Introduction
Mercury (Hg) pollution poses a significant threat to both the environment and plant growth. Hg is highly toxic and can accumulate in the food chain through methylation, bioaccumulation and biomagnification, potentially affecting animal and human health[
1,
2]. As a major source of food, industrial materials and livestock feed, maize plays a crucial role in global food production and human well-being. However, increasing industrial activities, automobile usage and pesticide applications have led to rising emissions of Hg gas and particles into the atmosphere. This atmospheric Hg eventually contaminates soil through deposition [
3,
4,
5]. Maize cultivation on contaminated soils introduces risks, as Hg can accumulate in plant tissues and enter the food chain[
6]. Inside plants, Hg disrupts critical physiological processes like water and nutrient uptake, transpiration and photosynthesis. It also impairs enzyme activity, slowing growth and decreasing biomass production, and can even cause mortality [
7]. The adverse effects of Hg toxicity extend to humans. Accumulation of Hg in vital organs such as the kidneys and central nervous system has been linked to harmful impacts [
1,
8]. Understanding the genetic basis of Hg accumulation in maize and developing varieties with reduced Hg uptake are essential strategies for mitigating these threats to both plant and human health.
Recent years have seen a growth in genetic studies investigating Hg accumulation mechanisms. For instance, quantitative trait locus mapping has identified regions associated with Hg tolerance in rice and maize[
9,
10]. Overexpression analyses have revealed genes that enhance Hg accumulation and tolerance in plants like rice, Arabidopsis and poplar [
11,
12,
13]. These findings provide valuable insights but also highlight the complexities of Hg accumulation in plants. Further genetic investigations are needed to better understand this process. GWAS, utilizing linkage disequilibrium (LD) have emerged as a powerful tool for dissecting genetic-phenotypic relationships. Compared to traditional linkage mapping, GWAS allows analysis of broader, more diverse populations with higher marker densities, improving mapping resolution to the single-gene level[
14]. Maize is well-suited for GWAS due to its rapid LD decay and abundant diversity [
15,
16]. The first maize GWAS in 2007 examined 8,590 loci in 553 elite maize inbred lines to identify genes related to oleic acid content in maize kernels[
17]. Subsequent studies have identified loci impacting oil concentration or fatty acid composition in kernels and identified QTLs related to arsenic content in various maize tissues[
16,
18].
The statistical power of GWAS depends on various factors, including population size, diversity, marker density, and choice of statistical models. By optimizing these aspects, more genetic determinants of target traits can be identified [
19]. Studies have demonstrated that analyzing large germplasm collections with high-density molecular markers can successfully identify genetic loci[
20]. Appropriate statistical models facilitate more comprehensive resolution of genetic structure and relationships[
21]. The GWAS method SUPER augmented power through model optimization [
22]. Enhancements in sequencing depth and marker density facilitate improved genomic coverage, enabling identification of both genes and non-genetic contributions to traits [
23]. Dissecting additional maize traits using an enlarged panel revealed further loci [
24]. Advancements in sequencing technology, reduced costs, and continuous GWAS algorithm improvements have made it an efficient approach for identifying genome-phenotype associations and genetic bases of complex traits [
25,
26].
In this study, we re-conducted a GWAS to dissect the genetic basis of Hg content in five tissues of the 230 maize inbred lines [
27]. Our aim was to leverage an expanded SNP panel and optimized statistical models to identify novel loci governing Hg levels in different tissues, enhancing understanding of this complex trait. Overall, characterizing the genetic basis of Hg accumulation in maize has important implications for breeding varieties with reduced Hg uptake and enhancing food safety and human health.
Materials and Methods
Plant materials and field trials
An association mapping panel (AMP) of 230 diverse maize inbred lines, encompassing temperate, tropical, and subtropical backgrounds, was utilized. The panel consisted of 151 inbred lines from temperate backgrounds and 79 from tropical/subtropical backgrounds. In 2012, the AMP underwent cultivation at two distinct locations, Xixian (XX) and Changge (CG), following a randomized complete block design with three replications. These locations were chosen specifically for sampling and evaluating arsenic (As) and mercury (Hg) content. The AMP had previously been employed in a GWAS study exploring the genetic basis of As and Hg accumulation in five maize tissues[
27]. Notably, the soil at XX and CG exhibited Hg contents of 457.57 ± 31.30 μg kg
−1 and 345.40 ± 22.24 μg kg
−1 (pH 6.5), respectively. Detailed information on maize inbred lines, trial specifics, and field management practices can be found in a previous study (Supplenentary Table S1, [
27]).
Measurement of Hg content
Hg content was collected from the kernel, axis, stem, bract, and leaf of the AMP at both XX and CG locations. The phenotypic measurement, as described previously [
27], utilized the same dataset for the current GWAS. To facilitate the GWAS, each combination of tissue (kernel, axis, stem, bract, and leaf) at each location (XX, CG, and BLUP) was treated as an individual phenotypic variable. For instance, "Axis_CG" represents the Hg content in the axis at the Changge location. In total, we obtained 15 phenotypic variables, including 10 for the five tissues at XX and CG locations and 5 representing the BLUP value of each inbred line across the two locations.
Genotype and GWAS
In this study, the AMP comprises 513 maize inbred lines extensively used in prior studies [
15]. To augment genotyping data, 556,809 SNPs (referred to as 0.55 M) with a minor allele frequency (MAF) above 0.05 were derived from this set of 513 lines. This dataset combines 56,110 SNPs from 513 lines and 1.03 million SNPs from 368 lines, a subset of the 513 lines. The integration of these datasets used a two-step imputation method based on Identity by Descent (IBD) and k-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) algorithms, as described previously [
24]. Notably, utilizing 0.55 M has demonstrated a significant enhancement in statistical power in GWAS for traits such as oil concentration and tocopherol content when compared to low-density markers like 56,110 SNPs [
28]. Additionally, a second genotype dataset, comprising 1.25 million SNPs (referred to as 1.25 M) with a MAF ≥ 0.05, was obtained through an effective imputation method integrating data from four genotyping platforms [
29], including Illumina Maize SNP50 BeadChip [
30], deep RNA-sequencing [
31], genotyping by sequencing (GBS) and Affymetrix Axiom Maize 600K array [
32]. This high-density genotype dataset has been successfully used in previous GWAS studies elucidating the genetic basis of traits such as oil concentration, amino acids, and arsenic content in maize kernel and other tissues [
18,
33,
34]. Both genotype datasets, 0.55M and 1.25M, were employed in the subsequent GWAS analysis of the current study, and they are available at
http://www.maizego.org/Resources.html.
GWAS of the 15 variables in the 230 inbred lines underwent analysis in several steps:
1) Multiple statistical models, namely 5PCs+K, Q, K, and Q+K, were employed. The 5PCs+K model controls both the top five principal components (PCs) and the Kinship matrix, as used in the study by Zhao et al[
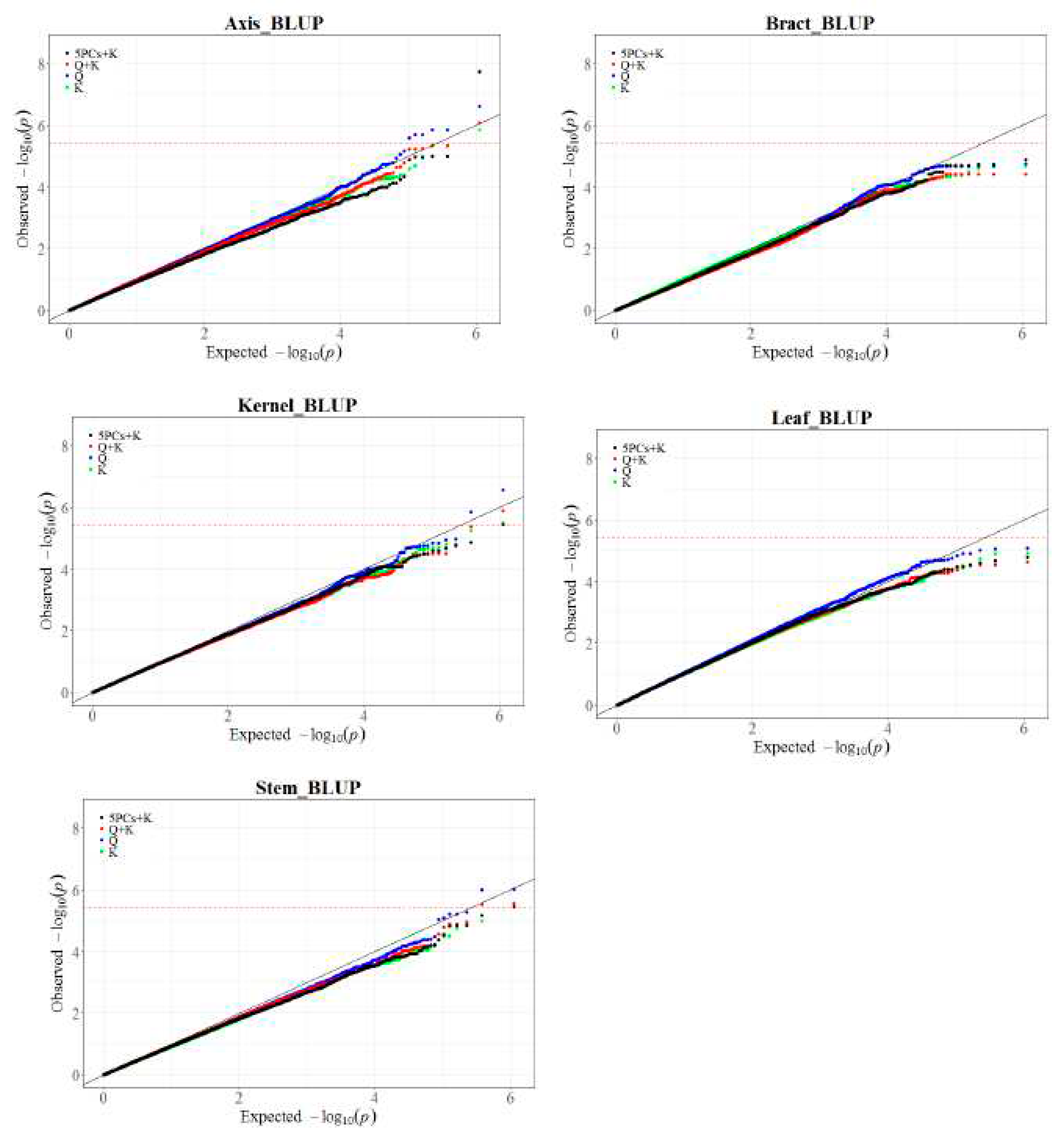
27]. The Q model controls only the population structure, the K model solely controls the Kinship matrix, and the Q+K model controls both the population structure and the Kinship matrix. These analyses utilized the 0.55 M genotypic datasets, and the optimal statistical model was chosen based on Quantile-Quantile (QQ) plots.
2) GWAS results under 0.55 M were compared between 5PCs+K and the optimal statistical model to assess whether changing the model could enhance the statistical power of GWAS.
3) Under the optimal statistical model, GWAS was conducted using an enlarged genotypic dataset (1.25 M). The results from GWAS with the 0.55M and 1.25M datasets were compared to determine if increasing marker density improved the statistical power of the analysis.
4) Finally, the GWAS results of the optimal statistical model under the enlarged 1.25 M genotypic dataset were used for subsequent analysis. The effective marker number (En) of the two genotypic datasets was calculated using GEC software. The result indicated that En was 490,548 for the 1.25 M dataset and 250,345 for the 0.55 M dataset. in addition, the software suggested a significance threshold of P≤ (1/En), which was used for the association analysis.
Candidate gene identification
In preceding studies, we employed a dataset of 1.25 million SNPs to investigate the linkage disequilibrium decay among 500 maize inbred lines. The results revealed an LD decay of approximately 30 kilobases (kb) with an R
2 value of 0.1. Consequently, a 30 kb interval around both the upstream and downstream regions of a significant SNP marker's physical position was defined as a locus. For gene identification within these identified loci from GWAS, we utilized the B73 reference genome (RefGen_v2) and obtained the maize whole-genome gene list from the Maize Genetics and Genomics Database (MaizeGDB,
http://www.maizegdb.org). This list was employed to search for candidate genes within each significant locus. The selection of the most likely candidate gene at each locus was based on functional annotations and expression profiles of the genes in different tissues of the maize inbred line B73.
Analysis of Expression Level Association of Candidate Genes
In our study, we performed an analysis to explore the association between gene expression levels and genetic variation (1.25M) using expression data from kernels collected 15 days after pollination in the 368 maize inbred lines. This analysis aimed to identify expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs), which are specific genetic loci associated with variations in gene expression. To assess the significance of these associations, we applied a stringent criterion, considering associations as significant only if they met the condition of P < 1/En, where En represents the effective marker number. This criterion ensures that only robust and biologically relevant associations between genetic variants (SNPs) and gene expression levels are deemed significant eQTLs.
Haplotype analyses of candidate genes
Based on the study's results, we performed a thorough screening of all single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within candidate genes using genotype data. Haplotypes were formed by combining Best Linear Unbiased Prediction (BLUP) values from the 230 inbred lines. Specifically, haplotypes with representation by more than 8 inbred lines were systematically chosen, and their differences were rigorously examined through a t-test, with a significance threshold set at P < 0.01. Additionally, we meticulously generated a Heatmap illustrating pairwise Linkage Disequilibrium using the "LDheatmap" package in the R statistical software[
35].
Results
Model comparison and selection
Previous research investigated the genetic factors influencing mercury (Hg) content in various maize tissues. However, limitations were identified in the statistical model used (5PCs+K), which exhibited excessive conservatism, leading to reduced detection of true associations (type II errors). Additionally, the significance threshold for declaring SNP-trait associations was relatively lenient[
36]. To address these limitations, we reanalyzed Hg content using different GWAS models and an enlarged SNP panel. We first analyzed Hg content using four statistical models (Q, K, Q+K, 5PCs+K) with 0.55 million SNPs. Examination of quantile-quantile (QQ) plots revealed the Q model consistently had the best fit to the data (
Figure 1, Supplementary Figure 2). Comparing results from the Q and 5PCs+K models affirmed the improved power of the Q model (Supplementary Figure 1). Using a Bonferroni-corrected significance threshold (P ≤ 1/EN
1, EN
1 = 250,345), the Q model identified 46 significant SNPs associated with 32 QTL, whereas 5PCs+K identified only three QTL (all also detected by Q). Similarly, Q model is also found to be superior to other models at 1.25M (Supplemental Figure 3).
Boosting GWAS Power through Increased Marker Density
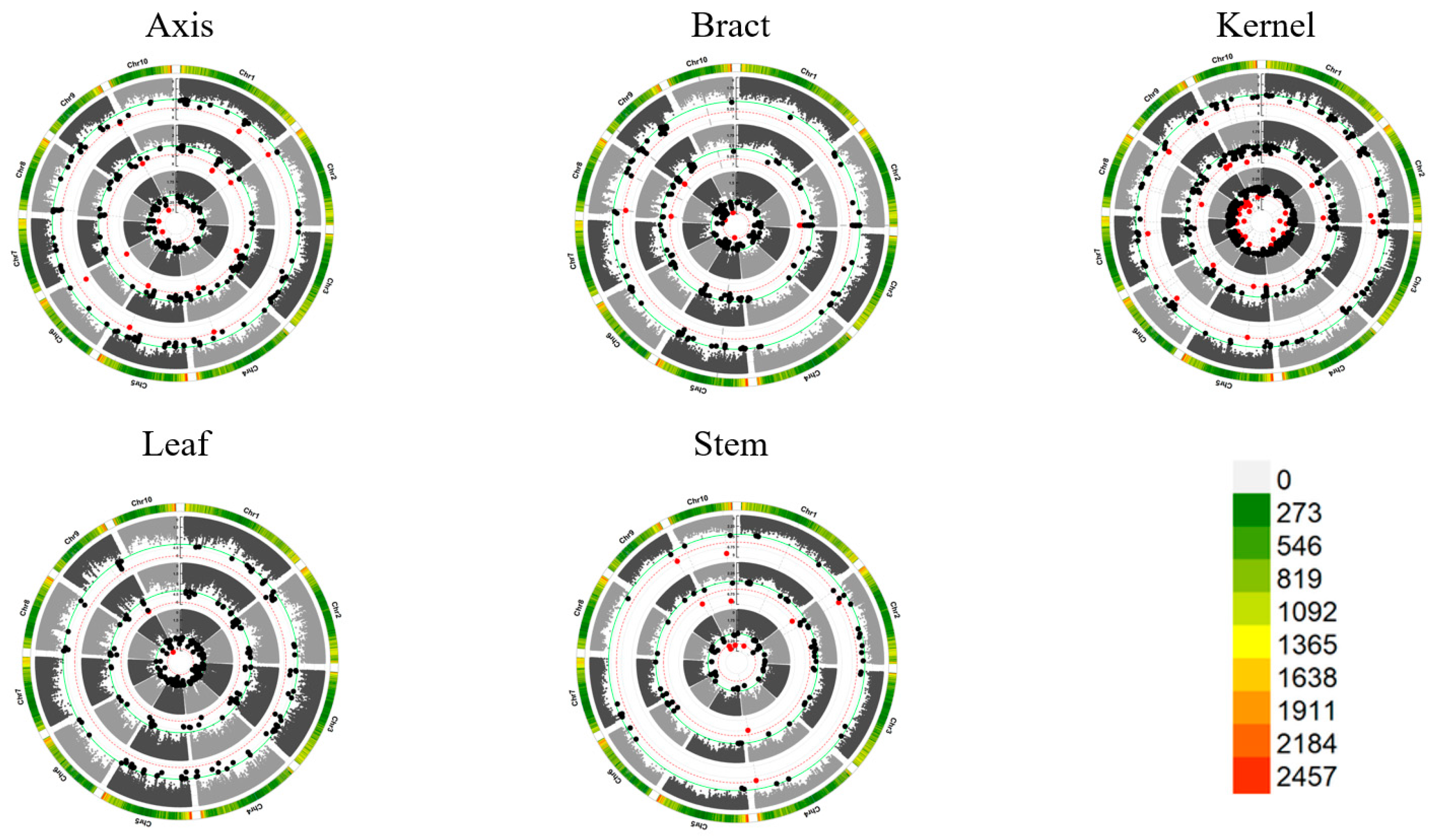
We then investigated whether increasing marker density could further improve power. Re-running GWAS with 1.25 million SNPs under the Q model revealed more significant SNPs than with 0.55 million SNPs (Supplemental Figures 4-5). Specifically, 1.25 million SNPs identified 111 significant SNPs associated with 78 QTL at (P ≤ 1/EN
2, EN
2 = 490,548,
Figure 2), versus 26 SNPs and 22 QTL with 0.55 million SNPs. These findings demonstrate that increasing marker density augments GWAS power to discover novel trait-associated loci.
Significant Loci and Tissue-Specific Variability
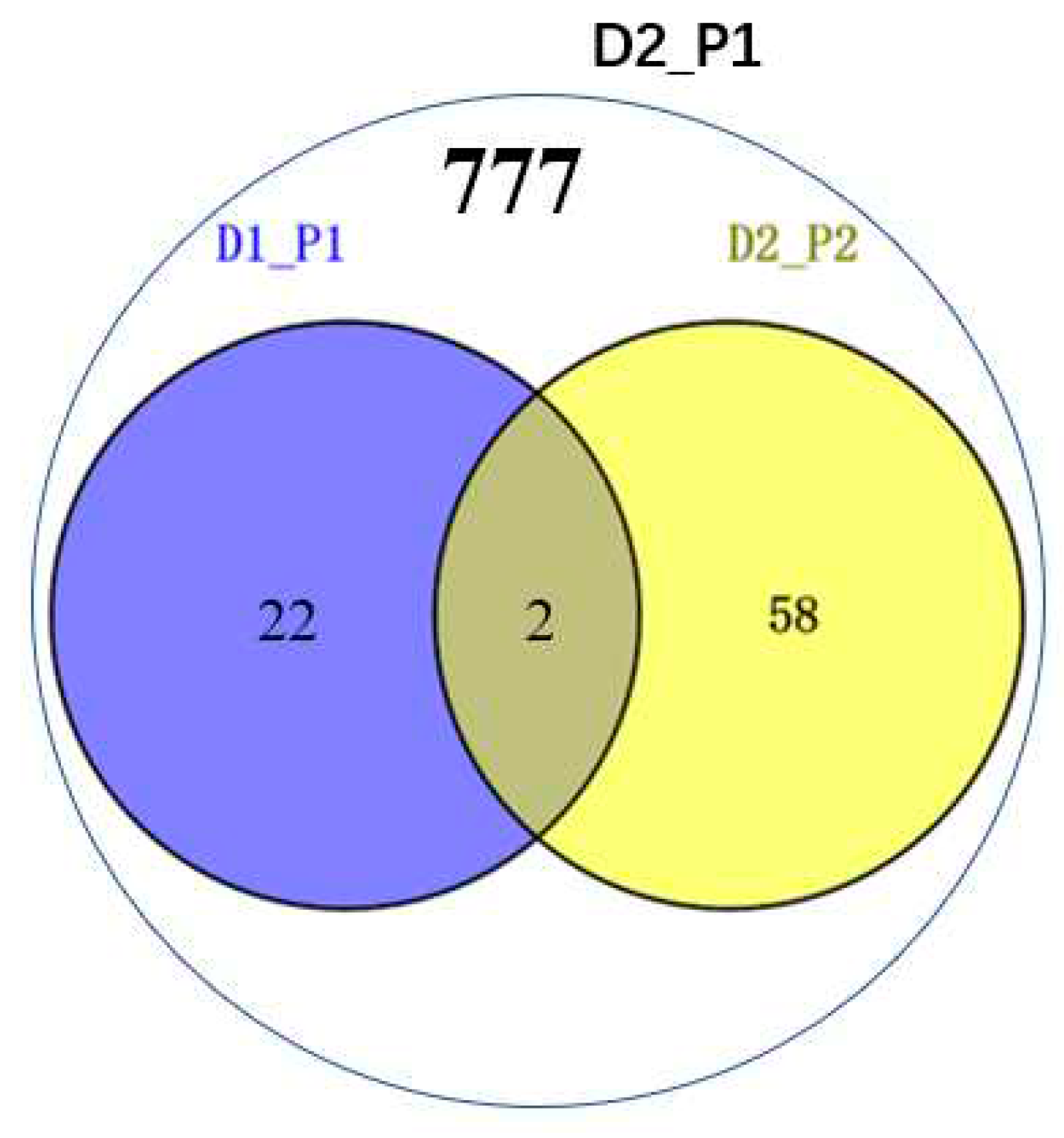
To assess the impact of increased marker density on GWAS detection efficiency, we conducted an analysis at a family-wise error rate of 0.05. In Dataset 1, we identified 24 non-redundant QTLs (P ≤ 4.0×10
-6, EN
1 = 250,345), and in Dataset 2, we identified 61 non-redundant QTL (P ≤ 2.0×10
-6, EN
2 =490,548). Only two loci were common between the two datasets. When the P-value was set to P ≤ 4.0×10
-6, consistent with Dataset 1, a total of 777 QTL were identified, including 24 non-redundant QTL from Dataset 1 (
Figure 3).
Expanding our analysis to different tissues revealed 111 SNP-trait associations across 78 loci categorized into 61 non-redundant QTL at a significance level of P ≤ 2.0×10-6 (
Table S2). Within the CG environment, 50 SNPs involving 34 loci were identified, each explaining phenotypic variation ranging from 8.38% to 24.30%. Notably, three significant SNPs associated with axis tissue were discovered across three QTLs, explaining phenotypic variance ranging from 10.3% to 24.3%, with a mean of 16.8%. Similar findings were observed for bract, kernel, leaf, and stem tissues. In the Xixian environment, 37 SNPs involving 25 loci were identified, each explaining 8.47% to 24.71% of the phenotypic variation. For each tissue, specific SNPs and QTLs were discovered, contributing to our understanding of the genetic basis of these traits. In the BLUP environment, 24 SNPs and 19 loci were identified, each explaining 9.70% to 23.27% of the variance. Comprehensive analysis across distinct tissues and locations enriched our understanding of the diverse landscape of significant loci, highlighting the genetic contributions to these traits.
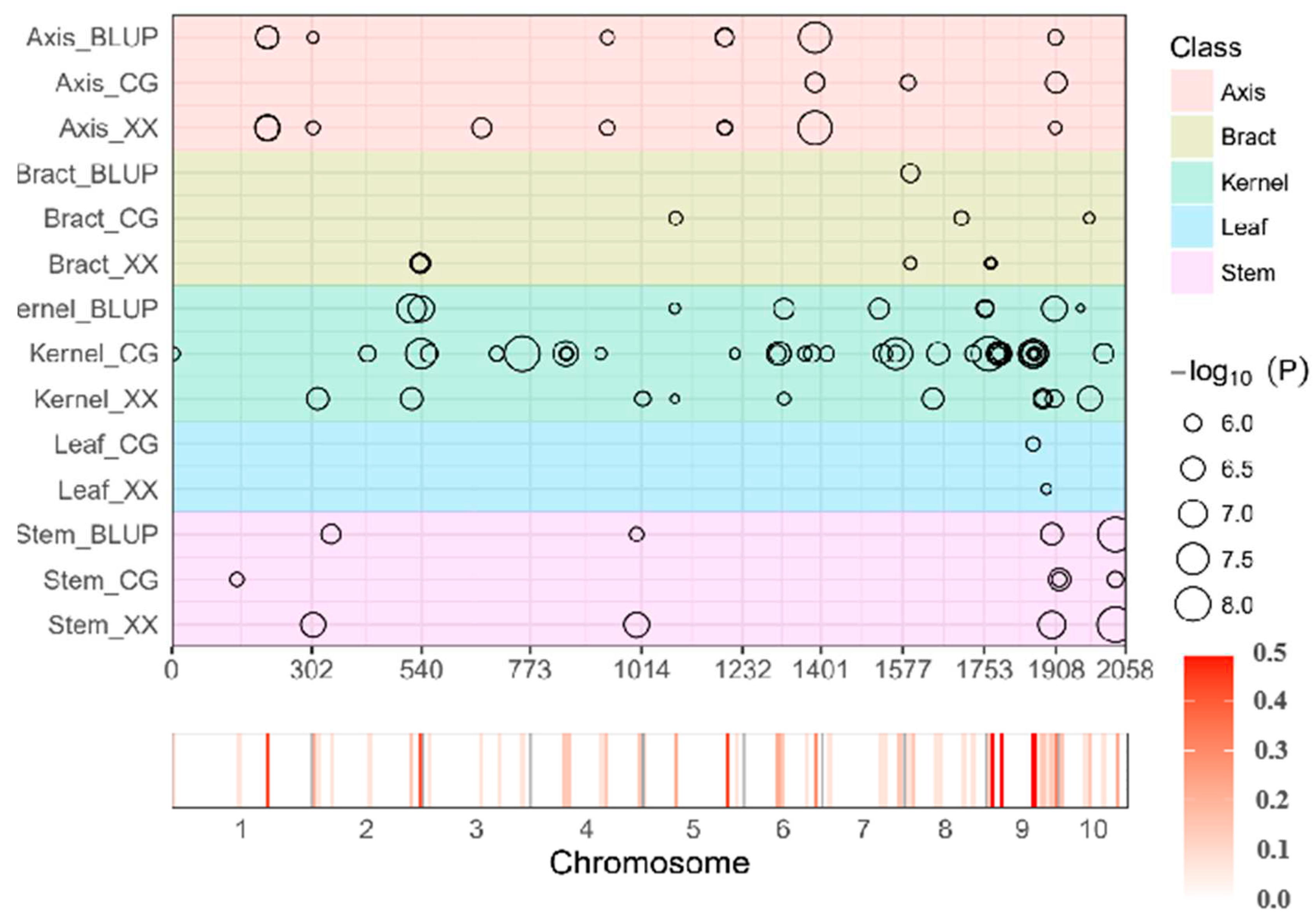
Simultaneous Identification of Significantly Mapped Loci Across Diverse Tissues and Environmental Conditions
Notably, we identified 15 non-redundant QTLs encompassing 36 SNP-trait associations consistently detected across tissues and environments (
Figure 4). Particularly noteworthy were non-redundant QTLs associated with stem tissue housing 3 QTLs within a 127.32 ~ 127.37Mb interval on chromosome 10. These QTLs were consistently identified in all environments, explaining sizable phenotypic variations. Another non-redundant QTL linked to axis tissue appeared in three environments within a 155.63 ~ 155.69Mb region on chromosome 6. The observed co-localization patterns indicate stability of these loci against environmental influences.
Functional Analysis of Identified Genes
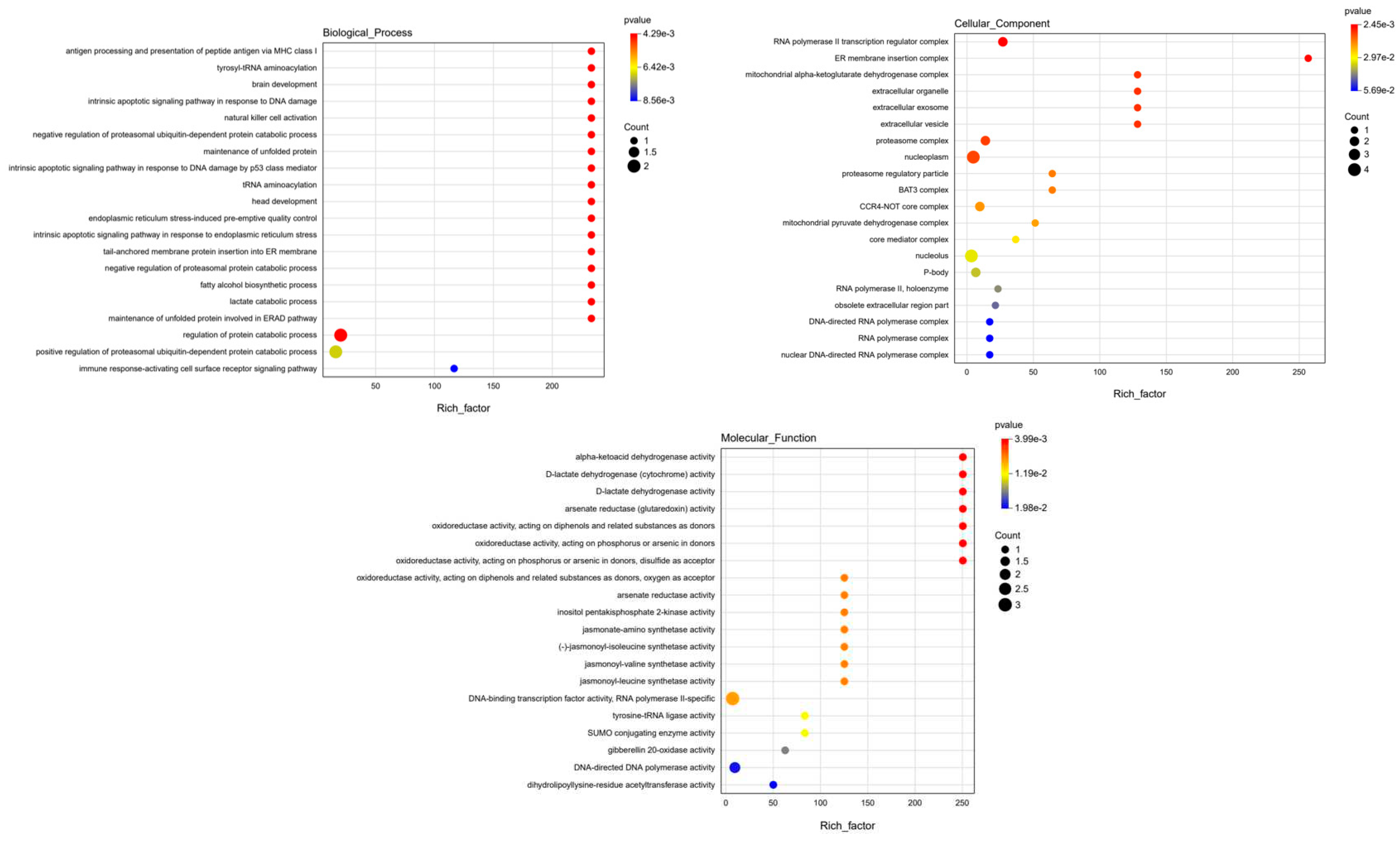
To pinpoint the most likely candidate gene and understand their molecular functions. Subsequently, we conducted Gene Ontology (GO) analysis to reveal the functions served by these genes (
Figure 5). Our analysis revealed that these genes predominantly cluster around essential molecular activities, including DNA binding, arsenate reductase (glutaredoxin) activity, jasmonate-amino synthetase activity and other functions. This GO analysis provides valuable insights into the molecular functions of these genes, shedding light on their involvement in the mechanisms of resistance to metal stress and significantly enhancing our understanding of their contributions to plant biology.
Candidate gene analysis
Our exploration into candidate genes within the co - located loci unveiled several noteworthy findings (
Table 1). For example, on chromosome 6
GRMZM2G440968 encodes a cysteine proteinase inhibitor, which may alleviate mercury toxicity by inhibiting cysteine, as indicated by its known role in detecting kidney damage [
37,
38]. Moving to chromosome 10,
GRMZM2G005633 encodes Endochitinase B, a pivotal player in bacterial adaptation to stresses, promoting plant growth and development [
39].
GRMZM2G125991 encodes endoglucanase 7-like, a cellulose-related enzyme potentially involved in responding to copper pollution in willow roots, impacting cellulase content [
40].
GRMZM2G125943 encodes a histidine kinase, recognized for its pivotal role in plant stress and hormone regulation. Previous studies have illuminated its involvement in responding to challenges such as cold stress and Cordyceps Sinensis mimicry [
41,
42].An intriguing observation comes from a locus (the peak SNP is chr5.S_2356674) on chromosome 5, exclusively detected in the XX environment, housing seven candidate genes. Notably,
GRMZM2G002805,
GRMZM2G144188 and
GRMZM2G144172 within this locus encode zinc finger proteins, known to play a role in alternative splicing under conditions of arsenic poisoning. Specifically, As
3+ can displace Zn
2+ in ZRANB2, leading to structural changes affecting protein function. Studies have also highlighted the impact of Hg (II) leading to structural changes affecting protein function [2-5]. Subsequently, 19 candidate genes were identified in 9 QTLs, involved in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. Further functional analysis, combining expression GWAS with the expression levels of 16 genes and 1.25M SNPs, revealed significant correlations for all 16 genes (Table 2). Haplotype analysis of
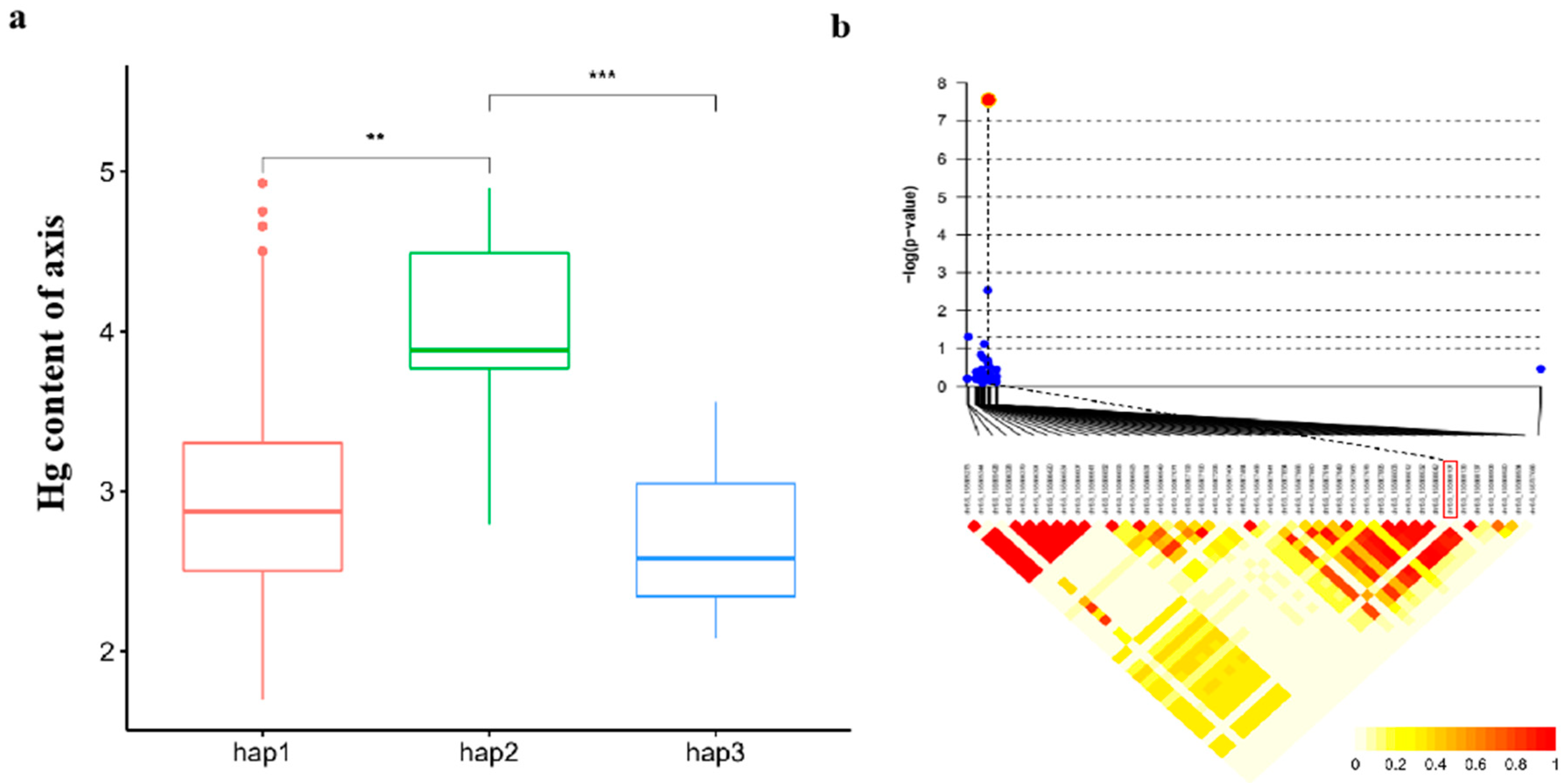
GRMZM2G440968 demonstrated three haplotypes, with Hap3 exhibited the lowest mercury content compared to other haplotypes. LD analysis within one LD decay distance (±30 kb) upstream and downstream of the lead SNP unveiled linkage relationships between them, emphasizing co - inheritance and linkage on the genome (
Figure 6). These findings provide valuable insights into the genetic mechanisms underlying various physiological and metabolic processes in maize
Discussion
In plant GWAS studies, maximizing statistical power is paramount. Different maize traits have varying sensitivities to different statistical models, a phenomenon intricately linked to population structure. Yang's seminal work underscored the pivotal role of selecting the most appropriate statistical model to augment GWAS statistical power[
24]. Extending this line of inquiry, Zhao et al. conducted a GWAS study on arsenic content across five maize tissues, meticulously assessing different statistical models to balance minimizing false positives and optimizing analysis sensitivity. Their findings illuminated that the K model and Q+K model exhibited excessive conservatism, potentially increasing type II errors. In contrast, the Q model emerged as the optimal choice, effectively controlling false positives while preserving power[
18].
In the present study, we encountered a similar scenario where both the K model and Q+K model demonstrated unwarranted stringency, while the Q model provided an ideal balance. Therefore, we selected the Q model to investigate the genetic basis of Hg content in five maize tissues. Using this model with 0.55M SNPs, we identified more significant SNPs and loci compared to the previous study. However, increasing marker density and population size can further enhance GWAS power, as demonstrated by others[
47,
24]. To explore this, we reanalyzed the data using 1.25M SNPs under the Q model. Directly comparing the results revealed substantial gains in power, with over double the number of significant SNPs and loci detected. This increase derives from a richer representation of the genome's genetic variation, consistent with prior reports. Innovative statistical models have also proven effective by optimizing genetic and pedigree relationships[
48]. Thus, both expanding genotype data and refining statistical models contribute synergistically to the increased statistical power of GWAS.
Analysis of candidate genes revealed several with notable functions. For example,
GRMZM2G162413 plays a key role in resisting ear rot and temperature stress [
49]. Another significant candidate,
GRMZM2G011520, encodes arsenate reductase critical for arsenic detoxification [
50].
GRMZM5G877941 links to growth inhibition and senescence under methylglyoxal stress [
51].
GRMZM2G150496 exhibits hypersensitivity to arsenate stress and reduced uptake compared to wild-type [
52]. The emerging candidate
GRMZM2G440968 encodes a cysteine proteinase inhibitor that may alleviate mercury toxicity by inhibiting cysteine, as indicated by its role in detecting kidney damage and ameliorating nephrotoxicity. we speculate that plants may undergo oxidative stress under mercury stress, leading to the production of reactive oxygen species and causing damage to cellular components. Cysteine proteinase inhibitors, by regulating the activity of cysteine proteinases, may help modulate the plant's response to oxidative stress and maintain cellular homeostasis under mercury exposure.
Mercury poisoning poses a substantial threat, with potential exposure pathways including ingestion through the food chain or contact with mercury-containing air, water, or specific occupational settings, leading to adverse effects on the nervous system [
8]. Intriguingly, research indicates that even mercury levels below 50 µg/g in hair can pose neurological risks, manifesting as sensory disturbances [
53]. Furthermore, studies underscore the neurobehavioral and neurochemical toxicity associated with prolonged low-dose cinnabar (HgS) exposure, shedding light on the sedative and neurotoxic effects of this mineral medicine [
54]. The primary approach to mitigating mercury poisoning involves chelation therapy, designed to enhance methylmercury excretion by forming complexes with mercury ions. However, existing chelating agents have limitations, including reduced therapeutic efficacy and the potential loss of essential elements like iron and calcium. Some chelating agents may even exhibit toxicity [
55,
56]. Consequently, effective mercury poisoning treatment remains a formidable challenge. Amid these challenges, the cultivation of mercury-tolerant maize emerges as a promising solution to address mercury poisoning. Additionally, exploration of organic selenium compounds and thiourea resin has shown promise in reducing methylmercury toxicity. However, these agents primarily focus on excretion rather than tissue repair. Research has also spotlighted the beneficial effects of natural plant extracts in mitigating the toxic impact of methylmercury and reducing metal neurotoxicity. Notably, garlic's mercaptans bind with methylmercury, reducing its toxicity. Fisetin, derived from various fruits, effectively reduces brain methylmercury accumulation and related toxicity. These findings open avenues for exploring natural substances in maize with therapeutic potential against mercury poisoning [
57,
58].
Conclusions
In this study, we leveraged an enlarged SNP panel comprising 1.25 million SNPs and improved statistical models to re-conduct a genome-wide association study of mercury content in five tissues of 230 maize inbred lines. Compared to prior research utilizing lower-density markers, our approach identified considerably more significant quantitative trait loci associated with mercury accumulation. Specifically, we uncovered 74 additional QTLs, for a total of 169 candidate genes implicated in mercury content, of which 142 have annotated functions. Notably, GRMZM2G440968, encoding a cysteine proteinase inhibitor, emerges as a potential key regulator in alleviating mercury toxicity in plants. By inhibiting cysteine proteinases, this gene may help mitigate the strong binding of mercury to cysteine thiolate anions in vital enzymes. Haplotype analysis showed lines containing haplotype 2 exhibited significantly higher mercury levels. Through enhanced marker density and improved modeling, our research provides deeper insights into the genetic mechanisms underlying mercury accumulation in maize. Ultimately, these findings are critical for developing maize varieties with reduced mercury content, thereby contributing to broader efforts of ensuring food safety and human health. In conclusion, we demonstrate that augmenting GWAS approaches can uncover additional genetic factors influencing metal stress tolerance in plants.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Table S1. Pedigree information of the 230 inbred lines used in this study. Table S2. List of candidate genes and their annotations. Figure S1. Comparison of Manhattan plots resulting from GWAS, based on 0.55M SNPs, using Q model and 5PCs+K model for mercury content in maize axis, stem, bract, leaf and kernel at BLUP environments. Figure S2. Comparison of Quantile-quantile (QQ) plots resulting from GWAS, based on 0.55M SNPs, using three models (Q, K and Q+K) for mercury content in maize axis, stem, bract, leaf, and kernel at three environments. Figure S3. Comparison of quantile-quantile (QQ) plots resulting from GWAS, based on 1.25M SNPs, using three models (Q, K and Q+K) for mercury content in maize axis, stem, bract, leaf, and kernel at three environments. Figure S4. Comparison of Quantile-quantile (QQ) plots resulting from GWAS, based on 0.55M SNPs and 1.25M SNPs, using Q model for mercury content in maize axis, stem, bract, leaf, and kernel at three environments. Figure S5. Comparison of Manhattan plots resulting from GWAS, based on 0.55M SNPs and 1.25M SNPs, using Q model for mercury content in maize axis, stem, bract, leaf, and kernel at three environments.
Author Contributions
XZ designed the study. XZ and JT supervised the study. XZ, JG, JL, JZ, YS, XJ, WL, HD, ZX, LS, JHS and ZF analyzed the data. XZ and JG prepared the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We thank research group of Prof. Jianbing Yan at Huazhong Agricultural University for providing genotypic data. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32171980), the Project funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M682295), the Henan Province Science and Technology Attack Project (232102110181), the Henan Provincial Higher Education Key Research Project(24B210003), the First-class postdoctoral research grant in Henan Province (202001032) and the Research start-up fund to youth talents of Henan Agricultural University (30500563).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Rahman, Z.; Singh, V.P. The relative impact of toxic heavy metals (THMs) (arsenic (As); cadmium (Cd); chromium (Cr)(VI); mercury (Hg); and lead (Pb)) on the total environment: an overview. Environ Monit Assess. 2019, 191, 419. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao R, Zhang J, Shi W, Wang Y, Tang Y, Liu Z, Sun W, Wang H, Guo J, Meng Y, Kang G, Jagadish KS, Yang Q. Mercury stress tolerance in wheat and maize is achieved by lignin accumulation controlled by nitric oxide. Environ Pollut. 2022, 307, 119488. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Z. Boerleider R; Roeleveld N; T.J. Scheepers P. Human biological monitoring of mercury for exposure assessment. AIMS Environmental Science. 2017, 4, 251–276. [CrossRef]
- Wang C; Wang Z; Gao Y; Zhang X. Planular-vertical distribution and pollution characteristics of cropland soil Hg and the estimated soil-air exchange fluxes of gaseous Hg over croplands in northern China. Environ Res. 2021, 195, 110810.
- Zhang L; Wong MH. Environmental mercury contamination in China: sources and impacts. Environ Int. 2017, 33, 108-121.
- Sun T, Wang Z, Zhang X, Niu Z, Chen J. Influences of high-level atmospheric gaseous elemental mercury on methylmercury accumulation in maize (Zea mays L.). Environ Pollut. 2020;265(Pt B):114890.
- Liu S; Wang X; Guo G; Yan Z. Status and environmental management of soil mercury pollution in China: A review. J Environ Manage. 2021, 277, 111442.
- Rocha J; Aschner M; Dorea JG; Ceccatelli S; Farina M; Silveira L. Mercury toxicity. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012, 831890.
- Wang C; Wang T; Mu P; Li Z; Yang L. Quantitative Trait Loci for Mercury Tolerance in Rice Seedlings. Rice Science. 2013, 20, 238–242.
- Fu Z; Li W; Zhang Q; Wang L; Zhang X; Song G; Fu Z; Ding D; Liu Z; Tang J. Quantitative trait loci for mercury accumulation in maize (Zea mays L.) identified using a RIL population. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107243.
- Hu T; Liu Y; Zhu S; Qin J; Li W; Zhou N. Overexpression of OsLea14-A improves the tolerance of rice and increases Hg accumulation under diverse stresses. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019, 26, 10537-10551.
- Sun L; Ma Y; Wang H; Huang W; Wang X; Han L; Sun W; Han E; Wang B. Overexpression of PtABCC1 contributes to mercury tolerance and accumulation in Arabidopsis and poplar. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018, 497, 997-1002.
- Xu S; Sun B; Wang R; He J; Xia B; Xue Y; Wang R. Overexpression of a bacterial mercury transporter MerT in Arabidopsis enhances mercury tolerance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017, 490, 528-534.
- Yu J; Buckler ES. Genetic association mapping and genome organization of maize. Curr Opin Biotechnol.2006, 17, 155–160.
- Xiao Y; Liu H; Wu L; Warburton M; Yan J. Genome-wide Association Studies in Maize: Praise and Stargaze. Mol Plant. 2017, 10:359-374.
- Li H; Peng Z; Yang X; Wang W; Fu J; Wang J; Han Y; Chai Y; Guo T; Yang N; Liu J; Warburton ML; Cheng Y; Hao X; Zhang P; Zhao J; Liu Y; Wang G; Li J; Yan J. Genome-wide association study dissects the genetic architecture of oil biosynthesis in maize kernels. Nat Genet. 2013, 45:43-50.
- Beló A; Zheng P; Luck S; Shen B; Meyer DJ; Li B; Tingey S; Rafalski A. Whole genome scan detects an allelic variant of fad2 associated with increased oleic acid levels in maize. Mol Genet Genomics. 2008, 279, 1–10.
- Zhao Z; Zhang H; Fu Z; Chen H; Lin Y; Yan P; Li W; Xie H; Guo Z; Zhang X; Tang J. Genetic-based dissection of arsenic accumulation in maize using a genome-wide association analysis method. Plant Biotechnol J. 2018, 16, 1085-1093.
- Korte A, Farlow A. The advantages and limitations of trait analysis with GWAS: a review. Plant Methods 2013, 9, 29.
- Huang X, Zhao Y, Wei X, Li C, Wang A, Zhao Q, Li W, Guo Y, Deng L, Zhu C, Fan D, Lu Y, Weng Q, Liu K, Zhou T, Jing Y, Si L, Dong G, Huang T, Lu T, Feng Q, Qian Q, Li J, Han B. Genome-wide association study of flowering time and grain yield traits in a worldwide collection of rice germplasm. Nat Genet. 2011, 44, 32-9.
- Wang SB, Feng JY, Ren WL, Huang B, Zhou L, Wen YJ, Zhang J, Dunwell JM, Xu S, Zhang YM. Improving power and accuracy of genome-wide association studies via a multi-locus mixed linear model methodology. Sci Rep. 2016, 6, 19444.
- Wang Q, Tian F, Pan Y, Buckler ES, Zhang Z. A SUPER powerful method for genome wide association study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107684.
- Li X, Zhu C, Yeh CT, Wu W, Takacs EM, Petsch KA, Tian F, Bai G, Buckler ES, Muehlbauer GJ, Timmermans MC, Scanlon MJ, Schnable PS, Yu J. Genic and nongenic contributions to natural variation of quantitative traits in maize. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 2436-44.
- Yang N; Lu Y; Yang X; Huang J; Zhou Y; Ali F; Wen W; Liu J; Li J; Yan J. Genome wide association studies using a new nonparametric model reveal the genetic architecture of 17 agronomic traits in an enlarged maize association panel. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004573. [CrossRef]
- Tian F; Bradbury P; Brown P; Hung H; Sun Q; Flint-Garcia S; Rocheford TR; McMullen MD; Holland JB; Buckler ES. Genome-wide association study of leaf architecture in the maize nested association mapping population. Nat Genet. 2011, 43, 159-162.
- Zhao K; Tung CW; Eizenga GC; Wright MH; Ali ML; Price AH; Norton GJ; Islam MR; Reynolds A; Mezey J; McClung AM; Bustamante CD; McCouch SR. Genome-wide association mapping reveals a rich genetic architecture of complex traits in Oryza sativa. Nat Commun. 2011, 2, 467.
- Zhao Z; Fu Z; Lin Y; Chen H; Liu K; Xing X; Liu Z; Li W; Tang J. Genome-wide association analysis identifies loci governing mercury accumulation in maize. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 247.
- Wang H; Xu S; Fan Y; Liu N; Zhan W; Liu H; Xiao Y; Li K; Pan Q; Li W; Deng M; Liu J; Jin M; Yang X; Li J; Li Q; Yan J. Beyond pathways: genetic dissection of tocopherol content in maize kernels by combining linkage and association analyses. Plant Biotechnol J. 2018, 16, 1464-1475. 1475.
- Liu H; Luo X; Niu L; Xiao Y; Chen L; Liu J; Wang X; Jin M; Li W; Zhang Q; Yan J. Distant eQTLs and Non-coding Sequences Play Critical Roles in Regulating Gene Expression and Quantitative Trait Variation in Maize. Mol Plant. 2017, 10, 414-426.
- Li Q; Yang X; Xu S; Cai Y; Zhang D; Han Y; Li L; Zhang Z; Gao S; Li J; Yan J. Genome-wide association studies identified three independent polymorphisms associated with alpha-tocopherol content in maize kernels. PLoS One 2012, 7, e36807.
- Fu J; Cheng Y; Linghu J; Yang X; Kang L; Zhang Z; Zhang J; He C; Du X; Peng Z; Wang B; Zhai L; Dai C; Xu J; Wang W; Li X; Zheng J; Chen L; Luo L; Liu J; Qian X; Yan J; Wang J; Wang G. RNA sequencing reveals the complex regulatory network in the maize kernel. Nat Commun. 2013, 4, 2832.
- Elshire R; Glaubitz J; Sun Q; Poland J; Kawamoto K; Buckler E; Mitchell S. A robust; simple genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) approach for high diversity species. PLoS One 2011, 6, e19379.
- Deng M; Li D; Luo J; Xiao Y; Liu H; Pan Q; Zhang X; Jin M; Zhao M; Yan J. The genetic architecture of amino acids dissection by association and linkage analysis in maize. Plant Biotechnol J. 2017, 15, 1250-1263.
- Liu H; Wang X; Warburton ML; Wen W; Jin M; Deng M; Liu J; Tong H; Pan Q; Yang X; Yan J. Genomic; Transcriptomic; and Phenomic Variation Reveals the Complex Adaptation of Modern Maize Breeding. Mol Plant. 2015, 8, 871-884.
- iu B; Zhang B; Yang Z; Liu Y; Yang S; Shi Y; Jiang C; Qin F. Manipulating ZmEXPA4 expression ameliorates the drought-induced prolonged anthesis and silking interval in maize. Plant Cell. 2021, 33, 2058-2071. 2071.
- Huang X; Wei X; Sang T; Zhao Q; Feng Q; Zhao Y; Li C; Zhu C; Lu T; Zhang Z; Li M; Fan D; Guo Y; Wang A; Wang L; Deng L; Li W; Lu Y; Weng Q; Liu K; Huang T; Zhou T; Jing Y; Li W; Lin Z; Buckler ES; Qian Q; Zhang QF; Li J; Han B. Genome-wide association studies of 14 agronomic traits in rice landraces. Nat Genet. 2010, 42, 961–967.
- Khorchid A; Ikura M. Bacterial histidine kinase as signal sensor and transducer. International. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006, 38, 307-312.
- Yu X; Meng X; Xu M; Zhang X; Zhang Y; Ding G; Huang S; Zhang A; Jia Z. Celastrol ameliorates cisplatin nephrotoxicity by inhibiting NF-kappaB and improving mitochondrial function. EBioMedicine 2018, 36, 266-280.
- Stratton A, Ericksen M, Harris TV, Symmonds N, Silverstein TP. Mercury(II) binds to both of chymotrypsin's histidines, causing inhibition followed by irreversible denaturation/aggregation. Protein Sci. 2017;26(2):292-305.
- Cao Y; Ma C; Chen H; Chen G; White JC; Xing B. Copper stress in flooded soil: Impact on enzyme activities; microbial community composition and diversity in the rhizosphere of Salix integra. Sci Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135350.
- Liu YN; Liu BY; Ma YC; Yang HL; Liu GQ. Analysis of reference genes stability and histidine kinase expression under cold stress in Cordyceps militaris. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0236898.
- Kumar M; Verslues P. Stress physiology functions of the Arabidopsis histidine kinase cytokinin receptors. Physiol Plant. 2015, 154, 369-380.
- Abbehausen C. Zinc finger domains as therapeutic targets for metal-based compounds - an update. Metallomics. 2019, 11, 15-28.
- Banerjee M; Ferragut Cardoso AP; Lykoudi A; Wilkey DW; Pan J; Watson WH; Garbett NC; Rai SN; Merchant ML; States JC. Arsenite Exposure Displaces Zinc from ZRANB2 Leading to Altered Splicing. Chem Res Toxicol. 2020, 33, 1403-1417.
- Razmiafshari M; Kao J; d'Avignon A; Zawia NH. NMR identification of heavy metal-binding sites in a synthetic zinc finger peptide: toxicological implications for the interactions of xenobiotic metals with zinc finger proteins. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2001, 172, 1-10.
- Sivo V; D'Abrosca G; Baglivo I; Iacovino R; Pedone PV; Fattorusso R; Russo L; Malgieri G; Isernia C. Ni(II); Hg(II); and Pb(II) Coordination in the Prokaryotic Zinc-Finger Ros87. Inorg Chem. 2019, 58, 1067-1080.
- Zhang X; Warburton ML; Setter T; Liu H; Xue Y; Yang N; Yan J; Xiao Y. Genome-wide association studies of drought-related metabolic changes in maize using an enlarged SNP panel. Theor Appl Genet. 2016, 129, 1449-63.
- Tibbs Cortes L; Zhang Z; Yu J. Status and prospects of genome-wide association studies in plants. Plant Genome. 2021, 14, e20077.
- Liao X; Sun J; Li Q; Ding W; Zhao B; Wang B; Zhou S; Wang H. ZmSIZ1a and ZmSIZ1b play an indispensable role in resistance against Fusarium ear rot in maize. Mol Plant Pathol. 2023, 24, 711-724.
- Kumari N; Jagadevan S. Genetic identification of arsenate reductase and arsenite oxidase in redox transformations carried out by arsenic metabolising prokaryotes - A comprehensive review. Chemosphere 2016, 163, 400-412.
- An B; Lan J; Deng X; Chen S; Ouyang C; Shi H; Yang J; Li Y. Silencing of D-Lactate Dehydrogenase Impedes Glyoxalase System and Leads to Methylglyoxal Accumulation and Growth Inhibition in Rice. Front Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2071.
- Sun Y; Xu W; Wu L; Wang R; He Z; Ma M. An Arabidopsis mutant of inositol pentakisphosphate 2-kinase AtIPK1 displays reduced arsenate tolerance. Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 39, 416-426.
- Maruyama K; Yorifuji T; Tsuda T; Sekikawa T; Nakadaira H; Saito H. Methyl mercury exposure at Niigata; Japan: results of neurological examinations of 103 adults. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012, 635075.
- Huang C; Liu S; Lin-Shiau S. Neurotoxicological effects of cinnabar (a Chinese mineral medicine; HgS) in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2007, 224, 192-201.
- Canabady-Rochelle LL; Harscoat-Schiavo C; Kessler V; Aymes A; Fournier F; Girardet JM. Determination of reducing power and metal chelating ability of antioxidant peptides: revisited methods. Food Chem. 2015, 183, 129-135.
- Torres-Fuentes C; Alaiz M; Vioque J. Iron-chelating activity of chickpea protein hydrolysate peptides. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 1585-1588.
- Chang J; Zhou Y; Wang Q; Aschner M; Lu R. Plant components can reduce methylmercury toxication: A mini-review. Biochimica et biophysica acta. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2019, 1863, 129290.
- Li Y; Takada M; Mizuno N. Premotor neurons projecting simultaneously to two orofacial motor nuclei by sending their branched axons. A study with a fluorescent retrograde double-labeling technique in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1993, 152, 29–32.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).