Submitted:
07 February 2024
Posted:
08 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of CS Nanoparticles
2.2. Characterization of Chitosan Nanoparticles
3. Results
3.1. XRD and TEM Analyses
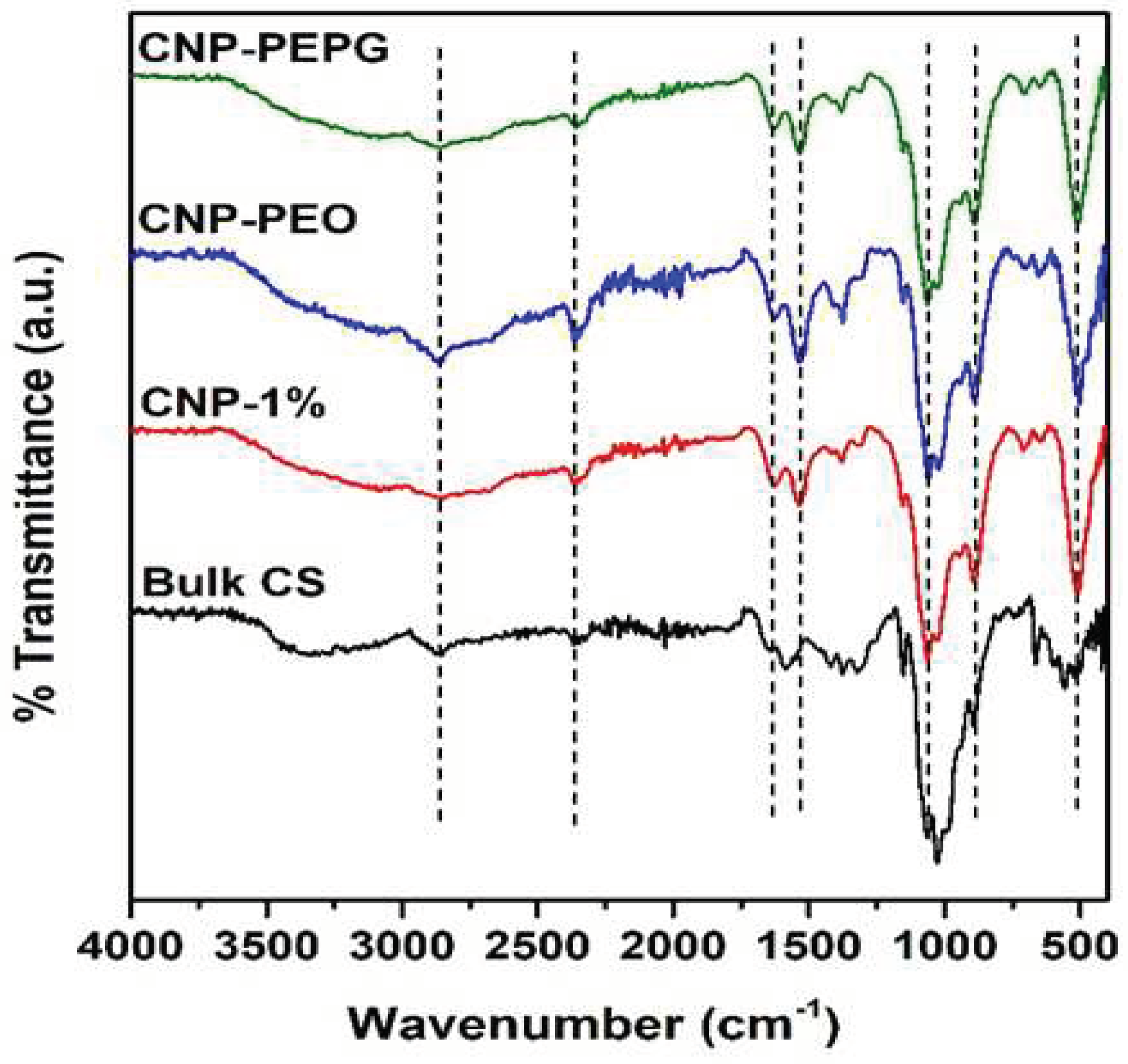
3.2. FTIR Spectroscopy Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jha, R.; Mayanovic, R. A. A Review of the Preparation, Characterization, and Applications of Chitosan Nanoparticles in Nanomedicine. Nanomaterials 2023, 13(8), 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, K.; Singh, S. K.; Mishra, D. N. Chitosan Nanoparticles: A Promising System in Novel Drug Delivery. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58(11), 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.; Syeda, J.; Wasan, K.; Wasan, E. An Overview of Chitosan Nanoparticles and Its Application in Non-Parenteral Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9(4), 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, U.; Chauhan, S.; Nagaich, U.; Jain, N. Current Advances in Chitosan Nanoparticles Based Drug Delivery and Targeting. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 9(2), 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z. Recent Advances of Chitosan Nanoparticles as Drug Carriers. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2011, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naskar, S.; Koutsu, K.; Sharma, S. Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Systems: A Review on Two Decades of Research. J. Drug Target. 2019, 27(4), 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Campos, A. M.; Sánchez, A.; Alonso, M. J. Chitosan Nanoparticles: A New Vehicle for the Improvement of the Delivery of Drugs to the Ocular Surface. Application to Cyclosporin A. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 224(1–2), 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, Q. Recent Development of Chitosan-Based Polyelectrolyte Complexes with Natural Polysaccharides for Drug Delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 64, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumirska, J.; Weinhold, M. X.; Thöming, J.; Stepnowski, P. Biomedical Activity of Chitin/Chitosan Based Materials- Influence of Physicochemical Properties Apart from Molecular Weight and Degree of N-Acetylation. Polymers (Basel). 2011, 3(4), 1875–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranaz, I.; Mengibar, M.; Harris, R.; Panos, I.; Miralles, B.; Acosta, N.; Galed, G.; Heras, A. Functional Characterization of Chitin and Chitosan. Curr. Chem. Biol. 2012, 3(2), 203–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumirska, J.; Czerwicka, M.; Kaczyński, Z.; Bychowska, A.; Brzozowski, K.; Thöming, J.; Stepnowski, P. Application of Spectroscopic Methods for Structural Analysis of Chitin and Chitosan. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8(5), 1567–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, R.; Maji, T. K.; Maji, T. K. Determination of Degree of Deacetylation of Chitosan and Their Effect on the Release Behavior of Essential Oil from Chitosan and Chitosan-Gelatin Complex Microcapsules. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Appl. 2013, 2(4), 4–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kasaai, M. R. Various Methods for Determination of the Degree of N-Acetylation of Chitin and Chitosan: A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57(5), 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi Kumar, M. N. V. Chitin and Chitosan Fibres: A Review. Bull. Mater. Sci. 1999, 22(5), 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Q.; Wang, T.; Cochrane, C.; McCarron, P. Modulation of Surface Charge, Particle Size and Morphological Properties of Chitosan-TPP Nanoparticles Intended for Gene Delivery. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2005, 44(2–3), 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, M. E. I.; Rabea, E. I. A Biopolymer Chitosan and Its Derivatives as Promising Antimicrobial Agents against Plant Pathogens and Their Applications in Crop Protection. Int. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2011, 2011, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divya, K.; Jisha, M. S. Chitosan Nanoparticles Preparation and Applications. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16(1), 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranaz, I.; Alcántara, A. R.; Civera, M. C.; Arias, C.; Elorza, B.; Caballero, A. H.; Acosta, N. Chitosan: An Overview of Its Properties and Applications. Polymers (Basel) 2021, 13(19). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamer, T. M.; Hassan, M. A.; Omer, A. M.; Valachová, K.; Eldin, M. S. M.; Collins, M. N.; Šoltés, L. Antibacterial and Antioxidative Activity of O-Amine Functionalized Chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 169, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Farias, B. S.; Sant’Anna Cadaval Junior, T. R.; de Almeida Pinto, L. A. Chitosan-Functionalized Nanofibers: A Comprehensive Review on Challenges and Prospects for Food Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and Chitosan: Properties and Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31(7), 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minke, R.; Blackwell, J. The Structure of α-Chitin. J. Mol. Biol. 1978, 120(2), 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchinatto, W. M.; Santos, D. M. dos; Fiamingo, A.; Bernardes-Filho, R.; Campana-Filho, S. P.; Azevedo, E. R. de; Colnago, L. A. Evaluation of Chitosan Crystallinity: A High-Resolution Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy Approach. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 250(July). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitri, E.; Juliastuti, S. R.; Handaratri, A.; Sumarno; Roesyadi, A. Degradation of Chitosan by Sonication in Very-Low-Concentration Acetic Acid. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 110, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikušová, V.; Mikuš, P. Advances in Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22(17), 9652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M. J.; Calvo, P.; Remun, C. Novel Hydrophilic Chitosan-polyethylene Oxide Nanoparticles as Protein Carriers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 63(1), 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, K.; Brown, W.; Almdal, K.; Alami, E.; Jada, A. Structure of PS-PEO Diblock Copolymers in Solution and the Bulk State Probed Using Dynamic Light-Scattering and Small-Angle Neutron-Scattering and Dynamic Mechanical Measurements. Langmuir 1997, 13(14), 3635–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbasizadeh, B.; Motasadizadeh, H.; Foroughi-Nia, B.; Farhadnejad, H. Tripolyphosphate-Crosslinked Chitosan/Poly (Ethylene Oxide) Electrospun Nanofibrous Mats as a Floating Gastro-Retentive Delivery System for Ranitidine Hydrochloride. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 153, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sazak, C.; Attar, A.; Yilmaz, A.; Altikatoglu Yapaoz, M. Biofabrication of Acer Palmatum-Mediated Multifunctional CuO Nanoparticles for Dye Removal, Antibacterial-Antifungal Activity, and Molecular Docking. ACS Omega 2023. [CrossRef]
- Zaman, M.; Butt, M. H.; Siddique, W.; Iqbal, M. O.; Nisar, N.; Mumtaz, A.; Nazeer, H. Y.; Alshammari, A.; Riaz, M. S. Fabrication of PEGylated Chitosan Nanoparticles Containing Tenofovir Alafenamide: Synthesis and Characterization. Molecules 2022, 27(23). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L, P.; MF, G.; CM, B.; G, Z.; MG, R.; DS, C.; RL, P.; BG, Z.; M, K.; MF, T.; V, R.; MM, S.; CT, F.; CC, F. Structure and Properties of Nanocrystalline Chitosan. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 1(1), 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustriane, C.; Dwivany, F. M.; Suendo, V.; Reza, M. Effect of Chitosan and Chitosan-Nanoparticles on Post Harvest Quality of Banana Fruits. J. Plant Biotechnol. 2018, 45(1), 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, M.; Agarwal, M. K.; Shrivastav, N.; Pandey, S.; Das, R.; Gaur, P. Preparation of Chitosan Nanoparticles and Their In-Vitro Characterization. Int. J. Life-Sciences Sci. Res. 2018, 4(2), 1713–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

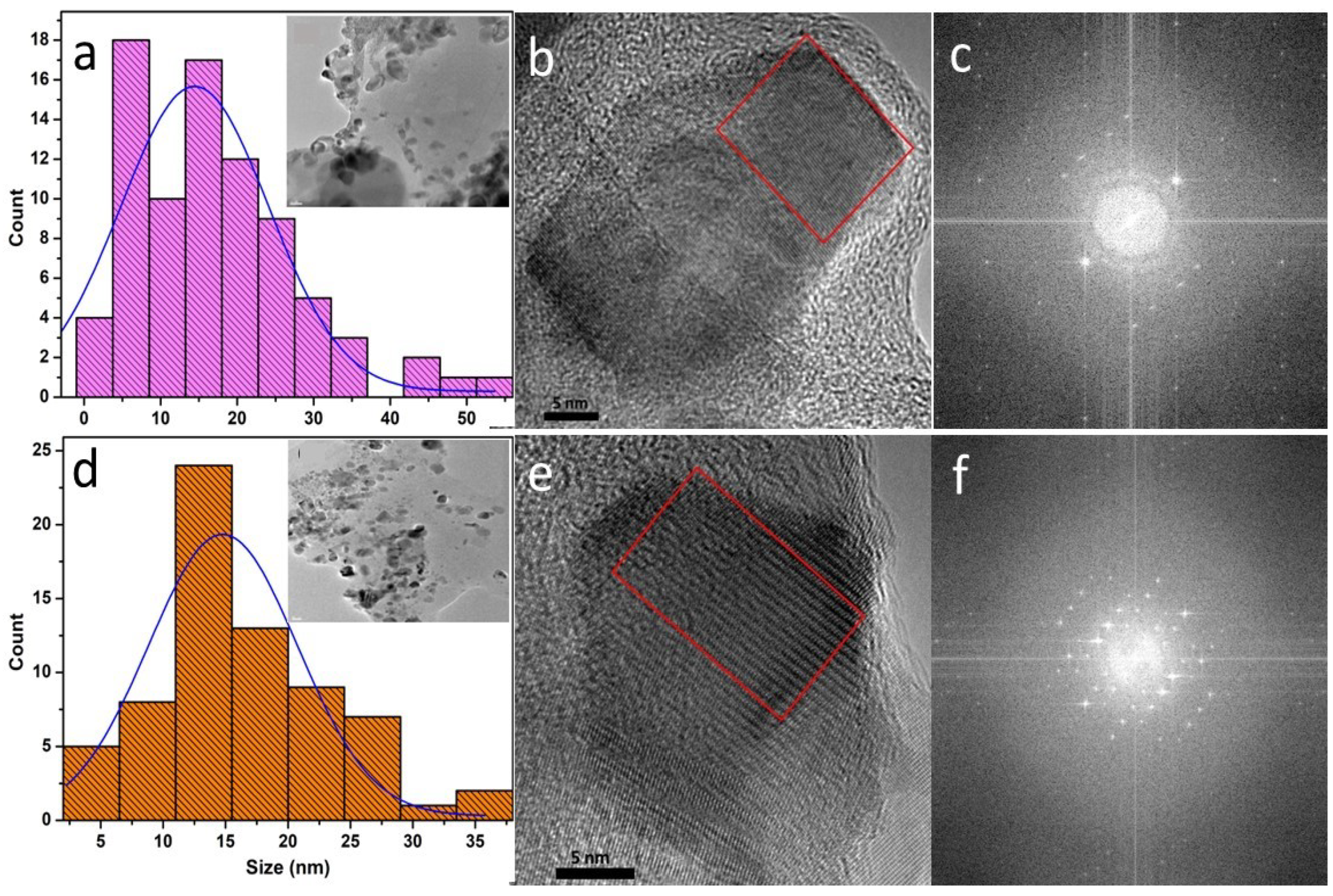
| Sample | Description | Mean size (nm) | FWHM (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNP-0.25% | 0.25% w/v CS-NPs | - | - |
| CNP-0.5% | 0.5% w/v CS-NPs | 13.1 | 15.4 |
| CNP-1.0% | 1.0% w/v CS-NPs | 14.4 | 22.7 |
| CNP-PEO | 1.0% w/v CS-NPs+PEO | 11.3 | 13.0 |
| CNP-PEPG | 1.0% w/v CS-NPs+PEO+PPG | 14.8 | 14.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





