1. Introduction
The development of today’s society is closely linked to two very important aspects, energy, and environmental sustainability. Conventional energy conversion systems use fossil fuels and are associated with greenhouse gas emissions and other atmospheric pollutants. These negative environmental impacts are increasing due to the growing demand for energy. The progressive depletion of fossil fuels and the growing concern about global warming and climate change have driven the search for renewable energy generation techniques. In addition to the growing energy demand, another consequence of the pace of development of today’s society is the increase in waste generation, there being a great concern to manage them in a sustainable and economically viable way. For these reasons, it is reasonable to think that one of the ways to make the development of society energetically and environmentally sustainable is the use of the maximum waste for energy production, since the benefit would be twofold: waste would be reduced and at the same time the consumption of natural resources would be reduced by producing and using an alternative energy.
Sewage sludge (SS) is one of the wastes whose production has significantly grown. Due to urbanization, industrialization, population expansion, an increase in the proportion of people using the sewer system, and better wastewater treatment facilities, the rate of sewage sludge (SS) creation is rising globally. Sewage sludge is a hazardous waste, which is produced by wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) [
1,
2]. The management and disposal of the large amount of sewage sludge generated are increasingly complicated due to the strict conditions imposed by current legislation regarding its disposal in landfills and its use as an agricultural fertilizer [
3]. Currently, 92.5% of Catalonia’s sewage sludge, of the total 120,000 tons of dry matter produced annually, is destined for soil application and 2.5% for landfill [
4]. For this reason, the implementation of new ways of valorization of sludge that cannot be destined to agriculture and/or landfills is relevant. One of these ways is gasification in order to produce syngas which could be used to produce chemicals, alternative fuels, hydrogen or combined head and power (CHP). The sewage sludge gasification process involves multiple reactions and transformations and is therefore considered a complex process. Thus, it is useful to use simulation models that help to study the system behavior and allow predicting the process efficiency under different operating conditions with high reliability and low cost [
5]. There are numerous process simulation software tools, among which Aspen Plus stands out for its flexibility and intuitive handling have been used by several authors.
Given that supercritical water gasification has emerged as preferred means of converting wet biomass to hydrogen-rich gases [
6], sewage sludge has been studied almost exclusively resorting to supercritical water gasification. For example, Qian et al. [
7] experimentally investigated the effects of moisture and pressure on mole fraction, yield, gasification efficiency of gaseous products from supercritical water gasification of sewage sludge. Ruya et al. [
8] simulated the supercritical water gasification of various sewage sludge for power generation in Aspen Plus. Chen et al. [
9] studied the sewage sludge gasification in supercritical water with high heating rate batch reactor. Hantoko et al. [
10] evaluated through experimental and thermodynamic analysis, the potential of sewage sludge for hydrogen-rich syngas production from supercritical water gasification. In this work, the sewage sludge will be subjected to autothermal gasification, which, as discussed by Ramos et al. [
11] requires the feedstock to be exposed to a drying process.
The thermochemical techniques for hydrogen production from biomass were reviewed by Pandey et al. [
12]. They found that the literature confirms that hydrogen obtained from biomass has high-energy efficiency and potential to reduce greenhouse gases. They also found that higher temperature, suitable steam to biomass ratio and catalyst type favor useful hydrogen yield. However, hydrogen is not available in sufficient amounts and production cost is still high. The hydrogen production costs issue based on three different gasification processes of high-moisture forest residues was studied by Martins et al. [
13]. They found that supercritical water gasification is the most suitable process for hydrogen production, with hydrogen yields of 0.844 Nm
3/kg. Hydrogen yields of 0.828 Nm
3/kg, and 0.758 Nm
3/kg were achieved for the conventional gasification and plasma gasification processes, respectively. Conventional gasification is viable for steam-to-biomass ratios below 3. Process intensification techniques applied to supercritical water gasification make this process viable for feed concentrations between 15 and 25%. Alves et al. [
14] develop a techno-economic analysis for a small-scale gasification plant processing mixtures of solid recovered fuels and sewage sludge, assuming a capacity of 883 kg/h and two different sale scenarios: production of electric energy, and production of hydrogen. Gasification tests and mass and energy flow analyses were carried out for the economic assessment. The results showed that both scenarios presented viability for implementation. Although the production of electric energy scenario was more attractive in the short-term period due to the lower payback period and higher internal rate of return, the other option was more favorable at the end of plant’s life once the net present value was greater. The exploration of conventional gasification of sewage sludge is a recent topic of research, mostly experimental studies. Kang et al. [
15] explored the catalytic gasification of sewage sludge using activated carbon and sawdust biochar catalysts, bed temperatures, and gasifying agents. The effects of the porosity of activated carbon on tar adsorption and cracking, and biochar containing alkali and alkaline earth metallic species were investigated. A catalyst bed temperature of 800ºC and particle size of 0.5-1.7 mm showed optimum conditions for increasing H
2 and CO content and decrease CO
2 fraction. The injection of steam had a positive effect on the H
2 amount, owing to the enhancement of water gas shift and hydrocarbon steam reforming reactions. Tezer et al. [
16] experimentally studied sewage sludge gasification carried out in two different fixed bed gasifiers, updraft and downdraft. The effect of temperature, gasification agents (air and pure oxygen), and their different flow rates on gasification efficiency are investigated. The maximum hydrogen content in syngas from updraft and downdraft gasifiers was achieved as 42 vol.% and 46 vol.% by using dry air as gasifying agent. Hydrogen content for updraft and downdraft gasifiers was also obtained as 40 vol.% and 45 vol.%, respectively in the case of pure oxygen. Carotenuto et al. [
1] developed a numerical model of sewage sludge gasification, based on a restricted chemical equilibrium approach in Aspen Plus. The novelty of this work consists of considering different sludge samples. The developed gasification model is used to identify optimum temperature (900°C) and equivalence ratio (0.2) through sensitivity analyses. Then the model is used to assess the combined heat and power generation potentiality of sewage sludge by integrating a gasifier with an internal combustion engine. They found that the energy recovery from sewage sludge through the proposed solution may supply near 50% of electrical energy demand to run wastewater treatment plants and from 60 to 75% of thermal energy needed for thermal drying of mechanically dewatered sewage sludge for gasification. Andrés et al. [
3] performed sewage sludge gasification assays in an atmospheric fluidized bed reactor using air and air-steam mixtures as the gasifying agents. The objective of this study is to determine the influence of dolomite, olivine and alumina catalysts in the product distribution and tar production during sewage sludge gasification. They show that dolomite has the highest activity in tar elimination, followed by alumina and olivine. In addition to improving tar removal, the presence of water vapor and the catalysts increased the content of hydrogen in the gases by nearly 60%.
This briefly state-of-the art shows that the sewage sludge conversion to hydrogen-rich gas is mostly approach using the supercritical water gasification. The economic studies on the high-moisture biomass also shows that conventional gasification is more suitable to the economic viability of a gasification plant producing hydrogen. Therefore, in this work, a thermodynamic equilibrium model has been developed using Aspen Plus® to simulate the air and steam gasification process of sewage sludge from a wastewater treatment plant in Catalonia (Spain). The main contribution of this work is to determine the potential of sewage sludge for hydrogen-rich gas production and provide fundamental data for economic studies of the implementation of this waste-to-energy technology.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Aspen Plus Model Description
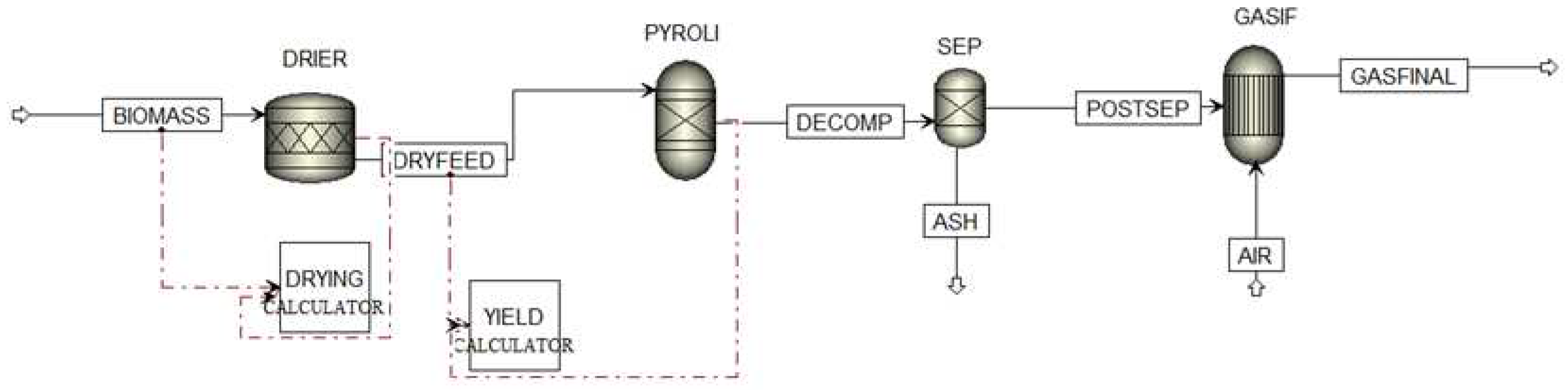
The model developed in this work is based on the thermodynamic equilibrium model. This model is independent of the gasifier design and is based on the minimization of the Gibbs free energy of the system. The gasifier is represented by multiple blocks, as seen in
Figure 1, that correspond to the different phases of the gasification process: the feed drying, the decomposition or pyrolysis and the gasification itself. The configuration starts by defining the components involved in the process. For the conventional components the RKS-BM property method, abbreviation of Redlich-Kwong-Soave equation of state with Boston Mathias modifications, is defined [
17]. For nonconventional components, biomass and ash, the only physical properties calculated are enthalpy and density as they do not participate in chemical or phase equilibrium. In this simulation, HCOALGEN and DCOALIGT models are used to calculate the enthalpy and density of biomass and ash based on the proximate, ultimate and sulphur analysis.
The first stage of the process occurs in the DRIER where the evaporation of moisture is simulated. It is necessary to define the water coefficient as 1/18 in the stoichiometric reactor (RStoic) unit, since the molecular weight of biomass and water are 1 g/mol [
18] and 18 g/mol, respectively. In addition, a Fortran subroutine calculator is implemented to control this drying process. The second stage occurs in the PYROLI where biomass is converted into its main components C, H, O, N, S, and ash, by specifying the yield distribution according to the biomass ultimate analysis. A Fortran subroutine calculator is implemented to control the decomposition. The resulting stream is directed to SEP where C, H
2, H
2O, O
2, N
2 are separated from the ash content which is discarded. The mixture is redirected to GASIF, where the reactions take place with the oxidizing agent, giving rise to the synthesis gas (GASFINAL).
2.2. Aspen Plus Model Validation
In order to validate the results of the developed model, the composition of the syngas is compared with the experimental results of Ong et al. [
19] and with a kinetic model developed by Rabea et al. [
20]. Both studies are based on the same biomass and conditions as the present study. The biomass used is wood chips, and the gasifying agent for the analysis is air. The ultimate and proximate analyses are presented in
Table 1.
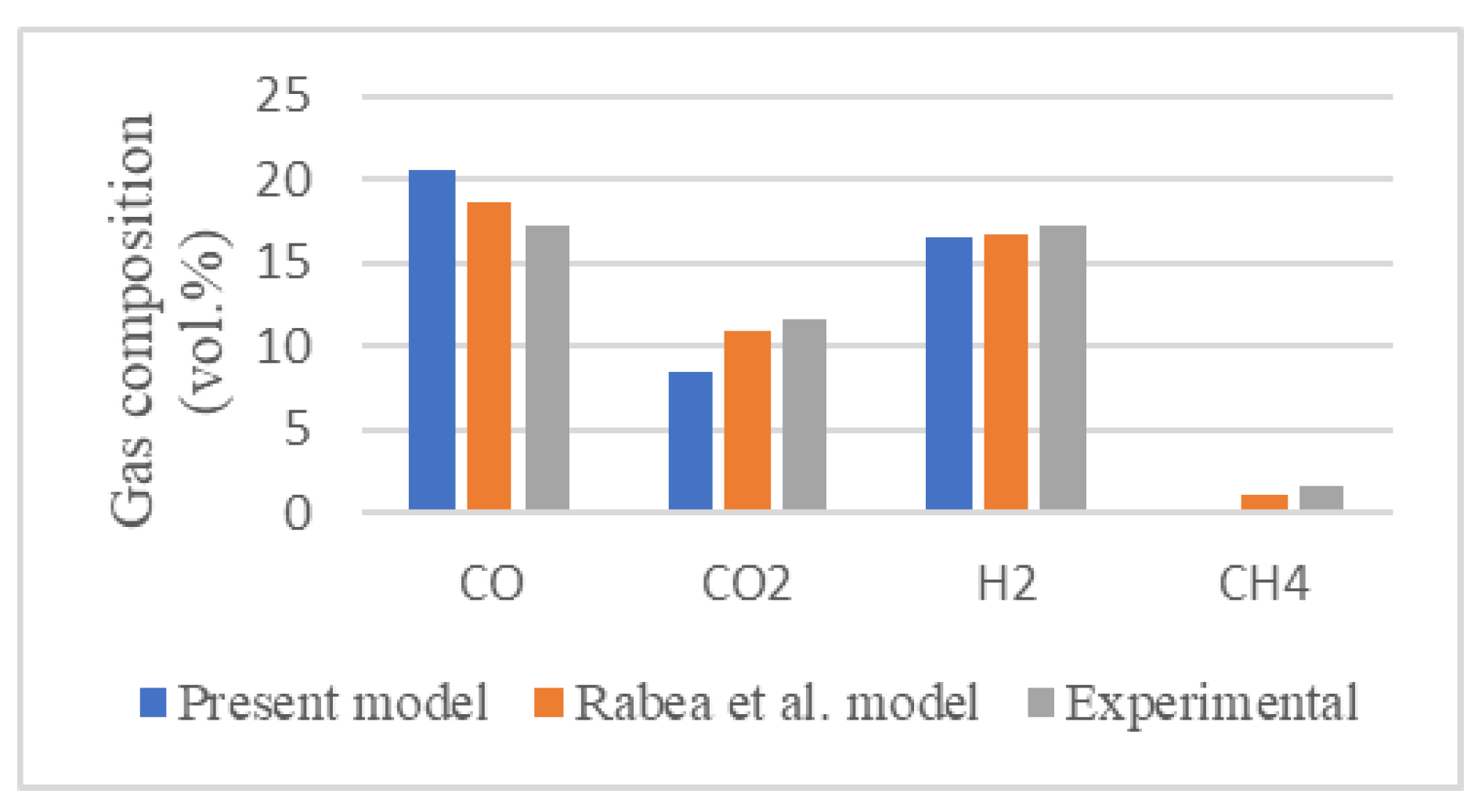
Figure 2 presents the molar fractions of the gas composition produced from the proposed model and the kinetic model of Rabea et al. [
20] against the experimental results of Ong et al. [
19] with an air flow rate of 7 l/s and a biomass flow rate of 16.2 kg/h at a gasifier temperature of 995ºC.
Relative error is used to determine the deviations between results and verify if the model is overestimating or underestimating them based on whether the relative error is positive or negative. The relative error is calculated as expressed in Eq. (1) and is present in
Table 2.
Relative errors below 25% are obtained for the main syngas species. Methane (CH
4) is not included in the comparison due to the near-zero molar fractions. The greater relative errors are obtained for CO
2, which occur frequently in thermodynamic equilibrium models [
21]. Besides that, the experimental work of Ong et al. [
19] does not provide an error analysis which could reduce the relative errors of the comparison.
These results indicate that the Aspen Plus-developed model can reproduce well the thermodynamic behavior of the gasification process, especially for the hydrogen molar fraction (< 5%), providing an effective tool for further estimations.
2.3. Aspen Plus Model Improvement
Since it is intended to perform the sensitivity analysis for both air and steam, a selector (SELT) is added to the model to easily switch from one gasifying agent to another. In addition, a separator (SEP1) is added at the gasifier outlet, which basically separates the components of interest from those that are not of interest. The final model used to perform both sensitivity analyses is shown in Error! Reference source not found..
2.4. Sewage Sludge Characterization
Dried sewage sludge was selected as waste biomass material for this study. Their origin is from an urban wastewater treatment plant in Catalonia (Spain), which proximate and ultimate analysis are presented in
Table 3.
The main chemical reactions that are performed in the gasification process and enthalpy of formation are depicted in
Table 4.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation Using Air as the Gasifying Agent
The composition and LHV of the syngas will be analyzed as a function of different process parameters: equivalence ratio, gasification temperature, and moisture content. The same conditions used for model validation (6.2 kg/h of sewage sludge and a gasifier temperature of 995°C) were used in this assessment, except for the gasification temperature.
3.1.1. Effect of Equivalence Ratio
The ER is defined as the ratio of the air-to-biomass ratio to the stoichiometric air-to- biomass ratio [
24]. The ER was adjusted by varying the air flow rate into the Gibbs reactor.
Figure 4 shows the effect of the ER on the syngas composition and LHV.
Figure 4 shows that an increase in the ER leads to a decrease in H
2 production due to a lower magnitude of the reforming reaction (R5) and the water-gas shift reaction (R6) versus the combustion reactions (R1, R2, and R3). The molar fraction of CO and CH
4 decreases because of the higher presence of oxygen, which promotes the oxidation of the carbon in the sewage sludge and part of the combustible gases to produce CO
2, which explains the increase of this compound in the syngas [
3,
25]. The reduction of H
2, CO, and CH
4 content leads to lower heating values in the produced syngas. Similar trends for the different syngas species with ER can be found in stated literature [
26,
27].
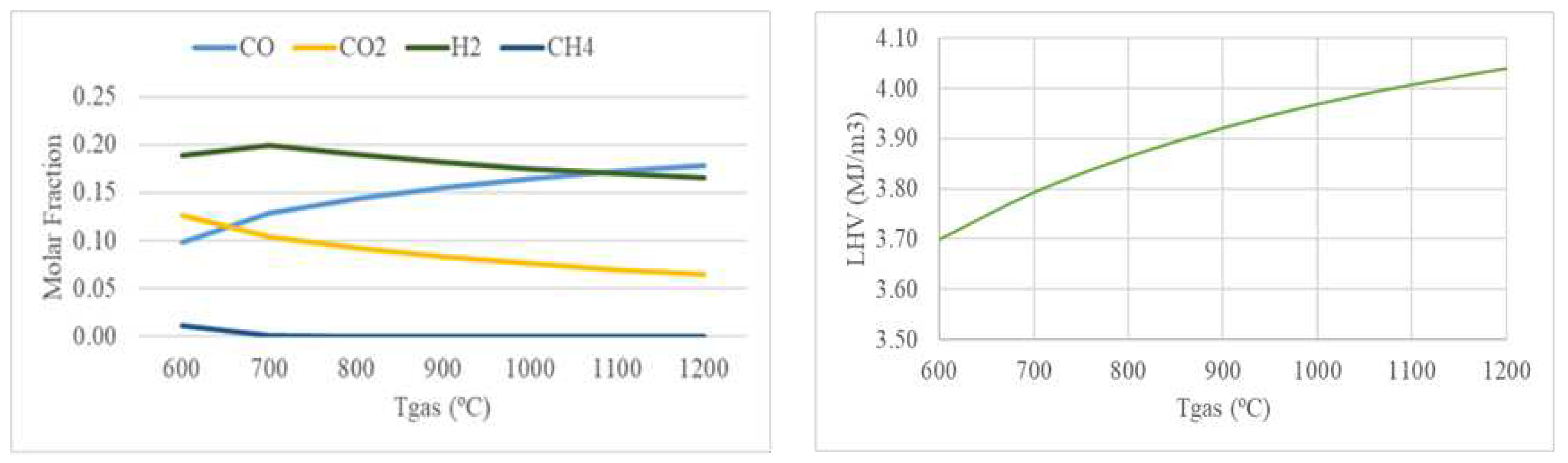
3.1.2. Effect of Gasification Temperature
According to Le Chatelier’s principle, high temperatures favor the products of endothermic reactions and reactants in exothermic reactions [
28].
Figure 5 shows the effect of the gasification temperature on the syngas composition and LHV.
Figure 5 shows that the molar fractions of CO and H
2 increase while CO
2 and CH
4 decrease due to the Boudouard reaction (R4), the reforming of the char reaction (R5), and the steam methane reforming reaction (R8) that are enhanced with increasing temperature. The change in H
2 trend may be due to the mutual effect of the reactions taking place in the gasifier. The water-gas shift reaction (R6) is successful at lower temperatures, creating syngas that is rich in H
2, but it is hampered at temperatures above 720 °C because the reverse reaction is encouraged, which reduces the amount of H
2 that is produced. Since CO increases more than H
2 drops, LHV increases with temperature above 700°C along with H
2 and CO. Similar trends for the different syngas species with temperature can be found in [
28,
29].
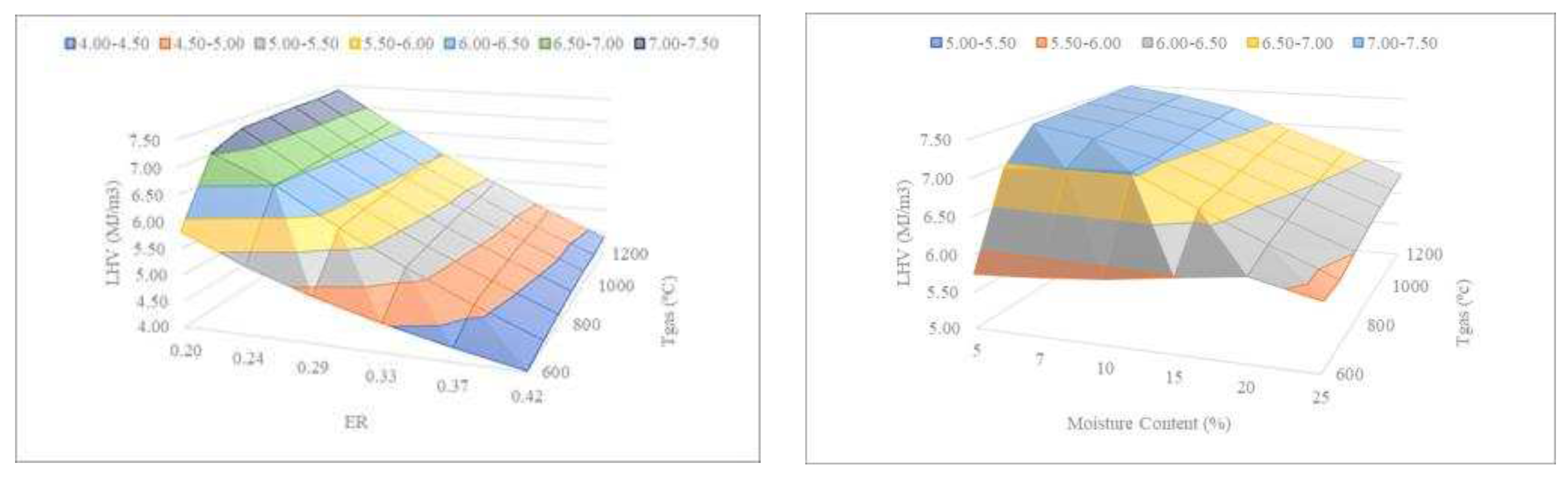
3.1.3. Correlation between Variables
The following assessment examines the correlation between the process parameters temperature, ER, and moisture content (
Figure 6) to determine the optimal conditions that maximize the LHV of the produced syngas.
Figure 6 shows that the lower the ER, the lower the temperature required by the gasifier to produce syngas with near the same LHV. This result is of great interest since the lower the temperature, the lower the energy, and the lower the operational expenditures. For example, an ER of 0.29 at Tgas = 1000ºC produces syngas with the same LHV as an ER of 0.24 at Tgas = 600-700ºC. It can also be observed in
Figure 6 that the lower the MC, the lower the temperature required by the gasifier to produce syngas with virtually the same LHV. For example, sewage sludge gasification with a MC of 15% at Tgas = 1200ºC produces syngas with almost the same LHV as sewage sludge with a MC of 10% at Tgas = 600-700ºC. It is known that moisture content considerably affects the gasification process because the water is vaporized in the reactor, absorbing heat, and reducing the temperature, while the generated steam can react with other compounds [
30]. The obtained trends for the effect of moisture content on the LHV of the syngas are confirmed by the literature [
30,
31].
3.2. Evaluation Using Steam as the Gasifying Agent
The composition and LHV of the syngas will be analyzed as a function of SBR, gasification temperature, and moisture content. The same conditions used for model validation (16.2 kg/h of sewage sludge and a gasifier temperature of 995°C) were used in this assessment, except for the gasification temperature.
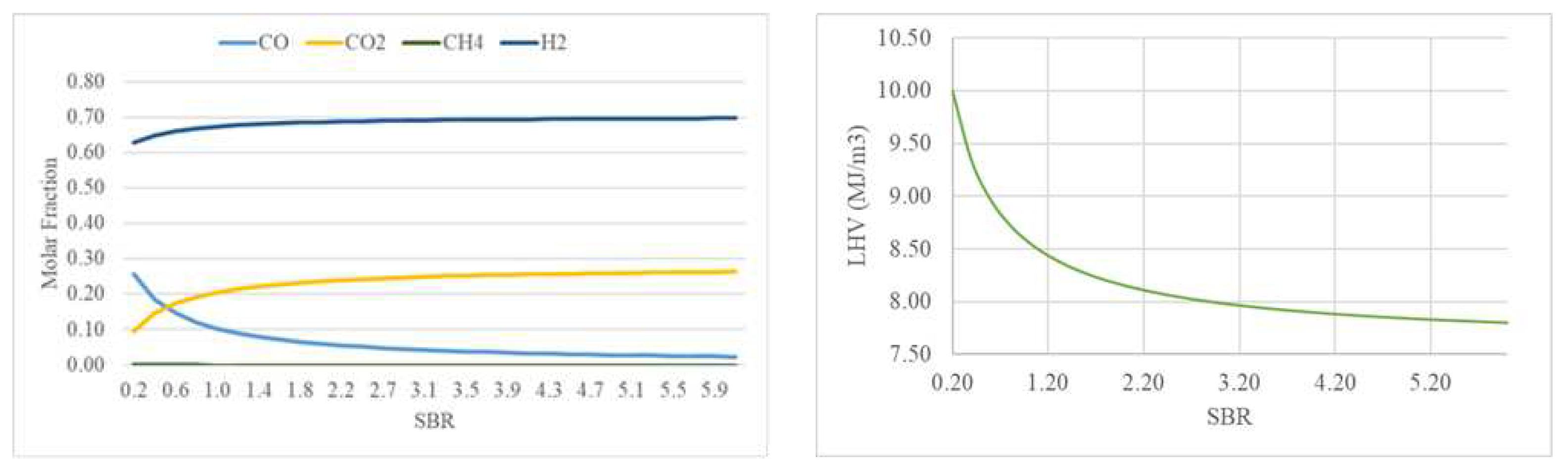
3.2.1. Effect of Steam-to-Biomass Ratio
Since more steam is added with increasing the SBR, it enhances the water-gas shift reaction (R6) and steam reforming reaction (R5) which result as an increase of H
2 and CO molar fractions [
28]. However, the CO concentration will decrease due to the water-gas shift reaction (R6) (since the temperature is 995ºC), which reduces the CO molar fraction concentration by reacting with the steam and increasing H
2 and CO
2 concentrations as seen in
Figure 7.
Regarding the CH
4 molar fraction, represents a very low percentage of the syngas composition and decreases very slowly as SBR increases, an expected behavior resulting from the steam methane reforming reaction (R8) reaction of the syngas. The LHV decreases with SBR because of CO decreasing more than H
2. Similar results for the different syngas species and LHV as a function of SBR can be found in [
28,
32].
3.2.2. Effect of Gasification Temperature
One of the most important parameters influencing syngas composition is gasification temperature. Because the main reactions of gasification are endothermic, raising temperature strengthens them [
27].
Figure 8 shows that the mole fractions of CO and H
2 increase up to 600°C because the reforming of the char reaction (R5) and the Boudouard reaction (R4) are endothermic and, therefore, the temperature increase causes an increase in CO and H2. The water-gas shift reaction (R6) is the dominant reaction above 750°C, so CO increases while CO
2 and H
2 decrease. Reactions (R5) and (R4) contribute to the increase in CO above 800°C. CH4 reduction is dictated by the methanation reaction (R7) and the steam methane reforming reaction (R8).
The LHV decreases until reaching the temperature of 700ºC because CH
4 decreases more than H
2 increases, but from then on, the LHV follows a clear increasing trend as H
2, and CO continue to increase while CH
4 keeps very low values. It can be said that the higher the temperature, the higher the LHV, but this does not imply higher H
2. Similar trends for the different syngas species and LHV as a function of temperature can be found in [
33,
34].
3.2.3. Correlation between Variables
The following assessment examines the correlation between the process parameters SBR, gasification temperature, and moisture content. The objective is to find the optimal conditions that maximize the syngas quality in terms of heating value and H
2 content.
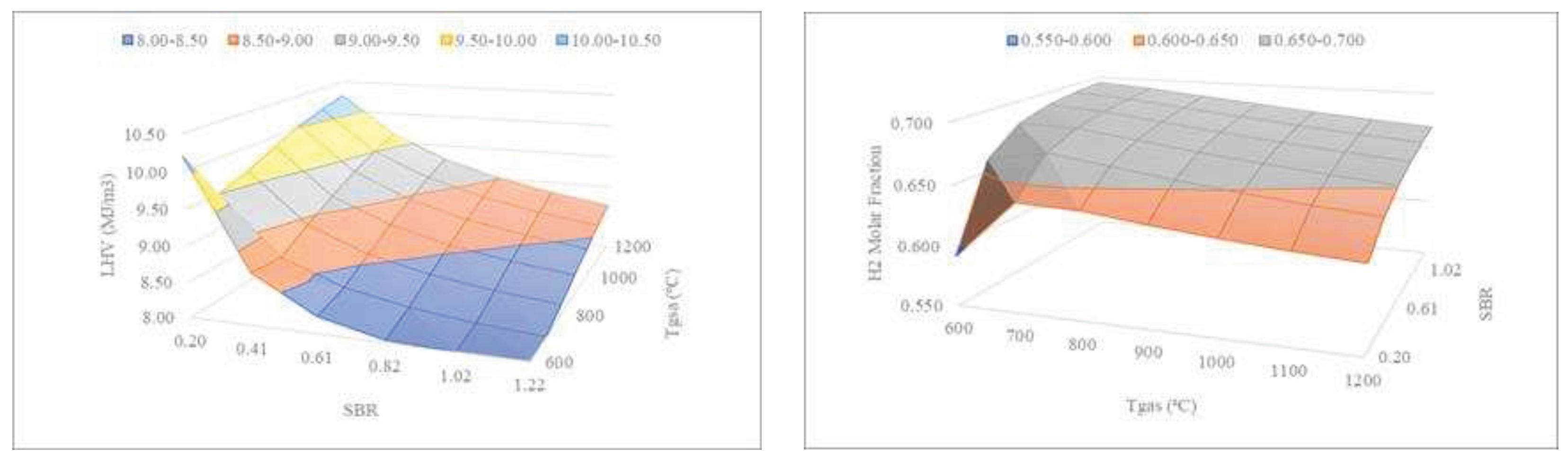
Figure 9 shows the combined effect of SBR and gasification temperature on the LHV and H
2 content of the syngas.
The results of
Figure 9 (left) show that the lower the SBR, the lower the temperature required by the gasifier to produce the same LHV. As mentioned before, lower temperatures are beneficial for the operational expenditures’ reduction. On the other hand, in
Figure 9 (right), it can be seen that the higher the SBR, the lower the temperature required by the gasifier to produce similar H
2 molar fractions.
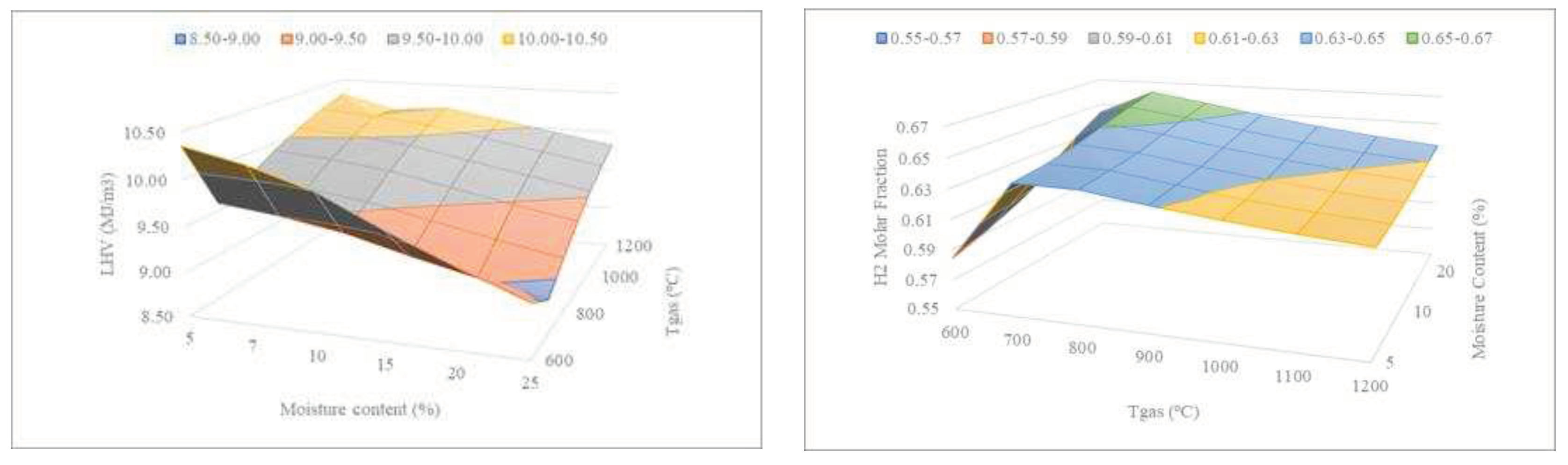
Figure 10 shows the combined effect of the sewage sludge moisture and temperature on the LHV and H
2 content of the syngas.
It can be observed that the lower the moisture content, the lower the temperature required to achieve similar LHV values. On the other hand, to obtain higher H
2 molar fractions, the higher the MC, the higher the H
2 molar fraction. The condition in which the maximum H
2 production is reached for high moisture content (20%) at a temperature of 700ºC. As has been reported elsewhere [
30,
35], higher moisture contents promote a slight increase in the H
2 molar fraction. This behavior can be explained based on the water-gas shift reaction (R6). When more moisture is present, CO levels decrease through their consumption, which subsequently raises the H
2 content [
36]. Regarding the effect of moisture content in the LHV, it can be seen that higher moisture contents lead to the decrease of LHV. Similar trends for LHV as a function of moisture can be found in the literature [
30,
31].
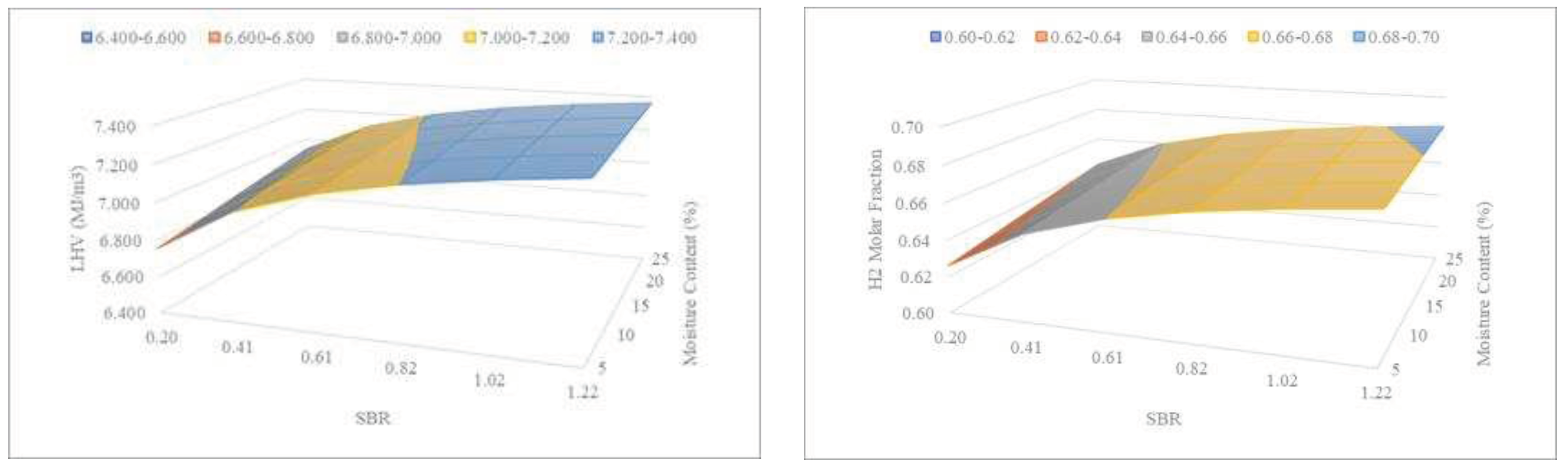
Figure 11 shows the combined effect of SBR and sewage sludge moisture content on the LHV and H
2 of the syngas.
From
Figure 11, it can be deduced that the higher the MC and the higher the SBR, the higher the LHV and H
2 values, but no relationship between MC and SBR is observed. The presence of moisture has a similar effect to that of steam addition.
4. Conclusions
In this work, a thermodynamic equilibrium model was developed using Aspen Plus® to simulate the air and steam gasification processes of sewage sludge from a wastewater treatment plant in Catalonia (Spain). A sensitivity analysis to various process parameters was performed to determine the optimal conditions for higher calorific value of the syngas and higher hydrogen molar fractions.
Air-blown sewage sludge gasification finds the highest LHV conditions under the minimum sewage sludge moisture content and equivalence ratio (and high temperature). Specifically, under conditions of ER = 0.2, MC = 5%, and Tgas = 1200ºC, it generates a syngas with a calorific value of 7.48 MJ/m3. On the other hand, using steam as the gasifying agent, the lower the SBR and the lower the MC, the higher the LHV (at high temperature). Working at SBR = 0.2, MC = 5%, and Tgas = 1200ºC generates syngas with a calorific value of 10.30 MJ/m3.
Under optimal operating conditions that maximize the LHV of the syngas and considering a moisture content of 7% in the dried sewage sludge, the LHV of the syngas is 7.37 MJ/m3 and 10.26 MJ/m3 when using air and steam as the gasifying agents, respectively.
The hydrogen molar fraction is maximized when steam is used as the gasifying agent in combination with high moisture contents of the sewage sludge, high steam-to-biomass ratios, and low gasification temperatures. Particularly, a moisture content of 25%, an SBR of 1.2, and a temperature of 600°C allow for a maximum H2 molar fraction of 69.7%.
From a technical point of view, for the implementation of gasification as an alternative method to sewage sludge treatment in the region of Catalonia (Spain), the present project suggests using steam as a gasifying agent instead of air since it provides a higher LHV of the syngas as well as a hydrogen-richer syngas. However, the economic aspect should also be considered when proposing such a paradigm shift to the sewage sludge treatment method. In this regard, our sensitivity analysis provides precious information regarding some gasification parameters that could be reduced without prejudice to the quality of the syngas while reducing operational expenditures. Our study demonstrated that the gasification temperature can be reduced without significantly decreasing the LHV (e.g., with an SBR of 0.2, MC of 7%, and Tgas = 1100ºC, the LHV is 10.15 MJ/m3 while with the same conditions but Tgas = 1200ºC, the LHV is 10.26 MJ/m3). Other examples can be given for moisture content and SBR ratio. Because these parameters are energy-intensive, it is worthwhile to reduce the sewage sludge pre-drying or inject less steam into the gasifier. Further studies should be carried out such as a cost-benefit study, which can be made using the developed tool. The main contribution of this work is to determine the potential of sewage sludge for hydrogen-rich gas production and provide fundamental data for economic studies of the implementation of this waste-to-energy technology.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.R. and E.M.; methodology, S.U.; software, A.R.; validation, E.M. and A.R.; formal analysis, E.M.; investigation, S.U.; writing—original draft preparation, S.U.; writing—review and editing, E.M.; supervision, A.R. and E.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Carotenuto, A.; Fraia, S.; Massarotti, N.; Sobek, S.; Uddin, M.R.; Vanoli, L.; Werle, S. Predictive modeling for energy recovery from sewage sludge gasification. Energy 2023, 263, 125838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, L.M.; Yabar, H.; Idaa, W.; Yuzir, A. Simulation of sewage sludge air gasification and application of electricity and steam generation: Case study of Pantai 1 sewage treatment plant. Energy Convers Manag 2022, 270, 116196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, J.M.; Narros, A.; Rodríguez, M.E. Behaviour of dolomite, olivine and alumina as primary catalysts in air–steam gasification of sewage sludge. Fuel 2011, 90, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agència Catalana de l’Aigua. La gestió dels biosòlids a Catalunya. Generalitat de Catalunya. 2019. Available online: https://aca.gencat.cat/web/.content/10_ACA/J_Publicacions/07-estudis-informes/10_gestio_biosolids_a_catalunya.pdf (accessed on 09 January 2023).
- Ahmed, T.Y.; Ahmad, M.M.; Yusup, S.; Inayat, A.; Khan, Z. Mathematical and computational approaches for design of biomass gasification for hydrogen production: A review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 2012, 16, 2304–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Gong, M.; Xing, X.; Wang, H.; Zeng, Y.; Xu, C.C. Supercritical water gasification of biomass model compounds: A review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 2020, 118, 09529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, B. Supercritical water gasification and partial oxidation of municipal sewage sludge: An experimental and thermodynamic study. Int J Hydrog Energy 2021, 46, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruya, P.M.; Purwadi, R.; Lim, S.S. Supercritical water gasification of sewage sludge for power generation–thermodynamic study on auto-thermal operation using Aspen Plus. Energy Convers Manag 2020, 206, 112458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yi, L.; Wei, W.; Jin, H.; Guo, L. Hydrogen production by sewage sludge gasification in supercritical water with high heating rate batch reactor. Energy 2022, 238, 121740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantoko, D.; Antoni; Kanchanatip, E.; Yan, M.; Weng, Z.; Gao, Z.; Zhong, Y. Assessment of sewage sludge gasification in supercritical water for H2-rich syngas production. Process Saf Environ Prot 2019, 131, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.; Monteiro, E.; Rouboa, A. Biomass pre-treatment techniques for the production of biofuels using thermal conversion methods – A review. Energy Convers Manag 2022, 270, 116271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, B.; Prajapati, Y.K.; Sheth, P.N. Recent progress in thermochemical techniques to produce hydrogen gas from biomass: A state of the art review. Int J Hydrog Energy 2019, 44, 25384–25415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.H.; Rouboa, A.; Monteiro, E. On the green hydrogen production through gasification processes: A techno-economic approach. J Clean Prod 2023, 383, 135476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, O.; Calado, L.; Panizio, R.M.; Gonçalves, M.; Monteiro, E.; Brito, P. Techno-economic study for a gasification plant processing residues of sewage sludge and solid recovered fuels. Waste Manag 2021, 131, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.S.; Farooq, A.; Valizadeh, B.; Lee, D.; Seo, M.W.; Jung, S.-C.; Hussain, M.; Kim, Y.M.; Khan, M.A.; Jeon, B-H.; Rhee, G.H.; Park, Y-K. Valorization of sewage sludge via air/steam gasification using activated carbon and biochar as catalysts. Int J Hydrog Energy 2024, 54, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezer, Ö.; Karabağ, N.; Öngen, A.; Ayol, A. Syngas production from municipal sewage sludge by gasification Process: Effects of fixed bed reactor types and gasification agents on syngas quality. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 2023, 56, 103042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.; Chen, G.; Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Xu, B. Biomass gasification-gas turbine combustion for power generation system model based on ASPEN PLUS. Sci Total Environ 2018, 628–629, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspen Technology, Inc. Aspen Plus 12.1 Getting Started Modeling Processes with Solids, Cambridge, USA. 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Maneerung, T.; Yao, Z.; Tong, Y.W.; Wang, C.-H.; Dai, Y. Co-gasification of woody biomass and sewage sludge in a fixed-bed downdraft gasifier. AIChE Journal 2015, 61, 2508–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabea, K.; Michailos, S.; Akram, M.; Hughes, K.J.; Ingham, D.; Pourkashanian, M. An improved kinetic modelling of woody biomass gasification in a downdraft reactor based on the pyrolysis gas evolution. Energy Convers Manag 2022, 258, 115495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.; Monteiro, E.; Brito, P.; Vilarinho, C. A Holistic Review on Biomass Gasification Modified Equilibrium Models. Energies 2019, 12, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molino, A.; Chianese, S.; Musmarra, D. Biomass gasification technology: The state of the art overview. J Energy Chem 2016, 25, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.; Monteiro, E.; Rouboa, A. Numerical approaches and comprehensive models for gasification process: A review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 2019, 110, 188–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, T.; Ramos, A.; Monteiro, E.; El-Salam, M.; Rouboa, A. Parametric studies in the gasification agent and fluidization velocity during oxygen-enriched gasification of biomass in a pilot-scale fluidized bed: Experimental and numerical assessment. Renew Energy 2020, 147, 2429–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, Pravir. In Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis and Torrefaction, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: London, UK, 2013.
- Couto, N.; Silva, V.; Monteiro, E.; Rouboa, A.; Brito, P. An experimental and numerical study on the Miscanthus gasification by using a pilot scale gasifier. Renew Energy 2017, 109, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, N.; Monteiro, E.; Silva, V.; Rouboa, A. Hydrogen-rich gas from gasification of Portuguese municipal solid wastes. Int J Hydrog Energy 2016, 41, 10619–10630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, R.; Monteiro, E.; Tabet, F.; Rouboa, A. Numerical investigation of optimum operating conditions for syngas and hydrogen production from biomass gasification using Aspen Plus. Renew Energy 2020, 146, 1309–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.; Monteiro, E.; Calado, L.; Silva, V.; Brito, P.; Vilarinho, C. Experimental and Modeling Analysis of Brewers’ Spent Grains Gasification in a Downdraft Reactor. Energies 2019, 12, 4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altafini, C.R.; Wander, P.R.; Barreto, R.M. Prediction of the working parameters of a wood waste gasifier through an equilibrium model. Energy Convers Manag 2003, 44, 2763–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarungthammachote, S.; Dutta, A. Thermodynamic equilibrium model and second law analysis of a downdraft waste gasifier. Energy 2007, 32, 1660–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.; Monteiro, E.; Brito, P.; Vilarinho, C. Experimental Analysis of Brewers’ Spent Grains Steam Gasification in an Allothermal Batch Reactor. Energies 2019, 12, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, N.; Ashraf, A.; Naveed, S.; Malik, A. Simulation of hybrid biomass gasification using Aspen plus: a comparative performance analysis for food, municipal solid and poultry waste. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 3962–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratieri, M.; Baggio, P.; Fiori, L.; Grigiante, M. Biomass as an energy source: Thermodynamic constraints on the performance of the conversion process. Bioresour Technol 2008, 99, 7063–7073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, E.; Ismail, T.M.; Ramos, A.; El-Salam, M.A.; Brito, P.; Rouboa, A. Experimental and modeling studies of Portuguese peach stone gasification on an autothermal bubbling fluidized bed pilot plant. Energy 2018, 142, 862–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKendry, P. Energy production from biomass (part 3): gasification technologies. Bioresour Technol 2002, 83, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).