Submitted:
02 February 2024
Posted:
05 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Literature Review
Introduction
Methodology
Results
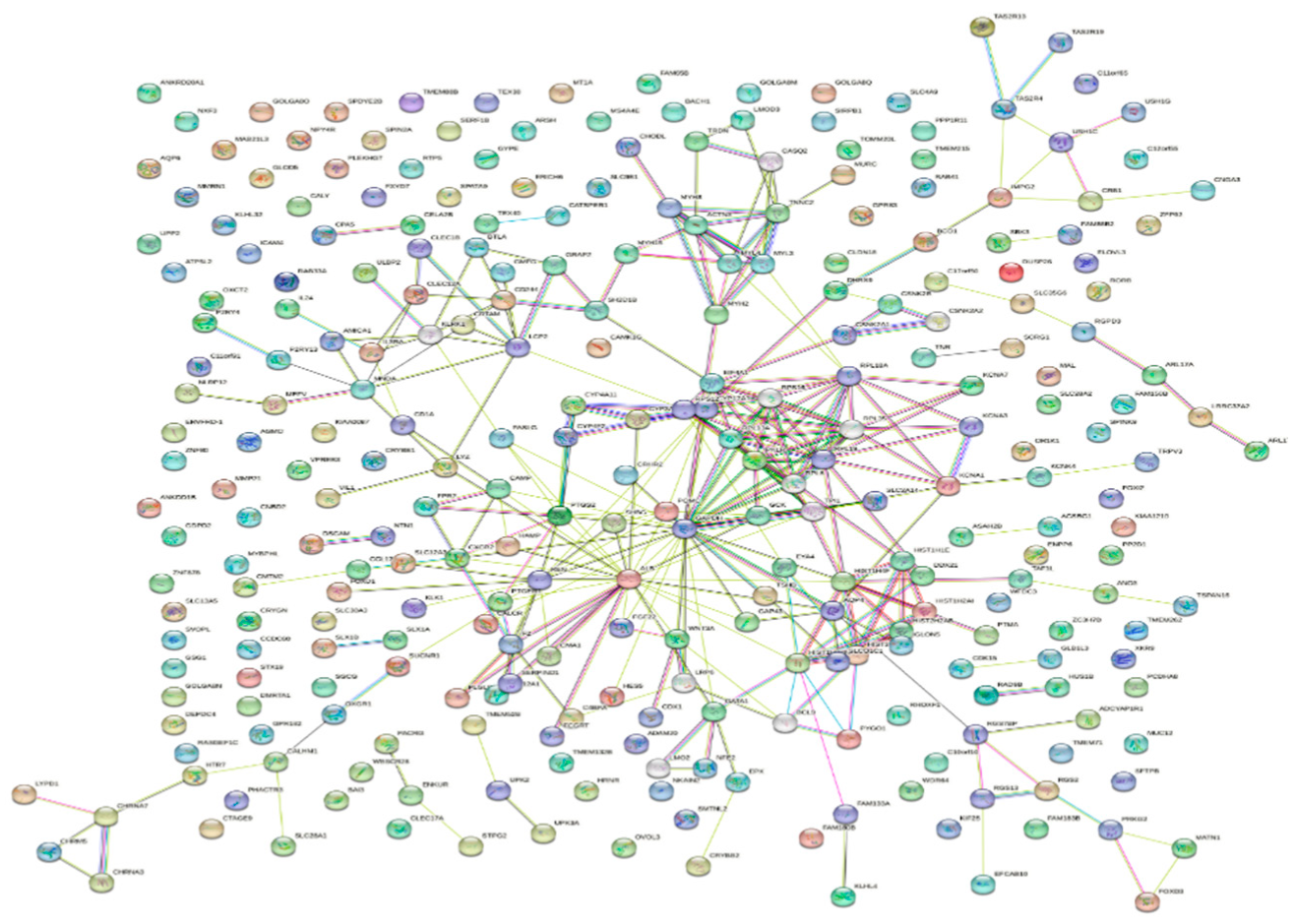
| Ensemble Ids | Category | Term description |
|---|---|---|
| ENSP00000258873 | Go Process | Very long-chain fatty acid metabolic process |
| ENSP00000422007 | Go Process | Regulation of oxidative phosphorylation |
| ENSP00000256389 | Go Process | Reproduction |
| ENSP00000483721 | Go Process | Developmental process involved in reproduction |
| ENSP00000341662 | Go Process | Lipid metabolic process |
| ENSP00000258873 | KEGG | Fatty acid biosynthesis, Fatty acid degradation, |
| ENSP00000422007 | KEGG | Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy |
| ENSP00000258168 | KEGG | Retinol metabolism, Metabolic pathways |
| ENSP00000356037 | KEGG | Complement and coagulation cascades, Pertussis |
| ENSP00000352561 | KEGG | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction |
| ENSP00000309052 | DISEASES | Complement component 2 deficiency, Male infertility |
| ENSP00000219244 | DISEASES | Skin disease, Atopic dermatitis, Allergic contact dermatitis |
| ENSP00000289429 | DISEASES | Immune system disease, Langerhans-cell histiocytosis |
| ENSP00000315602 | DISEASES | Lower respiratory tract disease, Nicotine dependence |
| ENSP00000407546 | DISEASES | Genetic disease, Chromosomal deletion syndrome, Chromosome 15q13.3 microdeletion syndrome |
| ENSP00000422007 | GO Function | Actin binding, Signaling receptor binding, Integrin binding |
| ENSP00000256389 | GO Function | Metalloendopeptidase activity, Catalytic activity |
| ENSP00000483721 | GO Function | Peptide receptor activity, G protein-coupled receptor activity |
| ENSP00000341662 | GO Function | Monooxygenase activity, Iron ion binding |
| ENSP00000295897 | GO Function | DNA binding, Copper ion binding |
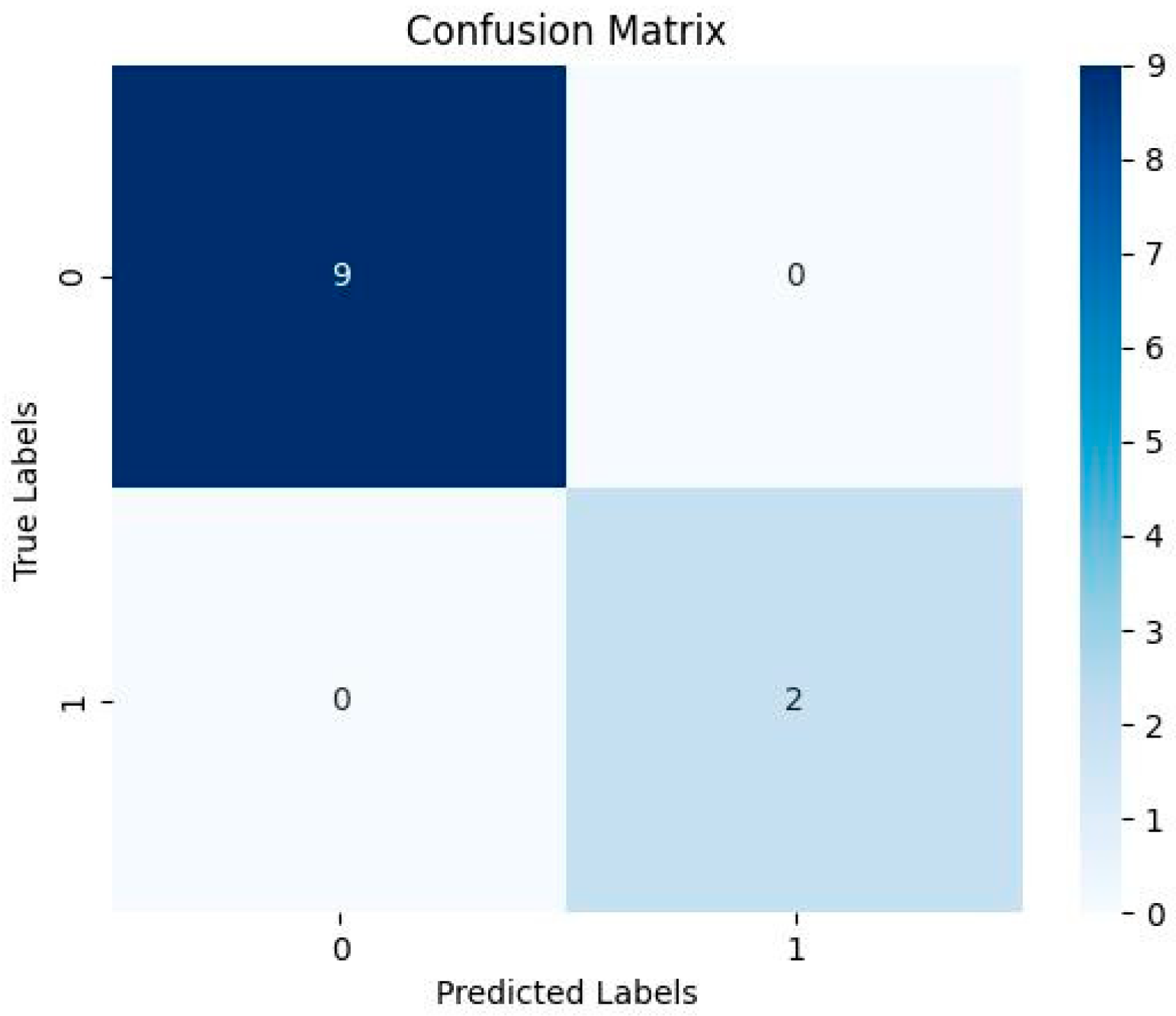
| Evaluation Matrices | Results |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | 0.8181818181818182 |
| Sensitivity | 0.0 |
| Specificity | 1.0 |
| Predicted positive | 0 |
| Predicted Negative | 11 |
| F1 Score | nan |
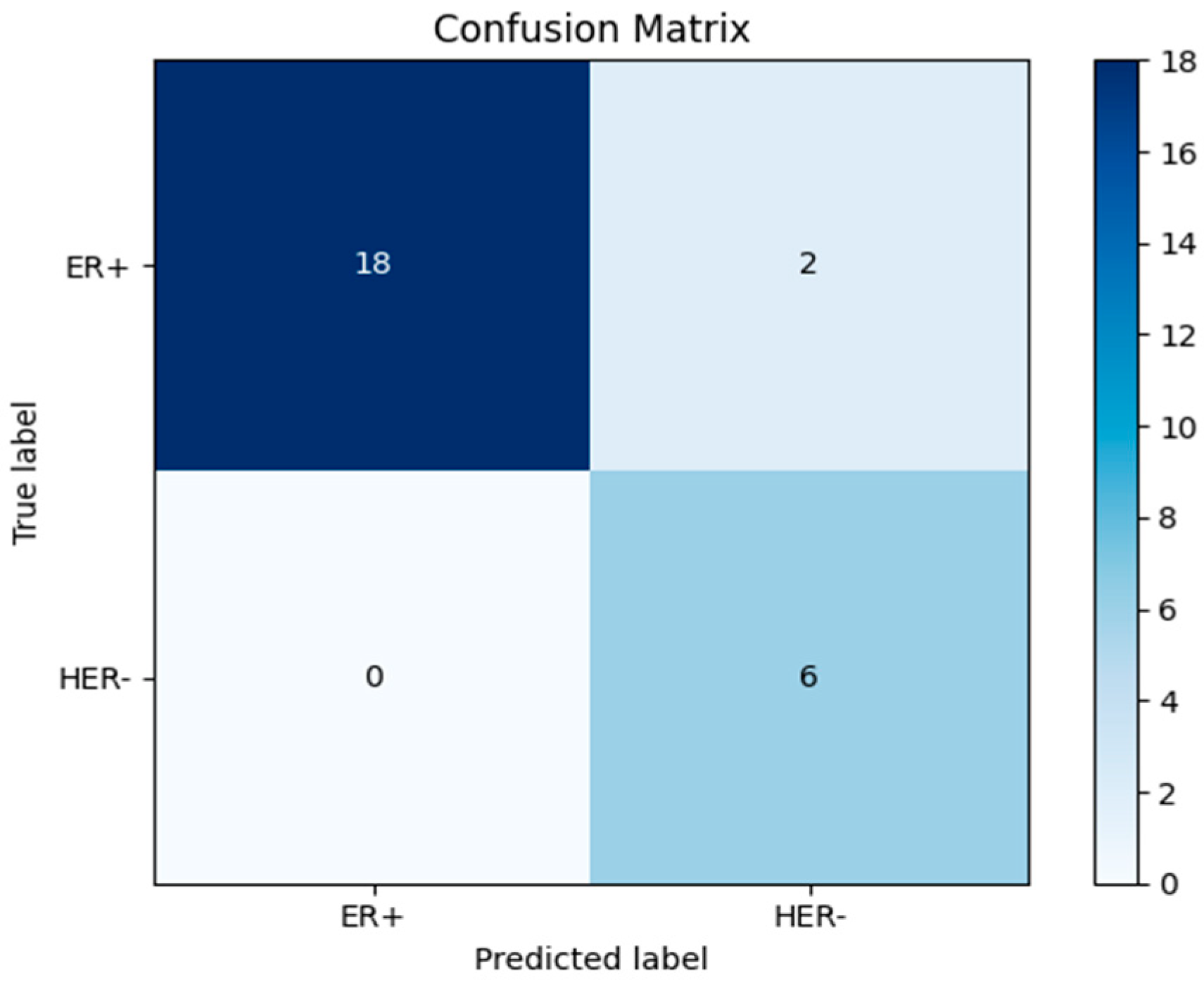
| Evaluation Metrics | Results |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | 0.9615384615384616 |
| Sensitivity ER+ | 0.95 |
| Sensitivity HER2- | 1.0 |
| Specificity ER+ | 0.95 |
| Specificity HER2- | 1.0 |
| Predicted positive ER+ | 1.0 |
| Predicted Negative HER2- | 0.95 |
| F1 Score | 0.9743589743589743 |
Discussion
Conclusion
References
- Atkins, H., Hayward, J. L., Klugman, D. J., & Wayte, A. B. (1972). Treatment of Early Breast Cancer: A Report After Ten Years of a Clinical Trial. British Medical Journal, 2(5811), 423–429. [CrossRef]
- Bafford, A. C., Burstein, H. J., Barkley, C. R., Smith, B. L., Lipsitz, S., Iglehart, J. D., Winer, E. P., & Golshan, M. (2009). Breast surgery in stage IV breast cancer: Impact of staging and patient selection on overall survival. In Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (Vol. 115, Issue 1, pp. 7–12). [CrossRef]
- Beňačka, R., Szabóová, D., Guľašová, Z., Hertelyová, Z., & Radoňák, J. (2022). Classic and New Markers in Diagnostics and Classification of Breast Cancer. In Cancers (Vol. 14, Issue 21). MDPI. [CrossRef]
- Brazma, A., Parkinson, H., Sarkans, U., Shojatalab, M., Vilo, J., Abeygunawardena, N., Holloway, E., Kapushesky, M., Kemmeren, P., Lara, G. G., Oezcimen, A., Rocca-Serra, P., & Sansone, S. A. (2003). ArrayExpress—a public repository for microarray gene expression data at the EBI. Nucleic Acids Research, 31(1), 68–71. [CrossRef]
- Cabral, A. H., Recine, M., Paramo, J. C., McPhee, M. M., Poppiti, R., & Mesko, T. W. (2003). Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: An Institutional Experience and Review of the Literature. The Breast Journal, 9(4), 298–301. [CrossRef]
- Cho, N. (2016). Molecular subtypes and imaging phenotypes of breast cancer. In Ultrasonography (Vol. 35, Issue 4, pp. 281–288). Korean Society of Ultrasound in Medicine. [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, G., Alako, B., Amid, C., Bower, L., Cerdeño-Tárraga, A., Cleland, I., Gibson, R., Goodgame, N., Jang, M., Kay, S., Leinonen, R., Lin, X., Lopez, R., McWilliam, H., Oisel, A., Pakseresht, N., Pallreddy, S., Park, Y., Plaister, S., … Zalunin, V. (2013). Facing growth in the European Nucleotide Archive. Nucleic Acids Research, 41(D1), D30–D35. [CrossRef]
- Colomer, R., Aranda-López, I., Albanell, J., García-Caballero, T., Ciruelos, E., López-García, M., Cortés, J., Rojo, F., Martín, M., & Palacios-Calvo, J. (2018). Biomarkers in breast cancer: A consensus statement by the Spanish Society of Medical Oncology and the Spanish Society of Pathology. In Clinical and Translational Oncology (Vol. 20, Issue 7, pp. 815–826). Springer-Verlag Italia s.r.l. [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y., Whiteman, M. K., Flaws, J. A., Langenberg, P., Tkaczuk, K. H., & Bush, T. L. (2002). Body mass and stage of breast cancer at diagnosis. International Journal of Cancer, 98(2), 279–283. [CrossRef]
- Fatima, N., Liu, L., Hong, S., & Ahmed, H. (2020). Prediction of Breast Cancer, Comparative Review of Machine Learning Techniques, and Their Analysis. IEEE Access, 8, 150360–150376. [CrossRef]
- Gajdos, C., Tartter, P. I., Bleiweiss, I. J., Bodian, C., & Brower, S. T. (2000). Stage 0 to stage III breast cancer in young women. Journal of the American College of Surgeons, 190(5), 523–529. [CrossRef]
- Grann, V. R., Troxel, A. B., Zojwalla, N. J., Jacobson, J. S., Hershman, D., & Neugut, A. I. (2005). Hormone receptor status and survival in a population-based cohort of patients with breast carcinoma. Cancer, 103(11), 2241–2251. [CrossRef]
- Haq, A. U., Li, J. P., Saboor, A., Khan, J., Wali, S., Ahmad, S., Ali, A., Khan, G. A., & Zhou, W. (2021). Detection of Breast Cancer through Clinical Data Using Supervised and Unsupervised Feature Selection Techniques. IEEE Access, 9, 22090–22105. [CrossRef]
- Harrison, P. W., Ahamed, A., Aslam, R., Alako, B. T. F., Burgin, J., Buso, N., Courtot, M., Fan, J., Gupta, D., Haseeb, M., Holt, S., Ibrahim, T., Ivanov, E., Jayathilaka, S., Kadhirvelu, V. B., Kumar, M., Lopez, R., Kay, S., Leinonen, R., … Cochrane, G. (2021). The European Nucleotide Archive in 2020. Nucleic Acids Research, 49(D1), D82–D85. [CrossRef]
- Hrdlickova, R., Toloue, M., & Tian, B. (2017). RNA-Seq methods for transcriptome analysis. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: RNA, 8(1), e1364. [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, N., & Iqbal, N. (2014). Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) in Cancers: Overexpression and Therapeutic Implications. Molecular Biology International, 2014, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Kukurba, K. R., & Montgomery, S. B. (2015). RNA Sequencing and Analysis. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols, 2015(11), pdb.top084970. [CrossRef]
- Li, J., Guan, X., Fan, Z., Ching, L. M., Li, Y., Wang, X., Cao, W. M., & Liu, D. X. (2020). Non-Invasive Biomarkers for Early Detection of Breast Cancer. Cancers 2020, Vol. 12, Page 2767, 12(10), 2767. [CrossRef]
- Łukasiewicz, S., Czeczelewski, M., Forma, A., Baj, J., Sitarz, R., & Stanisławek, A. (2021). Breast cancer—epidemiology, risk factors, classification, prognostic markers, and current treatment strategies—An updated review. In Cancers (Vol. 13, Issue 17). MDPI. [CrossRef]
- Ming, C., Viassolo, V., Probst-Hensch, N., Chappuis, P. O., Dinov, I. D., & Katapodi, M. C. (2019). Machine learning techniques for personalized breast cancer risk prediction: Comparison with the BCRAT and BOADICEA models. Breast Cancer Research, 21(1). [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, C. S., Chou, J. F., Wolden, S. L., Bernstein, J. L., Malhotra, J., Friedman, D. N., Mubdi, N. Z., Leisenring, W. M., Stovall, M., Hammond, S., Smith, S. A., Henderson, T. O., Boice, J. D., Hudson, M. M., Diller, L. R., Bhatia, S., Kenney, L. B., Neglia, J. P., Begg, C. B., … Oeffinger, K. C. (2014). Breast cancer after chest radiation therapy for childhood cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 32(21), 2217–2223. [CrossRef]
- Naz, S., Siddiqui, M., Memon, A. I., Bhatti, A. M., Hussain, Z. I., & . I. (2023). Analysis of Breast Cancer Receptors Status and Molecular Subtypes Among Female Population. Pakistan Journal of Medical and Health Sciences, 17(1), 656–658. [CrossRef]
- Olimjonova, K. A. K., Khusainova, G. O., & Khamzaeva, K. J. (2023). IDENTIFICATION OF THE PREVALENCE OF BREAST CANCER AMONG DIFFERENT AGE GROUPS OF THE POPULATION AND ITS PREVENTION (Vol. 4, Issue 3). [CrossRef]
- Osareh, A., & Shadgar, B. (2010). Machine learning techniques to diagnose breast cancer. 2010 5th International Symposium on Health Informatics and Bioinformatics, HIBIT 2010, 114–120. [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, H., Kapushesky, M., Shojatalab, M., Abeygunawardena, N., Coulson, R., Farne, A., Holloway, E., Kolesnykov, N., Lilja, P., Lukk, M., Mani, R., Rayner, T., Sharma, A., William, E., Sarkans, U., & Brazma, A. (2007). ArrayExpress—a public database of microarray experiments and gene expression profiles. Nucleic Acids Research, 35(suppl_1), D747–D750.
- Plasilova, M. L., Hayse, B., Killelea, B. K., Horowitz, N. R., Chagpar, A. B., & Lannin, D. R. (2016). Features of triple-negative breast cancer Analysis of 38,813 cases from the national cancer database. Medicine (United States), 95(35). [CrossRef]
- Pramod Shardul, B., & Dipak Sonar, A. (n.d.). The Review on types of Breast Cancer and Associated Risk Factors. Available online: www.ijfmr.com.
- Prognostic classification of breast ductal carcinoma-in-situ. (n.d.).
- Smolarz, B., Zadrożna Nowak, A., & Romanowicz, H. (2022). Breast Cancer—Epidemiology, Classification, Pathogenesis and Treatment (Review of Literature). In Cancers (Vol. 14, Issue 10). MDPI. [CrossRef]
- Sopik, V., & Narod, S. A. (2018). The relationship between tumour size, nodal status and distant metastases: on the origins of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, 170(3), 647–656. [CrossRef]
- Studham, M. E., Tjärnberg, A., Nordling, T. E. M., Nelander, S., & Sonnhammer, E. L. L. (2014). Functional association networks as priors for gene regulatory network inference. Bioinformatics, 30(12). [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D., Franceschini, A., Kuhn, M., Simonovic, M., Roth, A., Minguez, P., Doerks, T., Stark, M., Muller, J., Bork, P., Jensen, L. J., & Von Mering, C. (2011). The STRING database in 2011: functional interaction networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids Research, 39(suppl_1), D561–D568. [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D., Kirsch, R., Koutrouli, M., Nastou, K., Mehryary, F., Hachilif, R., Gable, A. L., Fang, T., Doncheva, N. T., Pyysalo, S., Bork, P., Jensen, L. J., & von Mering, C. (2023). The STRING database in 2023: protein–protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Research, 51(D1), D638–D646. [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D., Morris, J. H., Cook, H., Kuhn, M., Wyder, S., Simonovic, M., Santos, A., Doncheva, N. T., Roth, A., Bork, P., Jensen, L. J., & Von Mering, C. (2017). The STRING database in 2017: quality-controlled protein–protein association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Research, 45(D1), D362–D368. [CrossRef]
- Testa, U., Castelli, G., & Pelosi, E. (2020). Breast Cancer: A Molecularly Heterogenous Disease Needing Subtype-Specific Treatments. In Medical sciences (Basel, Switzerland) (Vol. 8, Issue 1). NLM (Medline). [CrossRef]
- Trabert, B., Sherman, M. E., Kannan, N., & Stanczyk, F. Z. (2020). Progesterone and Breast Cancer. Endocrine Reviews, 41(2), 320–344. [CrossRef]
- Wang, A. T., Vachon, C. M., Brandt, K. R., & Ghosh, K. (2014). Breast density and breast cancer risk: A practical review. In Mayo Clinic Proceedings (Vol. 89, Issue 4, pp. 548–557). Elsevier Ltd. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L., Wang, S., & Li, W. (2012). RSeQC: quality control of RNA-seq experiments. Bioinformatics, 28(16), 2184–2185. [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y., Lai, X., Yu, S., Chen, S., Ma, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, H., Zhu, X., Yao, L., & Zhang, J. (2014). Exosomal miR-221/222 enhances tamoxifen resistance in recipient ER-positive breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, 147(2), 423–431. [CrossRef]
- Wu, J., & Hicks, C. (2021). Breast Cancer Type Classification Using Machine Learning. Journal of Personalized Medicine 2021, Vol. 11, Page 61, 11(2), 61. [CrossRef]
- Yue, W., Wang, Z., Chen, H., Payne, A., & Liu, X. (2018). Machine Learning with Applications in Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis. Designs 2018, Vol. 2, Page 13, 2(2), 13. [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, N. H., Hashad, D., Saied, M. H., Hegazy, N., Elkayal, A., & Tayae, E. (2023). Genetic mutations in HER2-positive breast cancer: possible association with response to trastuzumab therapy. Human Genomics, 17(1), 43. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. (2023). Molecular Classification of Breast Cancer Relevance and Challenges. Archives of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, 147(1), 46–51. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X., Ying, J., Wang, F., Wang, J., & Yang, H. (2014). Estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 status in invasive breast cancer: a 3,198 cases study at National Cancer Center, China. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, 147(3), 551–555. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




