Submitted:
18 January 2024
Posted:
19 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Relative changes in blood metabolites
2.2. Exosomal miRNA expression in the serum samples of mCRPC
2.3. Correlations between miRs and metabolites levels
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study population
4.2.1. H-NMR metabolomics
4.3. Exosomal miRs expression
4.4. Statistical analysis
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bergengren, O.; Pekala, K.R.; Matsoukas, K.; Fainberg, J.; Mungovan, S.F.; Bratt, O.; Bray, F.; Brawley, O.; Luckenbaugh, A.N.; Mucci, L.; et al. 2022 Update on Prostate Cancer Epidemiology and Risk Factors-A Systematic Review. Eur Urol 2023, 84, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descotes, J.L. Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer. Asian J Urol 2019, 6, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubihal, V.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, R.; Seth, A.; Kumar, R.; Kaushal, S.; Sarangi, J.; Gupta, R.; Das, C. Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 68Ga Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen Positron Emission Tomography-Computed Tomography, and Respective Quantitative Parameters in Detection and Localization of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer in Intermediate- and High-Risk Group Patients: An Indian Demographic Study. Indian J Nucl Med 2021, 36, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoom, S.N.; Sundaram, K.M.; Ghanouni, P.; Fütterer, J.; Oto, A.; Ayyagari, R.; Sprenkle, P.; Weinreb, J.; Arora, S. Real-Time MRI-Guided Prostate Interventions. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, S.; Mercinelli, C.; Marandino, L.; Litterio, G.; Marchioni, M.; Schips, L. Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Insights on Current Therapy and Promising Experimental Drugs. Res Rep Urol 2023, 15, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, Z.W.; Allison, D.B.; Ellis, C.S. A Case Report of Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Harboring a PTEN Loss. Front Oncol 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottet, N.; van den Bergh, R.C.N.; Briers, E.; Van den Broeck, T.; Cumberbatch, M.G.; De Santis, M.; Fanti, S.; Fossati, N.; Gandaglia, G.; Gillessen, S.; et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer-2020 Update. Part 1: Screening, Diagnosis, and Local Treatment with Curative Intent. Eur Urol 2021, 79, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburg, O. On the Origin of Cancer Cells. Science 1956, 123, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, H.J.; Carvalho, T.M.A.; Fonseca, L.R.S.; Figueira, M.I.; Vaz, C.V.; Socorro, S. Revisiting Prostate Cancer Metabolism: From Metabolites to Disease and Therapy. Med Res Rev 2021, 41, 1499–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strmiska, V.; Michalek, P.; Eckschlager, T.; Stiborova, M.; Adam, V.; Krizkova, S.; Heger, Z. Prostate Cancer-Specific Hallmarks of Amino Acids Metabolism: Towards a Paradigm of Precision Medicine. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 2019, 1871, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, L.C.; Feng, P.; Milon, B.; Tan, M.; Franklin, R.B. Role of Zinc in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Prostate Cancer: Critical Issues to Resolve. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2004, 7, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twum-Ampofo, J.; Fu, D.X.; Passaniti, A.; Hussaind, A.; Siddiqui, M.M. Metabolic Targets for Potential Prostate Cancer Therapeutics. Curr Opin Oncol 2016, 28, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, A.M.K.; Puhr, M.; Stope, M.B.; Thomas, C.; Erb, H.H.H. Metabolic Changes during Prostate Cancer Development and Progression. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2023, 149, 2259–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, K.R.; Fenoglio-Preiser, C.; Sillerud, L.O. Differentiation of Human Tumors from Nonmalignant Tissue by Natural-Abundance 13C NMR Spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med 1988, 7, 384–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, H. Reprogramming of Glucose, Fatty Acid and Amino Acid Metabolism for Cancer Progression. Cell Mol Life Sci 2016, 73, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidan, H.E.; Abdul-Maksoud, R.S.; Elsayed, W.S.H.; Desoky, E.A.M. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Serum MiR-15a and MiR-16-1 Expression among Egyptian Patients with Prostate Cancer. IUBMB Life 2018, 70, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutruzzolà, F.; Giardina, G.; Marani, M.; Macone, A.; Paiardini, A.; Rinaldo, S.; Paone, A. Glucose Metabolism in the Progression of Prostate Cancer. Front Physiol 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santotoribio, J.D.; Jimenez-Romero, M.E. Serum Biomarkers of Inflammation for Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer in Patients with Nonspecific Elevations of Serum Prostate Specific Antigen Levels. Transl Cancer Res 2019, 8, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Cruz-López, K.G.; Castro-Muñoz, L.J.; Reyes-Hernández, D.O.; García-Carrancá, A.; Manzo-Merino, J. Lactate in the Regulation of Tumor Microenvironment and Therapeutic Approaches. Front Oncol 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetta, P.; Sriram, R.; Zadra, G. Lactate as Key Metabolite in Prostate Cancer Progression: What Are the Clinical Implications? Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.R.; Pinto, J.; Bastos, M. de L.; Carvalho, M.; Guedes de Pinho, P. NMR-Based Metabolomics Studies of Human Prostate Cancer Tissue. Metabolomics 2018, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessem, M.B.; Swanson, M.G.; Keshari, K.R.; Albers, M.J.; Joun, D.; Tabatabai, Z.L.; Simko, J.P.; Shinohara, K.; Nelson, S.J.; Vigneron, D.B.; et al. Evaluation of Lactate and Alanine as Metabolic Biomarkers of Prostate Cancer Using 1H HR-MAS Spectroscopy of Biopsy Tissues. Magn Reson Med 2008, 60, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Asten, J.J.A.; Cuijpers, V.; Hulsbergen-Van De Kaa, C.; Soede-Huijbregts, C.; Witjes, J.A.; Verhofstad, A.; Heerschap, A. High Resolution Magic Angle Spinning NMR Spectroscopy for Metabolic Assessment of Cancer Presence and Gleason Score in Human Prostate Needle Biopsies. MAGMA 2008, 21, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costello, L.C.; Franklin, R.B. The Clinical Relevance of the Metabolism of Prostate Cancer; Zinc and Tumor Suppression: Connecting the Dots. Mol Cancer 2006, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costello, L.C.; Franklin, R.B. Concepts of Citrate Production and Secretion by Prostate: 2. Hormonal Relationships in Normal and Neoplastic Prostate. Prostate 1991, 19, 181–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costello, L.C.; Franklin, R.B. Plasma Citrate Homeostasis: How It Is Regulated; And Its Physiological and Clinical Implications. An Important, But Neglected, Relationship In. HSOA J Hum Endocrinol 2016, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Yuan, X.H.; Wang, J.J.; Wang, Y.C.; Li, S.L.; Ding, J. The Diagnostic Value of MiRNA-141 in Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and PRISMA-Compliant Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, E19993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhu, Y.; Shao, X.; Cai, A.; Dong, B.; Xue, W.; Gao, H. Distinct Metabolic Signatures of Hormone-Sensitive and Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Revealed by a 1H NMR-Based Metabolomics of Biopsy Tissue. J Proteome Res 2020, 19, 3741–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Gupta, A.; Mandhani, A.; Sankhwar, S.N. NMR Spectroscopy of Filtered Serum of Prostate Cancer: A New Frontier in Metabolomics. Prostate 2016, 76, 1106–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, L.C.; Franklin, R.B.; Feng, P. Mitochondrial Function, Zinc, and Intermediary Metabolism Relationships in Normal Prostate and Prostate Cancer. Mitochondrion 2005, 5, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haferkamp, S.; Drexler, K.; Federlin, M.; Schlitt, H.J.; Berneburg, M.; Adamski, J.; Gaumann, A.; Geissler, E.K.; Ganapathy, V.; Parkinson, E.K.; et al. Extracellular Citrate Fuels Cancer Cell Metabolism and Growth. Front Cell Dev Biol 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mycielska, M.E.; Dettmer, K.; Rummele, P.; Schmidt, K.; Prehn, C.; Milenkovic, V.M.; Jagla, W.; Madej, G.M.; Lantow, M.; Schladt, M.; et al. Extracellular Citrate Affects Critical Elements of Cancer Cell Metabolism and Supports Cancer Development In Vivo. Cancer Res 2018, 78, 2513–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Icard, P.; Simula, L.; Zahn, G.; Alifano, M.; Mycielska, M.E. The Dual Role of Citrate in Cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 2023, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buszewska-Forajta, M.; Monedeiro, F.; Gołębiowski, A.; Adamczyk, P.; Buszewski, B. Citric Acid as a Potential Prostate Cancer Biomarker Determined in Various Biological Samples. Metabolites 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Mondul, A.M.; Weinstein, S.J.; Karoly, E.D.; Sampson, J.N.; Albanes, D. Prospective Serum Metabolomic Profile of Prostate Cancer by Size and Extent of Primary Tumor. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 45190–45199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitburn, J.; Edwards, C.M. Metabolism in the Tumour-Bone Microenvironment. Curr Osteoporos Rep 2021, 19, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.J.; Pollock, C.B.; Kelly, K. Mechanisms of Cancer Metastasis to the Bone. Cell Res 2005, 15, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Outschoorn, U.E.; Peiris-Pagés, M.; Pestell, R.G.; Sotgia, F.; Lisanti, M.P. Cancer Metabolism: A Therapeutic Perspective. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2017, 14, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarrah, R.W.; White, P.J. Branched-Chain Amino Acids in Cardiovascular Disease. Nat Rev Cardiol 2023, 20, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.K.; Okekunle, A.P.; Lee, J.E.; Sung, M.K.; Lim, Y.J. Role of Branched-Chain Amino Acid Metabolism in Tumor Development and Progression. J Cancer Prev 2021, 26, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericksen, R.E.; Lim, S.L.; McDonnell, E.; Shuen, W.H.; Vadiveloo, M.; White, P.J.; Ding, Z.; Kwok, R.; Lee, P.; Radda, G.K.; et al. Loss of BCAA Catabolism during Carcinogenesis Enhances MTORC1 Activity and Promotes Tumor Development and Progression. Cell Metab 2019, 29, 1151–1165.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, A.; Tsunoda, M.; Konuma, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Nagy, T.; Glushka, J.; Tayyari, F.; McSkimming, D.; Kannan, N.; Tojo, A.; et al. Cancer Progression by Reprogrammed BCAA Metabolism in Myeloid Leukaemia. Nature 2017, 545, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayers, J.R.; Wu, C.; Clish, C.B.; Kraft, P.; Torrence, M.E.; Fiske, B.P.; Yuan, C.; Bao, Y.; Townsend, M.K.; Tworoger, S.S.; et al. Elevation of Circulating Branched-Chain Amino Acids Is an Early Event in Human Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Development. Nat Med 2014, 20, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giskeødegård, G.F.; Hansen, A.F.; Bertilsson, H.; Gonzalez, S.V.; Kristiansen, K.A.; Bruheim, P.; Mjøs, S.A.; Angelsen, A.; Bathen, T.F.; Tessem, M.B. Metabolic Markers in Blood Can Separate Prostate Cancer from Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Br J Cancer 2015, 113, 1712–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dereziński, P.; Klupczynska, A.; Sawicki, W.; Pałka, J.A.; Kokot, Z.J. Amino Acid Profiles of Serum and Urine in Search for Prostate Cancer Biomarkers: A Pilot Study. Int J Med Sci 2017, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagi, Y.; Higashiyama, M.; Gochi, A.; Akaike, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Miura, T.; Saruki, N.; Bando, E.; Kimura, H.; Imamura, F.; et al. Plasma Free Amino Acid Profiling of Five Types of Cancer Patients and Its Application for Early Detection. PLoS One 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xia, B.; Zheng, H.; Ning, J.; Zhu, Y.; Shao, X.; Liu, B.; Dong, B.; Gao, H. Identification of Characteristic Metabolic Panels for Different Stages of Prostate Cancer by 1H NMR-Based Metabolomics Analysis. J Transl Med 2022, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, T.; Ferdous, G.; Tsuruta, T.; Satoh, T.; Baba, S.; Muto, T.; Ueno, A.; Kanai, Y.; Endou, H.; Okayasu, I. L-Type Amino-Acid Transporter 1 as a Novel Biomarker for High-Grade Malignancy in Prostate Cancer. Pathol Int 2009, 59, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wang, Y.; Luo, W. Multifaceted Role of Branched-Chain Amino Acid Metabolism in Cancer. Oncogene 2020, 39, 6747–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfried, T.N.; Flores, R.E.; Poff, A.M.; D’Agostino, D.P. Cancer as a Metabolic Disease: Implications for Novel Therapeutics. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puchalska, P.; Crawford, P.A. Multi-Dimensional Roles of Ketone Bodies in Fuel Metabolism, Signaling, and Therapeutics. Cell Metab 2017, 25, 262–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, C.Y.; Choe, W.; Yoon, K.S.; Ha, J.; Kim, S.S.; Yeo, E.J.; Kang, I. Molecular Mechanisms for Ketone Body Metabolism, Signaling Functions, and Therapeutic Potential in Cancer. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, L.M.; Uribe-Lewis, S.; Madhu, B.; Honess, D.J.; Stubbs, M.; Griffiths, J.R. The Action of β-Hydroxybutyrate on the Growth, Metabolism and Global Histone H3 Acetylation of Spontaneous Mouse Mammary Tumours: Evidence of a β-Hydroxybutyrate Paradox. Cancer Metab 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrere, G.; Alou, M.T.; Liu, P.; Goubet, A.G.; Fidelle, M.; Kepp, O.; Durand, S.; Iebba, V.; Fluckiger, A.; Daillère, R.; et al. Ketogenic Diet and Ketone Bodies Enhance the Anticancer Effects of PD-1 Blockade. JCI Insight 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraon, P.; Cretu, D.; Musrap, N.; Karagiannis, G.S.; Batruch, I.; Drabovich, A.P.; Van Der Kwast, T.; Mizokami, A.; Morrissey, C.; Jarvi, K.; et al. Quantitative Proteomics Reveals That Enzymes of the Ketogenic Pathway Are Associated with Prostate Cancer Progression. Mol Cell Proteomics 2013, 12, 1589–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labanca, E.; Bizzotto, J.; Sanchis, P.; Anselmino, N.; Yang, J.; Shepherd, P.D.A.; Paez, A.; Antico-Arciuch, V.; Lage-Vickers, S.; Hoang, A.G.; et al. Prostate Cancer Castrate Resistant Progression Usage of Non-Canonical Androgen Receptor Signaling and Ketone Body Fuel. Oncogene 2021, 40, 6284–6298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshii, Y.; Furukawa, T.; Saga, T.; Fujibayashi, Y. Acetate/Acetyl-CoA Metabolism Associated with Cancer Fatty Acid Synthesis: Overview and Application. Cancer Lett 2015, 356, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadra, G.; Loda, M. When Fat Goes down, Prostate Cancer Is on the Ropes. Mol Cell Oncol 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Gupta, S.; Mahdi, A.A. 1H NMR-Derived Serum Metabolomics of Leukoplakia and Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin Chim Acta 2015, 441, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Prakash, V.; Gupta, N.; Kumar, A.; Kant, R.; Kumar, D. Serum Metabolic Disturbances in Lung Cancer Investigated through an Elaborative NMR-Based Serum Metabolomics Approach. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 5510–5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Xiao, Y.; Shu, D.; Liang, X.; Hu, X.; Xie, Y.; Lin, D.; Li, H. Metabolomics Analysis in Serum from Patients with Colorectal Polyp and Colorectal Cancer by 1H-NMR Spectrometry. Dis Markers 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosios, A.M.; Vander Heiden, M.G. Acetate Metabolism in Cancer Cells. Cancer Metab 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqeilan, R.I.; Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. MiR-15a and MiR-16-1 in Cancer: Discovery, Function and Future Perspectives. Cell Death Differ 2010, 17, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Mao, Z.G.; Wang, X.; Du, Q.; Jian, M.; Zhu, D.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, H.J.; Zhu, Y.H. MicroRNAs and Target Genes in Pituitary Adenomas. Horm Metab Res 2018, 50, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Cho, S.; Park, Y.; Lee, J.; Park, J. Evaluation of Micro-RNA in Extracellular Vesicles from Blood of Patients with Prostate Cancer. PLoS One 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Chen, F.; Wang, K.; Song, Y.; Fei, X.; Wu, B. MiR-15a/MiR-16 Cluster Inhibits Invasion of Prostate Cancer Cells by Suppressing TGF-β Signaling Pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 2018, 104, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musumeci, M.; Coppola, V.; Addario, A.; Patrizii, M.; Maugeri-Saccá, M.; Memeo, L.; Colarossi, C.; Francescangeli, F.; Biffoni, M.; Collura, D.; et al. Control of Tumor and Microenvironment Cross-Talk by MiR-15a and MiR-16 in Prostate Cancer. Oncogene 2011, 30, 4231–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Shi, J.; Cao, P.; Wan, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Kridel, S.J.; Liu, W.; Xu, J.; et al. Fatty Acid Synthase Is a Primary Target of MiR-15a and MiR-16-1 in Breast Cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 78566–78576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.G.; Zhao, J.F.; Xiao, L.; Rao, W.Y.; Ran, C.; Xiao, Y.H. MicroRNA-19a-3p Suppresses Invasion and Metastasis of Prostate Cancer via Inhibiting SOX4. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2018, 22, 6245–6251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wa, Q.; Li, L.; Lin, H.; Peng, X.; Ren, D.; Huang, Y.; He, P.; Huang, S. Downregulation of MiR-19a-3p Promotes Invasion, Migration and Bone Metastasis via Activating TGF-β Signaling in Prostate Cancer. Oncol Rep 2018, 39, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schramedei, K.; Mörbt, N.; Pfeifer, G.; Läuter, J.; Rosolowski, M.; Tomm, J.M.; Von Bergen, M.; Horn, F.; Brocke-Heidrich, K. MicroRNA-21 Targets Tumor Suppressor Genes ANP32A and SMARCA4. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2975–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista-Sánchez, D.; Arriaga-Canon, C.; Pedroza-Torres, A.; De La Rosa-Velázquez, I.A.; González-Barrios, R.; Contreras-Espinosa, L.; Montiel-Manríquez, R.; Castro-Hernández, C.; Fragoso-Ontiveros, V.; Álvarez-Gómez, R.M.; et al. The Promising Role of MiR-21 as a Cancer Biomarker and Its Importance in RNA-Based Therapeutics. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Q.; Li, N.; Zhou, X. Increased MiR-21a Provides Metabolic Advantages through Suppression of FBP1 Expression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Am J Cancer Res 2017, 7, 2121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Shan, T.; Ma, J.; Lin, W.; Li, W.; Kang, Y. MiR-21-Mediated Metabolic Alteration of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Its Effect on Pancreatic Cancer Cell Behavior. Int J Biol Sci 2018, 14, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Cappello, T.; Wang, L. Emerging Role of MicroRNAs in Lipid Metabolism. Acta Pharm Sin B 2015, 5, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, K.; Wang, D.; Xu, H.; Mei, F.; Wu, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, B. MiR-21 Promotes Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells Growth by Regulating Fatty Acid Metabolism. Cancer Cell Int 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, M.; Mirdamadi, M.S.A.; Talebi, Y.; Khaniabad, N.; Banaei, G.; Daneii, P.; Gholami, S.; Ghorbani, A.; Tavakolpournegari, A.; Farsani, Z.M.; et al. Pre-Clinical and Clinical Importance of MiR-21 in Human Cancers: Tumorigenesis, Therapy Response, Delivery Approaches and Targeting Agents. Pharmacol Res 2023, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damodaran, M.; Chinambedu Dandapani, M.; SimonDuraiRaj; SandhyaSundaram; VenkatRamanan, S.; Ramachandran, I.; Venkatesan, V. Differentially Expressed MiR-20, MiR-21, MiR-100, MiR-125a and MiR-146a as a Potential Biomarker for Prostate Cancer. Mol Biol Rep 2021, 48, 3349–3356. [CrossRef]
- Joković, S.M.; Dobrijević, Z.; Kotarac, N.; Filipović, L.; Popović, M.; Korać, A.; Vuković, I.; Savić-Pavićević, D.; Brajušković, G. MiR-375 and MiR-21 as Potential Biomarkers of Prostate Cancer: Comparison of Matching Samples of Plasma and Exosomes. Genes (Basel) 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Gong, A.Y.; Eischeid, A.N.; Chen, D.; Deng, C.; Young, C.Y.F.; Chen, X.M. MiR-141 Modulates Androgen Receptor Transcriptional Activity in Human Prostate Cancer Cells through Targeting the Small Heterodimer Partner Protein. Prostate 2012, 72, 1514–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Baruah, M.M. The MicroRNA Signatures: Aberrantly Expressed MiRNAs in Prostate Cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 2019, 21, 126–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akalin, I.; Erol, B.; Aslan, E.; Ozkanli, S.S.; Efiloglu, O.; Yildirim, S.; Caskurlu, T.; Yildirim, A.; Karaman, M.I. A New Promising Pathway in Aggressive Prostate Cancer: Treg/Mir-Let8c/Lin28b. Arch Esp Urol 2022, 75, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagana Gowda, G.A.; Gowda, Y.N.; Raftery, D. Expanding the Limits of Human Blood Metabolite Quantitation Using NMR Spectroscopy. Anal Chem 2015, 87, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Guo, A.C.; Oler, E.; Wang, F.; Anjum, A.; Peters, H.; Dizon, R.; Sayeeda, Z.; Tian, S.; Lee, B.L.; et al. HMDB 5.0: The Human Metabolome Database for 2022. Nucleic Acids Res 2022, 50, D622–D631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarlinova, M.; Halasa, M.; Mistuna, D.; Musak, L.; Iliev, R.; Slaby, O.; Mazuchova, J.; Valentova, V.; Plank, L.; Halasova, E. MiR-21, MiR-221 and MiR-150 Are Deregulated in Peripheral Blood of Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Anticancer Res 2016, 36, 5449–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benko, J.; Sarlinova, M.; Mikusova, V.; Bolek, T.; Pec, M.J.; Halasova, E.; Galajda, P.; Samos, M.; Mokan, M. MiR-126 and MiR-146a as Markers of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Pilot Study. Bratisl Lek Listy 2023, 124, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, P.; Pandey, C.M.; Singh, U.; Gupta, A.; Sahu, C.; Keshri, A. Descriptive Statistics and Normality Tests for Statistical Data. Ann Card Anaesth 2019, 22, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ørsted, D.D.; Bojesen, S.E. The Link between Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Prostate Cancer. Nat Rev Urol 2013, 10, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
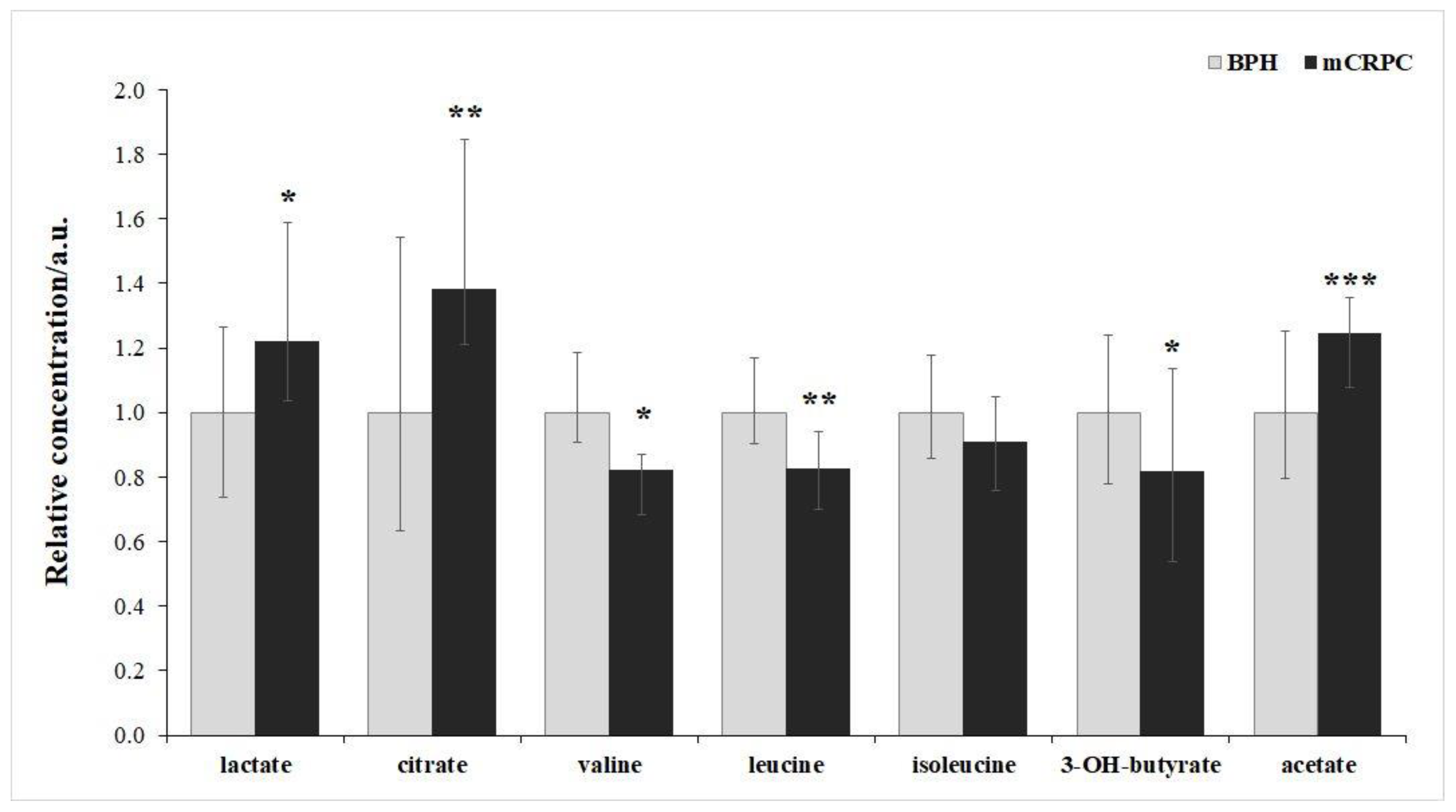
| Metabolite |
Percentage change mCRPC vs BPH group |
P-value |
| Lactate | 22% | 0.04 |
| Citrate | 38% | 0.003 |
| Valine | -18% | 0.02 |
| Leucine | -18% | 0.002 |
| Isoleucine | -11% | 0.06 |
| 3-hydroxybutyrate | -19% | 0.03 |
| Acetate | 24% | 0.00002 |
| miR | Fold regulation +/- |
P-value |
|---|---|---|
| miR-15a | -2.00 | 0.006 |
| miR-16 | -3.24 | 4.33 × 10-6 |
| miR-19a-3p | -2.78 | 1.11 ×10-5 |
| miR-21 | -2.39 | 0.003 |
| miR-141a-3p | +1.23 | 0.41 |
| miR-15a | miR-16 | miR-19a-3p | miR-21 | miR-141a-3p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-15a |
Pearson Corr. P-value |
1.00 - |
0.73 5.94×10-9 |
0.80 6.22×10-12 |
0.81 3.99×10-9 |
0.13 0.38 |
|
| miR-16 |
Pearson Corr. P-value |
0.73 5.94×10-9 |
1.00 - |
0.79 9.88×10-12 |
0.38 0.01 |
0.01 0.95 |
|
| miR-19a-3p |
Pearson Corr. P-value |
0.80 6.22×10-12 |
0.79 9.88 ×10-12 |
1.00 - |
0.72 7.44×10-9 |
0.22 0.13 |
|
| miR-21 |
Pearson Corr. P-value |
0.81 3.99×10-12 |
0.38 0.01 |
0.72 7.44×10-9 |
1.00 - |
0.29 0.04 |
|
| miR-141a-3p |
Pearson Corr. P-value |
0.13 0.38 |
0.01 0.95 |
0.22 0.13 |
0.29 0.04 |
1.00 - |
|
| miR-15a | miR-16 | miR-19a-3p | miR-21 | miR-141a-3p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lactate |
Pearson Corr. P-value |
0.35 0.01 |
0.31 0.03 |
0.33 0.03 |
0.27 0.06 |
0.01 0.92 |
| Citrate |
Pearson Corr. P-value |
-0.47 9.23×10-4 |
-0.24 0.11 |
-0.35 0.02 |
-0.47 7.61×10-4 |
-0.24 0.09 |
| Valine | Pearson Corr. P-value |
0.05 0.73 |
0.05 0.071 |
0.15 0.33 |
0.14 0.35 |
-0.09 0.55 |
| Leucine | Pearson Corr. P-value |
-0.04 0.78 |
-0.02 0.89 |
0.05 0.72 |
0.08 0.55 |
-0.09 0.55 |
| Isoleucine | Pearson Corr. P-value |
-0.23 0.11 |
-0.09 0.52 |
-0.07 0.62 |
-0.12 0.44 |
-0.08 0.59 |
| 3-hydroxybutyrate |
Pearson Corr. P-value |
0.28 0.05 |
0.09 0.51 |
0.17 0.24 |
0.33 0.03 |
0.05 0.72 |
| Acetate |
Pearson Corr. P-value |
0.16 0.29 |
0.01 0.96 |
0.30 0.04 |
0.46 0.001 |
0.42 0.003 |
| Glutamine |
Pearson Corr. P-value |
0.28 0.05 |
0.28 0.05 |
0.21 0.16 |
0.19 0.21 |
-0.14 0.36 |
| Lysine |
Pearson Corr. P-value |
-0.44 0.002 |
-0.22 0.14 |
-0.29 0.05 |
-0.39 0.006 |
-0.04 0.81 |
| mCRPC patients | BPH patients | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 51 | 48 | > 0.05 |
| Age (years, mean ± SD) Range |
73.5 ± 7.65 (58 - 85) |
67.5 ± 6.54 (55 - 84) |
< 0.05 |
| PSA (ng/ml, mean ± SD) Range |
103.5 ± 1478.7 (2.2 - 9506) |
3.29 ± 9.77 (0.2 – 66.5) |
< 0.05 |
|
T Staging T2 T3 T4 |
No. 2 35 14 |
N/A |
– |
|
N staging N0 N1 |
No. 40 11 |
N/A |
– |
|
M staging* M1a M1b M1c |
No. 8 51 4 |
N/A |
– |
| Gleason score 6 7 8 9 10 |
No. 1 9 17 20 4 |
N/A |
– |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





