Submitted:
15 January 2024
Posted:
15 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
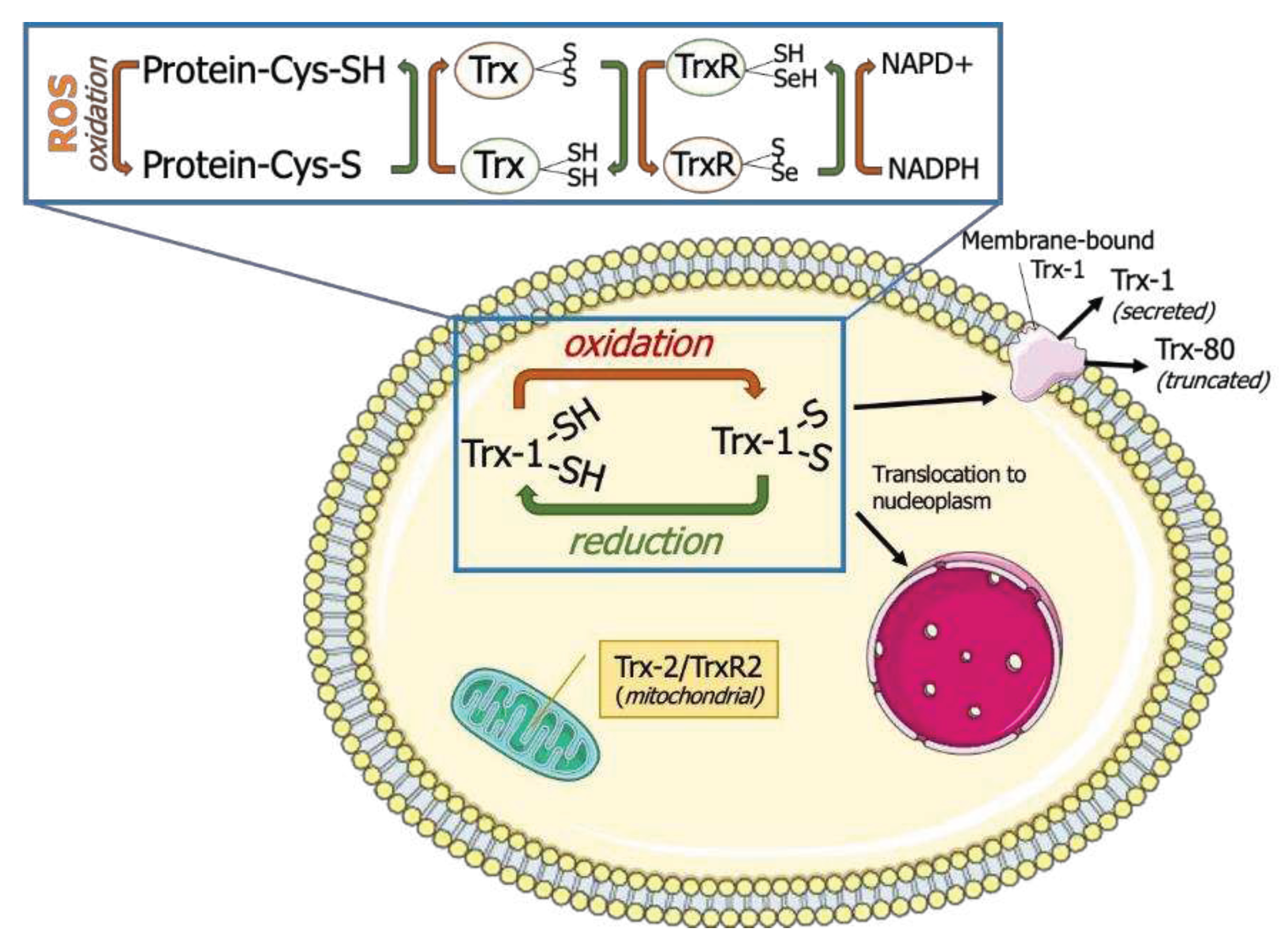
1.1. The Trx family of proteins
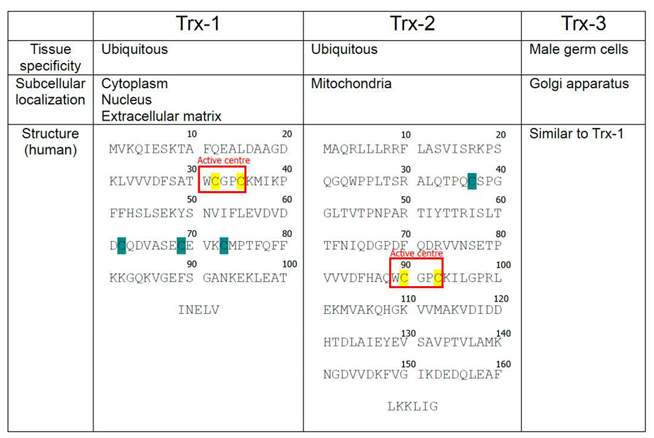
1.2. Isoforms of mammalian Trx
- Cysteines located within the active center of Thioredoxin-1 (Trx-1), Thioredoxin-2 (Trx-2), and Thioredoxin-3 (Trx-3) are highlighted with yellow, Cysteines outside of the active center are highlighted with Cyan.
2. Review of murine Trx1 system knockout models
2.1. Constitutive Trx1 and TrxR1 knockout
2.2. General inducible Trx1 knockout and dominant negative Trx1
2.3. Organ-specific Trx1/TrxR1 knockouts
2.3.1. Heart-specific depletion of Trx1 activity
2.3.2. Liver-specific Trx1 and TrxR1 knockouts
2.3.3. Pancreatic β-cell-specific TrxR1 knockout
2.3.4. T-Cell-specific TrxR1 knockout
2.3.5. Brain-specific Trx1 null-mutation
2.3.6. Brain- and neuron-specific knockouts of TrxR1
3. Concluding remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matsui M, Oshima M, Oshima H, et al. Early embryonic lethality caused by targeted disruption of the mouse thioredoxin gene. Dev Biol. 1996;178(1):179-185. [CrossRef]
- Bondareva AA, Capecchi MR, Iverson SV, et al. Effects of thioredoxin reductase-1 deletion on embryogenesis and transcriptome. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007;43(6):911-923. [CrossRef]
- Holmgren, A. Thioredoxin structure and mechanism: conformational changes on oxidation of the active-site sulfhydryls to a disulfide. Structure. 1995;3(3):239-243. [CrossRef]
- Perkins A, Nelson KJ, Parsonage D, Poole LB, Karplus PA. Peroxiredoxins: guardians against oxidative stress and modulators of peroxide signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 2015;40(8):435-445. [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara E, Masaki S, Matsuo Y, Chen Z, Tian H, Yodoi J. Thioredoxin/Txnip: redoxisome, as a redox switch for the pathogenesis of diseases. Front Immunol. 2014;4:514. Published 2014 Jan 9. [CrossRef]
- Borowiec AM, Właszczuk A, Olakowska E, Lewin-Kowalik J. TXNIP inhibition in the treatment of diabetes. Verapamil as a novel therapeutic modality in diabetic patients. Med Pharm Rep. 2022;95(3):243-250. [CrossRef]
- Medinas DB, Rozas P, Hetz C. Critical roles of protein disulfide isomerases in balancing proteostasis in the nervous system. J Biol Chem. 2022;298(7):102087. [CrossRef]
- Wang L, Wang CC. Oxidative protein folding fidelity and redoxtasis in the endoplasmic reticulum. Trends Biochem Sci. 2023;48(1):40-52. [CrossRef]
- Jiménez A, Zu W, Rawe VY, et al. Spermatocyte/spermatid-specific thioredoxin-3, a novel Golgi apparatus-associated thioredoxin, is a specific marker of aberrant spermatogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(33):34971-34982. [CrossRef]
- Ouyang Y, Peng Y, Li J, Holmgren A, Lu J. Modulation of thiol-dependent redox system by metal ions via thioredoxin and glutaredoxin systems. Metallomics. 2018;10(2):218-228. [CrossRef]
- Hasan AA, Kalinina E, Tatarskiy V, Shtil A. The Thioredoxin System of Mammalian Cells and Its Modulators. Biomedicines. 2022;10(7):1757. Published 2022 Jul 21. [CrossRef]
- Spyrou G, Enmark E, Miranda-Vizuete A, Gustafsson J. Cloning and expression of a novel mammalian thioredoxin. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(5):2936-2941. [CrossRef]
- Lowes DA, Galley HF. Mitochondrial protection by the thioredoxin-2 and glutathione systems in an in vitro endothelial model of sepsis. Biochem J. 2011;436(1):123-132. [CrossRef]
- Tanaka T, Hosoi F, Yamaguchi-Iwai Y, et al. Thioredoxin-2 (TRX-2) is an essential gene regulating mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. EMBO J. 2002;21(7):1695-1703. [CrossRef]
- Zhang R, Al-Lamki R, Bai L, et al. Thioredoxin-2 inhibits mitochondria-located ASK1-mediated apoptosis in a JNK-independent manner. Circ Res. 2004;94(11):1483-1491. [CrossRef]
- Damdimopoulos AE, Miranda-Vizuete A, Pelto-Huikko M, Gustafsson JA, Spyrou G. Human mitochondrial thioredoxin. Involvement in mitochondrial membrane potential and cell death. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(36):33249-33257. [CrossRef]
- Nonn L, Williams RR, Erickson RP, Powis G. The absence of mitochondrial thioredoxin 2 causes massive apoptosis, exencephaly, and early embryonic lethality in homozygous mice. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23(3):916-922. [CrossRef]
- Monteiro HP, Ogata FT, Stern A. Thioredoxin promotes survival signaling events under nitrosative/oxidative stress associated with cancer development. Biomed J. 2017;40(4):189-199. [CrossRef]
- Mougiakakos D, Johansson CC, Jitschin R, Böttcher M, Kiessling R. Increased thioredoxin-1 production in human naturally occurring regulatory T cells confers enhanced tolerance to oxidative stress. Blood. 2011;117(3):857-861. [CrossRef]
- Bertini R, Howard OM, Dong HF, et al. Thioredoxin, a redox enzyme released in infection and inflammation, is a unique chemoattractant for neutrophils, monocytes, and T cells. J Exp Med. 1999;189(11):1783-1789. [CrossRef]
- Rubartelli A, Bajetto A, Allavena G, Wollman E, Sitia R. Secretion of thioredoxin by normal and neoplastic cells through a leaderless secretory pathway. J Biol Chem. 1992;267(34):24161-24164.
- Arnér ES, Holmgren A. Physiological functions of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. Eur J Biochem. 2000;267(20):6102-6109. [CrossRef]
- Holmgren, A. Thioredoxin. 6. The amino acid sequence of the protein from escherichia coli B. Eur J Biochem. 1968;6(4):475-484. [CrossRef]
- Andoh T, Chock PB, Chiueh CC. The roles of thioredoxin in protection against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(12):9655-9660. [CrossRef]
- Haendeler J, Hoffmann J, Tischler V, Berk BC, Zeiher AM, Dimmeler S. Redox regulatory and anti-apoptotic functions of thioredoxin depend on S-nitrosylation at cysteine 69. Nat Cell Biol. 2002;4(10):743-749. [CrossRef]
- Tao L, Gao E, Bryan NS, et al. Cardioprotective effects of thioredoxin in myocardial ischemia and reperfusion: role of S-nitrosation [corrected] [published correction appears in Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Sep 14;101(37):13694]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(31):11471-11476. [CrossRef]
- Weichsel A, Brailey JL, Montfort WR. Buried S-nitrosocysteine revealed in crystal structures of human thioredoxin. Biochemistry. 2007;46(5):1219-1227. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y, Liu T, Wu C, Li H. A strategy for direct identification of protein S-nitrosylation sites by quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2008;19(9):1353-1360. [CrossRef]
- Wu C, Liu T, Chen W, et al. Redox regulatory mechanism of transnitrosylation by thioredoxin. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010;9(10):2262-2275. [CrossRef]
- Casagrande S, Bonetto V, Fratelli M, et al. Glutathionylation of human thioredoxin: a possible crosstalk between the glutathione and thioredoxin systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(15):9745-9749. [CrossRef]
- Go YM, Halvey PJ, Hansen JM, Reed M, Pohl J, Jones DP. Reactive aldehyde modification of thioredoxin-1 activates early steps of inflammation and cell adhesion. Am J Pathol. 2007;171(5):1670-1681. [CrossRef]
- Kim MK, Zhao L, Jeong S, et al. Structural and Biochemical Characterization of Thioredoxin-2 from Deinococcus radiodurans. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10(11):1843. Published 2021 Nov 20. [CrossRef]
- Lee S, Kim SM, Lee RT. Thioredoxin and thioredoxin target proteins: from molecular mechanisms to functional significance. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;18(10):1165-1207. [CrossRef]
- Ueno M, Masutani H, Arai RJ, et al. Thioredoxin-dependent redox regulation of p53-mediated p21 activation. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(50):35809-35815. [CrossRef]
- Liu Y, Min W. Thioredoxin promotes ASK1 ubiquitination and degradation to inhibit ASK1-mediated apoptosis in a redox activity-independent manner. Circ Res. 2002;90(12):1259-1266. [CrossRef]
- Hwang J, Suh HW, Jeon YH, et al. The structural basis for the negative regulation of thioredoxin by thioredoxin-interacting protein. Nat Commun. 2014;5:2958. [CrossRef]
- Akterin S, Cowburn RF, Miranda-Vizuete A, et al. Involvement of glutaredoxin-1 and thioredoxin-1 in beta-amyloid toxicity and Alzheimer's disease. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13(9):1454-1465. [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H. Extracellular functions of thioredoxin. Novartis Found Symp. 2008;291:184-224. [CrossRef]
- Saitoh M, Nishitoh H, Fujii M, et al. Mammalian thioredoxin is a direct inhibitor of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase (ASK) 1. EMBO J. 1998;17(9):2596-2606. [CrossRef]
- Chae JS, Gil Hwang S, Lim DS, Choi EJ. Thioredoxin-1 functions as a molecular switch regulating the oxidative stress-induced activation of MST1. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012;53(12):2335-2343. [CrossRef]
- Islam MI, Nagakannan P, Ogungbola O, Djordjevic J, Albensi BC, Eftekharpour E. Thioredoxin system as a gatekeeper in caspase-6 activation and nuclear lamina integrity: Implications for Alzheimer's disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;134:567-580. [CrossRef]
- Mitchell DA, Morton SU, Fernhoff NB, Marletta MA. Thioredoxin is required for S-nitrosation of procaspase-3 and the inhibition of apoptosis in Jurkat cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(28):11609-11614. [CrossRef]
- Oka SI, Chin A, Park JY, et al. Thioredoxin-1 maintains mitochondrial function via mechanistic target of rapamycin signalling in the heart. Cardiovasc Res. 2020;116(10):1742-1755. [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan N, Oka SI, Nah J, et al. Thioredoxin 1 promotes autophagy through transnitrosylation of Atg7 during myocardial ischemia. J Clin Invest. 2023;133(3):e162326. Published 2023 Feb 1. [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pérez ME, Zaffagnini M, Marchand CH, Crespo JL, Lemaire SD. The yeast autophagy protease Atg4 is regulated by thioredoxin. Autophagy. 2014;10(11):1953-1964. [CrossRef]
- Hu J, Liu J, Chen S, et al. Thioredoxin-1 regulates the autophagy induced by oxidative stress through LC3-II in human lens epithelial cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2023;50(6):476-485. [CrossRef]
- Wang X, Ling S, Zhao D, et al. Redox regulation of actin by thioredoxin-1 is mediated by the interaction of the proteins via cysteine 62. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2010;13(5):565-573. [CrossRef]
- Landino LM, Iwig JS, Kennett KL, Moynihan KL. Repair of peroxynitrite damage to tubulin by the thioredoxin reductase system. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004;36(4):497-506. [CrossRef]
- Morinaka A, Yamada M, Itofusa R, et al. Thioredoxin mediates oxidation-dependent phosphorylation of CRMP2 and growth cone collapse. Sci Signal. 2011;4(170):ra26. Published 2011 Apr 26. [CrossRef]
- Bai J, Nakamura H, Kwon YW, et al. Critical roles of thioredoxin in nerve growth factor-mediated signal transduction and neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells. J Neurosci. 2003;23(2):503-509. [CrossRef]
- Sartelet H, Rougemont AL, Fabre M, et al. Activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase/AKT pathway in neuroblastoma and its regulation by thioredoxin 1. Hum Pathol. 2011;42(11):1727-1739. [CrossRef]
- Chen B, Guan D, Cui ZJ, Wang X, Shen X. Thioredoxin 1 downregulates MCP-1 secretion and expression in human endothelial cells by suppressing nuclear translocation of activator protein 1 and redox factor-1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010;298(5):C1170-C1179. [CrossRef]
- Schenk H, Klein M, Erdbrügger W, Dröge W, Schulze-Osthoff K. Distinct effects of thioredoxin and antioxidants on the activation of transcription factors NF-kappa B and AP-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91(5):1672-1676. [CrossRef]
- Naranjo-Suarez S, Carlson BA, Tobe R, et al. Regulation of HIF-1α activity by overexpression of thioredoxin is independent of thioredoxin reductase status. Mol Cells. 2013;36(2):151-157. [CrossRef]
- Guo Y, Einhorn L, Kelley M, et al. Redox regulation of the embryonic stem cell transcription factor oct-4 by thioredoxin. Stem Cells. 2004;22(3):259-264. [CrossRef]
- Ago T, Liu T, Zhai P, et al. A redox-dependent pathway for regulating class II HDACs and cardiac hypertrophy. Cell. 2008;133(6):978-993. [CrossRef]
- Hansen JM, Watson WH, Jones DP. Compartmentation of Nrf-2 redox control: regulation of cytoplasmic activation by glutathione and DNA binding by thioredoxin-1. Toxicol Sci. 2004;82(1):308-317. [CrossRef]
- Makino Y, Yoshikawa N, Okamoto K, et al. Direct association with thioredoxin allows redox regulation of glucocorticoid receptor function. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(5):3182-3188. [CrossRef]
- Rao AK, Ziegler YS, McLeod IX, Yates JR, Nardulli AM. Thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase influence estrogen receptor alpha-mediated gene expression in human breast cancer cells. J Mol Endocrinol. 2009;43(6):251-261. [CrossRef]
- King BC, Nowakowska J, Karsten CM, Köhl J, Renström E, Blom AM. Truncated and full-length thioredoxin-1 have opposing activating and inhibitory properties for human complement with relevance to endothelial surfaces. J Immunol. 2012;188(8):4103-4112. [CrossRef]
- Nordberg J, Arnér ES. Reactive oxygen species, antioxidants, and the mammalian thioredoxin system. Free Radic Biol Med. 2001;31(11):1287-1312. [CrossRef]
- Prigge JR, Coppo L, Martin SS, et al. Hepatocyte Hyperproliferation upon Liver-Specific Co-disruption of Thioredoxin-1, Thioredoxin Reductase-1, and Glutathione Reductase. Cell Rep. 2017;19(13):2771-2781. [CrossRef]
- Du Y, Zhang H, Lu J, Holmgren A. Glutathione and glutaredoxin act as a backup of human thioredoxin reductase 1 to reduce thioredoxin 1 preventing cell death by aurothioglucose. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(45):38210-38219. [CrossRef]
- Nagakannan P, Iqbal MA, Yeung A, et al. Perturbation of redox balance after thioredoxin reductase deficiency interrupts autophagy-lysosomal degradation pathway and enhances cell death in nutritionally stressed SH-SY5Y cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016;101:53-70. [CrossRef]
- Shcholok T, Eftekharpour E. Cre-recombinase systems for induction of neuron-specific knockout models: a guide for biomedical researchers. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(2):273-279. [CrossRef]
- Jakupoglu C, Przemeck GK, Schneider M, et al. Cytoplasmic thioredoxin reductase is essential for embryogenesis but dispensable for cardiac development. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25(5):1980-1988. [CrossRef]
- Jabbar S, Mathews P, Wang X, et al. Thioredoxin-1 regulates self-renewal and differentiation of murine hematopoietic stem cells through p53 tumor suppressor. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2022;11(1):83. Published 2022 Oct 31. [CrossRef]
- Das, KC. Thioredoxin-deficient mice, a novel phenotype sensitive to ambient air and hypersensitive to hyperoxia-induced lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015;308(5):L429-L442. [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan N, Oka S, Sadoshima J. Modulation of signaling mechanisms in the heart by thioredoxin 1. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017;109:125-131. [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto M, Yang G, Hong C, et al. Inhibition of endogenous thioredoxin in the heart increases oxidative stress and cardiac hypertrophy. J Clin Invest. 2003;112(9):1395-1406. [CrossRef]
- Mutlak M, Kehat I. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 as regulators of cardiac hypertrophy. Front Pharmacol. 2015;6:149. Published 2015 Jul 24. [CrossRef]
- Chandra M, Escalante-Alcalde D, Bhuiyan MS, et al. Cardiac-specific inactivation of LPP3 in mice leads to myocardial dysfunction and heart failure. Redox Biol. 2018;14:261-271. [CrossRef]
- Mello T, Zanieri F, Ceni E, Galli A. Oxidative Stress in the Healthy and Wounded Hepatocyte: A Cellular Organelles Perspective. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:8327410. [CrossRef]
- Suvorova ES, Lucas O, Weisend CM, et al. Cytoprotective Nrf2 pathway is induced in chronically txnrd 1-deficient hepatocytes. PLoS One. 2009;4(7):e6158. Published 2009 Jul 7. [CrossRef]
- Rollins MF, van der Heide DM, Weisend CM, et al. Hepatocytes lacking thioredoxin reductase 1 have normal replicative potential during development and regeneration. J Cell Sci. 2010;123(Pt 14):2402-2412. [CrossRef]
- Iverson SV, Eriksson S, Xu J, et al. A Txnrd1-dependent metabolic switch alters hepatic lipogenesis, glycogen storage, and detoxification. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013;63:369-380. [CrossRef]
- Shearn CT, Anderson AL, Miller CG, et al. Thioredoxin reductase 1 regulates hepatic inflammation and macrophage activation during acute cholestatic liver injury. Hepatol Commun. 2023;7(1):e0020. Published 2023 Jan 10. [CrossRef]
- Lenzen, S. Chemistry and biology of reactive species with special reference to the antioxidative defence status in pancreatic β-cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017;1861(8):1929-1942. [CrossRef]
- Ghiselli A, Laurenti O, De Mattia G, Maiani G, Ferro-Luzzi A. Salicylate hydroxylation as an early marker of in vivo oxidative stress in diabetic patients. Free Radic Biol Med. 1992;13(6):621-626. [CrossRef]
- Gopaul NK, Anggård EE, Mallet AI, Betteridge DJ, Wolff SP, Nourooz-Zadeh J. Plasma 8-epi-PGF2 alpha levels are elevated in individuals with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. FEBS Lett. 1995;368(2):225-229. [CrossRef]
- Nourooz-Zadeh J, Tajaddini-Sarmadi J, McCarthy S, Betteridge DJ, Wolff SP. Elevated levels of authentic plasma hydroperoxides in NIDDM. Diabetes. 1995;44(9):1054-1058. [CrossRef]
- Ihara Y, Toyokuni S, Uchida K, et al. Hyperglycemia causes oxidative stress in pancreatic beta-cells of GK rats, a model of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 1999;48(4):927-932. [CrossRef]
- Shin CS, Moon BS, Park KS, et al. Serum 8-hydroxy-guanine levels are increased in diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2001;24(4):733-737. [CrossRef]
- Sakuraba H, Mizukami H, Yagihashi N, Wada R, Hanyu C, Yagihashi S. Reduced beta-cell mass and expression of oxidative stress-related DNA damage in the islet of Japanese Type II diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 2002;45(1):85-96. [CrossRef]
- Lenzen S, Drinkgern J, Tiedge M. Low antioxidant enzyme gene expression in pancreatic islets compared with various other mouse tissues. Free Radic Biol Med. 1996;20(3):463-466. [CrossRef]
- Lenzen, S. Oxidative stress: the vulnerable beta-cell. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008;36(Pt 3):343-347. [CrossRef]
- Minn AH, Hafele C, Shalev A. Thioredoxin-interacting protein is stimulated by glucose through a carbohydrate response element and induces beta-cell apoptosis. Endocrinology. 2005;146(5):2397-2405. [CrossRef]
- Stancill JS, Broniowska KA, Oleson BJ, Naatz A, Corbett JA. Pancreatic β-cells detoxify H2O2 through the peroxiredoxin/thioredoxin antioxidant system. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(13):4843-4853. [CrossRef]
- Stancill JS, Hansen PA, Mathison AJ, Schmidt EE, Corbett JA. Deletion of Thioredoxin Reductase Disrupts Redox Homeostasis and Impairs β-Cell Function. Function (Oxf). 2022;3(4):zqac034. Published 2022 Jul 4. [CrossRef]
- Oka S, Yoshihara E, Bizen-Abe A, et al. Thioredoxin binding protein-2/thioredoxin-interacting protein is a critical regulator of insulin secretion and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor function. Endocrinology. 2009;150(3):1225-1234. [CrossRef]
- Buck MD, O'Sullivan D, Pearce EL. T cell metabolism drives immunity. J Exp Med. 2015;212(9):1345-1360. [CrossRef]
- Wang R, Dillon CP, Shi LZ, et al. The transcription factor Myc controls metabolic reprogramming upon T lymphocyte activation. Immunity. 2011;35(6):871-882. [CrossRef]
- Muri J, Heer S, Matsushita M, et al. The thioredoxin-1 system is essential for fueling DNA synthesis during T-cell metabolic reprogramming and proliferation. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1851. Published 2018 May 10. [CrossRef]
- Holmgren A, Sengupta R. The use of thiols by ribonucleotide reductase. Free Radic Biol Med. 2010;49(11):1617-1628. [CrossRef]
- Uttara B, Singh AV, Zamboni P, Mahajan RT. Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: a review of upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2009;7(1):65-74. [CrossRef]
- Dringen, R. Metabolism and functions of glutathione in brain. Prog Neurobiol. 2000;62(6):649-671. [CrossRef]
- Lin MT, Beal MF. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature. 2006;443(7113):787-795. [CrossRef]
- Elfawy HA, Das B. Crosstalk between mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and age related neurodegenerative disease: Etiologies and therapeutic strategies. Life Sci. 2019;218:165-184. [CrossRef]
- Islam MI, Nagakannan P, Shcholok T, et al. Regulatory role of cathepsin L in induction of nuclear laminopathy in Alzheimer's disease. Aging Cell. 2022;21(1):e13531. [CrossRef]
- Ohmori I, Ouchida M, Imai H, Ishida S, Toyokuni S, Mashimo T. Thioredoxin deficiency increases oxidative stress and causes bilateral symmetrical degeneration in rat midbrain. Neurobiol Dis. 2022;175:105921. [CrossRef]
- Ohmori I, Ouchida M, Shinohara M, Kobayashi K, Ishida S, Mashimo T. Novel animal model of combined generalized and focal epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2022;63(7):e80-e85. [CrossRef]
- Mashimo T, Yanagihara K, Tokuda S, et al. An ENU-induced mutant archive for gene targeting in rats. Nat Genet. 2008;40(5):514-515. [CrossRef]
- Chatzikonstantinou, A. Epilepsy and the hippocampus. Front Neurol Neurosci. 2014;34:121-142. [CrossRef]
- Aksenov MY, Aksenova MV, Butterfield DA, Geddes JW, Markesbery WR. Protein oxidation in the brain in Alzheimer's disease. Neuroscience. 2001;103(2):373-383. [CrossRef]
- Soerensen J, Jakupoglu C, Beck H, et al. The role of thioredoxin reductases in brain development. PLoS One. 2008;3(3):e1813. Published 2008 Mar 19. [CrossRef]
- Drechsel DA, Patel M. Respiration-dependent H2O2 removal in brain mitochondria via the thioredoxin/peroxiredoxin system. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(36):27850-27858. [CrossRef]
 |
| Subcellular localization | Cell Function | Target | Cell type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cytoplasm | Antioxidative defence | Oxidized proteins |
All | Bertini et al. [20], Ueno et al. [34], Liu et al. [35], Hwang et al. [36], Akterin et al. [37], Nakamura et al. [38], Tao et al. [25], Arner et al. [22] |
| Apoptosis | ASK-1 | Mv1Lu (Mink Lung Epithelial Cells), L929 (mouse fibroblast cell line) and 293 (mouse fibroblast cell line) | Saitoh et al. [39] | |
| MST-1 | MEF (murine embryonic fibroblasts) | Chae et al. [40] | ||
| Casp-6 | SH-SY5Y (human neuroblastoma cells) | Islam et al. [41] | ||
| Casp-3 | Jurkat (immortalized human T-lymphocytes) | Mitchell et al. [42] | ||
| Autophagy | mTOR | Rat cardiomyocytes | Oka et al. [43] | |
| ATG7 | Rat cardiomyocytes | Nagarajan et al. [44] | ||
| ATG4 | Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Perez et al. [45] | ||
| LC III-B | HLE-B3 (human lens epithelial cells) | Hu et al. [46] | ||
| Cytoskeleton organization | Actin | SH-SY5Y (human neuroblastoma cells) | Wang et al. [47] | |
| Tubulin | Purified porcine tubulin | Landino et al. [48] | ||
| CRMP-2 | Embryonic DRG neurons from Sprague-Dawley rats | Morinaka et al. [49] | ||
| NGF | PC-12 (adrenal phaeochromocytoma cells) | Bai et al. [50] | ||
| Signalling transduction | AKT and PTEN | Neuroblastic neoplasms, and neuroblastoma cell lines | Sartelet et al. [51] | |
| Inflammation | Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) | Trx-1 Overexpressing/ knockdown EA.hy 926 and bovine aortic endothelial cells | Chen et al. [52] | |
| Immunomodulatory | Regulatory T-cells | Tregs (regulatory T-lymphocytes) | Mougiakakos et al. [19] | |
| Nucleus | Gene regulation | NFk-B, AP-1, and Ref-1 | L929 (mouse fibroblast cell line), HeLa (cervical cancer cells) COS-7 (African green monkey kidney fibroblast-like cells) | Chen et al., [52] Schenk et al. [53] |
| HIF-1a | HeLa (cervical cancer cells) | Naranjo-Suarez et al. [54] | ||
| Oct-4 | Embryonic stem cells | Guo et al. [55] | ||
| HDAC4 | Cardiac myocytes | Ago et al. [56] | ||
| DNA-binding | NRF-2 | HeLa (cervical cancer cells) | Hansen et al. [57] | |
| Transportation to nucleus | Glucocorticoid receptor | COS7 and CV-1 (African green monkey kidney fibroblast-like cells), HeLa (cervical cancer cells) | Makino et al. [58] | |
| Estrogen receptor | MCF-7 (breast cancer cells) | Rao et al. [59] | ||
| Cell membrane | Immunomodulatory | Complement deposition | HUVEC (human umbilical vein endothelial cells) | King et al. [60] |
| Extracellular matrix | Chemokine-like | Chemoattraction | human monocytes, PMNs, leucocytes | Bertini et al. [20] Nordberg et al. [61] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





