Submitted:
20 January 2024
Posted:
22 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Role of non-coding RNAs in hepatocarcinogenesis
3. Combination of non-coding RNAs-based strategies with TKIs in HCC
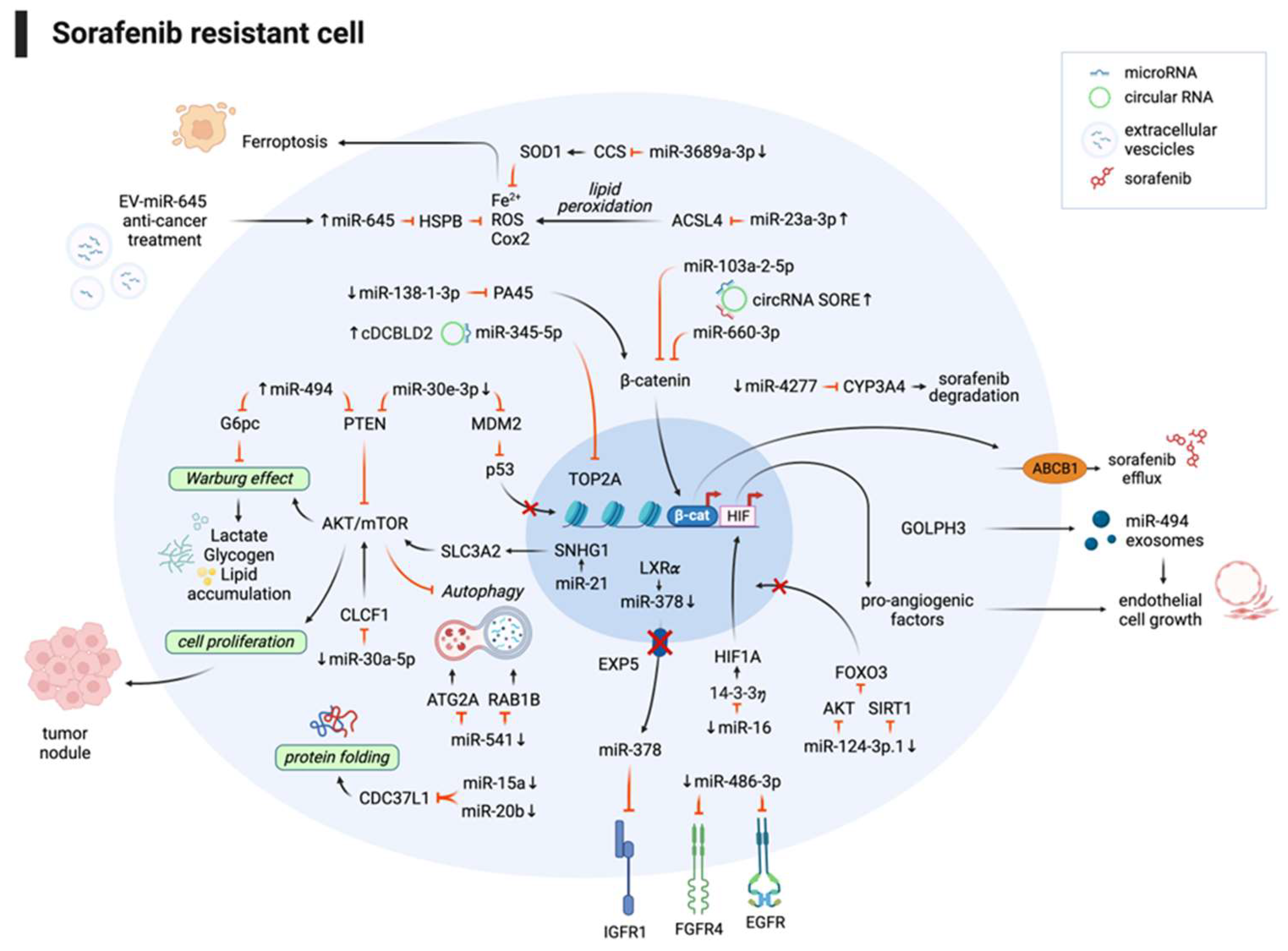
3.1. Non-coding RNAs and sorafenib combination improves the therapeutic response
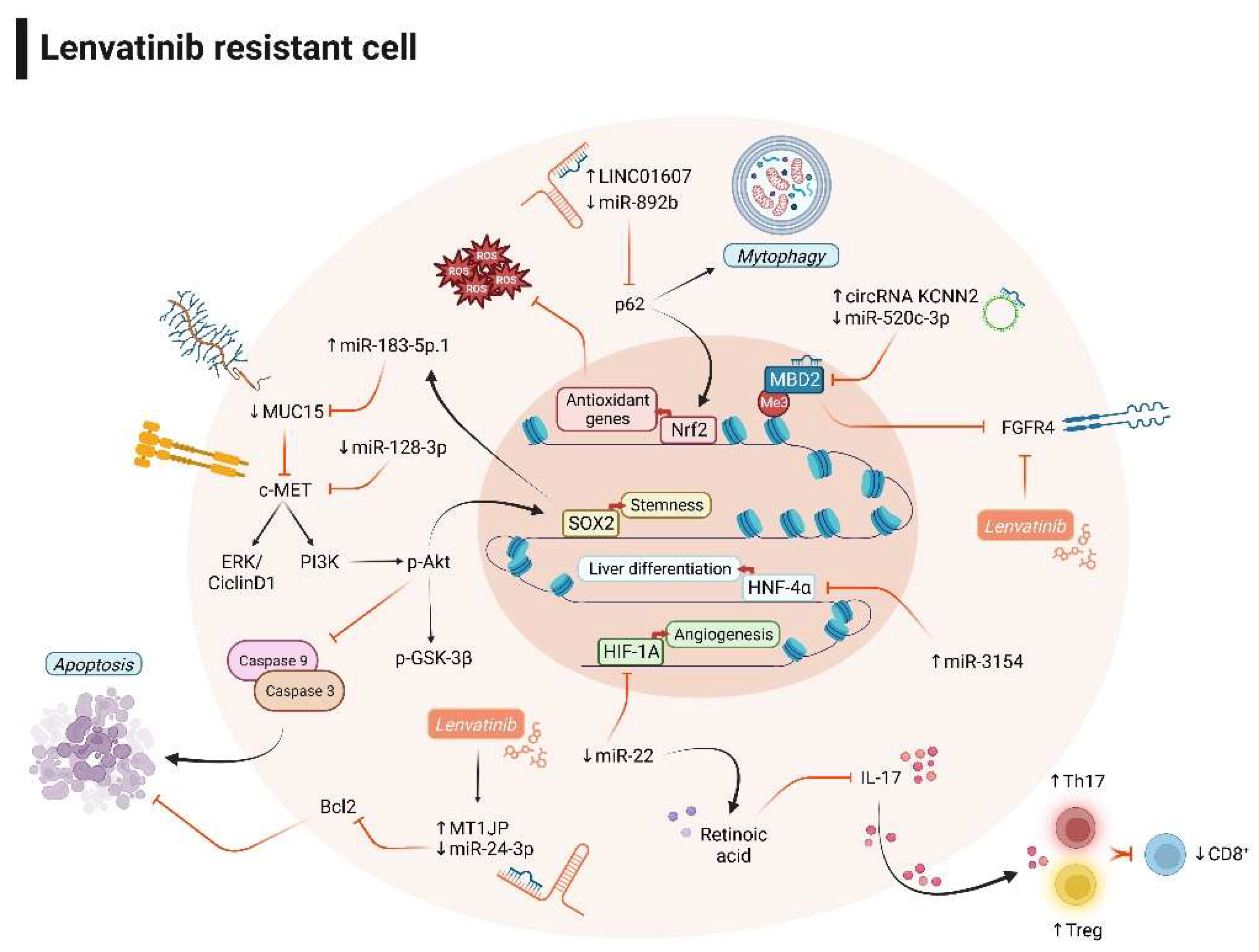
3.2. Non-coding RNAs and lenvatinib combination improves the therapeutic response
4. Combination of ncRNAs-based strategies and ICIs improves therapeutic efficacy in HCC preclinical models
5. Non-coding RNAs as biomarkers of treatment response in HCC
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.-F.; de Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.-L.; Forner, A.; et al. Sorafenib in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Qin, S.; Merle, P.; Granito, A.; Huang, Y.-H.; Bodoky, G.; Pracht, M.; Yokosuka, O.; Rosmorduc, O.; Breder, V.; et al. Regorafenib for Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Who Progressed on Sorafenib Treatment (RESORCE): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Han, K.-H.; Ikeda, K.; Piscaglia, F.; Baron, A.; Park, J.-W.; Han, G.; Jassem, J.; et al. Lenvatinib versus Sorafenib in First-Line Treatment of Patients with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Randomised Phase 3 Non-Inferiority Trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Meyer, T.; Cheng, A.-L.; El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Rimassa, L.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Cicin, I.; Merle, P.; Chen, Y.; Park, J.-W.; et al. Cabozantinib in Patients with Advanced and Progressing Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.X.; Kang, Y.-K.; Yen, C.-J.; Finn, R.S.; Galle, P.R.; Llovet, J.M.; Assenat, E.; Brandi, G.; Pracht, M.; Lim, H.Y.; et al. Ramucirumab after Sorafenib in Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Increased α-Fetoprotein Concentrations (REACH-2): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Chan, S.L.; Kudo, M.; Lau, G.; Kelley, R.K.; Furuse, J.; Sukeepaisarnjaroen, W.; Kang, Y.-K.; Dao, T.V.; De Toni, E.N.; et al. Phase 3 Randomized, Open-Label, Multicenter Study of Tremelimumab (T) and Durvalumab (D) as First-Line Therapy in Patients (Pts) with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma (uHCC): HIMALAYA. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 379–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reig, M.; Forner, A.; Rimola, J.; Ferrer-Fàbrega, J.; Burrel, M.; Garcia-Criado, Á.; Kelley, R.K.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Salem, R.; et al. BCLC Strategy for Prognosis Prediction and Treatment Recommendation: The 2022 Update. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, D.; Núñez, N.G.; Pinyol, R.; Govaere, O.; Pinter, M.; Szydlowska, M.; Gupta, R.; Qiu, M.; Deczkowska, A.; Weiner, A.; et al. NASH Limits Anti-Tumour Surveillance in Immunotherapy-Treated HCC. Nature 2021, 592, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, J.J.; Nandakumar, S.; Armenia, J.; Khalil, D.N.; Albano, M.; Ly, M.; Shia, J.; Hechtman, J.F.; Kundra, R.; El Dika, I.; et al. Prospective Genotyping of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Clinical Implications of Next-Generation Sequencing for Matching Patients to Targeted and Immune Therapies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 2116–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afra, F.; Mahboobipour, A.A.; Salehi Farid, A.; Ala, M. Recent Progress in the Immunotherapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Non-Coding RNA-Based Immunotherapy May Improve the Outcome. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornari, F.; Giovannini, C.; Piscaglia, F.; Gramantieri, L. Elucidating the Molecular Basis of Sorafenib Resistance in HCC: Current Findings and Future Directions. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2021, 8, 741–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattick, J.S.; Makunin, I.V. Non-Coding RNA. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15 Spec No 1, R17-29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteller, M. Non-Coding RNAs in Human Disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, K.; Bayraktar, R.; Ferracin, M.; Calin, G.A. Non-Coding RNAs in Disease: From Mechanisms to Therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, F.; Mendell, J.T. Functional Classification and Experimental Dissection of Long Noncoding RNAs. Cell 2018, 172, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhou, J.-K.; Peng, Y.; He, W.; Huang, C. The Role of Long Noncoding RNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Lyu, T.; Li, H.; Liu, C.; Xie, K.; Xu, L.; Li, W.; Liu, H.; Zhu, J.; Lyu, Y.; et al. LncRNA CEBPA-DT Promotes Liver Cancer Metastasis through DDR2/β-Catenin Activation via Interacting with hnRNPC. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Hu, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, P.; Xiong, H.; Zeng, Z.; Han, S.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; et al. LncRNA FTO-IT1 Promotes Glycolysis and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Modulating FTO-Mediated N6-Methyladenosine Modification on GLUT1 and PKM2. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.-Y.; Cai, Z.-R.; Liu, J.; Wang, D.-S.; Ju, H.-Q.; Xu, R.-H. Circular RNA: Metabolism, Functions and Interactions with Proteins. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Liang, M.; Liu, H.; Huang, J.; Li, P.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, X. CircRNA hsa_circRNA_104348 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression through Modulating miR-187-3p/RTKN2 Axis and Activating Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Long, H.; Zheng, Q.; Bo, X.; Xiao, X.; Li, B. Circular RNA circRHOT1 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Initiation of NR2F6 Expression. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.-Y.; Huang, Z.-L.; Huang, J.; Xu, B.; Huang, X.-Y.; Xu, Y.-H.; Zhou, J.; Tang, Z.-Y. Exosomal circRNA-100338 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastasis via Enhancing Invasiveness and Angiogenesis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, J.; Jung, S.; Keller, S.; Gregory, R.I.; Diederichs, S. Many Roads to Maturity: microRNA Biogenesis Pathways and Their Regulation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Liu, C.; Bi, Z.-Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.-L.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, W.; Song, Y.-Y.-Y.; Zhang, F.; et al. Comprehensive Landscape of Extracellular Vesicle-Derived RNAs in Cancer Initiation, Progression, Metastasis and Cancer Immunology. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ren, H.; Dai, B.; Li, J.; Shang, L.; Huang, J.; Shi, X. Hepatocellular Carcinoma-Derived Exosomal miRNA-21 Contributes to Tumor Progression by Converting Hepatocyte Stellate Cells to Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenouda, S.K.; Alahari, S.K. MicroRNA Function in Cancer: Oncogene or a Tumor Suppressor? Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009, 28, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornari, F.; Milazzo, M.; Galassi, M.; Callegari, E.; Veronese, A.; Miyaaki, H.; Sabbioni, S.; Mantovani, V.; Marasco, E.; Chieco, P.; et al. P53/Mdm2 Feedback Loop Sustains miR-221 Expression and Dictates the Response to Anticancer Treatments in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramantieri, L.; Pollutri, D.; Gagliardi, M.; Giovannini, C.; Quarta, S.; Ferracin, M.; Casadei-Gardini, A.; Callegari, E.; De Carolis, S.; Marinelli, S.; et al. MiR-30e-3p Influences Tumor Phenotype through MDM2/TP53 Axis and Predicts Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 1720–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA Signatures in Human Cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramantieri, L.; Ferracin, M.; Fornari, F.; Veronese, A.; Sabbioni, S.; Liu, C.-G.; Calin, G.A.; Giovannini, C.; Ferrazzi, E.; Grazi, G.L.; et al. Cyclin G1 Is a Target of miR-122a, a microRNA Frequently down-Regulated in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6092–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladeiro, Y.; Couchy, G.; Balabaud, C.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; Pelletier, L.; Rebouissou, S.; Zucman-Rossi, J. MicroRNA Profiling in Hepatocellular Tumors Is Associated with Clinical Features and Oncogene/Tumor Suppressor Gene Mutations. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1955–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budhu, A.; Jia, H.-L.; Forgues, M.; Liu, C.-G.; Goldstein, D.; Lam, A.; Zanetti, K.A.; Ye, Q.-H.; Qin, L.-X.; Croce, C.M.; et al. Identification of Metastasis-Related microRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2008, 47, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jopling, C.L.; Yi, M.; Lancaster, A.M.; Lemon, S.M.; Sarnow, P. Modulation of Hepatitis C Virus RNA Abundance by a Liver-Specific MicroRNA. Science 2005, 309, 1577–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmén, J.; Lindow, M.; Schütz, S.; Lawrence, M.; Petri, A.; Obad, S.; Lindholm, M.; Hedtjärn, M.; Hansen, H.F.; Berger, U.; et al. LNA-Mediated microRNA Silencing in Non-Human Primates. Nature 2008, 452, 896–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krützfeldt, J.; Rajewsky, N.; Braich, R.; Rajeev, K.G.; Tuschl, T.; Manoharan, M.; Stoffel, M. Silencing of microRNAs in Vivo with “Antagomirs”. Nature 2005, 438, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komoll, R.-M.; Hu, Q.; Olarewaju, O.; von Döhlen, L.; Yuan, Q.; Xie, Y.; Tsay, H.-C.; Daon, J.; Qin, R.; Manns, M.P.; et al. MicroRNA-342-3p Is a Potent Tumour Suppressor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, J.; Chivukula, R.R.; O’Donnell, K.A.; Wentzel, E.A.; Montgomery, C.L.; Hwang, H.-W.; Chang, T.-C.; Vivekanandan, P.; Torbenson, M.; Clark, K.R.; et al. Therapeutic microRNA Delivery Suppresses Tumorigenesis in a Murine Liver Cancer Model. Cell 2009, 137, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callegari, E.; Domenicali, M.; Shankaraiah, R.C.; D’Abundo, L.; Guerriero, P.; Giannone, F.; Baldassarre, M.; Bassi, C.; Elamin, B.K.; Zagatti, B.; et al. MicroRNA-Based Prophylaxis in a Mouse Model of Cirrhosis and Liver Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 14, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.S.; Kang, Y.-K.; Borad, M.; Sachdev, J.; Ejadi, S.; Lim, H.Y.; Brenner, A.J.; Park, K.; Lee, J.-L.; Kim, T.-Y.; et al. Phase 1 Study of MRX34, a Liposomal miR-34a Mimic, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA: Trends in Clinical Trials of Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy Strategies. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanuso, V.; Rimassa, L.; Braconi, C. The Rapidly Evolving Landscape of HCC: Selecting the Optimal Systemic Therapy. Hepatology 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, S.M.; Carter, C.; Tang, L.; Wilkie, D.; McNabola, A.; Rong, H.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Vincent, P.; McHugh, M.; et al. BAY 43-9006 Exhibits Broad Spectrum Oral Antitumor Activity and Targets the RAF/MEK/ERK Pathway and Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Involved in Tumor Progression and Angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7099–7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, J.M.; Burchard, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, A.M.; Wong, K.F.; Shek, F.H.; Lee, N.P.; Fan, S.T.; Poon, R.T.; Ivanovska, I.; et al. DLK1-DIO3 Genomic Imprinted microRNA Cluster at 14q32.2 Defines a Stemlike Subtype of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Associated with Poor Survival. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 30706–30713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.; Balakrishnan, A.; Huskey, N.; Jones, K.D.; Jodari, M.; Ng, R.; Song, G.; Riordan, J.; Anderton, B.; Cheung, S.-T.; et al. MicroRNA-494 within an Oncogenic microRNA Megacluster Regulates G1/S Transition in Liver Tumorigenesis through Suppression of Mutated in Colorectal Cancer. Hepatology 2014, 59, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollutri, D.; Patrizi, C.; Marinelli, S.; Giovannini, C.; Trombetta, E.; Giannone, F.A.; Baldassarre, M.; Quarta, S.; Vandewynckel, Y.P.; Vandierendonck, A.; et al. The Epigenetically Regulated miR-494 Associates with Stem-Cell Phenotype and Induces Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yin, Z.; Qi, Y.; Peng, H.; Ma, W.; Wang, R.; Li, W. Golgi Phosphoprotein 3 Promotes Angiogenesis and Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Upregulating Exosomal miR-494-3p. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, G.; Liu, Y.; Fang, X.; Liu, Y.; Fang, L.; Lin, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, N. Tumor-Derived microRNA-494 Promotes Angiogenesis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Angiogenesis 2015, 18, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Jiang, F.; Yang, Y.; Huang, G.; Pu, F.; Liu, Q.; Chen, L.; Ju, L.; Lu, M.; Zhou, F.; et al. 14-3-3η Is a Novel Growth-Promoting and Angiogenic Factor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Shan, W.; Yang, Y.; Jin, M.; Dai, Y.; Yang, H.; Jiao, R.; Xia, Y.; Liu, Q.; Ju, L.; et al. Reversal of Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Epigenetically Regulated Disruption of 14-3-3η/Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yu, S.; Chen, J.; Quan, M.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y. miR-15a and miR-20b Sensitize Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells to Sorafenib through Repressing CDC37L1 and Consequent PPIA Downregulation. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Chan, Y.-T.; Wu, J.; Feng, Z.; Yuan, H.; Li, Q.; Xing, T.; Xu, L.; Zhang, C.; Tan, H.-Y.; et al. CRISPR/Cas9 Screens Unravel miR-3689a-3p Regulating Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Suppressing CCS/SOD1-Dependent Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress. Drug Resist. Updat. 2023, 71, 101015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Lee, D.; Law, C.-T.; Zhang, M.S.; Shen, J.; Chin, D.W.-C.; Zhang, A.; Tsang, F.H.-C.; Wong, C.L.-S.; Ng, I.O.-L.; et al. Genome-Wide CRISPR/Cas9 Library Screening Identified PHGDH as a Critical Driver for Sorafenib Resistance in HCC. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, A.; Chevalier, N.; Calderoni, M.; Dubuis, G.; Dormond, O.; Ziros, P.G.; Sykiotis, G.P.; Widmann, C. CRISPR/Cas9 Genome-Wide Screening Identifies KEAP1 as a Sorafenib, Lenvatinib, and Regorafenib Sensitivity Gene in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 7058–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander Heiden, M.G.; Cantley, L.C.; Thompson, C.B. Understanding the Warburg Effect: The Metabolic Requirements of Cell Proliferation. Science 2009, 324, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zuo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, G.; Zhang, L.; Wu, J.; Wang, X. MiR-3662 Suppresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth through Inhibition of HIF-1α-Mediated Warburg Effect. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Xiao, X.; Han, Y.; Fan, D.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, L. MiR-3662 Suppresses Cell Growth, Invasion and Glucose Metabolism by Targeting HK2 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Neoplasma 2020, 67, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamini, C.; Leoni, I.; Rizzardi, N.; Melli, M.; Galvani, G.; Coada, C.A.; Giovannini, C.; Monti, E.; Liparulo, I.; Valenti, F.; et al. MiR-494 Induces Metabolic Changes through G6pc Targeting and Modulates Sorafenib Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tan, X.; Luo, J.; Yao, H.; Si, Z.; Tong, J.-S. The miR-30a-5p/CLCF1 Axis Regulates Sorafenib Resistance and Aerobic Glycolysis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, P.-Y.; Yang, G.-M.; Gurunathan, S. A Comprehensive Review on the Composition, Biogenesis, Purification, and Multifunctional Role of Exosome as Delivery Vehicles for Cancer Therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicodemou, A.; Bernátová, S.; Čeháková, M.; Danišovič, Ľ. Emerging Roles of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal-Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Liu, H.; Zuo, H. Engineered Small Extracellular Vesicles Loaded with miR-654-5p Promote Ferroptosis by Targeting HSPB1 to Alleviate Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Chan, Y.-T.; Tan, H.-Y.; Zhang, C.; Guo, W.; Xu, Y.; Sharma, R.; Chen, Z.-S.; Zheng, Y.-C.; Wang, N.; et al. Epigenetic Regulation of Ferroptosis via ETS1/miR-23a-3p/ACSL4 Axis Mediates Sorafenib Resistance in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eun, J.W.; Yoon, J.H.; Ahn, H.R.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.B.; Lim, S.B.; Park, W.; Kang, T.W.; Baek, G.O.; Yoon, M.G.; et al. Cancer-Associated Fibroblast-Derived Secreted Phosphoprotein 1 Contributes to Resistance of Hepatocellular Carcinoma to Sorafenib and Lenvatinib. Cancer Commun. 2023, 43, 455–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornari, F.; Gramantieri, L.; Callegari, E.; Shankaraiah, R.C.; Piscaglia, F.; Negrini, M.; Giovannini, C. MicroRNAs in Animal Models of HCC. Cancers 2019, 11, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.-B.; Wu, H.-M.; He, Y.-C.; Huang, Z.-T.; Weng, Y.-H.; Li, H.; Liang, C.; Yu, W.-M.; Chen, W. MiRNA-124-3p.1 Sensitizes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells to Sorafenib by Regulating FOXO3a by Targeting AKT2 and SIRT1. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tovar, V.; Cornella, H.; Moeini, A.; Vidal, S.; Hoshida, Y.; Sia, D.; Peix, J.; Cabellos, L.; Alsinet, C.; Torrecilla, S.; et al. Tumour Initiating Cells and IGF/FGF Signalling Contribute to Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gut 2017, 66, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Huang, J.; Ma, L.; Shan, J.; Shen, J.; Yang, Z.; Liu, L.; Luo, Y.; Yao, C.; Qian, C. MicroRNA-122 Confers Sorafenib Resistance to Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Targeting IGF-1R to Regulate RAS/RAF/ERK Signaling Pathways. Cancer Lett. 2016, 371, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Xia, S.; Liang, Y.; Ji, L.; Pan, Y.; Jiang, S.; Wan, Z.; Tao, L.; Chen, J.; Lin, C.; et al. LXR Activation Potentiates Sorafenib Sensitivity in HCC by Activating microRNA-378a Transcription. Theranostics 2020, 10, 8834–8850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Lin, Z.; Wan, Z.; Xia, S.; Jiang, S.; Cen, D.; Cai, L.; Xu, J.; Cai, X. miR-486-3p Mediates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Sorafenib Resistance by Targeting FGFR4 and EGFR. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wan, Z.; Tang, M.; Lin, Z.; Jiang, S.; Ji, L.; Gorshkov, K.; Mao, Q.; Xia, S.; Cen, D.; et al. N6-Methyladenosine-Modified CircRNA-SORE Sustains Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Regulating β-Catenin Signaling. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, Y.; Chen, T.; Zheng, L.; Cai, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Tao, L.; Xu, J.; Ji, L.; Cai, X. cDCBLD2 Mediates Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Sponging miR-345-5p Binding to the TOP2A Coding Sequence. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 4608–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Dong, X.; He, C.; Tan, G.; Li, Z.; Zhai, B.; Feng, J.; Jiang, X.; Liu, C.; Jiang, H.; et al. LncRNA SNHG1 Contributes to Sorafenib Resistance by Activating the Akt Pathway and Is Positively Regulated by miR-21 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, B.; Hu, F.; Jiang, X.; Xu, J.; Zhao, D.; Liu, B.; Pan, S.; Dong, X.; Tan, G.; Wei, Z.; et al. Inhibition of Akt Reverses the Acquired Resistance to Sorafenib by Switching Protective Autophagy to Autophagic Cell Death in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 1589–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.-P.; Liu, J.-P.; Feng, J.-F.; Zhu, C.-P.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, W.-P.; Ding, J.; Huang, C.-K.; Cui, Y.-L.; Ding, C.-H.; et al. miR-541 Potentiates the Response of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma to Sorafenib Treatment by Inhibiting Autophagy. Gut 2020, 69, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Sun, H.; Jiang, Q.; Chai, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, B.; You, S.; Li, B.; Hao, J.; et al. Hsa-miR-4277 Decelerates the Metabolism or Clearance of Sorafenib in HCC Cells and Enhances the Sensitivity of HCC Cells to Sorafenib by Targeting Cyp3a4. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 735447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-T.; Mou, J.; Pan, Y.-J.; Huo, F.-C.; Du, W.-Q.; Liang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.-S.; Pei, D.-S. MicroRNA-138-1-3p Sensitizes Sorafenib to Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting PAK5 Mediated β-Catenin/ABCB1 Signaling Pathway. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 28, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spallanzani, A.; Orsi, G.; Andrikou, K.; Gelsomino, F.; Rimini, M.; Riggi, L.; Cascinu, S. Lenvatinib as a Therapy for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2018, 18, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladd, A.D.; Duarte, S.; Sahin, I.; Zarrinpar, A. Mechanisms of Drug Resistance in HCC. Hepatology 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wei, L.; Han, T.; Ding, S. miR-3154 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression via Suppressing HNF4α. Carcinogenesis 2022, 43, 1002–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.-Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.-Y.; Hu, L.; Li, L.; Sun, H.-Y.; Jiang, F.; Zhao, J.; Liu, G.-M.-Y.; Tang, J.; et al. MUC15 Inhibits Dimerization of EGFR and PI3K-AKT Signaling and Is Associated with Aggressive Hepatocellular Carcinomas in Patients. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 1436–1448.e1-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, P.; Li, H.; Cheng, Z.; Xiang, D.; Wang, R. Downregulation of MUC15 by miR-183-5p.1 Promotes Liver Tumor-Initiating Cells Properties and Tumorigenesis via Regulating c-MET/PI3K/AKT/SOX2 Axis. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Jiang, W.; Han, P.; Zhang, J.; Tong, L.; Sun, X. MicroRNA-128-3p Mediates Lenvatinib Resistance of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Downregulating c-Met. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2022, 9, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Yin, J.; Ma, L.; Liu, M.; Zhou, X.; Xian, L.; Li, P.; Tan, X.; et al. circKCNN2 Suppresses the Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma at Least Partially via Regulating miR-520c-3p/Methyl-DNA-Binding Domain Protein 2 Axis. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Yu, J.; Lu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, F.; Sun, L.; Guo, Z.; Hou, G.; et al. MT1JP-Mediated miR-24-3p/BCL2L2 Axis Promotes Lenvatinib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Inhibiting Apoptosis. Cell. Oncol. 2021, 44, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, H.; Zhu, J.; Lu, Y.; Cheng, F.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, J.; Cai, G.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Targeting LINC01607 Sensitizes Hepatocellular Carcinoma to Lenvatinib via Suppressing Mitophagy. Cancer Lett. 2023, 576, 216405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Setayesh, T.; Vaziri, F.; Wu, X.; Hwang, S.T.; Chen, X.; Yvonne Wan, Y.-J. miR-22 Gene Therapy Treats HCC by Promoting Anti-Tumor Immunity and Enhancing Metabolism. Mol. Ther. 2023, 31, 1829–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Iwama, H.; Fujita, K.; Kobara, H.; Nishiyama, N.; Fujihara, S.; Goda, Y.; Yoneyama, H.; Morishita, A.; Tani, J.; et al. Evaluating the Effect of Lenvatinib on Sorafenib-Resistant Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Wang, X.; Steer, C.J.; Song, G. MicroRNA-206 Promotes the Recruitment of CD8+ T Cells by Driving M1 Polarisation of Kupffer Cells. Gut 2022, 71, 1642–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Chang, C.W.; Steer, C.J.; Wang, X.W.; Song, G. MicroRNA-15a/16-1 Prevents Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Disrupting the Communication Between Kupffer Cells and Regulatory T Cells. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wenes, M.; Romero, P.; Huang, S.C.-C.; Fendt, S.-M.; Ho, P.-C. Navigating Metabolic Pathways to Enhance Antitumour Immunity and Immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 425–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, J.; Mao, J.; Zuo, X. CircRHBDD1 Augments Metabolic Rewiring and Restricts Immunotherapy Efficacy via m6A Modification in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2022, 24, 755–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Xia, P.; Chen, X.; Ma, W.; Yuan, Y. ncRNA-Mediated Fatty Acid Metabolism Reprogramming in HCC. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 34, 278–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.; Yi, J.; Jiang, J.; Zou, Z.; Mo, Y.; Ren, Q.; Lin, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J. Identification and Validation of a Fatty Acid Metabolism-Related lncRNA Signature as a Predictor for Prognosis and Immunotherapy in Patients with Liver Cancer. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, J.; Shen, X.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, J. LncRNA SNHG1 Upregulates FANCD2 and G6PD to Suppress Ferroptosis by Sponging miR-199a-5p/3p in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Drug Discov. Ther. 2023, 17, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.-Y.; Zhang, P.-F.; Wei, C.-Y.; Peng, R.; Lu, J.-C.; Gao, C.; Cai, J.-B.; Yang, X.; Fan, J.; Ke, A.-W.; et al. Circular RNA circMET Drives Immunosuppression and Anti-PD1 Therapy Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via the miR-30-5p/Snail/DPP4 Axis. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollande, C.; Boussier, J.; Ziai, J.; Nozawa, T.; Bondet, V.; Phung, W.; Lu, B.; Duffy, D.; Paradis, V.; Mallet, V.; et al. Inhibition of the Dipeptidyl Peptidase DPP4 (CD26) Reveals IL-33-Dependent Eosinophil-Mediated Control of Tumor Growth. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Pan, T.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, G.; Xu, Q.; Li, S.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA LINC01132 Enhances Immunosuppression and Therapy Resistance via NRF1/DPP4 Axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Mackowiak, B.; Feng, D.; Lu, H.; Guan, Y.; Lehner, T.; Pan, H.; Wang, X.W.; He, Y.; Gao, B. MicroRNA-223 Attenuates Hepatocarcinogenesis by Blocking Hypoxia-Driven Angiogenesis and Immunosuppression. Gut 2023, 72, 1942–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Tang, X.; Ren, Y.; Yang, Y.; Song, F.; Fu, J.; Liu, S.; Yu, M.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; et al. An RNA-RNA Crosstalk Network Involving HMGB1 and RICTOR Facilitates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tumorigenesis by Promoting Glutamine Metabolism and Impedes Immunotherapy by PD-L1+ Exosomes Activity. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, H.; Li, L.; Yin, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wang, L.; Mang, Y.; Gao, Y.; et al. Exosome-Derived circCCAR1 Promotes CD8 + T-Cell Dysfunction and Anti-PD1 Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.-F.; Gao, C.; Huang, X.-Y.; Lu, J.-C.; Guo, X.-J.; Shi, G.-M.; Cai, J.-B.; Ke, A.-W. Cancer Cell-Derived Exosomal circUHRF1 Induces Natural Killer Cell Exhaustion and May Cause Resistance to Anti-PD1 Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.-R.; Cai, J.-B.; Shi, G.-M.; Yang, Y.-F.; Huang, X.-Y.; Zhang, C.; Dong, R.-Z.; Wei, C.-Y.; Li, T.; Ke, A.-W.; et al. Oncogenic miR-93-5p/Gal-9 Axis Drives CD8 (+) T-Cell Inactivation and Is a Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2023, 564, 216186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Wang, X.; Lv, L.; Liu, J.; Xing, H.; Song, Y.; Xie, M.; Lei, T.; Zhang, N.; Yang, M. The Emerging Role of microRNAs and Long Noncoding RNAs in Drug Resistance of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O’Briant, K.C.; Allen, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as Stable Blood-Based Markers for Cancer Detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miotto, E.; Saccenti, E.; Lupini, L.; Callegari, E.; Negrini, M.; Ferracin, M. Quantification of Circulating miRNAs by Droplet Digital PCR: Comparison of EvaGreen- and TaqMan-Based Chemistries. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2014, 23, 2638–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greten, T.F.; Villanueva, A.; Korangy, F.; Ruf, B.; Yarchoan, M.; Ma, L.; Ruppin, E.; Wang, X.W. Biomarkers for Immunotherapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 780–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wu, F.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Rong, D.; Reiter, F.P.; et al. The Mechanisms of Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Theoretical Basis and Therapeutic Aspects. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornari, F.; Pollutri, D.; Patrizi, C.; La Bella, T.; Marinelli, S.; Casadei Gardini, A.; Marisi, G.; Baron Toaldo, M.; Baglioni, M.; Salvatore, V.; et al. In Hepatocellular Carcinoma miR-221 Modulates Sorafenib Resistance through Inhibition of Caspase-3-Mediated Apoptosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3953–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Cruz-Ojeda, P.; Schmid, T.; Boix, L.; Moreno, M.; Sapena, V.; Praena-Fernández, J.M.; Castell, F.J.; Falcón-Pérez, J.M.; Reig, M.; Brüne, B.; et al. miR-200c-3p, miR-222-5p, and miR-512-3p Constitute a Biomarker Signature of Sorafenib Effectiveness in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells 2022, 11, 2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Tussy, P.; Rodríguez-Agudo, R.; Fernández-Ramos, D.; Barbier-Torres, L.; Zubiete-Franco, I.; Davalillo, S.L. de; Herraez, E.; Goikoetxea-Usandizaga, N.; Lachiondo-Ortega, S.; Simón, J.; et al. Anti-miR-518d-5p Overcomes Liver Tumor Cell Death Resistance through Mitochondrial Activity. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, N.; Arizumi, T.; Hagiwara, S.; Ida, H.; Sakurai, T.; Kudo, M. MicroRNAs for the Prediction of Early Response to Sorafenib Treatment in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2017, 6, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.-Y.; Chen, P.-S.; Lin, L.-I.; Lee, B.-S.; Ling, A.; Cheng, A.-L.; Hsu, C.; Ou, D.-L. Low miR-10b-3p Associated with Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 1806–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.-P.; Wang, C.-Y.; Jin, X.-H.; Li, M.; Wang, F.-W.; Huang, W.-J.; Yun, J.-P.; Xu, R.-H.; Cai, Q.-Q.; Xie, D. Acidic Microenvironment Up-Regulates Exosomal miR-21 and miR-10b in Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma to Promote Cancer Cell Proliferation and Metastasis. Theranostics 2019, 9, 1965–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.S.; Kudo, M.; Cheng, A.-L.; Wyrwicz, L.; Ngan, R.K.C.; Blanc, J.-F.; Baron, A.D.; Vogel, A.; Ikeda, M.; Piscaglia, F.; et al. Pharmacodynamic Biomarkers Predictive of Survival Benefit with Lenvatinib in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From the Phase III REFLECT Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 4848–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teufel, M.; Seidel, H.; Köchert, K.; Meinhardt, G.; Finn, R.S.; Llovet, J.M.; Bruix, J. Biomarkers Associated With Response to Regorafenib in Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1731–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshida, Y.; Toffanin, S.; Lachenmayer, A.; Villanueva, A.; Minguez, B.; Llovet, J.M. Molecular Classification and Novel Targets in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Recent Advancements. Semin. Liver Dis. 2010, 30, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Non-coding RNA | Target gene/sponged miRNA/other targets | Experimental in vivo models | Therapeutic/experimental strategy | Effect on immune cells | Treatment combination | Ref. N. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-206 | Klf4/CCL2 | AKT/Ras and Sleeping Beauty transposon hydrodynamic injection in FVB/NJ mice | Mini-circle and Sleeping Beauty hydrodynamic injection for miR-206 overexpression | Decreased Treg recruitment | None | 90 |
| miR-15a/16-1 | Nf-kB/CCL22 | AKT/Ras, Myc hydrodynamic injection in FVB/NJ mice | Hydrodynamic injection for miRNA overexpression | M1 macrophage polarization | None | 91 |
| circRHBDD1 | YTHDF1/PIK3R1 | PDX NOD/SCID, BALBc mice; Hepa1-6 cells in xenograft C57BL/6 mice | circRHBDD1 interference vector | N/A | Anti-PD1 | 93 |
| circMET | miR-30-5p/SNAI1/DPP4/CXCL10 | Hepa1-6 cells in xenograft C57BL/6 mice | Sitagliptin (DPP4 inhibitor) | Increased CD8+ T cells recruitment | Anti-PD1 | 97 |
| LINC01132 | NRF1/DPP4 | PDX nude mice; Hepa1-6 cells in C57BL/6 xenograft mice | LINC01132 adenovirus interference vector | Increased CD8+ T cells recruitment | Anti-PD-L1 | 99 |
| miR-223 | HIF1/CD39/CD73 | miR-223 KO mice + DEN or CCL4; C57BL/4J mice + DEN+CCl4 | miR-223 adenovirus vector | Decreased PD1/PD-L1 expression | None | 100 |
| CircCCAR1 | miR-127-5p/WTAP | HCCLM3 cells in BALBc, HuNSG xenograft mice | circCCAR1 overexpression vector | CD8+ T cells dysfunction | Anti-PD1 | 102 |
| circUHRF1 | miR-449c-5p/TIM3 | HCCLM3 cells in NOD/SCID xenograft mice | circUHRF1 interference vector | Increased NK activity | Anti-PD1 | 103 |
| miRNA name | Blood specimen | Timepoint of analysis | Circulating levels in responders | Treatment | Ref. N. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-221 | Serum | Basal On treatment (2 m) |
Low High |
Sorafenib | 110 |
|
miR-200c-3p miR-222-5p miR-512-3p |
Plasma | Basal On treatment (1 m) On treatment (1 m) |
High Low Low |
Sorafenib | 111 |
| miR-30e-3p | Serum | On treatment (2 m) | Low | Sorafenib | 29 |
| miR-518d-5p | Serum | Basal | Low | Sorafenib | 112 |
| miR-181a-5p | Serum | Basal | High | Sorafenib | 113 |
| miR-10b-3p | Serum | Basal | High | Sorafenib | 114 |
| miR-494 | Serum | Basal | Low | Sorafenib | 59 |
|
miR-30a, miR-122, miR-125b, miR-200a, miR-347b; miR-15b, miR-107, miR-320; miR-645 |
Plasma | Basal | High Low Absent |
Regorafenib | 117 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





