Submitted:
08 February 2024
Posted:
09 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. A Brief Overview of BDNF Functions
1.2. Pain as a Complex and Multifaceted Sensory Experience
1.3. Overview of the Anatomical Arrangement of Pain Pathways
1.3.1. Somatic Pain Pathways – Subcortical Structures
1.3.2. Visceral Pain Pathways – Subcortical Structures
1.3.3. Cortical Structures
2. Role of BDNF in Nociception and Pain: Insights and Mechanisms
2.1. BDNF in Pain Pathways Neurons
2.1.1. Primary Sensory Neurons
2.1.2. Second-Order Neurons
2.1.3. Higher-Order Neurons
- Cerebral cortex
- Amygdala
- Brainstem
2.2. Neuronal Mechanisms
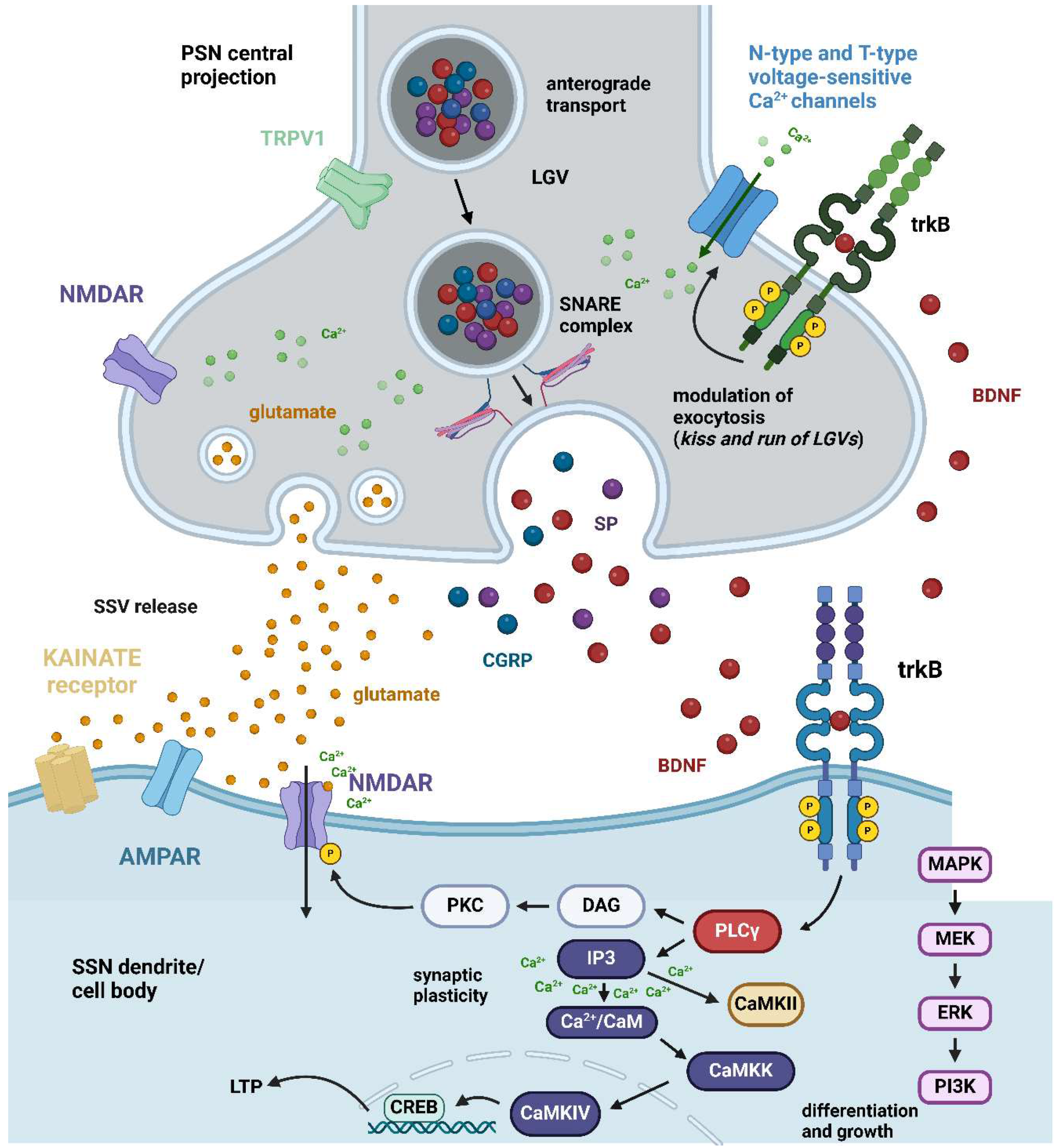
2.2.1. Ex Vivo Studies on Nociceptive/Pain Modulation by Mature BDNF
2.2.2. In Vivo Studies on Inflammatory Pain Modulation by Mature BDNF
- DRG/Spinal cord
- Trigeminal system
2.2.3. Modulation of Inflammatory Pain by proBDNF In Vivo
2.2.4. In Vivo Studies on Neuropathic Pain Modulation by Mature BDNF
- DRG/Spinal cord
- Trigeminal system
2.3. BDNF in Glia and Other Cells of Relevance in Nociceptive/Pain Pathways – Localization and Mechanisms
2.3.1. Glial Cells
- Schwann cells
- Microglia
- Astrocytes
- Oligodendroglia
2.3.2. Immune Cells
2.4. BDNF Polymorphisms Related to Pain Signaling
3. BDNF and Neuronal Sensitization
3.1. Peripheral Sensitization
3.2. Central Sensitization
3.3. Hyperalgesic Priming in the Spinal Cord Dorsal Horn
4. Implications for Pain Management
5. Clinical Trials
6. Conclusion
Abbreviations
References
- Ateaque, S.; Merkouris, S.; Barde, Y.A. Neurotrophin signalling in the human nervous system. Front Mol Neurosci 2023, 16, 1225373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arévalo, J.C.; Deogracias, R. Mechanisms Controlling the Expression and Secretion of BDNF. Biomolecules 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Siao, C.J.; Nagappan, G.; Marinic, T.; Jing, D.; McGrath, K.; Chen, Z.Y.; Mark, W.; Tessarollo, L.; Lee, F.S.; et al. Neuronal release of proBDNF. Nat.Neurosci. 2009, 12, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.S.; Kavalali, E.T.; Monteggia, L.M. BDNF signaling in context: From synaptic regulation to psychiatric disorders. Cell 2022, 185, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Nagappan, G.; Lu, Y. BDNF and Synaptic Plasticity, Cognitive Function, and Dysfunction. In Neurotrophic Factors; Lewin, G.R., Carter, B.D., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2014; pp. 223–250. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda, M.; Morici, J.F.; Zanoni, M.B.; Bekinschtein, P. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor: A Key Molecule for Memory in the Healthy and the Pathological Brain. Front Cell Neurosci 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagahara, A.H.; Merrill, D.A.; Coppola, G.; Tsukada, S.; Schroeder, B.E.; Shaked, G.M.; Wang, L.; Blesch, A.; Kim, A.; Conner, J.M.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rodent and primate models of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Med 2009, 15, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palasz, E.; Wysocka, A.; Gasiorowska, A.; Chalimoniuk, M.; Niewiadomski, W.; Niewiadomska, G. BDNF as a Promising Therapeutic Agent in Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccato, C.; Ciammola, A.; Rigamonti, D.; Leavitt, B.R.; Goffredo, D.; Conti, L.; MacDonald, M.E.; Friedlander, R.M.; Silani, V.; Hayden, M.R.; et al. Loss of huntingtin-mediated BDNF gene transcription in Huntington’s disease. Science 2001, 293, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, Z.-Y.A.; Byrne, L.M.; Rodrigues, F.B.; Tortelli, R.; Johnson, E.B.; Foiani, M.S.; Arridge, M.; De Vita, E.; Scahill, R.I.; Heslegrave, A.; et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma is not a biomarker for Huntington’s disease. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, J.; Noakes, P.G.; Bellingham, M.C. The Role of Altered BDNF/TrkB Signaling in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front Cell Neurosci 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riolo, G.; Ricci, C.; De Angelis, N.; Marzocchi, C.; Guerrera, G.; Borsellino, G.; Giannini, F.; Battistini, S. BDNF and Pro-BDNF in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A New Perspective for Biomarkers of Neurodegeneration. Brain Sci 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, R.S.; Monteggia, L.M. A neurotrophic model for stress-related mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry 2006, 59, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinowich, K.; Manji, H.; Lu, B. New insights into BDNF function in depression and anxiety. Nat Neurosci 2007, 10, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merighi, A. Neuropeptides and Coexistence. In Reference Module in Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Psychology; Elsevier, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Raja, S.N.; Carr, D.B.; Cohen, M.; Finnerup, N.B.; Flor, H.; Gibson, S.; Keefe, F.J.; Mogil, J.S.; Ringkamp, M.; Sluka, K.A.; et al. The revised International Association for the Study of Pain definition of pain: concepts, challenges, and compromises. Pain 2020, 161, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, S.A.; Herr, M.J. Physiology, Nociception. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island (FL), 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Dubin, A.E.; Patapoutian, A. Nociceptors: the sensors of the pain pathway. J Clin Invest 2010, 120, 3760–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias, B.; Merighi, A. Capsaicin, Nociception and Pain. Molecules 2016, 21, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, B.A. Pain and emotion interactions in subregions of the cingulate gyrus. Nat Rev Neurosci 2005, 6, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grichnik, K.P.; Ferrante, F.M. The difference between acute and chronic pain. Mt Sinai J Med 1991, 58, 217–220. [Google Scholar]
- Merighi, A.; Salio, C.; Ghirri, A.; Lossi, L.; Ferrini, F.; Betelli, C.; Bardoni, R. BDNF as a pain modulator. Prog.Neurobiol. 2008, 85, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, P.M. Somatic Pain. In Encyclopedia of Pain; Schmidt, R.F., Willis, W.D., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2007; pp. 2190–2192. [Google Scholar]
- Price, D.D. Psychological and neural mechanisms of the affective dimension of pain. Science 2000, 288, 1769–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, G.J.; Averill, S.; Shortland, P.J.; Yan, Q.; Priestley, J.V. Axotomy results in major changes in BDNF expression by dorsal root ganglion cells: BDNF expression in large trkB and trkC cells, in pericellular baskets, and in projections to deep dorsal horn and dorsal column nuclei. Eur.J.Neurosci. 1999, 11, 3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudspith, M.J.; Siddall, P.J.; Munglani, R. Chapter 23—Physiology of pain. In Foundations of Anesthesia, 2nd ed.; Hemmings, H.C., Hopkins, P.M., Eds.; Mosby: Edinburgh, 2006; pp. 267–285. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.Y.; Wang, J.; Gwak, Y.S. Gracile neurons contribute to the maintenance of neuropathic pain in peripheral and central neuropathic models. J Neurotrauma 2012, 29, 2587–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebhart, G.F. Visceral Pain. In Encyclopedia of Neuroscience; Squire, L.R., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, 2009; pp. 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Vardeh, D.; Naranjo, J.F. Peripheral and Central Sensitization. In Pain Medicine: An Essential Review; Yong, R.J., Nguyen, M., Nelson, E., Urman, R.D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2017; pp. 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Kim, H.J.; Back, S.K.; Na, H.S. Common and discrete mechanisms underlying chronic pain and itch: peripheral and central sensitization. Pflügers Archiv—European Journal of Physiology 2021, 473, 1603–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, M.F.; Hügle, T.; Morlion, B.; Koltzenburg, M.; Chapman, V.; MaassenVanDenBrink, A.; Lane, N.E.; Perrot, S.; Zieglgänsberger, W. Neurogenic inflammation as a novel treatment target for chronic pain syndromes. Exp Neurol 2022, 356, 114108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikandar, S.; Minett, M.S.; Millet, Q.; Santana-Varela, S.; Lau, J.; Wood, J.N.; Zhao, J. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor derived from sensory neurons plays a critical role in chronic pain. Brain 2018, 141, 1028–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altar, C.A.; Cai, N.; Bliven, T.; Juhasz, M.; Conner, J.M.; Acheson, A.L.; Lindsay, R.M.; Wiegand, S.J. Anterograde transport of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its role in the brain. Nature 1997, 389, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bartheld, C.S.; Wang, X.; Butowt, R. Anterograde axonal transport, transcytosis, and recycling of neurotrophic factors: the concept of trophic currencies in neural networks. Mol.Neurobiol. 2001, 24, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.F.; Song, X.Y.; Zhong, J.H.; Barati, S.; Zhou, F.H.; Johnson, S.M. Distribution and localization of pro-brain-derived neurotrophic factor-like immunoreactivity in the peripheral and central nervous system of the adult rat. J.Neurochem. 2004, 91, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conner, J.M.; Lauterborn, J.C.; Yan, Q.; Gall, C.M.; Varon, S. Distribution of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) protein and mRNA in the normal adult rat CNS: evidence for anterograde axonal transport. J.Neurosci. 1997, 17, 2295–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohara, K.; Kitamura, A.; Morishima, M.; Tsumoto, T. Activity-dependent transfer of brain-derived neurotrophic factor to postsynaptic neurons. Science 2001, 291, 2419–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, B.J.; Bradbury, E.J.; Bennett, D.L.; Trivedi, P.M.; Dassan, P.; French, J.; Shelton, D.B.; McMahon, S.B.; Thompson, S.W. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor modulates nociceptive sensory inputs and NMDA-evoked responses in the rat spinal cord. J.Neurosci. 1999, 19, 5138–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, G.J.; Averill, S.; Nitkunan, A.; Rattray, M.; Bennett, D.L.H.; Yan, Q.; Priestley, J.V. Nerve growth factor treatment increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor selectively in trk-A expressing dorsal root ganglion cells and in their central terminations within the spinal cord. J.Neurosci. 1997, 17, 8476–8490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bothwell, M. Recent advances in understanding context-dependent mechanisms controlling neurotrophin signaling and function. F1000Research 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.-F.; Rush, R.A. Endogenous brain-derived neurothrophic factor is anterogradely transported in primary sensory neurons. Neuroscience 1996, 74, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.F.; Chie, E.T.; Rush, R.A. Distribution of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in cranial and spinal ganglia. Exp Neurol 1998, 149, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, H.; Terayama, R.; Yamaai, T.; Yan, Z.; Sugimoto, T. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor-immunoreactive neurons in the rat vagal and glossopharyngeal sensory ganglia; co-expression with other neurochemical substances. Brain Res. 2007, 1155, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, J. An immunohistochemical and quantitative examination of dorsal root ganglion neuronal subpopulations. J Neurosci 1985, 5, 2051–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallemend, F.; Ernfors, P. Molecular interactions underlying the specification of sensory neurons. Trends Neurosci 2012, 35, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Cai, B.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X. Somatosensory neuron types and their neural networks as revealed via single-cell transcriptomics. Trends Neurosci 2023, 46, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeiren, S.; Bellefroid, E.J.; Desiderio, S. Vertebrate Sensory Ganglia: Common and Divergent Features of the Transcriptional Programs Generating Their Functional Specialization. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capra, N.F.; Wax, T.D. Distribution and central projections of primary afferent neurons that innervate the masseter muscle and mandibular periodontium: a double-label study. J Comp Neurol 1989, 279, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, J.L.; Solé-Magdalena, A.; Menéndez, I.; de Vicente, J.C.; Vega, J.A. Connections between the facial and trigeminal nerves: Anatomical basis for facial muscle proprioception. JPRAS Open 2017, 12, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfini, M.C.; Mantilleri, A.; Gaillard, S.; Hao, J.; Reynders, A.; Malapert, P.; Alonso, S.; Francois, A.; Barrere, C.; Seal, R.; et al. TAFA4, a Chemokine-like Protein, Modulates Injury-Induced Mechanical and Chemical Pain Hypersensitivity in Mice. Cell Reports 2013, 5, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, E.C.; Ernfors, P. Dorsal Root Ganglion Neuron Types and Their Functional Specialization. In The Oxford Handbook of the Neurobiology of Pain; Wood, J.N., Ed.; Oxford University Press, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kupari, J.; Häring, M.; Agirre, E.; Castelo-Branco, G.; Ernfors, P. An Atlas of Vagal Sensory Neurons and Their Molecular Specialization. Cell Rep 2019, 27, 2508–2523.e2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Averill, S.; McMahon, S.B.; Clary, D.O.; Reichardt, L.F.; Priestley, J.V. Immunocytochemical localization of trkA receptors in chemically identified subgroups of adult rat sensory neurons. Eur.J.Neurosci. 1995, 7, 1484–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, S.N. Phenotype and Function of Somatic Primary Afferent Nociceptive Neurones with C-, Aδ- or Aα/β-Fibres. Exp Physiol 2002, 87, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merighi, A.; Polak, J.M.; Gibson, S.J.; Gulbenkian, S.; Valentino, K.L.; Peirone, S.M. Ultrastructural studies on calcitonin gene-related peptide-, tachykinins- and somatostatin-immunoreactive neurones in rat dorsal root ganglia: Evidence for the colocalisation of different peptides in single secretory granules. Cell Tiss.Res. 1988, 254, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merighi, A. The histology, physiology, neurochemistry and circuitry of the substantia gelatinosa Rolandi (lamina II) in mammalian spinal cord. Prog.Neurobiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salio, C.; Lossi, L.; Ferrini, F.; Merighi, A. Ultrastructural evidence for a pre- and post-synaptic localization of full length trkB receptors in substantia gelatinosa (lamina II) of rat and mouse spinal cord. Eur.J.Neurosci. 2005, 22, 1951–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salio, C.; Averill, S.; Priestley, J.V.; Merighi, A. Costorage of BDNF and neuropeptides within individual dense-core vesicles in central and peripheral neurons. Dev.Neurobiol. 2007, 67, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merighi, A.; Bardoni, R.; Salio, C.; Lossi, L.; Ferrini, F.; Prandini, M.; Zonta, M.; Gustincich, S.; Carmignoto, G. Presynaptic functional trkB receptors mediate the release of excitatory neurotransmitters from primary afferent terminals in lamina II (substantia gelatinosa) of postnatal rat spinal cord. Dev.Neurobiol. 2008, 68, 457–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salio, C.; Ferrini, F. BDNF and GDNF expression in discrete populations of nociceptors. Ann.Anat. 2016, 207, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, C.M.; Gulick, M.A.; Yu, S.J.; Grider, J.R.; Murthy, K.S.; Kuemmerle, J.F.; Akbarali, H.I.; Qiao, L.Y. Up-regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in primary afferent pathway regulates colon-to-bladder cross-sensitization in rat. J Neuroinflammation 2012, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, S.O.; Kim, J.K.; Hong, H.S.; Kim, D.S.; Cho, H.J. Expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rat dorsal root ganglia, spinal cord and gracile nuclei in experimental models of neuropathic pain. Neuroscience 2001, 107, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-T.; Ro, L.-S.; Wang, H.-L.; Chen, J.-C. Up-regulation of dorsal root ganglia BDNF and trkB receptor in inflammatory pain: an in vivo and in vitrostudy. Journal of Neuroinflammation 2011, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.J.; Kim, J.K.; Zhou, X.F.; Rush, R.A. Increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor immunoreactivity in rat dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord following peripheral inflammation. Brain Res. 1997, 764, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomotsuka, N.; Kaku, R.; Obata, N.; Matsuoka, Y.; Kanzaki, H.; Taniguchi, A.; Muto, N.; Omiya, H.; Itano, Y.; Sato, T.; et al. Up-regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the dorsal root ganglion of the rat bone cancer pain model. Journal of pain research 2014, 7, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, P.M.E. CHAPTER 26—Trigeminal Sensory System. In The Rat Nervous System, 3rd ed.; Paxinos, G., Ed.; Academic Press: Burlington, 2004; pp. 817–851. [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa, H.; Yabuuchi, T.; Jin, H.W.; Terayama, R.; Yamaai, T.; Deguchi, T.; Kamioka, H.; Takano-Yamamoto, T.; Sugimoto, T. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor-immunoreactive primary sensory neurons in the rat trigeminal ganglion and trigeminal sensory nuclei. Brain Res. 2006, 1081, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buldyrev, I.; Tanner, N.M.; Hsieh, H.y.; Dodd, E.G.; Nguyen, L.T.; Balkowiec, A. Calcitonin gene-related peptide enhances release of native brain-derived neurotrophic factor from trigeminal ganglion neurons. Journal of Neurochemistry 2006, 99, 1338–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usoskin, D.; Furlan, A.; Islam, S.; Abdo, H.; Lonnerberg, P.; Lou, D.; Hjerling-Leffler, J.; Haeggstrom, J.; Kharchenko, O.; Kharchenko, P.V.; et al. Unbiased classification of sensory neuron types by large-scale single-cell RNA sequencing. Nat.Neurosci. 2015, 18, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kollarik, M.; Ru, F.; Sun, H.; McNeil, B.; Dong, X.; Stephens, G.; Korolevich, S.; Brohawn, P.; Kolbeck, R.; et al. Distinct and common expression of receptors for inflammatory mediators in vagal nodose versus jugular capsaicin-sensitive/TRPV1-positive neurons detected by low input RNA sequencing. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0185985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta, T.S.; Haider, B.; Adamovich-Zeitlin, R.; Chen, A.C.; Chaudhry, S.; Zanos, T.P. Calcium imaging and analysis of the jugular-nodose ganglia enables identification of distinct vagal sensory neuron subsets. 2023, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, R.; Zaidi, S.I.; Mayer, C.; Katz, D.M. BDNF is a target-derived survival factor for arterial baroreceptor and chemoafferent primary sensory neurons. J Neurosci 1999, 19, 2131–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, C.G.; Hasser, E.M.; Kunze, D.L.; Katz, D.M.; Kline, D.D. Endogenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the nucleus tractus solitarius tonically regulates synaptic and autonomic function. J Neurosci 2011, 31, 12318–12329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, K.; Lin, W.K.; Rancillac, A.; Fan, M.; Snollaerts, T.; Sordoillet, V.; Hamon, M.; Smith, G.M.; Lenkei, Z.; Pezet, S. BDNF-dependent plasticity induced by peripheral inflammation in the primary sensory and the cingulate cortex triggers cold allodynia and reveals a major role for endogenous BDNF as a tuner of the affective aspect of pain. J Neurosci 2014, 34, 14739–14751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Ma, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, M. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the rostral anterior cingulate cortex (rACC) contributes to neuropathic spontaneous pain-related aversion via NR2B receptors. Brain Res Bull 2016, 127, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Chen, B.; Jia, G.; Xu, R.; Xia, Y.; Lai, C.; Li, G.; Li, W.; Han, Y. Reduced BDNF expression in the auditory cortex contributed to neonatal pain-induced hearing impairment and dendritic pruning deficiency in mice. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2023, 48, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Yue, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Han, B.; Cui, S.; Liu, F.Y.; Wan, Y.; Yi, M. Spontaneous Pain Disrupts Ventral Hippocampal CA1-Infralimbic Cortex Connectivity and Modulates Pain Progression in Rats with Peripheral Inflammation. Cell Rep 2019, 29, 1579–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, E.K.; Bian, Z.X.; Xu, H.X.; Sung, J.J. Neonatal maternal separation increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor and tyrosine kinase receptor B expression in the descending pain modulatory system. Neurosignals 2009, 17, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Liu, R.; Guo, F.; Wen, M.Q.; Ma, X.L.; Li, K.Y.; Sun, H.; Xu, C.L. Parabrachial nucleus circuit governs neuropathic pain-like behavior. 2020, 11, 5974. [CrossRef]
- Sarhan, M.; Pawlowski, S.A.; Barthas, F.; Yalcin, I.; Kaufling, J.; Dardente, H.; Zachariou, V.; Dileone, R.J.; Barrot, M.; Veinante, P. BDNF parabrachio-amygdaloid pathway in morphine-induced analgesia. Int.J.Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 16, 1649–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, K.; Yamanaka, H.; Dai, Y.; Tachibana, T.; Fukuoka, T. Differential activation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase in primary afferent neurons regulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression after peripheral inflammation and nerve injury. J.Neurosci. 2003, 23, 4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, L.-y.; Gulick, M.A.; Bowers, J.; Kuemmerle, J.F.; Grider, J.R. Differential changes in brain-derived neurotrophic factor and extracellular signal-regulated kinase in rat primary afferent pathways with colitis. Neurogastroenterology & Motility 2008, 20, 928–938. [Google Scholar]
- Garraway, S.M.; Petruska, J.C.; Mendell, L.M. BDNF sensitizes the response of lamina II neurons to high threshold primary afferent inputs. Eur.J Neurosci. 2003, 18, 2467–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garraway, S.M.; Anderson, A.J.; Mendell, L.M. BDNF-induced facilitation of afferent-evoked responses in lamina II neurons is reduced after neonatal spinal cord contusion injury. J.Neurophysiol. 2005, 94, 1798–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaksh, T.L. Calcium Channels As Therapeutic Targets in Neuropathic Pain. The Journal of Pain 2006, 7, S13–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garraway, S.M.; Huie, J.R. Spinal Plasticity and Behavior: BDNF-Induced Neuromodulation in Uninjured and Injured Spinal Cord. Neural Plast 2016, 2016, 9857201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezet, S.; Malcangio, M.; McMahon, S.B. BDNF: a neuromodulator in nociceptive pathways? Brain Res.Brain Res.Rev. 2002, 40, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merighi, A.; Carmignoto, G.; Gobbo, S.; Lossi, L.; Salio, C.; Vergnano, A.M.; Zonta, M. Neurotrophins in spinal cord nociceptive pathways. Prog.Brain Res. 2004, 146, 291–321. [Google Scholar]
- Pezet, S.; McMahon, S.B. NEUROTROPHINS: Mediators and Modulators of Pain. Annual Review of Neuroscience 2006, 29, 507–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembo, T.; Braz, J.M. Primary Afferent-Derived BDNF Contributes Minimally to the Processing of Pain and Itch. 2018, 5. [CrossRef]
- Lossi, L.; Merighi, A. The Use of ex Vivo Rodent Platforms in Neuroscience Translational Research With Attention to the 3Rs Philosophy. Frontiers in Veterinary Science 2018, 5, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, V.B.; Moran, T.D.; Balasubramanyan, S.; Alier, K.A.; Dryden, W.F.; Colmers, W.F.; Smith, P.A. Substantia Gelatinosa neurons in defined-medium organotypic slice culture are similar to those in acute slices from young adult rats. Pain. 2006, 121, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, B.J.; Bradbury, E.J.; Bennett, D.L.; Trivedi, P.M.; Dassan, P.; French, J.; Shelton, D.B.; McMahon, S.B.; Thompson, S.W. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor modulates nociceptive sensory inputs and NMDA-evoked responses in the rat spinal cord. J Neurosci. 1999, 19, 5138–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Walwyn, W.; Ennes, H.S.; Kim, H.; McRoberts, J.A.; Marvizón, J.C. BDNF released during neuropathic pain potentiates NMDA receptors in primary afferent terminals. Eur J Neurosci 2014, 39, 1439–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biggs, J.E.; Lu, V.B.; Kim, H.J.; Lai, A.; Todd, K.G.; Ballanyi, K.; Colmers, W.F.; Smith, P.A. Defined Medium Organotypic Cultures of Spinal Cord Put ‘Pain in a Dish’. In Isolated Central Nervous System Circuits; Ballanyi, K., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, 2012; pp. 405–436. [Google Scholar]
- Biggs, J.E.; Lu, V.B.; Stebbing, M.J.; Balasubramanyan, S.; Smith, P.A. Is BDNF sufficient for information transfer between microglia and dorsal horn neurons during the onset of central sensitization? Mol.Pain 2010, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.A. BDNF: No gain without pain? Neuroscience 2014, 283, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Lei, Y.; Tian, Y.; Xu, S.; Shen, X.; Wu, H.; Bao, S.; Wang, F. The etiological contribution of GABAergic plasticity to the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain. Mol Pain 2019, 15, 1744806919847366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezet, S.; Cunningham, J.; Patel, J.; Grist, J.; Gavazzi, I.; Lever, I.J.; Malcangio, M. BDNF modulates sensory neuron synaptic activity by a facilitation of GABA transmission in the dorsal horn. Mol.Cell Neurosci. 2002, 21, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardoni, R.; Ghirri, A.; Salio, C.; Prandini, M.; Merighi, A. BDNF-mediated modulation of GABA and glycine release in dorsal horn lamina II from postnatal rats. Dev.Neurobiol. 2007, 67, 960–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, V.B.; Colmers, W.F.; Smith, P.A. Long-term actions of BDNF on inhibitory synaptic transmission in identified neurons of the rat substantia gelatinosa. Journal of Neurophysiology 2012, 108, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedek, A.; Xu, J.; Lorenzo, L.; Godin, A.G.; Kandegedara, C.M.; Glavina, G.; Landrigan, J.A.; Lombroso, P.J.; De Koninck, Y.; Tsai, E.C.; et al. Sexual dimorphism in a neuronal mechanism of spinal hyperexcitability across rodent and human models of pathological pain. Brain 2022, 145, 1124–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Seereeram, A.; Nassar, M.A.; Levato, A.; Pezet, S. Nociceptor-derived brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates acute and inflammatory but not neuropathic pain. Mol.Cell Neurosci. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groth, R.; Aanonsen, L. Spinal brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) produces hyperalgesia in normal mice while antisense directed against either BDNF or trkB, prevent inflammation-induced hyperalgesia. Pain 2002, 100, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slack, S.E.; Thompson, S.W. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces NMDA receptor 1 phosphorylation in rat spinal cord. Neuroreport 2002, 13, 1967–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matayoshi, S.; Jiang, N.; Katafuchi, T.; Koga, K.; Furue, H.; Yasaka, T.; Nakatsuka, T.; Zhou, X.F.; Kawasaki, Y.; Tanaka, N.; et al. Actions of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on spinal nociceptive transmission during inflammation in the rat. J.Physiol. 2005, 569, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalisse, S.; Hua, J.; Lenoir, M.; Linck, N.; Rassendren, F. Sensory neuronal P2RX4 receptors controls BDNF signaling in inflammatory pain. 2018, 8, 964. [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.K.; Noble, D.J.; Parvin, S.; Jang, K.; Garraway, S.M. Pharmacogenetic inhibition of TrkB signaling in adult mice attenuates mechanical hypersensitivity and improves locomotor function after spinal cord injury. Front Cell Neurosci 2022, 16, 987236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonomini, F.; Favero, G.; Castrezzati, S.; Borsani, E. Role of Neurotrophins in Orofacial Pain Modulation: A Review of the Latest Discoveries. International journal of molecular sciences 2023, 24, 12438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradnam, L.; Barry, C. The role of the trigeminal sensory nuclear complex in the pathophysiology of craniocervical dystonia. J Neurosci 2013, 33, 18358–18367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, M.; Takahashi, M.; Kitagawa, J.; Kanazawa, T.; Nasu, M.; Matsumoto, S. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhances the excitability of small-diameter trigeminal ganglion neurons projecting to the trigeminal nucleus interpolaris/caudalis transition zone following masseter muscle inflammation. Mol Pain 2013, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayson, M.; Arris, D. Oral squamous cell carcinoma-released brain-derived neurotrophic factor contributes to oral cancer pain by peripheral tropomyosin receptor kinase B activation. 2022, 163, 496–507. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wei, Y.; Pu, Y.; Jiang, D.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, J. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulation of T-type Ca<sup>2+</sup> channels in sensory neurons contributes to increased peripheral pain sensitivity. Science signaling 2019, 12, eaaw2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chung, M.-K. Orthodontic force induces nerve injury-like transcriptomic changes driven by TRPV1-expressing afferents in mouse trigeminal ganglia. Molecular Pain 2020, 16, 1744806920973141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshida, T.; Maruta, T.; Tanaka, N.; Hidaka, K.; Kurogi, M.; Nemoto, T.; Yanagita, T.; Takeya, R.; Tsuneyoshi, I. Changes in TRPV1 Receptor, CGRP, and BDNF Expression in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion with Resiniferatoxin-Induced Neuropathic Pain: Modulation by Pulsed Radiofrequency Applied to the Sciatic Nerve. Acta Med Okayama 2023, 77, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooshki, R.; Abbasnejad, M.; Mahani, S.E.; Raoof, M.; Aghtaei, M.M.M.; Dabiri, S. Orexin-A inhibits capsaicin-induced changes in cyclooxygenase-2 and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in trigeminal nucleus caudalis of rats. Korean J Pain 2018, 31, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarabelot, V.L.; de Oliveira, C.; Medeiros, L.F.; de Macedo, I.C.; Cioato, S.G.; Adachi, L.N.S.; Paz, A.H.; de Souza, A.; Caumo, W.; Torres, I.L.S. Transcranial direct-current stimulation reduces nociceptive behaviour in an orofacial pain model. J Oral Rehabil 2019, 46, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Z. PACAP6-38 improves nitroglycerin-induced central sensitization by modulating synaptic plasticity at the trigeminal nucleus caudalis in a male rat model of chronic migraine. The Journal of Headache and Pain 2023, 24, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, L.; Li, M.; Wang, S.; Long, T.; He, W.; Kong, X.; Qin, G.; et al. P2X4-receptor participates in EAAT3 regulation via BDNF-TrkB signaling in a model of trigeminal allodynia. Mol Pain 2018, 14, 1744806918795930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Zhong, X.L.; Zhou, F.H.; Li, J.Y.; Zhou, P.; Xu, J.M.; Song, B.; Li, C.Q.; Zhou, X.F.; Dai, R.P. Peripheral Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor Precursor Regulates Pain as an Inflammatory Mediator. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 27171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkowiec, A.; Katz, D.M. Activity-dependent release of endogenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor from primary sensory neurons detected by ELISA in situ. J Neurosci. 2000, 20, 7417–7423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Ieraci, A.; Teng, H.; Dall, H.; Meng, C.X.; Herrera, D.G.; Nykjaer, A.; Hempstead, B.L.; Lee, F.S. Sortilin controls intracellular sorting of brain-derived neurotrophic factor to the regulated secretory pathway. J Neurosci 2005, 25, 6156–6166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, I.H.T.; Liu, X.; Zou, Y.; Liu, T.; Hu, W.; Chan, H.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Kou, S.; et al. A Novel Peptide Interfering with proBDNF-Sortilin Interaction Alleviates Chronic Inflammatory Pain. Theranostics 2019, 9, 1651–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.R.; Ding, H.J.; Yu, M.; Zhou, F.H.; Han, C.Y.; Liang, R.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Meng, F.J.; Wang, S.; et al. proBDNF/p75NTR promotes rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory response by activating proinflammatory cytokines. Faseb j 2022, 36, e22180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liu, T.; Sun, J.; Zhao, S. Up-Regulation of ProBDNF/p75(NTR) Signaling in Spinal Cord Drives Inflammatory Pain in Male Rats. 2023, 16, 95–107. [CrossRef]
- Theodosiou, M.; Rush, A.R.; Zhou, F.X.; Hu, D.; Walker, S.J.; Tracey, J.D. Hyperalgesia due to nerve damage: role of nerve growth factor. Pain 1999, 81, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yajima, Y.; Narita, M.; Narita, M.; Matsumoto, N.; Suzuki, T. Involvement of a spinal brain-derived neurotrophic factor/full-length TrkB pathway in the development of nerve injury-induced thermal hyperalgesia in mice. Brain Res. 2002, 958, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yajima, Y.; Narita, M.; Usui, A.; Kaneko, C.; Miyatake, M. Direct evidence for the involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the development of a neuropathic pain-like state in mice. J.Neurochem. 2005, 93, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.F.; Deng, Y.S.; Xian, C.J.; Zhong, J.H. Neurotrophins from dorsal root ganglia trigger allodynia after spinal nerve injury in rats. Eur.J.Neurosci. 2000, 12, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, S.J.; Liao, F.F.; Dang, W.H.; Ding, X.; Liu, X.D.; Cai, J.; Han, J.S.; Wan, Y.; Xing, G.G. Contribution of the spinal cord BDNF to the development of neuropathic pain by activation of the NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in rats with spinal nerve ligation. Exp Neurol 2010, 222, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miletic, G.; Miletic, V. Increases in the concentration of brain derived neurotrophic factor in the lumbar spinal dorsal horn are associated with pain behavior following chronic constriction injury in rats. Neurosci.Lett. 2002, 319, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obata, K.; Yamanaka, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Dai, Y.; Mizushima, T.; Katsura, H.; Fukuoka, T.; Tokunaga, A.; Noguchi, K. Role of mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in injured and intact primary afferent neurons for mechanical and heat hypersensitivity after spinal nerve ligation. J Neurosci 2004, 24, 10211–10222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, K.; Noguchi, K. BDNF in sensory neurons and chronic pain. Neurosci.Res. 2006, 55, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, K.; Yamanaka, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Dai, Y.; Mizushima, T.; Katsura, H.; Fukuoka, T.; Tokunaga, A.; Noguchi, K. The effect of site and type of nerve injury on the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the dorsal root ganglion and on neuropathic pain behavior. Neuroscience 2006, 137, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanelderen, P.; Rouwette, T.; Kozicz, T.; Roubos, E.; Van Zundert, J.; Heylen, R.; Vissers, K. The role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in different animal models of neuropathic pain. Eur J Pain 2010, 14, 473.e471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.M.; Mitchell, V.A.; White, D.M.; Rush, R.A.; Duggan, A.W. Release of immunoreactive brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the spinal cord of the rat following sciatic nerve transection. Brain Res 2001, 899, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Cai, J.; Li, S.; Liu, X.D.; Wan, Y.; Xing, G.G. BDNF contributes to the development of neuropathic pain by induction of spinal long-term potentiation via SHP2 associated GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors activation in rats with spinal nerve ligation. Neurobiol Dis 2015, 73, 428–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, M.E.; Xu, J.; Dedek, A.; Li, Y.; Sengar, A.S.; Beggs, S.; Lombroso, P.J.; Salter, M.W. Potentiation of Synaptic GluN2B NMDAR Currents by Fyn Kinase Is Gated through BDNF-Mediated Disinhibition in Spinal Pain Processing. Cell Reports 2016, 17, 2753–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedek, A.; Xu, J.; Kandegedara, C.M.; Lorenzo, L.; Godin, A.G.; De Koninck, Y.; Lombroso, P.J.; Tsai, E.C.; Hildebrand, M.E. Loss of STEP61 couples disinhibition to N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor potentiation in rodent and human spinal pain processing. Brain 2019, 142, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.T.; Guo, D.; Campanelli, D.; Frattini, F.; Mayer, F.; Zhou, L.; Kuner, R.; Heppenstall, P.A.; Knipper, M.; Hu, J. Presynaptic GABAergic inhibition regulated by BDNF contributes to neuropathic pain induction. Nat Commun 2014, 5, 5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.Y.; Hsieh, M.C.; Yeh, C.M.; Yang, P.S.; Cheng, J.K.; Wang, H.H.; Lin, K.H.; Nie, S.T.; Lin, T.B.; Peng, H.Y. MicroRNA-489-3p attenuates neuropathic allodynia by regulating oncoprotein DEK/TET1-dependent epigenetic modification in the dorsal horn. Neuropharmacology 2022, 210, 109028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phạm, T.L.; Noh, C.; Neupane, C.; Sharma, R.; Shin, H.J.; Park, K.D.; Lee, C.J.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, J.B. MAO-B Inhibitor, KDS2010, Alleviates Spinal Nerve Ligation-induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats Through Competitively Blocking the BDNF/TrkB/NR2B Signaling. J Pain 2022, 23, 2092–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Guo, H.; Liu, P.; Ma, M.; Wang, Y. Resolvin D1 attenuates mechanical allodynia after burn injury: Involvement of spinal glia, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor/tropomyosin-related kinase B signaling. Mol Pain 2023, 19, 17448069231159970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Liu, F.; Fang, Z.H.; Li, Y.L.; Liao, H.L.; Song, Q.X.; Zhou, C.; Shen, J.F. Differential roles of NMDAR subunits 2A and 2B in mediating peripheral and central sensitization contributing to orofacial neuropathic pain. Brain, behavior, and immunity 2022, 106, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finamor, F.; Scarabelot, V.L.; Medeiros, L.F.; Stein, D.J.; da Silva, M.D.; Callai, E.; Caumo, W.; de Souza, A.; Torres, I.L.S. Involvement of GABAergic, glutamatergic, opioidergic, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor systems in the trigeminal neuropathic pain process. Neuroscience Letters 2023, 793, 136970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, C.L.; Medeiros, L.F.; de Souza, V.S.; Lopes, B.C.; de Oliveira, F.F.; Marques, L.X.; da Silva Torres, I.L.; de Souza, A. LOW-DOSE NALTREXONE REVERSES FACIAL MECHANICAL ALLODYNIA IN A RAT MODEL OF TRIGEMINAL NEURALGIA. Neurosci Lett 2020, 736, 135248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Xu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Bai, Q.; Li, Z. The cAMP Response Element- Binding Protein/Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Pathway in Anterior Cingulate Cortex Regulates Neuropathic Pain and Anxiodepression Like Behaviors in Rats. Front Mol Neurosci 2022, 15, 831151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakkar, B.; Acevedo, E.O. BDNF as a biomarker for neuropathic pain: Consideration of mechanisms of action and associated measurement challenges. Brain Behav 2023, 13, e2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malcangio, M. Microglia and chronic pain. PAIN 2016, 157, 1002–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.-R.; Berta, T.; Nedergaard, M. Glia and pain: Is chronic pain a gliopathy? PAIN 2013, 154, S10–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apfel, S.C.; Wright, D.E.; Wiideman, A.M.; Dormia, C.; Snider, W.D.; Kessler, J.A. Nerve growth factor regulates the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA in the peripheral nervous system. Mol.Cell Neurosci. 1996, 7, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coull, J.A.; Beggs, S.; Boudreau, D.; Boivin, D.; Tsuda, M. BDNF from microglia causes the shift in neuronal anion gradient underlying neuropathic pain. Nature 2005, 438, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmann, L.; Hatcher, J.P.; Hughes, J.P.; Chaumont, S.; Green, P.J.; Conquet, F.; Buell, G.N.; Reeve, A.J.; Chessell, I.P.; Rassendren, F. Up-regulation of P2X4 receptors in spinal microglia after peripheral nerve injury mediates BDNF release and neuropathic pain. J Neurosci 2008, 28, 11263–11268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boakye, P.A.; Tang, S.J.; Smith, P.A. Mediators of Neuropathic Pain; Focus on Spinal Microglia, CSF-1, BDNF, CCL21, TNF-α, Wnt Ligands, and Interleukin 1β. Front Pain Res (Lausanne) 2021, 2, 698157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofroniew, M.V.; Vinters, H.V. Astrocytes: biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol 2010, 119, 7–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albini, M.; Krawczun-Rygmaczewska, A.; Cesca, F. Astrocytes and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Neuroscience Research 2023, 197, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.; Gould, E.; Xu, J.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, J.H. Oligodendrocytes regulate presynaptic properties and neurotransmission through BDNF signaling in the mouse brainstem. 2019, 8. [CrossRef]
- Atta, A.A.; Ibrahim, W.W.; Mohamed, A.F.; Abdelkader, N.F. Microglia polarization in nociplastic pain: mechanisms and perspectives. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 1053–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcangio, M. Role of the immune system in neuropathic pain. Scandinavian Journal of Pain 2020, 20, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, T.; Beggs, S.; Wan, X.; Salter, M.W. P2X4-receptor-mediated synthesis and release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in microglia is dependent on calcium and p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J Neurosci 2009, 29, 3518–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonalume, V.; Caffino, L.; Castelnovo, L.F.; Faroni, A.; Giavarini, F.; Liu, S.; Caruso, D.; Schmelz, M.; Fumagalli, F.; Carr, R.W.; et al. Schwann Cell Autocrine and Paracrine Regulatory Mechanisms, Mediated by Allopregnanolone and BDNF, Modulate PKCε in Peripheral Sensory Neurons. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, C.A.N.; Suppian, R.; Ab Aziz, C.B.; Long, I. Ifenprodil Reduced Expression of Activated Microglia, BDNF and DREAM Proteins in the Spinal Cord Following Formalin Injection During the Early Stage of Painful Diabetic Neuropathy in Rats. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience 2021, 71, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, L.; Done, J.D.; Schaeffer, A.J.; Thumbikat, P. Experimental autoimmune prostatitis induces microglial activation in the spinal cord. The Prostate 2015, 75, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.-t.; Wu, J.-r.; Chen, Z.-y.; Liu, Z.-x.; Miao, B. Effects of dexmedetomidine on P2X4Rs, p38-MAPK and BDNF in spinal microglia in rats with spared nerve injury. Brain Research 2014, 1568, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Jin, J.; Chen, K.; You, S.; Zhang, H.; Sideris, A.; Norcini, M.; Recio-Pinto, E.; Wang, J.; Gan, W.B.; et al. BDNF produced by cerebral microglia promotes cortical plasticity and pain hypersensitivity after peripheral nerve injury. PLoS Biol 2021, 19, e3001337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harty, B.L.; Monk, K.R. Unwrapping the unappreciated: recent progress in Remak Schwann cell biology. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2017, 47, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.F.; Wu, F.; Jin, Z.H.; Gu, Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Fei, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.X.; Xing, L.Y.; Zhao, Y.Y.; et al. Overexpression of P2X4 receptor in Schwann cells promotes motor and sensory functional recovery and remyelination via BDNF secretion after nerve injury. Glia 2019, 67, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez, K.T.; Mohammad, H.; Sweitzer, S.M. Protein kinase C in pain: involvement of multiple isoforms. Pharmacol Res 2007, 55, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.-Y.; Zhou, T.-H.; Chen, B.-K.; Liu, Z.-X. Schwann cells and trigeminal neuralgia. Molecular Pain 2020, 16, 1744806920963809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crotti, A.; Ransohoff, R.M. Microglial Physiology and Pathophysiology: Insights from Genome-wide Transcriptional Profiling. Immunity 2016, 44, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Qadri, Y.J.; Serhan, C.N.; Ji, R.R. Microglia in Pain: Detrimental and Protective Roles in Pathogenesis and Resolution of Pain. Neuron 2018, 100, 1292–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber-Schoffnegger, D.; Drdla-Schutting, R.; Hönigsperger, C.; Wunderbaldinger, G.; Gassner, M.; Sandkühler, J. Induction of thermal hyperalgesia and synaptic long-term potentiation in the spinal cord lamina I by TNF-α and IL-1β is mediated by glial cells. J Neurosci 2013, 33, 6540–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decosterd, I.; Ji, R.-R.; Suter, M.R.; Wen, Y.-R. Do glial cells control pain? Neuron Glia Biology 2007, 3, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrini, F.; De Koninck, Y. Microglia control neuronal network excitability via BDNF signalling. Neural Plast 2013, 2013, 429815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boakye, P.A.; Rancic, V.; Whitlock, K.H.; Simmons, D.; Longo, F.M.; Ballanyi, K.; Smith, P.A. Receptor dependence of BDNF actions in superficial dorsal horn: relation to central sensitization and actions of macrophage colony stimulating factor 1. J Neurophysiol 2019, 121, 2308–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, V.B.; Ballanyi, K.; Colmers, W.F.; Smith, P.A. Neuron type-specific effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rat superficial dorsal horn and their relevance to ‘central sensitization’. J Physiol 2007, 584, 543–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, V.B.; Biggs, J.E.; Stebbing, M.J.; Balasubramanyan, S.; Todd, K.G.; Lai, A.Y.; Colmers, W.F.; Dawbarn, D.; Ballanyi, K.; Smith, P.A. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor drives the changes in excitatory synaptic transmission in the rat superficial dorsal horn that follow sciatic nerve injury. J Physiol 2009, 587, 1013–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, H.; Ji, R.R.; Kohno, T.; Moore, K.A.; Ataka, T.; Wakai, A.; Okamoto, M.; Woolf, C.J. Removal of GABAergic inhibition facilitates polysynaptic A fiber-mediated excitatory transmission to the superficial spinal dorsal horn. Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience 2003, 24, 818–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Yu, X.; Chen, P.; Jin, K.; Zhou, J.; Wang, G.; Yu, J.; Wu, T.; Wang, Y.; Lin, F.; et al. BDNF-TrkB signaling pathway-mediated microglial activation induces neuronal KCC2 downregulation contributing to dynamic allodynia following spared nerve injury. Mol Pain 2023, 19, 17448069231185439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarei, M.; Sabetkasaei, M.; Moini Zanjani, T.; Sahebi Vaighan, N. The effect of microglial inhibition on the expression of BDNF, KCC2, and GABAA receptor before and after the establishment of CCI-induced neuropathic pain model. Fundamental & Clinical Pharmacology 2022, 36, 277–285. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.J.; Peng, J.; Xu, Y.N.; Zeng, W.J.; Zhang, J.; Wei, X.; Mai, C.L.; Lin, Z.J.; Liu, Y.; Murugan, M.; et al. Microglia Are Indispensable for Synaptic Plasticity in the Spinal Dorsal Horn and Chronic Pain. Cell Rep 2019, 27, 3844–3859.e3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapplebeck, J.C.S.; Beggs, S.; Salter, M.W. Sex differences in pain: a tale of two immune cells. PAIN 2016, 157, S2–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paige, C.; Plasencia-Fernandez, I.; Kume, M.; Papalampropoulou-Tsiridou, M.; Lorenzo, L.E.; David, E.T.; He, L.; Mejia, G.L.; Driskill, C.; Ferrini, F.; et al. A Female-Specific Role for Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP) in Rodent Pain Models. J Neurosci 2022, 42, 1930–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardell, L.R.; Vanderah, T.W.; Gardell, S.E.; Wang, R.; Ossipov, M.H.; Lai, J.; Porreca, F. Enhanced Evoked Excitatory Transmitter Release in Experimental Neuropathy Requires Descending Facilitation. The Journal of Neuroscience 2003, 23, 8370–8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Chen, J.; Su, M.; Lin, Z.; Zhan, H.; Yang, F.; Li, W.; Xie, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. BDNF promotes activation of astrocytes and microglia contributing to neuroinflammation and mechanical allodynia in cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis. J Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, L.; Xu, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Huang, W. Interaction between astrocytic colony stimulating factor and its receptor on microglia mediates central sensitization and behavioral hypersensitivity in chronic post ischemic pain model. Brain, behavior, and immunity 2018, 68, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Z.; Kuhn, J.A.; Wang, X.; Colquitt, B.; Solorzano, C.; Vaman, S.; Guan, A.K.; Evans-Reinsch, Z.; Braz, J.; Devor, M.; et al. Injured sensory neuron-derived CSF1 induces microglial proliferation and DAP12-dependent pain. 2016, 19, 94–101. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhong, L.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, W.; Tang, S.J. Neuron activity-induced Wnt signaling up-regulates expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the pain neural circuit. 2018, 293, 15641–15651. [CrossRef]
- Charles, A.C.; Merrill, J.E.; Dirksen, E.R.; Sanderson, M.J. Intercellular signaling in glial cells: calcium waves and oscillations in response to mechanical stimulation and glutamate. Neuron 1991, 6, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedergaard, M.; Ransom, B.; Goldman, S.A. New roles for astrocytes: redefining the functional architecture of the brain. Trends Neurosci 2003, 26, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafra, F.; Lindholm, D.; Castren, E.; Hartikka, J.; Thoenen, H. Regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor mRNA in primary cultures of hippocampal neurons and astrocytes. The Journal of Neuroscience 1992, 12, 4793–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.P.; Sheng, J.G.; Mitsuo, K.; Shirabe, S.; Nishiyama, N. Trophic factor production by reactive astrocytes in injured brain. Ann.NY Acad.Sci. 1993, 679, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, J.P.; Nishiyama, N. Neurotrophic factor gene expression in astrocytes during development and following injury. Brain Research Bulletin 1994, 35, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderson, R.F.; Curtis, R.; Alterman, A.L.; Lindsay, R.M.; DiStefano, P.S. Truncated TrkB mediates the endocytosis and release of BDNF and neurotrophin-4/5 by rat astrocytes and Schwann cells in vitro. Brain Research 2000, 871, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Matyas, J.J.; Renn, C.L. Function and Mechanisms of Truncated BDNF Receptor TrkB. T1 in Neuropathic Pain. 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinboshi, M.; Mukai, T.; Nagao, Y.; Matsuba, Y.; Tsuji, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Tokudome, K.; Shimizu, S.; Ito, H.; Ikeda, A.; et al. Inhibition of Inwardly Rectifying Potassium (Kir) 4.1 Channels Facilitates Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Expression in Astrocytes. Frontiers in molecular neuroscience 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milligan, E.D.; Watkins, L.R. Pathological and protective roles of glia in chronic pain. Nat Rev Neurosci 2009, 10, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renn, C.L.; Leitch, C.C.; Dorsey, S.G. In Vivo Evidence that Truncated Trkb.T1 Participates in Nociception. Molecular Pain 2009, 5, 1744–8069–1745-1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Renn, C.L.; Faden, A.I.; Dorsey, S.G. TrkB.T1 contributes to neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury through regulation of cell cycle pathways. J Neurosci 2013, 33, 12447–12463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyas, J.J.; O’Driscoll, C.M.; Yu, L. Truncated TrkB.T1-Mediated Astrocyte Dysfunction Contributes to Impaired Motor Function and Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury. 2017, 37, 3956–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.; Shao, L.; Jiang, G.-T.; Min, J.-W.; Mei, X.-Y.; He, X.-H.; Liu, W.-H.; Huang, W.-X.; Peng, B.-W. TRPV1 mediates astrocyte activation and interleukin-1β release induced by hypoxic ischemia (HI). Journal of Neuroinflammation 2019, 16, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradl, M.; Lassmann, H. Oligodendrocytes: biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol 2010, 119, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, K.D.; Dreyfus, C.F.; Black, I.B. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglia/macrophages after spinal cord injury. Neurobiol Dis 2000, 7, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malta, I.; Moraes, T.; Rodrigues, G.; Franco, P.; Galdino, G. The role of oligodendrocytes in chronic pain: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Journal of physiology and pharmacology: An official journal of the Polish Physiological Society 2019, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Dubner, R. Interactions between the immune and nervous systems in pain. Nat Med 2010, 16, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahashi, T.; Fujimura, H.; Altar, C.A.; Li, J.; Kambayashi, J.; Tandon, N.N.; Sun, B. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize and secrete brain-derived neurotrophic factor. FEBS Lett 2000, 470, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.A. Neuropathic pain; what we know and what we should do about it. Frontiers in pain research (Lausanne, Switzerland) 2023, 4, 1220034. [CrossRef]
- Dimmek, D.J.; Korallus, C.; Buyny, S.; Christoph, G.; Lichtinghagen, R.; Jacobs, R. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Immune Cells in Osteoarthritis, Chronic Low Back Pain, and Chronic Widespread Pain Patients: Association with Anxiety and Depression. 2021, 57. [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-R.; Ding, H.-J.; Yu, M.; Zhou, F.-H.; Han, C.-Y.; Liang, R.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Zhang, X.-L.; Meng, F.-J.; Wang, S.; et al. proBDNF/p75NTR promotes rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory response by activating proinflammatory cytokines. The FASEB Journal 2022, 36, e22180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staszkiewicz, R.; Gładysz, D.; Gralewski, M.; Garczarek, M.; Gadzieliński, M.; Grabarek, B.O. Pathomechanism of the IVDs Degeneration and the Role of Neurotrophic Factors and Concentration of Selected Elements in Genesis of Low Back Pain. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 2023, 24, 1164–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisiewski, L.E.; Jacobsen, H.E.; Viola, D.C.M.; Kenawy, H.M.; Kiridly, D.N.; Chahine, N.O. Intradiscal inflammatory stimulation induces spinal pain behavior and intervertebral disc degeneration in vivo. The FASEB Journal 2024, 38, e23364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheorghe, R.O.; Grosu, A.V.; Magercu, M.; Ghenghea, M.S.; Zbarcea, C.E.; Tanase, A.; Negres, S.; Filippi, A.; Chiritoiu, G.; Gherghiceanu, M.; et al. Switching Rat Resident Macrophages from M1 to M2 Phenotype by Iba1 Silencing Has Analgesic Effects in SNL-Induced Neuropathic Pain. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Y.; Muley, M.M.; Beggs, S.; Salter, M.W. Microglia-independent peripheral neuropathic pain in male and female mice. Pain 2022, 163, e1129–e1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buskila, D. Genetics of chronic pain states. Best practice & research clinical rheumatology 2007, 21, 535–547. [Google Scholar]
- Fillingim, R.; Wallace, M.; Herbstman, D.; Ribeiro-Dasilva, M.; Staud, R. Genetic contributions to pain: a review of findings in humans. Oral Diseases 2008, 14, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappoli, N.; Tabolacci, E.; Aceto, P.; Dello Russo, C. The emerging role of the BDNF-TrkB signaling pathway in the modulation of pain perception. Journal of neuroimmunology 2020, 349, 577406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, M.F.; Kojima, M.; Callicott, J.H.; Goldberg, T.E.; Kolachana, B.S.; Bertolino, A.; Zaitsev, E.; Gold, B.; Goldman, D.; Dean, M.; et al. The BDNF val66met polymorphism affects activity-dependent secretion of BDNF and human memory and hippocampal function. Cell 2003, 112, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempstead, B.L. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor: Three Ligands, Many Actions. Transactions of the American Clinical and Climatological Association 2015, 126, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, X.; Jia, M.; Yu, H.; Lichtner, P.; Shi, Y.; Meng, Z.; Kou, S.; Ho, I.H.T.; Jia, B.; et al. Targeted Genotyping Identifies Susceptibility Locus in Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor Gene for Chronic Postsurgical Pain. Anesthesiology 2018, 128, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossen, H.; Kenis, G.; Rutten, B.; van Os, J.; Hermens, H.; Lousberg, R. The Genetic Influence on the Cortical Processing of Experimental Pain and the Moderating Effect of Pain Status. PLOS ONE 2010, 5, e13641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polli, A.; Ghosh, M.; Bakusic, J.; Ickmans, K.; Monteyne, D.; Velkeniers, B.; Bekaert, B.; Godderis, L.; Nijs, J. DNA Methylation and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Expression Account for Symptoms and Widespread Hyperalgesia in Patients With Chronic Fatigue Syndrome and Comorbid Fibromyalgia. Arthritis & Rheumatology 2020, 72, 1936–1944. [Google Scholar]
- Chau, C.M.; Cepeda, I.L.; Devlin, A.M.; Weinberg, J.; Grunau, R.E. The Val66Met brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene variant interacts with early pain exposure to predict cortisol dysregulation in 7-year-old children born very preterm: Implications for cognition. Neuroscience 2017, 342, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, D.D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Lee, F.S.; Chen, Z.Y. Variant brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism alters vulnerability to stress and response to antidepressants. J.Neurosci. 2012, 32, 4092–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, F.T.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Rebello-Sanchez, I.; Castelo-Branco, L.; de Melo, P.S.; Parente, J.; Cardenas-Rojas, A.; Firigato, I.; Pessotto, A.V.; Imamura, M.; et al. Association of Mu opioid receptor (A118G) and BDNF (G196A) polymorphisms with rehabilitation-induced cortical inhibition and analgesic response in chronic osteoarthritis pain. International journal of clinical and health psychology: IJCHP 2023, 23, 100330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, F.T.; Marques, L.M.; Pessotto, A.V.; Barbosa, S.P.; Imamura, M.; Simis, M.; Fregni, F.; Battistella, L. OPRM1 and BDNF polymorphisms associated with a compensatory neurophysiologic signature in knee osteoarthritis patients. Neurophysiologie clinique = Clinical neurophysiology 2023, 53, 102917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, L.P.; Medeiros, L.F. Fibromyalgia: A Review of Related Polymorphisms and Clinical Relevance. 2021, 93, e20210618. [CrossRef]
- Behnoush, A.H.; Khalaji, A.; Khanmohammadi, S.; Alehossein, P.; Saeedian, B.; Shobeiri, P.; Teixeira, A.L.; Rezaei, N. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in fibromyalgia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of its role as a potential biomarker. PloS One 2023, 18, e0296103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumbauer, K.M.; Ramesh, D.; Perry, M.; Carney, K.B.; Julian, T.; Glidden, N.; Dorsey, S.G.; Starkweather, A.R.; Young, E.E. Contribution of COMT and BDNF Genotype and Expression to the Risk of Transition From Acute to Chronic Low Back Pain. The Clinical journal of pain 2020, 36, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, A.S.; Antunes, F.T.T.; Ferraz, C.; de Souza, A.H.; Simon, D. The genetic influence of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism in chronic low back pain. Advances in rheumatology (London, England) 2021, 61, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, T.; Von Ah, D.; Li, X.; Xiang, L.; Kwiat, C.; Nguyen, C.; Hsiao, C.P.; Saligan, L.N. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor rs6265 polymorphism is associated with severe cancer-related fatigue and neuropathic pain in female cancer survivors. Journal of cancer survivorship: Research and practice 2023. [CrossRef]
- Azoulay, D.; Abed, S.; Sfadi, A.; Sheleg, O.; Shaoul, E.; Shehadeh, M.; Kaykov, E.; Nodelman, M.; Bashkin, A. Low brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein levels and single-nucleotide polymorphism Val66Met are associated with peripheral neuropathy in type II diabetic patients. Acta diabetologica 2020, 57, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandasamy, R.; Price, T.J. The pharmacology of nociceptor priming. Handbook of experimental pharmacology 2015, 227, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melemedjian, O.K.; Tillu, D.V.; Asiedu, M.N.; Mandell, E.K.; Moy, J.K.; Blute, V.M.; Taylor, C.J.; Ghosh, S.; Price, T.J. BDNF regulates atypical PKC at spinal synapses to initiate and maintain a centralized chronic pain state. Mol Pain 2013, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouin, O.; L’Herondelle, K.; Lebonvallet, N.; Le Gall-Ianotto, C.; Sakka, M.; Buhé, V.; Plée-Gautier, E.; Carré, J.-L.; Lefeuvre, L.; Misery, L.; et al. TRPV1 and TRPA1 in cutaneous neurogenic and chronic inflammation: pro-inflammatory response induced by their activation and their sensitization. Protein & Cell 2017, 8, 644–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmelz, M. Itch and pain. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 2010, 34, 171–176. [Google Scholar]
- Pezet, S.; McMahon, S.B. Neurotrophins: mediators and modulators of pain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 29, 507–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtori, S.; Takahashi, K.; Moriya, H. Inflammatory pain mediated by a phenotypic switch in brain-derived neurotrophic factor-immunoreactive dorsal root ganglion neurons innervating the lumbar facet joints in rats. Neurosci Lett 2002, 323, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.F.; Chie, E.T.; Deng, Y.S.; Zhong, J.H.; Xue, Q.; Rush, R.A.; Xian, C.J. Injured primary sensory neurons switch phenotype for brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the rat. Neuroscience 1999, 92, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannion, R.J.; Costigan, M.; Decosterd, I.; Amaya, F.; Ma, Q.P. Neurotrophins: peripherally and centrally acting modulators of tactile stimulus-induced inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA 1999, 96, 9385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distefano, P.S.; Friedman, B.; Radziejewski, C.; Alexander, C.; Boland, P.; Schick, C.M.; Lindsay, R.M.; Wiegand, S.J. The neurotrophins BDNF, NT-3, and NGF display distinct patterns of retrograde axonal transport in peripheral and central neurons. Neuron 1992, 8, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heppenstall, P.A.; Lewin, G.R. Neurotrophins, nociceptors and pain. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 2000, 13, 573–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Park, M.J.; Kim, D.S. Nerve growth factor activates brain-derived neurotrophic factor promoter IV via extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase 1/2 in PC12 cells. Mol Cells 2006, 21, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, S.; Schmelz, M.; McGlone, F.; Turner, G.; Rukwied, R. Facilitated neurotrophin release in sensitized human skin. European Journal of Pain 2009, 13, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, K.; Dubner, R. Pain Facilitation and Activity-Dependent Plasticity in Pain Modulatory Circuitry: Role of BDNF-TrkB Signaling and NMDA Receptors. Mol.Neurobiol. 2007, 35, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.-G.; Zhou, L.-J. Long-term Potentiation at Spinal C-fiber Synapses: A Target for Pathological Pain. Current Pharmaceutical Design 2015, 21, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Cai, J.; Feng, Z.B.; Jin, Z.R.; Liu, B.H.; Zhao, H.Y.; Jing, H.B.; Wei, T.J.; Yang, G.N.; Liu, L.Y.; et al. BDNF Contributes to Spinal Long-Term Potentiation and Mechanical Hypersensitivity Via Fyn-Mediated Phosphorylation of NMDA Receptor GluN2B Subunit at Tyrosine 1472 in Rats Following Spinal Nerve Ligation. Neurochem Res 2017, 42, 2712–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandkühler, J.; Gruber-Schoffnegger, D. Hyperalgesia by synaptic long-term potentiation (LTP): an update. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2012, 12, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.J.; Ren, W.J.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, T.; Wei, X.H.; Xin, W.J.; Liu, C.C.; Zhou, L.H.; Li, Y.Y.; Liu, X.G. Limited BDNF contributes to the failure of injury to skin afferents to produce a neuropathic pain condition. Pain 2010, 148, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, S.E.; Pezet, S.; McMahon, S.B.; Thompson, S.W.; Malcangio, M. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces NMDA receptor subunit one phosphorylation via ERK and PKC in the rat spinal cord. Eur.J Neurosci. 2004, 20, 1769–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.J.; Zhong, Y.; Ren, W.J.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, X.G. BDNF induces late-phase LTP of C-fiber evoked field potentials in rat spinal dorsal horn. Exp Neurol 2008, 212, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Hou, W.; Liu, R.; Gao, Y.; Kong, X.; Yang, L.; Shi, Z.; Li, W.; Zheng, H.; Jiang, S.; et al. PAR2-mediated upregulation of BDNF contributes to central sensitization in bone cancer pain. Mol Pain 2014, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.J.; Yang, T.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y.; Xin, W.J.; Chen, Y.; Pang, R.P.; Zang, Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Liu, X.G. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor contributes to spinal long-term potentiation and mechanical hypersensitivity by activation of spinal microglia in rat. Brain Behav.Immun. 2011, 25, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retamal, J.; Reyes, A.; Ramirez, P.; Bravo, D.; Hernandez, A.; Pelissier, T.; Villanueva, L.; Constandil, L. Burst-Like Subcutaneous Electrical Stimulation Induces BDNF-Mediated, Cyclotraxin B-Sensitive Central Sensitization in Rat Spinal Cord. Front Pharmacol 2018, 9, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Arconada, I.; Benedet, T.; Roza, C.; Torres, B.; Barrio, J.; Krzyzanowska, A.; Avendaño, C.; Mellström, B.; Lopez-Garcia, J.A.; Naranjo, J.R. DREAM regulates BDNF-dependent spinal sensitization. Mol Pain 2010, 6, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.J.; Lee, K.H.; Grau, J.W. Complete spinal cord injury (SCI) transforms how brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) affects nociceptive sensitization. Exp Neurol 2017, 288, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, T.J.; Ghosh, S. ZIPping to pain relief: the role (or not) of PKMζ in chronic pain. Mol Pain 2013, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacktor, T.C. How does PKMζ maintain long-term memory? Nat Rev Neurosci 2011, 12, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croll, S.D.; Chesnutt, C.R.; Rudge, J.S.; Acheson, A.; Ryan, T.E.; Siuciak, J.A.; DiStefano, P.S.; Wiegand, S.J.; Lindsay, R.M. Co-infusion with a TrkB-Fc receptor body carrier enhances BDNF distribution in the adult rat brain. Exp Neurol 1998, 152, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgado, C.; Pereira-Terra, P.; Cruz, C.D.; Tavares, I. Minocycline completely reverses mechanical hyperalgesia in diabetic rats through microglia-induced changes in the expression of the potassium chloride co-transporter 2 (KCC2) at the spinal cord. Diabetes, obesity & metabolism 2011, 13, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moy, J.K.; Szabo-Pardi, T.; Tillu, D.V.; Megat, S.; Pradhan, G.; Kume, M.; Asiedu, M.N.; Burton, M.D.; Dussor, G.; Price, T.J. Temporal and sex differences in the role of BDNF/TrkB signaling in hyperalgesic priming in mice and rats. Neurobiology of pain (Cambridge, Mass.) 2019, 5, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, A.; Lin, J.C. Modulation of neurotrophin signaling by monoclonal antibodies. Handbook of experimental pharmacology 2014, 220, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazorla, M.; Prémont, J.; Mann, A.; Girard, N.; Kellendonk, C.; Rognan, D. Identification of a low-molecular weight TrkB antagonist with anxiolytic and antidepressant activity in mice. J Clin Invest 2011, 121, 1846–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazorla, M.; Arrang, J.M.; Prémont, J. Pharmacological characterization of six trkB antibodies reveals a novel class of functional agents for the study of the BDNF receptor. Br J Pharmacol 2011, 162, 947–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrini, F.; Trang, T.; Mattioli, T.A.; Laffray, S.; Del’Guidice, T.; Lorenzo, L.E.; Castonguay, A.; Doyon, N.; Zhang, W.; Godin, A.G.; et al. Morphine hyperalgesia gated through microglia-mediated disruption of neuronal Cl⁻ homeostasis. Nat Neurosci 2013, 16, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazorla, M.; Jouvenceau, A.; Rose, C.; Guilloux, J.P.; Pilon, C.; Dranovsky, A.; Prémont, J. Cyclotraxin-B, the first highly potent and selective TrkB inhibitor, has anxiolytic properties in mice. PLoS One 2010, 5, e9777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, H.C.; Kuan, Y.H.; Shyu, B.C. Targeting brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the medial thalamus for the treatment of central poststroke pain in a rodent model. Pain 2017, 158, 1302–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constandil, L.; Goich, M.; Hernández, A.; Bourgeais, L.; Cazorla, M.; Hamon, M.; Villanueva, L.; Pelissier, T. Cyclotraxin-B, a new TrkB antagonist, and glial blockade by propentofylline, equally prevent and reverse cold allodynia induced by BDNF or partial infraorbital nerve constriction in mice. J Pain 2012, 13, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M’Dahoma, S.; Barthélemy, S.; Tromilin, C.; Jeanson, T.; Viguier, F.; Michot, B.; Pezet, S.; Hamon, M.; Bourgoin, S. Respective pharmacological features of neuropathic-like pain evoked by intrathecal BDNF versus sciatic nerve ligation in rats. European neuropsychopharmacology: The journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 25, 2118–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Zhang, Y.W.; Gu, Q.; Yuan, T.J.; Fan, B.Q. Alteration of neural activity and neuroinflammatory factors in the insular cortex of mice with corneal neuropathic pain. Genes, brain, and behavior 2023, 22, e12842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, T.; Colciago, A.; Montagnani Marelli, M.; Moretti, R.M.; Magnaghi, V. Protein kinase C epsilon activation regulates proliferation, migration, and epithelial to mesenchymal-like transition in rat Schwann cells. Front Cell Neurosci 2023, 17, 1237479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Tang, Y.; Dai, H.; Cao, Y.; Sun, P.; Chen, Y.; Chen, A.; Lin, C. Blockade of BDNF signalling attenuates chronic visceral hypersensitivity in an IBS-like rat model. European journal of pain (London, England) 2020, 24, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhao, W.; Chen, D.; Zhou, D.; Gao, Y.; Bian, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xia, S.H. Disinhibition of Mesolimbic Dopamine Circuit by the Lateral Hypothalamus Regulates Pain Sensation. J Neurosci 2023, 43, 4525–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Yan, X.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Li, T. Transcranial direct current stimulation attenuates chronic pain in knee osteoarthritis by modulating BDNF/TrkB signaling in the descending pain modulation system. Neurosci Lett 2023, 810, 137320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. Exploring the role and mechanisms of diallyl trisulfide and diallyl disulfide in chronic constriction-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Korean J Pain 2020, 33, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, K.; Lesnak, J.B.; Plumb, A.N.; Janowski, A.J.; Smith, A.F.; Hill, J.K.; Sluka, K.A. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor contributes to activity-induced muscle pain in male but not female mice. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, B.; Sun, P.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Y.; Ai-Qin, C.; Chen, Y.; Lin, C. Spinal P2X4 Receptors Involved in Visceral Hypersensitivity of Neonatal Maternal Separation Rats. 2023, 19, 113–122. [CrossRef]
- Hsiang, H.W.; Girard, B.M.; Ratkovits, L.; Campbell, S.E.; Vizzard, M.A. Effects of pharmacological neurotrophin receptor inhibition on bladder function in female mice with cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis. Frontiers in urology 2022, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, T.; He, W.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, D.; Qin, G.; Chen, L.; Zhou, J. Microglia P2X4R-BDNF signalling contributes to central sensitization in a recurrent nitroglycerin-induced chronic migraine model. J Headache Pain 2020, 21, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chodroff, L.; Bendele, M.; Valenzuela, V.; Henry, M.; Ruparel, S. EXPRESS: BDNF Signaling Contributes to Oral Cancer Pain in a Preclinical Orthotopic Rodent Model. Mol Pain 2016, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.M.; Pan, W.; Xu, N.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Zhang, G.F.; Shen, J.C. Environmental enrichment improves long-term memory impairment and aberrant synaptic plasticity by BDNF/TrkB signaling in nerve-injured mice. Neurosci Lett 2019, 694, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.Y.; Sun, Y.; Shi, X.Y.; Sahbaie, P.; Clark, J.D. Epigenetic regulation of spinal cord gene expression controls opioid-induced hyperalgesia. Mol Pain 2014, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Yang, C.; Li, S.; Zhan, G.; Zhang, J.; Huang, N.; Du, X.; Xu, H.; Hashimoto, K.; Luo, A. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor-TrkB signaling in the medial prefrontal cortex plays a role in the anhedonia-like phenotype after spared nerve injury. European archives of psychiatry and clinical neuroscience 2020, 270, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahbaie, P.; Liang, D.Y.; Shi, X.Y.; Sun, Y.; Clark, J.D. Epigenetic regulation of spinal cord gene expression contributes to enhanced postoperative pain and analgesic tolerance subsequent to continuous opioid exposure. Mol Pain 2016, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Lin, Y.M.; Winston, J.H.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Huang, L.-H.M.; Shi, X.Z. Role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the pathogenesis of distention-associated abdominal pain in bowel obstruction. Neurogastroenterology and motility 2018, 30, e13373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillu, D.V.; Hassler, S.N.; Burgos-Vega, C.C.; Quinn, T.L.; Sorge, R.E.; Dussor, G.; Boitano, S.; Vagner, J.; Price, T.J. Protease-activated receptor 2 activation is sufficient to induce the transition to a chronic pain state. Pain 2015, 156, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, F.; Liu, X.; Ma, C.; Zhao, J. Surgical incision induces learning impairment in mice partially through inhibition of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling pathway in the hippocampus and amygdala. Mol Pain 2018, 14, 1744806918805902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Lakkaniga, N.R.; Carlomagno, F.; Santoro, M.; McDonald, N.Q.; Lv, F.; Gunaganti, N.; Frett, B.; Li, H.Y. Insights into Current Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase (TRK) Inhibitors: Development and Clinical Application. J Med Chem 2019, 62, 1731–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachel, S.J.; Sanders, J.M.; Henze, D.A.; Rudd, M.T.; Su, H.P.; Li, Y.; Nanda, K.K.; Egbertson, M.S.; Manley, P.J.; Jones, K.L.; et al. Maximizing diversity from a kinase screen: identification of novel and selective pan-Trk inhibitors for chronic pain. J Med Chem 2014, 57, 5800–5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeles, T.S.; Yang, S.X.; Steffler, C.; Dionne, C.A. Kinetics of trkA tyrosine kinase activity and inhibition by K-252a. Arch Biochem Biophys 1998, 349, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, J.H.; Toma, H.; Shenoy, M.; He, Z.J.; Zou, L.; Xiao, S.Y.; Micci, M.A.; Pasricha, P.J. Acute pancreatitis results in referred mechanical hypersensitivity and neuropeptide up-regulation that can be suppressed by the protein kinase inhibitor k252a. J Pain 2003, 4, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias, B.; Allen, S.; Dawbarn, D.; Charrua, A.; Cruz, F.; Cruz, C.D. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, acting at the spinal cord level, participates in bladder hyperactivity and referred pain during chronic bladder inflammation. Neuroscience 2013, 234, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miletic, G.; Miletic, V. Loose ligation of the sciatic nerve is associated with TrkB receptor-dependent decreases in KCC2 protein levels in the ipsilateral spinal dorsal horn. Pain 2008, 137, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.H.; Zhang, X.Q.; Xue, Q.S.; Yan, L.; Huang, J.L.; Zhang, S.; Shao, H.J.; Lu, H.; Wang, W.Y.; Yu, B.W. The BDNF/TrkB signaling pathway is involved in heat hyperalgesia mediated by Cdk5 in rats. PLoS One 2014, 9, e85536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, M.; Shiraishi, Y.; Ozaki, N.; Hayashi, K.; Hori, K.; Ichiyanagi, M.; Sugiura, Y. Nerve growth factor and associated nerve sprouting contribute to local mechanical hyperalgesia in a rat model of bone injury. Eur J Pain 2012, 16, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Lv, L.; Duan, W.; Bai, R.; Meng, Z.; Shao, X. Involvement of the BDNF-TrkB-KCC2 pathway in neuropathic pain after brachial plexus avulsion. Brain Behav 2022, 12, e2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroki, T.; Suto, T.; Ohta, J.; Saito, S.; Obata, H. Spinal γ-Aminobutyric Acid Interneuron Plasticity Is Involved in the Reduced Analgesic Effects of Morphine on Neuropathic Pain. J Pain 2022, 23, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Reis, R.C.; Kopruszinski, C.M.; Nones, C.F.M.; Aguiar, D.A.; Chichorro, J.G. The opposing contribution of neurotrophin-3 and nerve growth factor to orofacial heat hyperalgesia in rats. Behav Pharmacol 2020, 31, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, B.; Yin, Y.; Mao, G.; Zhao, B.; Wu, J.; Shi, H.; Fei, S. The implication of transient receptor potential canonical 6 in BDNF-induced mechanical allodynia in rat model of diabetic neuropathic pain. Life Sci 2021, 273, 119308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, J.J.; Jaworski, C.; Tung, D.; Wängler, C.; Wängler, B.; Schirrmacher, R. Tropomyosin receptor kinase inhibitors: an updated patent review for 2016-2019. Expert Opin Ther Pat 2020, 30, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, J.J.; Schirrmacher, R.; Farrell, K.; Bernard-Gauthier, V. Tropomyosin receptor kinase inhibitors: an updated patent review for 2010-2016—Part II. Expert Opin Ther Pat 2017, 27, 831–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, J.J.; Schirrmacher, R.; Farrell, K.; Bernard-Gauthier, V. Tropomyosin receptor kinase inhibitors: an updated patent review for 2010-2016—Part I. Expert Opin Ther Pat 2017, 27, 733–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yu, D.; Lamb, M.L. Trk kinase inhibitors as new treatments for cancer and pain. Expert Opin Ther Pat 2009, 19, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghilardi, J.R.; Freeman, K.T.; Jimenez-Andrade, J.M.; Mantyh, W.G.; Bloom, A.P.; Bouhana, K.S.; Trollinger, D.; Winkler, J.; Lee, P.; Andrews, S.W.; et al. Sustained blockade of neurotrophin receptors TrkA, TrkB and TrkC reduces non-malignant skeletal pain but not the maintenance of sensory and sympathetic nerve fibers. Bone 2011, 48, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skerratt, S.E.; Andrews, M.; Bagal, S.K.; Bilsland, J.; Brown, D.; Bungay, P.J.; Cole, S.; Gibson, K.R.; Jones, R.; Morao, I.; et al. The Discovery of a Potent, Selective, and Peripherally Restricted Pan-Trk Inhibitor (PF-06273340) for the Treatment of Pain. J Med Chem 2016, 59, 10084–10099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiguro, N.; Oyama, S.; Higashi, R.; Yanagida, K. Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of ONO-4474, an Orally Available Pan-Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase Inhibitor, in Japanese Patients With Moderate to Severe Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Parallel-Group Comparative Study. J Clin Pharmacol 2020, 60, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulle, F.; Kenis, G.; Cazorla, M.; Hamon, M.; Steinbusch, H.W.; Lanfumey, L.; van den Hove, D.L. TrkB inhibition as a therapeutic target for CNS-related disorders. Prog Neurobiol 2012, 98, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggs, S.; Trang, T.; Salter, M.W. P2X4R+ microglia drive neuropathic pain. Nat Neurosci 2012, 15, 1068–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyon, N.; Ferrini, F.; Gagnon, M.; De Koninck, Y. Treating pathological pain: is KCC2 the key to the gate? Expert Rev Neurother 2013, 13, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnon, M.; Bergeron, M.J.; Lavertu, G.; Castonguay, A.; Tripathy, S.; Bonin, R.P.; Perez-Sanchez, J.; Boudreau, D.; Wang, B.; Dumas, L.; et al. Chloride extrusion enhancers as novel therapeutics for neurological diseases. Nat Med 2013, 19, 1524–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laske, C.; Stransky, E.; Eschweiler, G.W.; Klein, R.; Wittorf, A.; Leyhe, T.; Richartz, E.; Köhler, N.; Bartels, M.; Buchkremer, G.; et al. Increased BDNF serum concentration in fibromyalgia with or without depression or antidepressants. Journal of Psychiatric Research 2007, 41, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Zanette, S.A.; Vercelino, R.; Laste, G.; Rozisky, J.R.; Schwertner, A.; Machado, C.B.; Xavier, F.; de Souza, I.C.C.; Deitos, A.; Torres, I.L.S.; et al. Melatonin analgesia is associated with improvement of the descending endogenous pain-modulating system in fibromyalgia: a phase II, randomized, double-dummy, controlled trial. BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology 2014, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablochkova, A.; Bäckryd, E.; Kosek, E.; Mannerkorpi, K.; Ernberg, M.; Gerdle, B.; Ghafouri, B. Unaltered low nerve growth factor and high brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in plasma from patients with fibromyalgia after a 15-week progressive resistance exercise. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2019, 51, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brietzke, A.P.; Zortea, M.; Carvalho, F.; Sanches, P.R.S.; Silva, D.P.J.; Torres, I.; Fregni, F.; Caumo, W. Large Treatment Effect With Extended Home-Based Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Over Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex in Fibromyalgia: A Proof of Concept Sham-Randomized Clinical Study. J Pain 2020, 21, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caumo, W.; Alves, R.L.; Vicuña, P.; Alves, C.F.d.S.; Ramalho, L.; Sanches, P.R.S.; Silva, D.P.; da Silva Torres, I.L.; Fregni, F. Impact of Bifrontal Home-Based Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation in Pain Catastrophizing and Disability due to Pain in Fibromyalgia: A Randomized, Double-Blind Sham-Controlled Study. The Journal of Pain 2022, 23, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, L.C.; Leite, F.M.; da Graça, L.; Tarragó, M.; Zanette, S.A.; de Souza, A.; Castro, S.M.; Caumo, W. BDNF and serum S100B levels according the spectrum of structural pathology in chronic pain patients. Neuroscience Letters 2019, 706, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolmeister, A.S.; Schiavo, C.L.; Nazário, K.C.K.; Castro, S.M.d.J.; de Souza, A.; Caetani, R.P.; Caumo, W.; Stefani, L.C. The Brief Measure of Emotional Preoperative Stress (B-MEPS) as a new predictive tool for postoperative pain: A prospective observational cohort study. PLOS ONE 2020, 15, e0227441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.C.S.; Zortea, M.; Souza, A.; Santos, V.; Biazús, J.V.; Torres, I.L.S.; Fregni, F.; Caumo, W. Clinical impact of melatonin on breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy; effects on cognition, sleep and depressive symptoms: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. PLOS ONE 2020, 15, e0231379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Agnol, L.; Medeiros, L.F.; Torres, I.L.S.; Deitos, A.; Brietzke, A.; Laste, G.; de Souza, A.; Vieira, J.L.; Fregni, F.; Caumo, W. Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Increases the Corticospinal Inhibition and the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Chronic Myofascial Pain Syndrome: An Explanatory Double-Blinded, Randomized, Sham-Controlled Trial. The Journal of Pain 2014, 15, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassot, M.; Dussan-Sarria, J.A.; Sehn, F.C.; Deitos, A.; de Souza, A.; Vercelino, R.; Torres, I.L.S.; Fregni, F.; Caumo, W. Electroacupuncture analgesia is associated with increased serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor in chronic tension-type headache: a randomized, sham controlled, crossover trial. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2015, 15, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.-H.; Liu, H.-T.; Kuo, H.-C. Decrease of Urinary Nerve Growth Factor but Not Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Patients with Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Treated with Hyaluronic Acid. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e91609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, L.F.; Caumo, W.; Dussán-Sarria, J.; Deitos, A.; Brietzke, A.; Laste, G.; Campos-Carraro, C.; de Souza, A.; Scarabelot, V.L.; Cioato, S.G.; et al. Effect of Deep Intramuscular Stimulation and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Neurophysiological Biomarkers in Chronic Myofascial Pain Syndrome. Pain Medicine 2016, 17, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, A.K.; Lakshman, K.; Sharma, T.; Gupta, N.; Banerjee, B.D.; Singal, A. Modulation of serum BDNF levels in postherpetic neuralgia following pulsed radiofrequency of intercostal nerve and pregabalin. Pain Management 2016, 6, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Wang, M.-H.; Wang, X.-B.; Liu, L.; Wu, J.-L.; Yang, X.-L.; Liu, X.-R.; Zhang, C.-X. Effect of intraoperative application of ketamine on postoperative depressed mood in patients undergoing elective orthopedic surgery. Journal of Anesthesia 2016, 30, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, H.; Sesterhenn, R.B.; Souza, A.d.; Souza, A.C.d.; Alves, M.; Machado, J.C.; Burger, N.B.; Torres, I.L.d.S.; Stefani, L.C.; Fregni, F.; et al. Preoperative transcranial direct current stimulation: Exploration of a novel strategy to enhance neuroplasticity before surgery to control postoperative pain. A randomized sham-controlled study. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0187013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.-G.; Sun, W.; Ju, F.; Wang, H.; Sun, X.-L.; Mou, X.; Yuan, H. Analgesic Effects of Directed Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Acute Neuropathic Pain After Spinal Cord Injury. Pain Medicine 2019, 21, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govil, M.; Mukhopadhyay, N.; Holwerda, T.; Sluka, K.; Rakel, B.; Schutte, D.L. Effects of genotype on TENS effectiveness in controlling knee pain in persons with mild to moderate osteoarthritis. European Journal of Pain 2020, 24, 398–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltran Serrano, G.; Pooch Rodrigues, L.; Schein, B.; Zortea, M.; Torres, I.L.S.; Fregni, F.; Caumo, W. The Hypnotic Analgesia Suggestion Mitigated the Effect of the Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on the Descending Pain Modulatory System: A Proof of Concept Study. J Pain Res 2020, 13, 2297–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paula, T.M.H.d.; Castro, M.S.; Medeiros, L.F.; Paludo, R.H.; Couto, F.F.; Costa, T.R.d.; Fortes, J.P.; Salbego, M.d.O.; Behnck, G.S.; Moura, T.A.M.d.; et al. Association of low-dose naltrexone and transcranial direct current stimulation in fibromyalgia: a randomized, double-blinded, parallel clinical trial. Brazilian Journal of Anesthesiology (English Edition) 2023, 73, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Marin, J.; Andrés-Rodríguez, L.; Tops, M.; Luciano, J.V.; Navarro-Gil, M.; Feliu-Soler, A.; López-del-Hoyo, Y.; Garcia-Campayo, J. Effects of attachment-based compassion therapy (ABCT) on brain-derived neurotrophic factor and low-grade inflammation among fibromyalgia patients: A randomized controlled trial. Scientific Reports 2019, 9, 15639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bonaventura, S.; Fernández Carnero, J.; Ferrer-Peña, R. Can a specific biobehavioral-based therapeutic education program lead to changes in pain perception and brain plasticity biomarkers in chronic pain patients? A study protocol for a randomized clinical trial. PLOS ONE 2024, 19, e0289430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polacchini, A.; Metelli, G.; Francavilla, R.; Baj, G.; Florean, M.; Mascaretti, L.G.; Tongiorgi, E. A method for reproducible measurements of serum BDNF: comparison of the performance of six commercial assays. Sci Rep 2015, 5, 17989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salio, C.; Ferrini, F.; Muthuraju, S.; Merighi, A. Presynaptic modulation of spinal nociceptive transmission by glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF). J.Neurosci. 2014, 34, 13819–13833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrini, F.; Salio, C.; Boggio, E.M.; Merighi, A. Interplay of BDNF and GDNF in the Mature Spinal Somatosensory System and Its Potential Therapeutic Relevance. Curr Neuropharmacol 2021, 19, 1225–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merighi, A. Cross Talk of BDNF and GDNF in Spinal Substantia Gelatinosa (Lamina II): Focus on Circuitry. Adv Exp Med Biol 2021, 1331, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
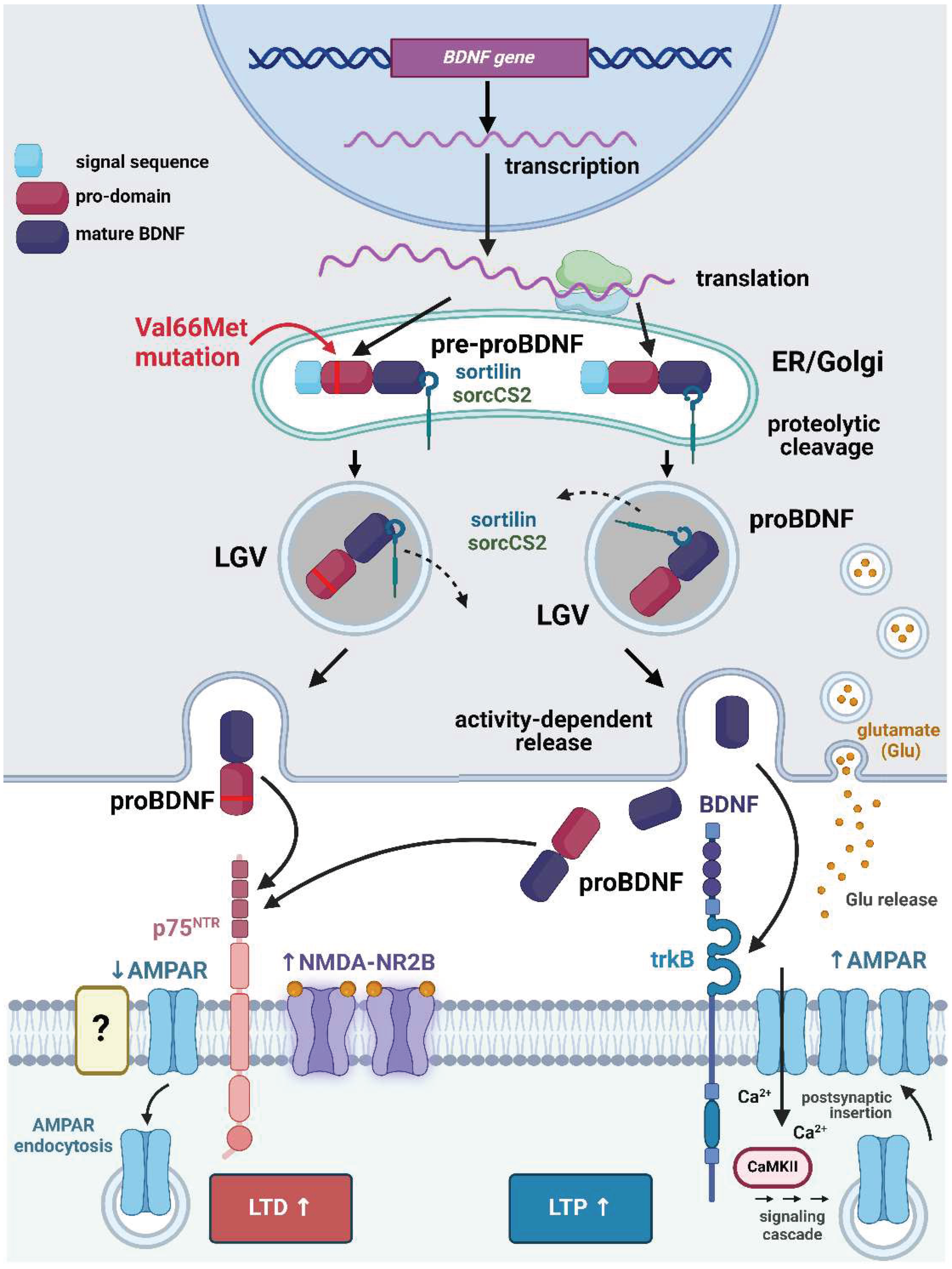
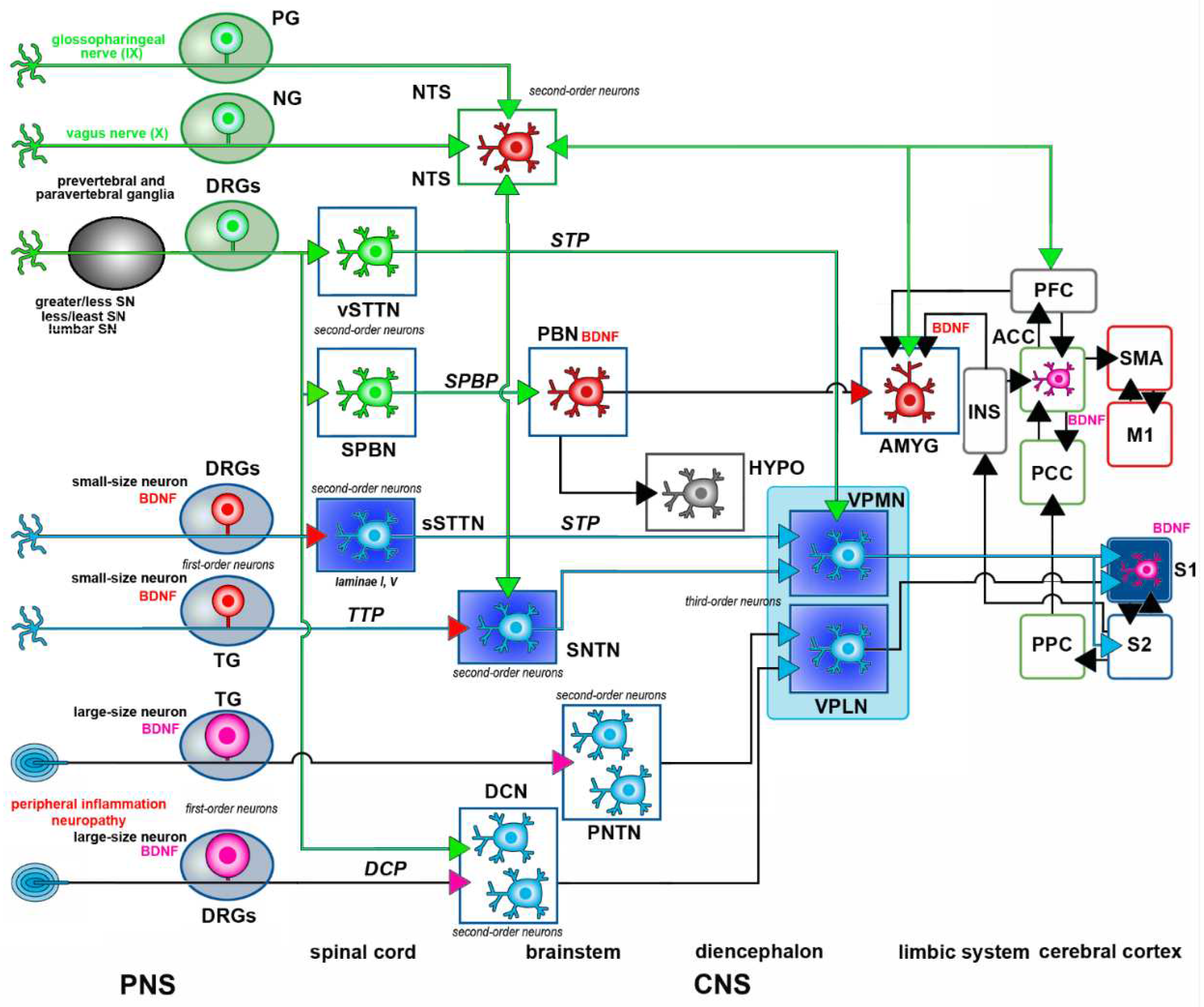
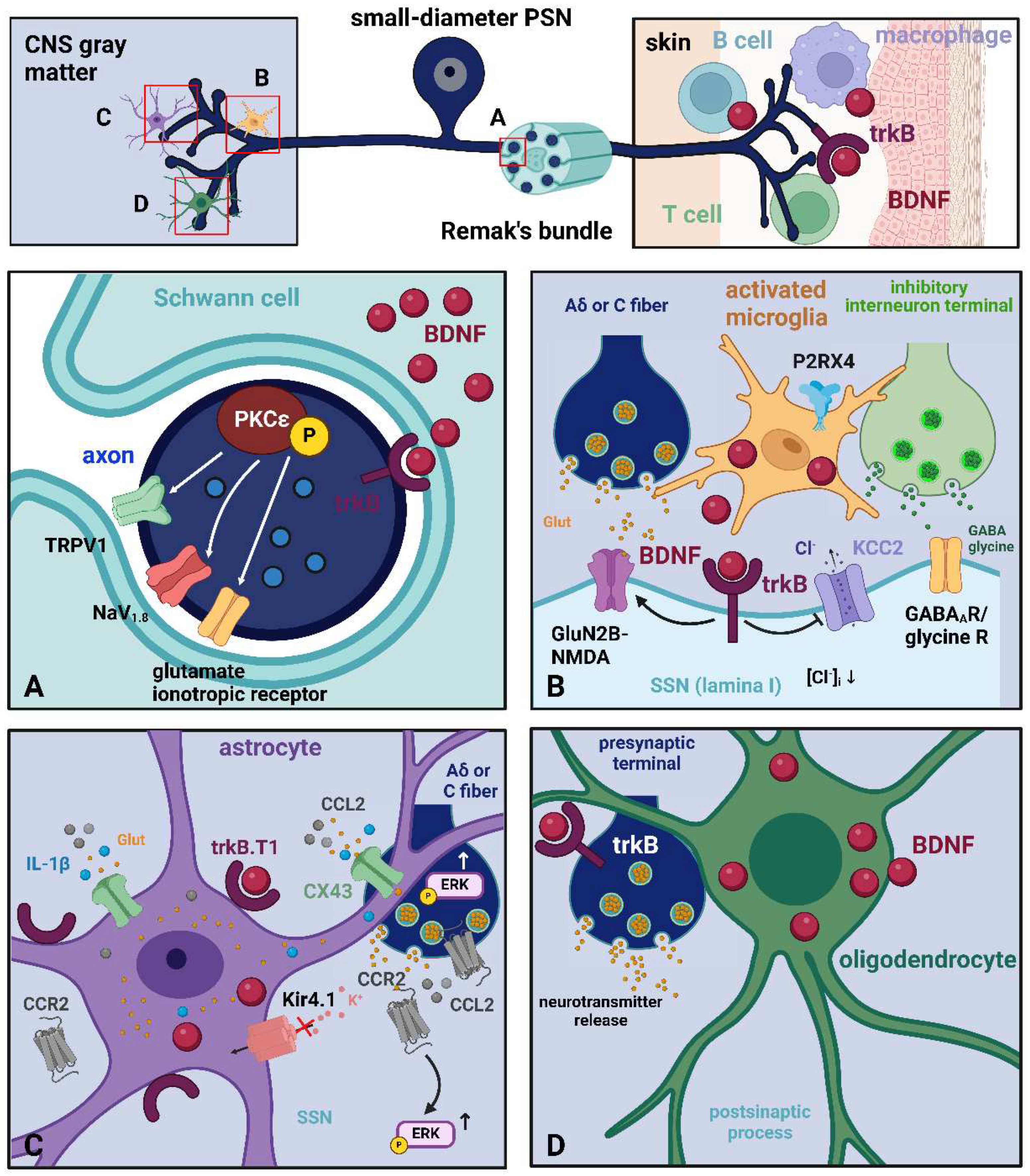
| Location | Type of neurons | Function | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| DRGs | Small-to-medium-size PSNs | Nociception | [57–59] |
| DRGs | Small-to-medium-size PSNs | Inflammatory nociception | [81] |
| JG (X) | Small-to-medium-size PSNs | Nociception | [43] |
| TG (V) | Small-to-medium-size PSNs | Nociception | [67,68] |
| DRGs | Large-size PSNs | Nociception (after injury) | [62] |
| SNTN | SSNs | Localization study | [36] |
| CN | SSNs | Localization study | [36] |
| PBN | Projection neurons | Nociception | [36] |
| S1 | Cortical neurons | Inflammatory/neuropathic pain | [74] |
| Au1 | Cortical neurons | Chronic pain | [76] |
| ACC | Cortical neurons | Inflammatory/neuropathic pain | [74,75] |
| Location | Type of neurons | Function | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| DRGs | Small-to-medium-size PSNs | Nociception | [82] |
| NG (X) | Small-to-medium-size PSNs | Chemoafferent neurons | [43,72] |
| PG (IX) | Small-to-medium-size PSNs | Chemoafferent neurons | [43,72] |
| NTS | Small-to-medium-size SSNs | Modulation of cardiovascular afferents | [36,73] |
| AMY | Projection neurons to PBN | Hyperalgesia | [78] |
| Location | Type of cells | Function | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| PNS | Schwann cells | Modulation of nociception | [161] |
| DH | Activated microglia (OX-42+/ Iba1+) | Inflammatory/neuropathic pain | [162,163,164] |
| SNTN | Microglia (Iba1+) | Nociception (allodynia) | [119] |
| Au1 | Astrocytes (GFAP+) | Chronic pain | [76] |
| ACC | Astrocytes (GFAP+) | ||
| S1 | Astrocytes (GFAP+) Microglia (Iba1+) |
Inflammatory/neuropathic pain | [74,165] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





