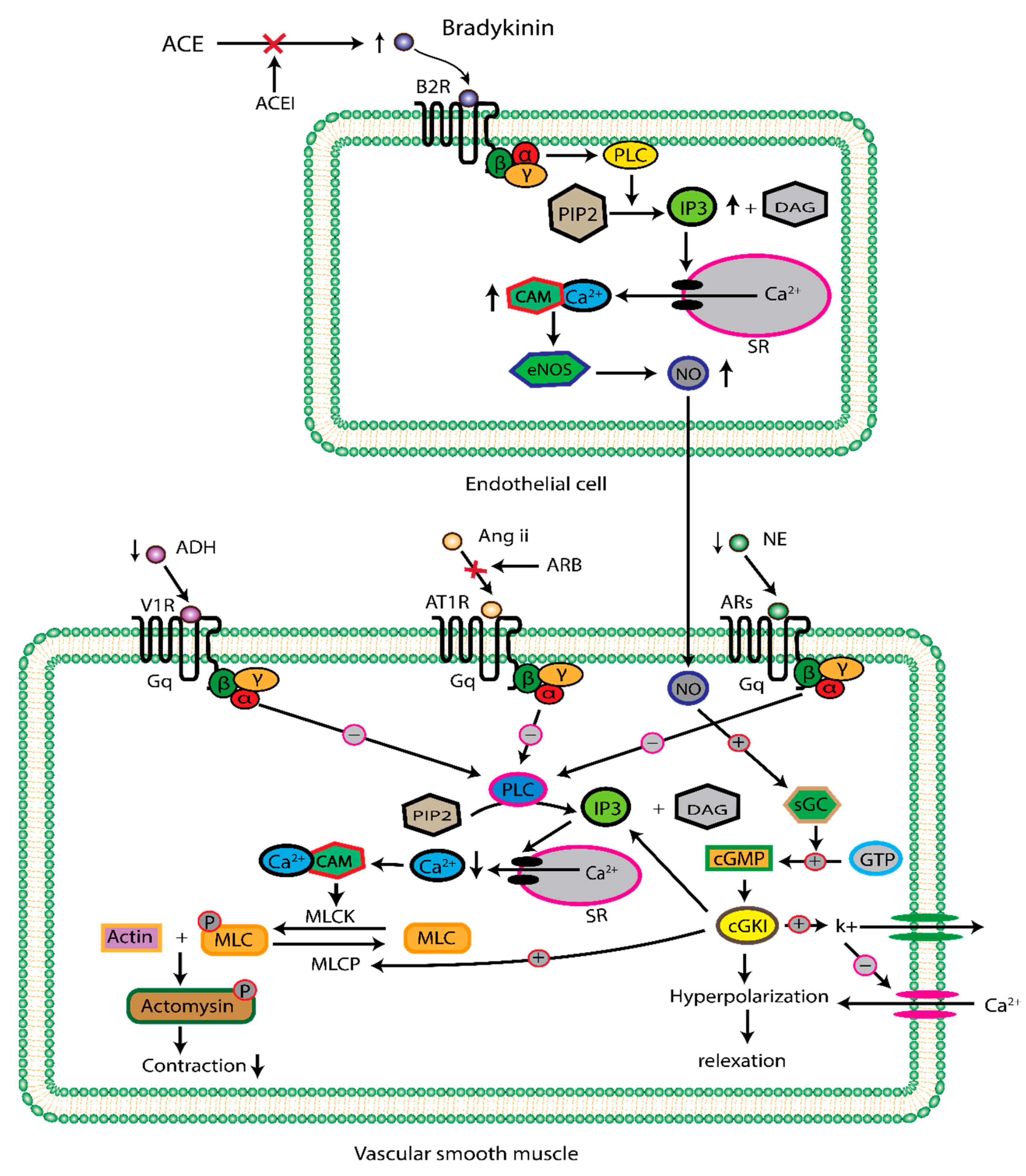
2.1. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System
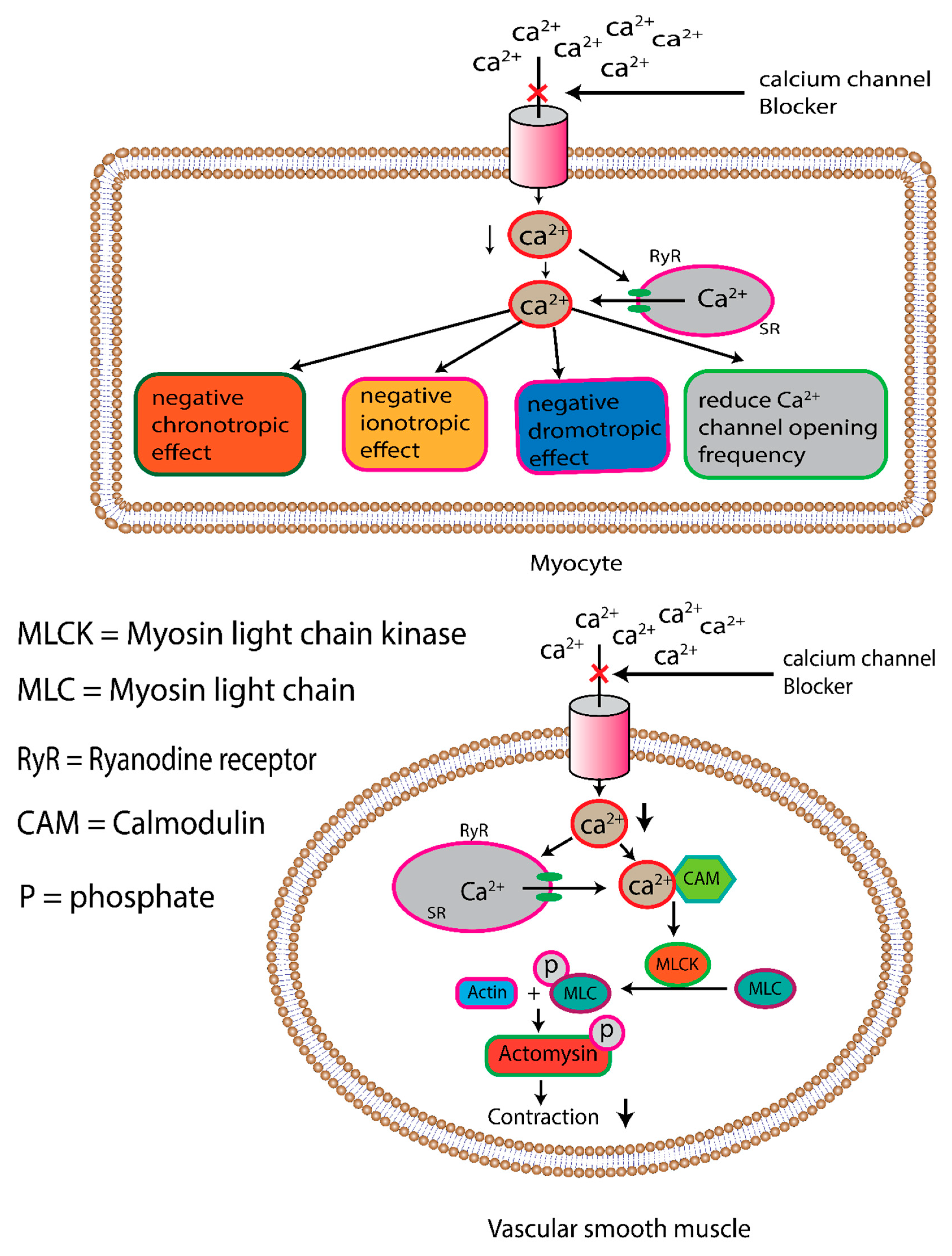
2.2. Calcium Channel Blocker
2.3. Diuretic
3. Clinical Trial Evaluation
3.1. Perindopril/Indapamide vs. Placebo (PROGRESS TRAIL)
3.2. Perindopril/Indapamide vs. Placebo (ADVANCE TRAIL)
3.3. Perindopril/Indapamide vs. Placebo (HYVET TRAIL)
3.4. Losartan/Hydrochlorothiazide vs. Atenolol/Hydrochlorothiazide (LIFE TRAIL)
3.5. A Calcium Antagonist vs. Non-Calcium Antagonist (INVEST TRAIL)
3.6. Amlodipine-Based Regiment vs. Atenolol Based Regiment (ASCOT-BPLA TRAIL)
3.7. Benazepril/Amlodipine vs. Benazepril/Hydrochlorothiazide (ACCOMPLISH TRAIL)
3.8. Benazepril/Amlodipine vs. Benazepril/Hydrochlorothiazide (ACCOMPLISH TRAIL)
| class | Cmax | F | T1/2 | VD | Proteinbinding | CLr | Refer-ence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
CCB Amlodipine |
6-8h |
64% |
40-50h |
21L/kg |
98% |
0.23-0.4L/h/kg |
[159] |
| Felodipine | 0.5-5h | 15% | 25 h | 10 L/kg | >99 | 1-1.5 L/min | [160] |
| Verapamil | 2.2h | 20% | 2.7-4.8h | 310-406 L | 90% | 875 ml/min | [161] |
|
ARB Olmesartan medoxomil/ Olmesartan |
1.7–2.5h |
26% |
15 h |
35L |
99.7% |
1.31 L/h |
[162, 163] |
| valsartan | 2h | 23% | 6.1h | 17L | 85-99% | 2.2 L/h | [164] |
| Telmisartan | 1h | 43% | 24h | 500L | >99% | >800ml/min | [165] |
| Candesartan cilexetil/candesartan | 3,5-6h | 40% | 3.5-11h | 0.13L/kg | 99.5% | 0.0222 L/h/kg | [166, 167] |
| Eprosartan | 1-2h | 13% | 5-9h | 13L | 98% | 130ml/min | [168] |
| Irbesartan | 1.3-3h | 60-80% | 11-18h | 53-93L | 90% | 167ml/min | [166] |
| Losartan | 1-2h | 33% | 1.7-2.1h | 34.4 ± 17.9L | 98.6–98.8% | 4.3-5.6L/h | [169] |
|
ACEI Benazepril/Benazeprilat |
1.5h |
37% |
22.3h |
8.7L |
95% |
1.4-1.7L/h |
[170] |
| Captopril | 0.75-1h | 65% | 2h | 0.8 L/kg | 23-31% | 0.7L/h/kg | [171] |
| Enalapril/ enalaprilat | 4h | 36-44% | 11h | 50% | 8-9.5L/h | [172,173] | |
| Fosinopril/Fosinoprilat | 2.8-3.1h | 25-29% | 11.5-12h | 9.8-10.6L | 95-99.8% | 1.55-2.35 L/h | [174] |
| Lisinopril | 8h | 20-28% | 12.6h | 24L | no | 6.36L/h | [175] |
| Quinapril/quinaprilat | 2.5h | 50-60% | 3.2h | 13.9L | 97% | 68 ml/min. | [176] |
| Diuretics hydrochlorothiazide |
1.5-4h |
60-70% |
5.6-14.8h |
275.3 L |
40-68% |
[177] |
| Combination type | Dose (mg) | Trade name | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
|
CCB + ACEI Amlodipine-benazepril Hydrochloride |
2.5/10, 5/10, 5/20, 10/20 | Lotrel | $14 ($215)- $16 ($390) |
| Enalaprilmaleate-felodipine | 5/5 | Lexxel | |
| Trandolapril-verapamil | 2/180, 1/240, 2/240, 4/240 | Tarka | $47 ($185)- $65 ($185) |
|
CCB + ARB Amlodipine/Olmesartan medoxomil |
5/20,5/40,10/20,10/40 |
Azor |
$23 ($280)- $28 ($350) |
| Amlodipine/Valsartan |
5/160,320/5,10/160,10/320 | Exforge | $20 ($270)- $25 ($385) |
| Amlodipine/Telmisartan | 5/40,5/80,10/40,10/80 | Twynsta | $50 (NA)- $55 ($240) |
|
Diuretic + ACEI Benazepril-hydrochlorothiazide |
5/6.25, 10/12.5, 20/12.5, 20/25 | Lotensin HCT | $21 (NA)- $24 (NA) |
| Captopril-hydrochlorothiazide | 25/15, 25/25, 50/15, 50/25 | Capozide | |
| Enalapril-hydrochlorothiazide | 5/12.5, 10/25 | Vaseretic | $10 (NA)- $10 ($395) |
| Fosinopril-hydrochlorothiazide | 10/12.5, 20/12.5 | Monopril/HCT | |
| Lisinopril-hydrochlorothiazid | 10/12.5, 20/12.5, 20/25 | Prinzide, Zestoretic | $4 ($400)- $6 ($400) |
| Moexipril-hydrochlorothiazide | 7.5/12.5, 15/25 | Uniretic | |
| Quinapril-hydrochlorothiazide | 10/12.5, 20/12.5, 20/25 | Accuretic | $17 ($150) |
|
Diuretic + ARB Candesartan-hydrochlorothiazide |
16/12.5, 32/12.5,32/25 |
Atacand HCT | $48 ($150)- $50 ($165) |
| Eprosartan-hydrochlorothiazide | 600/12.5, 600/25 | Teveten-HCT | |
| Irbesartan-hydrochlorothiazide | 150/12.5, 300/12.5 | Avalide | $15 ($235)- $20 ($255) |
| Losartan-hydrochlorothiazide | 50/12.5, 100/12.5,100/25 | Hyzaar | $4 ($130)- $9 ($175) |
| Olmesartan medoxomil-hydrochlorothiazide | 20/12.5,40/12.5,40/25 | Benicar HCT | $14 ($225)- $16 ($310) |
| Telmisartan-hydrochlorothiazide | 40/12.5, 80/12.5 | Micardis-HCT | $47 ($220) |
| Valsartan-hydrochlorothiazide | 80/12.5, 160/12.5, 160/25,320/12.5,320/25 | Diovan-HCT | $14 ($270)- $18 ($420) |
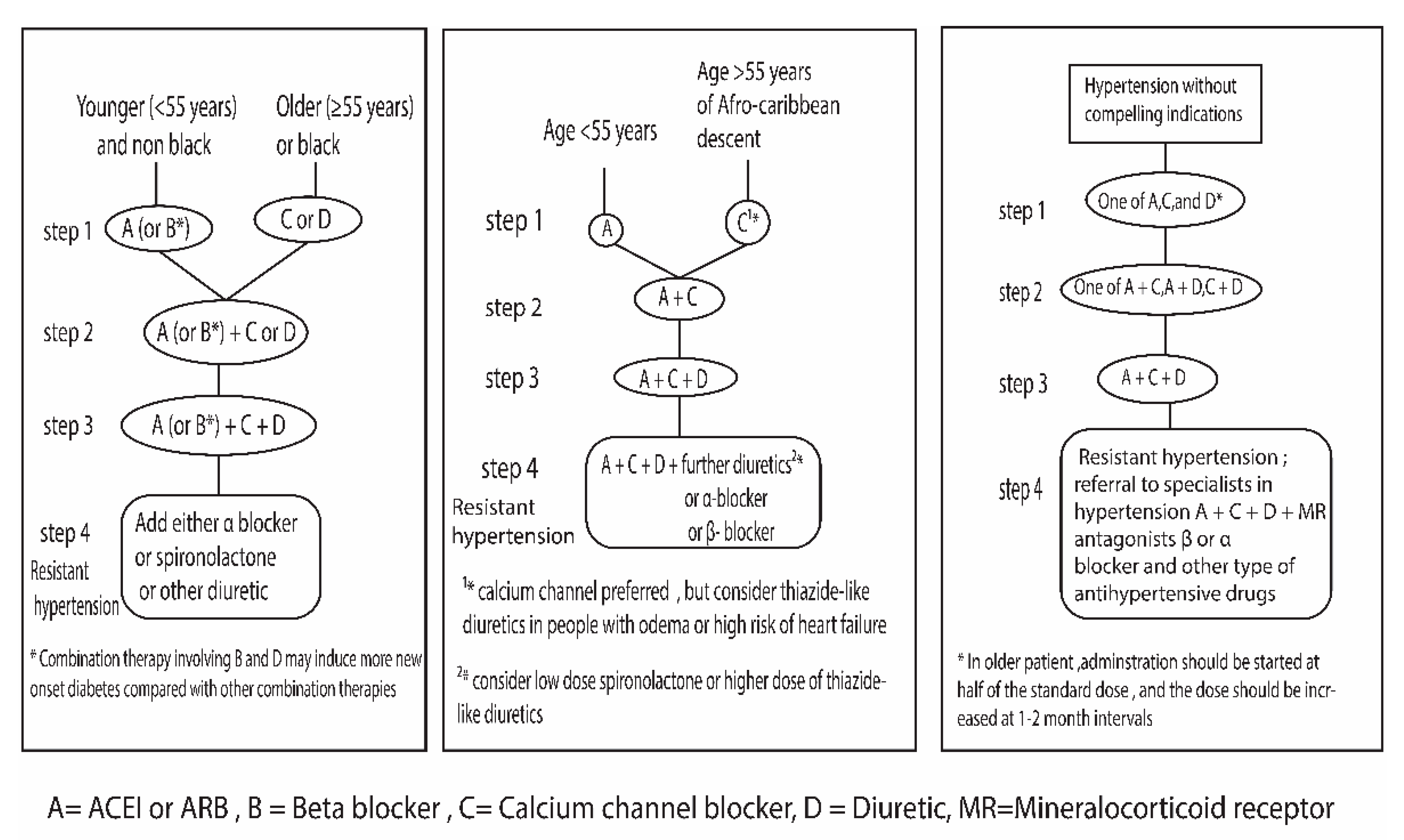
4. Pharmacological Treatment Strategy
5. Conclusions
Data Availability Statment
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaziano, T. , Reddy, K. S., Paccaud, F., Horton, S., & Chaturvedi, V. (2006). Cardiovascular disease. Disease Control Priorities in Developing Countries. 2nd edition.
- Nabel, E. G. (2003). Cardiovascular disease. New England Journal of Medicine, 349(1), 60-72.
- Kannel, W.B. Hypertension as a Risk Factor for Cardiac Events—Epidemiologic Results of Long-Term Studies. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1993, 21 (Suppl. S2), S27–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snow, P.J.D.; Jones, A.M.; Daber, K.S. Coronary disease: a pathological study. Br. Heart J. 1955, 17, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, A. Coronary heart disease: Overview. Lancet 1996, 348, S1–S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P.; Theroux, P. Pathophysiology of coronary artery disease. Circulation 2005, 111, 3481–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, M., Oktay, A. A., Stewart, M. H., Milani, R. V., Ventura, H. O., & Lavie, C. J. (2020). Left ventricular hypertrophy and hypertension. Progress in cardiovascular diseases, 63(1), 10-21.
- Maganti, K.; Rigolin, V.H.; Sarano, M.E.; Bonow, R.O. Valvular Heart Disease: Diagnosis and Management. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2010, 85, 483–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijesurendra, R. S. , & Casadei, B. (2019). Mechanisms of atrial fibrillation. Heart.
- Wijesurendra, R.S.; Casadei, B. Atrial fibrillation: effects beyond the atrium? Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 105, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markus, H.S. Cerebral perfusion and stroke. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, V.; Chowdhary, A.; Farrar, B.; Nagaraja, H.; Braun, J.; Kanard, R.; Novak, P.; Slivka, A. Altered cerebral vasoregulation in hypertension and stroke. Neurology 2003, 60, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albright Jr, R. C. (2001, January). Acute renal failure: a practical update. In Mayo Clinic Proceedings (Vol. 76, No. 1, pp. 67-74). Elsevier.
- Bellomo, R.; Kellum, J.A.; Ronco, C. Defining acute renal failure: physiological principles. Intensiv. Care Med. 2003, 30, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, R. G. (1998). Chronic renal failure—a vasculopathic state. New England Journal of Medicine, 339(12), 841-843.
- Kjeldsen, S.E. Hypertension and cardiovascular risk: General aspects. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 129, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, K.T.; Bundy, J.D.; Kelly, T.N.; Reed, J.; Kearney, P.M.; Reynolds, K.; Chen, J.; He, J. Abstract 16828: Global Disparities of Hypertension Prevalence and Control: A Systematic Analysis of Population-based Studies From 90 Countries. Circulation 2016, 134, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fryar, C.D.; Ostchega, Y.; Hales, C.; Zhang, G.; Kruszon-Moran, D. Hypertension Prevalence and Control Among Adults: United States, 2015-2016. . 2017, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, K.T.; Stefanescu, A.; He, J. The global epidemiology of hypertension. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, J. (2013). Epidemiology of hypertension. Clinical Queries: Nephrology, 2(2), 56-61.
- Giles, T.D.; Materson, B.J.; Cohn, J.N.; Kostis, J.B. Definition and Classification of Hypertension: An Update. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2009, 11, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzo, J. L. , Sica, D. A., & Black, H. R. (Eds.). (2008). Hypertension primer. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- Beevers, G., Lip, G. Y., & O’Brien, E. (2001). The pathophysiology of hypertension. Bmj, 322(7291), 912-916.
- Messerli, F. H., Williams, B., & Ritz, E. (2007). Essential hypertension. The Lancet, 370(9587), 591-603.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. (2019). Hypertension in adults: diagnosis and management. London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (UK).
- James, P. A. , Oparil, S., Carter, B. L., Cushman, W. C., Dennison-Himmelfarb, C., Handler, J.,... & Ortiz, E. (2014). 2014 evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). Jama, 311(5), 507-520.
- Watkins, P. J. , Drury, P. L., & Taylor, K. W. (1990). Diabetes and its management. Boston: Blackwell Scientific.
- Forbes, J.M.; Cooper, M.E. Mechanisms of Diabetic Complications. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 137–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K., Jafar, T. H., Nitsch, D., Neuen, B. L., & Perkovic, V. (2021). Chronic kidney disease. The lancet, 398(10302), 786-802.
- Webster, A. C., Nagler, E. V., Morton, R. L., & Masson, P. (2017). Chronic kidney disease. The lancet, 389(10075), 1238-1252.
- Levey, A. S., & Coresh, J. (2012). Chronic kidney disease. The lancet, 379(9811), 165-180.
- Cohn, J.N. Blood pressure and cardiac performance. Am. J. Med. 1973, 55, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loushin, M. K., Quill, J. L., & Iaizzo, P. A. (2015). Mechanical aspects of cardiac performance. Handbook of cardiac anatomy, physiology, and devices, 335-360.
- Touyz, R.M.; Alves-Lopes, R.; Rios, F.J.; Camargo, L.L.; Anagnostopoulou, A.; Arner, A.; Montezano, A.C. Vascular smooth muscle contraction in hypertension. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, S.K.; Surks, H.K.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Blanton, R.; Jamnongjit, M.; Aronovitz, M.; Baur, W.; Ohtani, K.; Wilkerson, M.K.; et al. High blood pressure arising from a defect in vascular function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2008, 105, 6702–6707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beevers, G., Lip, G. Y., & O’Brien, E. (2001). The pathophysiology of hypertension. Bmj, 322(7291), 912-916.
- Hingorani, A.D.; Sharma, P.; Jia, H.; Hopper, R.; Brown, M.J. Blood Pressure and the M235T Polymorphism of the Angiotensinogen Gene. Hypertension 1996, 28, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canbakan, B. (2013). Rational approaches to the treatment of hypertension: drug therapy—monotherapy, combination, or fixed-dose combination?. Kidney international supplements, 3(4), 349-351.
- Guerrero-García, C., & Rubio-Guerra, A. F. (2018). Combination therapy in the treatment of hypertension. Drugs in context, 7.
- Chalmers, J. The Place of Combination Therapy in the Treatment of Hypertension in 1993. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 1993, 15, 1299–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradman, A. H., Basile, J. N., Carter, B. L., Bakris, G. L., & American Society of Hypertension Writing Group. (2010). Combination therapy in hypertension. Journal of the American Society of Hypertension, 4(2), 90-98.
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Rosei, E.A.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; De Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Society of Hypertension (ESH). Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3021–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, L.S.; Schulz, R.M. Patient compliance—an overview. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 1992, 17, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackwell, B. Patient compliance. New Engl. J. Med. 1973, 289, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahuddin, A.; Mushtaq, M.; Materson, B.J. Combination therapy for hypertension 2013: An update. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2013, 7, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, S.; Kalra, B.; Agrawal, N. Combination therapy in hypertension: An update. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2010, 2, 44–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorostidi, M., & de la Sierra, A. (2013). Combination therapy in hypertension. Advances in therapy, 30, 320-336.
- Chaszczewska-Markowska, M.; Sagan, M.; Bogunia-Kubik, K. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) – physiology and molecular mechanisms of functioning. Postepy Hig. I Med. Doswiadczalnej 2016, 70, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atlas, S.A. The Renin-Angiotensin Aldosterone System: Pathophysiological Role and Pharmacologic Inhibition. J. Manag. Care Pharm. 2007, 13, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thatcher, S. E. (2017). A brief introduction into the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system: new and old techniques. The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System: Methods and Protocols, 1-19.
- Schweda, F. Salt feedback on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Pfl?gers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2015, 467, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taugner, R., & Hackenthal, E. (1988). On the character of the secretory granules in juxtaglomerular epithelioid cells. International review of cytology, 110, 93-131.
- Barajas, L. (1979). Anatomy of the juxtaglomerular apparatus. American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology, 237(5), F333-F343.
- Schweda, F. Schweda, F., Friis, U., Wagner, C., Skott, O., & Kurtz, A. (2007). Renin release. Physiology, 22(5), 310-319.
- Trerattanavong, K. , & Chen, J. (2023). Biochemistry, Renin. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.
- Morgan, L. , Pipkin, F. B., & Kalsheker, N. (1996). Angiotensinogen: molecular biology, biochemistry and physiology. The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology, 28(11), 1211-1222.
- Lu, H.; A Cassis, L.; Kooi, C.W.V.; Daugherty, A. Structure and functions of angiotensinogen. Hypertens. Res. 2016, 39, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeunemaitre, X.; Soubrier, F.; Kotelevtsev, Y.V.; Lifton, R.P.; Williams, C.S.; Charru, A.; Hunt, S.C.; Hopkins, P.N.; Williams, R.R.; Lalouel, J.-M.; et al. Molecular basis of human hypertension: Role of angiotensinogen. Cell 1992, 71, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Lu, H.; Cassis, L.A.; Daugherty, A. Molecular and Pathophysiological Features of Angiotensinogen: A Mini Review. Am. Chin. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, M. E. , & Sigmund, C. D. (2006). Genetic basis of hypertension: revisiting angiotensinogen. Hypertension, 48(1), 14-20.
- Wu, C.; Lu, H.; Cassis, L.A.; Daugherty, A. Molecular and Pathophysiological Features of Angiotensinogen: A Mini Review. Am. Chin. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griendling, K.; Murphy, T.J.; Alexander, R.W. Molecular biology of the renin-angiotensin system. Circulation 1993, 87, 1816–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparks, M. A. , Crowley, S. D., Gurley, S. B., Mirotsou, M., & Coffman, T. M. (2014). Classical renin-angiotensin system in kidney physiology. Comprehensive Physiology, 4(3), 1201.
- Dorer, F.E.; Kahn, J.R.; Lentz, K.E.; Levine, M.; Skeggs, L.T. Hydrolysis of Bradykinin by Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme. Circ. Res. 1974, 34, 824–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirahanchi, Y., & Sharma, S. (2019). Physiology, Bradykinin.
- Ng, K.K.F.; Vane, J.R. Conversion of Angiotensin I to Angiotensin II. Nature 1967, 216, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdös, E.G. Conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II. Am. J. Med. 1976, 60, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountain, J. H. , Kaur, J., & Lappin, S. L. (2023). Physiology, renin angiotensin system. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing.
- Peti-Peterdi, J.; Harris, R.C. Macula Densa Sensing and Signaling Mechanisms of Renin Release. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1093–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, T. , Chung, O., Csikos, T., Culman, J., Gallinat, S., Gohlke, P.,... & Zhu, Y. Z. (1996). Angiotensin receptors. Journal of hypertension. Supplement: official journal of the International Society of Hypertension, 14(5), S95-103.
- Greindling, K.K.; Lassegue, B.; Alexander, R.W. Angiotensin Receptors and Their Therapeutic Implications. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1996, 36, 281–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greindling, K.K.; Lassegue, B.; Alexander, R.W. Angiotensin Receptors and Their Therapeutic Implications. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1996, 36, 281–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrion, D. , Kubis, N., & Lévy, B. I. (2001). Physiological and pathophysiological functions of the AT2 subtype receptor of angiotensin II: from large arteries to the microcirculation. Hypertension, 38(5), 1150-1157.
- Padia, S.H.; Carey, R.M. AT2 receptors: beneficial counter-regulatory role in cardiovascular and renal function. Pfl?gers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2013, 465, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, M. , Musumeci, B., De Paolis, P., Savoia, C., & Morganti, A. (2003). Angiotensin II AT2 receptor subtype: an uprising frontier in cardiovascular disease?. Journal of hypertension, 21(8), 1429-1443.
- Kostenis, E.; Milligan, G.; Christopoulos, A.; Sanchez-Ferrer, C.F.; Heringer-Walther, S.; Sexton, P.M.; Gembardt, F.; Kellett, E.; Martini, L.; Vanderheyden, P.; et al. G-Protein–Coupled Receptor Mas Is a Physiological Antagonist of the Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor. Circulation 2005, 111, 1806–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oro, C.; Qian, H.; Thomas, W.G. Type 1 angiotensin receptor pharmacology: Signaling beyond G proteins. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 113, 210–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiriet, M. Signaling at the Cell Surface in the Circulatory and Ventilatory Systems; Springer Nature: Dordrecht, GX, Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cat, A.N.D.; Touyz, R.M. Cell Signaling of Angiotensin II on Vascular Tone: Novel Mechanisms. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2011, 13, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadir, P. M. , Periasamy, A., Carey, R. M., & Siragy, H. M. (2006). Angiotensin II type 2 receptor–bradykinin B2 receptor functional heterodimerization. Hypertension, 48(2), 316-322.
- Duka, A. , Duka, I., Gao, G., Shenouda, S., Gavras, I., & Gavras, H. (2006). Role of bradykinin B1 and B2 receptors in normal blood pressure regulation. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, 291(2), E268-E274.
- Bernier, S.G.; Haldar, S.; Michel, T. Bradykinin-regulated Interactions of the Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Pathway with the Endothelial Nitric-oxide Synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 30707–30715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daiber, A.; Münzel, T. Organic Nitrate Therapy, Nitrate Tolerance, and Nitrate-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction: Emphasis on Redox Biology and Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2015, 23, 899–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maron, B.A.; Michel, T. Subcellular Localization of Oxidants and Redox Modulation of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase. Circ. J. 2012, 76, 2497–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocco, D.M.; Clark, B.J. Regulation of the Acute Production of Steroids in Steroidogenic Cells*. Endocr. Rev. 1996, 17, 221–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lymperopoulos, A.; Rengo, G.; Zincarelli, C.; Kim, J.; Soltys, S.; Koch, W.J. An adrenal β-arrestin 1-mediated signaling pathway underlies angiotensin II-induced aldosterone production in vitro and in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2009, 106, 5825–5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollag, W. B. (2011). Regulation of aldosterone synthesis and secretion. Comprehensive physiology, 4(3), 1017-1055.
- Bollag, W. B. (2011). Regulation of aldosterone synthesis and secretion. Comprehensive physiology, 4(3), 1017-1055.
- Scott, J. H., Menouar, M. A., & Dunn, R. J. (2017). Physiology, aldosterone.
- Pearce, D.; Soundararajan, R.; Trimpert, C.; Kashlan, O.B.; Deen, P.M.; Kohan, D.E. Collecting Duct Principal Cell Transport Processes and Their Regulation. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandgren, J. A. , Linggonegoro, D. W., Zhang, S. Y., Sapouckey, S. A., Claflin, K. E., Pearson, N. A.,... & Grobe, J. L. (2018). Fluid and Electrolyte Homeostasis: Angiotensin AT1A receptors expressed in vasopressin-producing cells of the supraoptic nucleus contribute to osmotic control of vasopressin. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 314(6), R770.
- Okuya, S.; Inenaga, K.; Kaneko, T.; Yamashita, H. Angiotensin II sensitive neurons in the supraoptic nucleus, subfornical organ and anteroventral third ventricle of rats in vitro. Brain Res. 1987, 402, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuzzo, B. , Padala, S. A., & Lappin, S. L. (2023). Physiology, vasopressin. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing.
- Hanoune, J. (2010). Vasopressin receptors, the signalling cascade and mechanisms of action. Perspectives on Vasopressin.
- Morla, L. , Edwards, A., & Crambert, G. (2016). New insights into sodium transport regulation in the distal nephron: Role of G-protein coupled receptors. World journal of biological chemistry, 7(1), 44.
- Severs, W.B.; Summy-Long, J. The role of angiotensin in thirst. Life Sci. 1975, 17, 1513–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzsimons, J. T. (1998). Angiotensin, thirst, and sodium appetite. Physiological reviews, 78(3), 583-686.
- Dibona, G. F. (2013). Sympathetic nervous system and hypertension. Hypertension, 61(3), 556-560.
- Dibona, G. F. (2004). The sympathetic nervous system and hypertension: recent developments. Hypertension, 43(2), 147-150.
- Esler, M. The sympathetic system and hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 2000, 13, 99S–105S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wnorowski, A. , & Jozwiak, K. (2014). Homo-and hetero-oligomerization of β2-adrenergic receptor in receptor trafficking, signaling pathways and receptor pharmacology. Cellular Signalling, 26(10), 2259-2265.
- Ecker, P. M. , Lin, C. C., Powers, J., Kobilka, B. K., Dubin, A. M., & Bernstein, D. (2006). Effect of targeted deletions of β1-and β2-adrenergic-receptor subtypes on heart rate variability. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 290(1), H192-H199.
- Woo, A.Y.H.; Xiao, R.-P. β-Adrenergic receptor subtype signaling in heart: From bench to bedside. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefkowitz, R. J. , Rockman, H. A., & Koch, W. J. (2000). Catecholamines, cardiac β-adrenergic receptors, and heart failure. Circulation, 101(14), 1634-1637.
- Stiles, G.L.; Caron, M.G.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Beta-adrenergic receptors: biochemical mechanisms of physiological regulation. Physiol. Rev. 1984, 64, 661–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, G.D. Neural control of the circulation. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2011, 35, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, G. Renin–angiotensin–sympathetic crosstalks in hypertension: reappraising the relevance of peripheral interactions. J. Hypertens. 2001, 19, 1713–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldehni, F.; Tang, T.; Madsen, K.; Plattner, M.; Schreiber, A.; Friis, U.G.; Hammond, H.K.; Han, P.L.; Schweda, F. Stimulation of Renin Secretion by Catecholamines Is Dependent on Adenylyl Cyclases 5 and 6. Hypertension 2011, 57, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messerli, F. H. , Bangalore, S., Bavishi, C., & Rimoldi, S. F. (2018). Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in hypertension: to use or not to use?. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 71(13), 1474-1482.
- Uehara, Y.; Miura, S.-I.; Yahiro, E.; Saku, K. Non-ACE Pathway-induced Angiotensin II Production. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 3054–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallberg, P.; Nagy, J.; Karawajczyk, M.; Nordang, L.; Islander, G.; Norling, P.; Johansson, H.-E.; Kämpe, M.; Hugosson, S.; Yue, Q.-Y.; et al. Comparison of Clinical Factors Between Patients With Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor–Induced Angioedema and Cough. Ann. Pharmacother. 2017, 51, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles, N. R. , Cerezo, I., & Hernandez-Gallego, R. (2014). Renin–angiotensin system blocking drugs. Journal of cardiovascular pharmacology and therapeutics, 19(1), 14-33.
- Hernández-Hernández, R.; Sosa-Canache, B.; Velasco, M.; Armas-Hernández, M.J.; Armas-Padilla, M.C.; Cammarata, R. Angiotensin II receptor antagonists role in arterial hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2002, 16, S93–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantzaris, N.-D.; Karanikolas, E.; Tsiotsios, K.; Velissaris, D. Renin Inhibition with Aliskiren: A Decade of Clinical Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trimarchi, H. Role of aliskiren in blood pressure control and renoprotection. Int. J. Nephrol. Renov. Dis. 2011, 4, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D. , & Dimri, M. (2020). Biochemistry, Calcium Channels.
- Catterall, W.A.; Perez-Reyes, E.; Snutch, T.P.; Striessnig, J. International Union of Pharmacology. XLVIII. Nomenclature and Structure-Function Relationships of Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Yan, Z.; Li, Z.; Qian, X.; Lu, S.; Dong, M.; Zhou, Q.; Yan, N. Structure of the voltage-gated calcium channel Cav1.1 at 3.6 Å resolution. Nature 2016, 537, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertel, E.A.; Campbell, K.P.; Harpold, M.M.; Hofmann, F.; Mori, Y.; Perez-Reyes, E.; Schwartz, A.; Snutch, T.P.; Tanabe, T.; Birnbaumer, L.; et al. Nomenclature of Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels. Neuron 2000, 25, 533–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolphin, A.C. Voltage-gated calcium channels and their auxiliary subunits: physiology and pathophysiology and pharmacology. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 5369–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Seeley, S.; Schulz, C.; Fisher, J.; Rao, S.G. Calcium Channels in the Heart: Disease States and Drugs. Cells 2022, 11, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hockerman, G.H.; Peterson, B.Z.; Johnson, B.D.; Catterall, W.A. Molecular determinants of drug binding and action on l-type calcium channels. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1997, 37, 361–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neagoe, A. M. , Rexhaj, E., Grossman, E., & Messerli, F. H. (2019). Beta blockers and calcium channel blockers. Cardiovascular Hemodynamics: An Introductory Guide, 73-88.
- Weir, M.R. Calcium Channel Blockers: Their Pharmacologic and Therapeutic Role in Hypertension. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2007, 7, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H. , & Zeltser, R. (2023). Antihypertensive medications.[Updated 2022 May 15]. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing.
- Elliott, W. J., & Ram, C. V. S. (2011). Calcium channel blockers. The Journal of Clinical Hypertension, 13(9), 687.
- Padilla, M.C.A.; Armas-Hernández, M.J.; Hernández, R.H.; Israili, Z.H.; Valasco, M. Update of Diuretics in the Treatment of Hypertension. Am. J. Ther. 2007, 14, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamargo, J.; Segura, J.; Ruilope, L.M. Diuretics in the treatment of hypertension. Part 2: loop diuretics and potassium-sparing agents. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2014, 15, 605–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roush, G.C.; Sica, D.A. Diuretics for Hypertension: A Review and Update. Am. J. Hypertens. 2016, 29, 1130–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNally, R.J.; Morselli, F.; Farukh, B.; Chowienczyk, P.J.; Faconti, L. A review of the prescribing trend of thiazide-type and thiazide-like diuretics in hypertension: A UK perspective. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 85, 2707–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W. , Ma, H., Cao, L., Yan, W., & Yang, J. (2017). Comparison of thiazide-like diuretics versus thiazide-type diuretics: a meta-analysis. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine, 21(11), 2634-2642.
- Rapoport, R.M.; Soleimani, M. Mechanism of Thiazide Diuretic Arterial Pressure Reduction: The Search Continues. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blowey, D. L. (2016). Diuretics in the treatment of hypertension. Pediatric nephrology, 31, 2223-2233.
- Duarte, J.D.; Cooper-DeHoff, R.M. Mechanisms for blood pressure lowering and metabolic effects of thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2010, 8, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, B. L. , Ernst, M. E., & Cohen, J. D. (2004). Hydrochlorothiazide versus chlorthalidone: evidence supporting their interchangeability. Hypertension, 43(1), 4-9.
- Wiggam, M. I. , Bell, P. M., Sheridan, B., Walmsley, A., & Atkinson, A. B. (1999). Low dose bendrofluazide (1.25 mg) effectively lowers blood pressure over 24 h: results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study. American journal of hypertension, 12(5), 528-531.
- Peterzan, M.A.; Hardy, R.; Chaturvedi, N.; Hughes, A.D. Meta-Analysis of Dose-Response Relationships for Hydrochlorothiazide, Chlorthalidone, and Bendroflumethiazide on Blood Pressure, Serum Potassium, and Urate. Hypertension 2012, 59, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, E., Verdecchia, P., Shamiss, A., Angeli, F., & Reboldi, G. (2011). Diuretic treatment of hypertension. Diabetes care, 34(Suppl 2), S313.
- Rockhold, R.W. Thiazide diuretics and male sexual dysfunction. Drug Dev. Res. 1992, 25, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krane, R. J., Goldstein, I., & de Tejada, I. S. (1989). Impotence. New England Journal of Medicine, 321(24), 1648-1659.
- Ravioli, S. , Bahmad, S., Funk, G. C., Schwarz, C., Exadaktylos, A., & Lindner, G. (2021). Risk of electrolyte disorders, syncope, and falls in patients taking thiazide diuretics: results of a cross-sectional study. The American Journal of Medicine, 134(9), 1148-1154.
- Akbari, P. , & Khorasani-Zadeh, A. (2023). Thiazide Diuretics. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.
- Nochaiwong, S.; Chuamanochan, M.; Ruengorn, C.; Noppakun, K.; Awiphan, R.; Phosuya, C.; Tovanabutra, N.; Chiewchanvit, S.; Sood, M.M.; Hutton, B.; et al. Use of Thiazide Diuretics and Risk of All Types of Skin Cancers: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malha, L.; Mann, S.J. Loop Diuretics in the Treatment of Hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2016, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickkers, P.; Dormans, T.P.J.; Russel, F.G.M.; Hughes, A.D.; Thien, T.; Schaper, N.; Smits, P. Direct Vascular Effects of Furosemide in Humans. Circulation 1997, 96, 1847–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musini, V. M. , Rezapour, P., Wright, J. M., Bassett, K., & Jauca, C. D. (2015). Blood pressure-lowering efficacy of loop diuretics for primary hypertension. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, (5).
- Blowey, D. L. (2016). Diuretics in the treatment of hypertension. Pediatric nephrology, 31, 2223-2233.
- Sica, D. A., Carter, B., Cushman, W., & Hamm, L. (2011). Thiazide and loop diuretics. The journal of clinical hypertension, 13(9), 639-643.
- Huxel, C. , Raja, A., & Ollivierre-Lawrence, M. D. (2023). Loop diuretics. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing.
- Calhoun, D.A.; White, W.B. Effectiveness of the selective aldosterone blocker, eplerenone, in patients with resistant hypertension. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2008, 2, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PROGRESS Collaborative Group. (2001). Randomised trial of a perindopril-based blood-pressure-lowering regimen among 6105 individuals with previous stroke or transient ischaemic attack. The Lancet, 358(9287), 1033-1041.
- Patel, A. Effects of a fixed combination of perindopril and indapamide on macrovascular and microvascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (the ADVANCE trial): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2007, 370, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckett, N.S.; Peters, R.; Fletcher, A.E.; Staessen, J.A.; Liu, L.; Dumitrascu, D.; Stoyanovsky, V.; Antikainen, R.L.; Nikitin, Y.; Anderson, C.; et al. Treatment of Hypertension in Patients 80 Years of Age or Older. New Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlöf, B.; Devereux, R.B.; E Kjeldsen, S.; Julius, S.; Beevers, G.; de Faire, U.; Fyhrquist, F.; Ibsen, H.; Kristiansson, K.; Lederballe-Pedersen, O.; et al. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in the Losartan Intervention For Endpoint reduction in hypertension study (LIFE): a randomised trial against atenolol. Lancet 2002, 359, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepine, C. J. , Handberg, E. M., Cooper-DeHoff, R. M., Marks, R. G., Kowey, P., Messerli, F. H.,... & INVEST Investigators. (2003). A calcium antagonist vs a non–calcium antagonist hypertension treatment strategy for patients with coronary artery disease: the International Verapamil-Trandolapril Study (INVEST): a randomized controlled trial. Jama, 290(21), 2805-2816.
- Dahlöf, B.; Sever, P.S.; Poulter, N.R.; Wedel, H.; Beevers, D.G.; Caulfield, M.; Collins, R.; E Kjeldsen, S.; Kristinsson, A.; McInnes, G.T.; et al. Prevention of cardiovascular events with an antihypertensive regimen of amlodipine adding perindopril as required versus atenolol adding bendroflumethiazide as required, in the Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial-Blood Pressure Lowering Arm (ASCOT-BPLA): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2005, 366, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamerson, K.; Weber, M.A.; Bakris, G.L.; Dahlöf, B.; Pitt, B.; Shi, V.; Hester, A.; Gupte, J.; Gatlin, M.; Velazquez, E.J. Benazepril plus Amlodipine or Hydrochlorothiazide for Hypertension in High-Risk Patients. New Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2417–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakris, G.L.; A Sarafidis, P.; Weir, M.R.; Dahlöf, B.; Pitt, B.; Jamerson, K.; Velazquez, E.J.; Staikos-Byrne, L.; Kelly, R.Y.; Shi, V.; et al. Renal outcomes with different fixed-dose combination therapies in patients with hypertension at high risk for cardiovascular events (ACCOMPLISH): a prespecified secondary analysis of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010, 375, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, P.A.; Elliott, H.L. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Amlodipine. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1992, 22, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, B. , Lundborg, P., & Regårdh, C. G. (1987). Clinical pharmacokinetics of felodipine: a summary. Drugs, 34, 16-27.
- Hamann, S.R.; Blouin, R.A.; McAllister, R.G., Jr. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Verapamil. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1984, 9, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, L. J. , & McCormack, P. L. (2008). Olmesartan medoxomil: a review of its use in the management of hypertension. Drugs, 68, 1239-1272.
- Warner, G. T., & Jarvis, B. (2002). Olmesartan medoxomil. Drugs, 62, 1345-1353.
- Markham, A. , & Goa, K. L. (1997). Valsartan: a review of its pharmacology and therapeutic use in essential hypertension. Drugs, 54, 299-311.
- McClellan, K. J. , & Markham, A. (1998). Telmisartan. Drugs, 56(6).
- Israili, Z.H. Clinical pharmacokinetics of angiotensin II (AT1) receptor blockers in hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2000, 14 (Suppl. 1), S73–S86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleiter, C.H.; Mörike, K.E. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Candesartan. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2002, 41, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottorff, M. B. , & Tenero, D. M. (1999). Pharmacokinetics of eprosartan in healthy subjects, patients with hypertension, and special populations. Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy, 19(4P2), 73S-78S.
- A Sica, D.; Gehr, T.W.B.; Ghosh, S. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Losartan. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2005, 44, 797–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balfour, J. A. , & Goa, K. L. (1991). Benazepril: a review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic efficacy in hypertension and congestive heart failure. Drugs, 42, 511-539.
- Duchin, K.L.; McKinstry, D.N.; Cohen, A.I.; Migdalof, B.H. Pharmacokinetics of Captopril in Healthy Subjects and in Patients with Cardiovascular Diseases. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1988, 14, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, H. J. , Cirillo, V. J., & Irvin, J. D. (1985). Enalapril: a review of human pharmacology. Drugs, 30, 13-24.
- Todd, P. A. , & Goa, K. L. (1992). Enalapril: a reappraisal of its pharmacology and therapeutic use in hypertension. Drugs, 43, 346-381.
- Murdoch, D. , & McTavish, D. (1992). Fosinopril: a review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic potential in essential hypertension. Drugs, 43, 123-140.
- Goa, K. L. , Balfour, J. A., & Zuanetti, G. (1996). Lisinopril: a review of its pharmacology and clinical efficacy in the early management of acute myocardial infarction. Drugs, 52(4), 564-588.
- Kieback, A. G. , Felix, S. B., & Reffelmann, T. (2009). Quinaprilat: a review of its pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, toxicological data and clinical application. Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology, 5(10), 1337-1347.
- Commander, S.J.; Wu, H.; Boakye-Agyeman, F.; Melloni, C.; Hornik, C.D.; Zimmerman, K.; Al-Uzri, A.; Mendley, S.R.; Harper, B.; Cohen-Wolkowiez, M.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of Hydrochlorothiazide in Children: A Potential Surrogate for Renal Secretion Maturation. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 61, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chobanian, A. V., Bakris, G. L., Black, H. R., Cushman, W. C., Green, L. A., Izzo Jr, J. L., ... & National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating Committee. (2003). Seventh report of the joint national committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure. hypertension, 42(6), 1206-1252.
- Smith, D.K.; Lennon, R.P.; Carlsgaard, P.B. Managing Hypertension Using Combination Therapy. 2020, 101, 341–349.
- Williams, B.; Poulter, N.R.; Brown, M.J.; Davis, M.; McInnes, G.T.; Potter, J.F.; Sever, P.S.; Thom, S.M. British Hypertension Society guidelines for hypertension management 2004 (BHS-IV): summary. BMJ 2004, 328, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umemura, S.; Arima, H.; Arima, S.; Asayama, K.; Dohi, Y.; Hirooka, Y.; Horio, T.; Hoshide, S.; Ikeda, S.; Ishimitsu, T.; et al. The Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension (JSH 2019). Hypertens. Res. 2019, 42, 1235–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





