Submitted:
07 February 2024
Posted:
08 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
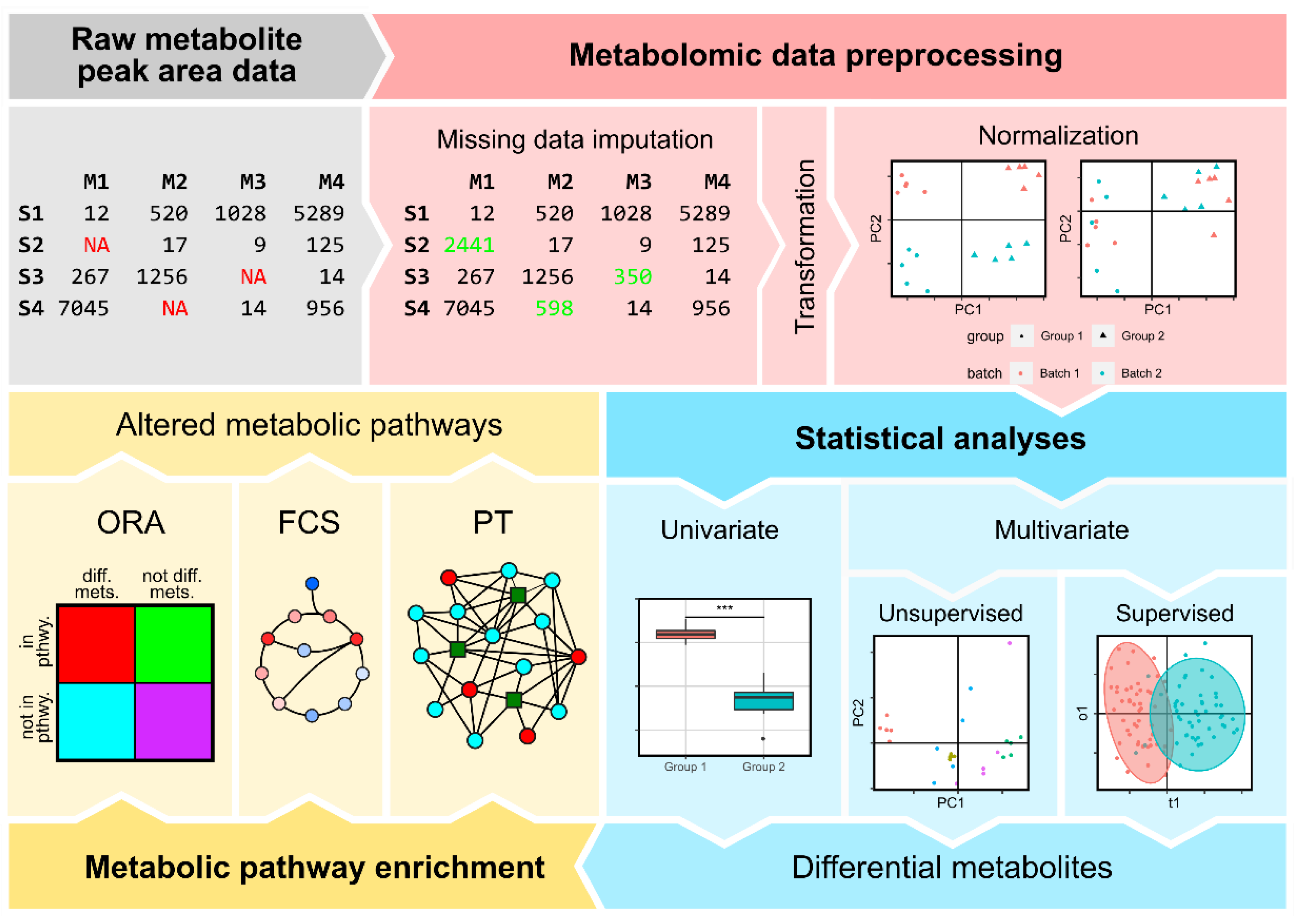
2. Data Preprocessing
2.1. Metabolite Imputation
2.2. Normalization
2.2.1. Normalization Methods
2.2.2. Assessment of Post-Acquisition Normalization Effectivity
3. Statistical Analysis of Metabolomics Data
3.1. Univariate Analyses
3.2. Multivariate Analyses
3.2.1. Non-Supervised Multivariate Analyses
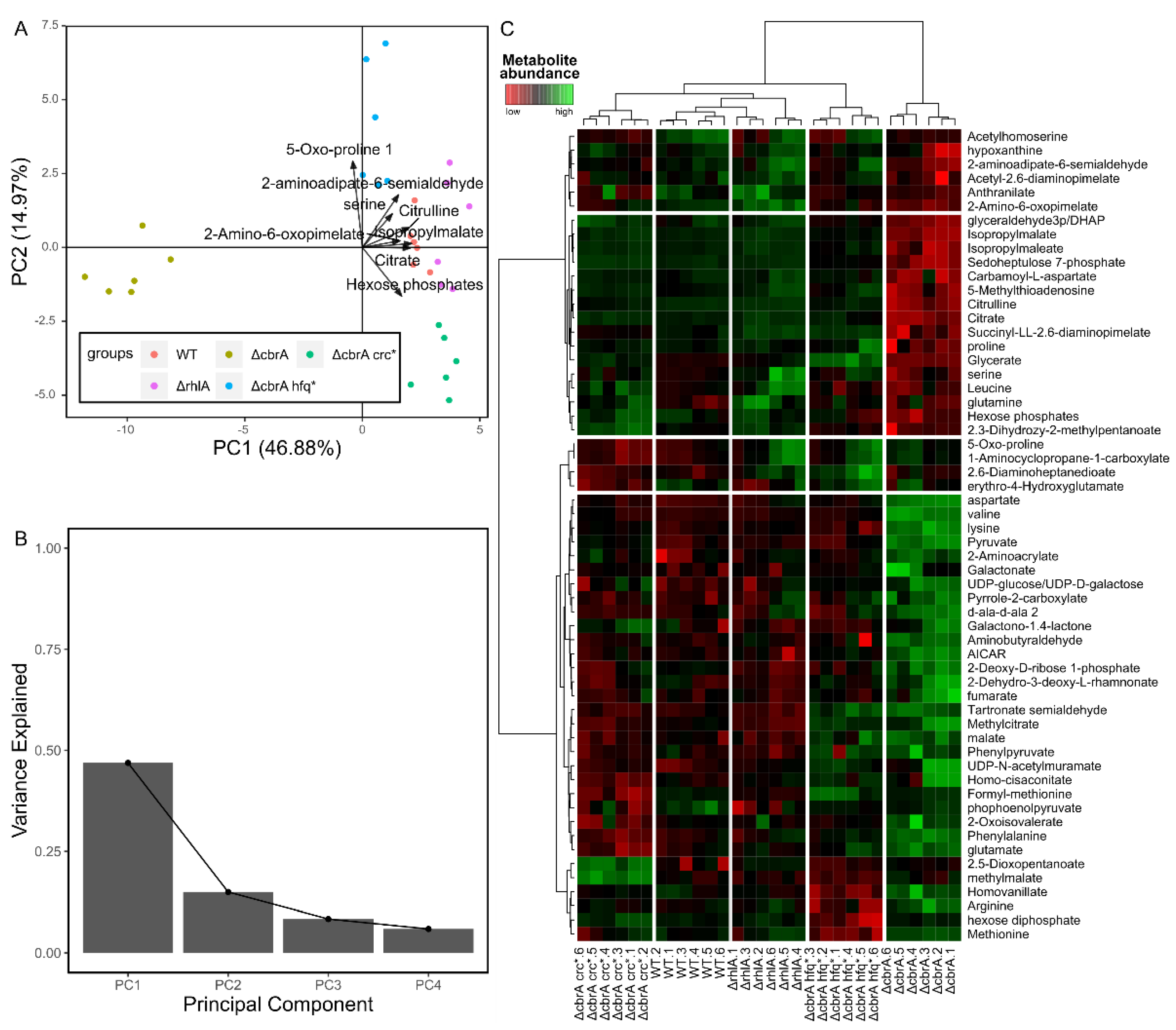
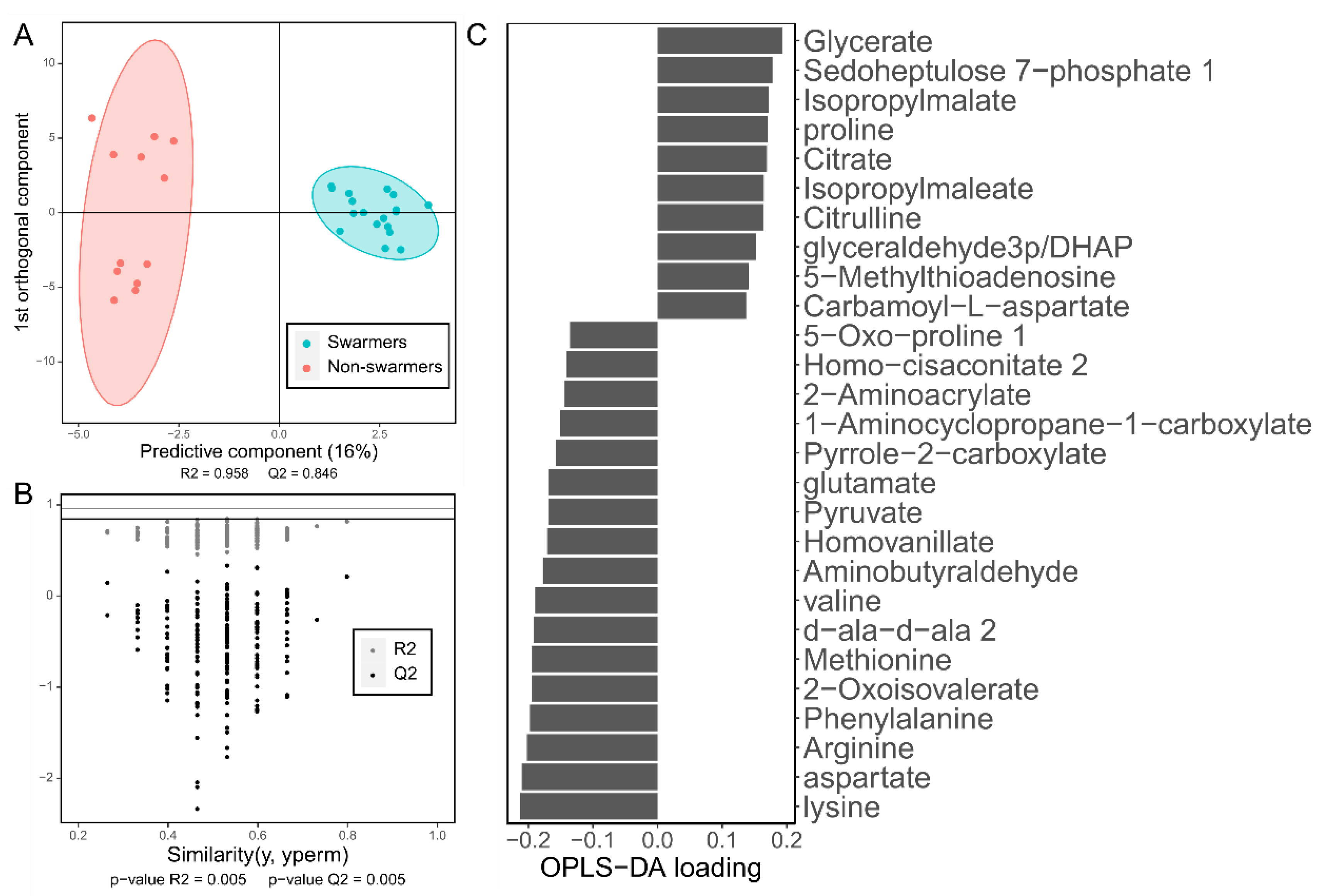
3.2.2. Supervised Multivariate Approaches
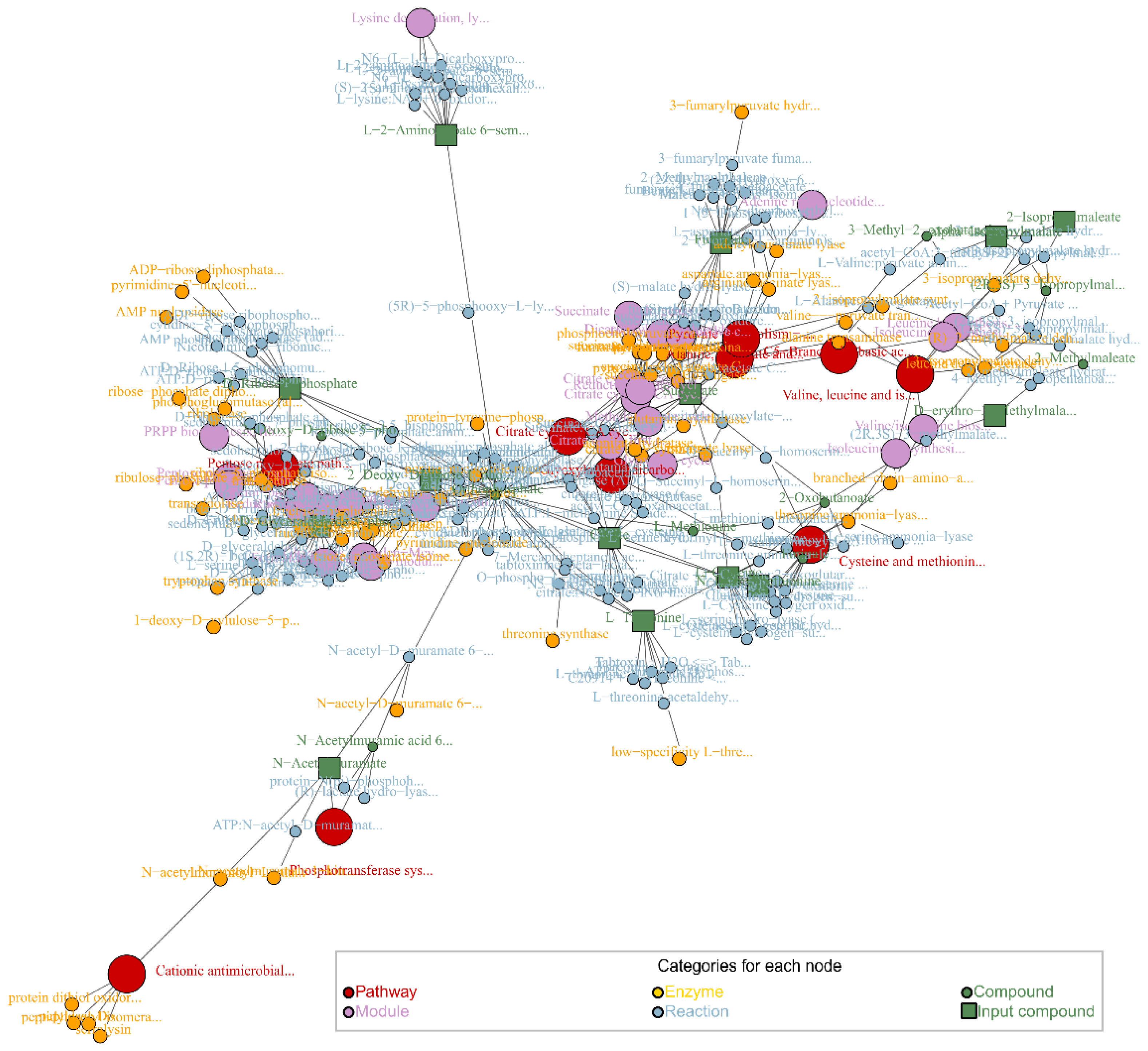
4. Metabolic Pathway Enrichment
4.1. Over-Representation Analysis (ORA)
4.2. Functional Class Scoring (FCS)
4.3. Pathway Topology (PT)
5. Generating Insight when Metabolomic Data Is Not Available: Genome-Scale Metabolic Models
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oliver, S.G.; Winson, M.K.; Kell, D.B.; Baganz, F. Systematic Functional Analysis of the Yeast Genome. Trends Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics – the Link between Genotypes and Phenotypes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 48, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, A.J. Molecular Genetic Studies of Complex Phenotypes. Transl. Res. 2012, 159, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulianello, L.; Canard, C.; Köhler, T.; Caille, D.; Lacroix, J.S.; Meda, P. Rhamnolipids Are Virulence Factors That Promote Early Infiltration of Primary Human Airway Epithelia by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 3134–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, M.E.; Caiazza, N.C.; O’Toole, G.A. Rhamnolipid Surfactant Production Affects Biofilm Architecture in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa PAO1. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiazza, N.C.; Shanks, R.M.Q.; O’Toole, G.A. Rhamnolipids Modulate Swarming Motility Patterns of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 7351–7361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabra, W.; Kim, E.J.; Zeng, A.P. Physiological Responses of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa PAO1 to Oxidative Stress in Controlled Microaerobic and Aerobic Cultures. Microbiology 2002, 148, 3195–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Nair, S.; Ghosh, S. Pathogenesis in Tuberculosis: Transcriptomic Approaches to Unraveling Virulence Mechanisms and Finding New Drug Targets. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 463–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galagan, J.E.; Minch, K.; Peterson, M.; Lyubetskaya, A.; Azizi, E.; Sweet, L.; Gomes, A.; Rustad, T.; Dolganov, G.; Glotova, I.; et al. The Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Regulatory Network and Hypoxia. Nature 2013, 499, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghunandanan, S.; Jose, L.; Gopinath, V.; Kumar, R.A. Comparative Label-Free Lipidomic Analysis of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis during Dormancy and Reactivation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, D.; Li, X.; Shen, J.; Xia, X. Microbial Metabolomics: From Novel Technologies to Diversified Applications. TrAC - Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 148, 116540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emwas, A.H.; Roy, R.; McKay, R.T.; Tenori, L.; Saccenti, E.; Nagana Gowda, G.A.; Raftery, D.; Alahmari, F.; Jaremko, L.; Jaremko, M.; et al. Nmr Spectroscopy for Metabolomics Research. Metabolites 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Liang, Y.; Dunn, W.B.; Shen, H.; Kell, D.B. Comparative Evaluation of Software for Deconvolution of Metabolomics Data Based on GC-TOF-MS. TrAC - Trends Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver Fiehn Metabolomics by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry: The Combination of Targeted and Untargeted Profiling; 2017; Vol. 7; ISBN 0471142727.
- Perez, E.R.; Knapp, J.A.; Horn, C.K.; Stillman, S.L.; Evans, J.E.; Arfsten, D.P. Comparison of LC-MS-MS and GC-MS Analysis of Benzodiazepine Compounds Included in the Drug Demand Reduction Urinalysis Program. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2016, 40, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Idle, J.R. LC-MS-Based Metabolomics in Drug Metabolism. Drug Metab. Rev. 2007, 39, 581–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Benton, H.P.; Siuzdak, G. Bioinformatics: The next Frontier of Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edison, A.S.; Colonna, M.; Gouveia, G.J.; Holderman, N.R.; Judge, M.T.; Shen, X.; Zhang, S. NMR: Unique Strengths That Enhance Modern Metabolomics Research. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 478–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, I.; Climaco Pinto, R.; Graça, G. Metabolomics Data Preprocessing: From Raw Data to Features for Statistical Analysis. Compr. Anal. Chem. 2018, 82, 197–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Marsal, S.; Julià, A. Analytical Methods in Untargeted Metabolomics: State of the Art in 2015. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrydziuszko, O.; Viant, M.R. Missing Values in Mass Spectrometry Based Metabolomics: An Undervalued Step in the Data Processing Pipeline. Metabolomics 2012, 8, S161–S174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, J.; Meng, X.L. Applications of Multiple Imputation in Medical Studies: From AIDS to NHANES. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 1999, 8, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijlsma, S.; Bobeldijk, I.; Verheij, E.R.; Ramaker, R.; Kochhar, S.; Macdonald, I.A.; Van Ommen, B.; Smilde, A.K. Large-Scale Human Metabolomics Studies: A Strategy for Data (Pre-) Processing and Validation. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokla, M.; Virtanen, J.; Kolehmainen, M.; Paananen, J.; Hanhineva, K. Random Forest-Based Imputation Outperforms Other Methods for Imputing LC-MS Metabolomics Data: A Comparative Study. BMC Bioinformatics 2019, 20, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Lynn, H.S. Accuracy of Random-Forest-Based Imputation of Missing Data in the Presence of Non-Normality, Non-Linearity, and Interaction. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2020, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.Y.; Huang, M.W.; Ke, S.W.; Tsai, C.F. The Distance Function Effect on K-Nearest Neighbor Classification for Medical Datasets. Springerplus 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Golub, G.H.; Park, H. Missing Value Estimation for DNA Microarray Gene Expression Data: Local Least Squares Imputation. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troyanskaya, O.; Cantor, M.; Sherlock, G.; Brown, P.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Botstein, D.; Altman, R.B. Missing Value Estimation Methods for DNA Microarrays. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oba, S.; Sato, M.A.; Takemasa, I.; Monden, M.; Matsubara, K.I.; Ishii, S. A Bayesian Missing Value Estimation Method for Gene Expression Profile Data. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 2088–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilin, A.; Raiko, T. Practical Approaches to Principal Component Analysis in the Presence of Missing Values. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2010, 11, 1957–2000. [Google Scholar]
- Leek, J.T.; Scharpf, R.B.; Bravo, H.C.; Simcha, D.; Langmead, B.; Johnson, W.E.; Geman, D.; Baggerly, K.; Irizarry, R.A. Tackling the Widespread and Critical Impact of Batch Effects in High-Throughput Data. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marioni, J.C.; Mason, C.E.; Mane, S.M.; Stephens, M.; Gilad, Y. RNA-Seq: An Assessment of Technical Reproducibility and Comparison with Gene Expression Arrays. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpievitch, Y. V.; Dabney, A.R.; Smith, R.D. Normalization and Missing Value Imputation for Label-Free LC-MS Analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 2012, 13, S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandesompele, J.; De Preter, K.; Pattyn, F.; Poppe, B.; Van Roy, N.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F. Accurate Normalization of Real-Time Quantitative RT-PCR Data by Geometric Averaging of Multiple Internal Control Genes. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2002, 3, research0034.1–research0034.11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiśniewski, J.R.; Mann, M. A Proteomics Approach to the Protein Normalization Problem: Selection of Unvarying Proteins for MS-Based Proteomics and Western Blotting. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 2321–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, L. Sample Normalization Methods in Quantitative Metabolomics. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1430, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, P.; Lv, M.; Guo, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, F. Influences of Normalization Method on Biomarker Discovery in Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry-Based Untargeted Metabolomics: What Should Be Considered? Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 5342–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmerman, L.; De Livera, A.M.; Browne, J.B.; Sheedy, J.R.; Callahan, D.L.; Nahid, A.; De Souza, D.P.; Schoofs, L.; Tull, D.L.; McConville, M.J.; et al. Cross-Platform Urine Metabolomics of Experimental Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes. J. Diabetes Metab. 2012, S6:002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Livera, A.M.; Sysi-Aho, M.; Jacob, L.; Gagnon-Bartsch, J.A.; Castillo, S.; Simpson, J.A.; Speed, T.P. Statistical Methods for Handling Unwanted Variation in Metabolomics Data. Ann. Chem. 2015, 87, 3606–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmands, W.M.B.; Ferrari, P.; Scalbert, A. Normalization to Specific Gravity Prior to Analysis Improves Information Recovery from High Resolution Mass Spectrometry Metabolomic Profiles of Human Urine. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 10925–10931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinowska, R.; Trygg, J.; Wolf-Watz, H.; Mortiz, T.; Surowiec, I. Optimization of a Sample Preparation Method for the Metabolomic Analysis of Clinically Relevant Bacteria. J. Microbiol. Methods 2011, 87, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shen, G.; Zhang, R.; He, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, W.; Chen, X.; Song, Y.; Abliz, Z. Combination of Injection Volume Calibration by Creatinine and MS Signals’ Normalization to Overcome Urine Variability in LC-MS-Based Metabolomics Studies. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 7659–7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Livera, A.M.; Dias, D.A.; De Souza, D.; Rupasinghe, T.; Pyke, J.; Tull, D.; Roessner, U.; McConville, M.; Speed, T.P. Normalizing and Integrating Metabolomics Data. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 10768–10776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, J.; Claggett, B.L.; Henglin, M.; Kim, A.; Ovsak, G.; Kim, N.; Deng, K.; Rao, K.; Tyagi, O.; Watrous, J.D.; et al. Statistical Workflow for Feature Selection in Human Metabolomics Data. Metabolites 2019, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, R.A.; Hoefsloot, H.C.J.; Westerhuis, J.A.; Smilde, A.K.; van der Werf, M.J. Centering, Scaling, and Transformations: Improving the Biological Information Content of Metabolomics Data. BMC Genomics 2006, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Livera, A.M.; Olshansky, G.; Simpson, J.A.; Creek, D.J. NormalizeMets: Assessing, Selecting and Implementing Statistical Methods for Normalizing Metabolomics Data. Metabolomics 2018, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sysi-Aho, M.; Katajamaa, M.; Yetukuri, L.; Orešič, M. Normalization Method for Metabolomics Data Using Optimal Selection of Multiple Internal Standards. BMC Bioinformatics 2007, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grocholska, P.; Bachor, R. Trends in the Hydrogen−deuterium Exchange at the Carbon Centers. Preparation of Internal Standards for Quantitative Analysis by Lc-Ms. Molecules 2021, 26, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullberg, J.; Jonsson, P.; Nordström, A.; Sjöström, M.; Moritz, T. Design of Experiments: An Efficient Strategy to Identify Factors Influencing Extraction and Derivatization of Arabidopsis Thaliana Samples in Metabolomic Studies with Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 331, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.H.; Lin, D.L.; Chang, W.-T.; Liu, C.; Tsay, W.-I.; Li, J.-H.; Kuo, T.-L. Isotopically Labeled Analogues for Drug Quantitation. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 618A–626A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redestig, H.; Fukushima, A.; Stenlund, H.; Moritz, T.; Arita, M.; Saito, K.; Kusano, M. Compensation for Systematic Cross-Contribution Improves Normalization of Mass Spectrometry Based Metabolomics Data. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 7974–7980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon-Bartsch, J.A.; Speed, T.P. Using Control Genes to Correct for Unwanted Variation in Microarray Data. Biostatistics 2012, 13, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, G.; Liao, C.; Lindberg, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Rhee, K.; Pinto, F.; Yan, J.; Xavier, J.B. Evolution and Regulation of Microbial Secondary Metabolism. Elife 2022, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.; Begley, P.; Zelena, E.; Francis-Mcintyre, S.; Anderson, N.; Brown, M.; Knowles, J.D.; Halsall, A.; Haselden, J.N.; et al. Procedures for Large-Scale Metabolic Profiling of Serum and Plasma Using Gas Chromatography and Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Mass Spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1060–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangster, T.; Major, H.; Plumb, R.; Wilson, A.J.; Wilson, I.D. A Pragmatic and Readily Implemented Quality Control Strategy for HPLC-MS and GC-MS-Based Metabonomic Analysis. Analyst 2006, 131, 1075–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gika, H.G.; Theodoridis, G.A.; Wingate, J.E.; Wilson, I.D. Within-Day Reproducibility of an HPLC-MS-Based Method for Metabonomic Analysis: Application to Human Urine. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 3291–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadhurst, D.; Goodacre, R.; Reinke, S.N.; Kuligowski, J.; Wilson, I.D.; Lewis, M.R.; Dunn, W.B. Guidelines and Considerations for the Use of System Suitability and Quality Control Samples in Mass Spectrometry Assays Applied in Untargeted Clinical Metabolomic Studies. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffman, C.; Petrick, L.; Perttula, K.; Yano, Y.; Carlsson, H.; Whitehead, T.; Metayer, C.; Hayes, J.; Rappaport, S.; Dudoit, S. Filtering Procedures for Untargeted Lc-Ms Metabolomics Data. BMC Bioinformatics 2019, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begley, P.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Halsall, A.; Tseng, A.; Knowles, J.; HUSERMET Consortium; Goodacre, R. ; Kell, D.B. Development and Performance of a Gas Chromatography-Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Analysis for Large-Scale Nontargeted Metabolomic Studies of Human Serum. anal 2009, 81, 7038–7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelena, E.; Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Carroll, K.M.; Begley, P.; O’Hagan, S.; Knowles, J.D.; Halsall, A.; HUSERMET Consortium; et al. Development of a Robust and Repeatable UPLC-MS Method for the Long-Term Metabolomic Study of Human Serum. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousseeuw, P.J. Silhouettes: A Graphical Aid to the Interpretation and Validation of Cluster Analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 1987, 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Livera, A.M.; Olshansky, M.; Speed, T.P. Statistical Analysis of Metabolomics Data. In Metabolomics Tools for Natural Product Discovery; 2013; pp. 291–307. [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen, P.; Gommers, R.; Oliphant, T.E.; Haberland, M.; Reddy, T.; Cournapeau, D.; Burovski, E.; Peterson, P.; Weckesser, W.; Bright, J.; et al. Author Correction: SciPy 1.0: Fundamental Algorithms for Scientific Computing in Python. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D Graphics Environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokal, R.R.; Rohlf, F.J. Biometry. The Principles and Practice of Statistics in Biological Research.; Third Edit.; W. H. Freeman and Company: New York, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bewick, V.; Cheek, L.; Ball, J. Statistics Review 14: Logistic Regression. Crit. Care 2005, 9, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadhurst, D.I.; Kell, D.B. Statistical Strategies for Avoiding False Discoveries in Metabolomics and Related Experiments. Metabolomics 2006, 2, 171–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccenti, E.; Hoefsloot, H.C.J.; Smilde, A.K.; Westerhuis, J.A.; Hendriks, M.M.W.B. Reflections on Univariate and Multivariate Analysis of Metabolomics Data. Metabolomics 2014, 10, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worley, B.; Powers, R. Multivariate Analysis in Metabolomics. Curr. Metabolomics 2013, 1, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şenbabaoğlu, Y.; Michailidis, G.; Li, J.Z. Critical Limitations of Consensus Clustering in Class Discovery. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, C.R.; David, W.; Russ, D.; Goldmann, K.; Ehrenstein, M.; Pitzalis, C.; Lewis, M.; Barnes, M. M3C: Monte Carlo Reference-Based Consensus Clustering. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, K.E.; Monaco, H.T.; Deforet, M.; Yan, J.; Wang, Z.; Rhee, K.; Xavier, J.B. Metabolism and the Evolution of Social Behavior. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 2367–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-Learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkerson, M.D.; Hayes, D.N. ConsensusClusterPlus : A Class Discovery Tool with Confidence Assessments and Item Tracking. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1572–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, S.; Sjöström, M.; Eriksson, L. PLS-Regression: A Basic Tool of Chemometrics. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2001, 58, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trygg, J.; Wold, S. Orthogonal Projections to Latent Structures (O-PLS). J. Chemom. 2002, 16, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, T.; Liland, K.H.; Snipen, L.; Sæbø, S. A Review of Variable Selection Methods in Partial Least Squares Regression. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2012, 118, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, A.; Shankar, A.; Chatterjee, A.; More, T.H.; Bose, T.; Dutta, A.; Balakrishnan, K.; Madugulla, L.; Rapole, S.; Mande, S.S.; et al. Rewiring of Metabolic Network in Mycobacterium Tuberculosis during Adaptation to Different Stresses. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, S.; Li, R.; Xia, H.; Jie, Z.; Wen, B.; Chen, X.; Yan, W.; Fan, Y.; et al. Integrated Metabolomics and Metagenomics Analysis of Plasma and Urine Identified Microbial Metabolites Associated with Coronary Heart Disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Chi, Y.H.; Niu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Y.L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.B.; Zhang, C.E.; Li, J.Y.; Wang, L.F.; et al. Metabolomics Coupled with Multivariate Data and Pathway Analysis on Potential Biomarkers in Cholestasis and Intervention Effect of Paeonia Lactiflora Pall. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymańska, E.; Saccenti, E.; Smilde, A.K.; Westerhuis, J.A. Double-Check: Validation of Diagnostic Statistics for PLS-DA Models in Metabolomics Studies. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.H.; Olshen, R.A.; Stone, C.J. Classification and Regression Trees; Chapman & Hall/CRC, 1984; ISBN 0412048418. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Bagging Predictors. Mach. Learn. 1996, 24, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amit, Y.; Geman, D. Shape Quantization and Recognition with Randomized Trees. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1545–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devroye, L.; Lugosi, G. Consistency of Random Forests and Other Averaging Classifiers. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 2015–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S; Fourth edi.; Springer: New York, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Thévenot, E.A.; Roux, A.; Xu, Y.; Ezan, E.; Junot, C. Analysis of the Human Adult Urinary Metabolome Variations with Age, Body Mass Index, and Gender by Implementing a Comprehensive Workflow for Univariate and OPLS Statistical Analyses. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 3322–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mevik, B.-H.; Wehrens, R. The Pls Package: Principal Component and Partial Least Squares Regression in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BiRG - Wright State University Pyopls. Available online: https://pypi.org/project/pyopls/.
- Kuhn, M. Building Predictive Models in R Using the Caret Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 28, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and Regression by RandomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, P.; Sirota, M.; Butte, A.J. Ten Years of Pathway Analysis: Current Approaches and Outstanding Challenges. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeman, J.J.; Bühlmann, P. Analyzing Gene Expression Data in Terms of Gene Sets: Methodological Issues. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. ClusterProfiler: An R Package for Comparing Biological Themes among Gene Clusters. Omi. A J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, F.; Ovens, K.; Hogan, D.J.; Kusalik, A.J. Gene Set Analysis: Challenges, Opportunities, and Future Research. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mootha, V.K.; Lindgren, C.M.; Eriksson, K.F.; Subramanian, A.; Sihag, S.; Lehar, J.; Puigserver, P.; Carlsson, E.; Ridderstråle, M.; Laurila, E.; et al. PGC-1α-Responsive Genes Involved in Oxidative Phosphorylation Are Coordinately Downregulated in Human Diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Chong, J.; Zhou, G.; De Lima Morais, D.A.; Chang, L.; Barrette, M.; Gauthier, C.; Jacques, P.É.; Li, S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 5.0: Narrowing the Gap between Raw Spectra and Functional Insights. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W388–W396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Chong, J.; Li, S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalystR 3.0: Toward an Optimized Workflow for Global Metabolomics. Metabolites 2020, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomfohr, J.; Lu, J.; Kepler, T.B. Pathway Level Analysis of Gene Expression Using Singular Value Decomposition. BMC Bioinformatics 2005, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLuskey, K.; Wandy, J.; Vincent, I.; Hooft, J.J.J. va. der; Rogers, S.; Burgess, K.; Daly, R. Ranking Metabolite Sets by Their Activity Levels. Metabolites 2021, 11, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shojaie, A.; Michailidis, G. Analysis of Gene Sets Based on the Underlying Regulatory Network. J. Comput. Biol. 2009, 16, 407–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellstern, M.; Ma, J.; Yue, K.; Shojaie, A. Netgsa: Fast Computation and Interactive Visualization for Topology-Based Pathway Enrichment Analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1008979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picart-Armada, S.; Fernández-Albert, F.; Vinaixa, M.; Yanes, O.; Perera-Lluna, A. FELLA: An R Package to Enrich Metabolomics Data. BMC Bioinformatics 2018, 19, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, L.; Neuvial, P.; Dudoit, S. More Power via Graph-Structured Tests for Differential Expression of Gene Networks. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2012, 6, 561–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, G.; Ruiz-Rodríguez, P.; Renau-Mínguez, C.; Pinto, F.R.; Coscollá, M. In Silico Exploration of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Metabolic Networks Shows Host-Associated Convergent Fluxomic Phenotypes. Biomolecules 2022, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baart, G.J.; Martens, D.E. Genome-Scale Metabolic Models: Reconstruction and Analysis. In Neisseria meningiditis: Advanced Methods and Protocols; Christodoulides, M., Ed.; Humana Press, 2011; pp. 107–126. [Google Scholar]
- Santamaria, G.; Liao, C.; Wang, Z.; Rhee, K.; Pinto, F.; Yan, J.; Xavier, J.B. Evolution and Regulation of Microbial Secondary Metabolism. bioRxiv 2021, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartell, J.A.; Blazier, A.S.; Yen, P.; Thøgersen, J.C.; Jelsbak, L.; Goldberg, J.B.; Papin, J.A. Reconstruction of the Metabolic Network of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa to Interrogate Virulence Factor Synthesis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, J.S.; Palsson, B.O. Systems Properties of the Haemophilus Influenzae Rd Metabolic Genbotype. Mol. Biol. 1999, 274, 17410–17416. [Google Scholar]
- Karp, P.D.; Weaver, D.; Latendresse, M. How Accurate Is Automated Gap Filling of Metabolic Models ? 2018, 1–11.
- Palsson, B.Ø. Systems Biology: Properties of Reconstructed Networks; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 2006; ISBN 9780521859035. [Google Scholar]
- Varma, A.; Palsson, B.Ø. Metabolic Flux Balancing: Basic Concepts, Scientific and Practical Use. Nat. Biotechnol. 1994, 12, 994–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feist, A.M.; Palsson, B.Ø. The Biomass Objective Function. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2010, 13, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuetz, R.; Kuepfer, L.; Sauer, U. Systematic Evaluation of Objective Functions for Predicting Intracellular Fluxes in Escherichia Coli. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2007, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piddington, D.L.; Kashkouli, A.; Buchmeier, N.A. Growth of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis in a Defined Medium Is Very Restricted by Acid PH and Mg 2 Levels Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Grows within the Phagocytic Vacuoles of Macrophages, Where It Encounters a Moderately Acidic and Possibly Nutrient-Restricted. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 4518–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, K.E.; Monaco, H.; van Ditmarsch, D.; Deforet, M.; Xavier, J.B. Integration of Metabolic and Quorum Sensing Signals Governing the Decision to Cooperate in a Bacterial Social Trait. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, H.A.; Dyson, B.C.; Vass, L.; Johnson, G.N.; Schwartz, J.M. Flux Sampling Is a Powerful Tool to Study Metabolism under Changing Environmental Conditions. npj Syst. Biol. Appl. 2019, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiback, S.J.; Famili, I.; Greenberg, H.J.; Palsson, B. Monte Carlo Sampling Can Be Used to Determine the Size and Shape of the Steady-State Flux Space. J. Theor. Biol. 2004, 228, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S. Emerging Applications of Metabolomics in Drug Discovery and Precision Medicine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Øyås, O.; Borrell, S.; Trauner, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Feldmann, J.; Liphardt, T.; Gagneux, S.; Stelling, J.; Sauer, U.; Zampieri, M. Model-Based Integration of Genomics and Metabolomics Reveals SNP Functionality in Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2020, 117, 8494–8502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




