Submitted:
01 February 2024
Posted:
02 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
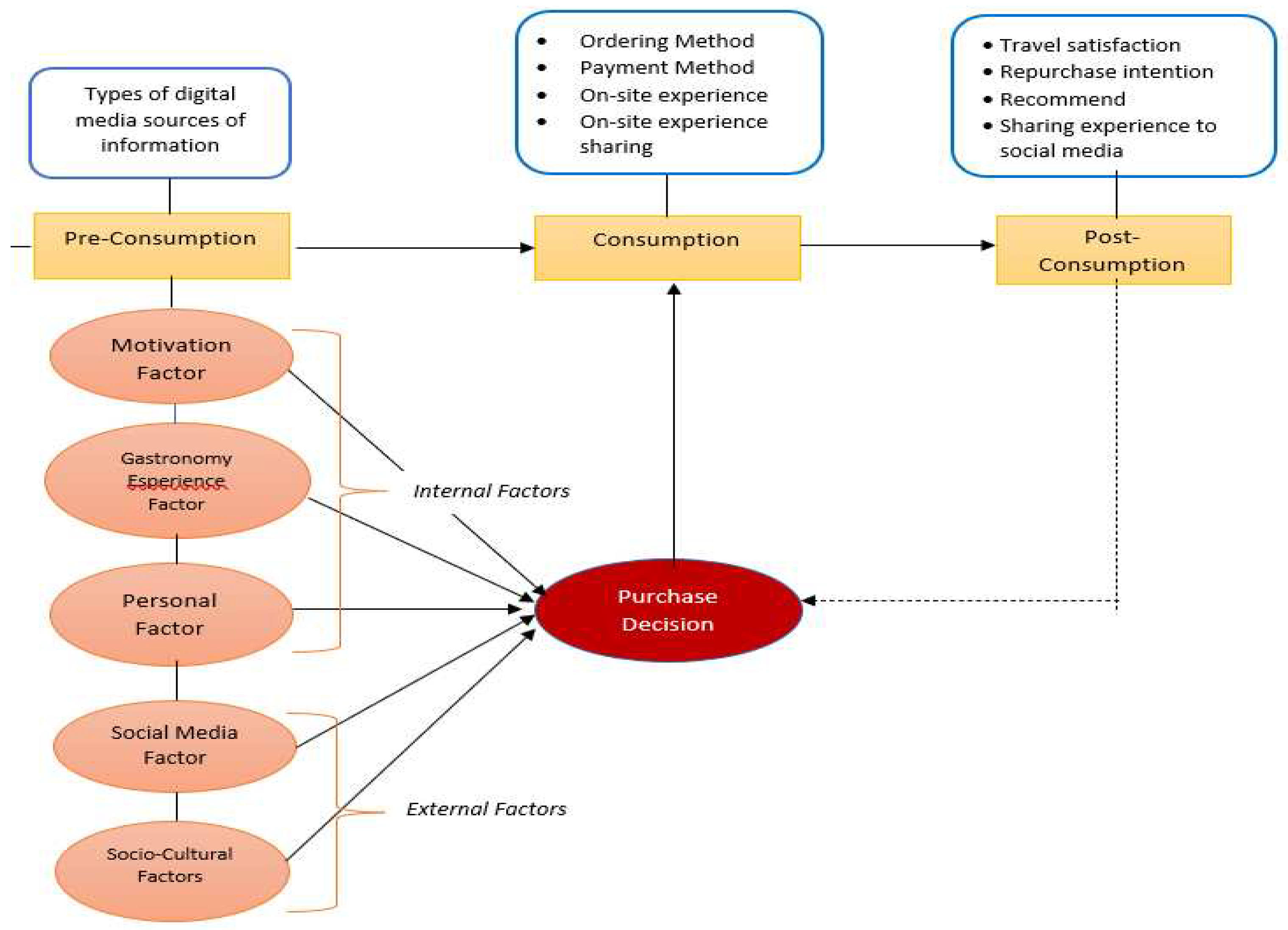
2.1. Local culinary
2.2. Pre-consumption behavior
- Cultural factors include culture, subculture, and social class.
- Social factors such as social groups and networks, family, and socioeconomic status.
- Individual factors such as occupation, age and stage of life, financial situation, lifestyle, and personality.
- Psychological factors such as motivation, perception, the learning process, beliefs, and attitudes.
- H1: There is a positive influence of personal factors on local culinary purchasing decisions.
- H2: There is a positive influence of motivational factors on local culinary purchasing decisions.
- H3: There is a positive influence of gastronomic experience on local culinary purchasing decisions.
- H4: There is a positive influence of social media factors on local culinary purchasing decisions.
- H5: There is a positive influence of socio-cultural factors on local culinary purchasing decisions.
- H6: There is an influence of internal factors on local culinary purchasing decisions.
- H7: There is the influence of external factors on local culinary purchasing decisions.
- H8: There is the influence of internal and external factors simultaneously on purchasing decisions.
2.3. On-consumption behavior
2.4. Post-consumption behavior
3. Methods
4. Results
4.1. Tourist consumption behavior in the Pre-Consumption Stage
Tourist Demographics
4.2. Factors influencing local culinary purchasing decisions at destination
4.2.1. Outer model analysis
4.2.2. Inner model analysis
- H1 is accepted because personal factors (PF) have a positive influence on purchasing decisions (PD).
- H2 is accepted because motivational factors (MF) have positive influence on purchasing decisions (PD)
- H3 is accepted because the gastronomic experience factor (GEF) has a positive influence on purchasing decisions (PD)
- H4 is accepted because the social media factor (SMF) has a positive influence on purchasing decisions (PD)
- H5 is accepted because socio-cultural factors (SCF) have a positive influence on purchasing decisions (PD)
- Purchase decision factor (PD) has a positive influence on consumption (CON)
- Consumption (CON) has a positive influence on post consumption (PCO)
4.3. Tourist consumption behavior in the Consumption Stage
4.4. Tourist consumption behavior in the Post-Consumption Stage
4.5. Goodness of fit behavior model of local culinary consumption in destinations
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fields K. Demand for the gastronomy tourism product: motivational factors. In: Tourism and Gastronomy. London: Routledge; 2002. p. 37–50.
- Sánchez-Cañizares, S.M López-Guzmán T. Gastronomy as a Tourism Resource: Profile of the Culinary Tourist. Curr Issues Tour. 2012;15(3):229–45. [CrossRef]
- Pieniak Z, Verbeke W, Vanhonacker F, Guererro L, Hersleth M. Assosiations between traditional food consumption and motives for food choice in six European countries. Appetite. 2009;53(1):101–8. [CrossRef]
- Rosana FR, Widyastuti RA. Asosiasi Franchise Keluhkan Asing Kuasai Waralaba di RI [Internet]. bisnis.tempo.co. 2019 [cited 2020 Jul 7]. Available from: https://bisnis.tempo.co/read/1275873/asosiasi-franchise-keluhkan-asing-kuasai-pasar-waralaba-di-ri/full&view=ok.
- Lestari M. Coba Tebak Ada Berapa Jumlah Kuliner di Indonesia? [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2022 Mar 19]. Available from: https://food.detik.com/berita-boga/d-4529131/coba-tebak-ada-berapa-jumlah-kuliner-di-indonesia.
- Mak AH., Lumbers M, Eves A, Chang RC. Factors influencing tourist food consumption. Int J Hosp Manag. 2012;31:928–36. [CrossRef]
- Damanik D, Wachyuni SS, Wiweka K, Setiawan A. The Influence of Social Media on the Domestic Tourist’s Travel Motivation Case Study: Kota Tua Jakarta, Indonesia. Curr J Appl Sci Technol [Internet]. 2019;36(6):1–14. [CrossRef]
- Damanik J, Priyambodo T., Wibowo M., Pitanatri PD., Wachyuni S. Travel behaviour differences among Indonesian youth in Generations Y and Z: pre-, during and post-travel. Consum Behav Tour Hosp [Internet]. 2023;18(1):35–48. Available from: https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/CBTH-07-2021-0184/full/html.
- Wachyuni SS, Wiweka K, Liman M. Pengaruh Online Distribution Channels (ODS) Terhadap Hotel Revenue. J Tour Econ. 2018;1(2):1–9. [CrossRef]
- Kyomba M., Spencer J., Muresherwa G. Indirect Versus Direct Bookings: Hotel Customer Motivations for Online Reservations at Travel Agencies in the Cape. Ceconomica. Acta Univ Danubius [Internet]. 2022;18(5). Available from: https://dj.univ-danubius.ro/index.php/AUDOE/article/download.
- Tandon A., Kaur P, Bhatt Y, Mäntymäki M, Dhir A. Why do People Purchase from Food Delivery apss? A consumer value perspective. J Retail Consum Serv. 2021;63. [CrossRef]
- No Liling J., Lyawati M, Lim S, Lim T, Jiang K. Pengaruh Youtube Vloggers terhadap Food Branding. J Pemasar Kompetitif [Internet]. 2022;6(1). Available from: https://openjournal.unpam.ac.id/index.php/JPK/article/view/20848. [CrossRef]
- Cleave P. Food as a leisure pursuit, a United Kingdom perspective. Ann Leis Res. 2019;1–18. [CrossRef]
- Horng J., Tsai CT. Government websites for promoting East Asian culinary tourism: a cross-national analysis. Tour Manag. 2010;31(1):74–85. [CrossRef]
- Okumus F, Kock G, Scantlebury M., Okumus B. Using local cuisines when promoting small Caribbean island destinations. J Travel Tour Mark. 2013;30(410–429). [CrossRef]
- Jia S. Measuring tourists’ meal experience by mining online user generated content about restaurants. Scand J Hosp Tour. 2019;19(4):371–89. [CrossRef]
- Sarinastiti EN, Vardhani N. Co-Branding Online Food Delivery: Perubahan Model Bisnis Wisata Kuliner Lokal Khas Yogyakarta. J Pemikir dan Penelit Bisnis dan Kewirausahaan. 2018;3(3).
- Kim G, Eves A, Scarles C. Building a model of local food consumption on trips and Holidays: A grounded theory approach. Int J Hosp Manag. 2009;28(4):423 –431. [CrossRef]
- Suntikul W, Pratt S, Chong YW. Factors that Influence Chinese Outbound Tourists’ Intention to Consume Local Food. J China Tour Res. 2020;16(2):230–47. [CrossRef]
- Bjork P, Raisanen H. Local food: a source for destination attraction. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag. 2015;28(1):177–94. [CrossRef]
- Hariyanto B. Makalah Pangan Lokal disajikan dalam Acara Kuliah Umum di Jurusan Gizi. Malang; 2017.
- Santoso U, Gardjito M, Harmayani E. Makanan Tradisional Indonesia Seri 2: Makanan Tradisional yang Populer (Sup, Mi, Set Menu Nasi, Nasi Goreng, dan Makanan Berbasis Sayur). Yogyakarta: UGM Press; 2017.
- Freidberg S. Editorial Not all sweetness and light: New cultural geographies of food. Soc Cult Geogr. 2003;4(1). [CrossRef]
- Hall CM, Sharples L. The Consumption of Experience or the Experience of Consumption? An Introduction to The Tourism of Taste In. C Food Tourism Around The World. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann; 2003.
- Henderson JC. Food tourism reviewed. Br Food Journa. 2009;111(4):317 –326. [CrossRef]
- Gardjito M. Gastronomi Indonesia Jilid 1. Yogyakarta: Global Pustaka Utama; 2019.
- Hall CM, Sharples L, Mitchell R, Macionis N, Cambourne B. Food tourism around the world: Development, management and markets. Oxford: Butterworth Heinemann; 2003.
- Chiou W., Wan C., Lee H. Virtual experience vs. brochures in the advertisement of scenic spots: How cognitive preferences and order effects influence advertising effects on consumers. Tour Manag. 2008;29(1):146–50. [CrossRef]
- Kruizinga L, Vries D, Gensler S, Leeflang PS. Popularity of Brand Posts on Brand Fan Pages: An Investigation of the Effects of Social Media Marketing. J Interact Mark. 2012;26(2):83–91. [CrossRef]
- Tsiotsou RH, Wirtz J. Consumer behavior in a service context. In: Handbook of developments in consumer behaviour. 2012. p. 147–201.
- Kotler P, Amstrong G. Principles of Marketing. London: Pearson Education Limited; 2018.
- Kivela J, Crotts JC. Tourism and Gastronomy: Gastronomy’s Influence on How Tourists Experience a Destination. J Hosp Tour Res. 2006;30(3):354–77. [CrossRef]
- Kim J, Ritchie J., McCormick B. Development of a scale to measure memorable tourism experiences. J Travel Res. 2012;51(1):12–25. [CrossRef]
- Williams HA, Yuan JJ. Attributes Of Memorable Gastro- Tourists ’ Experiences. J Hosp Tour Res. 2018;XX(X):1–22. [CrossRef]
- Taprial, Varinder, Kanwar P. Understanding Social Media. London: Ventus. Publishing ApS; 2012.
- Tsiotsou R., Wirtz J. The Three-Stage Model of Service Consumption. In: The Handbook of Service Business Management, Marketing, Innovation and Internationalisation. United Kingdom: Edward Elgar; 2015.
- Kim YG, Eves A, Scarles C. Building a model of local food consumption on trips and holidays : A grounded theory approach. Int J Hosp Manag. 2009;28:423–31. [CrossRef]
- Sekaran U. Metode Penelitian Bisnis. Jakarta: Salemba Empat; 2006.
- Chin WW. The partial least squares approach for structural equation modeling. In: Modern methods for business research. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers; 1998. p. 295–336.
- Oblinger D, Oblinger J. Is It Age or IT: First Steps Toward Understanding the Net Generation. In: Educating the net generation [Internet]. 2005. Available from: https://studentconduct.tamucc.edu/assets/IsItAge.pdf.
- Bencsik A, Juhász T, Horváth-Csikós G. Y and Z Generations at Workplaces. J Compet. 2016;6(3):90–106. [CrossRef]
- Harsana M. Persepsi Wisatawan Terhadap Wisata Kuliner di Kabupaten Sleman. In: Seminar Nasional 2011 “Wonderful Indonesia.” Yogyakarta: UNY; 2011.
- Hall CM, Sharples L. The Consumption of Experience or the Experience of Consumption? An Introduction to The Tourism of Taste. Food Touri. Oxford: Butterworth Heinemann; 2003.
- Bjork P, Raisanen H. Local food: a source for destination attraction. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag. 2016;28(1):177–94. [CrossRef]
- Nield K, Kozak M, LeGrys G. The role of food service in tourist satisfaction. Int J Hosp Manag. 2000;19:375–84. [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein J. Dining out : a sociology of modern manners. New Yor: University Press; 1989.
- Eertmans A, Baeyens F, Van den Bergh O. Food likes and their relative importance in human eating behavior: review and preliminary suggestions for health promotion. Heal Educ Res. 2001;16(4):443–56. [CrossRef]
- Bell R, Meiselman H. The role of eating environments in determining food choice in D.W Marshall. In: Food choice and the consumer. London: Chapman and Hall; 1995. p. 292–310.
- Sloan D. The Postmodern Palate: Dining Out in The Individualized Era. In: Culinary Taste Consumer Behavior in the International Restaurant Sector. Oxford: Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann; 2003.
- Seymour D. The Social Contruction of Taste. In: Culinary Taste Consumer Behavior in the International Restaurant Sector. Burlington: Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann; 2004.
- Pérez Gálvez JC, Granda MJ, López-Guzmán T, Coronel JR. Local gastronomy, culture and tourism sustainable cities: The behavior of the American tourist. Sustain Cities Soc [Internet]. 2017;32(April):604–12. [CrossRef]
- Wachyuni S, Yusuf L. Camera Eat First: Tourist Motivation in Sharing Food Photograph on Instagram. Int J Tour Hosp Rev. 2021;8(1):62–70. [CrossRef]
- Waini PS. Preferensi Enterpreneur dalam menggunakan alat pembayaran (Studi Kasus di Kota Bengkulu). Institut agama islam negeri (IAIN) Bengkulu; 2020.
- Richard M. Masyarakat Indonesia Lebih Doyan Transaksi NonTunai. Jumlahnya Tertinggi di Asean! [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2022 Apr 5]. Available from: https://finansial.bisnis.com/read/20210224/90/1360517/masyarakat-indonesia-lebih-doyan-transaksi-nontunai-jumlahnya-tertinggi-di-asean.
- Majid MA., Alias MA., Samsudin A, Chik CT. Assessing customer-based brand equity ratings in family restaurant. Procedia Econ Financ. 2016;37:183–9. [CrossRef]
- Pham LT., Do H., Phung T. The Effect of Brand Equity and Perceived Value on Customer Revisit Intention: A Study in Quick-Service Restaurants in Vietnam. Acta Oeconomica Pragensia. 2016;2016(5):14–30. [CrossRef]
- Baym NK. Personal connections in the digital age. Cambridge: Polity; 2010.
- Harmayani E, Sari P. Kebijakan, Regulasi, dan Kelembagaan Boga dan Upaboga di Indonesia. In: Ragam Makanan Kita: Gastronomi & Kuliner Nusantara [Internet]. PRISMA Jurnal Pemikiran Sosial Ekonomi Vol 40 No 1; 2021. Available from: https://prismajurnal.com/edition/29.
| Profile and Characteristics | Option | Sample | Percentage (%) |
| Age | 17-26 years old | 263 | 54.60 |
| 27-33 years old | 73 | 15.10 | |
| 34-39 years old | 50 | 10.40 | |
| 40-46 years old | 43 | 8.90 | |
| >46 years old | 53 | 11.00 | |
| Gender | Female | 280 | 58.10 |
| Male | 199 | 41.30 | |
| Choose not to answer | 3 | 0.60 | |
| Status | Married | 175 | 36.30 |
| Single | 295 | 61.20 | |
| Choose not to answer | 12 | 2.50 | |
| Education | Diploma | 151 | 31.30 |
| Bachelors | 187 | 38.80 | |
| Master’s degree | 117 | 24.30 | |
| Doctoral degree | 27 | 5.60 | |
| Occupation | Civil servant | 41 | 8.50 |
| Private employees | 111 | 23.00 | |
| Entrepreneur | 127 | 26.30 | |
| Lecturer | 15 | 3.10 | |
| Part time worker | 7 | 1.50 | |
| Student | 141 | 29.25 | |
| Other | 40 | 8.29 | |
| Revenue | Low | 212 | 44.00 |
| Middle | 97 | 40.80 | |
| High | 73 | 15.10 | |
| Domicile | DKI Jakarta | 108 | 22.00 |
| Banten | 89 | 18.00 | |
| West java | 113 | 23.00 | |
| Yogyakarta | 38 | 8.00 | |
| Central java | 18 | 4.00 | |
| East java | 11 | 2.00 | |
| Bali | 30 | 6.00 | |
| Nusa Tenggara | 2 | 0.40 | |
| Sumatra | 61 | 13.00 | |
| Kalimantan | 2 | 0,40 | |
| Sulawesi | 9 | 2.00 | |
| Papua | 1 | 0,20 |
| Original Sample (O) | Sample Mean (M) | Standard Deviation (STDEV) | T Statistics (|O/STDEV|) | P Values | |
| CON-> PCO | 0.638 | 0.641 | 0.040 | 15.828 | 0.000 |
| SMF -> PD | 0.155 | 0.154 | 0.054 | 2.872 | 0.004 |
| MF -> PD | 0.221 | 0.221 | 0.063 | 3.531 | 0.000 |
| GEF -> PD | 0.166 | 0.168 | 0.073 | 2.267 | 0.024 |
| PF-> PD | 0.222 | 0.224 | 0.048 | 4.635 | 0.000 |
| SCF -> PD | 0.150 | 0.149 | 0.051 | 2.965 | 0.003 |
| PD -> CON | 0.482 | 0.484 | 0.046 | 10.524 | 0.000 |
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | Sig. | ||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | ||||
| 1 | (Constant) | .092 | .164 | .561 | .575 | |
| Internal factors | .667 | .055 | .549 | 12.063 | .000 | |
| External factors | .293 | .056 | .238 | 5.228 | .000 | |
| a. Dependent Variable: Purchasing Decisions | ||||||
| No | Variable and indicator | Average |
| A | On Site Experience | |
| 1 | The flavors (color, aroma, taste, texture) of local cuisine are interesting and delicious | 4.45 |
| 2 | The atmosphere of a local culinary restaurant is comfortable and memorable | 4.36 |
| 3 | Local culinary restaurant service is good | 4.29 |
| 4 | Local culinary restaurant employees are friendly and have good communication skills | 4.26 |
| 5 | Prices are in accordance with the local culinary products offered | 4.29 |
| 6 | The waiter gives recommendations for local culinary excellence | 4.19 |
| 7 | Local culinary image or reputation can increase consumer prestige | 4.33 |
| 8 | I feel like a family when I visit a local culinary restaurant | 4.20 |
| 9 | Local culinary restaurants have up-to-date information through social media | 4.00 |
| B | Sharing Experience On Site | |
| 1 | I share my eating experience live on social media when consuming local culinary delights at destinations | 3.38 |
| 2 | I do not share any experiences at culinary tourism locations | 2.95 |
| No | Variable and indicator | Average |
| A | Travel Satisfaction | |
| 1 | I feel satisfied traveling after consuming local culinary at the destination | 4.30 |
| B | Repurchase | |
| 1 | I will repurchase local culinary at the destination on my next visit | 4.18 |
| C | Recommendation | |
| 1 | I will give recommendations to friends and relatives about the local dishes that I have tried | 4.40 |
| D | Post-Consumption Experience Sharing | |
| 1 | I will share this local culinary experience with digital media | 3.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





