Submitted:
13 February 2024
Posted:
14 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
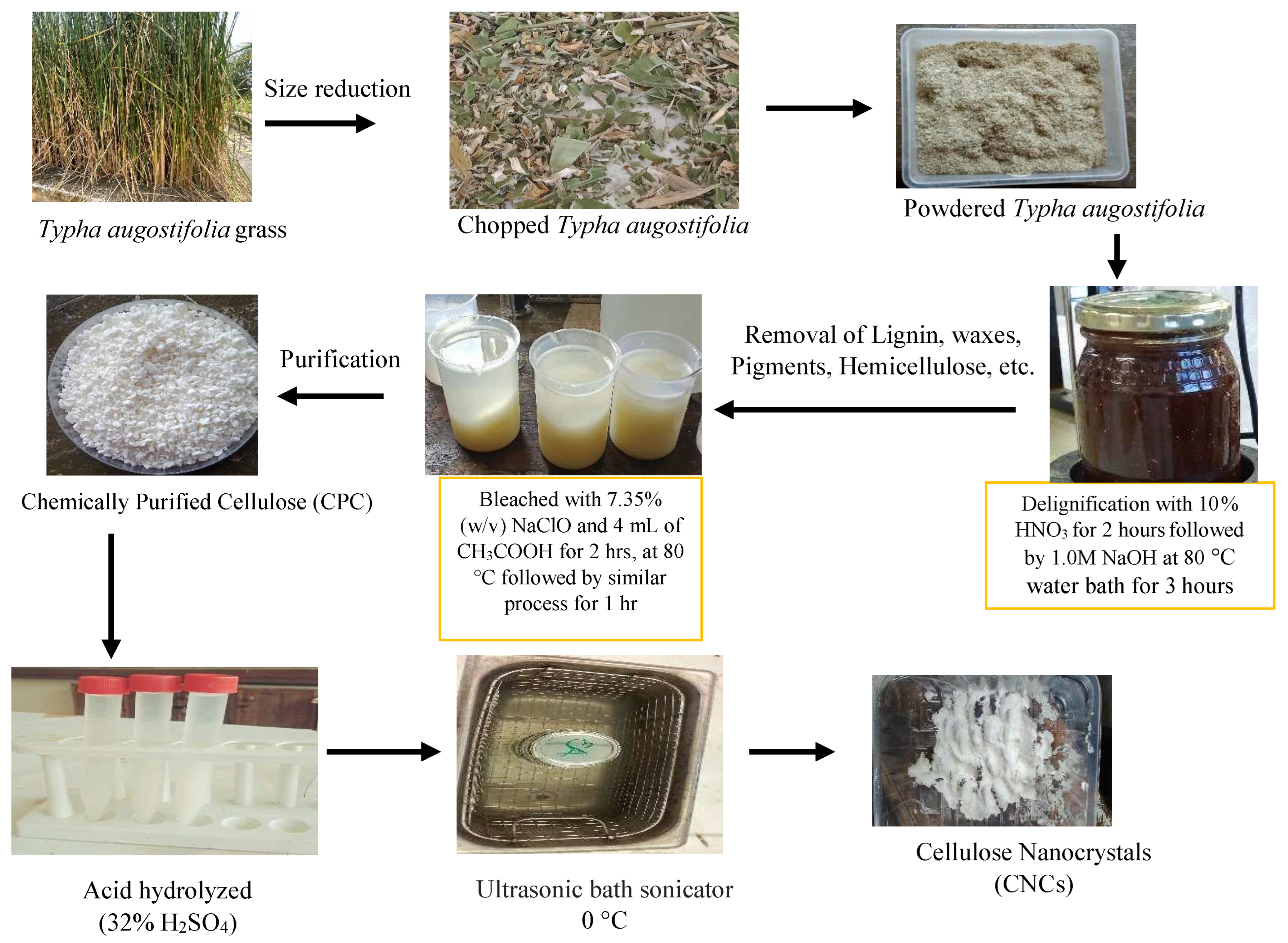
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Dewaxing and Delignification
2.2.2. Chemical Purification (Bleaching)
2.2.3. Synthesis of Nanocellulose
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Analysis
2.3.2. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
2.3.3. Scanning Electron Microscope-Electron Dispersive Spectroscopy (SEM-EDS) Analysis
2.3.4. Thermogravimetric (TGA) Analysis
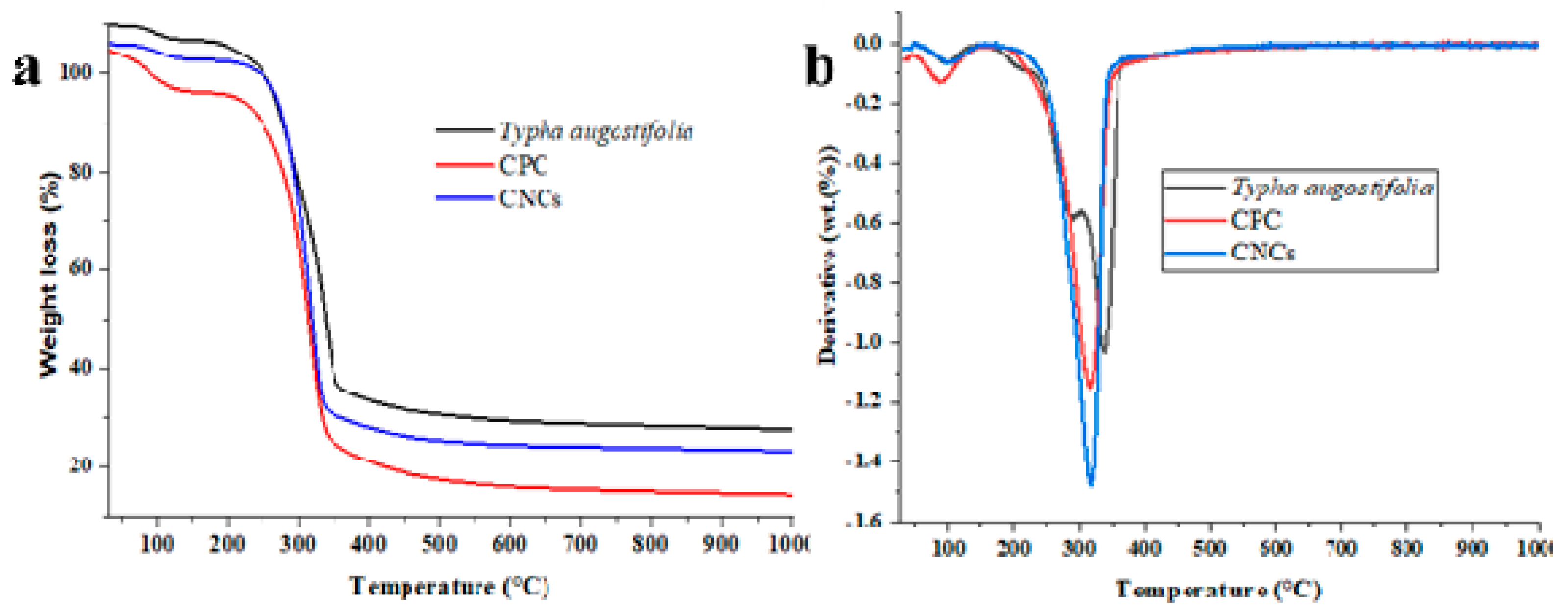
3. Results
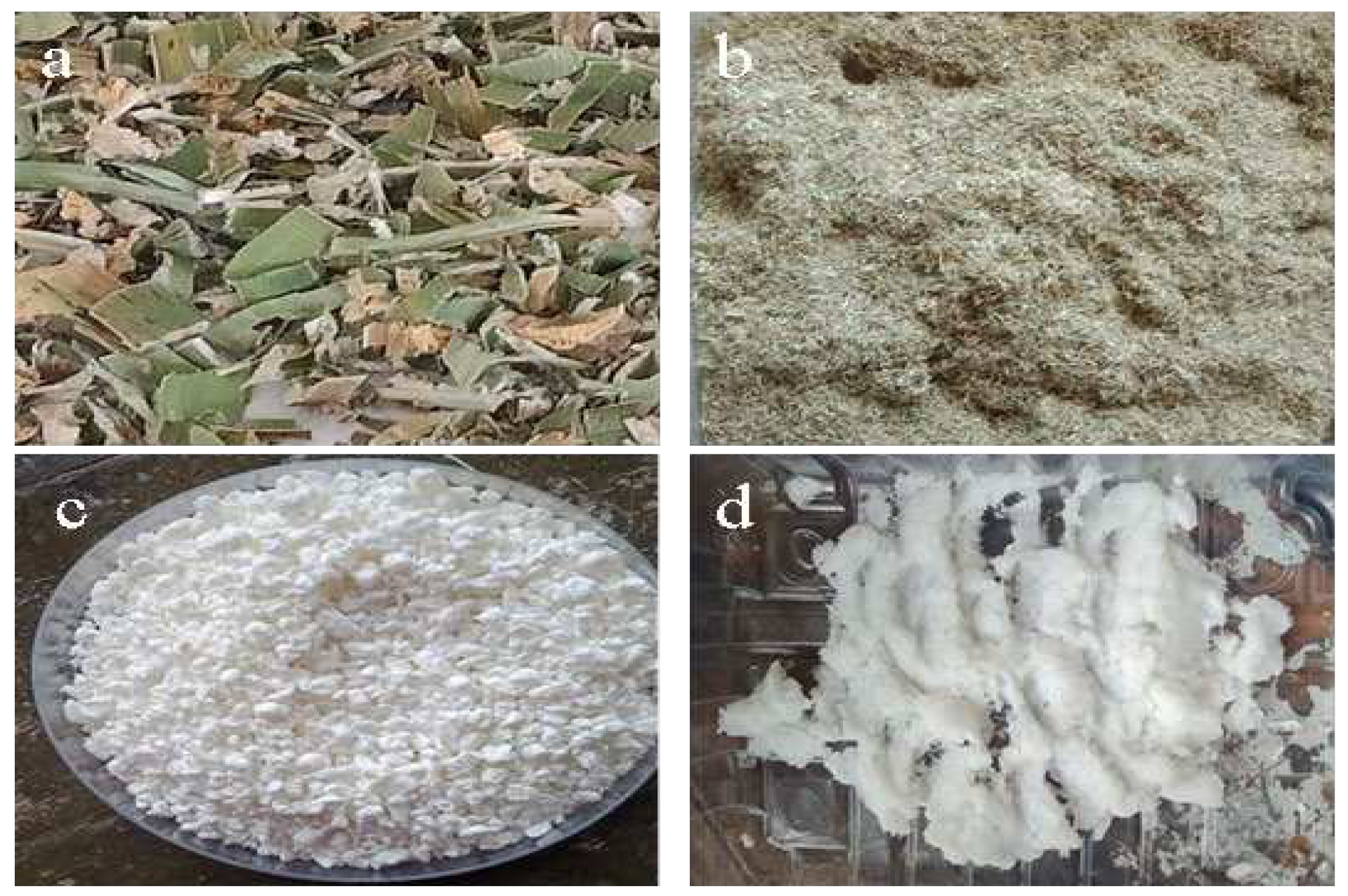
3.1. Physical Appearance
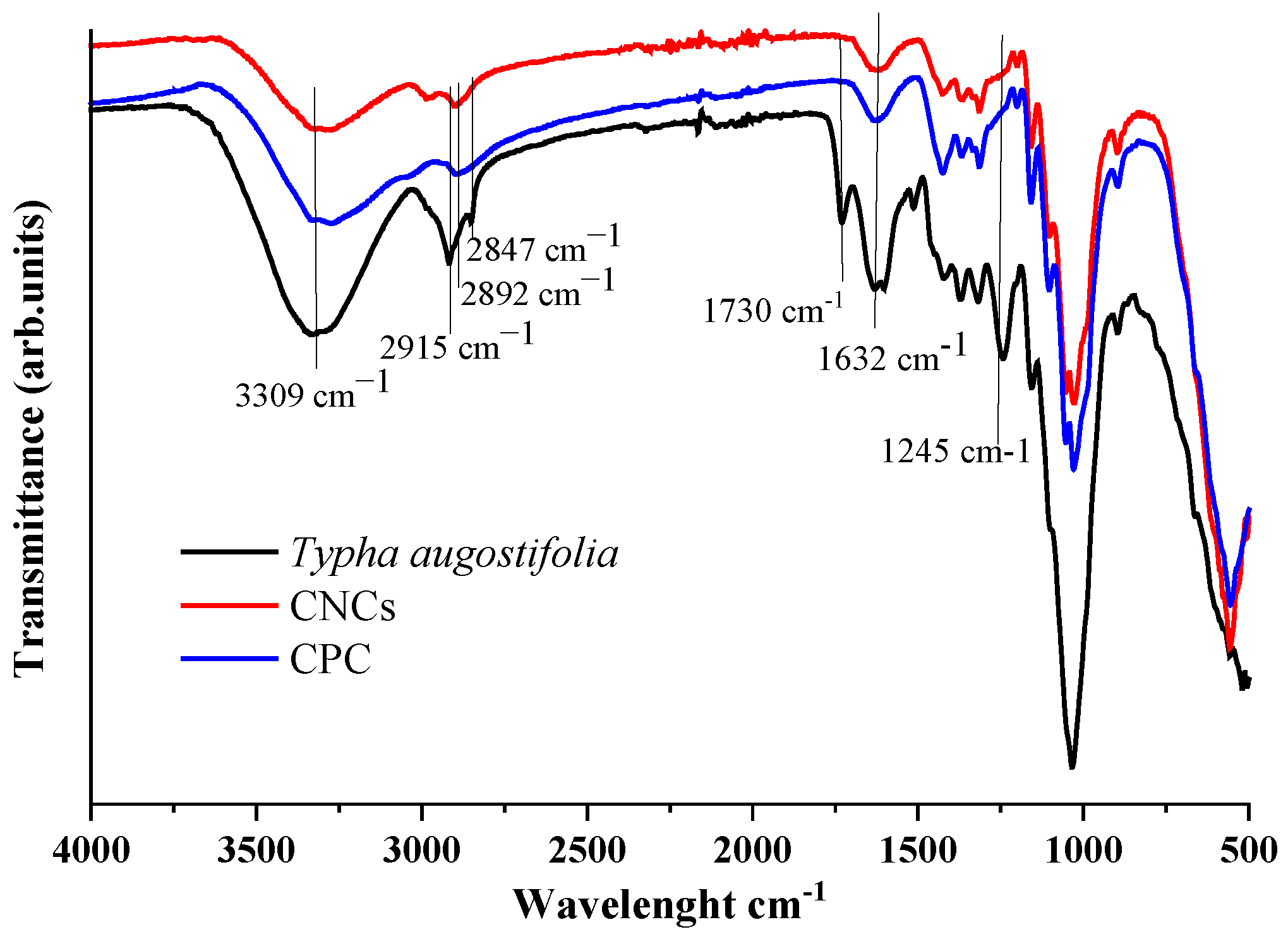
3.2. Functional Group Analysis (FTIR)
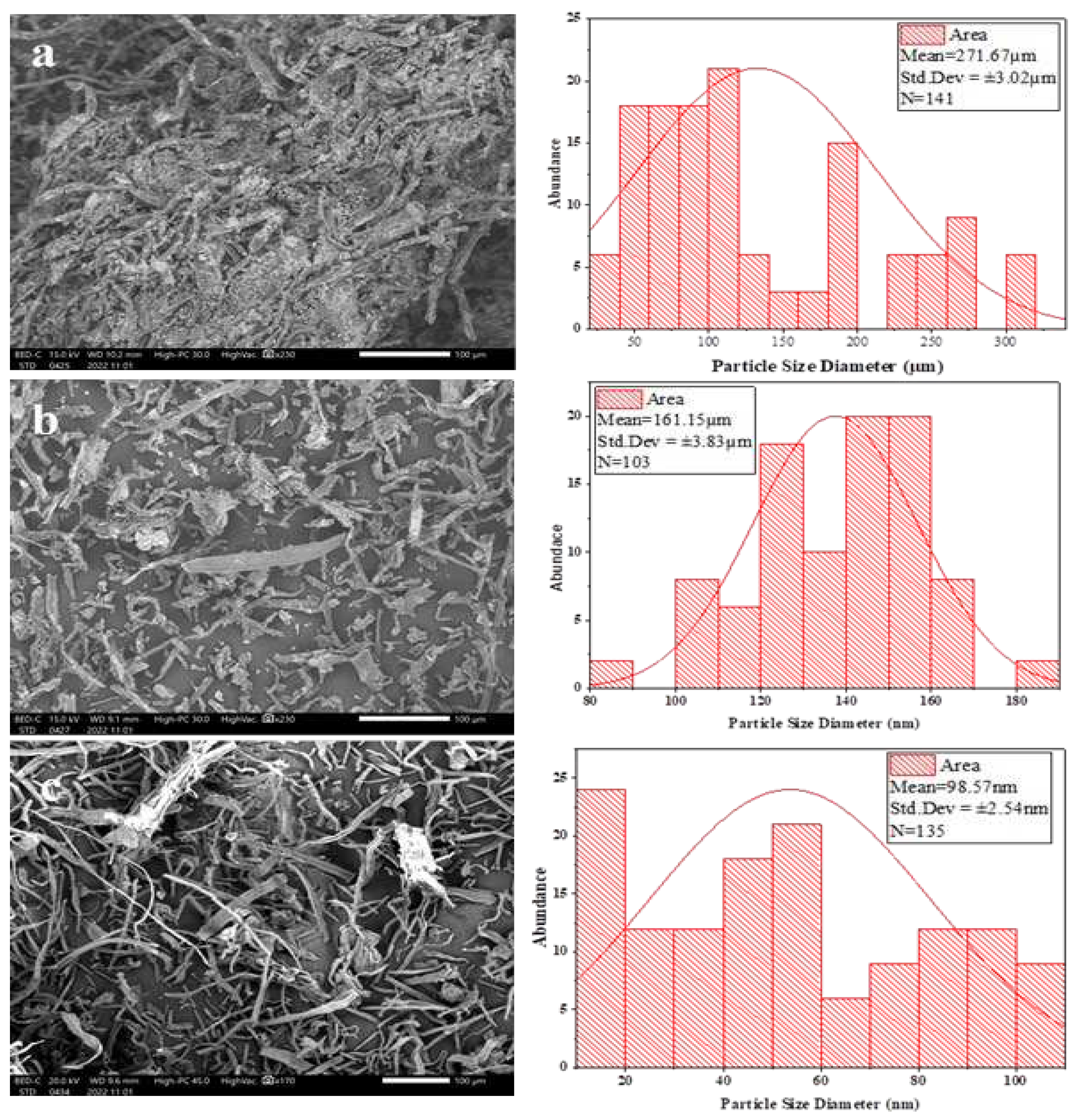
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
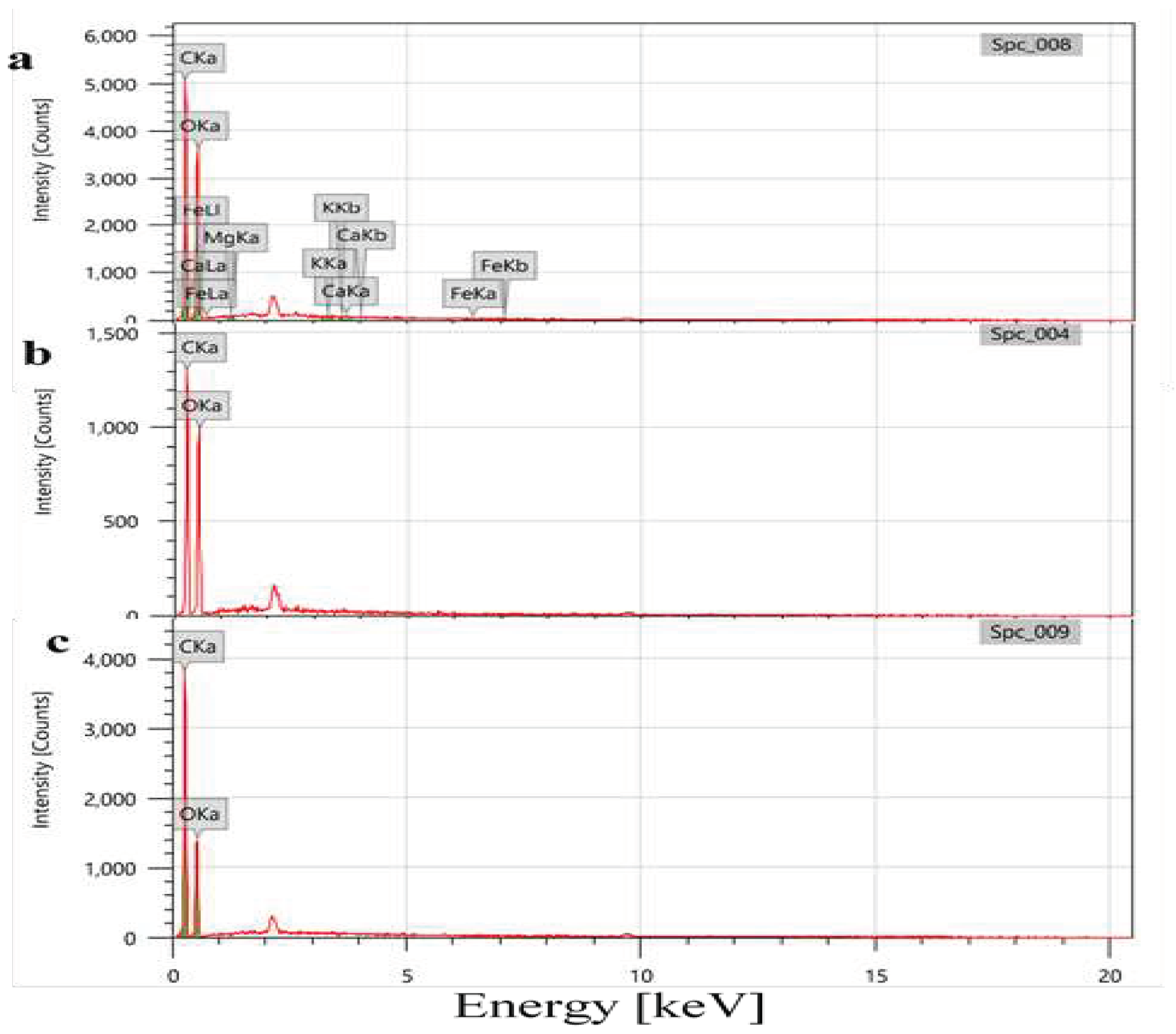
3.4. Elemental Analysis
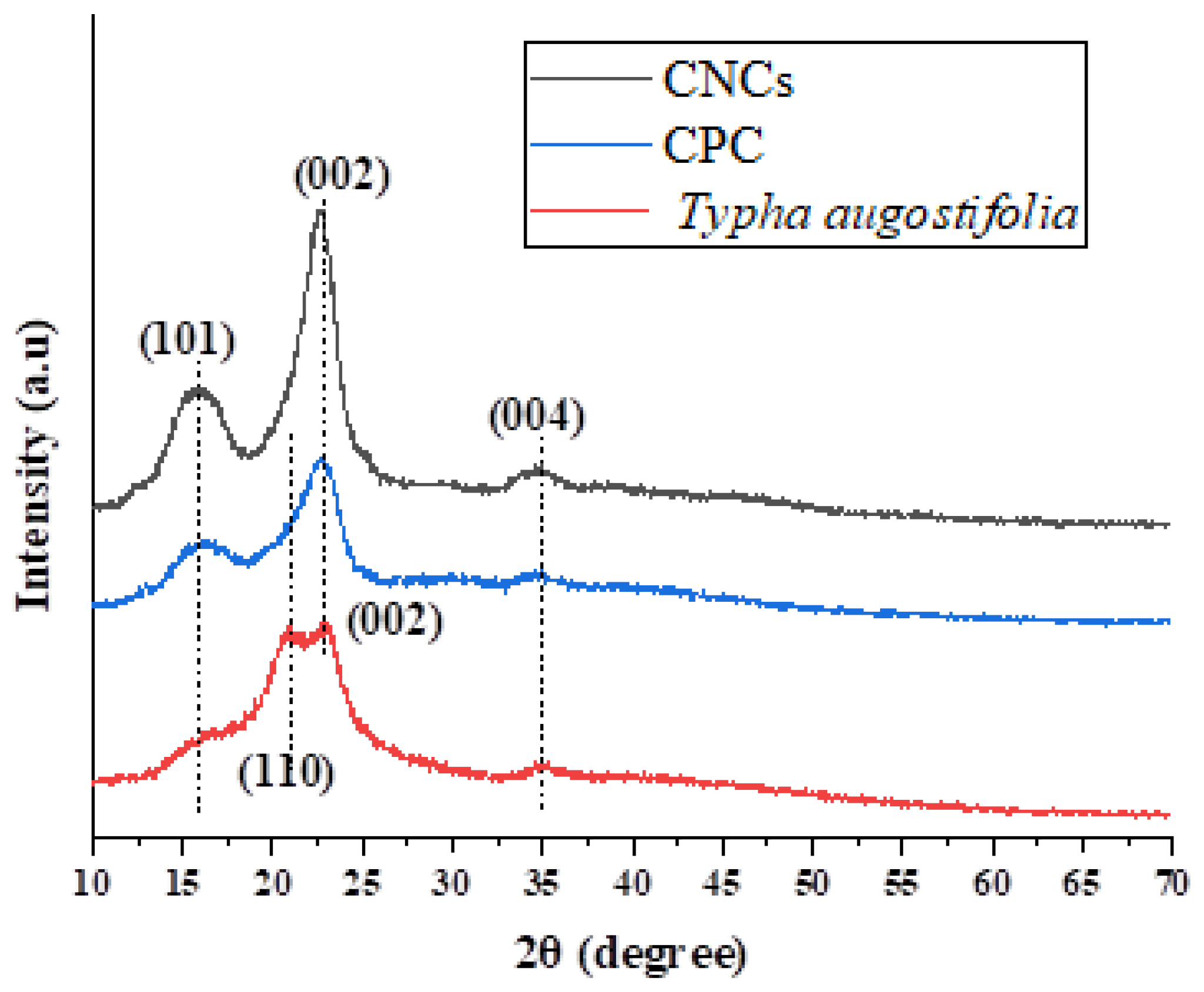
3.5. Crystalline Structure Analysis X-ray Diffraction
3.6. Thermal Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Almasi, H. Biodegradable Polymers. Biodegrad.-Life Sci. 2013, 141–185. [Google Scholar]
- Siqueira, G.; Bras, J.; Dufresne, A. Cellulosic Bionanocomposites: A Review of Preparation, Properties and Applications. Polymers 2010, 2, 728–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trache, D.; Hussin, M.H.; Chuin, C.T.H.; Sabar, S.; Fazita, M.N.; Taiwo, O.F.; Hassan, T.M.; Haafiz, M.M. Microcrystalline Cellulose: Isolation, Characterization and Bio-Composites Application—A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 789–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Verma, R.K. Taxonomical and Pharmacological Status of Typha: A Review. Ann. Plant Sci. 2018, 7, 2101–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragán, E.U.P.; Guerrero, C.F.C.; Zamudio, A.M.; Cepeda, A.B.M.; Heinze, T.; Koschella, A. Isolation of Cellulose Nanocrystals from Typha Domingensis Named Southern Cattail Using a Batch Reactor. Fibers Polym. 2019, 20, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kian, L.K.; Jawaid, M.; Ariffin, H.; Alothman, O.Y. Isolation and Characterization of Microcrystalline Cellulose from Roselle Fibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; He, B.; Zhao, L. Isolation and Characterization of Microcrystalline Cellulose from Cotton Stalk Waste. BioResources 2019, 14, 3231–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlou, S.; Suter, E.; Alfred, M.; Rutto, H.; Omwoyo, W. In Situ Capping of Silver Nanoparticles with Cellulosic Matrices from Wheat Straws in Enhancing Their Antimicrobial Activity: Synthesis and Characterization. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2023, 58, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.K.; Wesley, O.N.; Nathan, O.; Moloto, M.J. Chemically Purified Cellulose and Its Nanocrystals from Sugarcane Baggase: Isolation and Characterization. Heliyon 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, B.S.J.; Venkatachalam, S. A Neoteric Approach for the Complete Valorization of Typha Angustifolia Leaf Biomass: A Drive towards Environmental Sustainability. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 318, 115579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.M.; Elkomy, R.G.; El-Sheekh, M.M. Bioactive Compounds from Components of Marine Ecosystem. Mar. Ecosyst. A Unique Source Valuab. Bioact. Compd. 2023, 3, 206–256. [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi, T.; Shimamura, S.; Nakazono, M.; Mochizuki, T. Aerenchyma Formation in Crop Species: A Review. Field Crops Res. 2013, 152, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patro, A.; Dwivedi, S.; Panja, R.; Saket, P.; Gupta, S.; Mittal, Y.; Saeed, T.; Martínez, F.; Yadav, A.K. Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Management: Basic Design, Abiotic and Biotic Components, and Their Interactive Functions. In Material-Microbes Interactions; Elsevier, 315; Volume 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Baldawi, I.A. Removal of 1, 2-Dichloroethane from Real Industrial Wastewater Using a Sub-Surface Batch System with Typha Angustifolia L. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namasivayam, S.K.R.; Prakash, P.; Babu, V.; Paul, E.J.; Bharani, R.A.; Kumar, J.A.; Kavisri, M.; Moovendhan, M. Aquatic Biomass Cellulose Fabrication into Cellulose Nanocomposite and Its Application in Water Purification. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 136386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Amri, A.; Bensalah, J.; Idrissi, A.; Lamya, K.; Ouass, A.; Bouzakraoui, S.; Zarrouk, A.; Lebkiri, A. Adsorption of a Cationic Dye (Methylene Bleu) by Typha Latifolia: Equilibrium, Kinetic, Thermodynamic and DFT Calculations. Chem. Data Collect. 2022, 38, 100834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ievinsh, G. Halophytic Clonal Plant Species: Important Functional Aspects for Existence in Heterogeneous Saline Habitats. Plants 2023, 12, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulandari, W.T.; Rochliadi, A.; Arcana, I.M. Nanocellulose Prepared by Acid Hydrolysis of Isolated Cellulose from Sugarcane Bagasse. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing, 2016; Volume 107, p. 012045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trache, D.; Hussin, M.H.; Chuin, C.T.H.; Sabar, S.; Fazita, M.N.; Taiwo, O.F.; Hassan, T.M.; Haafiz, M.M. Microcrystalline Cellulose: Isolation, Characterization and Bio-Composites Application—A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 789–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Negi, Y.S.; Upadhyaya, J.S. Studies on Characterization of Corn Cob Based Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. Lett 2010, 1, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trache, D.; Hussin, M.H.; Haafiz, M.M.; Thakur, V.K. Recent Progress in Cellulose Nanocrystals: Sources and Production. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 1763–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeasmin, S. Study of Acid Hydrolysis Based Synthesis of Microcrystalline and Nanocrystalline Cellulose from Local Lignocellulosic Materials. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hokkanen, S.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. A Review on Modification Methods to Cellulose-Based Adsorbents to Improve Adsorption Capacity. Water research 2016, 91, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Thabit, N.Y.; Judeh, A.A.; Hakeem, A.S.; Ul-Hamid, A.; Umar, Y.; Ahmad, A. Isolation and Characterization of Microcrystalline Cellulose from Date Seeds (Phoenix dactylifera L.). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Guo, X.; Wang, S.; Yin, Y. Effects of Ultrasonic Treatment during Acid Hydrolysis on the Yield, Particle Size and Structure of Cellulose Nanocrystals. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 135, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johar, N.; Ahmad, I.; Dufresne, A. Extraction, Preparation and Characterization of Cellulose Fibres and Nanocrystals from Rice Husk. Ind. Crops Prod. 2012, 37, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trache, D.; Hussin, M.H.; Haafiz, M.M.; Thakur, V.K. Recent Progress in Cellulose Nanocrystals: Sources and Production. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 1763–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarchoun, A.F.; Trache, D.; Klapötke, T.M.; Derradji, M.; Bessa, W. Ecofriendly Isolation and Characterization of Microcrystalline Cellulose from Giant Reed Using Various Acidic Media. Cellulose 2019, 26, 7635–7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adawiyah, R.; Suryanti, V. Preparation and Characterization of Microcrystalline Cellulose from Lembang (Typha angustifolia L.). In Proceedings of the Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing, 2022; Volume 2190, p. 012007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khili, F.; Borges, J.; Almeida, P.L.; Boukherroub, R.; Omrani, A.D. Extraction of Cellulose Nanocrystals with Structure I and II and Their Applications for Reduction of Graphene Oxide and Nanocomposite Elaboration. Waste Biomass Valor 2019, 10, 1913–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guna, V.; Ilangovan, M.; Adithya, K.; Koushik, C.V.A.; Srinivas, C.V.; Yogesh, S.; Nagananda, G.S.; Venkatesh, K.; Reddy, N. Biofibers and Biocomposites from Sabai Grass: A Unique Renewable Resource. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 218, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouhou, M.C.; Abdelmoumen, S.; Thomas, S.; Attia, H.; Ghorbel, D. Use of green chemistry methods in the extraction of dietary fibers from cactus rackets (Opuntia ficus indica): Structural and microstructural studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Weng, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhai, S.; Wang, C.; Xu, R.; Guo, Y. Characterization of potential cellulose fiber from Luffa vine: A study on physicochemical and structural properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 2247–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chilukoti, G.R.; Mandapati, R.N. Characterization of Cellulosic Leaf Fiber from the Typha Angustifolia Plant. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 2516–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniyi, A.G.; Adeyanju, C.A.; Emenike, E.C.; Otoikhian, S.K.; Ogunniyi, S.; Iwuozor, K.O.; Raji, A.A. Thermal Energy Recovery and Valorisation of Delonix Regia Stem for Biochar Production. Environ. Chall. 2022, 9, 100630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Thabit, N.Y.; Judeh, A.A.; Hakeem, A.S.; Ul-Hamid, A.; Umar, Y.; Ahmad, A. Isolation and Characterization of Microcrystalline Cellulose from Date Seeds (Phoenix dactylifera L.). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


|
Sample |
2θ (Amorphous) (°) | 2θ (002) (°) | Crystallinity Index (CrI %) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Degree | Intensity, Iam | Degree | Intensity, I002 | ||
| Typha augostifolia | 21.00 | 376 | 34.97 | 658 | 42.86 |
| CPC | 22.58 | 287 | 34.73 | 868 | 66.94 |
| CNCs | 22.64 | 211 | 34.84 | 934 | 77.41 |
| Temperature | CPC (°C) | CNCs (°C) | Typha augostifolia (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tonset | 253.24 | 239.01 | 229.28 |
| Tendset | 339.56 | 344.45 | 354.06 |
| Td | 315.19 | 315.18 | 298.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





