Submitted:
06 February 2024
Posted:
08 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Antibodies and Inhibitors
2.3. Cell Lysis and Western Blot Analysis
2.4. Analyzing apoptosis by Annexin V/propidium iodide staining
2.5. Cell Viability Assay
2.6. Tumor Xenograft Formation in Mice
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
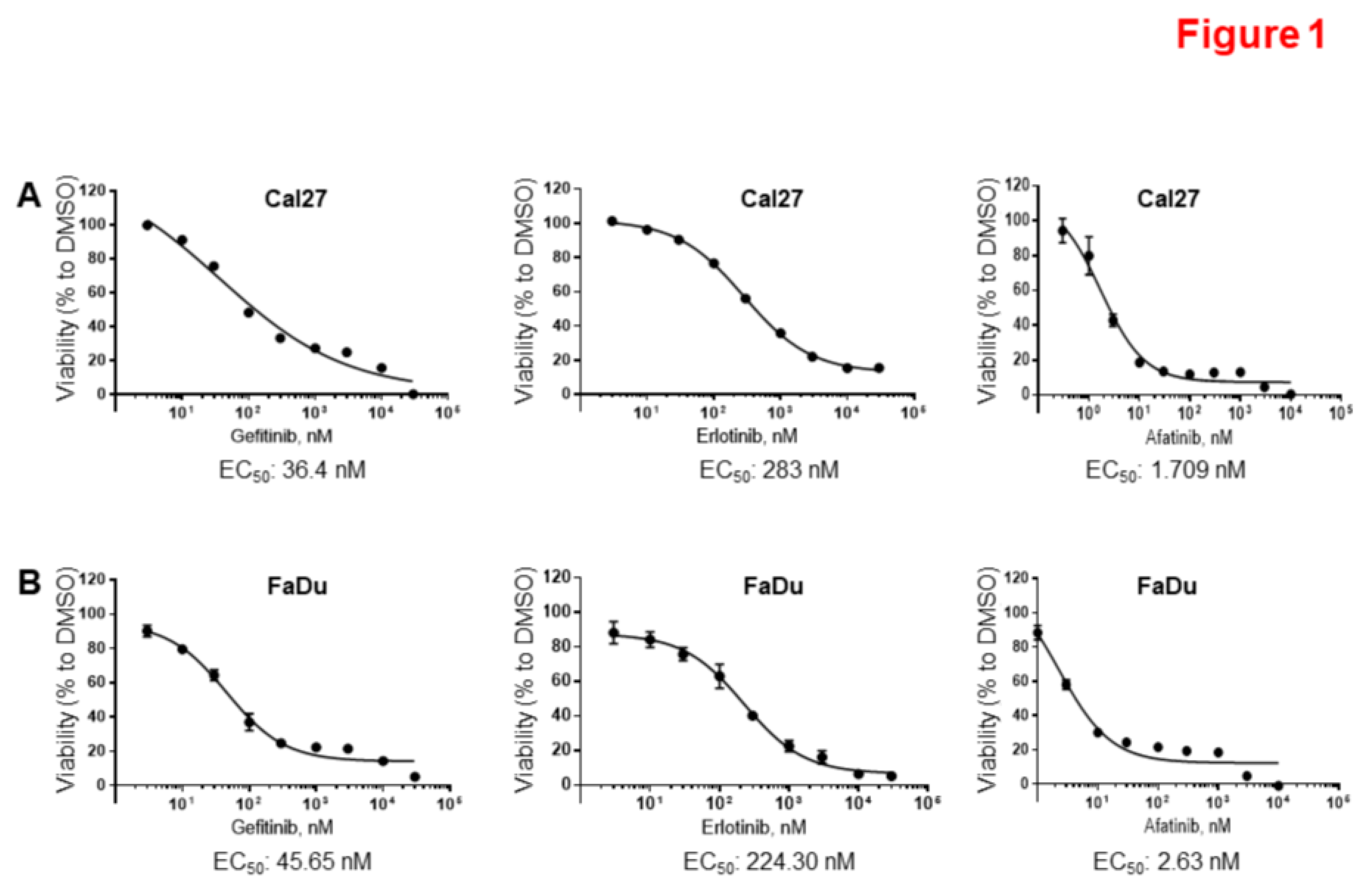
3.1. HPV-Negative HNSCC Cell Lines are Sensitive to Afatinib.
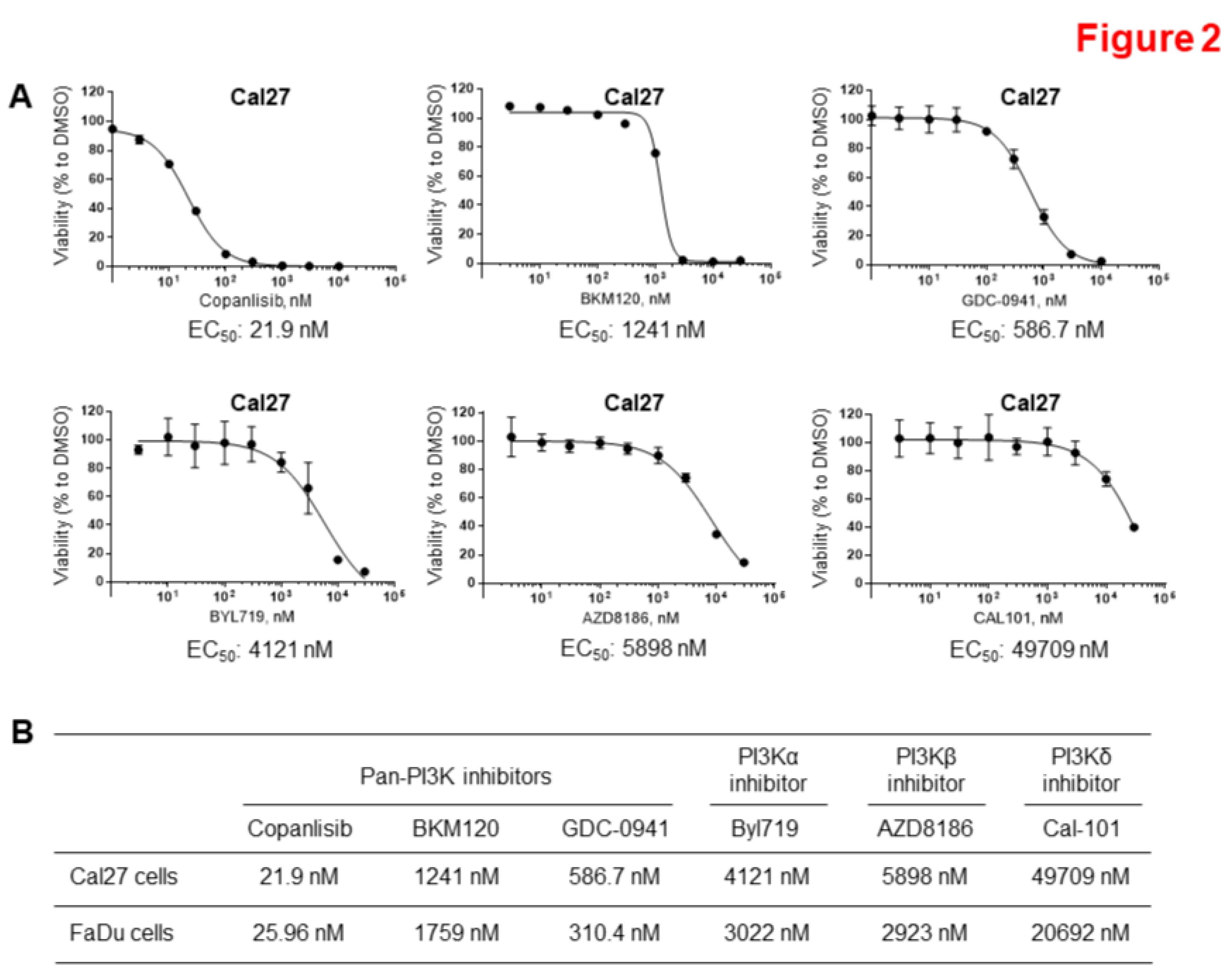
3.2. Copanlisib is the Most Effective PI3K Inhibitor to Suppress HPV-Negative HNSCC Proliferation.
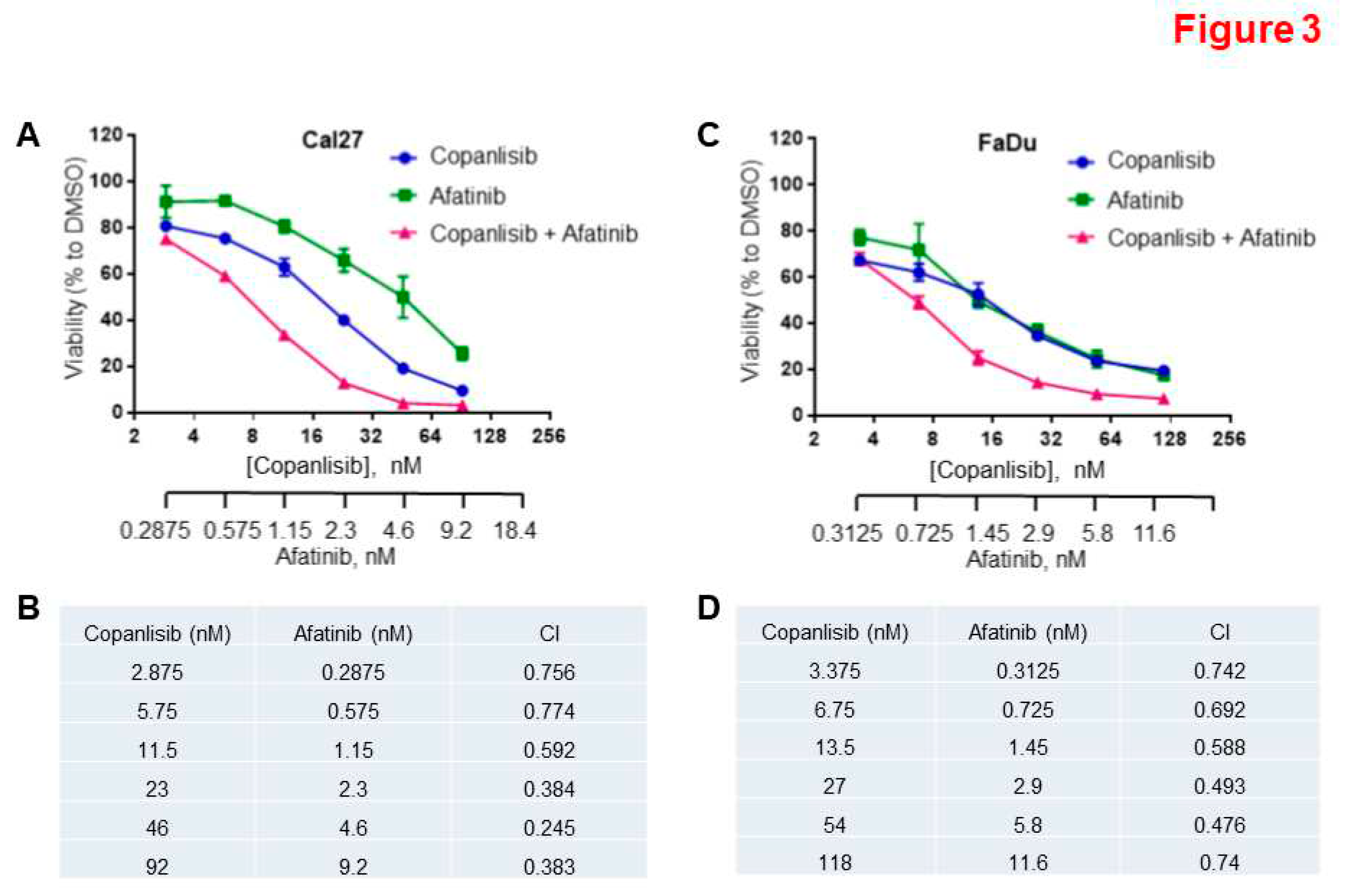
3.3. Synergistic Inhibition of Cell Proliferation by a Combination of Afatinib and Copanlisib.
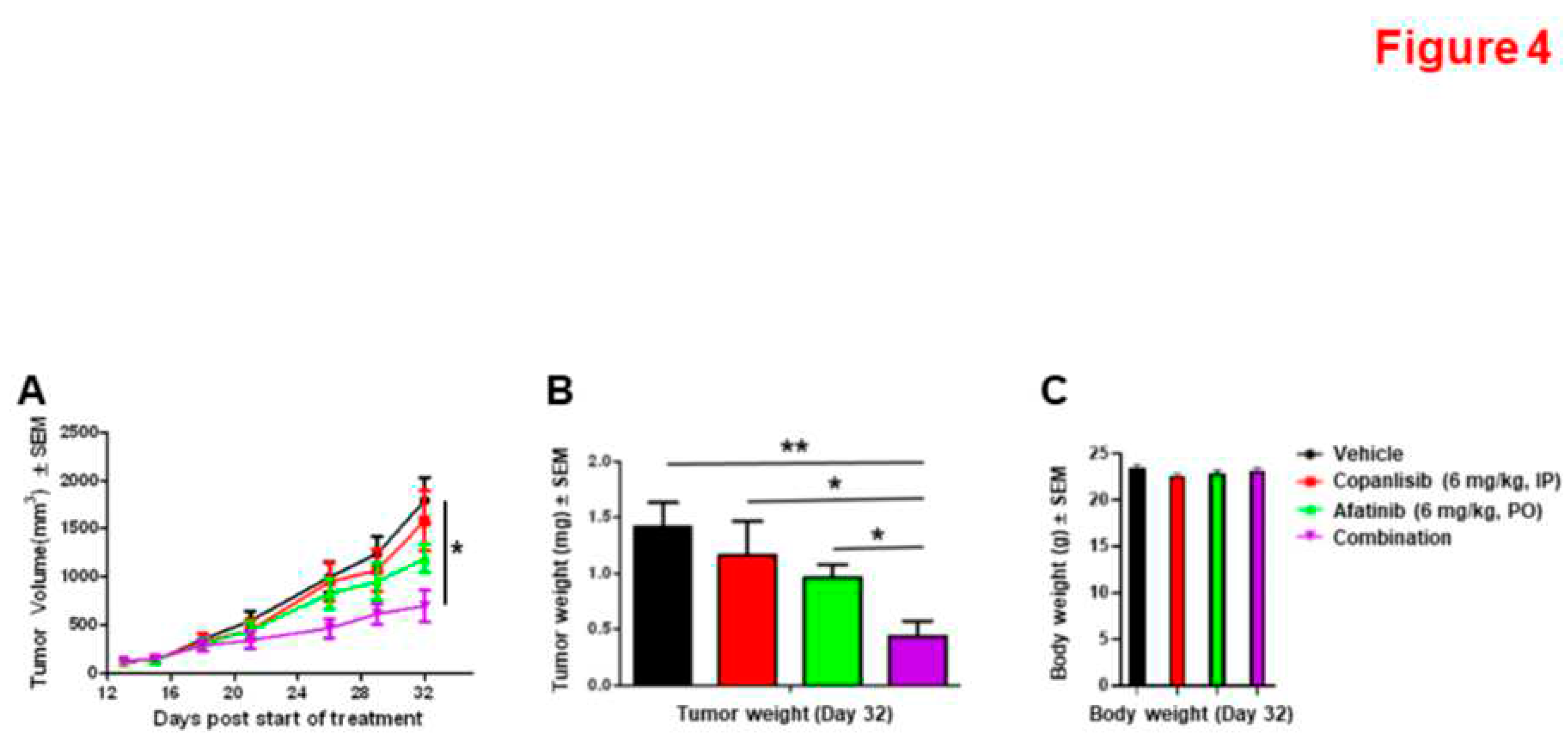
3.4. Synergistic Inhibition of Xenograft Tumor Growth by the Combination of Afatinib and Copanlisib in Mice.
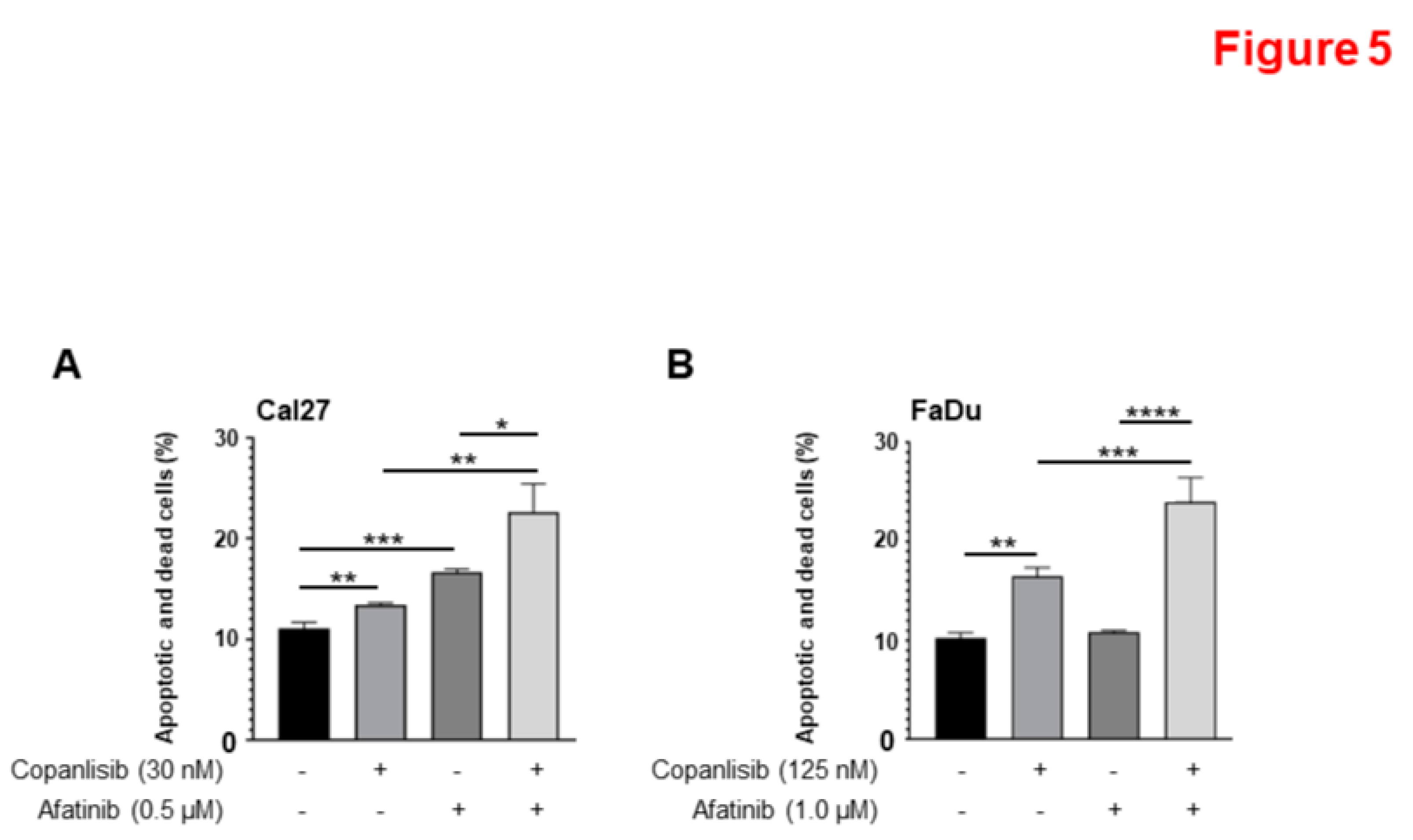
3.5. A combination of Afatinib and Copanlisib Induces Apoptosis.
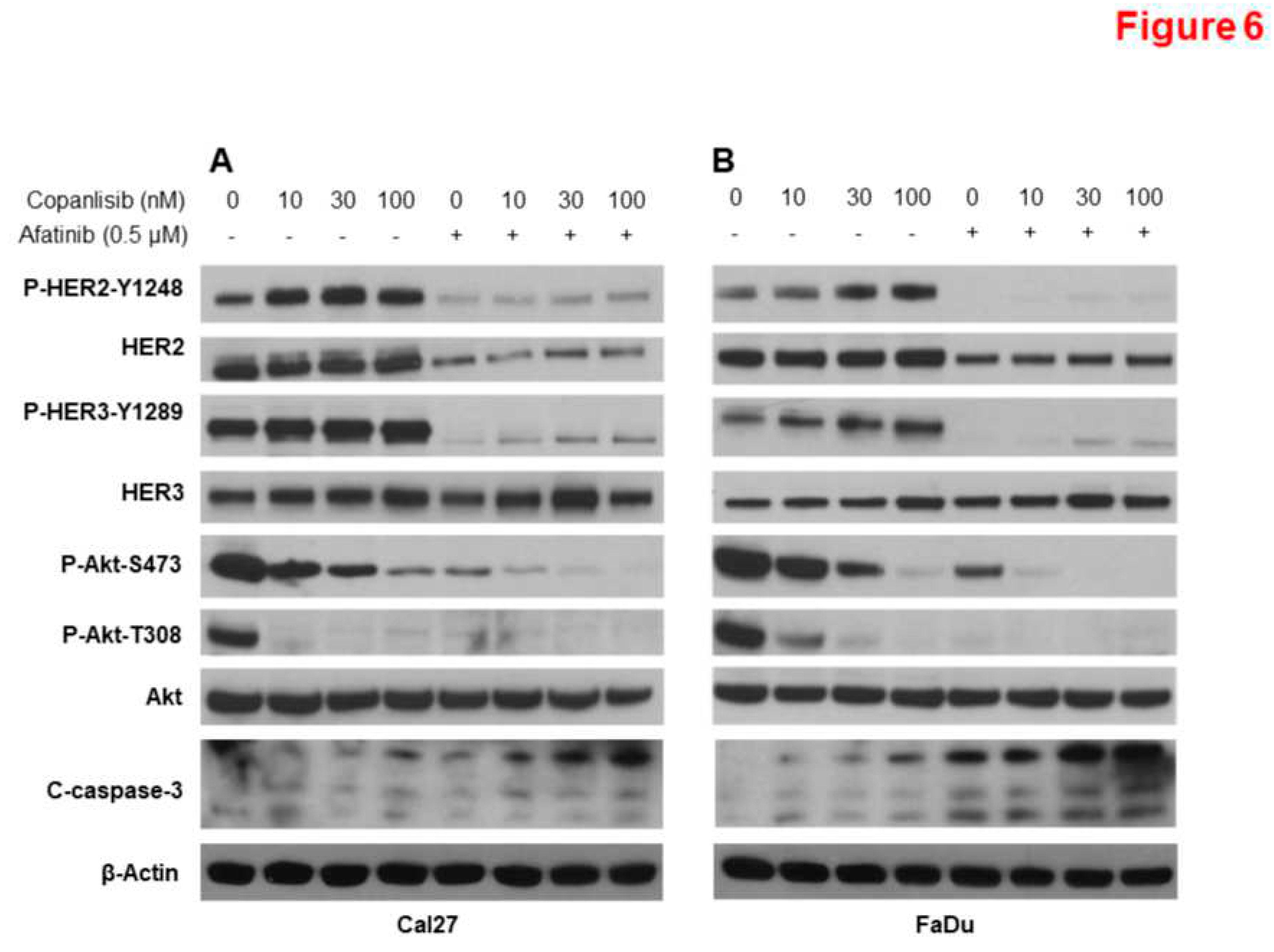
3.6. Combination of Afatinib and Copanlisib Completely Inhibits ErbB and PI3K Pathways Resulting in Induction of Caspase Cleavage.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Grant Support
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, C.S. Molecular landscape of head and neck cancer and implications for therapy. Ann Transl Med 2021, 9, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsouk, A.; Aluru, J.S.; Rawla, P.; Saginala, K.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Prevention of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Med Sci (Basel) 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashibe, M.; Boffetta, P.; Zaridze, D.; Shangina, O.; Szeszenia-Dabrowska, N.; Mates, D.; Fabiánová, E.; Rudnai, P.; Brennan, P. Contribution of tobacco and alcohol to the high rates of squamous cell carcinoma of the supraglottis and glottis in Central Europe. American journal of epidemiology 2007, 165, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashibe, M.; Brennan, P.; Benhamou, S.; Castellsague, X.; Chen, C.; Curado, M.P.; Dal Maso, L.; Daudt, A.W.; Fabianova, E.; Fernandez, L.; et al. Alcohol drinking in never users of tobacco, cigarette smoking in never drinkers, and the risk of head and neck cancer: pooled analysis in the International Head and Neck Cancer Epidemiology Consortium. Journal of the National Cancer Institute 2007, 99, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaryouh, H.; De Pauw, I.; Baysal, H.; Peeters, M.; Vermorken, J.B.; Lardon, F.; Wouters, A. Recent insights in the PI3K/Akt pathway as a promising therapeutic target in combination with EGFR-targeting agents to treat head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Med Res Rev 2022, 42, 112–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, T.; Li, S.; Henry, L.E.; Liu, S.; Sartor, M.A. Molecular Tumor Subtypes of HPV-Positive Head and Neck Cancers: Biological Characteristics and Implications for Clinical Outcomes. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, S.F.; Vu, L.; Spanos, W.C.; Pyeon, D. The Key Differences between Human Papillomavirus-Positive and -Negative Head and Neck Cancers: Biological and Clinical Implications. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennessey, P.T.; Westra, W.H.; Califano, J.A. Human papillomavirus and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: recent evidence and clinical implications. J Dent Res 2009, 88, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.C. The relation between human papillomavirus (HPV) and oropharyngeal cancer: a review. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milas, L.; Mason, K.A.; Liao, Z.; Ang, K.K. Chemoradiotherapy: emerging treatment improvement strategies. Head & neck 2003, 25, 152–167. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.S.; Johnson, D.E.; Grandis, J.R. An update: emerging drugs to treat squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Expert opinion on emerging drugs 2018, 23, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perri, F.; Ionna, F.; Longo, F.; Della Vittoria Scarpati, G.; De Angelis, C.; Ottaiano, A.; Botti, G.; Caponigro, F. Immune Response Against Head and Neck Cancer: Biological Mechanisms and Implication on Therapy. Translational oncology 2019, 13, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Grandis, J.R. Emerging drugs for head and neck cancer. Expert opinion on emerging drugs 2015, 20, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.J.; Chiosea, S.I.; Grandis, J.R. Molecular changes in the multistage pathogenesis of head and neck cancer. Cancer biomarkers : section A of Disease markers 2010, 9, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafinski, M.E.; Ferris, R.L.; Ferrone, S.; Grandis, J.R. Epidermal growth factor receptor targeted therapy of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Head & neck 2010, 32, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Cheng, H.; Roberts, T.M.; Zhao, J.J. Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer. Nature reviews Drug discovery 2009, 8, 627–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, P.; Wang, Z. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Cell Proliferation Signaling Pathways. Cancers (Basel) 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alorabi, M.; Shonka, N.A.; Ganti, A.K. EGFR monoclonal antibodies in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: What is their current role? Critical reviews in oncology/hematology 2016, 99, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaszczak, W.; Barczak, W.; Wegner, A.; Golusinski, W.; Suchorska, W.M. Clinical value of monoclonal antibodies and tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Medical oncology (Northwood, London, England) 2017, 34, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, R.; Cohen, R.B.; Burtness, B.A. The role of cetuximab for the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Clinical advances in hematology & oncology : H&O 2008, 6, 742–750. [Google Scholar]
- Argiris A, Heron DE, Smith RP, Kim S, Gibson MK, Lai SY, Branstetter BF, Posluszny DM, Wang L, Seethala RR.; et al. Induction docetaxel, cisplatin, and cetuximab followed by concurrent radiotherapy, cisplatin, and cetuximab and maintenance cetuximab in patients with locally advanced head and neck cancer. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2010, 28, 5294–5300. [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.J.; Ko, A.; Kil, S.H.; Mallen-St Clair, J.; Shin, D.S.; Wang, M.B.; Srivatsan, E.S. EGFR pathway targeting drugs in head and neck cancer in the era of immunotherapy. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 2023, 1878, 188827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; He, J.; Li, B.; Zheng, Y.; Li, K.; Zou, S.; Chen, L. Efficacy and Safety of Gefitinib in Patients with Advanced Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Oncol, 6273. [Google Scholar]
- Sacco, A.G.; Worden, F.P. Molecularly targeted therapy for the treatment of head and neck cancer: a review of the ErbB family inhibitors. OncoTargets and therapy 2016, 9, 1927–1943. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rysman, B.; Mouawad, F.; Gros, A.; Lansiaux, A.; Chevalier, D.; Meignan, S. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 3 in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Head Neck 2016, 38 (Suppl 1), E2412–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palumbo, C.; Benvenuto, M.; Focaccetti, C.; Albonici, L.; Cifaldi, L.; Rufini, A.; Nardozi, D.; Angiolini, V.; Bei, A.; Masuelli, L.; et al. Recent findings on the impact of ErbB receptors status on prognosis and therapy of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Front Med (Lausanne) 2023, 10, 1066021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specenier, P.; Vermorken, J. Afatinib in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Expert opinion on pharmacotherapy 2016, 17, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machiels, J.P.; Haddad, R.I.; Fayette, J.; Licitra, L.F.; Tahara, M.; Vermorken, J.B.; Clement, P.M.; Gauler, T.; Cupissol, D.; Grau, J.J.; et al. Afatinib versus methotrexate as second-line treatment in patients with recurrent or metastatic squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck progressing on or after platinum-based therapy (LUX-Head & Neck 1): an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2015, 16, 583–594. [Google Scholar]
- Kao, H.F.; Liao, B.C.; Huang, Y.L.; Huang, H.C.; Chen, C.N.; Chen, T.C.; Hong, Y.J.; Chan, C.Y.; Chia, J.S.; Hong, R.L. Afatinib and Pembrolizumab for Recurrent or Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ALPHA Study): A Phase II Study with Biomarker Analysis. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2022, 28, 1560–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Ahn, M.J.; Chan, A.; Wang, C.H.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, S.B.; Bello, M.; Arora, R.S.; Zhang, Q.; He, X.; et al. Afatinib versus methotrexate as second-line treatment in Asian patients with recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck progressing on or after platinum-based therapy (LUX-Head & Neck 3): an open-label, randomised phase III trial. Ann Oncol 2019, 30, 1831–1839. [Google Scholar]
- Haddad, R.; Guigay, J.; Keilholz, U.; Clement, P.M.; Fayette, J.; de Souza Viana, L.; Rolland, F.; Cupissol, D.; Geoffrois, L.; Kornek, G.; et al. Afatinib as second-line treatment in patients with recurrent/metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: Subgroup analyses of treatment adherence, safety and mode of afatinib administration in the LUX-Head and Neck 1 trial. Oral Oncol 2019, 97, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellor, P.; Furber, L.A.; Nyarko, J.N.; Anderson, D.H. Multiple roles for the p85α isoform in the regulation and function of PI3K signalling and receptor trafficking. The Biochemical journal 2012, 441, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, V.W.; Hedberg, M.L.; Li, H.; Vangara, B.S.; Pendleton, K.; Zeng, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Du, Y.; Gilbert, B.R.; et al. Frequent mutation of the PI3K pathway in head and neck cancer defines predictive biomarkers. Cancer Discov 2013, 3, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburrino, A.; Molinolo, A.A.; Salerno, P.; Chernock, R.D.; Raffeld, M.; Xi, L.; Gutkind, J.S.; Moley, J.F.; Wells, S.A.; Jr Santoro, M. Activation of the mTOR pathway in primary medullary thyroid carcinoma and lymph node metastases. Clin Cancer Res 2012, 18, 3532–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancox U, Cosulich S, Hanson L, Trigwell C, Lenaghan C, Ellston R, Dry H, Crafter C, Barlaam B, Fitzek M.; et al. Inhibition of PI3Kbeta signaling with AZD8186 inhibits growth of PTEN-deficient breast and prostate tumors alone and in combination with docetaxel. Molecular cancer therapeutics 2015, 14, 48–58. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer discovery 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poetsch, M.; Lorenz, G.; Kleist, B. Detection of new PTEN/MMAC1 mutations in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas with loss of chromosome 10. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2002, 132, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangale, Z.; Prass, C.; Carlson, A.; Tikishvili, E.; Degrado, J.; Lanchbury, J.; Stone, S. A robust immunohistochemical assay for detecting PTEN expression in human tumors. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2011, 19, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squarize, C.H.; Castilho, R.M.; Abrahao, A.C.; Molinolo, A.; Lingen, M.W.; Gutkind, J.S. PTEN deficiency contributes to the development and progression of head and neck cancer. Neoplasia (New York, NY) 2013, 15, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psyrri, A.; Seiwert, T.Y.; Jimeno, A. Molecular pathways in head and neck cancer: EGFR, PI3K, and more. American Society of Clinical Oncology educational book American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting 2013, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquard, F.E.; Jucker, M. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling as a molecular target in head and neck cancer. Biochemical pharmacology 2020, 172, 113729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzuto, F.; Buonaguro, L.; Caponigro, F.; Ionna, F.; Starita, N.; Annunziata, C.; Buonaguro, F.M.; Tornesello, M.L. Update on Head and Neck Cancer: Current Knowledge on Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Molecular Features and Novel Therapies. Oncology 2015, 89, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Liao, J.; Schumaker, L.; Carter-Cooper, B.; Lapidus, R.G.; Fan, X.; Gaykalova, D.A.; Mehra, R.; Cullen, K.J.; Dan, H. Simultaneously targeting ErbB family kinases and PI3K in HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 2022, 131, 105939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Liao, J.; Carter-Cooper, B.A.; Lapidus, R.G.; Cullen, K.J.; Dan, H. Regulation of cisplatin-resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by the SRC/ETS-1 signaling pathway. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, L.M.; Geng, X.; Bonazzi, V.F.; Ju, R.J.; Mahon, C.E.; Cummings, M.C.; Stephenson, S.A.; Pollock, P.M. PI3K Inhibitors Synergize with FGFR Inhibitors to Enhance Antitumor Responses in FGFR2(mutant) Endometrial Cancers. Mol Cancer Ther 2017, 16, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.C. Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer research 2010, 70, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarty, A.; Sánchez, V.; Kuba, M.G.; Rinehart, C.; Arteaga, C.L. Feedback upregulation of HER3 (ErbB3) expression and activity attenuates antitumor effect of PI3K inhibitors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2012, 109, 2718–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meister, K.S.; Godse, N.R.; Khan, N.I.; Hedberg, M.L.; Kemp, C.; Kulkarni, S.; Alvarado, D.; LaVallee, T.; Kim, S.; Grandis, J.R.; et al. HER3 targeting potentiates growth suppressive effects of the PI3K inhibitor BYL719 in pre-clinical models of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Scientific reports 2019, 9, 9130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaryouh, H.; Van Loenhout, J.; Peeters, M.; Vermorken, J.B.; Lardon, F.; Wouters, A. Co-Targeting the EGFR and PI3K/Akt Pathway to Overcome Therapeutic Resistance in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: What about Autophagy? Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaryouh, H.; De Pauw, I.; Baysal, H.; Pauwels, P.; Peeters, M.; Vermorken, J.B.; Lardon, F.; Wouters, A. The Role of Akt in Acquired Cetuximab Resistant Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An In Vitro Study on a Novel Combination Strategy. Front Oncol 2021, 11, 697967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mock, A.; Plath, M.; Moratin, J.; Tapken, M.J.; Jäger, D.; Krauss, J.; Fröhling, S.; Hess, J.; Zaoui, K. EGFR and PI3K Pathway Activities Might Guide Drug Repurposing in HPV-Negative Head and Neck Cancers. Front Oncol 2021, 11, 678966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izumi, H.; Wang, Z.; Goto, Y.; Ando, T.; Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Johnson, D.E.; Grandis, J.R.; Gutkind, J.S. Pathway-Specific Genome Editing of PI3K/mTOR Tumor Suppressor Genes Reveals that PTEN Loss Contributes to Cetuximab Resistance in Head and Neck Cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 2020, 19, 1562–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, R.S.; Garrett, J.T.; Sánchez, V.; Stanford, J.C.; Young, C.; Chakrabarty, A.; Rinehart, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Greenberger, L.; et al. ErbB3 ablation impairs PI3K/Akt-dependent mammary tumorigenesis. Cancer research 2011, 71, 3941–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, R.; Patel, H.; Alanazi, S.; Yuan, L.; Garrett, J.T. HER3 signaling and targeted therapy in cancer. Oncol Rev 2018, 12, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrett, J.T.; Sutton, C.R.; Kurupi, R.; Bialucha, C.U.; Ettenberg, S.A.; Collins, S.D.; Sheng, Q.; Wallweber, J.; Defazio-Eli, L.; Arteaga, C.L. Combination of antibody that inhibits ligand-independent HER3 dimerization and a p110α inhibitor potently blocks PI3K signaling and growth of HER2+ breast cancers. Cancer research 2013, 73, 6013–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milewska, M.; Cremona, M.; Morgan, C.; O'Shea, J.; Carr, A.; Vellanki, S.H.; Hopkins, A.M.; Toomey, S.; Madden, S.F.; Hennessy, B.T.; et al. Development of a personalized therapeutic strategy for ERBB-gene-mutated cancers. Ther Adv Med Oncol 2018, 10, 1758834017746040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari Dilmaghani, N.; Safaroghli-Azar, A.; Pourbagheri-Sigaroodi, A.; Bashash, D. The PI3K/Akt/mTORC signaling axis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Possibilities for therapeutic interventions either as single agents or in combination with conventional therapies. IUBMB Life 2021, 73, 618–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.; Kang, H.; Mehra, R. Targeting phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Cancers of the head & neck 2018, 3, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Suh, K.J.; Sung, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Han, S.H.; Lee, H.S.; Min, A.; Kang, M.H.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, S.H.; et al. EGFR or HER2 inhibition modulates the tumor microenvironment by suppression of PD-L1 and cytokines release. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 63901–63910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler M, Schulz D, Piendl G, Brockhoff G, Eichberger J, Menevse AN, Beckhove P, Hautmann M, Reichert TE, Ettl T.; et al. Buparlisib modulates PD-L1 expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Exp Cell Res 2020, 396, 112259. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




