Submitted:
05 February 2024
Posted:
06 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case selection
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. BMD assessment
2.4. Statistical analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nuti R, Brandi ML, Checchia G, Di Munno O, Dominguez L, Falaschi P, et al. Guidelines for the management of osteoporosis and fragility fractures. Intern Emerg Med 2019;14:85–102. [CrossRef]
- Johnston CB, Dagar M. Osteoporosis in Older Adults. Medical Clinics of North America 2020;104:873–84. [CrossRef]
- Piscitelli P, Neglia C, Feola M, Rizzo E, Argentiero A, Ascolese M, et al. Updated incidence and costs of hip fractures in elderly Italian population. Aging Clin Exp Res 2020;32:2587–93. [CrossRef]
- Davies MJ, Aroda VR, Collins BS, Gabbay RA, Green J, Maruthur NM, et al. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2022. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia 2022;65:1925–66. [CrossRef]
- Lovic D, Piperidou A, Zografou I, Grassos H, Pittaras A, Manolis A. The Growing Epidemic of Diabetes Mellitus. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 2020;18:104–9. [CrossRef]
- Ministero della Salute, Relazione al Parlamento 2021 sullo stato delle conoscenze e delle nuove acquisizioni in tema di diabete mellito - Legge 16 marzo 1987, n. 115, recante “Disposizioni per la prevenzione e la cura del diabete mellito” https://www.salute.gov.it/portale/documentazione/p6_2_2_1.jsp?lingua=italiano&id=3229. n.d.
- Dal Canto E, Ceriello A, Rydén L, Ferrini M, Hansen TB, Schnell O, et al. Diabetes as a cardiovascular risk factor: An overview of global trends of macro and micro vascular complications. Eur J Prev Cardiol 2019;26:25–32. [CrossRef]
- Napoli N, Chandran M, Pierroz DD, Abrahamsen B, Schwartz A V., Ferrari SL. Mechanisms of diabetes mellitus-induced bone fragility. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2017;13:208–19. [CrossRef]
- Hofbauer LC, Busse B, Eastell R, Ferrari S, Frost M, Müller R, et al. Bone fragility in diabetes: novel concepts and clinical implications. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2022;10:207–20. [CrossRef]
- Napoli N, Incalzi RA, De Gennaro G, Marcocci C, Marfella R, Papalia R, et al. Bone fragility in patients with diabetes mellitus: A consensus statement from the working group of the Italian Diabetes Society (SID), Italian Society of Endocrinology (SIE), Italian Society of Gerontology and Geriatrics (SIGG), Italian Society of Orthopaedics and Traumatology (SIOT). Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2021;31:1375–90. [CrossRef]
- Janghorbani M, Van Dam RM, Willett WC, Hu FB. Systematic Review of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Risk of Fracture. Am J Epidemiol 2007;166:495–505. [CrossRef]
- Weber DR, Haynes K, Leonard MB, Willi SM, Denburg MR. Type1Diabetes IsAssociatedWith an Increased Risk of Fracture Across theLifeSpan:APopulation- Based Cohort Study Using The Health Improvement Network (THIN). Diabetes Care 2015;38:1913–20. [CrossRef]
- Van Hulten V, Rasmussen N, Driessen JHM, Burden AM, Kvist A, van den Bergh JP. Fracture Patterns in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Narrative Review of Recent Literature. Curr Osteoporos Rep 2021;19:644–55. [CrossRef]
- Bai J, Gao Q, Wang C, Dai J. Diabetes mellitus and risk of low-energy fracture: a meta-analysis. Aging Clin Exp Res 2020;32:2173–86. [CrossRef]
- Wang H, Ba Y, Xing Q, Du J-L. Diabetes mellitus and the risk of fractures at specific sites: a meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2019;9:e024067. [CrossRef]
- Palermo A, D’Onofrio L, Buzzetti R, Manfrini S, Napoli N. Pathophysiology of Bone Fragility in Patients with Diabetes. Calcif Tissue Int 2017;100:122–32. [CrossRef]
- Eller-Vainicher C, Cairoli E, Grassi G, Grassi F, Catalano A, Merlotti D, et al. Pathophysiology and Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Bone Fragility. J Diabetes Res 2020;2020:7608964. [CrossRef]
- Hamann C, Kirschner S, Günther KP, Hofbauer LC. Bone, sweet bone - Osteoporotic fractures in diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2012;8:297–305. [CrossRef]
- Napoli N, Strotmeyer ES, Ensrud KE, Sellmeyer DE, Bauer DC, Hoffman AR, et al. Fracture risk in diabetic elderly men: The MrOS study. Diabetologia 2014;57:2057–65. [CrossRef]
- Valderrábano RJ, Linares MI. Diabetes mellitus and bone health: epidemiology, etiology and implications for fracture risk stratification. Clin Diabetes Endocrinol 2018;4:9. [CrossRef]
- Krugh M, Langaker MD. Krugh M, Langaker MD. Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry. 2023 Jun 5. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan–. PMID: 30085584. 2023.
- Bonds DE, Larson JC, Schwartz A V, Strotmeyer ES, Robbins J, Rodriguez BL, et al. Risk of fracture in women with type 2 diabetes: the Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006;91:3404–10. [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal R, Cibula D, Ghosh C, Weinstock RS, Moses AM. Bone quality assessment in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Osteoporos Int 2014;25:1969–73. [CrossRef]
- Silva BC, Leslie WD, Resch H, Lamy O, Lesnyak O, Binkley N, et al. Trabecular bone score: A noninvasive analytical method based upon the DXA image. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research 2014;29:518–30. [CrossRef]
- McCloskey E V, Odén A, Harvey NC, Leslie WD, Hans D, Johansson H, et al. A Meta-Analysis of Trabecular Bone Score in Fracture Risk Prediction and Its Relationship to FRAX. J Bone Miner Res 2016;31:940–8. [CrossRef]
- Ho-Pham LT, Nguyen T V. Association between trabecular bone score and type 2 diabetes: a quantitative update of evidence. Osteoporosis International 2019;30:2079–85. [CrossRef]
- Guglielmi G, Diacinti D, van Kuijk C, Aparisi F, Krestan C, Adams JE, et al. Vertebral morphometry: current methods and recent advances. Eur Radiol 2008;18:1484–96. [CrossRef]
- The jamovi project (2022). jamovi. (Version 2.3) [Computer Software]. Retrieved from https://www.jamovi.org. n.d.
- Janghorbani M, Feskanich D, Willett WC, Hu F. Prospective study of diabetes and risk of hip fracture: the Nurses’ Health Study. Diabetes Care 2006;29:1573–8. [CrossRef]
- Leslie WD, Krieg MA, Hans D. Clinical factors associated with trabecular bone score. Journal of Clinical Densitometry 2013;16:374–9. [CrossRef]
- Palermo A, Tuccinardi D, Defeudis G, Watanabe M, D’Onofrio L, Lauria Pantano A, et al. BMI and BMD: The Potential Interplay between Obesity and Bone Fragility. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2016;13. [CrossRef]
- Gortler H, Rusyn J, Godbout C, Chahal J, Schemitsch EH, Nauth A. Diabetes and Healing Outcomes in Lower Extremity Fractures: A Systematic Review. Injury 2018;49:177–83. [CrossRef]
- Norris R, Parker M. Diabetes mellitus and hip fracture: a study of 5966 cases. Injury 2011;42:1313–6. [CrossRef]
| Variables | Total |
|---|---|
| Participants n. (%) | 713 |
| Males n. (%) | 27 (3.8) |
| Median Age (years ± IQR) | 81 ± 11 |
| Median BMI (kg/m2 ± IQR) | 23.7 ± 4.34 |
| Median age at the time of first fracture (years ± IQR) | 71 ± 12 |
| Median BMD lumbar spine (g/cm2 ± IQR) | 0.771 ± 0.180 |
| Median BMD femoral neck (g/cm2 ± IQR) | 0.573 ± 0.112 |
|
Median BMD total hip (g/cm2 ± IQR) |
0.713 ± 0.139 |
| Median TBS ± IQR | 1.240 ± 0.125 |
| Family history of Osteoporosis n. (%) | 199 (27.9) |
| Smoking habit n. (%) | 130 (18.2) |
| Alcohol excess n. (%) | 7 (1) |
| RA n. (%) | 29 (4.1) |
| COPD n. (%) | 44 (6.2) |
| Cortisone therapy n. (%) | 40 (5.6) |
| Vertebral fractures n. (%) | 593 (83.2) |
| Hip fractures n. (%) | 36 (5) |
| Both vertebral and hip fractures n. (%) | 32 (4.5) |
| Non-vertebral - non-hip fractures n. (%) | 59 (8.3) |
| Patients with DM n. | 77 |
|---|---|
| Type 2 DM n. (%) | 70 (90.9) |
| Median Duration of DM ± IQR | 15 ± 10 |
| Median HbA1c mmol/mol ± IQR | 50 ± 12 |
| Median HbA1c % ± IQR | 6.8 ± 1.1 |
| Nutritional therapy n. (%) | 10 (13) |
| Oral hypoglycemic drugs n. (%) | 45 (58) |
| Insulin n. (%) | 17 (22) |
| Insulin + oral hypoglycemic drugs n. (%) | 5 (7) |
| Coronary heart disease n. (%) | 15 (19.5) |
| Carotid artery atheromasia - peripheral arterial disease n. (%) | 30 (39) |
| Peripheral Neuropathy n. (%) | 15 (19.5) |
| Retinopathy n. (%) | 8 (10.4) |
| Nephropathy n. (%) | 16 (20.8) |
| Variables | DM+ | DM- | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Participants n. (%) | 77 (10.8) | 636 (89.2) | |
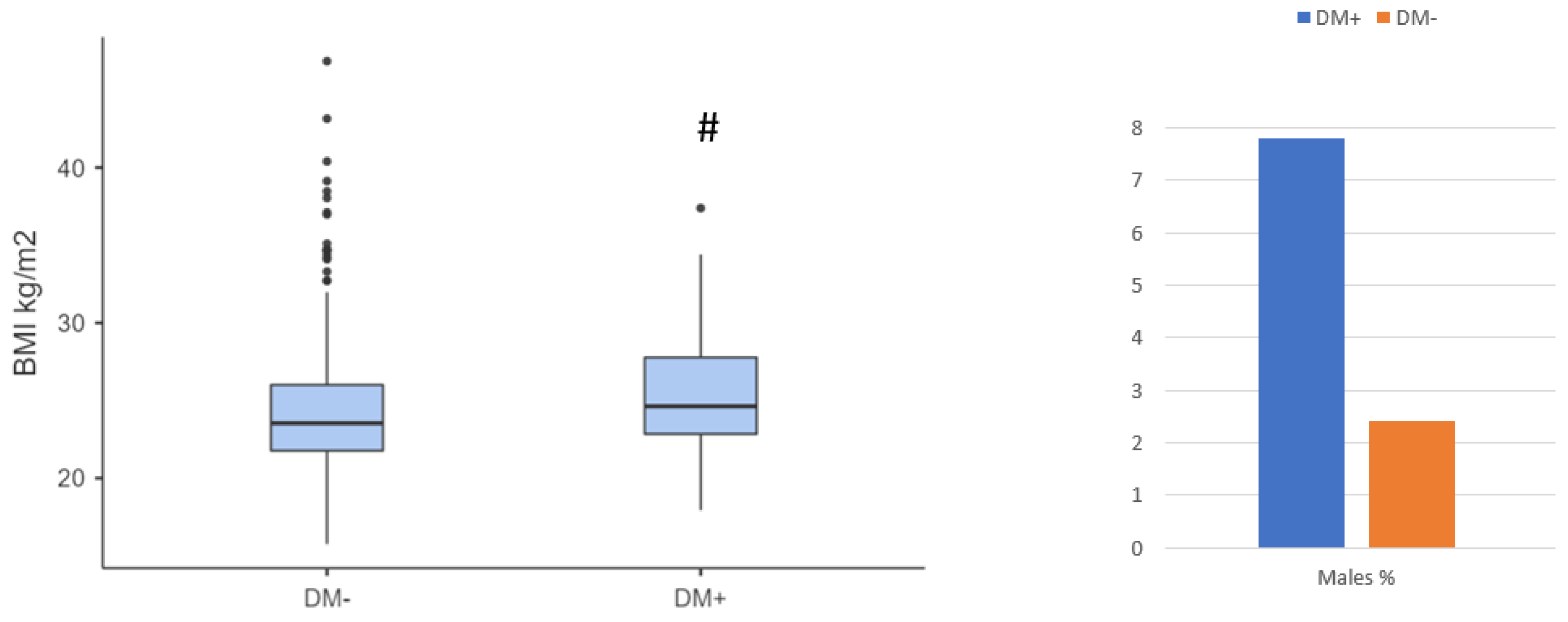
| Males n. (%) | 6 (7.8) | 21 (3.3) | 0.051 |
| Median Age (years ± IQR) | 82 ± 8 | 80 ± 12 | 0.221 |
| Median BMI (kg/m2 ± IQR) | 24.6 ± 4.94 | 23.5 ± 4.24 | <0.001 |
| Median age at the time of first fracture (years ± IQR) | 72 ± 14 | 71 ± 12 | 0.674 |
|
Median BMD lumbar spine (g/cm2 ± IQR) Median TBS ± IQR |
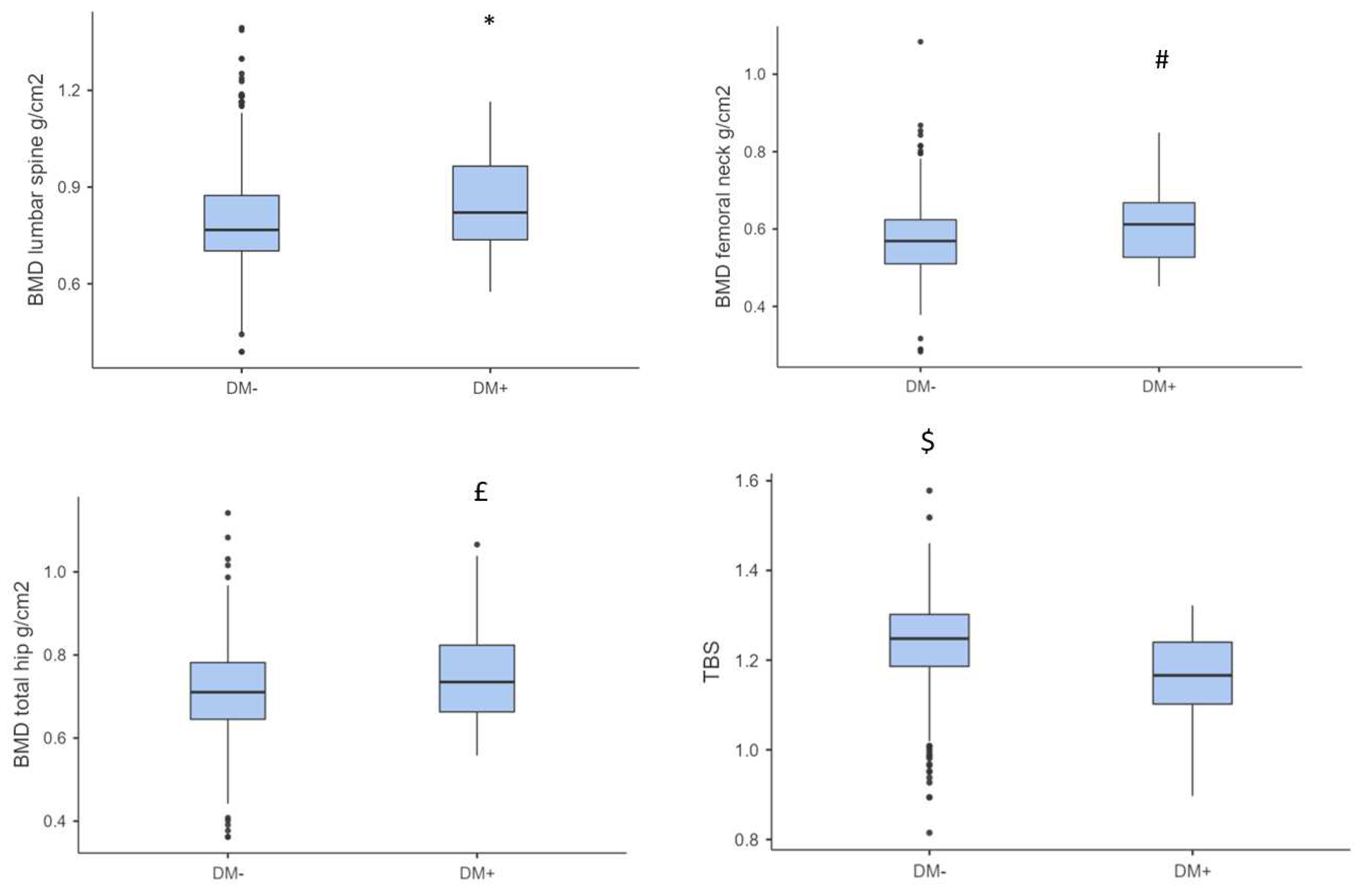
0.821 ± 0.229 | 0.767 ± 0.172 | 0.002 |
| Median BMD femoral neck (g/cm2 ± IQR) | 0.612 ± 0.141 | 0.569 ± 0.114 | 0.007 |
| Median BMD total hip (g/cm2 ± IQR) | 0.735 ± 0.161 | 0.710 ± 0.137 | 0.031 |
| Median TBS ± IQR | 1.170 ± 0.138 | 1.250 ± 0.116 | <0.001 |
| Family history of Osteoporosis n. (%) | 1 (1.3) | 198 (31.1) | <0.001 |
| Smoking habit n. (%) | 21 (27.3) | 109 (17.1) | 0.030 |
| Alcohol excess n. (%) | 0 (0) | 7 (1.1) | 0.355 |
| RA n. (%) | 2 (2.6) | 27 (4.2) | 0.489 |
| COPD n. (%) | 4 (5.2) | 40 (6.3) | 0.706 |
| Cortisone therapy n. (%) | 0 (0) | 40 (6.3) | 0.024 |
| Vertebral fractures n. (%) | 59 (76.6) | 534 (84) | 0.104 |
| Hip fractures n. (%) | 5 (6.5) | 31 (4.9) | 0.540 |
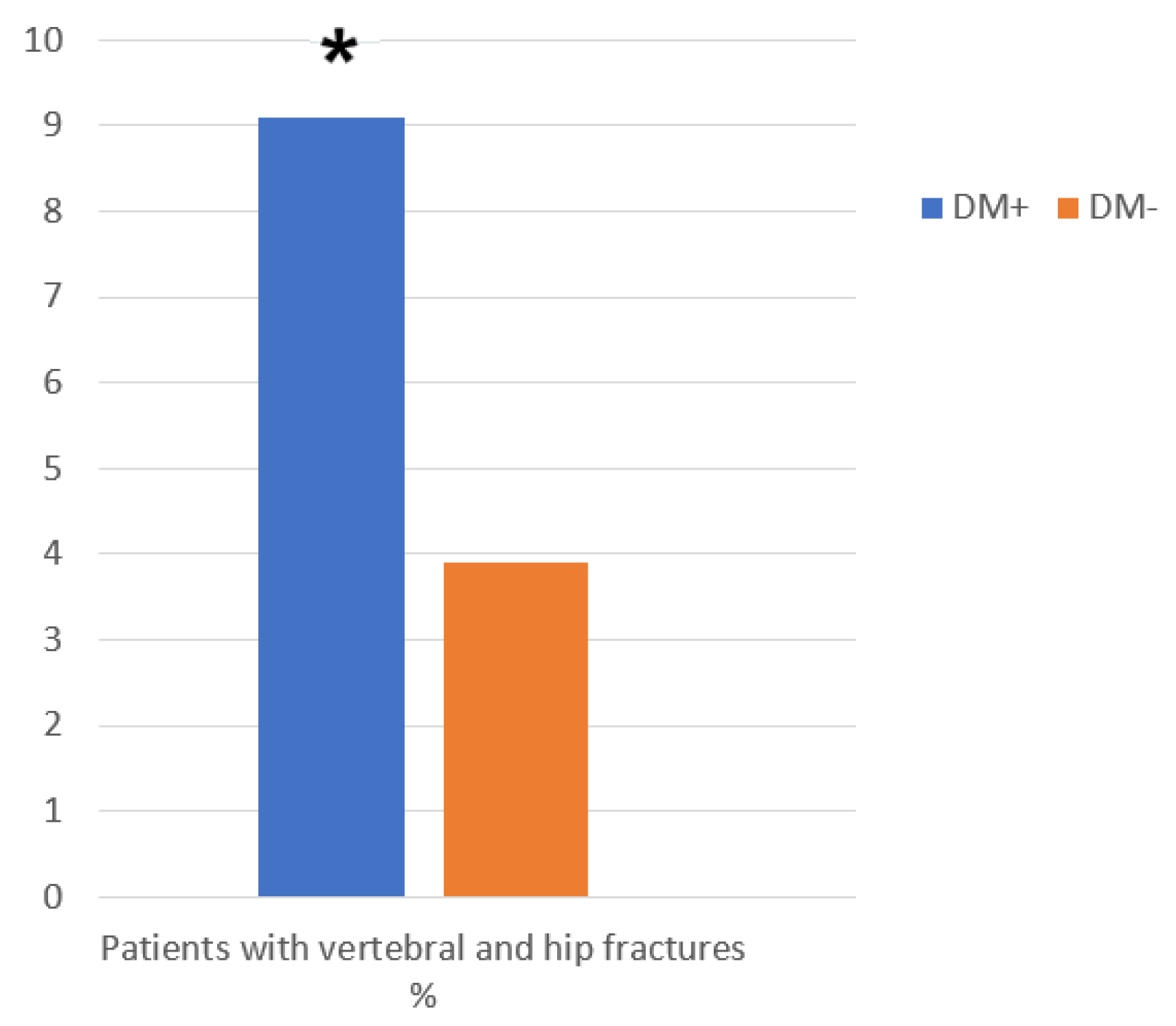
| Both vertebral and hip fractures n. (%) | 7 (9.1) | 25 (3.9) | 0.039 |
| Non-vertebral - non-hip fractures n. (%) | 6 (7.8) | 53 (8.3) | 0.871 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




