Submitted:
19 January 2024
Posted:
23 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
- A.
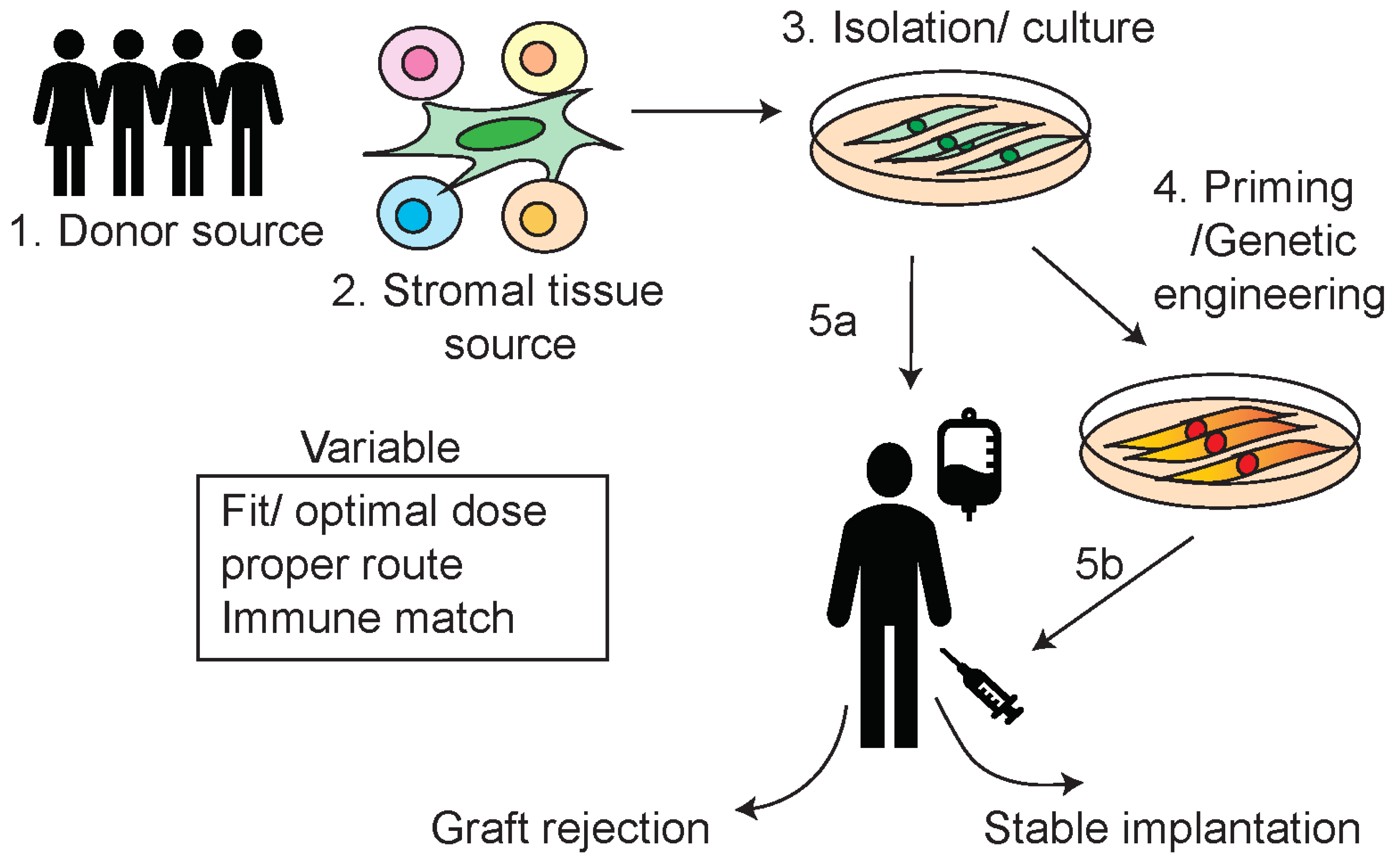
- Cell processing and mode of delivery: current status and translational hurdles
- MSCs’ tissue source
- 2.
- MSCs’ immunogenicity
- 3.
- MSCs administration routes:
- 4.
- Optimal Timing/ dose/ fitness of MSCs
- B.
- Improvement of MSCs application in tissue injury
Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Francois, M.; et al. Cryopreserved mesenchymal stromal cells display impaired immunosuppressive properties as a result of heat-shock response and impaired interferon-gamma licensing. Cytotherapy 2012, 14, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Cao, W.; Shi, Y. Plasticity of mesenchymal stem cells in immunomodulation: pathological and therapeutic implications. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, H.M.; E Haynesworth, S.; Gerson, S.L.; Rosenthal, N.S.; I Caplan, A. Ex vivo expansion and subsequent infusion of human bone marrow-derived stromal progenitor cells (mesenchymal progenitor cells): implications for therapeutic use. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995, 16, 557–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mastrolia, I.; Foppiani, E.M.; Murgia, A.; Candini, O.; Samarelli, A.V.; Grisendi, G.; Veronesi, E.; Horwitz, E.M.; Dominici, M. Challenges in Clinical Development of Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells: Concise Review. STEM CELLS Transl. Med. 2019, 8, 1135–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, J.; Galipeau, J. Mesenchymal stromal cell therapeutic potency is dependent upon viability, route of delivery, and immune match. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 1987–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galipeau, J.; Sensébé, L. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Clinical Challenges and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galipeau, J., et al. (2021) Mesenchymal stromal cell variables influencing clinical potency: the impact of viability, fitness, route of administration and host predisposition. Cytotherapy. [CrossRef]
- Galipeau, J.; Krampera, M.; Leblanc, K.; Nolta, J.A.; Phinney, D.G.; Shi, Y.; Tarte, K.; Viswanathan, S.; Martin, I. Mesenchymal stromal cell variables influencing clinical potency: the impact of viability, fitness, route of administration and host predisposition. Cytotherapy 2021, 23, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini-Asl, S.-K.; Mehrabani, D.; Karimi-Busheri, F. Therapeutic Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Ulcerative Colitis: A Review on Achievements and Challenges. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 9, 3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, L.M.; et al. Multiple infusions of mesenchymal stromal cells induce sustained remission in children with steroid-refractory, grade III-IV acute graft-versus-host disease. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 163, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtzberg, J.; et al. Allogeneic human mesenchymal stem cell therapy (remestemcel-L, Prochymal) as a rescue agent for severe refractory acute graft-versus-host disease in pediatric patients. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014, 20, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosser, S.; Dennler, C.; Schweizer, R.; Eberli, D.; Stein, J.V.; Enzmann, V.; Giovanoli, P.; Erni, D.; Plock, J.A. Paracrine effects of mesenchymal stem cells enhance vascular regeneration in ischemic murine skin. Microvasc. Res. 2012, 83, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweizer, R.; Kamat, P.; Schweizer, D.; Dennler, C.; Zhang, S.; Schnider, J.T.; Salemi, S.; Giovanoli, P.; Eberli, D.; Enzmann, V.; et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells improve vascular regeneration and reduce leukocyte-endothelium activation in critical ischemic murine skin in a dose-dependent manner. Cytotherapy 2014, 16, 1345–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Zeng, X.; Guo, W.; Jin, Y.; Wang, S.; Tian, R.; Han, Y.; Guo, L.; Han, J.; et al. Efficient lung cancer-targeted drug delivery via a nanoparticle/MSC system. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, I.; Subbarao, R.B.; Rho, G.J. Human mesenchymal stem cells - current trends and future prospective. Biosci. Rep. 2015, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez Vallone, V.B.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and their use in therapy: what has been achieved? Differ. ; Res. Biol. Divers. 2013, 85, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szala, S.; Wisniewska, E.; Czapla, J. [Mesenchymal stromal cells]. Postep. Hig. I Med. Dosw. 2014, 68:1287-1298. [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Zhang, N.; Marsano, A.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G.; Zhang, Y.; Lopez, M.J. In Vitro Mesenchymal Trilineage Differentiation and Extracellular Matrix Production by Adipose and Bone Marrow Derived Adult Equine Multipotent Stromal Cells on a Collagen Scaffold. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2013, 9, 858–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Ankrum, J.; Ong, J.F.; Karp, J.M. Mesenchymal stem cells: immune evasive, not immune privileged. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Blanc, K.; Tammik, C.; Rosendahl, K.; Zetterberg, E.; Ringden, O. HLA expression and immunologic properties of differentiated and undifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells. Exp. Hematol. 2003, 31, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schu, S.; Nosov, M.; O'Flynn, L.; Shaw, G.; Treacy, O.; Barry, F.; Murphy, M.; O'Brien, T.; Ritter, T. Immunogenicity of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2012, 16, 2094–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangi, L.; Margalit, R.; Reich-Zeliger, S.; Bachar-Lustig, E.; Beilhack, A.; Negrin, R.; Reisner, Y. Direct Imaging of Immune Rejection and Memory Induction by Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. STEM CELLS 2009, 27, 2865–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, A.K.; Fortier, L.A.; Antczak, D.F.; Schnabel, L.V. Immunoprivileged no more: measuring the immunogenicity of allogeneic adult mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Németh, K.; Leelahavanichkul, A.; Yuen, P.S.; Mayer, B.; Parmelee, A.; Doi, K.; Robey, P.G.; Leelahavanichkul, K.; Koller, B.H.; Brown, J.M.; et al. Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate sepsis via prostaglandin E2–dependent reprogramming of host macrophages to increase their interleukin-10 production. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, T.S.; Bertolino, G.M.; Giacomini, C.; Bornhäuser, M.; Dazzi, F.; Galleu, A. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells for Graft Versus Host Disease: Mechanism-Based Biomarkers. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, F.J.; Aigner, L. Adult mesenchymal stem cell therapy for myelin repair in Multiple Sclerosis. Biol. Res. 2012, 45, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangera, A.; Chapple, C.R. Tissue engineering in urethral reconstruction—an update. Asian J. Androl. 2013, 15, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caplan, H.; Olson, S.D.; Kumar, A.; George, M.; Prabhakara, K.S.; Wenzel, P.; Bedi, S.; Toledano-Furman, N.E.; Triolo, F.; Kamhieh-Milz, J.; et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapeutic Delivery: Translational Challenges to Clinical Application. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Yu, X.; Xu, R.; Fang, Y.; Qian, X.; Liu, S.; Teng, J.; Ding, X. Maximum Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Rat Model of Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: Renal Artery Administration with Optimal Numbers. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e92347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, B.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y. Strategies to Optimize Adult Stem Cell Therapy for Tissue Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braid, L.R.; Wood, C.A.; Wiese, D.M.; Ford, B.N. Intramuscular administration potentiates extended dwell time of mesenchymal stromal cells compared to other routes. Cytotherapy 2018, 20, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Hou, X.; Wang, B.; Chi, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z. Intramuscular injection of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells improves cardiac function in dilated cardiomyopathy rats. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, B. Intramuscular injection of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells with small gap neurorrhaphy for peripheral nerve repair. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 585, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvinen, T.; Jarvinen, M.; Kalimo, H. Regeneration of injured skeletal muscle after the injury. Muscle Ligaments Tendons J. 2013, 03, 337–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deten, A.; Volz, H.C.; Briest, W.; Zimmer, H.-G. Cardiac cytokine expression is upregulated in the acute phase after myocardial infarction. Experimental studies in rats. Cardiovasc. Res. 2002, 55, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, C.; Wienhold, D.; Benken, N.; Eggersmann, C.; Thüroff, J. Definition of overactive bladder and epidemiology of urinary incontinence. Urology 1997, 50, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Ren, L. Optimization of the adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell delivery time for radiation-induced lung fibrosis treatment in rats. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Koppen, A. , et al. Healthy bone marrow cells reduce progression of kidney failure better than CKD bone marrow cells in rats with established chronic kidney disease. Cell Transplant. 2012, 21, 2299–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.R.; Pollock, K.; Hubel, A.; McKenna, D. Mesenchymal stem or stromal cells: a review of clinical applications and manufacturing practices. Transfusion 2014, 54, 1418–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnadurai, R.; et al. Cryopreserved Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Are Susceptible to T-Cell Mediated Apoptosis Which Is Partly Rescued by IFNgamma Licensing. Stem Cells 2016, 34, 2429–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moll, G.; et al. Cryopreserved or Fresh Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Only a Matter of Taste or Key to Unleash the Full Clinical Potential of MSC Therapy? Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 951, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sensebé, L.; Tarte, K.; Galipeau, J.; Krampera, M.; Martin, I.; Phinney, D.G.; Shi, Y. Limited Acquisition of Chromosomal Aberrations in Human Adult Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 10, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galipeau, J. The mesenchymal stromal cells dilemma--does a negative phase III trial of random donor mesenchymal stromal cells in steroid-resistant graft-versus-host disease represent a death knell or a bump in the road? Cytotherapy 2013, 15, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bahr, L.; et al. Long-term complications, immunologic effects, and role of passage for outcome in mesenchymal stromal cell therapy. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. : J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2012, 18, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, A.; Tao, C.; Li, X.; Jin, P. The role of SDF-1-CXCR4/CXCR7 axis in biological behaviors of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 improve early liver regeneration of small-for-size liver grafts. Liver Transplant. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Study Liver Dis. Int. Liver Transplant. Soc. 2013, 19, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Zhang, G.; Wang, F.; Liu, H.; Liu, L.; Han, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, J. Protective Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cells with CXCR4 Up-Regulation in a Rat Renal Transplantation Model. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e82949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Choi, E.; Cha, M.-J.; Hwang, K.-C. Cell Adhesion and Long-Term Survival of Transplanted Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Prerequisite for Cell Therapy. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.-W.; Chang, W.; Song, B.-W.; Song, H.; Lim, S.; Kim, H.-J.; Cha, M.-J.; Choi, E.; Im, S.-H.; Chang, B.-C.; et al. Integrin-Linked Kinase Is Required in Hypoxic Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Strengthening Cell Adhesion to Ischemic Myocardium. STEM CELLS 2009, 27, 1358–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Yoon, Y.M.; Lee, S.H. Hypoxic Preconditioning Promotes the Bioactivities of Mesenchymal Stem Cells via the HIF-1α-GRP78-Akt Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Guo, J.; Mao, R.; Chao, K.; Chen, B.-L.; He, Y.; Zeng, Z.-R.; Zhang, S.-H.; Chen, M.-H. TLR3 preconditioning enhances the therapeutic efficacy of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in TNBS-induced colitis via the TLR3-Jagged-1-Notch-1 pathway. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 727–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, N.; et al. TNF-alpha/IL-1beta-licensed mesenchymal stromal cells promote corneal allograft survival via myeloid cell-mediated induction of Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells in the lung. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2019, 33, 9404–9421. [Google Scholar]
- Francois, M.; Romieu-Mourez, R.; Li, M.; Galipeau, J. Human MSC suppression correlates with cytokine induction of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and bystander M2 macrophage differentiation. Mol. Ther. : J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2012, 20, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrero, R.; et al. IL1beta induces mesenchymal stem cells migration and leucocyte chemotaxis through NF-kappaB. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2012, 8, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, X.; Ding, Y.; Xu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, F. Enhanced cell survival and paracrine effects of mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing hepatocyte growth factor promote cardioprotection in myocardial infarction. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 344, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, B.; Li, F.; Fang, J.; Xu, L.; Sun, C.; Han, J.; Hua, T.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Z.; Jiang, X. Hypoxia inducible factor 1α promotes survival of mesenchymal stem cells under hypoxia. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, B.; Hua, T.; Li, F.; Han, J.; Fang, J.; Xu, L.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Z.; Jiang, X. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 α protects mesenchymal stem cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury via autophagy induction and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 2492–2499. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, S.M. , et al. Enhanced proliferation and differentiation of Oct4- and Sox2-overexpressing human adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2014, 46, e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-J.; Choi, J.-H.; Jung, J.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, G.J. Changes in PTTG1 by human TERT gene expression modulate the self-renewal of placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2014, 357, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-C.; Chen, C.-L.; Liu, H.-C.; Lee, Y.-T.; Wang, H.-W.; Hou, L.-T.; Hung, S.-C. Overexpression of hTERT increases stem-like properties and decreases spontaneous differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cell lines. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 17, 64–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, H.; Qiu, W.; Li, C.; Flyvbjerg, A.; Abdallah, B.M.; Kassem, M. Telomerase activity promotes osteoblast differentiation by modulating IGF-signaling pathway. Biogerontology 2015, 16, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noone, C.; Kihm, A.; English, K.; O'Dea, S.; Mahon, B.P. IFN-gamma stimulated human umbilical-tissue-derived cells potently suppress NK activation and resist NK-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. Stem cells and development 2013, 22, 3003–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W. , et al. Infusion of mesenchymal stem cells and rapamycin synergize to attenuate alloimmune responses and promote cardiac allograft tolerance. Am. J. Transplant. : Off. J. Am. Soc. Transplant. Am. Soc. Transpl. Surg. 2009, 9, 1760–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Garza-Rodea, A.S. , et al. Exploitation of herpesvirus immune evasion strategies to modify the immunogenicity of human mesenchymal stem cell transplants. PloS one 2011, 6, e14493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.P. , et al. Class II transactivator knockdown limits major histocompatibility complex II expression, diminishes immune rejection, and improves survival of allogeneic bone marrow stem cells in the infarcted heart. FASEB J. : Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2016, 30, 3069–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galipeau, J.; Krampera, M.; Barrett, J.; Dazzi, F.; Deans, R.J.; DeBruijn, J.; Dominici, M.; Fibbe, W.E.; Gee, A.P.; Gimble, J.M.; et al. International Society for Cellular Therapy perspective on immune functional assays for mesenchymal stromal cells as potency release criterion for advanced phase clinical trials. Cytotherapy 2016, 18, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnadurai, R.; Rajan, D.; Qayed, M.; Arafat, D.; Garcia, M.; Liu, Y.; Kugathasan, S.; Anderson, L.J.; Gibson, G.; Galipeau, J. Potency Analysis of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Using a Combinatorial Assay Matrix Approach. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 2504–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| MSCs Functionality | Therapeutic Outcome |
|---|---|
| Immunomodulatory | reduce tissue inflammation during colitis (9) Resolving acute steroid-refractory graft vs. host disease (10, 11) |
| Angiogenic/vascular regeneration & and tissue healing | vascular regeneration in ischemic murine skin (12) Angiogenesis in myocardial infarction (13) |
| Anti-cancer drug delivery agent | MSCs as a drug carrier to deliver chemotherapeutic agent Docetaxel (DTX) to lung tumors (14) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




