1. Introduction
Pressure ulcers (PUs) [
1] are injuries to the skin and underlying tissues, mainly caused by prolonged pressure. These are common on the skin covering bony prominences of the body, such as elbows, hips or tailbone. PUs can cause swelling, warmth and pain in the affected area, among other symptoms [
2]. They tend to heal slowly and, if left untreated, they can progressively damage deep tissues (including muscles and bones), making them a significant health problem. The impact of PUs extends beyond patients, affecting their families and overloading the resources of healthcare and socio-health systems [
3,
4]. Because of this, PUs are considered adverse outcomes in clinical practice and need to be avoided.
The prevention of PUs should be, therefore, a priority for nurses, healthcare professionals and organizations around the world [
5]. Nevertheless, the economic cost in healthcare systems of PUs prevention measures for patients at risk is usually lower than the cost of other treatments [
3,
6]. Despite the scientific evidence that has been generated over the years to improve prevention and treatment strategies, patients with PUs or those at risk of developing them do not always receive the most effective interventions. Decision-making in this field depends on the actions of professionals, their knowledge, attitudes, skills and other external conditions [
7,
8] This variability in nursing practice, influenced by individual choices, highlights the importance of effective and efficient interventions in PU prevention.8 In this context, a better understanding of the risk level associated with PUs enable healthcare professionals to make informed decisions and avoid counterproductive practices.
Thus, knowing the risk level of PUs is crucial for nursing praxis as it enables various applications for prevention and treatment. One of the main preventive measures against the development of PUs is the usage of special pressure management surfaces [
9,
10], such as beds, mattresses and cushions. The selection of the appropriate support surfaces based on the risk level is essential for the prevention of PUs, since it allows a distribution of pressure adapted to the needs of each patient [
11]. For example, the Spanish national group GNEAUPP,
12 which is devoted to the study and advice on PUs and chronic wounds, proposes assigning support surfaces to patients based on four levels of PU risk: no risk, mild risk, moderate risk and high risk. Consequently, patients without risk of PUs may benefit from static mattresses, while high-risk patients may require additional resources such as replacement mattresses, flotation systems or fluidized beds [
12]. On the other hand, it is also important to prioritize the allocation of resources based on risk levels in healthcare facilities facing limitations. The identification of high-risk patients makes it possible to allocate resources, such as support surfaces, in order to optimize their usage and guarantee an efficient care. Risk levels can also be used to implement other personalized preventive strategies, such as promoting regular repositioning or encouraging the appropriate nutrition and hydration [
13]. Additionally, monitoring high-risk patients allows for early detection of PUs through periodic examinations, enabling prompt interventions to prevent progression. Despite the above, determining the risk level of PUs is often a complex task. In this scenario, prediction models can be a useful alternative to estimate the risk level and make informed decisions for patients.
The main aim of this paper is to propose interpretable prediction models that assist nursing professionals to estimate the risk level of PUs in each patient. This, in turn, will facilitate effective interventions, including the selection of support surfaces and other relevant applications. For this purpose, data from 16,215 patients in Granada (Spain) have been collected, focusing mainly on indicators that are quickly identifiable in practice by nursing professionals, such as mobility, activity and skin humidity [
4] The data treated present a common problem in nursing classification datasets, such as the presence of class imbalance [
14]. In order address this issue, the dataset is preprocessed and various oversampling configurations are studied to determine the best one allowing to improve data quality before modeling [
15]. From the preprocessed data, a classification model based on decision trees has been created using the well-known Classification and Regression Trees (CART) [
16] algorithm with the aim of predicting the risk level of developing PUs in each patient. Furthermore, to improve the interpretability of the model and its practical usage, this research proposes a tabular visualization format for the classifier. The models built are evaluated in terms of their classification performance using a stratified cross-validation scheme [
17].
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. First, the dataset and the methods used for the construction of the classification models are described. Then, the visual resources for estimating the risk level of PUs, which can be applied to the selection of support surfaces and other relevant interventions, are presented. Finally, the results obtained are discussed and the conclusions of this work are summarized, highlighting its main findings.
2. Data Collection and Methods
This section describes how the data collection process used in this paper was carried out, as well as the methods used to build the classification models. Thus, the data gathering procedure and the characteristics of the final dataset are presented initially, followed by a description of the algorithms involved in building the classifiers.
2.1. Dataset description
The study associated with this research has been carried out in accordance with the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki [
18] and is approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee at the Andalusian Public Health System (AP-0086-2016), located in Spain. For data collection, a chronic wound registration system (SIRUPP), which is integrated into the Diraya health history application from the Andalusian Public Health System, is used. Data from 16,215 patients, who belong to the Granada-Metropolitan Primary Healthcare District in Granada (Spain), are collected. Their mean age is 84.13 years, with 30.2% of the patients being men and 69.8% women. Three indicators were analyzed for each of the patients under study: the degree of mobility, the degree of activity and the degree of moisture in the skin. These characteristics were specially chosen because they are easily and quickly identifiable by the nursing professional and have shown to provide competitive results in previous works focused on predicting the presence/absence of pressure ulcer risk.4 Note that this paper represents a significant advancement over these previous works as it focuses on determining the precise risk level of PUs, a task that is more complex and has numerous practical applications, as discussed earlier.
After this, following the recommendations of risk levels of PUs provided by GNEAUPP,12 the risk level for each patient was determined using the Braden scale [
19]: patients with a score of 19 or more are labeled as no risk, patients with a score between 15 and 18 as mild risk, patients with a score between 13 and 14 as moderate risk and, finally, patients with a score of 12 or less are labeled as high risk. A descriptive analysis of the input indicators (skin moisture, activity and mobility) and the output class (pressure ulcer risk) is shown in
Table 1.
The results in
Table 1 show that most of the patients in the study have a mild risk of suffering from PUs (43.50%), whereas the highest risks occur in 29.54% of them. Skin moisture seems to be a recurring theme, since 60.71% of patients present it, at least, occasionally. The activity of the patients is also characterized mainly by walking occasionally (44.05% of observations), although cases in which most of the time they are saddled (26.20%) or bedridden (10.27%) are also frequent. Finally, the patient’s mobility is usually very limited (44.35%), which may be another influential factor in the appearance of PUs.
2.2. Methodology for building the decision tree models
In order to create the decision tree models that allow estimating the risk level of suffering from PUs based on the indicators of skin moisture, activity and mobility, a methodology consisting of two main stages is designed:
Data preprocessing. Before building the final model to predict the risk level of PUs, the dataset is preprocessed to improve the quality of the information used by the classification algorithms in the subsequent phase. This stage primarily focuses on mitigating the issue of class imbalance [
20] in the original dataset, as the distribution of classes is significantly uneven.
Model building. After preprocessing the data, we proceed to create the classification model, which enables the estimation of the risk level for each patient in developing PUs. The model is built using a decision tree generator algorithm [
16,
21], whose output is easily interpretable and applicable in a multitude of contexts.
Data preprocessing: As shown in
Table 1, the dataset obtained is characterized by being imbalanced [
14]. This fact indicates that the data present an unequal distribution among classes [
15], implying that the percentage of observations at each PUs risk level is quite uneven. For example, the class high risk represents 13.07% of the observations, whereas the class mild risk represents 43.50%. In classification datasets, this problem may involve that the models that are built from the data are more prone to predict the majority classes, while reducing the importance of minority ones. In order to avoid the negative effect of imbalanced data in the construction of classifiers, it is common to apply preprocessing techniques known as resampling methods [
15,
20]. These aim to balance the number of observations between the different classes. Thus, once the data are preprocessed, classifier construction algorithms can be applied more reliably.
In order to balance the number of observations in the minority classes, the random oversampling [
20] technique is used. It is a simple but efficient resampling method that is commonly used with imbalanced classification data with categorical attributes. This mainly consists of choosing a minority class and replicating samples of such class to increase its size. For example, in order to balance the class high risk, random observations from this class are iteratively selected and replicated until the same number of observations from the majority class (mild risk) is reached.
An important aspect to consider when dealing with imbalanced classification problems is the number of classes in the dataset. In binary problems, it is often sufficient to oversample the minority class to match the size of the majority class, which provides good results in most cases [
22]. However, in the case of multi-class problems, previous works have shown that it is interesting to analyze the classes and samples to oversample [
15]. Therefore, this research studies different oversampling configurations by preprocessing different combinations of classes, aiming to select the configuration that achieves the greatest improvement in data quality for building the decision trees. Each configuration involves preprocessing some of the minority classes in the dataset, that is, the classes high risk (13.07%), moderate risk (16.47%) and no risk (26.96%), until they reach the size of the majority class (mild risk). This procedure will allow minority but relevant classes to be more representative within the dataset for building the classification model later.
Model building: After balancing the data, a decision tree building algorithm [
21,
23] is used to create the classification model. There exist a multitude of classification approaches based on the creation of decision trees, such as Random Forest (RF) [
24], XGBoost [
25] or bagging methods [
26]. Among them, this research uses the CART 16,21 algorithm, which can be considered the basis of many other decision tree techniques, due to two main reasons: (i) it is widely used in other medical research works employing data science techniques [
27,
28,
29]; and (ii) it is easily interpretable, unlike other ensemble-based models like the aforementioned RF or XGBoost [
24,
25].
The classifier created by CART is represented as a binary tree. Each node in the tree involves a single input attribute (that is, skin moisture, activity or mobility in our case) and its branches show the values this variable can take (that is, its different modalities shown in
Table 1). Leaf nodes contain the output class that will be used to perform PUs risk level prediction. In order to create this binary tree, CART divides the attribute space into different regions allowing the observations to be categorized into different classes. These regions are defined using a greedy scheme based on a binary recursive partitioning, which searches all the attributes for the value that most reduces the impurity in the nodes (the level of mixing in the class labels of the observations in each of them) [
16]. For this, different metrics can be used, such as the deviation function or the Gini index [
16], considered in this research.
As a result of the recursive partitioning, CART repeatedly divides the dataset according to impurity reduction until a stopping criterion is satisfied. Among the most usual stopping criteria is considering the minimum number of observations of a node to be partitioned. If the amount of data in a node is not enough, the split can be stopped. Another common procedure is applying a pruning procedure to the tree that allows removing some of the nodes, making the final model more interpretable and reducing its overfitting to the training data. In this context, it is usual to use a complexity parameter that penalizes the tree for having too many splits. This research considers 20 observations per node in the stopping criterion and a complexity parameter 0.01.
The classification performance of the decision tree model is estimated using two metrics: accuracy and geometric mean. Accuracy is a commonly used measure in standard classification tasks, whereas the geometric mean is particularly suitable for imbalanced classification problems. The use of both metrics provides a comprehensive evaluation of the performance of the model across different aspects. In order to ensure robustness, the evaluation is conducted by averaging the test results of 10 runs of a 10-fold cross-validation (10-fcv) [
17].
3. Interpretable Models for Pressure Ulcer Risk Level Prediction
This section presents the classification models built from the data. First, the different oversampling configurations are studied, as well as their impact on the classification performance in order to select the best preprocessing approach. Then, the decision tree generated by CART is analyzed. Finally, a new way of visualizing the information of the classification model in the form of table is proposed, aiming to provide a more straightforward and interpretable representation for healthcare professionals.
3.1. Analysis of oversampling configurations
This section presents the results obtained from different oversampling configurations and their impact on the classification performance.
Table 2 provides the oversampling configurations for each risk level and the corresponding values of accuracy (ACC) and geometric mean (GM) for the decision trees using 10 runs of a 10-fcv. The Oversampling rows indicate whether each class (no risk, mild risk, moderate risk and high risk) are oversampled or not.
The analysis of the results in
Table 2 shows that most of the oversampling configurations achieve relatively high accuracy scores, ranging from 0.7000 to 0.7378. This finding indicates that the decision trees built from oversampled data provide promising results in predicting the risk levels of PUs. However, some oversampling configurations, such as those considering high risk with oversampling and moderate risk without oversampling, obtain a geometric mean of 0. This fact suggests that these configurations encounter difficulties in effectively addressing the imbalanced nature of the dataset. On the other hand, the preprocessing configurations including the oversampling of the minority classes (both moderate risk and high risk) achieve the highest geometric mean scores (0.7333 and 0.7356), which indicates that simultaneously oversampling the two highest risk levels of PUs has a positive impact on the classification performance.
Thus, the analysis of the oversampling configurations highlights the importance of addressing the class imbalance problem in the dataset. The classification models achieve a better performance when the minority classes are oversampled, as indicated by the higher accuracies and geometric means. Since the preprocessing that improves the classification performance the most is the one that oversamples all minority classes, we will choose this configuration to be used in the following sections when building the decision trees.
3.2. Decision tree for pressure ulcer risk level estimation
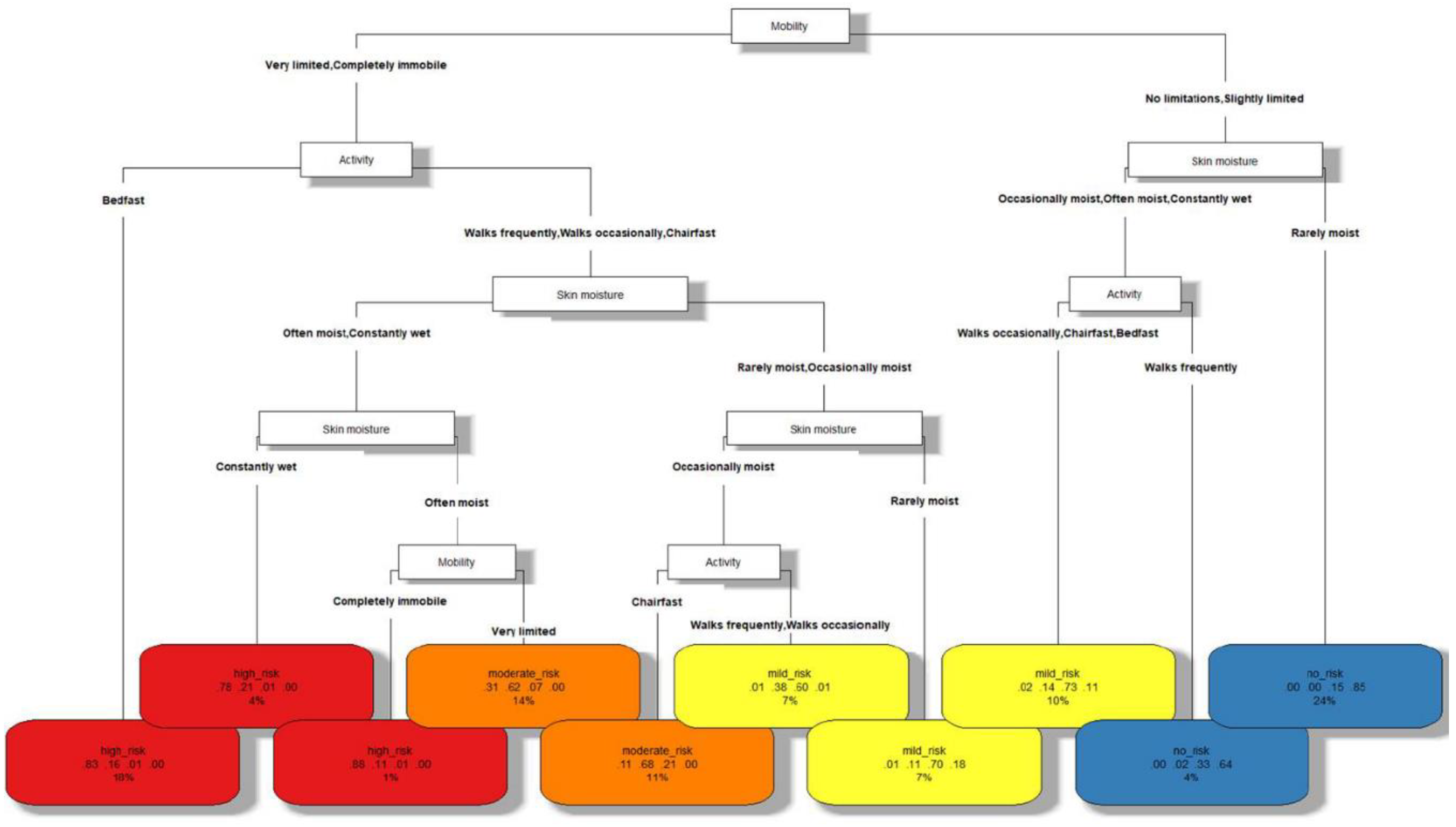
The decision tree built with CART distinguishing among the different risk levels of PUs is shown in
Figure 1. As shown in
Table 2, its classification accuracy is 0.7378 and its geometric mean is 0.7356. These scores, considering the complexity of the problem addressed, the ease of evaluation in practice of the indicators used and the interpretability of the resulting model, demonstrate a competitive performance. The elements that are part of this model are described below:
1. Each node in the tree represents a characteristic of the patient (mobility, activity or skin moisture), whereas the leaves of the tree (at the bottom level) represent the different risk levels of PUs (no risk, mild risk, moderate risk or high risk).
2. The branches of the tree that depart from each node A represent values that the characteristic A of the patient can take.
3. In the leaf nodes, a label with the risk level of PUs is found in the first row. A different color has been associated with each of them: blue for no risk, yellow for mild risk, orange for moderate risk and red for high risk.
4. The second row of each leaf shows 4 numbers in the interval [0, 1]. These can be viewed as the confidence of the model by classifying the observations at that leaf into the different classes, in order of high risk, moderate risk, mild risk and no risk.
5. The third row of each leaf represents the percentage of the total observations classified in such leaf, which can be seen as the frequency of occurrence of the corresponding patient profile in practice.
Note that the consultation of the confidences and the percentage of observations in each leaf node by the healthcare professional can provide important additional information when making the final decision in each case. For example, the sixth leaf node (starting from the left) with a mild risk has a frequency of occurrence of 7%, which can be considered as an indicator of dealing with a relatively common patient profile in practice. On the other hand, it can be observed that, although the patient profile corresponding to this leaf probably has a mild risk of suffering from PUs (confidence 0.6), it must be taken into account that a moderate risk is also highly possible (confidence 0.38). These results can indicate to the professional that, although the risk is probably mild risk and preventive measures (such as support surfaces) could be adapted to this risk level, special attention should be paid in case that additional measures corresponding to the level of moderate risk are required.
In order to use the tree, the nursing professional starts from the root node (in the top of the tree) and descends through its branches until reaching a particular leaf. Going through each node we have a characteristic, and through each of its branches the values that it must meet. Finally, leaf nodes indicate the class corresponding to the patients with such profile. Thus, observing the classification model, the characteristics of the following PUs risk profiles can be distinguished:
1. Characteristics of patients without risk of pressure ulcer. According to the decision tree, these patients are characterized by a mobility with no limitations or slightly limited. Also, either their skin is rarely moist or they walk frequently.
2. Characteristics of patients with mild risk of pressure ulcer. If the conditions of skin moisture and activity of the previous point are not met, patients have a mild risk of suffering from pressure ulcers. On the other hand, when mobility is quite limited (very limited or completely immobile), but patients are not bedridden and their skin is rarely moist, they are also at mild risk. This risk is also present if they are not saddled or bedridden and their skin is occasionally wet.
3. Characteristics of patients with moderate risk of pressure ulcer. If patients’ mobility is very limited and their skin is often moist (but they are not bedridden), they are at moderate risk for pressure ulcers. On the other hand, patients with very limited mobility or completely immobile, who are saddled and their skin is occasionally moist, are also at this risk level.
4. Characteristics of patients with high risk of pressure ulcer. Patients with very limited mobility or completely immobile, who are bedridden or whose skin is constantly wet are at high risk of pressure ulcers. Also, if they are not bedridden and their skin is slightly less moist (that is, often moist), but they are completely immobile, they are also at high risk.
The study of the aforementioned profiles in clinical practice makes it possible to identify the main characteristics of patients at each level of PUs risk based on the indicators studied, which are easily recognizable by nursing professionals through direct observation of the patient. In turn, this information can be used as a complement to the experience of nurses in making decisions related to these patients, including the selection of support surfaces and other relevant applications.
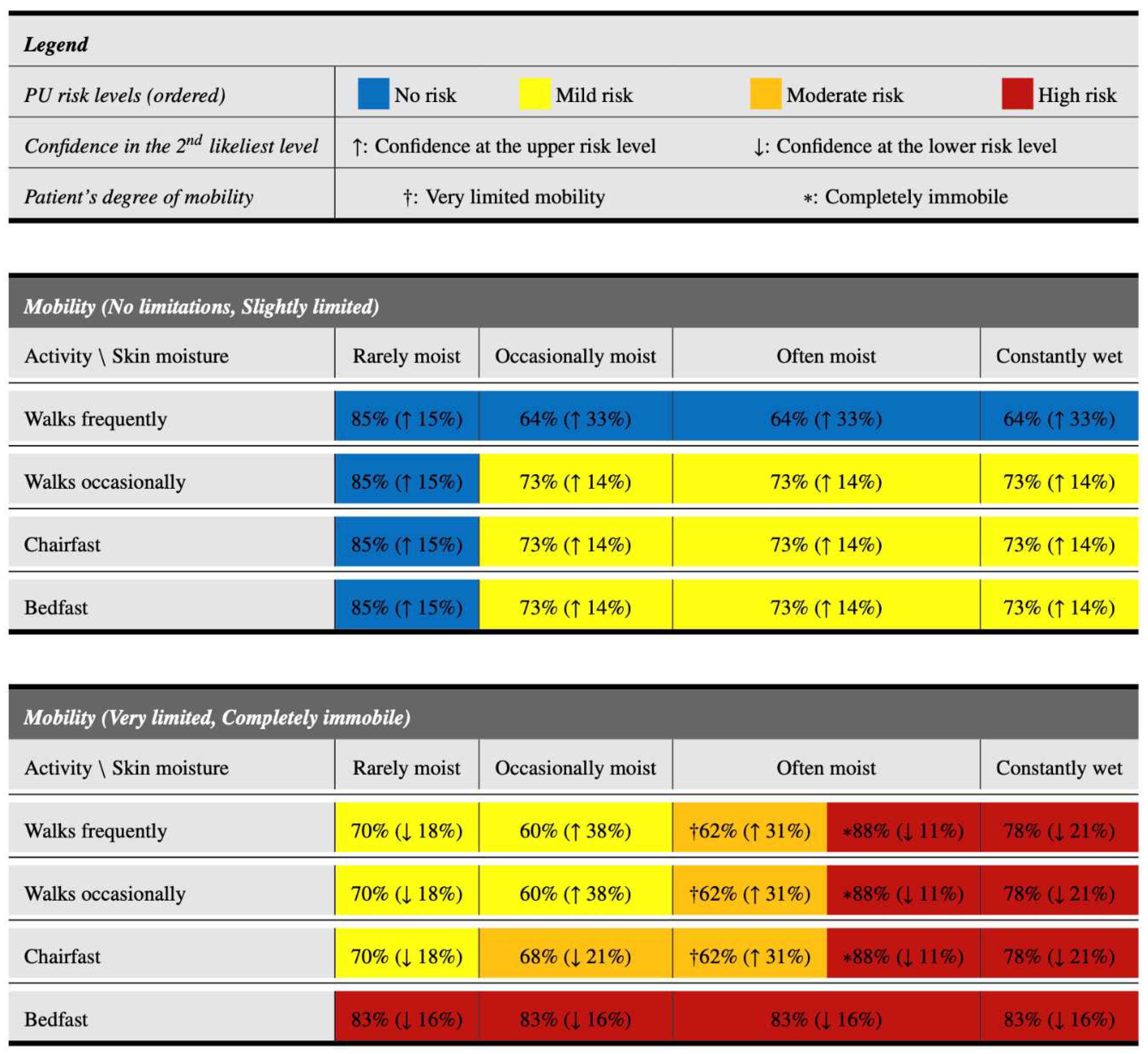
3.4. A tabular visualization resource to increase interpretability
Nursing professionals often face the challenge of making timely decisions for a large number of patients to prevent the occurrence of PUs. The usage of instruments, such as the one previously presented, can help them make decisions in less time, since they are based on objective and quickly identifiable characteristics. This section proposes a novel resource, in tabular form, which aims to further simplify and speed up the decision-making process. This resource, which is based on the information shown in
Figure 1 but in a more interpretable way, is presented in
Figure 2. It has the following characteristics:
1. Excluding the legend at the top, it is divided into two main parts, depending on the mobility of the patient. The upper part focuses on patients with acceptable mobility (no limitations or slightly limited), whereas the lower part focuses on patients with greater mobility problems (very limited or completely immobile).
2. Within each part, it is possible to easily identify the level of activity of the patient (in the rows), as well as the level of moisture of the skin (in the columns). Thus, all the characteristics that determine the patient’s profile are determined.
3. Once the patient’s profile has been identified, the corresponding cell in the table provides information on their risk level of developing PUs. Its color indicates the most probable risk level: blue for patients with no risk, yellow for patients with mild risk, orange for patients with moderate risk and red for patients with high risk.
4. Within each cell there is also a main percentage (outside the parentheses). This indicates the confidence of the classification model that the patient has the level of PU risk indicated by the color.
5. Finally, within each cell there is also a second percentage in parentheses, accompanied by an arrow. This percentage indicates the confidence in the second most likely risk level, while the arrow (↑ or ↓) indicates if this second level is the upper (↑) or lower (↓) level with respect to the main level expected for that profile. Risk levels are considered in order of no risk, mild risk, moderate risk and high risk.
As can be appreciated, the tabular model presented in this section allows a rapid categorization of PU risk levels simply by identifying the appropriate row and column to determine the patient’s profile. In addition, it maintains useful information that can be employed by nurses, such as the confidences in the most likely PUs risk levels based on the profile. Thus, for example, among patients with very limited mobility or completely immobile who walk frequently, both those with rarely moist and occasionally moist skin have a mild risk of PUs. The former have a 70% probability of being at this risk level, with a tendency to a no risk level (18%). However, in patients with occasionally moist skin, the probability of being in mild risk level is lower (60%) and there is a high tendency to present a moderate risk level of PUs (38%).
4. Discussion
In the field of health research, applications where data science models are used are becoming more frequent [
30,
31]. One specific area in which these techniques are applied is in the prevention and management of Pus [
32,
33,
34]. For example, Ting and Garnett [
32] conducted a systematic review to evaluate the impact of e-health decision support technologies on the prevention and management of PUs. The review highlighted the usability and accuracy of these methods in improving clinician adherence to prevention practices and reducing healthcare costs. Lee et al. [
34] utilized data-mining techniques to identify risk factors related to different stages of PUs. On the other hand, among data science methods, decision trees [
21,
23] provide particular benefits in this context, since they are characterized by simultaneously offering classifiers with predictive quality and interpretability. For example, risk factors for PUs were analyzed using demographic, laboratory and Braden variables by Raju et al. [
35], whereas decision trees were also used by Moon and Lee [
36] on data with numerous variables on patients in long-term care facilities.
Decision support models that assist nursing professionals in estimating the risk level of PUs for each patient and, consequently, in making informed decisions regarding appropriate interventions, can facilitate their work. This paper has proposed a model based on decision trees that allows distinguishing four levels of PU risk in patients based on three characteristics easily observable by nurses (mobility, activity and skin moisture). This differentiation into four risk levels enables the selection of suitable interventions, including the usage of appropriate special support surfaces, in accordance with expert guidelines on PUs prevention and treatment (such as those provided by the technical document of the Spanish national group GNEAUPP) [
12].
As previously mentioned, interpretable classification models, such as decision trees, are commonly applied in clinical practice where the professional often needs to know the reasons for the decision provided. However, it should be noted that there are other, more elaborate classification algorithms, such as XGBoost [
25] or RF [
24], which could provide more accurate classification results at the cost of interpretability. This fact may imply that the clinical application of these non-interpretable models is not as simple and efficient in all healthcare settings as the models presented in this research.
A possible limitation of the present work is the cross-sectional nature of the study, which has involved the usage of the Braden scale to label patients according to the risk level of suffering from PUs. It is interesting to extend this research over time through a longitudinal study, so that the final labeling of patients more accurately reflects the reality of whether they finally suffered from PUs in the future, also including the degree of severity of the lesions.
5. Conclusions
This research has proposed the usage of classification models based on decision trees to predict the risk level of developing PUs. Being able to estimate the risk level of PUs is especially useful, for example, to assign the special support surfaces to be used for each patient according to their needs. The use of models that help the nursing professional in this context can save time and resources in their choices and serve as an instrument to prevent possible unwanted situations that may arise in the future. In addition to presenting these models, one of the main objectives of this work is to make them highly interpretable by nurses. To this end, the models have been developed based on characteristics that are easily identifiable by professionals, such as skin moisture, mobility and activity of each patient. Furthermore, this work has helped to train professionals in the use of this type of instruments, explaining their operation in a simple way to favor the efficient use of these resources.
After preprocessing the dataset to overcome the imbalance learning problem, a decision tree model has been built to classify the risk levels of PUs. This model has been created with the well-known CART algorithm, whose resulting tree can be easily interpreted. This allows nurses to know the characteristics of the patient that are indicators of a potential risk level of PUs. The model built also offers different confidences that the patients in each profile may belong to different risk levels, which can be used as additional information when making the decision about the appropriate interventions to use.
Although the presented decision tree is interpretable, its structure and binary character give rise to improvements to increase its practical possibilities. For this reason, this work has also proposed a form of tabular visualization of the extracted decision tree with the aim of further improving its interpretability and applicability in real-world situations. This way of presenting the model in tabular form, which maintains information useful to the nurses (such as the confidences in the most probable risk levels), makes it possible to quickly determine the risk level of PUs for each patient simply by locating the row and the column of the table associated with the patient’s profile.
Thus, the models presented in this paper are characterized by being simple and interpretable and they will serve as a support instrument for the nursing professional to decide efficiently which may be the most appropriate interventions according to the patient’s needs. Furthermore, the proposed models could be easily included within clinical practice guidelines where decision-making regarding the choice of resources and other preventive measures is organized.
In future work, we plan to study within the clinical setting whether these models lead to significant reductions in PUs cases in patients at risk by assigning the most appropriate support surfaces in each case. Furthermore, it is interesting to delve into other aspects of data preprocessing in order to further improve the models created, in addition to the class imbalance that has been addressed, such as overlapping among classes or noise [
37].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, EV-S and CD-N; methodology, JAS and JLR-B; software, JAS and JLR-B; validation, EV-S and CD-N.; formal analysis, JAS and JLR-B; investigation, EV-S, EM-R and CD-N; resources, EV-S, EM-R and CD-N; data curation, JAS and JLR-B; writing—original draft preparation, JAS and EM-R.; writing—review and editing, JAS and JLR-B.; visualization, EV-S, EM-R and CD-N; supervision, EV-S and CD-N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study associated with this research has been carried out in accordance with the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki and is approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee at the Andalusian Public Health System (AP-0086-2016), located in Spain.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data available under request to the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Mervis JS, Phillips TJ. Pressure ulcers: Prevention and management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81(4):893-902. [CrossRef]
- Cornish L. Preventing and managing pressure ulcers in patients receiving palliative care. Nurs Older People. 2021;33(4):34-41. [CrossRef]
- Mervis JS, Phillips TJ. Pressure ulcers: Pathophysiology, epidemiology, risk factors, and presentation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81(4):881-890. [CrossRef]
- Vera-Salmerón E, Domínguez-Nogueira C, Romero-Béjar JL, Sáez JA, Mota-Romero E. Decision-tree-based approach for pressure ulcer risk assessment in immobilized patients. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(18):11161. [CrossRef]
- Nani FS, Stéfani KC, Busnardo FF, et al. Ulcer pressure prevention and opportunity for innovation during the COVID-19 crisis. Clinics. 2020;75:e2292. [CrossRef]
- McEvoy N, Avsar P, Patton D, Curley G, Kearney CJ, Moore Z. The economic impact of pressure ulcers among patients in intensive care units. A systematic review. J Tissue Viability. 2021;30(2):168-177. [CrossRef]
- De Meyer D, Verhaeghe S, Van Hecke A, Beeckman D. Knowledge of nurses and nursing assistants about pressure ulcer prevention: A survey in 16 Belgian hospitals using the PUKAT 2.0 tool. J Tissue Viability. 2019;28(2):59-69. [CrossRef]
- Moya-Suárez AB, Canca-Sánchez JC, Enríquez de Luna-Rodríguez M, Aranda-Gallardo M, Morales-Asencio JM. Factors associated with variability in the prevention of pressure ulcers. J Tissue Viability. 2018;27(4):211-216. [CrossRef]
- Soppi E, Knuuti J, Kalliokoski K. Positron emission tomography study of effects of two pressure-relieving support surfaces on pressure ulcer development. J Wound Care. 2021;30(1):54-62. [CrossRef]
- Boyle CJ, Carpanen D, Pandelani T, Higgins CA, Masen MA, Masouros SD. Lateral pressure equalisation as a principle for designing support surfaces to prevent deep tissue pressure ulcers. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(1):e0227064. [CrossRef]
- McInnes E, Jammali-Blasi A, Bell-Syer SE, Leung V. Support surfaces for treating pressure ulcers. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;Issue 10:CD009490. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Palma M, López-Casanova P, García-Molina P, Ibars-Moncasi P. Superficies Especiales Para El Manejo de La Presión En Prevención y Tratamiento de Las Úlceras Por Presión. Logroño: Serie Documentos Técnicos GNEAUPP no XIII. Grupo Nacional para el Estudio y Asesoramiento en Úlceras por Presión y Heridas Crónicas; 2011.
- Headlam J, Illsley A. Pressure ulcers: An overview. Br J Hosp Med. 2020;81(12):1-9. [CrossRef]
- Li Y, Hsu WW, Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. A classification for complex imbalanced data in disease screening and early diagnosis. Stat Med. 2022;41(19):3679-3695. [CrossRef]
- Sáez JA, Krawczyk B, Woźniak M. Analyzing the oversampling of different classes and types of examples in multi-class imbalanced datasets. Pattern Recognit. 2016;57:164-178. [CrossRef]
- Breiman L, Friedman J, Olshen R, Stone C. Classification and Regression Trees. Boca Raton, FL, USA: Chapman and Hall/CRC; 2017.
- Fontanari T, Fróes TC, Recamonde-Mendoza M. Cross-validation strategies for balanced and imbalanced datasets. Lect Notes Comput Sci. 2022;13653 LNAI:626-640.
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA. 2013;310:2191-2194. [CrossRef]
- Delmore BA, Ayello EA. Braden Scales for Pressure Injury Risk Assessment. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2023;36(6):332-335. [CrossRef]
- Branco P, Torgo L, Ribeiro RP. A survey of predictive modeling on imbalanced domains. ACM Comput Surv. 2017;49(2):1-50 (article no. 31). [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman RK, Nowalk MP, Bear T, et al. Proposed clinical indicators for efficient screening and testing for COVID-19 infection using Classification and Regression Trees (CART) analysis. Hum Vaccines Immunother. 2021;17(4):1109-1112. [CrossRef]
- Pan T, Zhao J, Wu W, Yang J. Learning imbalanced datasets based on SMOTE and Gaussian distribution. Inf Sci. 2020;512:1214-1233. [CrossRef]
- Im EO, Yi JS, Chee W. A Decision Tree Analysis on the Impact of a Technology-Based Program on Symptom Distress: Asian American Breast Cancer Survivors. CIN Comput Inform Nurs. 2022;40(7):487-496. [CrossRef]
- Hansch R. Handbook of Random Forests: Theory and Applications for Remote Sensing. World Scientific Publishing, Singapore; 2018.
- Cherif IL, Kortebi A. On using extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) machine learning algorithm for home network traffic classification. In: 2019 Wireless Days. ; 2019:1-6. [CrossRef]
- 26. Sun J, Lang J, Fujita H, Li H. Imbalanced enterprise credit evaluation with DTE-SBD: Decision tree ensemble based on SMOTE and bagging with differentiated sampling rates. Inf Sci. 2018;425:76-91. [CrossRef]
- Sun D, Zhao H, Zhang Z. Classification and regression tree (CART) model to assist clinical prediction for tracheostomy in patients with traumatic cervical spinal cord injury: A 7-year study of 340 patients. Eur Spine J. 2022;31(5):1283-1290. [CrossRef]
- Li X, Wu X, Qian J, et al. Differentiation of lacrimal gland tumors using the multi-model MRI: Classification and regression tree (CART)-based analysis. Acta Radiol. 2022;63(7):923-932. [CrossRef]
- Cheng Z, Nakatsugawa M, Hu C, et al. Evaluation of classification and regression tree (CART) model in weight loss prediction following head and neck cancer radiation therapy. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2018;3(3):346-355. [CrossRef]
- Bergquist S, Brooks GA, Landrum MB, Keating NL, Rose S. Uncertainty in lung cancer stage for survival estimation via set-valued classification. Stat Med. 2022;41(19):3772-3788. [CrossRef]
- Doubleday K, Zhou J, Zhou H, Fu H. Risk controlled decision trees and random forests for precision Medicine. Stat Med. 2022;41(4):719-735. [CrossRef]
- Ting JJ, Garnett A. E-health decision support technologies in the prevention and management of pressure ulcers: A systematic review. CIN Comput Inform Nurs. 2021;39(12):955-973. [CrossRef]
- Kim MS, Ryu JM, Choi BK. Development and Effectiveness of a Clinical Decision Support System for Pressure Ulcer Prevention Care Using Machine Learning: A Quasi-experimental Study. CIN Comput Inform Nurs. 2023;41(4):236-245. [CrossRef]
- Lee TT, Lin KC, Mills ME, Kuo YH. Factors related to the prevention and management of pressure ulcers. CIN Comput Inform Nurs. 2012;30(9):489-495. [CrossRef]
- Raju D, Su X, Patrician PA, Loan LA, McCarthy MS. Exploring factors associated with pressure ulcers: A data mining approach. Int J Nurs Stud. 2015;52:102-111. [CrossRef]
- Moon M, Lee SK. Applying of decision tree analysis to risk factors associated with pressure ulcers in long-term care facilities. Healthc Inform Res. 2017;23:43-52. [CrossRef]
- Sáez JA. Noise models in classification: Unified nomenclature, extended taxonomy and pragmatic categorization. Mathematics. 2022;10(20):3736. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
 indicates that the corresponding class is oversampled, whereas
indicates that the corresponding class is oversampled, whereas  indicates that the class is not preprocessed.
indicates that the class is not preprocessed.
 indicates that the corresponding class is oversampled, whereas
indicates that the corresponding class is oversampled, whereas  indicates that the class is not preprocessed.
indicates that the class is not preprocessed.




































