Submitted:
10 January 2024
Posted:
11 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
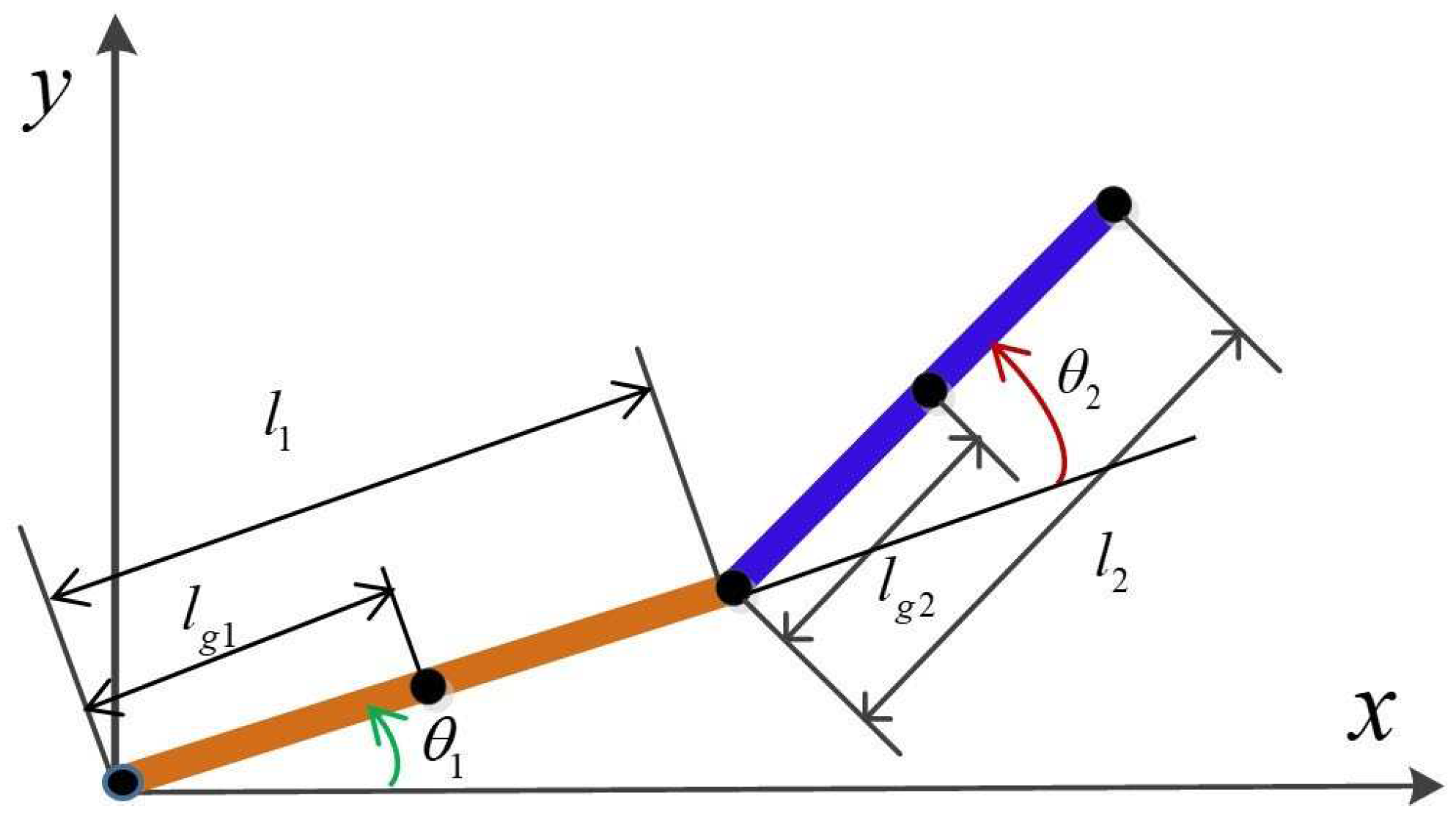
2. Robot planar dynamic model
3. Two structure diagrams for robot control using iterative learning method
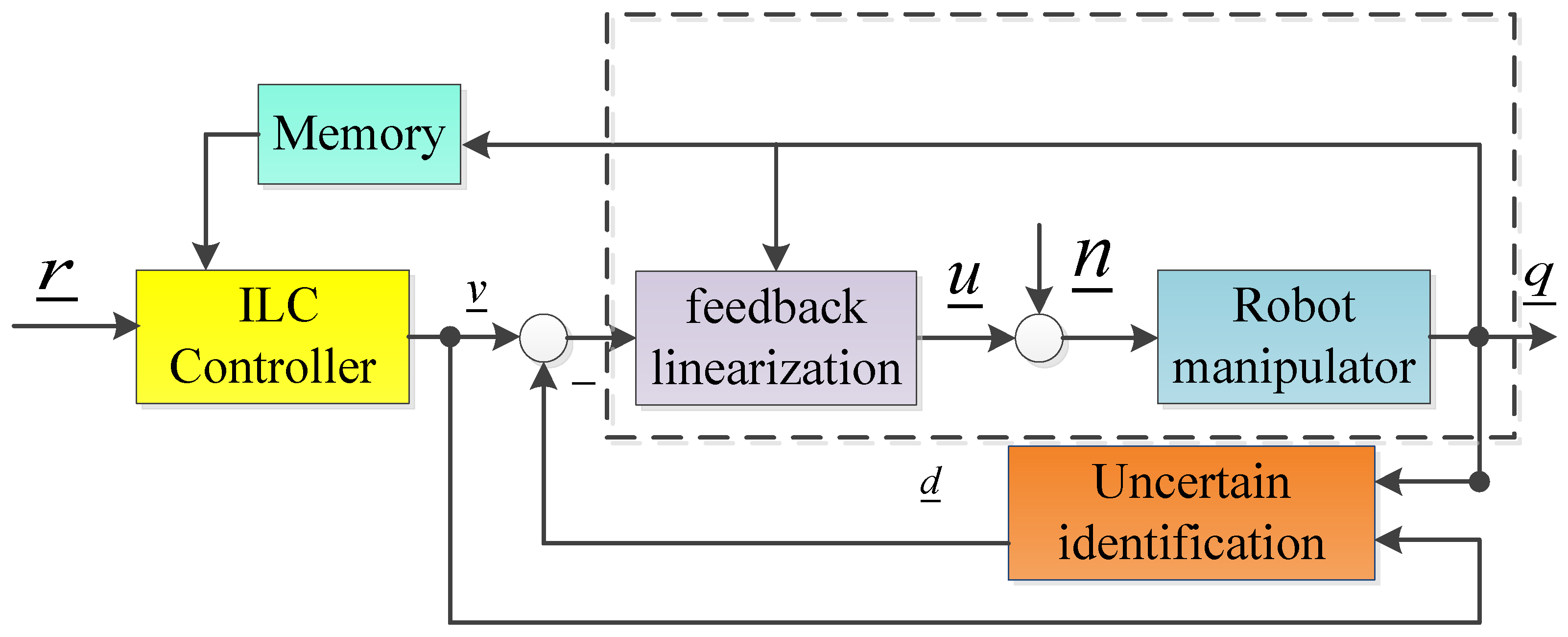
4. Structure the first diagram for robot control the iterative learning method
4.1. Algorithm content according to the first control diagram
| 1 | Assign Choose ; Calcutate . Choose K; Assign small value . |
| 2 | while continue the control do |
| 3 | fordo |
| 4 | Send to into uncertain control (9) and determine . |
| 5 | Calcutate . |
| 6 | Establish and calcutate . |
| 7 | end for |
| 8 | Set up the sum vector. từ , theo (11) |
| 9 | Update vector from its existing value according to (10) that is, calculate the values., |
| 10 | Set |
| 11 | end while |
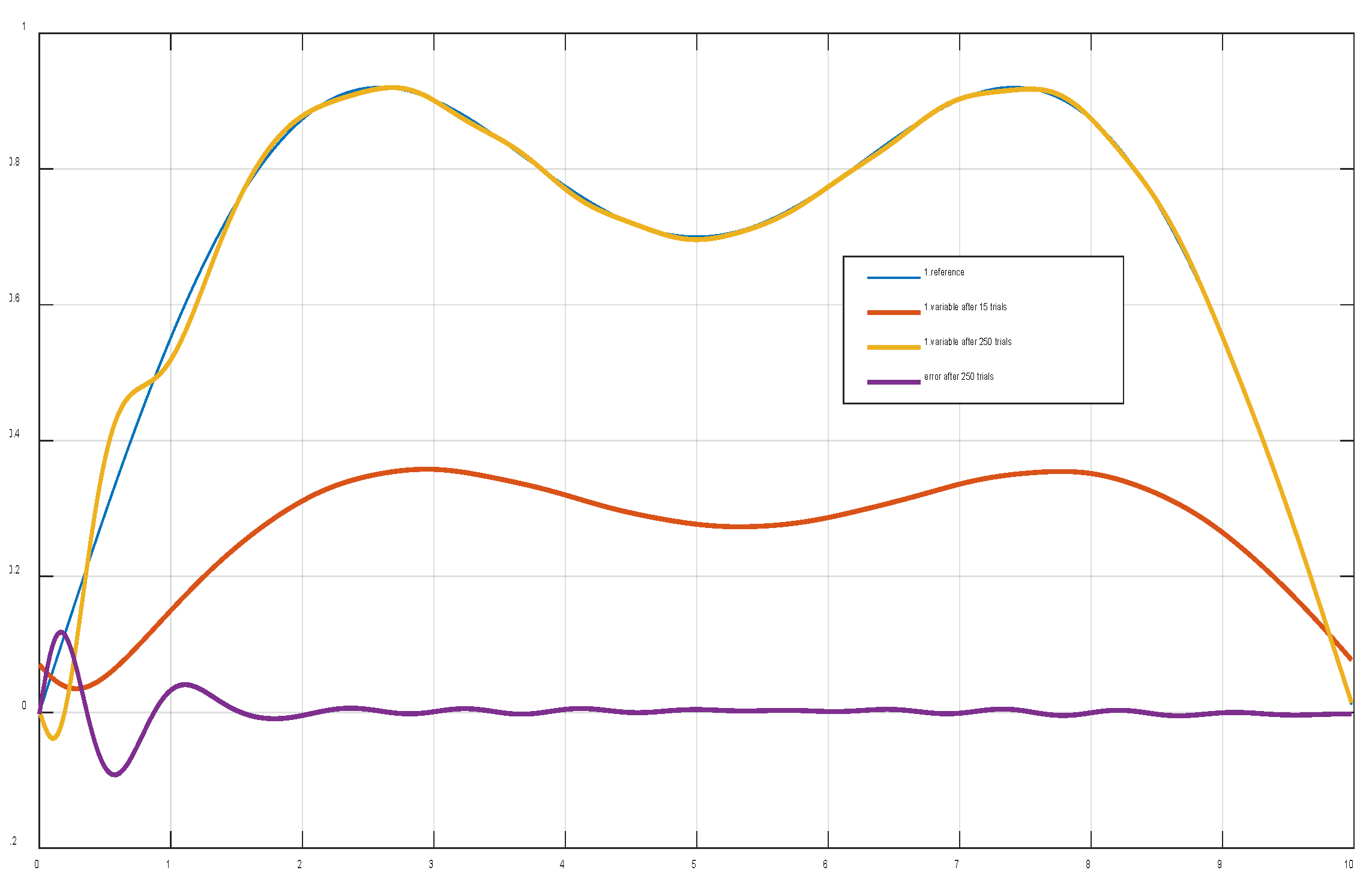
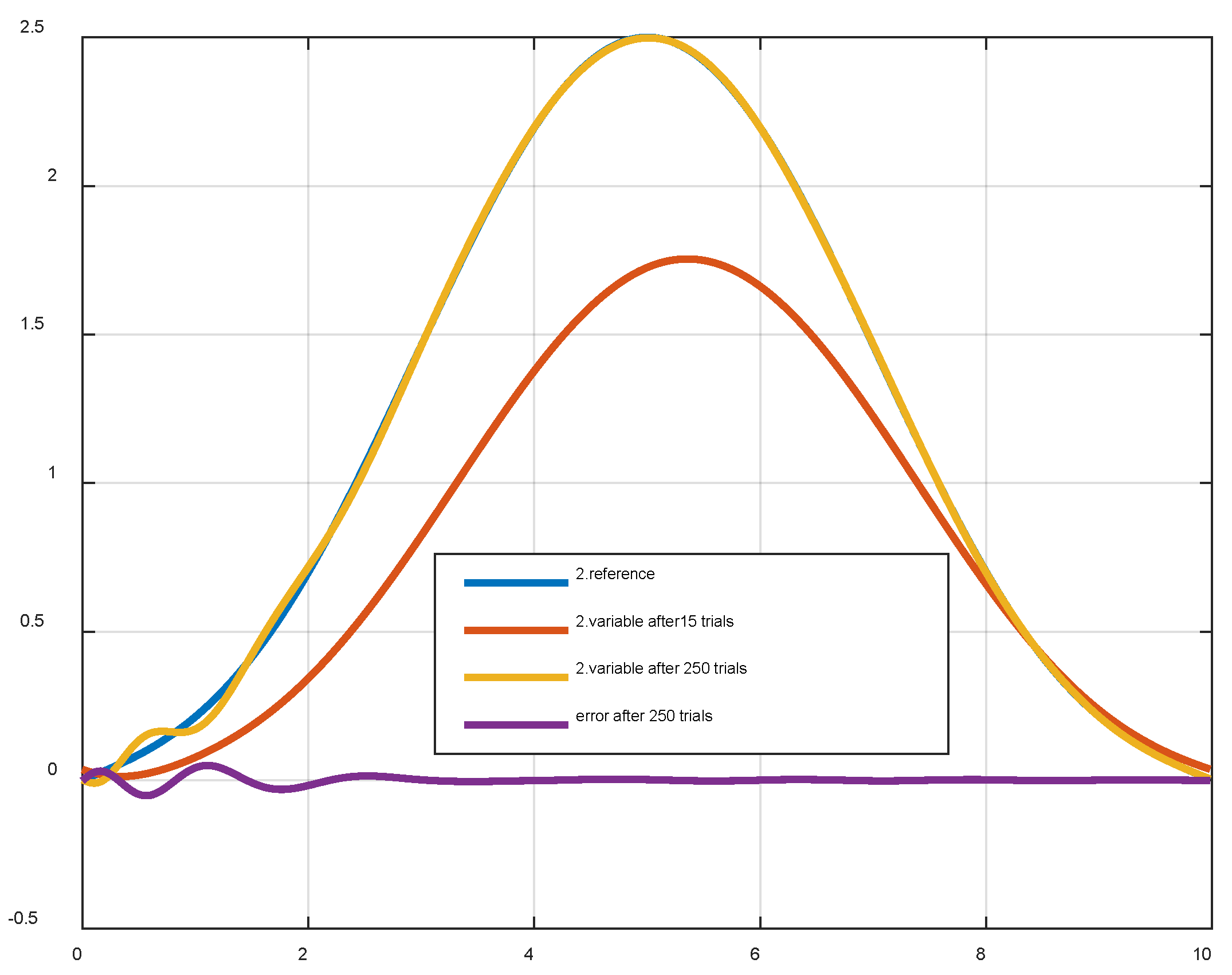
4.2. Applied to robot control
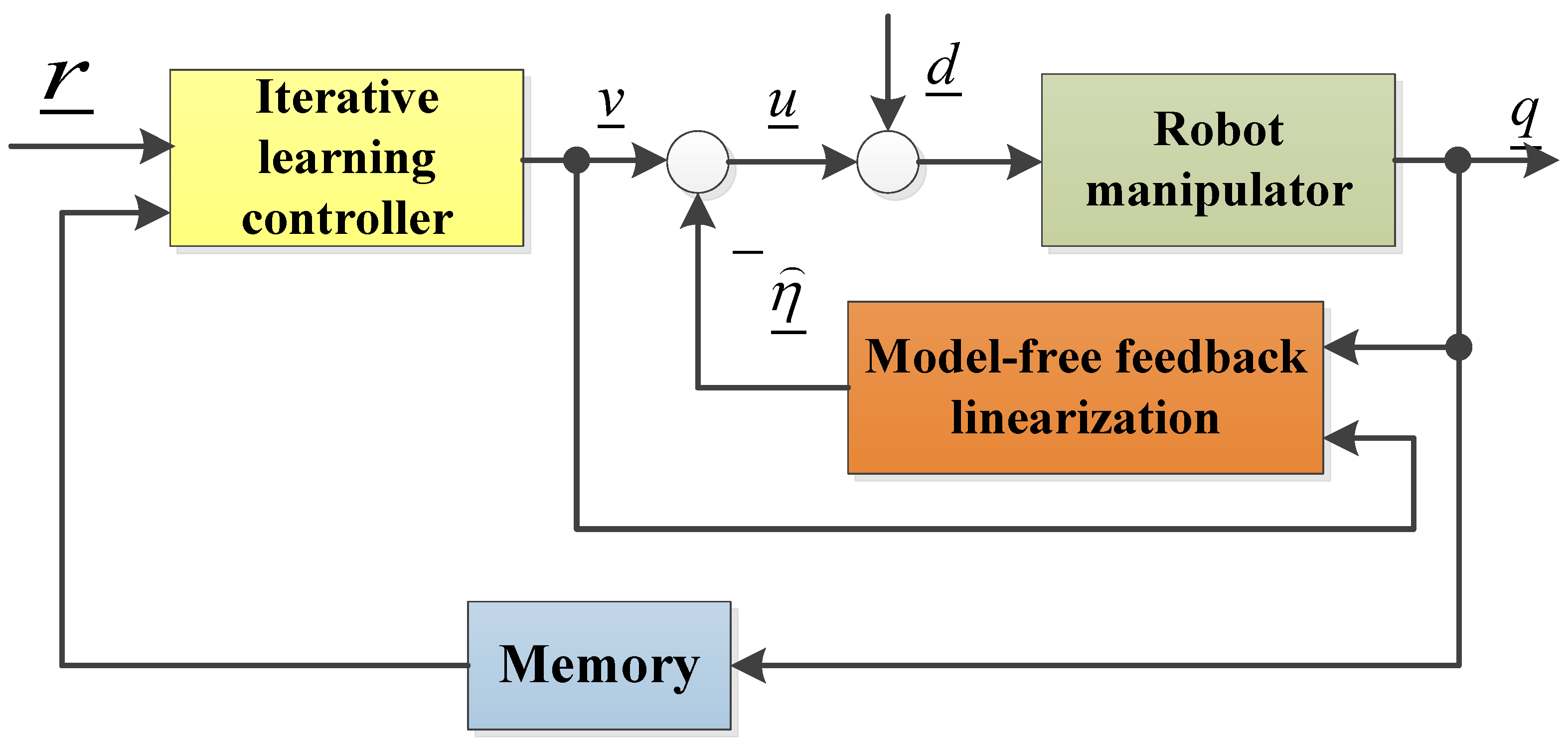
5. The structure of the second iterative learning controller with model-free determination of optimal learning parameters for industrial robot
5.1. Algorithm content according to the first control diagram
5.2. Feedback linearization for internal loop control using model-free disturbance compensation
5.3. Outer loop control is by iterative learning controller design.
5.4. Control algorithm and performance of closed – loop system
| 1 | Choose two matrices ,, given in (25) become Hurwitz . Determine given in (25) and given in (28). Choose . Calculate . Determine given in (23) Choose learning and tracking error . Assign . Choose learning parameter K so that Φ of (16) becomes Schur. |
| 2 | while continue the control do |
| 3 | fordo |
| 4 | Send to robot for a whilr of . measure , . |
| 5 | calculate . |
| 6 | end for |
| 7 | establish . |
| 8 | calculate and |
| 9 | end while |
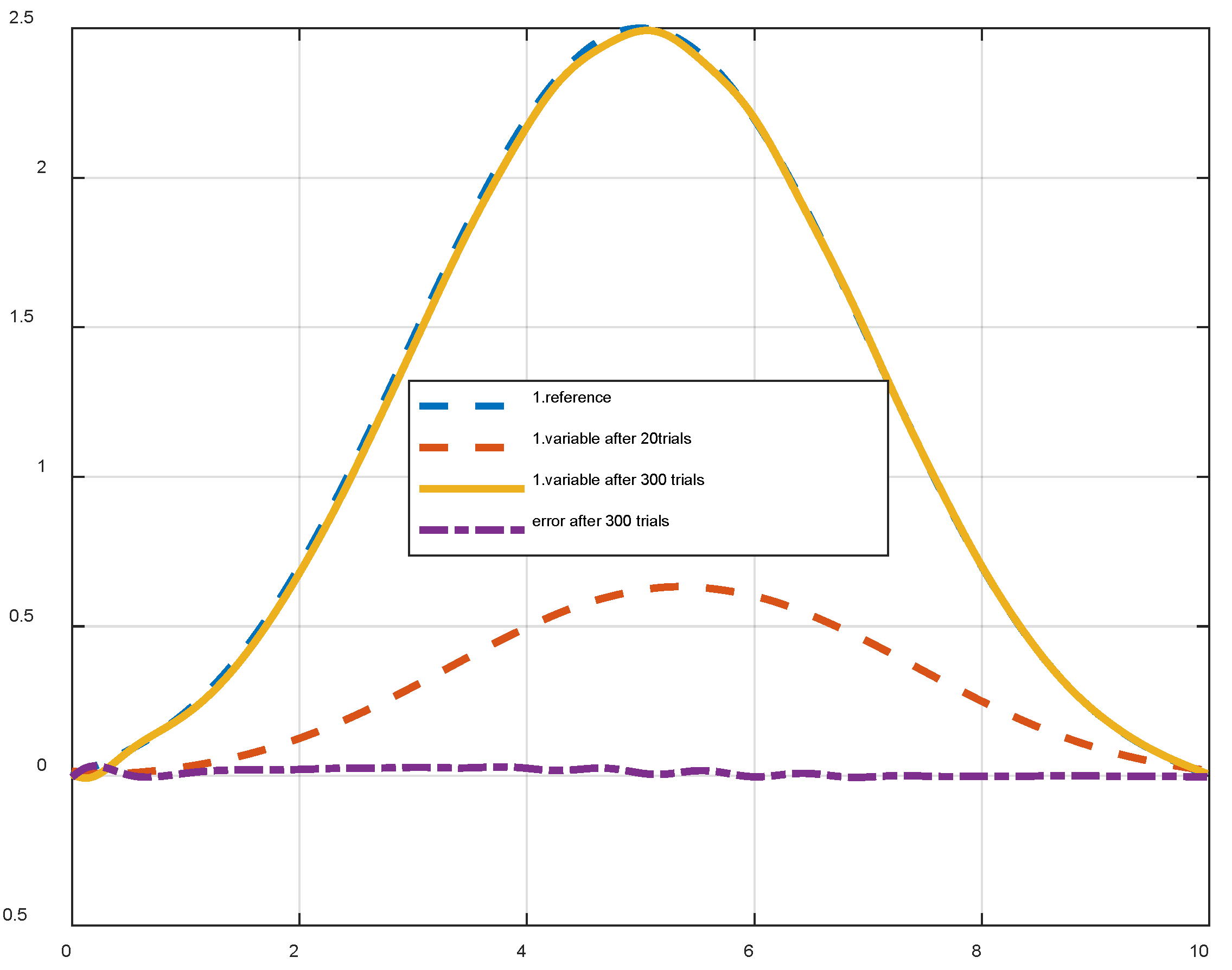
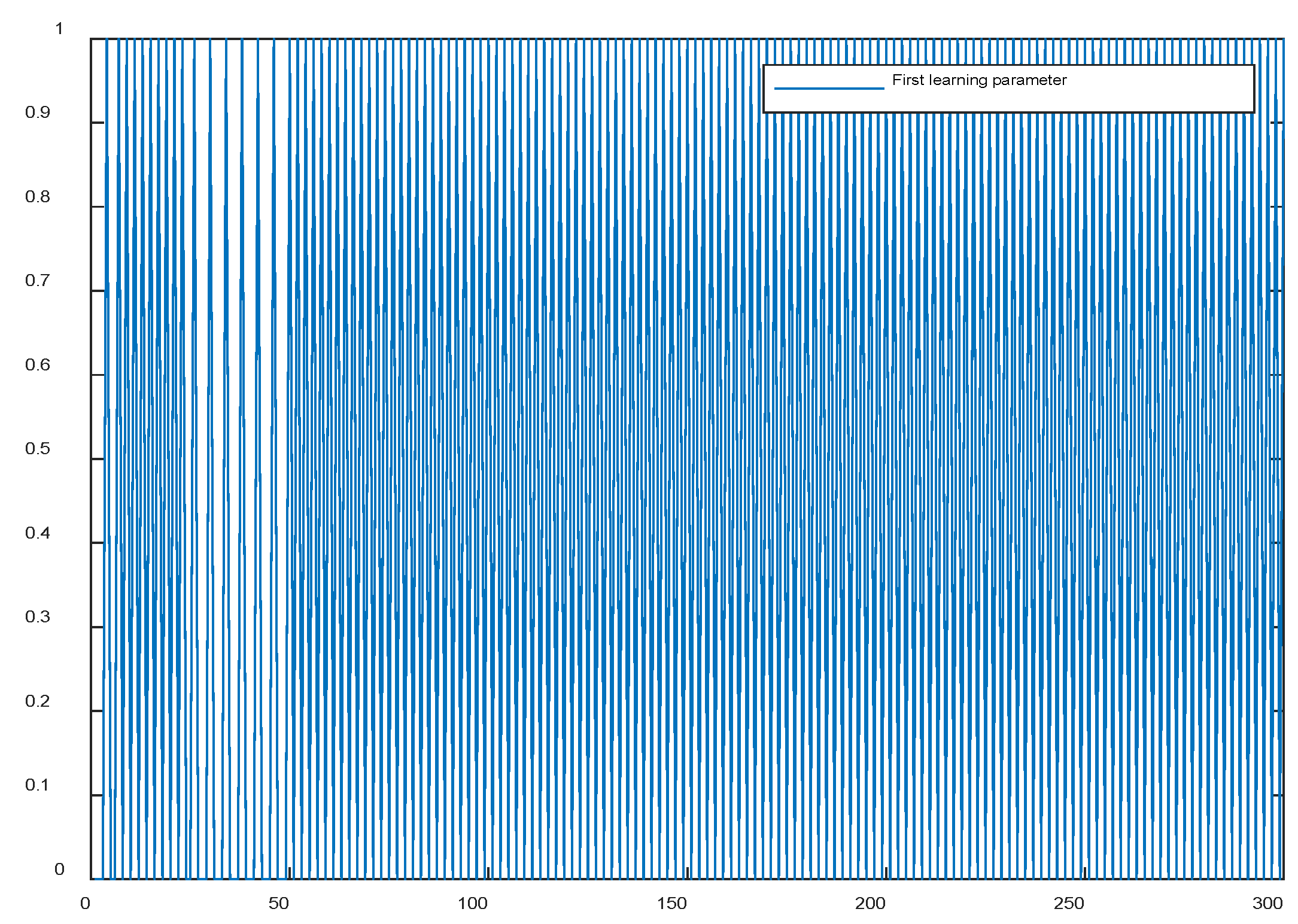
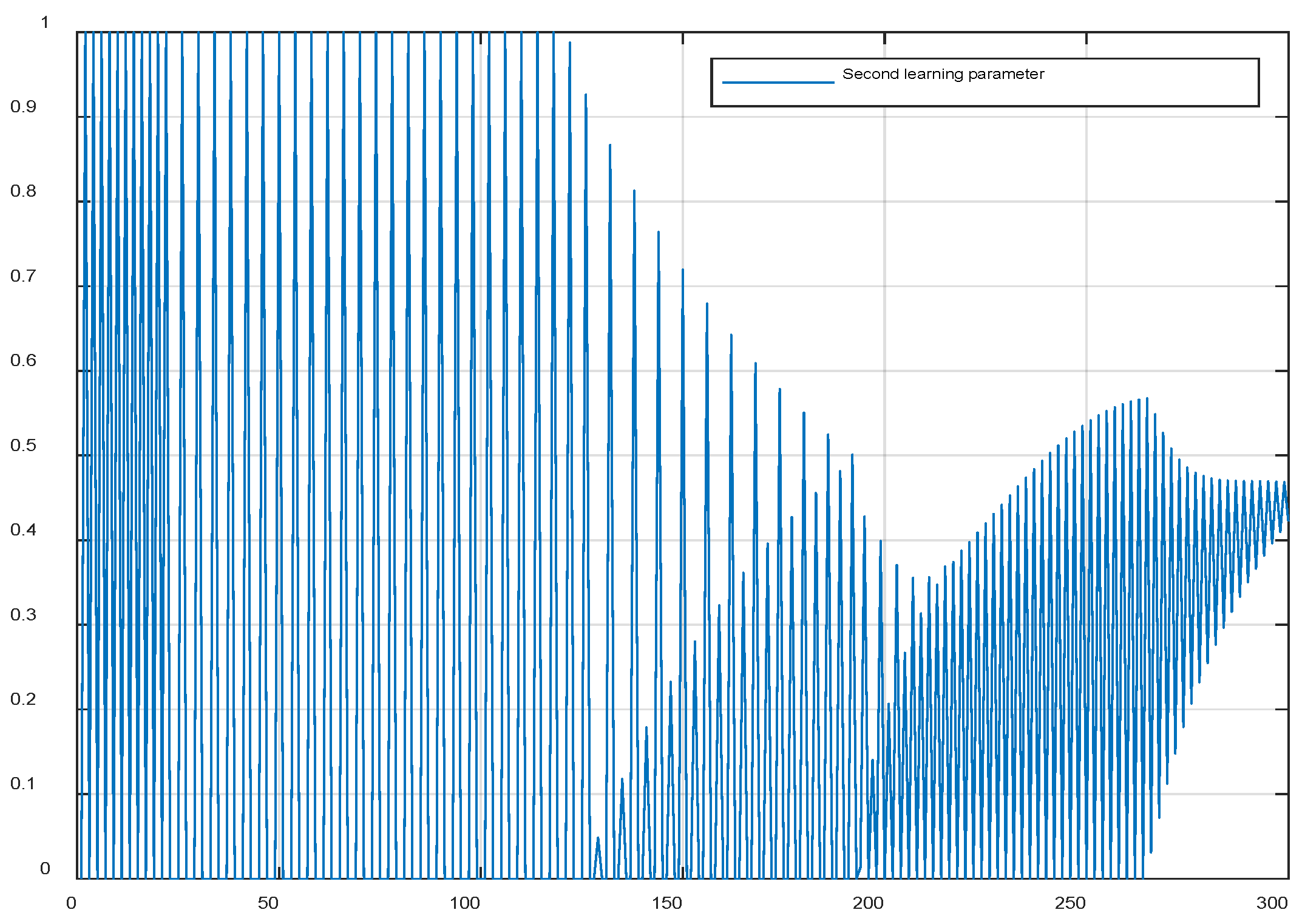
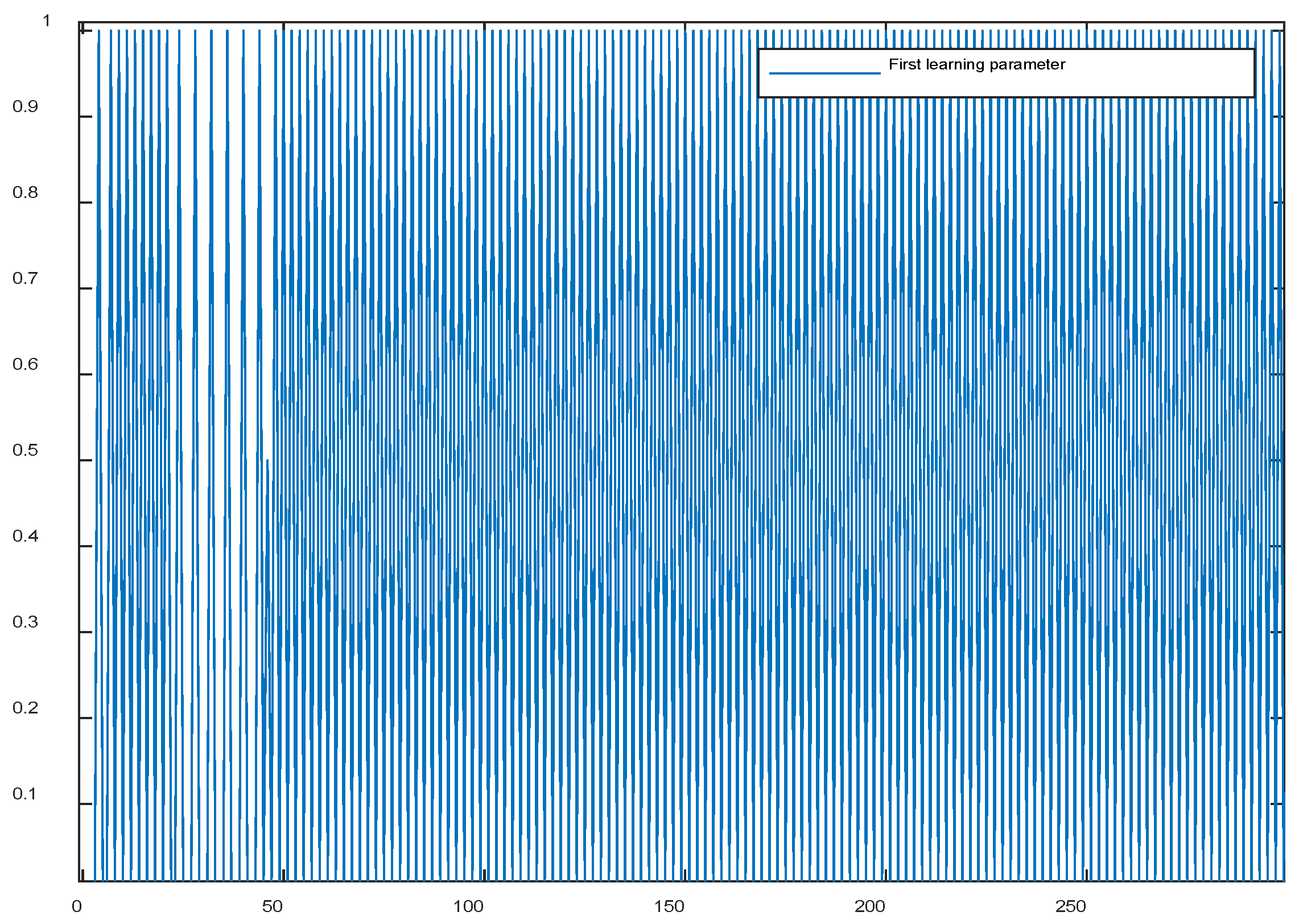
5.5. Applied to robot control
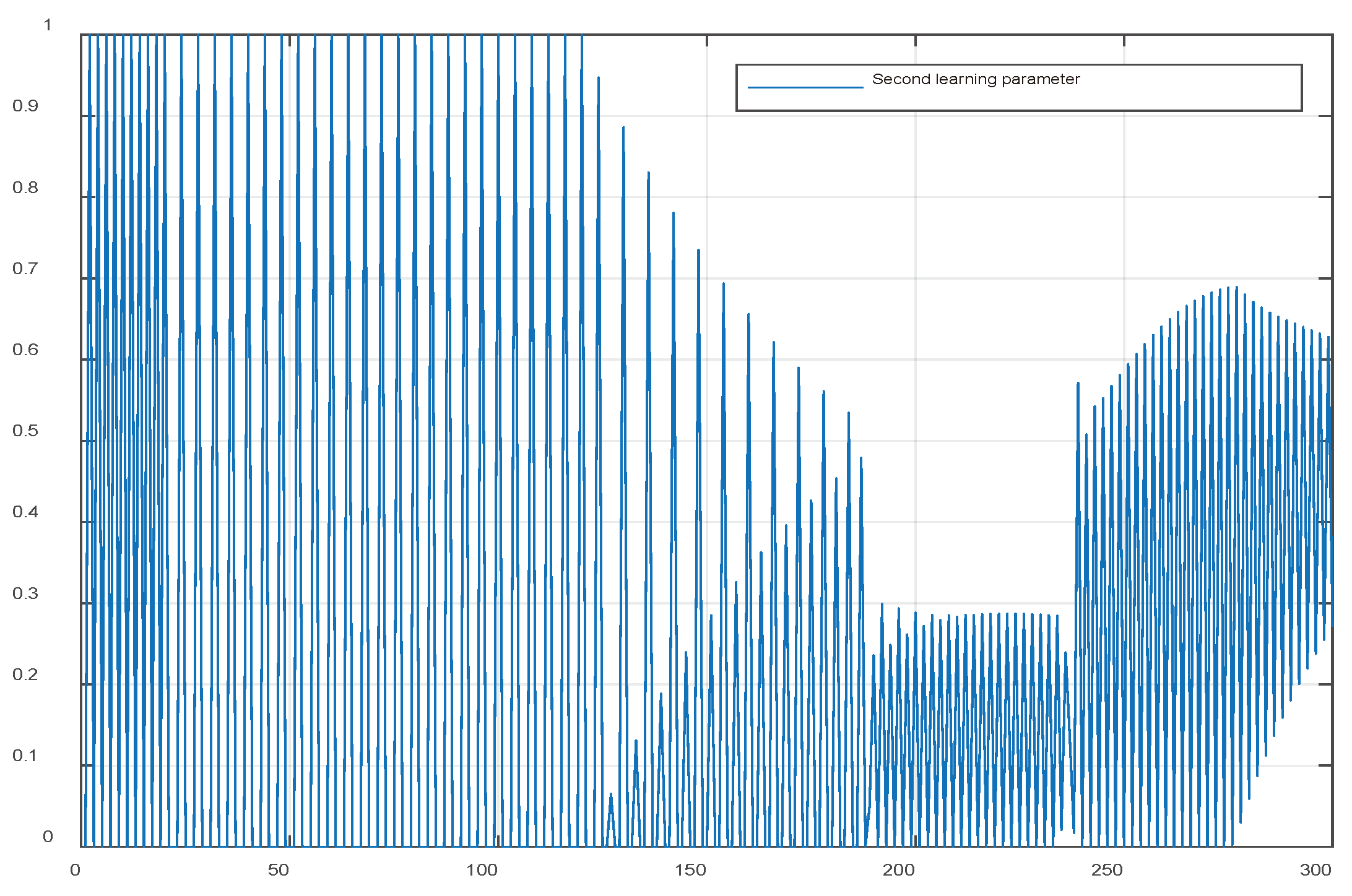
6. The structure of the second iterative learning controller with model-free determination of online learning parameters for industrial robot
6.1. Control the inner loop
6.2. Outer loop control is by iterative learning controller design.
| 1 | Choose two matrices ,, in (6), which become Hurwitz and a sufficiently small constant . Calculate . Determine Choose learning and tracking error . Assign the robot's initial state and initial output to the outer loop controller (iterative learning controller) |
| 2 | while keeping the controls in place |
| 3 | for do |
| 4 | send to robot for a while of . measure and . determine . |
| 5 | Calculate . |
| 6 | end for |
| 7 | establish . |
| 8 | Calculate or and |
| 9 | end while |
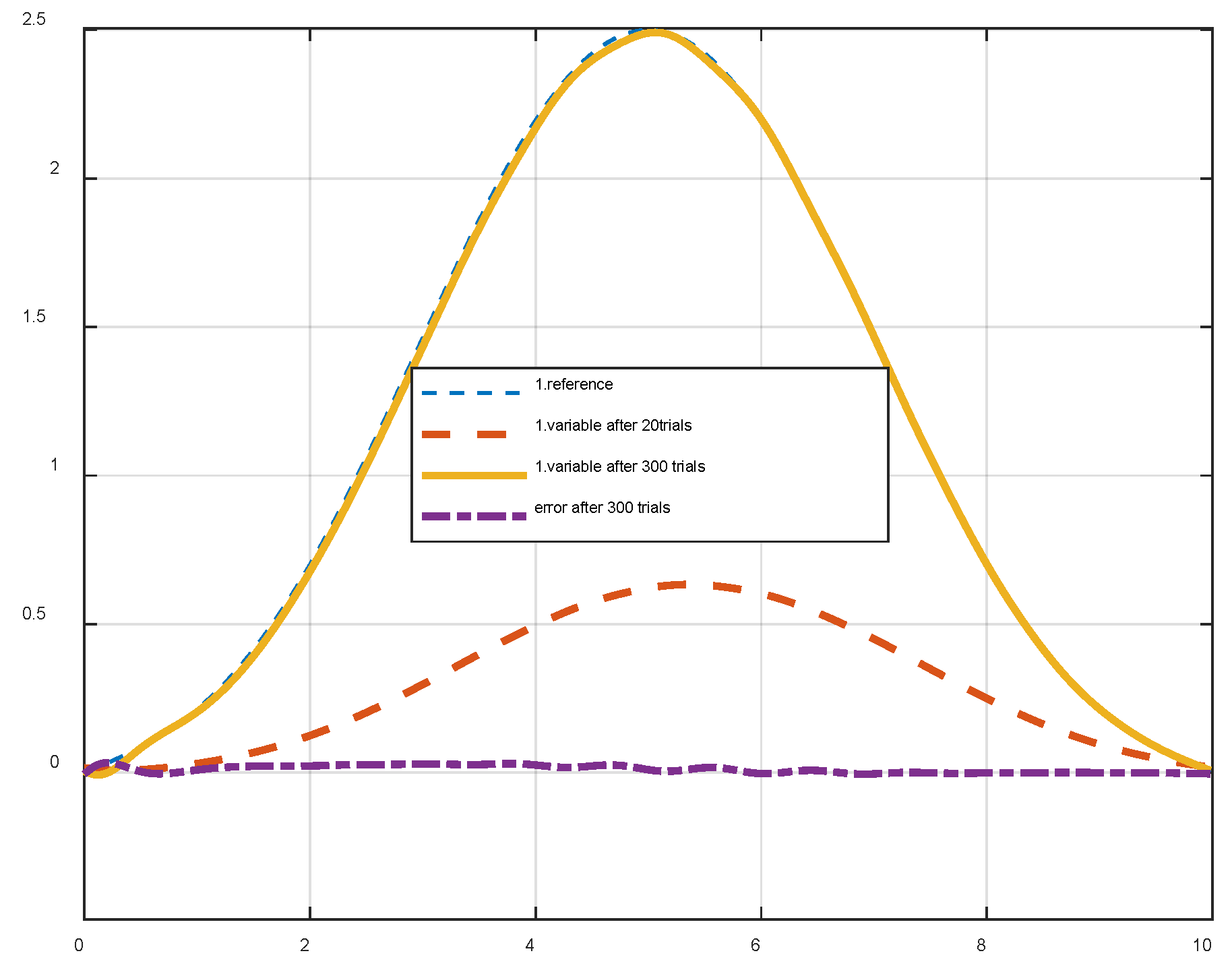
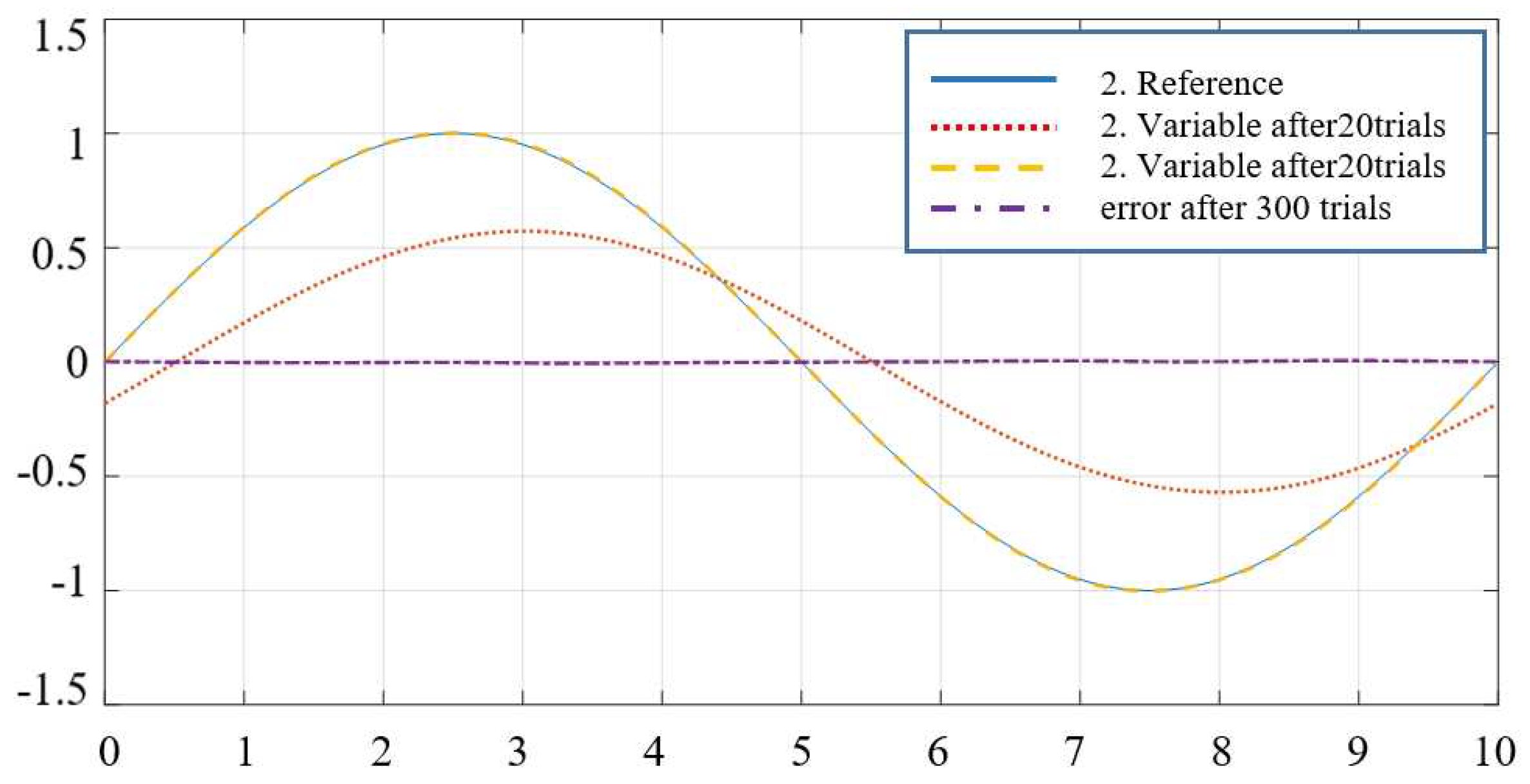
6.3. Applied to robot control
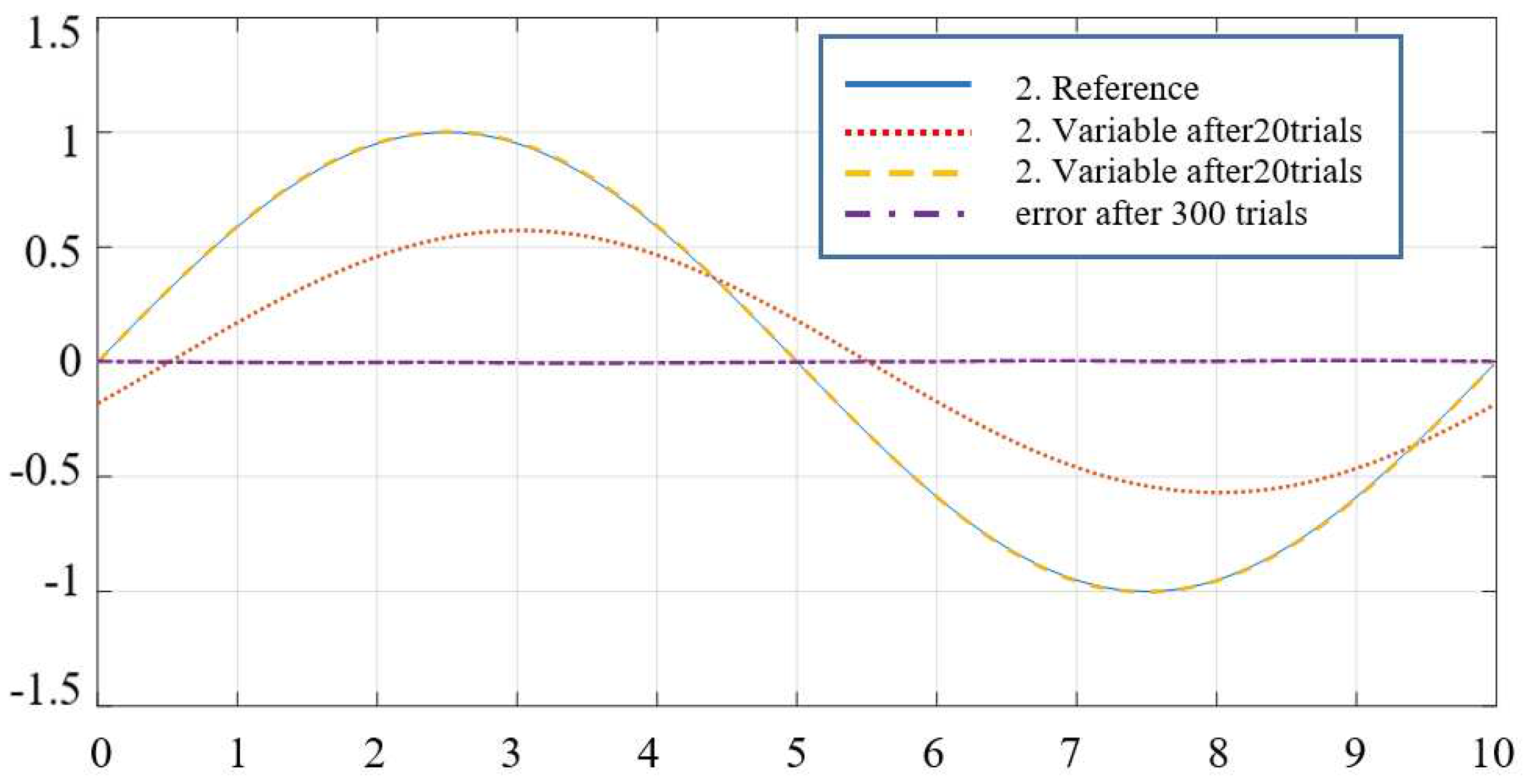
7. Conclusions
References
- L.Lewis, D.M. L.Lewis, D.M. Dawson and C.T.Abdallah, “ Robot manipulator control theory and practice”, Marcel Dekker, 2004.
- W. Spong, S. W. Spong, S. Hutchinson, and M. Vidyasagar,” Rovot modeling and control”, New York, Wiley, 2006.
- Z. S. Jiang, F. Z. S. Jiang, F. Xei, X. Wang anf Z. Li, “Adaptive dynamic sliding mode control for space manipulator with external disturbance”, Journal of Control and, 2019.
- Goel, A Swarup, “MIMO uncertain nonlinear system control via adaptive hight-order super twisting sliding mode and its application to robotic manipulator”, Journal Control Autom. Electr. Syst., 28, 36-49, 2017.
- Wang, Y et.al.; “Servy on iterative leaning control, repetitive control and run to run control. Journal of process control”, 19, (10), 589-1600, 2009.
- R. Lee, L. R. Lee, L. Sun, Z. Wang, M.Tomizuka,” AdaptivebILCcontrol of robot manipulators for friction compensation”. IFAC PapersOnline 52 (15), 175-180, 2019.
- F. Boiakrif, D. F. Boiakrif, D.Boukhetala and F.Boudjema Velocity observer-based ILCcontrol for robot manipulators. F Bouakrif, D Boukhetala, F Boudjema. International Journal of Systems Science 44 (2), 214,222, 2013.
- Nguyen, P.D.; Nguyen, N.H. Adaptive control for nonlinear non-autonomous systems with unknown input disturbance. Int. J. Control. 2021, 95, 3416–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyasenthil, R.; Choi, S.-B. A Robust Controller for Multivariable Model Matching System Utilizing a Quantitative Feedback Theory: Application to Magnetic Levitation. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.D.; Nguyen, N.H. Adaptive control for nonlinear non-autonomous systems with unknown input disturbance. Int. J. Control. 2021, 95, 3416–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K. G. Tran, N. H. K. G. Tran, N. H. Nguyen, P. D. Nguyen “Observer based controller two - wheeled inverted robots with unknown input disturbance and model uncertainty”, Journal of Control Science and Engineering, 1-12, 2020.
- Husnain, S.; Abdulkader, R. Fractional Order Modeling and Control of an Articulated Robotic Arm. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2023, 13, 12026–12032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouari, L.; Chtourou, S.; Ben Ayed, M.; Alshaya, S.A. A Comparative Study of Computer-Aided Engineering Techniques for Robot Arm Applications. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2020, 10, 6526–6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ayed, M.; Zouari, L.; Abid, M. Software In the Loop Simulation for Robot Manipulators. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2017, 7, 2017–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, D.M.; Tuy, T.X.; Phuoc, P.D. A Study on the Response of the Rehabilitation Lower Device using Sliding Mode Controller. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2021, 11, 7446–7451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
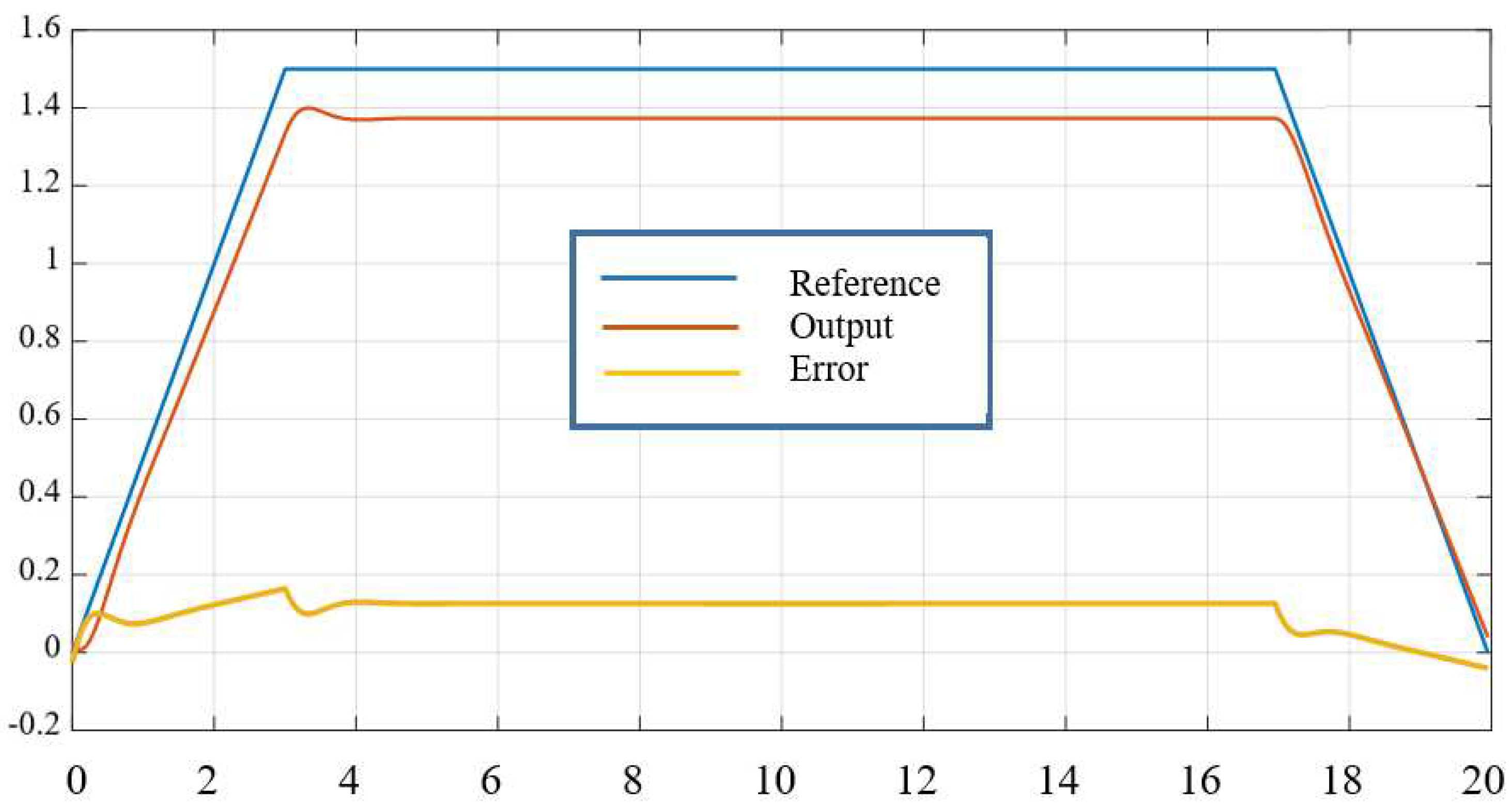
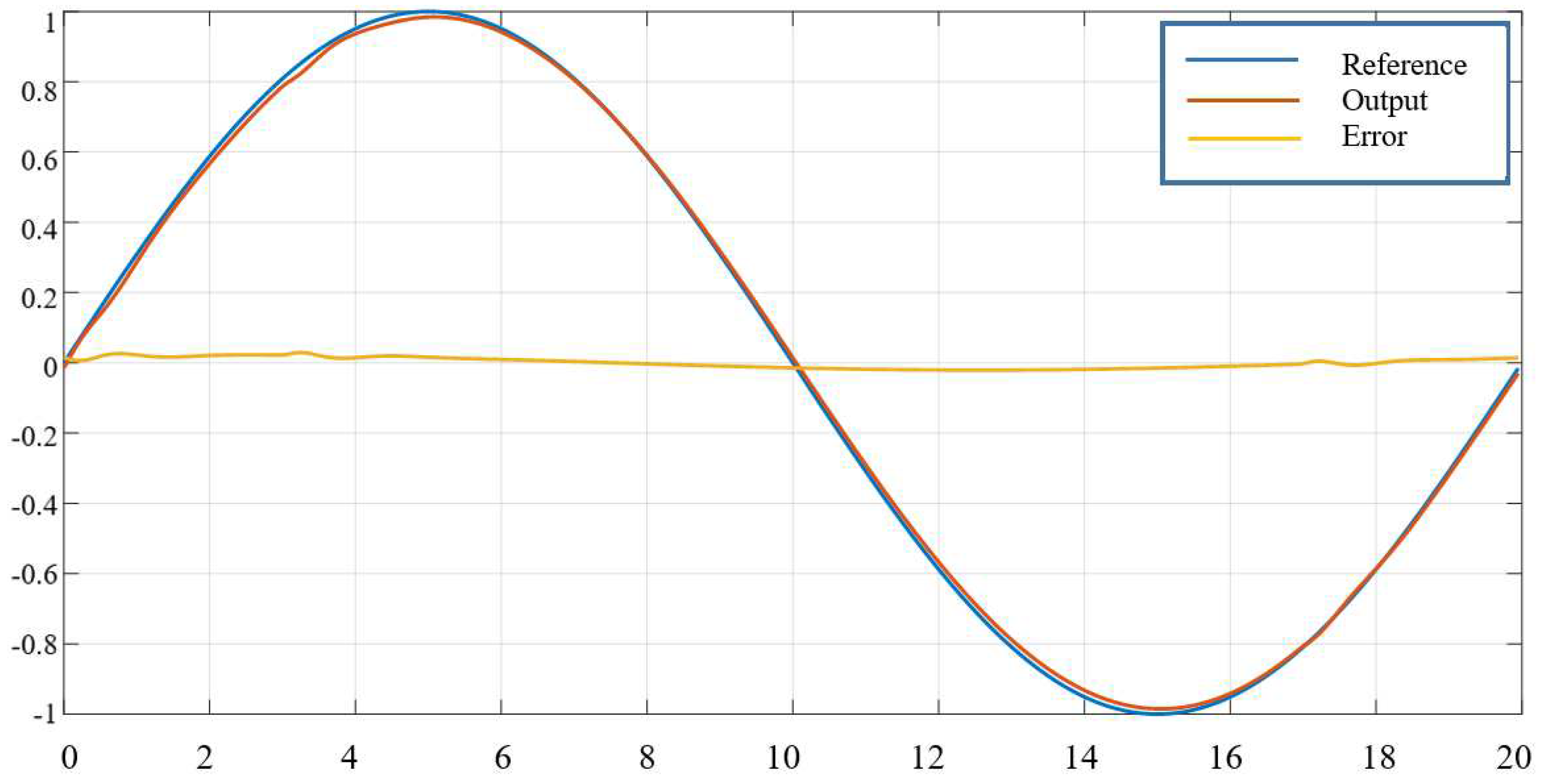
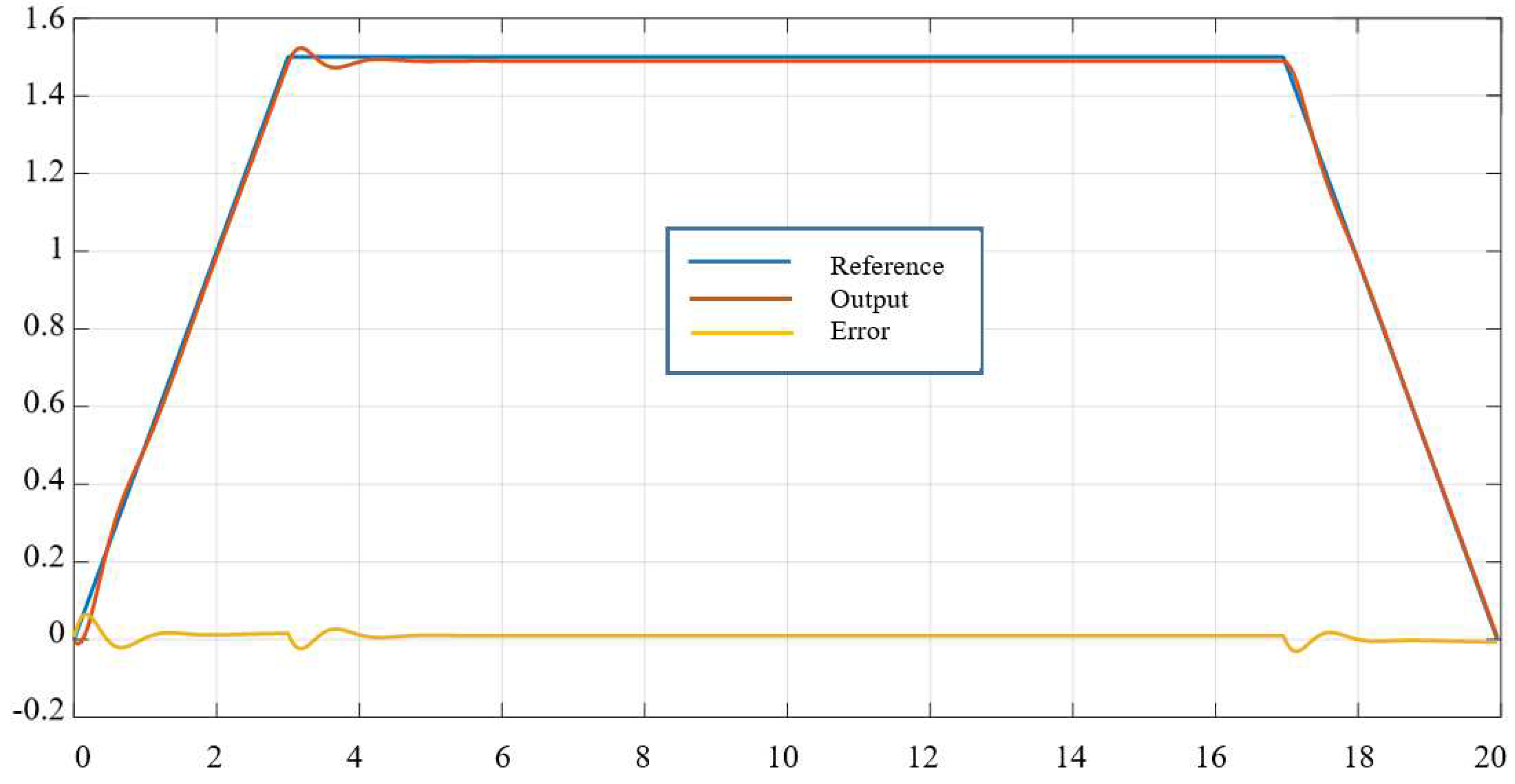
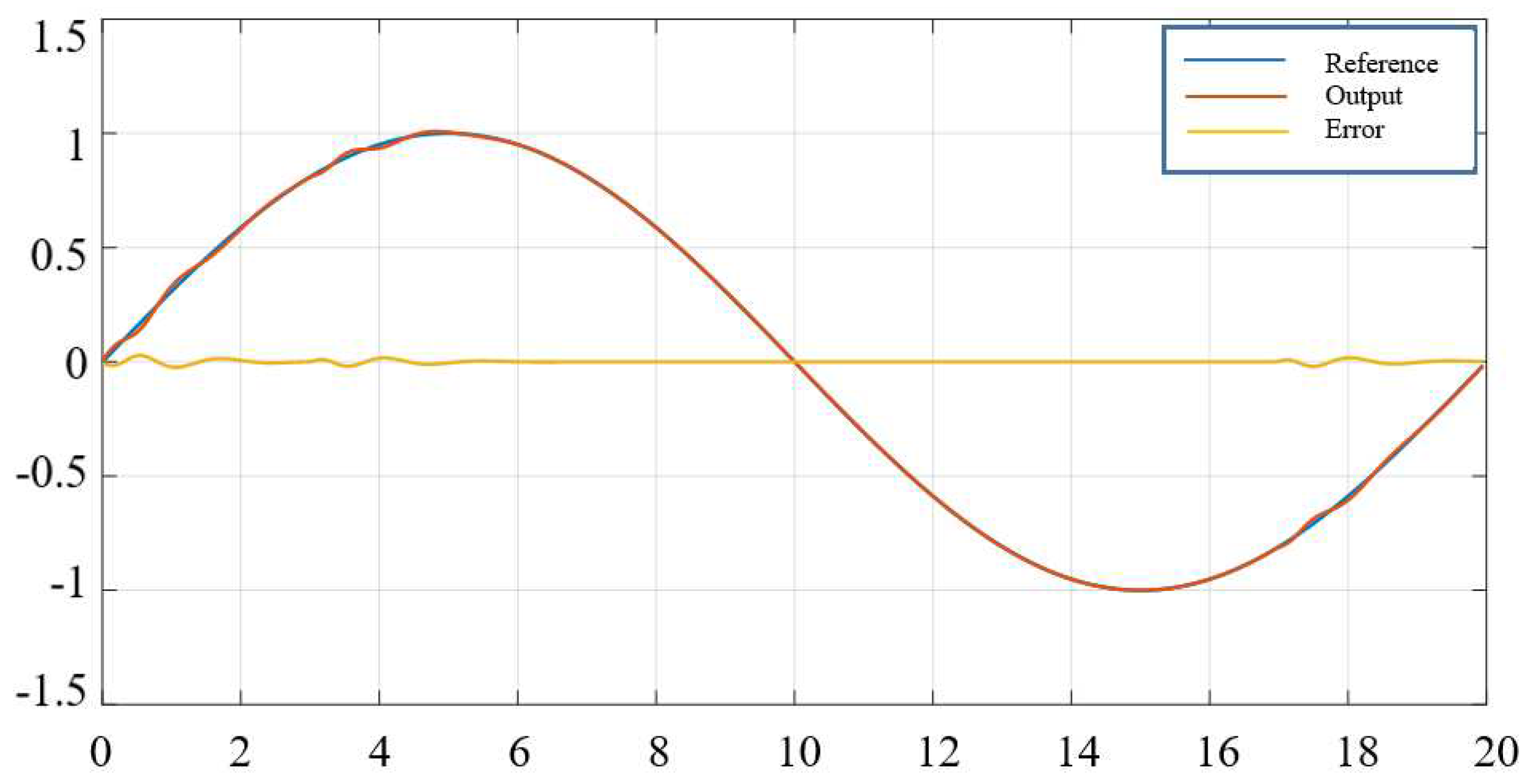
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




