1. Introduction
The process of pollination involves the transfer of pollen grains from the anther, the male portion of a flower, to the female part (stigma) of the same or another plant. There are two types of pollination form: i) self-pollination (autogamy), in which pollen is deposited on the stigma of the same or another flower on the same plant, and ii) cross-pollination (allogamy), in which pollen is transferred from one plant to the flower of a genetically different plant or cultivar. Walnut trees are self-compatible, but they require cross-pollination with another walnut tree to produce nuts due to protandrous, meaning that the male flowers mature – release pollen before the female flowers become receptive, and pollen shedding occurs before female bloom begins or protogynous, meaning that the female flower begins opening – become receptive - prior to the pollen shedding. Cross-pollination involves transferring pollen from the male flowers of one walnut tree to the female flowers of another. This can occur naturally, with the help of the wind (wind-blown pollen), or insects such as bees, or artificially, through the process of hand pollination [
1].
On walnut trees, the pollen is produced in catkins which may also be colonized with
Xanthomonas arboricola pv.
juglandis, the caused agent of walnut blight disease [
2,
3]. Mainly the disease can affect the leaves, stems, and nuts of the tree, leading to reduced yield and poor-quality nuts.
Xanthomonas arboricola pv
. juglandis is primarily spread by water, either through rain or irrigation, and can be more severe during warm and wet weather [
4,
5].
Once the bacterium enters the tree tissues, it can survive and spread within the tree through the sap. To prevent and control X. arboricola pv. juglandis, farmers can use a combination of cultural and chemical control measures. This may include removing infected plant material, managing irrigation practices to reduce water on the foliage, and applying copper-based fungicides during the dormant season or at the first signs of infection. Here, it is important to note that the overuse of chemical control measures can lead to the development of resistant strains of the bacterium, so it is important to use a holistic approach to disease management that incorporates a variety of methods. Additionally, early detection and rapid response to infected trees can help limit the spread of the disease to other trees in the orchard.
Research has shown that inoculum of
X. arboricola pv.
juglandis is also disseminated through pollen [
3,
6]. Those evidence-based early detections of developmental-behavioral problems in primary infection of
X. arboricola pv.
juglandis on plant symptomless materials such as catkins and pollen besides the symptomatic materials (leaves and fruits and other plant debris) should be considered.
Pathogenic bacteria and pollen are two distinct biological entities that are not directly related to each other. While pathogenic bacteria and pollen are not directly related, they can sometimes interact in certain situations. For example, pollen can sometimes serve as a carrier for pathogenic bacteria. Pollen of
Actinidia spp., is a good substrate for
Pseudomonas syringae pv.
actinidiae colonization and survival and as a pathway for its spread [
7]. Therefore, pollen may be a conduit for the spread of
P. syringae pv.
actinidiae and kiwifruit bacterial canker. [
7]. Further, pollen dispersal has been presented for Erwinia amylovora of pome fruits [
8], and for
X. arboricola pv.
juglandis of walnut [
9,
10]. Moreover, pollen was recognized as a possible pathway for
X. arboricola pv.
juglandis, although further studies were suggested to confirm if pollen could spread the pathogen [
3]. Viable pathogenic bacterium such as
X. arboricola pv.
juglandis were often isolated from pollen and infected pollen also represents a potential route of introduction into healthy walnut groves even in case of mechanical pollination [
3,
6]. Considering walnut cv. Chandler and cv. Serr results showed that pollen was recognized as a possible pathway for
X. arboricola pv.
juglandis [
3].
Therefore, the survival of the bacterium
X. arboricola pv.
juglandis in catkin buds and catkins should be checked before the bacterium overwinters in blighted leaf and catkin buds. When water carries the bacteria to the leaves and stigmatic surfaces of the flowers, the blight spreads from these reservoirs. When catkins open and staminate flowers release pollen, the disease may also spread through the air. Contaminated pollen may be carried by air winds and deposited on any young growing parts of the tree [
4].
In our view, these parameters are important and will be further analyzed in this review paper. Further, we will try to answer what are the advantages of pollination drones and how they can help to prevent or reduce the risk of the walnut blight disease. In the end, we have designed a path-planning algorithm for a pollination robot that involves determining the disease inoculum and an optimal route for the robot to pollinate flowers efficiently.
2. Walnut Blight Prevention
Walnut Blight and Conditions
Typically, the cycles of walnut blight bacteria are dependent upon weather conditions and rainfall during the growing season. Infrequent rainfall during the spring may lead to monocyclic progress, while frequent spring rainfall tends to favor polycyclic disease epidemics. Rainfalls during late spring (after leaf growth) have been reported to favor the spread of the
X. arboricola pv.
juglandis bacterium, which causes serious damage to trees, and it is responsible for significant crop losses, which can reach more than 50% of nut drops [
11].
All aerial walnut organs, including as catkins, female flowers, leaves, and fruit, are infected [
3]. Necrotic lesions on the fruit, twigs, and foliage are characteristic disease symptoms. Leaf lesions consist of small water-soaked spots, surrounded by chlorotic halos that extend to become brown necrotic lesions. Fruit lesions begin as tiny, water-soaked spots and develop into pericarp and inner nut tissue necrosis, which results in early fruit drop. After shell hardening, infections often only impact the epicarp [
12].
Cankers serve as a source of inoculum for leaves and nutlet infections [
4,
13,
14]. Populations of
X. arboricola pv.
juglandis found on dormant buds serve as the primary inoculum for nut infections [
13]. Tissues that have recently been infected can as secondary sources of inoculum for the pathogen. Pollen released from infected catkins plays a role in pathogen dissemination [
2,
13]. The bacterium is transmitted through moisture, particularly through the combined action of wind and rain [
15]. The cultivars Chandler and Vina exhibit a significant susceptibility to
X. arboricola pv.
juglandis, thus demonstrating the potential of these cultivars to be infected with
X. arboricola pv.
juglandis under conditions favorable for the disease [
5,
13,
16]. The cultivars terminal fruit fulness cultivars Milotai, Marbot, Sibisel, and Ronde de Montignac and the lateral fruit fulness cultivars Chandler, Sunland, and Techama were found to be highly susceptible cultivars, making it possible to serve as a host response to bacterial blight infections at different leaf and fruit growth stages [
12].
Overall, the degree of infection caused by X. arboricola pv. juglandis bacterium depends on: a) the quantity of the pathogen presented in individual catkin buds and catkins (inoculum), b) the quantity of walnut blight cankers present on certain walnut varieties, c) the environmental conditions such as rain, which plays a significant role in spreading bacteria and aiding infection and d) the early leafing varieties that are most severely affected.
Besides the favorable conditions for the disease, research suggests that pollen released from infected catkins plays a role in pathogen dissemination [
13,
14]. Aerial dissemination of infected pollen from diseased catkins may also transmit the bacterium,
X. arboricola pv.
juglandis, to pistil-late flowers. However, this source of inoculum might be region specific [
17] or by different origin of the propagation material [
18]. Up today new evidence, provides data that infections depend on pollen, especially in walnut orchards with varieties where catkins emerge before the pistillate flowers i.e., cv. Chandler. Indeed, pollen is important for spreading bacteria and aiding infection [
3]. Even more, the isolation of
X. arboricola pv.
juglandis, in late winter-early spring led to the finding that primary inoculum is present in buds (overwintering), catkins, and female flowers [
4,
13].
So, it's crucial to select walnut varieties resistant to bacterial blight and to implement good orchard management techniques, such as pruning and fertilization to keep trees healthy and less susceptible to disease. Moreover, one should be aware of pollen released from infected catkins, which contributes to the spread of the pathogen
X. arboricola pv.
juglandis. If bacterial blight is present in the orchard, it may be necessary to apply fungicides or use other treatments to prevent the disease from spreading, such as artificial techniques for cross-pollination, which probably has a direct cause or prevent bacterial blight in walnut trees. Apart from the infected catkins with
X. arboricola pv.
juglandis which plays a role in pathogen dissemination, walnuts produce pollen that is desiccation intolerant. Pollen that do not have homeostatic mechanisms for maintaining a constant water content also die rapidly after opening of the anther or after pollen dispersal [
19]. The previously described ‘partially hydrated’ or, more precisely, desiccation sensitive pollen of this type may have served as the connection point with
X. arboricola pv.
juglandis when the environmental conditions such as temperature, and relative humidity, can affect pollination processes or are highly favorable for the pathogen growth in plants [
19].
However, this pollen’s property related to walnut blight disease during the flower cycle when the daily temperature and leaf wetness are more favorable for
X. arboricola pv.
juglandis has not been supported with detailed experimental data. The epiphytic colonization of the stigmas of the kiwifruit flower, inoculated by pollen contaminated with the GFPuv-labelled
Pseudomonas syringae pv.
actinidae (Psa), responsible for the bacterial canker of the kiwifruit, concluded that the Psa, is often transmitted to the stigma by pollen contamination [
20]. Further, it is well known that plants employ sexual mimicry, and flowers mimic the mating signals of their pollinator insects. Based on the mimicry phenomenon, researchers demonstrated that fire blight, a serious disease of apple and pear trees, requires the combination of open blossoms, warm temperatures, and wet weather. The disease spreads rapidly from flower to flower by wind-driven or splashing moisture and by pollinating bees or other insects. So, the specific mimic odors which serve as a tool to enhance honeybee foraging and pollination activities in pear and apple crops spread serious diseases such as a fire blight of pear and apple trees [
21,
22]. So, concerning the walnut blight disease, fundamental questions are: is flower/corolla closure linked to a decrease in viability of desiccation-sensitive pollen? Is this disease related to other pollination activities or phenomena such as mimicry or dissemination by the wind?
As far as walnut plants it concerns, if pollen is served as a possible pathway for the dissemination of X. arboricola pv. juglandis and walnut blight disease, to prevent the disease from spreading, apart fungicides it is necessary to used artificial techniques for cross-pollination as mentioned above with uninfected pollen (pollen that is free from the above pathogen or diseases).
3. Walnut buds: bloom, and pollination events - Cross-Pollination
Walnuts are monoecious and have male and female flowers on the same tree. Male flowers are formed in structures called catkins. They developed directly on the prior year’s growth and are easy to identify by eye. At leaf out, the preformed shoot develops, and compound leaves start to grow before the pistillate (female) flowers form. That’s explains why walnut cultivars are indicated by both their leaf out date and bloom date. Female flowers are only receptive to pollination for a short time. In particular, pollen shed from staminate (male) flowers during anthesis is spread by wind (wind-blown pollen), and remains viable for a short time, generally up to 48 hours. As already mentioned, walnut is self-compatible but have adapted a mechanism called dichogamy to reduce the degree of inbreeding. Walnuts are classified as heterodichogamous, however, the majority of commercial walnut cultivars such as Chandler and Serr are protandrous, meaning that the male flowers mature and pollen shed occurs before the female bloom begins. So protandrous cultivars i.e. Serr may be a large contributor to protogynous cultivar pollination. In most walnut-growing regions, dichogamy is the reason for including pollinizers in orchards. Moreover, in certain cultivars such as Serr, an excessive of pollen on pistillate flowers (too much pollen), has been identified to be the cause of pistillate flower abortion [
1].
During cross-pollination, pollen is transferred from the male reproductive organ (stamen) of one plant to the female reproductive organ (pistil) of another plant of the same species, resulting in fertilization and the production of seeds. In the case of nut trees like walnuts, cross-pollination is necessary for the trees to produce nuts. Cross-pollination can occur naturally through the action of wind or insects such as bees, or it can be done artificially through hand pollination, in which pollen is manually transferred from one tree to another. Natural cross-pollination can be affected by factors such as the proximity of the trees, the timing of flowering, and the presence of pollinators.
Walnuts, require cross-pollination for optimal nut production. Cross-pollination increases the genetic diversity of the trees and can lead to larger and more flavorful fruit. However, not all nut tree varieties are compatible for cross-pollination. It's important to choose compatible varieties and to plant them close enough for natural cross-pollination to occur. In some cases, artificial pollination may be necessary to ensure adequate pollination and fruit set. This is especially true in orchards where natural pollinators are scarce or when the weather is unfavorable for pollination. Artificial pollination involves manually transferring pollen from the male flowers of one tree to the female flowers of another. As mentioned above walnut trees are probably requiring cross-pollination with another walnut tree to produce nuts and minimize the bacterial risk contamination. This can occur naturally, or artificially with air vehicles, or through the process of hand pollination or design specific aerial pollination systems for walnut trees.
4. Artificial Pollination - Artificial Pollination Technology
Pollination is critical for many crops for successful production. To avoid pollination failure by weather events or bloom asynchrony on both insects, and wind-based pollination systems, plants require artificial pollination systems that can provide the security of yield crops [
23].
There are various reasons for resorting to artificial pollination, including:
Crop Yield Enhancement: In agriculture, artificial pollination is sometimes employed to increase crop yields. This can be particularly important for crops where natural pollination may be insufficient [
24].
Control of Pollination: Artificial pollination allows for precise control over the pollination process. This is useful in hybrid seed production, where specific traits can be selected [
25].
Overcoming Pollination Challenges: Some crops may face challenges with natural pollination due to factors like low insect activity, unfavorable weather conditions i.e., wind, or geographic isolation. Artificial pollination can overcome these challenges [
26].
Biotechnological Research: In scientific research, artificial pollination can be used to study plant genetics, breeding, and other aspects of plant biology [
27].
Artificial pollination technology involves various methods and tools designed to facilitate the pollination process in plants by assisting the natural transfer of pollen. Some of the technologies and techniques used for artificial pollination include:
Drones: Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), or drones, equipped with special devices can be used for pollination. These devices may carry pollen and release it over crops i.e., walnut trees, or mimicking the action of bees or other pollinators [
28].
Robotic Pollinators: Small robots designed to mimic the behavior of natural pollinators can navigate through crops, transferring pollen between flowers. These robots are often equipped with cameras and sensors to identify and locate flowers [
29].
Spraying Devices: Some systems involve the use of sprayers to disperse pollen over crops. These devices can be mounted on tractors or other vehicles, releasing pollen in a controlled manner [
30].
Electrostatic Pollination: This method uses an electrostatic charge to adhere pollen to flowers. The charged pollen is attracted to the stigma, increasing the chances of successful pollination [
31].
Vibrational Devices: Certain crops respond well to vibrational stimulation, which can be achieved through devices that vibrate the flowers, causing the release of pollen [
32].
Artificial Flowers: In controlled environments like greenhouses, artificial flowers containing pollen can be placed strategically to enhance pollination [
33].
Automated Pollination Systems: Some systems use automated robotic arms or other mechanical devices to transfer pollen between flowers. These systems can be programmed to work efficiently and quickly [
34].
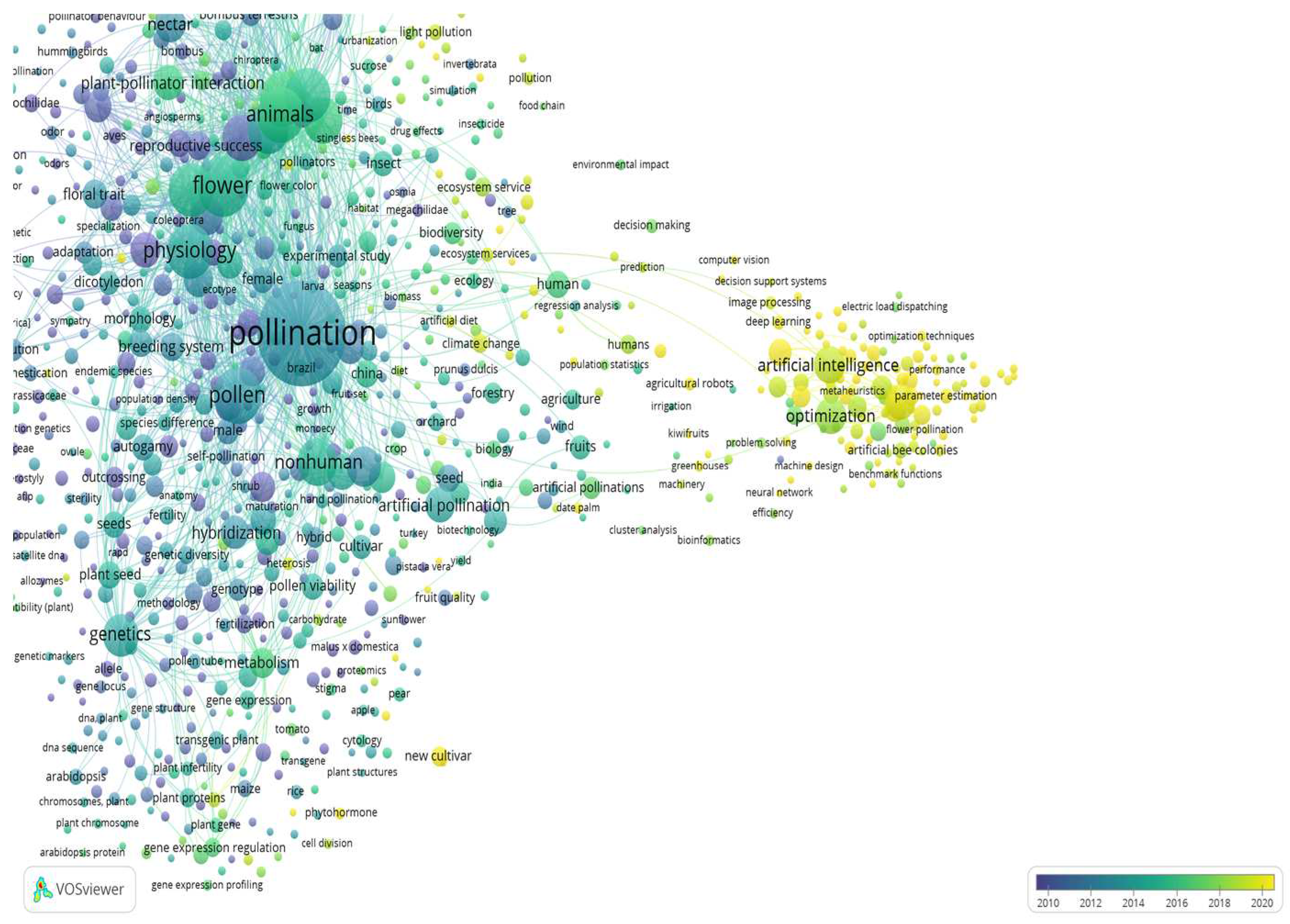
The development of artificial pollination technologies is driven by the need to address challenges such as declining bee populations, environmental factors and the increasing demand for efficient and reliable pollination in agriculture. By using the VOS viewer mapping software and the Scopus bibliographic database based on the search strategy criteria “Artificial and Pollination and Technologies” (
Figure 1), the above mentioned technologies show promise but they are still in the early stages of development (Co-keyword: artificial intelligence,
Figure 1), and may vary in effectiveness (Co-keyword: optimization,
Figure 1), depending on the specific crop, environmental conditions and probably other parameters such as the disease inoculum [
35,
36,
37,
38,
39].
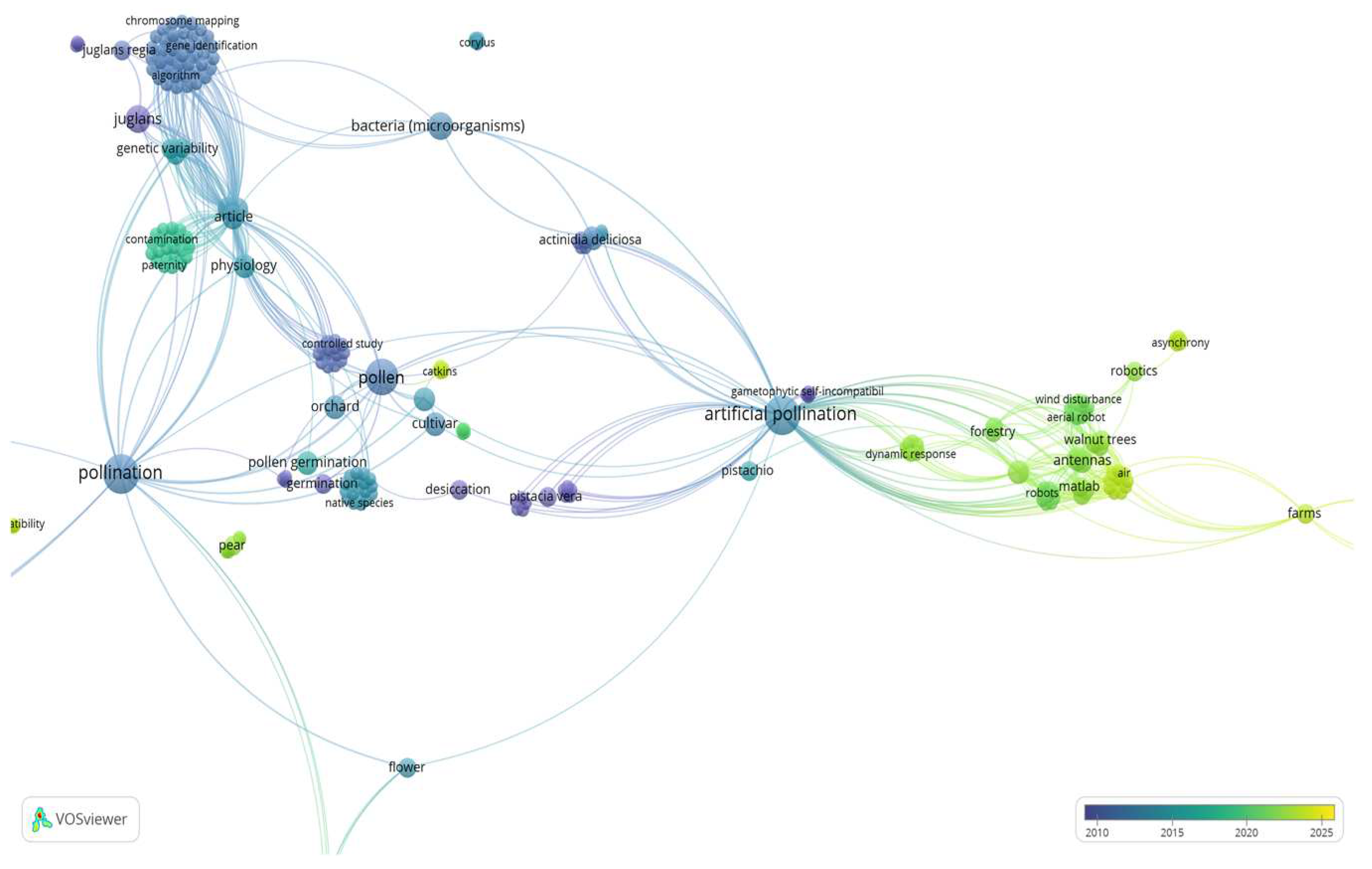
Furthermore, it's important to note that while artificial pollination can be a useful tool in certain situations such as for walnut trees, apart robotics (Co-keyword: artificial robots,
Figure 2), modeling (Co-keyword: Matlab,
Figure 2) or the agriculture drones (Co-keyword: agriculture drones, Figure2), the pollen germination (Co-keyword: pollen germination,
Figure 2), and the knowledge of pollen as a possible pathway for the dissemination of bacterial diseases of other crops such as pear of kiwifruit plant (Co-keywords: pear and Actinidia deliciosa,
Figure 2), remain crucial for maintaining information for design and manufacture of aerial pollinator robot for walnut trees.
The keywords for “Artificial” and “Pollination and Technologies and Walnut” were presented as 13 clusters defined by 310 keywords (items), which contributed a total 100%, as presented in
Figure 2.
Cluster 1 (
Figure 3), is defined by 52 keywords (items), with keywords including “matlab”, “adams matlab cosimulation”, “computational fluid dynamics”, “cosimulation”, “flight simulators”, “flying robots”, “quad rotors” “aerial robot”, “robotics”, “agricultural robots”, “system stability”, “vibration analysis”, “vibration transmissibility”, “software testing”, “antennas”, “artificial pollinations”, “fruit production”, “ population growth”, “population statistics”, “walnut pollinator”, “crop growth”, “wind disturbance”, etc.
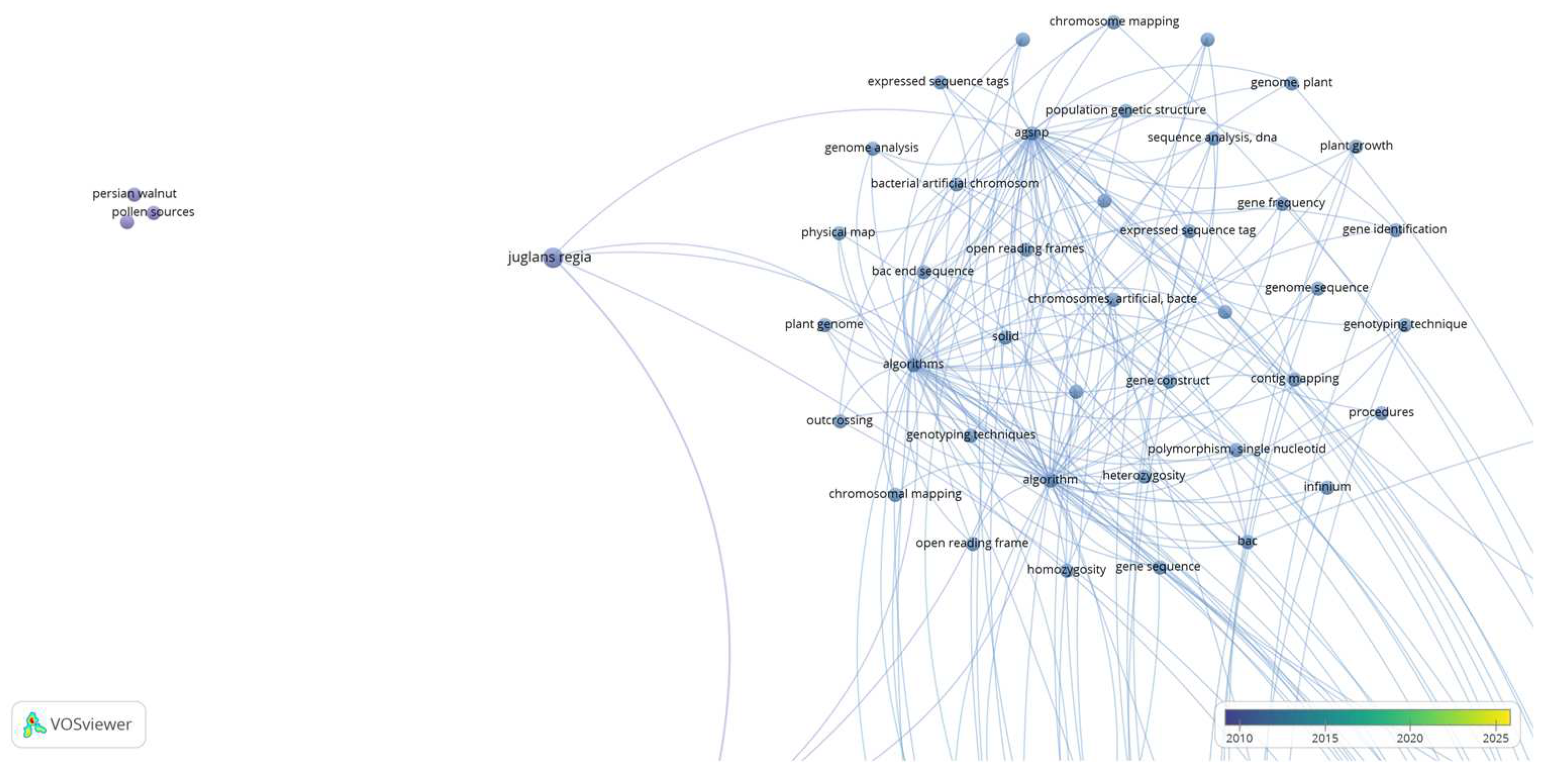
Cluster 2 (
Figure 4), is defined by 45 keywords (items), with keywords including “algorithms”, “bacterial artificial chromosome”, “chromosomes, artificial, bacterial”, “contig mapping”, “expressed sequence tags”, “genome analysis”, “genotyping techniques”, “heterozygosity”, “homozygosity”, “physical map”, “plant genome”, “plant growth”, “pollen sources”, “population genetic structure”, “sequence analysis, dna”, “single nucleotide polymorphism”, “vegetative propagation”, etc.
Based on the above observations, cluster 1 and 2 (
Figure 3 and
Figure 4), “Artificial Pollination Technologies” include knowledge of: a) mechanical pollination technology i.e., aerial vehicles (UAVs), robotic and autonomous pollinators (hardware), and basic simulation methodologies for controlling a quadrotor (software). b) Mother nature pollination technology i.e., pollen (pollen germination), crop (cultivars), microorganisms (bacteria).
Based on simulation methodologies for controlling a quadrotor, MATLAB provides a solution of standard flower pollination algorithms with more information on Nature Optimization Algorithms provided in a book entitled “Nature-Inspired Optimization Algorithms”. In detail, the flower pollination algorithm (FPA) is a population-based metaheuristic optimization algorithm derived from the evolution of flowering plants [
40]. Following its original development, FRA was modified and hybridized to improve its performance for different optimization problems such as the bee-pollinator concept to solve the data clustering problem [
41]. A modified version of the FPA, which utilizes the crossover techniques for resolving multidimensional knapsack problems, was also developed [43]. Keeping the above-mentioned facts in view, we believe that an algorithm such as the FPA, should be used for a pollination robot to prevent or reduce the risk of the walnut blight disease.
In addition to the FPA, the bacterial microbiota associated with flower pollen is influenced by the pollination type and exhibits a significant degree of diversity and species-specificity [
42]. So, for microbes–pollen interaction presumably we must know the sequencing of 16S rRNA gene amplicon libraries to identify dominant microbe (-s) phylum and core microbiome of pollen from different walnut cultivars. Since pollen-associated bacteria may have a potential impact on walnut blight disease pollen microbial communities from different walnut cultivars are necessary or need to identify. That information could play a significant role in the flower pollination algorithm and develop a strategy that leads to new valuable information on walnut cultivars microbes–pollen interaction during pollination.
Moreover, considering the algorithm-based approach, is necessary to provide criteria for the aerial robot path. Basic simulation steps helped determine pollen streams under the quadrotor, unmanned aerial vehicle [
28]. Those steps are the following:
5. Machine Learning and Pollination
Machine learning (ML) can play a significant role in the context of pollination, offering innovative solutions and insights to address challenges and optimize pollination processes. Below several ways in which machine learning is applied to pollination are mentioned:
Predictive modeling: ML algorithms can analyze historical data on pollination success, environmental conditions, crop yields, and phenology to create predictive models. These models can help predict optimal times for pollination, considering factors such as weather patterns, bloom asynchrony, and the availability of pollinators [
43,
44,
45].
Automated monitoring: ML-powered monitoring systems can analyze images or sensor data to track the health and development of crops. This real-time monitoring allows for the early detection of issues related to pollination, such as low pollination rates or the presence of pests that could affect pollinators [
46,
47].
Optimizing pollination strategies: Machine learning algorithms can optimize artificial pollination strategies based on a variety of factors [
48,
49]. These include the type of crop, environmental conditions, and the efficiency of different pollination methods [
50,
51]. This can lead to more targeted and effective pollination efforts [
52].
Identification of pollinator behavior: ML can be used to analyze the behavior of natural pollinators, such as bees, by processing video footage or sensor data. Understanding pollinator behavior can provide insights into their preferences, movement patterns, and efficiency in pollinating specific crops [
53,
54].
Genetic analysis: Machine learning techniques can analyze genetic data related to plant characteristics, including traits associated with pollination [
55,
56]. This information can contribute to breeding programs aimed at developing crops that are more resilient to environmental challenges and more compatible with artificial pollination methods [
57,
58].
Decision support systems: ML-based decision support systems can assist farmers in making informed choices related to pollination strategies. These systems can consider a range of variables and provide recommendations for optimal pollination practices [
59,
60].
Data integration: Machine learning excels at integrating and analyzing large datasets from various sources. In the context of pollination, this can include data on weather conditions, soil quality, plant health, and more. The integrated data can provide a comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing pollination success [
61,
62,
63].
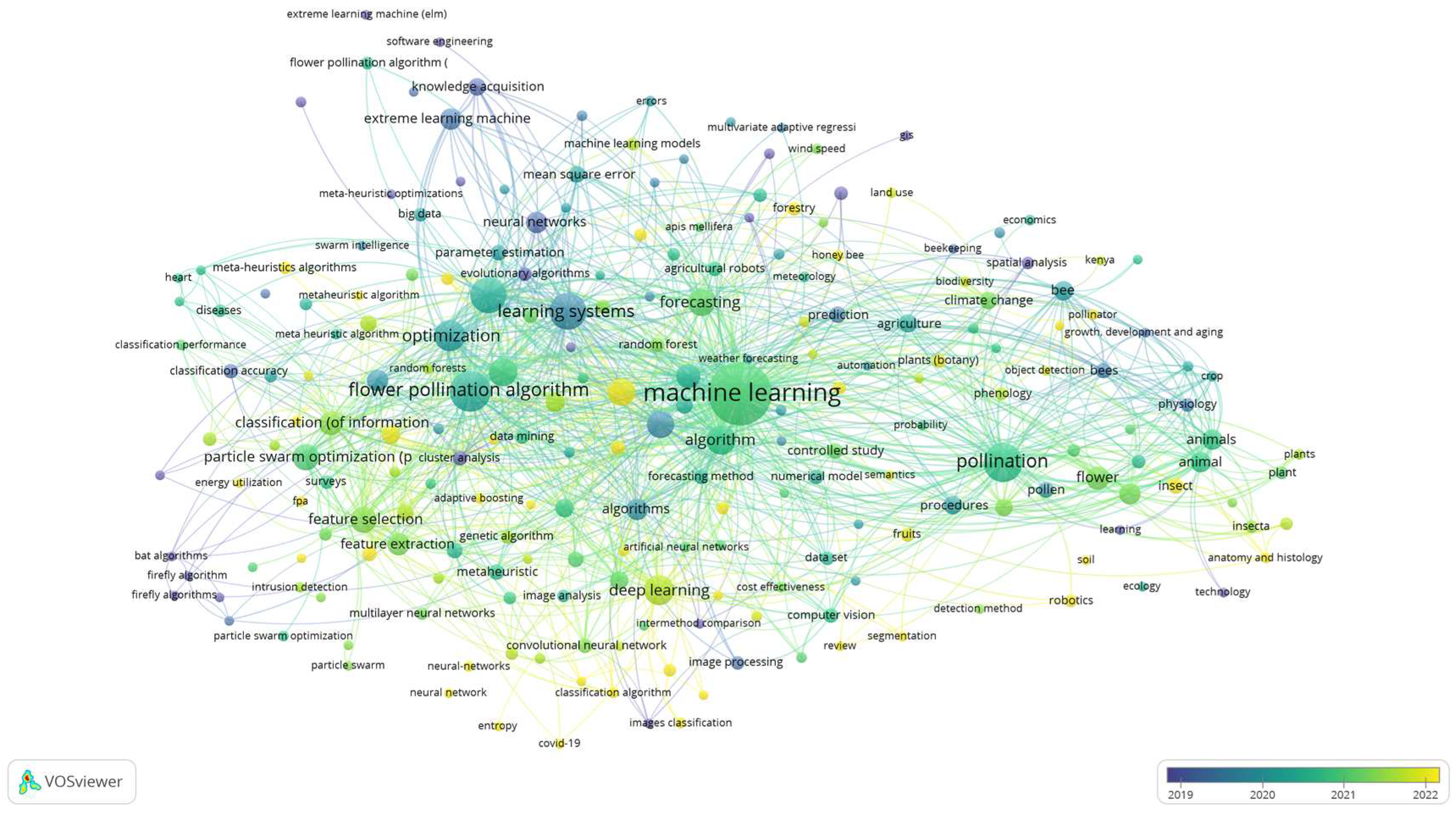
While machine learning holds great promise in improving pollination processes, it's essential to recognize the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration between machine learning and pollination as presented with VOS viewer analysis in
Figure 5. Based on
Figure 5, up today knowledge, 2022, (
Figure 5 items with yellow dots) requires: “anatomy and histology”, “classification of information”, “classification algorithms”, “image classification”, “neural networks”, “population statistics”, “robotics”, “machine learning”, “deep learning” and “meta-heuristic algorithms” (
Figure 5, items with yellow dots).
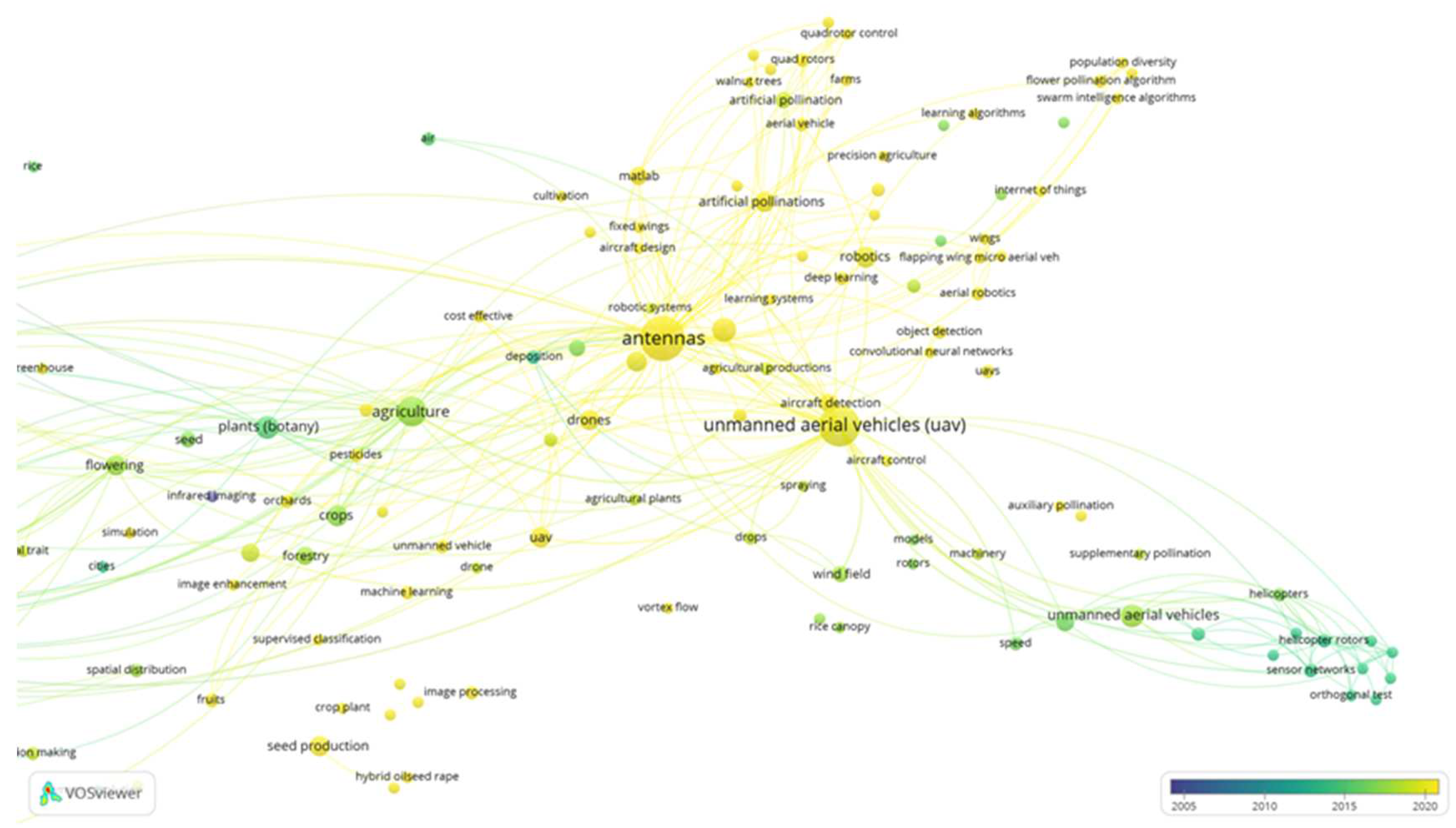
Even more, using the VOS viewer mapping software and the Scopus bibliographic database based on the search strategy criteria “Aerial and Pollination” (
Figure 6), all the above-mentioned criteria or technologies show promise but they still require important improvements such as “antennas”, “aircraft detection”, “aircraft control”, “MATLAB”, “internet of thinks”, “population diversity”, “flower population algorithm", “swarm intelligence algorithm", “learning algorithm", “learning systems", “deep learning”, “quadrotor control”, “image enhancement”, “auxiliary pollination:, “supplementary pollination” and “convolutional neural networks”,
Figure 6 (items with yellow dots).
6. Walnut Pollination. Model to prevent or reduce the risk of the walnut blight disease (our view).
Developing a walnut pollination model involves creating and a predictive framework that considers various factors influencing the pollination of walnut trees [
29,
41]. Keeping in mind the success of the walnut pollination model (
Figure 1,
Figure 2,
Figure 3,
Figure 4,
Figure 5 and
Figure 6) and based on the above paragraph we illustrate the following flowchart (6 steps, state of the art flowchart), which provides a general guideline for conducting a state-of-the-art analysis for a pollination robot to prevent or reduce the risk of the walnut blight disease.
State of the Art Flowchart
1st Step. Walnuts: budbreak, bloom, and pollination growth stages
1.1. Identify spring bud break, leaf emergence and anthesis growth stages of the walnut cultivars.
1.2. Understanding how plants grow and develop during bud break-up, anthesis, and pollination.
1.3. Understanding protandrous, protogynous mechanisms prior to the pollen shedding.
2nd Step. Study the bacterial microbiotas associated with the pollen
2.1. Identify the “core” pollen microbiota.
2.2. Compare bacterial abundance and diversity between walnut cultivars.
2.3. Assess the impact of the pollination type on the variability of the pollen microbiotas.
2.4. Estimate the role of X. arboricola pv. juglandis to stigma by contaminated pollen.
3rd Step. State of Walnut Pollination – Develop Pollination Algorithms
3.1. Check reservoir cultivars i.e. Chandler of inoculum presence.
3.2. Check for conditions that encourage the disease to spread such as moisture, and especially the combined action of wind and rain.
3.3. Check for air-borne inoculum when catkins open.
3.4. Check for pistil- late flowers.
3.5. Collect and store uninfected pollen.
4th Step. State of Walnut Pollination – Develop Pollination Algorithms
4.1. Set genetic algorithm for ‘mutation’, ‘selection’, ‘recombination’ based to pollen – microbes’ interaction.
4.2. Use metaheuristic algorithms which included differential evolution
4.3. Use the appropriate flower pollination algorithm which is inspired by the pollination process.
5th Step. Design of an Autonomous Precision Pollination Robot
5.1. Quadrotor (pollinating drone) to carry pollen grains.
5.2. Pollinating drone to make an ideal delivery system, landing on the pistil of a flower to result in pollination.
5.3. Drone technique would need some refinement in localization and mapping and control.
5.4. Metaheuristic optimization algorithm to find the best (feasible) solution out of all possible solutions of pollination optimization problem.
6th Step. Algorithm Optimization
6.1. Analyze historical data on pollination success, environmental conditions, and crop yields (machine learning)
6.2. Use flower pollination algorithm parameters tuning (formulating the above steps mainly step 1 and 2 due to climate change).
6.3. Start the process from step 3 and improve equipment at step 4 and 5.
7. Conclusions
Evidence to date is convincing that microbes such as the bacterium X. arboricola pv. juglandis, occur in pollen and influence walnut blight disease. Research showed that X. arboricola pv. juglandis the causing agent of walnut blight can affect the leaves, stems and nuts of the tree even pollen. In this review we present a flow diagram of a new artificial pollinator that we assume can reduce the spread of the disease in the orchard. Considering the knowledge of a solution to overcome this bacterial plant infection, VOS viewer suggests that the foundation for a new, more sophisticated and efficient walnut pollination model to prevent or reduce the risk of the walnut blight disease is possible. So, the purpose of the ideas presented here was to facilitate a description of such a pollination model with fundamental components, the identification of the ‘core’ pollen microbiota, specify an appropriate flower pollination algorithm, design an autonomous precision pollination robot and minimize the average errors of flower pollination algorithm parameters through machine learning and meta-heuristic algorithms.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.V., I.M. and T.S.; methodology, I.M. and I.V.; software, I.V.; validation, I.M., I.V.; formal analysis, I.V.; investigation, I.M., I.V. and T.S.; resources, I.V.; data curation, I.M., I.V.; writing—original draft preparation, I.V, T.S. and I.M.; writing— review and editing, I.V, T.S. and I.M.; visualization, I.V., I.M.; supervision, I.M., I.V. and T.S.; project administration, I.M., I.V.; funding acquisition, I.M., I.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work has received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Polito, V.S.; Pinney, K.; Weinbaum, S.; Aradhya, M.K.; Dangl, J.; Yanknin, Y.; Grant, J.A. Walnut pollination dynamics: pollen flow in walnut orchards. Acta Hortic. 2005, 705, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ark, P.A. Further evidence of pollen dissemination of walnut blight. Phytopathology. 1944, 34, 329–334. [Google Scholar]
- Kałużna, M.; Fischer-Le Saux, M.; Pothier, J.F.; Jacques, M.A.; Obradović, A.; Tavares, F.; Stefani, E. Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis and pv. corylina: Brothers or distant relatives? Genetic clues, epidemiology, and insights for disease management. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 22, 1481–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulrean, E.N.; Schroth, M.N. Ecology of Xanthomonas campestris pv. juglandis on Persian (English) Walnuts. Phytopathology. 1982, 72, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, M.D.; Evans, K. Epidemiology and status of walnut blight in Australia. J. Plant Pathol. 2010, 92, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Giovanardi, D.; Bonneau, S.; Gironde, S.; Saux, M.F.; Manceau, C.; Stefani, E. Morphological and genotypic features of Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis populations from walnut groves in Romagna region, Italy. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2016, 145, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tontou, R.; Giovanardi, D.; Stefani, E. Pollen as a possible pathway for the dissemination of Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinide and bacterial canker of kiwifruit. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2014, 53, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Zwet, T.; Bell, R.L. Survival of Erwinia amylovora on apple and pear pollen. Acta Hortic. 1992, 338, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcin, A.; El-Maataoui, M.; Tichadou, S.; Prunet, J.P.; Ginibre, T.; Penet, C. Walnut blight, new knowledge for an old disease: summary of research (1995‒2000). Infos-Ctifl. 2001, 171, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Giovanardi, D.; Dallai, D.; Stefani, E. Population features of Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis and epidemiology of walnut blight in Romagna (Italy). Petria -13th Congress of the Mediterranean Phytopathological Union 2010, 20(2), 96‒97.
- Chevallier, A.; Bray, O.; Prunet, J.P.; Giraud, M. Factors influencing walnut blight symptoms emergence and development. Acta Hortic. 2010, 861, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagelas, I.; Rumbos, C.I.; Tsiantos, J.A. Variation in disease development among persian walnut cultivars, selections and crosses when inoculated with Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis in Greece. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 94, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moragrega, C.; Llorente, I. Effects of leaf wetness duration, temperature, and host phenological stage on infection of walnut by Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis. Plants 2023, 12(15), 2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindow, S.; Olson, W.; Buchner, R. Colonization of dormant walnut buds by Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis is predictive of subsequent disease. Phytopathology 2014, 104, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchner, R.P.; Gilles, C.; Olson, W.H.; Adaskaveg, J.E.; Lindow, S.E.; Koutsoukis, R. Spray timing and materials for walnut blight (Xanthomonas campestris pv. juglandis, Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis) control in northern California USA. Acta Hortic. 2010, 861, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adaskaveg, J.E.; Förster, H.; Thompson, D.; Enns, J.; Connell, J.; Buchner, R. Epidemiology and management of walnut blight. Walnut Res. Reports. California Walnut Board. Sacramento, CA, USA, 2009, 241–257.
- Miller, P.W.; Bollen, W.B. Walnut bacteriosis and its control. U.S. Dept. Agr., Bur. Plant Industry, Soils and Agr. Eng. Oregon State College, Corvallis. Agr. Expt. Sta. Tech. Bul. 9.
- Giovanardi, D.; Bonneau, S.; Gironde, S.; Saux, M.F.; Manceau, C.; Stefani, E. Morphological and genotypic features of Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis populations from walnut groves in Romagna region, Italy. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2016, 145, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchi, G.G.; Piotto, B.; Nepi, M.; Baskin, C.C.; Baskin, J.M.; Pacini, E. Pollen and seed desiccation tolerance in relation to degree of developmental arrest, dispersal, and survival. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62(15), 5267–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, I.; Cellini, A.; Sangiorgio, D.; Vanneste, J.; Scortichini, M.; Balestra, G.; Spinelli, F. Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae: ecology, infection dynamics and disease epidemiology. Microb. Ecol. 2020, 80, 81–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, W.M.; Arenas, A.; Díaz, P.C.; Susic Martin, C.; Corriale, M.J. In-hive learning of specific mimic odours as a tool to enhance honey bee foraging and pollination activities in pear and apple crops. Sci. Rep 2022, 12 (1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroncelli, A. Puopolo, G. This tree is on fire: a review on the ecology of Erwinia amylovora, the causal agent of fire blight disease. J. Plant Pathol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broussard, M.A.; Coates, M.; Martinsen, P. Artificial pollination technologies: A review. Agronomy 2023, 13(5), 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, H.; Siopa, C.; Casais, V.; Castro, M.; Loureiro, J.; Gaspar, H.; Castro, S. Pollination as a key management tool in crop production: Kiwifruit orchards as a study case. Sci. Hort. 2021, 290(80), 110533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurz, A.; Grass, I.; Tscharntke, T. Hand pollination of global crops – A systematic review. Basic Applied Ecol. 2021, 56, 299–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H. Advanced technologies for pollination in plant factories. Plant Factory Using Artif. Light. 2019, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frachon, L.; Stirling, S.; Schiestl, F.P. , Dudareva, N. Combining biotechnology and evolution for understanding the mechanisms of pollinator attraction. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 70, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazinani, M.; Zarafshan, P.; Dehghani, M.; Vahdati, K.; Etezadi, H. Design and analysis of an aerial pollination system for walnut trees. Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 225(1), 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, S.G. , Neumann, P.; Vaissière, B.E.; Vereecken, N.J. Robotic bees for crop pollination: Why drones cannot replace biodiversity. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 665–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Douzals, J.; Lan, Y.; Cotteux, E.; Delpuech, X.; Pouxviel, G.; Zhan, Y. Characteristics of unmanned aerial spraying systems and related spray drift: A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; Lan, Y.; Wang, L.; Lu, X.; Yan, K.; Deng, J.; Zeng, W. Development and prospect of UAV-based aerial electrostatic spray technology in China. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.; Dunno, K.D.; Singh, M.; Yuan, L.; Lu, L. Development of a drone’s vibration, shock, and atmospheric profiles. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, A.L.; Papaj, D.R. Artificial pollen dispensing flowers and feeders for bee behaviour experiments. J. Pollinat. Ecol. 2016, 18, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Huo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Y.; He, Z.; Cui, Y. Design of a lightweight robotic arm for kiwifruit pollination. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 198, 107114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2009, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orduña-Malea, E.; Costas, R. Link-based approach to study scientific software usage: The case of VOSviewer. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 8153–8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, H.; Silva, É.R.; Lessa, M.; Proença, D.; Bartholo, R. VOSviewer and Bibliometrix. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. 2022, 110, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagelas, I.; Leontopoulos, S. A bibliometric analysis and a citation mapping process for the role of soil recycled organic matter and microbe interaction due to climate change using scopus database. Agric. Eng. 2023, 5, 581–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykas, C.; Vagelas, I. Innovations in agriculture for sustainable Agro-systems. Agronomy 2023, 13(9), 2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergos, P.E.; Yang, X. Flower pollination algorithm parameters tuning. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 14429–14447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhou, Y.; Qiao, S.; Huang, K. Flower pollination algorithm with bee pollinator for cluster analysis. Inf. Proc. Lett. 2016, 116, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambika Manirajan, B.; Ratering, S.; Rusch, V.; Schwiertz, A.; Geissler-Plaum, R.; Cardinale, M.; Schnell, S. Bacterial microbiota associated with flower pollen is influenced by pollination type, and shows a high degree of diversity and species-specificity. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18(12), 5161–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, D.R. Predicting plant reproductive success from models of competition for pollination. Oikos 1986, 47, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez, A.; di Virgilio, A.; Tiribelli, F.; Geslin, B. Simulation models to predict pollination success in apple orchards: a useful tool to test management practices. Apidologie 2018, 49, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, M.; Piot, N.; Vanbesien, S.; Meys, J.; Smagghe, G.; Baets, B.D. Pairwise learning for predicting pollination interactions based on traits and phylogeny. Ecol. Modell. 2021, 451, 109508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegoraro, L.; Hidalgo, O.; Leitch, I.J.; Pellicer, J.; Barlow, S.E. Automated video monitoring of insect pollinators in the field. Emerg. Top. Life Sci. 2020, 4, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, T.N.; Rustia, D.J.; Yang, E.; Lin, T. Automated monitoring and analyses of honey bee pollen foraging behavior using a deep learning-based imaging system. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 187, 106239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVetter, L.W.; Chabert, S.; Milbrath, M.O.; Mallinger, R.E.; Walters, J.; Isaacs, R.; Galinato, S.P.; Kogan, C.J.; Brouwer, K.; Melathopoulos, A.; Eeraerts, M. Toward evidence-based decision support systems to optimize pollination and yields in highbush blueberry. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, C.M. Fruit set is moderately dependent on insect pollinators in strawberry and is limited by the availability of pollen under natural open conditions. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 98(3), 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingley, A.; Anwar, S.; Kristiansen, P.; Warwick, N.W.; Wang, C.; Sindel, B.M.; Cazzonelli, C.I. Precision pollination strategies for advancing horticultural tomato crop production. Agronomy 2022, 12(2), 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraguri, T., Shimizu, H., Kimura, T., Matsuda, T., Maruta, K., Takemura, Y., Ohya, T., Takanashi, T. Autonomous drone-based pollination system using AI classifier to replace bees for greenhouse tomato cultivation. IEEE Access, 2023, 11, 99352–99364. [CrossRef]
- Cong, W.; Dupont, Y.L.; Søegaard, K.; Eriksen, J. Optimizing yield and flower resources for pollinators in intensively managed multi-species grasslands. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 302, 107062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajnberg, E.; Tel-Zur, N.; Shapira, I.; Lebber, Y.; Lev-Yadun, S.; Zurgil, U.; Reisman-Berman, O.; Keasar, T. Pollinator behavior drives sexual specializations in the hermaphrodite flowers of a heterodichogamous tree. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauer, A.C.; Kokko, H.; Schiestl, F.P. Pollinator behaviour and resource limitation maintain honest floral signalling. Funct. Ecol. 2021, 35(11), 2536–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Byers, K.J.; Bradshaw, H.D. The genetic control of flower-pollinator specificity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2013, 16(4), 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, J.P.; Sytsma, K.J. Complex interactions underlie the correlated evolution of floral traits and their association with pollinators in a clade with diverse pollination systems. Evolution. 2021, 75(6), 1431–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feigs, J.T.; Holzhauer, S.I.; Huang, S.; Brunet, J.; Diekmann, M.; Hedwall, P.; Kramp, K.; Naaf, T. Pollinator movement activity influences genetic diversity and differentiation of spatially isolated populations of clonal forest herbs. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opedal, Ø.H.; Pérez-Barrales, R.; Brito, V.L.; Muchhala, N.; Capó, M.; Dellinger, A.S. Pollen as the link between floral phenotype and fitness. Am. J. Bot. 2023, 110(6), e16200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barons, M.J.; Shenvi, A. Where the bee sucks - a dynamic bayesian network approach to decision support for pollinator abundance strategies. ArXiv abs. 2022, 2212.03179. [CrossRef]
- Lonsdorf, E.V.; Kremen, C.; Ricketts, T.H.; Winfree, R.; Williams, N.M.; Greenleaf, S.S. Modelling pollination services across agricultural landscapes. Ann. Bot. 2009, 103(9), 1589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.P.; Salim, J.A.; Trekels, M.; Groom, Q.J.; Parr, C.S.; Soares, F.M.; Agostini, K.; Saraiva, A.; Molloy, L.; Hodson, S.; Gregory, A. Plant-pollinator interaction data: A case study of the WorldFAIR project. Biodivers. Inf. Sci. Stand. 2022, 6, e94310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, J.A.; Zermoglio, P.F.; Drucker, D.P.; Soares, F.M.; Saraiva, A.M.; Agostini, K.; Freitas, L.; Wolowski, M.; Rech, A.R.; Maués, M.M.; Varassin, I.G. Plant-pollinator vocabulary - a contribution to interaction data standardization. Biodivers. Inf. Sci. Stand. 2021, D2021 5, e75636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, J.A.; Saraiva, A.M.; Zermoglio, P.F.; Agostini, K; Wolowski, M.; Drucker, D.P.; Soares, F.M.; Bergamo, P.J.; Varassin, I.G.; Freitas, L.; et al. Data standardization of plant–pollinator interactions. GigaScience 2022, 11, giac043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).