1. Introduction
Transarterial radioembolization (TARE) is a minimally invasive procedure that uses radioactive microspheres to deliver targeted radiation therapy to tumors in the liver [
1]. The radiolabelling nuclide of the microspheres is Yttrium-90 (90Y) which is a beta-emitter (2.280 MeV (Emax)) with a half-life of 64.1 hours, decaying to zirconium-90, a reasonably high linear energy transfer (LET) and an approximate emission range of 5 mm [
2]. 90Y-loaded microspheres are injected into the hepatic artery, the main blood vessel that supplies blood to the liver. This allows the microspheres to be delivered directly to the tumor, with little exposure to surrounding healthy tissues. This is because β radiation has a short penetration range, meaning that it only travels a short distance before it is absorbed by tissue [
3].
There has been a growing usage of TARE by means of
90Y glass or resin microspheres in patients affected by hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) or unresectable colorectal cancer (CRC) liver metastases in the last decade [
4]. Glass microspheres offer the advantage of delivering a specific radiation dose with a reduced number of particles, which can potentially minimize embolic effects. Therefore, they are considered a more appropriate option in situations where achieving early stasis or addressing reflux is a concern, especially in cases of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein invasion and for radiation segmentectomy. In contrast, resin microspheres have a lower activity per particle, necessitating a higher number of particles to achieve the same radiation dose. As a result, resin microspheres are typically preferred for larger tumors and those with high arterial flow [
5].
While TARE proved to be an effective first- or second-line treatment in patients with advanced HCC [
6], the Resin trial demonstrated in a multicentre cohort of 498 patients that TARE is an effective second-line treatment for patients with CRC liver metastases [
7]. Indeed, liver is thought to be the predominant site of metastatic dissemination for CRC in approximately 60% of people [
8]. Surgical removal of CRC liver metastases has shown promising 5-year survival rates of 20-70%, making it the preferred treatment option for suitable patients. However, due to technical constraints and the severity of the disease, a significant portion (70-80%) of individuals with extensive liver metastases are unable to undergo surgery [
9].
There is expanding evidence that TARE provides a longer time to progression compared to transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) in patients with HCC [
8]. Similarly, in patients with CRC liver metastases, according to the results of the EPOCH trial including 428 patients, TARE reduces the risk of disease progression or death compared to chemotherapy alone [
8]. Although there is mounting evidence with regards to the beneficial effect of TARE in HCC and CRC liver metastases, there are still limited medical centres with trained personnel to perform TARE.
The aim of this study was investigate the influence of additional treatments, injected activity, mean dose delivered to the tumor on OS of patients treated with 90Y microspheres.
2. Materials and Methods
Patients
The database of our centre was interrogated to retrieve patients who had undergone TARE with 90Y glass or resin microspheres. The eligibility criteria for enrolment to the study were: age ≥ 18 years, histologically proven or imaging-based diagnosis of unresectable HCC or CRC liver metastasis; life expectancy > 6 months; preserved liver function with Child–Pugh Class A or B; Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status ≤ 2; bilirubin < 2.0 mg/dL, albumin > 2.0 g/dL; availability of pre-treatment hepatic angioscintigraphy with 99mTc-macroaggregated albumin (MAA); a post-radioembolization 90Y PET/CT scan carried out within 12 hours from TARE; information on additional treatment beyond TARE and a minimum follow-up of 24 months. Patient with CRC liver metastases had undergone surgical removal of the primary tumor.
Main exclusion criteria included previous radiotherapy to the liver, ascites, unresolved toxicity from first-line therapy, extra-hepatic metastases, or contraindications to angiography. The following patient information were also retrieved from the hospital database: sex; age; administered activity and mean dose to the tumor at of 90Y-loaded microspheres; date of cancer-specific death.
Ethical approval for conducting the study was waived by the local Ethics Committee in view of the retrospective nature of the study (n.1007, 31st May 2023).
Pre-Treatment Imaging
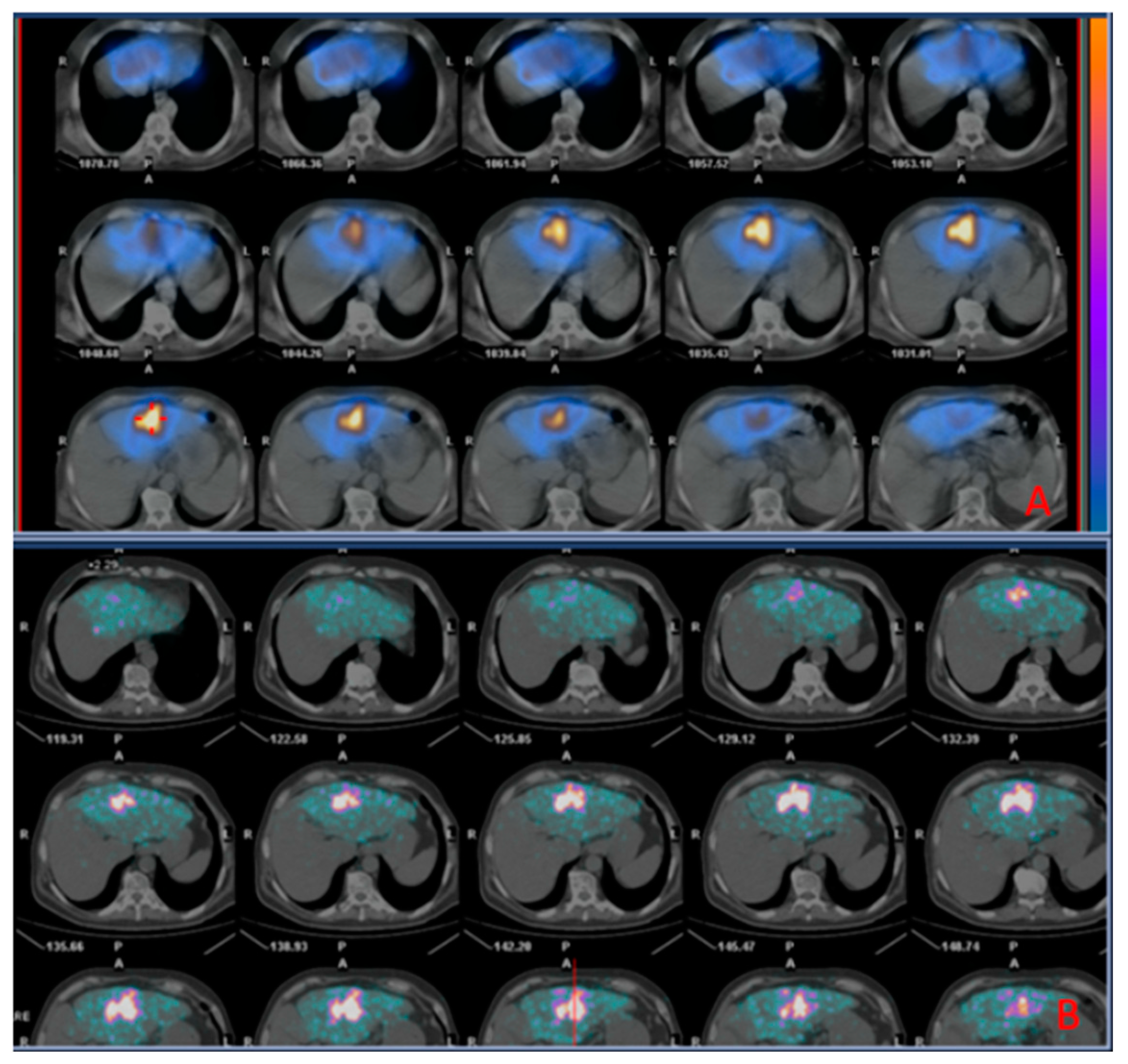
Before TARE, all patients underwent at our centre an angiography of the hepatic vasculature for treatment planning and a liver angioscintigraphy with 99mTc-MAA (fixed dose: 185 MBq) to evaluate the percentage of injected activity shunted to the lungs and foresee the distribution of the 90Y-TARE spheres. These procedures were performed in a fully equipped Innova angiography suite (General Electric Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI).
The 99mTc-MAA scan was acquired on a dual-head gamma camera (Infinia; General Electric Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI, USA) using a high-resolution, low-energy collimator. Whole-body anterior and posterior projections of the superior abdominal regions were obtained using 120-second planar pictures, with the energy window set at 140 ± 10 keV. Ninety-nine step-and-shoot mode projections were recorded in 360 degrees (10 s per step) for the SPECT/CT using a 256 × 256 matrix. Each 99mTc-MAA scan was reviewed jointly by two board certified nuclear medicine physicians, both with >5 years of experience on a XELERIS-1.123 GE workstation (GE medical systems, Milwaukee, USA). The CT and 99mTc-MAA SPECT/CT scans were analysed and compared jointly by an interventional radiologist and a nuclear medicine physician to evaluate the uptake of 9mTc MAA within the tumor area (CT-MAA agreement) and classified as positive or negative for presence of shunts to the lungs. In the case of no evidence of hepato-pulmonary shunts, patients were submitted to 90Y-TARE within 21 days from the 99mTc-MAA scan.
90Y-TARE Procedure
Pre-procedural exams to complete staging included baseline imaging studies: liver sonography, clinical and laboratory examination, contrast-enhanced CT (ce-CT), and [18F]FDG PET/CT. After selective catheterization of the right/left hepatic artery to assess the vascular, tumor anatomy and blood-flow, the patient was administered with either 90Y- resin spheres (SIR-Spheres; Sirtex Medical, Sydney, Australia) or 90Y-glass microspheres (Therasphere; Boston Scientific, USA). The choice of the radiopharmaceutical between 90Y- resin spheres and 90Y-glass microspheres was made based on a multidisciplinary discussion among the nuclear medicine physician, the interventional radiologist and the physicist.
The prescribed 90Y activity was determined on the basis of a dosimetric estimation on a commercial software as the patient-specific activity. Administered activity and mean dose to the tumor were calculated in order to achieve a desirable minimal dose of 120 Gy.
Post-Treatment Imaging
After 90Y-TARE procedure, all subjects underwent a 90Y-PET/CT scan within 4-12 hours to assess the microsphere distribution pattern. The PET/CT scan was carried out using a PET/CT scanner (GE Discovery STE, GE Healthcare). The first procedure was a CT scan (140 kVp, 30-300 mA, 3.75-mm slice thickness). After that, an OSEM algorithm was integrated to reconstruct the PET image (15 min per bed position).
The 99mTc-MAA SPECT/CT and 90Y PECT/CT scans were compared to evaluate the overlap of the distribution between MAA particles and microspheres.
Statistics
OS of each patient was retrieved based on the time interccured from the date of TARE and the date of death at the last available follow-up. OS of the different groups of patients, based on pathology (HCC patients vs. patients with CRC liver metastases) and additional treatment (patients receiving only TARE and patients receiving TARE and additional treatments) were compared (p<0.05). A bivariate correlation (p<0.05) was used to investigate the association between injected activity and OS, and between mean dose delivered to the tumor and OS. Statistics were performed using MedCalc 11.3.8.0 (MedCalc Software, Mariakerke, Belgium).
3. Results
From a total of 150 patients who had undergone TARE, 39 patients with complete datasets (liver angioscintigraphy, post-radioembolization 90Y PET/CT scan and clinical information listed in the eligibility criteria) were retrieved (Sex: 27 M, 12 F; mean age: 61.26 ± 14.95 years; 23 with unresectabile HCC and 16 with liver metastases from CRC).
The median follow-up from TARE to the last available record (April 2023) was 69 months (range: 39-91 months). Mean administered activity was 2.2 ± 0.9 GBq; mean dose to the tumor was 282.68 Gy. Ten of 16 patients with liver metastases from CRC had additional treatments with Sorafenib (n=7), or Regorafenib (n=2) or both (n=1).
Patients with HCC demonstrated a significantly longer OS than those with liver metastasis from CRC (22.66±19.11 vs. 10.41±8.75 months; p=0.022).
Patients with HCC
Among patients with HCC, subjects receiving TARE and additional treatment (n=8) demonstrated a trend for longer OS than HCC patients receiving only TARE (n=15; 31.07±18.20 months vs. 18.20±18.66; p=0.13); in the whole group of HCC patients there was a trend towards a direct correlation between mean dose to the tumor and OS (R=0.45, p=0.118).
4. Discussion
TARE is an effective therapy that can be used to shrink tumors before surgery or liver transplantation. It is also a bridging and downstaging therapy, meaning that it can help patients who are not yet eligible for surgery or transplantation to become eligible [
10].
TARE has been traditionally used to treat advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), but recent improvements in the technique have made it effective for treating solitary HCC as well. Furthermore, it is a safe procedure when performed in the context of an expert multidisciplinary team. Alternative embolization treatments include conventional transarterial chemoembolization (cTACE), and drug-eluting beads (DEB-TACE) [
8]. TARE has significantly less complications than conventional transarterial chemoembolization (cTACE), drug-eluting beads (DEB-TACE) in patients with HCC [
11].
In our center experience, patients undergoing TARE with either resin- or glass-
90Y-spheres showed an OS comparable with those reported in literature (22.66±19.11 for patients with HCC and 10.41±8.75 months for patients with liver metastases from CRC). Interestingly, the effect of additional treatments resulted more beneficial in the group of patients with liver metastases from CRC (23.50±19.76 months vs. 8.54±5.31 not receiving a concomitant pharmacological treatment). In keeping with the literature, in the group of patients with liver metastases from CRC there was a correlation between injected activity and OS and between mean activity reaching the tumor and OS [
12].
The efficacy of TARE as second-line treatment in chemorefractory hepatic metastases from CRC has been widely reported [
4]. The additional treatments in our patient cohort included Sorafenib, Regorafenib or combination of both. Also in our study patients with CRC liver metastases presented a longer survival in presence of additional treatments.
Conversely, a significant improvement of OS and a correlation between injected activity and OS and between mean activity and OS were not proved in patients with HCC. Given the existence of a statistical trend, we suppose the lack of statistical significance may be attributed due to the limited number of the patient sample.
Person-related predictors of unfavourable outcome in patients undergoing TARE include older age (>70 years) [
13,
14], male sex [
15], higher tumor grade, size, and stage, lack of treatment with surgery or systemic therapy, and presence of lymphatic or vascular invasion [
16], Child-Pugh score (CPS: B or C vs. A), Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance status (ECOG-PS: 2 or 1 vs. 0) [
17,
18]. Other factors that positively influence survival in patients receiving TARE are administered activity and mean dose to the tumor [
19]. All these variables might have influenced the individual survival in our patient cohort, but in order to assess their real importance they would need to be tested in studies with larger patient samples.
5. Conclusions
Patients with HCC receiving TARE achieved a longer OS than those with liver metastases from colon cancer. Additional treatments and increasing injected activity and mean dose to the tumor may be beneficial for outcome, especially in patients with liver metastases from CRC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.Q. and D.S.; methodology, F.D.; software, F.D.; validation, A.C., F.V. and G.M.; formal analysis, N.Q.; investigation, S.I.; resources, A.C.; data curation, V.P. and E.M.; writing—original draft preparation, N.Q.; writing—review and editing, A.C.; visualization, M.R.B.; supervision, M.G.B, E.B. and F.B.; project administration, G.F.; funding acquisition, F.L and A.M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical approval for conducting the study was waived by the local Ethics Committee in view of the retrospective nature of the study. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from the patients to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
Data can be provided upon reasonable request bona fide.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Mikell, J.K.; Dewaraja, Y.K.; Owen, D. Transarterial radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic metastases: Clinical aspects and dosimetry models. Seminars in radiation oncology 2020, 30, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgouros, G.; Bodei, L.; McDevitt, M.R.; Nedrow, J.R. Radiopharmaceutical therapy in cancer: Clinical advances and challenges. Nature reviews. Drug discovery 2020, 19, 589–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casáns-Tormo, I.; Guijarro-Rosaleny, J.; Lluch-García, P.; Rodríguez-Parra, H.; Roselló-Keränen, S.; Asensio-Valero, L. Evaluation of results after 112 radioembolizations with 90y-microspheres. Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition) 2023, 42, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmons, E.C.; Bishay, S.; Du, L.; Krebs, H.; Gandhi, R.T.; Collins, Z.S.; O'Hara, R.; Akhter, N.M.; Wang, E.A.; Grilli, C.; et al. Survival and toxicities after (90)y transarterial radioembolization of metastatic colorectal cancer in the resin registry. Radiology 2022, 305, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boas, F.E.; Bodei, L.; Sofocleous, C.T. Radioembolization of colorectal liver metastases: Indications, technique, and outcomes. J Nucl Med 2017, 58, 104s–111s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangro, B.; Iñarrairaegui, M.; Bilbao, J.I. Radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of hepatology 2012, 56, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, V. Transarterial radioembolization for colorectal cancer liver metastases is effective as a second-line treatment. Radiology: Imaging Cancer 2023, 5, e239003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulcahy, M.F.; Mahvash, A.; Pracht, M.; Montazeri, A.H.; Bandula, S.; Martin, R.C.G., 2nd; Herrmann, K.; Brown, E.; Zuckerman, D.; Wilson, G.; et al. Radioembolization with chemotherapy for colorectal liver metastases: A randomized, open-label, international, multicenter, phase iii trial. J Clin Oncol 2021, 39, 3897–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeyarajah, D.R.; Doyle, M.B.M.; Espat, N.J.; Hansen, P.D.; Iannitti, D.A.; Kim, J.; Thambi-Pillai, T.; Visser, B.C. Role of yttrium-90 selective internal radiation therapy in the treatment of liver-dominant metastatic colorectal cancer: An evidence-based expert consensus algorithm. Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology 2020, 11, 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yue, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Cai, P. Imaging evaluation following transarterial radioembolization with yttrium-90 microspheres downstaging hepatocellular carcinoma: The first case in china. Quant Imaging Med Surg 2023, 13, 2744–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Liang, J.; Qu, Z.; Yang, F.; Liao, Z.; Gou, H. Transarterial strategies for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review. PloS one 2020, 15, e0227475. [Google Scholar]
- van den Hoven, A.F.; Rosenbaum, C.E.; Elias, S.G.; de Jong, H.W.; Koopman, M.; Verkooijen, H.M.; Alavi, A.; van den Bosch, M.A.; Lam, M.G. Insights into the dose-response relationship of radioembolization with resin 90y-microspheres: A prospective cohort study in patients with colorectal cancer liver metastases. J Nucl Med 2016, 57, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, L.; Bagni, O.; Notarianni, E.; Saltarelli, A.; Ambrogi, C.; Schillaci, O. Pet/ct with (18)f-choline or (18)f-fdg in hepatocellular carcinoma submitted to (90)y-tare: A real-world study. Biomedicines 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, T.S.; Rhee, H.; Kim, G.M.; Kim, S.U.; Kim, B.K.; Park, J.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Han, K.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y. Alpha-fetoprotein, des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin, and modified recist response as predictors of survival after transarterial radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of vascular and interventional radiology : JVIR 2019, 30, 1194–1200.e1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohme, S.; Bou Samra, P.; Kaltenmeier, C.; Chidi, A.P.; Varley, P.R.; Tsung, A. Radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: A nationwide 10-year experience. Journal of vascular and interventional radiology : JVIR 2018, 29, 912–919.e912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Heller, M.; Lokken, R.P.; Fidelman, N.; Lam, A. Socioeconomic and survival analysis of radioembolization in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A propensity score-adjusted study. Journal of vascular and interventional radiology : JVIR 2023, 34, 815–823.e811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, M.A.; Wongjarupong, N.; Hassan, M.A.; Taha, W.; Abdalla, A.; Bampoh, S.; Onyirioha, K.; Nelson, M.; Glubranson, L.A.; Wiseman, G.A.; et al. The efficacy, safety, and predictors of outcomes of transarterial radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective study. Expert review of gastroenterology & hepatology 2020, 14, 619–629. [Google Scholar]
- Kolligs, F.; Arnold, D.; Golfieri, R.; Pech, M.; Peynircioglu, B.; Pfammatter, T.; Ronot, M.; Sangro, B.; Schaefer, N.; Maleux, G.; et al. Factors impacting survival after transarterial radioembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Results from the prospective cirt study. JHEP reports : innovation in hepatology 2023, 5, 100633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, A.L.; Dieudonné, A.; Ronot, M.; Sanchez, M.; Pereira, H.; Chatellier, G.; Garin, E.; Castera, L.; Lebtahi, R.; Vilgrain, V. Relationship of tumor radiation-absorbed dose to survival and response in hepatocellular carcinoma treated with transarterial radioembolization with (90)y in the sarah study. Radiology 2020, 296, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).