Submitted:
18 January 2024
Posted:
19 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
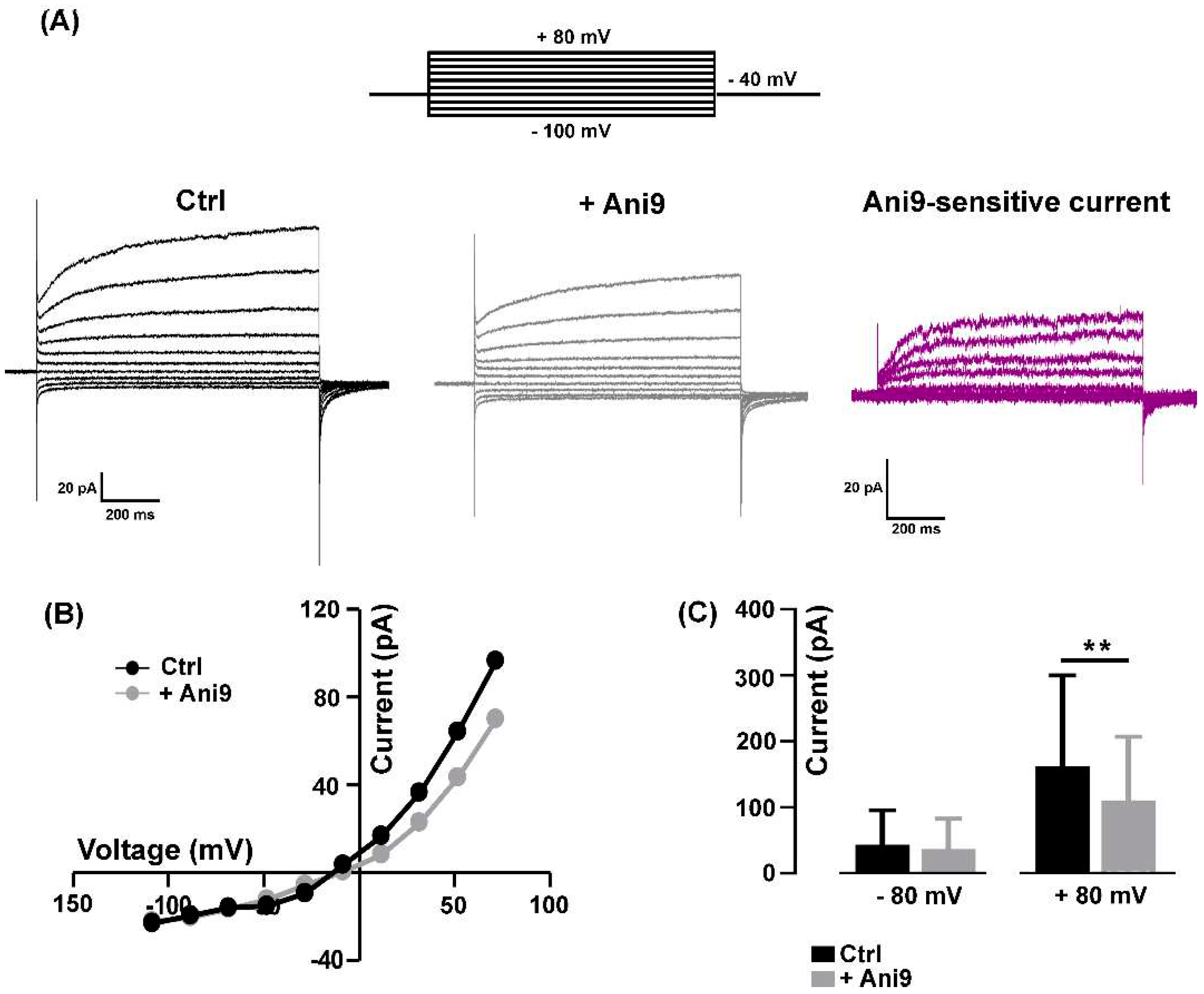
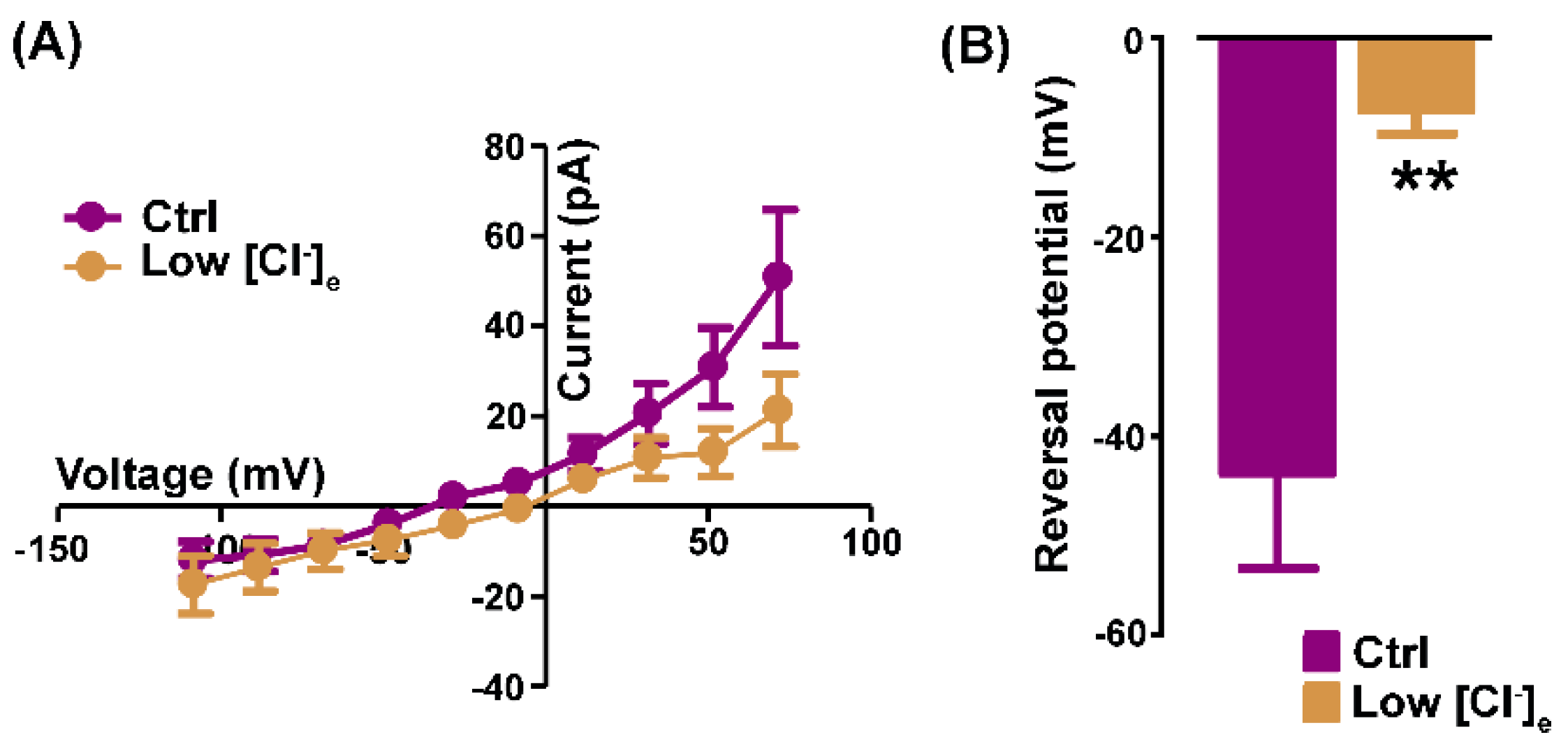
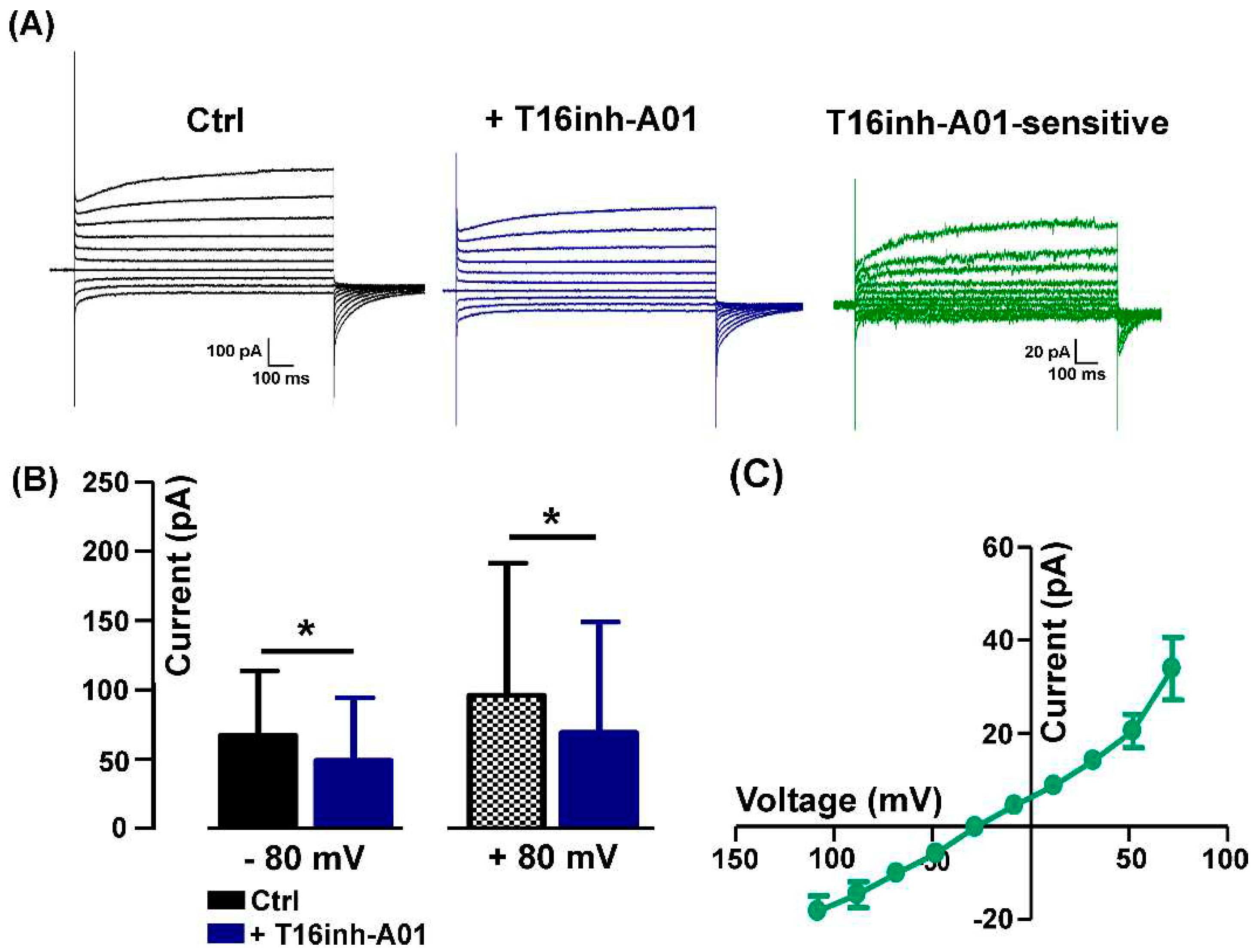
2.1. Pharmacological identification of TMEM16A currents in mouse skeletal myocytes
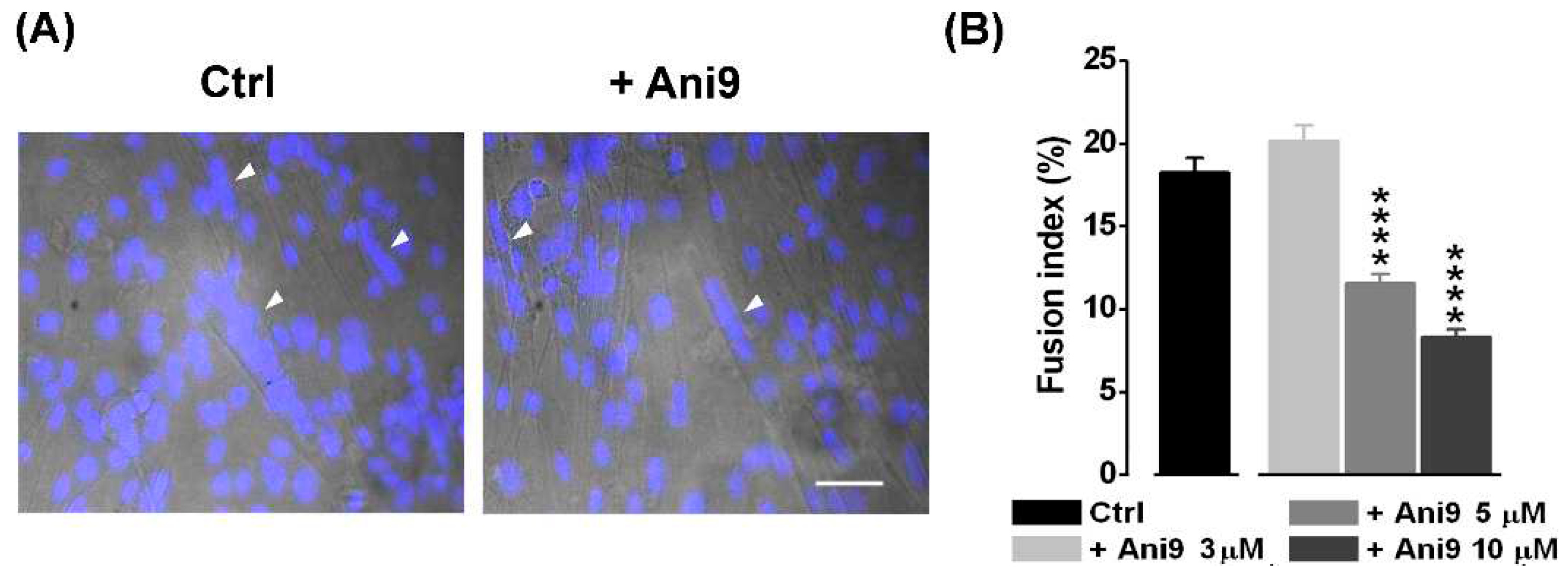
2.2. The blockage of TMEM16A currents reduces myoblast fusion
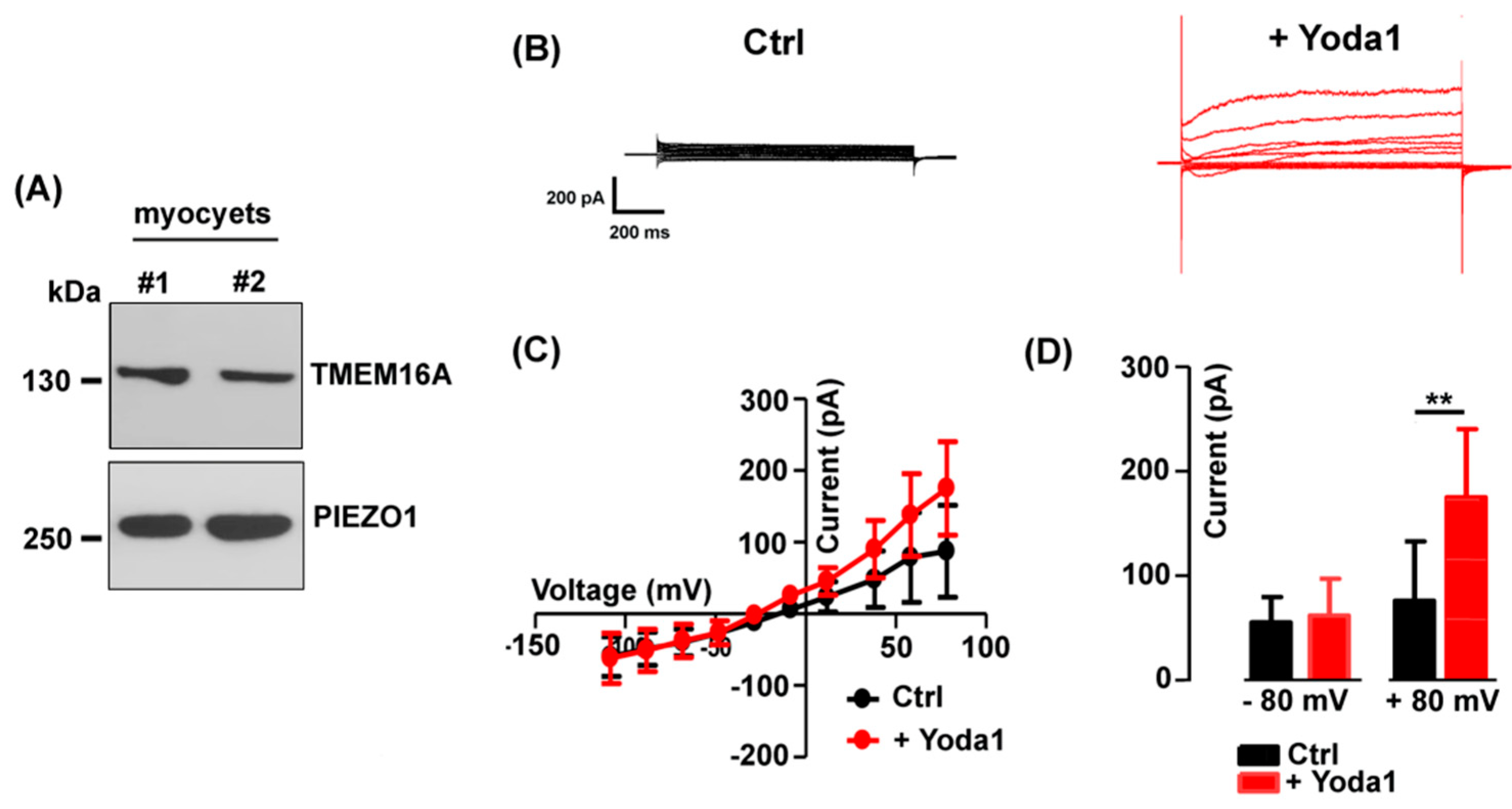
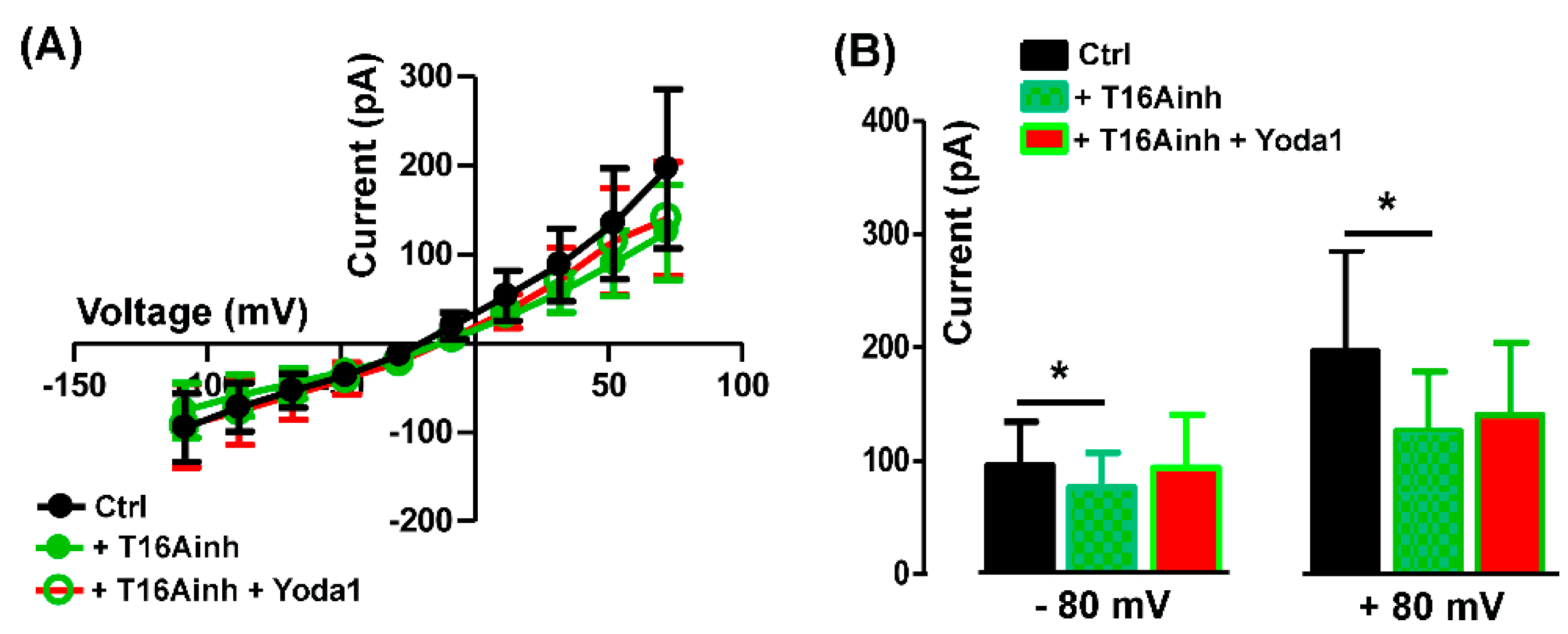
2.3. TheTMEM16A currents are modulated by the Piezo1 agonist Yoda1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell cultures
4.2. Electrophysiological recordings
4.3. Western blotting
4.4. Fusion index
4.5. Statistical analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mauro, A. Satellite cell of skeletal muscle fibers. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961, 9, 493–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennelly, C.; Soker, S. Bioelectric Properties of Myogenic Progenitor Cells. Bioelectricity. 2019, 1, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miledi, R. A calcium-dependent transient outward current in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982, 215, 491–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barish, M.E. A transient calcium-dependent chloride current in the immature Xenopus oocyte. J Physiol. 1983, 342, 309–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, J.A.; Cozens, A.L.; Schulman, H.; Gruenert, D.C.; Stryer, L.; Gardner, P. Activation of chloride channels in normal and cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells by multifunctional calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Nature. 1991, 349, 793–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Shah, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lees, M.; Fu, Z.; Lippiat, J.D.; Beech, D.J.; Sivaprasadarao, A.; Baldwin, S.A.; Zhang, H.; Gamper, N. Activation of the Cl- channel ANO1 by localized calcium signals in nociceptive sensory neurons requires coupling with the IP3 receptor. Sci Signal. 2013, 6, ra73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Large, W.A.; Wang, Q. Characteristics and physiological role of the Ca(2+)-activated Cl- conductance in smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1996, 271, C435–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frings, S.; Reuter, D.; Kleene, S.J. Neuronal Ca2+ -activated Cl- channels--homing in on an elusive channel species. Prog Neurobiol. 2000, 60, 247–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauner, S.; Lissmann, J.; Jeridi, S.; Frings, S.; Mohrlen, F. Expression patterns of anoctamin 1 and anoctamin 2 chloride channels in the mammalian nose. Cell Tissue Res. 2012, 347, 327–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, D.K.; Menini, A. Developmental expression of the calcium-activated chloride channels TMEM16A and TMEM16B in the mouse olfactory epithelium. Dev Neurobiol. 2014, 74, 657–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrera, L.; Zegarra-Moran, O.; Galietta, L.J. Ca2+-activated Cl- channels. Compr Physiol. 2011, 1, 2155–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmeyer, K.; Ortland, C.; Jentsch, T.J. Primary structure and functional expression of a developmentally regulated skeletal muscle chloride channel. Nature. 1991, 354, 301–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretag, A.H. Muscle chloride channels. Physiol Rev. 1987, 67, 618–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardouille, C.; Vullhorst, D.; Jockusch, H. Expression of chloride channel 1 mRNA in cultured myogenic cells: a marker of myotube maturation. FEBS Lett. 1996, 396, 177–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedemonte, N.; Galietta, LJ. Structure and function of TMEM16 proteins (anoctamins). Physiol Rev. 2014, 94, 419–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, B.C.; Cheng, T.; Jan, Y.N.; Jan, L.Y. Expression cloning of TMEM16A as a calcium-activated chloride channel subunit. Cell. 2008, 134, 1019–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caputo, A.; Caci, E.; Ferrera, L.; Pedemonte, N.; Barsanti, C.; Sondo, E.; Pfeffer, U.; Ravazzolo, R.; Zegarra-Moran, O.; Galietta, L.J. TMEM16A, a membrane protein associated with calcium-dependent chloride channel activity. Science. 2008, 322, 590–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.D.; Cho, H.; Koo, J.Y.; Tak, M.H.; Cho, Y.; Shim, W.S.; Park, S.P.; Lee, J.; Lee, B.; Kim, B.M.; Raouf, R.; Shin, Y.K.; Oh, U. TMEM16A confers receptor-activated calcium-dependent chloride conductance. Nature. 2008, 455, 1210–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, E.; Fedigan, S.; Webb, T.; Hollywood, M.A.; Thornbury, K.D.; McHale, N.G.; Sergeant, G.P. Pharmacological characterization of TMEM16A currents. Channels (Austin). 2014, 8, 308–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hume R.I., Thomas S,A. A calcium- and voltage-dependent chloride current in developing chick skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1989, 417, 241-61. [CrossRef]
- Dayal, A.; Ng, S.F.J.; Grabner, M. Ca2+-activated Cl- channel TMEM16A/ANO1 identified in zebrafish skeletal muscle is crucial for action potential acceleration. Nat Commun. 2019, 10, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Cui, C.C.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.H.; Fan, C.E.; Chen, Y.C.; Fan, H.W.; Hu, B.X.; Shi, M.Y.; Sun, Z.Y.; Wang, P.; Ma, T.X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, M.S.; Chen, H.Q. Intracellular TMEM16A is necessary for myogenesis of skeletal muscle. Science. 2022, 25, 105446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosutti, A.; Giniatullin, A.; Odnoshivkina, Y.; Giudice, L.; Malm, T.; Sciancalepore, M.; Giniatullin, R.; D'Andrea, P.; Lorenzon, P.; Bernareggi, A. "Time window" effect of Yoda1-evoked Piezo1 channel activity during mouse skeletal muscle differentiation. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2021, 233, e13702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernareggi, A.; Bosutti, A.; Massaria, G.; Giniatullin, R.; Malm, T.; Sciancalepore, M.; Lorenzon, P. The State of the Art of Piezo1 Channels in Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciancalepore, M.; Massaria, G.; Tramer, F.; Zacchi, P.; Lorenzon, P.; Bernareggi, A. A preliminary study on the role of Piezo1 channels in myokine release from cultured mouse myotubes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022, 623, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coste, B.; Mathur, J.; Schmidt, M.; Earley, T.J.; Ranade, S.; Petrus, M.J.; Dubin, A.E.; Patapoutian, A. Piezo1 and Piezo2 are essential components of distinct mechanically activated cation channels. Science 2010, 330, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahalan, S.M.; Lukacs, V.; Ranade, S.S.; Chien, S.; Bandell, M.; Patapoutian, A. Piezo1 links mechanical forces to red blood cell volume. Elife. 2015, 4, e07370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnanasambandam, R.; Bae, C.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Sachs, F. Ionic Selectivity and Permeation Properties of Human PIEZO1 Channels. PLoS One. 2015, 10, e0125503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vladislav Chubinskiy-Nadezhdin, V.; Semenova, S.; Vasileva, V.; Shatrova, A.; Pugovkina, N.; Negulyaev, Y.; Negulyaev Y. Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry Contributes to Piezo1-Induced Ca2+ Increase in Human Endometrial Stem Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syeda, R.; Xu, J.; Dubin, A.E.; Coste, B.; Mathur, J.; Huynh, T.; Matzen, J.; Lao, J.; Tully, D.C.; Engels, I.H.; Petrassi, H.M.; Schumacher, A.M.; Montal, M.; Bandell, M.; Patapoutian, A. Chemical activation of the mechanotransduction channel Piezo1. Elife. 2015, 4, e07369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centeio, R.; Cabrita, I.; Benedetto, R.; Talbi, K.; Ousingsawat, J.; Schreiber, R.; Sullivan, J.K.; Kunzelmann, K. Pharmacological Inhibition and Activation of the Ca2+ Activated Cl- Channel TMEM16A. Int J Mol Sci. 2020, 21, 2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdivieso, Á.G.; Santa-Coloma, T.A. The chloride anion as a signalling effector. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2019, 94, 1839–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Lee, H.K.; Park, J.; Jeon, D.K.; Jo, S.; Jo, M.; Namkung, W. Ani9, A Novel Potent Small-Molecule ANO1 Inhibitor with Negligible Effect on ANO2. PLoS One. 2016, 11, e0155771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Ryu, S.; Sim, K.; Song, C.; Shin, I.; Kim, S.S.; Lee, Y.-S; Park, J.-Y; Sim, T. Anti-glioma effects of 2-aminothiophene-3-carboxamide derivatives, ANO1 channel blockers. Eur. J. Med Chem. 2020, 208, 112688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wozniak, K.L.; Phelps, W.A.; Tembo, M.; Lee, M.T.; Carlson, A.E. The TMEM16A channel mediates the fast polyspermy block in Xenopus laevis. J Gen Physiol. 2018, 150, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroon, M.; Klein-Nulend, J.; Bakker, A.D.; Jin, J.; Seddiqi, H.; Offringa, C.; de Wit, G.M.J.; Le Grand, F.; Giordani, L.; Liu, K.J.; Knight, R.D.; Jaspers, R.T. Myofiber stretch induces tensile and shear deformation of muscle stem cells in their native niche. Biophys J. 2021, 120, 2665–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seale, P.; Rudnicki, M.A. A new look at the origin, function, and "stem-cell" status of muscle satellite cells. Dev Biol. 2000, 218, 115–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawke, T.J.; Garry, D.J. Myogenic satellite cells: physiology to molecular biology. J Appl Physiol. 2001, 91, 534–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botello-Smith W.M.; Jiang W.; Zhang H.; OzkN ad; Lin Y.C.; Pham C.N.; Lacroix J.J.; Luo Y. A mechanism for the activation of the mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel by the small molecule Yoda1. Nature Communications 2019, 10:, 4503. [CrossRef]
- Wijerathne T.D.; Alper A.D.; Lacroix J.J. Yoda1’s energetic footprint on Piezo1 channels and its modulation by voltage and temperature. PNAS 119, e2202269119. [CrossRef]
- Bernheim, L.; Liu, J.H.; Hamann, M.; Haenggeli, C.A.; Fischer-Lougheed, J.; Bader, C.R. Contribution of a non-inactivating potassium current to the resting membrane potential of fusion-competent human myoblasts. J Physiol. 1996, 493, 129–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijlenga, P.; Occhiodoro, T.; Liu, J.H.; Bader, C.R.; Bernheim, L.; Fischer-Lougheed, J. An ether -à-go-go K+ current, Ih-eag, contributes to the hyperpolarization of human fusion-competent myoblasts. J Physiol. 1998, 512, 317–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Bijlenga, P.; Fischer-Lougheed, J.; Occhiodoro, T.; Kaelin, A.; Bader, C.R.; Bernheim, L. Role of an inward rectifier K+ current and of hyperpolarization in human myoblast fusion. J Physiol. 1998, 510, 467–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; König, B.; Stauber, T. LRRC8 channel activation and reduction in cytosolic chloride concentration during early differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020, 532, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulhunty, A.F. The dependence of membrane potential on extracellular chloride concentration in mammalian skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1978, 276, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, A.K.; Fambrough, D.M. Electrophysiological properties of the membrane and acetylcholine receptor in developingrat and chick myotubes. J Gen Physiol. 1975, 66, 327–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spector, I.; Prives, J.M. Development of electrophysiological and biochemical membrane properties during differentiation of embryonic skeletal muscle in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977, 74, 5166–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauber, T.; Jentsch, T.J. Chloride in vesicular trafficking and function. Annu Rev Physiol. 2013, 75, 453–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Ye, W.; Wang, W.J.; Sison, E.S.; Jan, Y.N.; Jan, LY. Cytoplasmic Cl- couples membrane remodeling to epithelial morphogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017, 114, E11161–E11169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irintchev, A.; Langer, M.; Zweyer, M.; Theisen, R.; Wernig, A. Functional improvement of damaged adult mouse muscle by implantation of primary myoblasts. J Physiol. 1997, 500, 775–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, P.H. JPCalc, a software package for calculating liquid junction potential corrections in patch-clamp, intracellular, epithelial and bilayer measurements and for correcting junction potential measurements. J Neurosci Methods. 1994, 51, 107–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; Tinevez, J.Y.; White, D.J.; Hartenstein, V.; Eliceiri, K.; Tomancak, P.; Cardona, A. Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat Methods. 2012, 9, 676–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




