Submitted:
06 January 2024
Posted:
08 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. The ALK structural biology
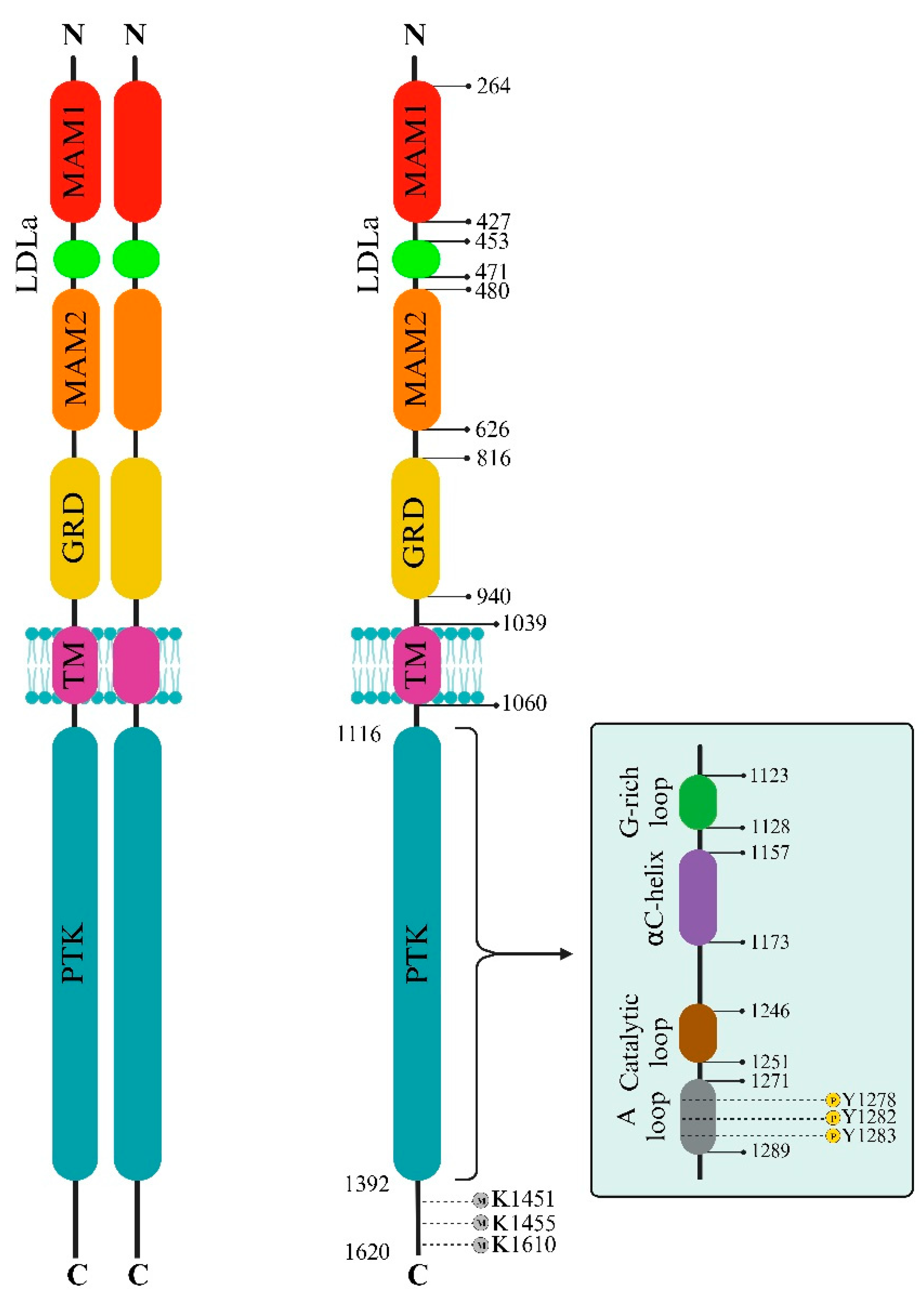
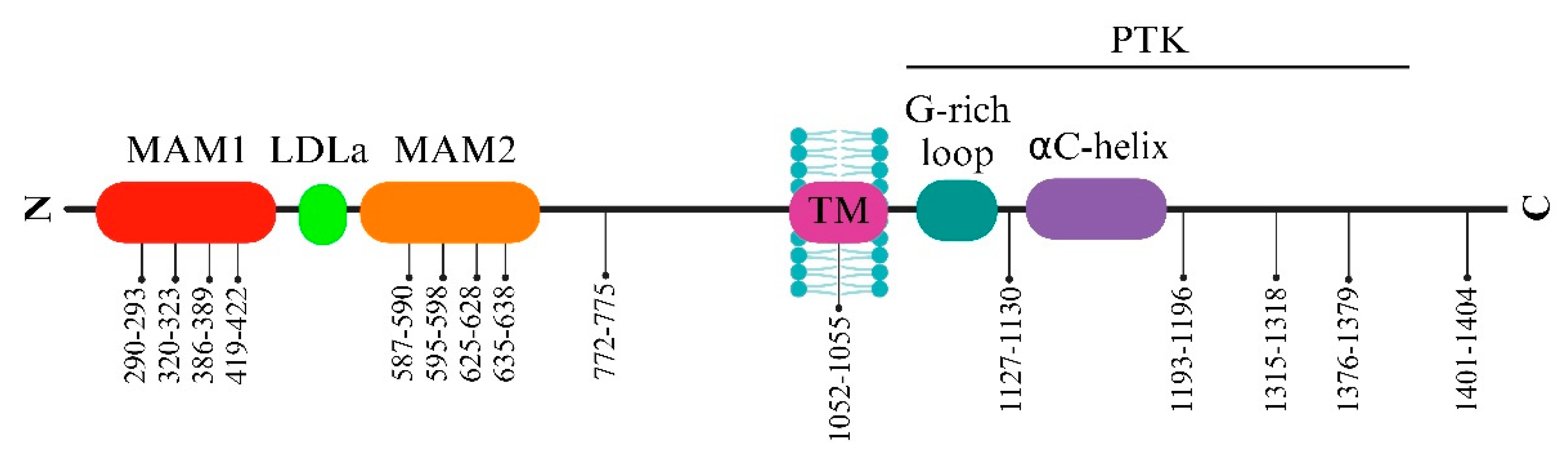
2.1. ALK extracellular side
2.2. ALK intracellular side
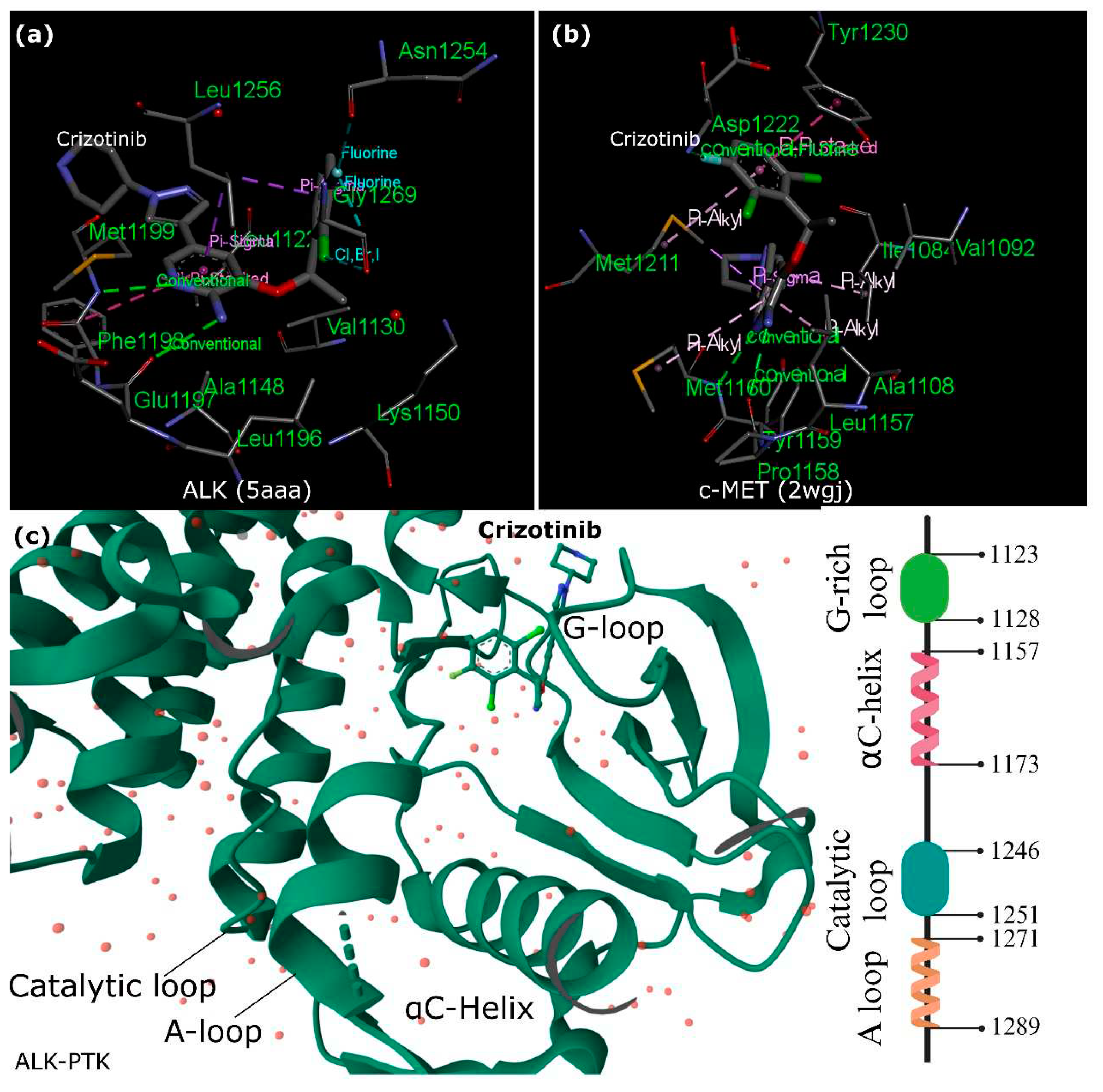
2.3. Crizotinib and ALK vs. c-MET
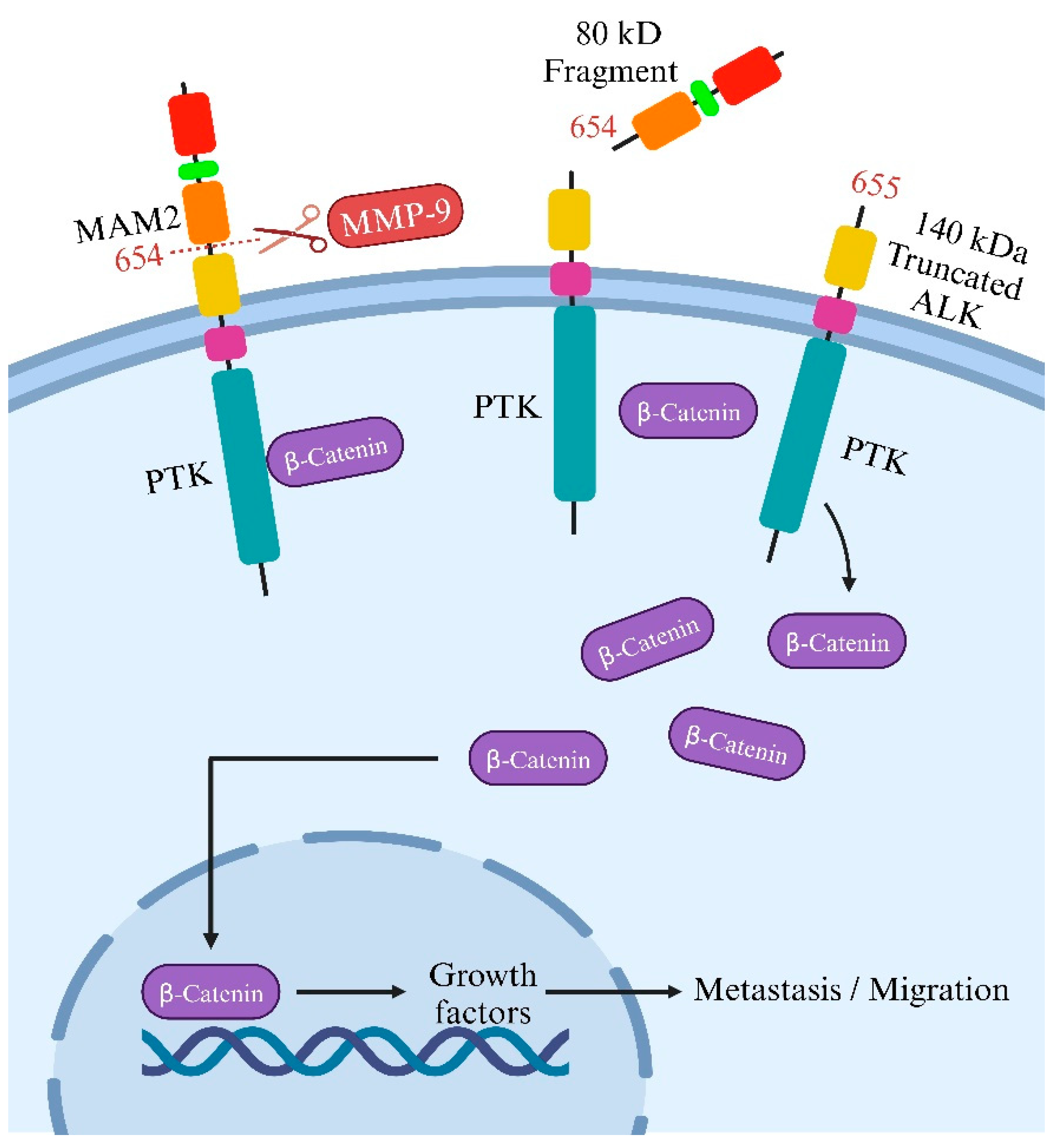
3. ALK cleavage and modifications
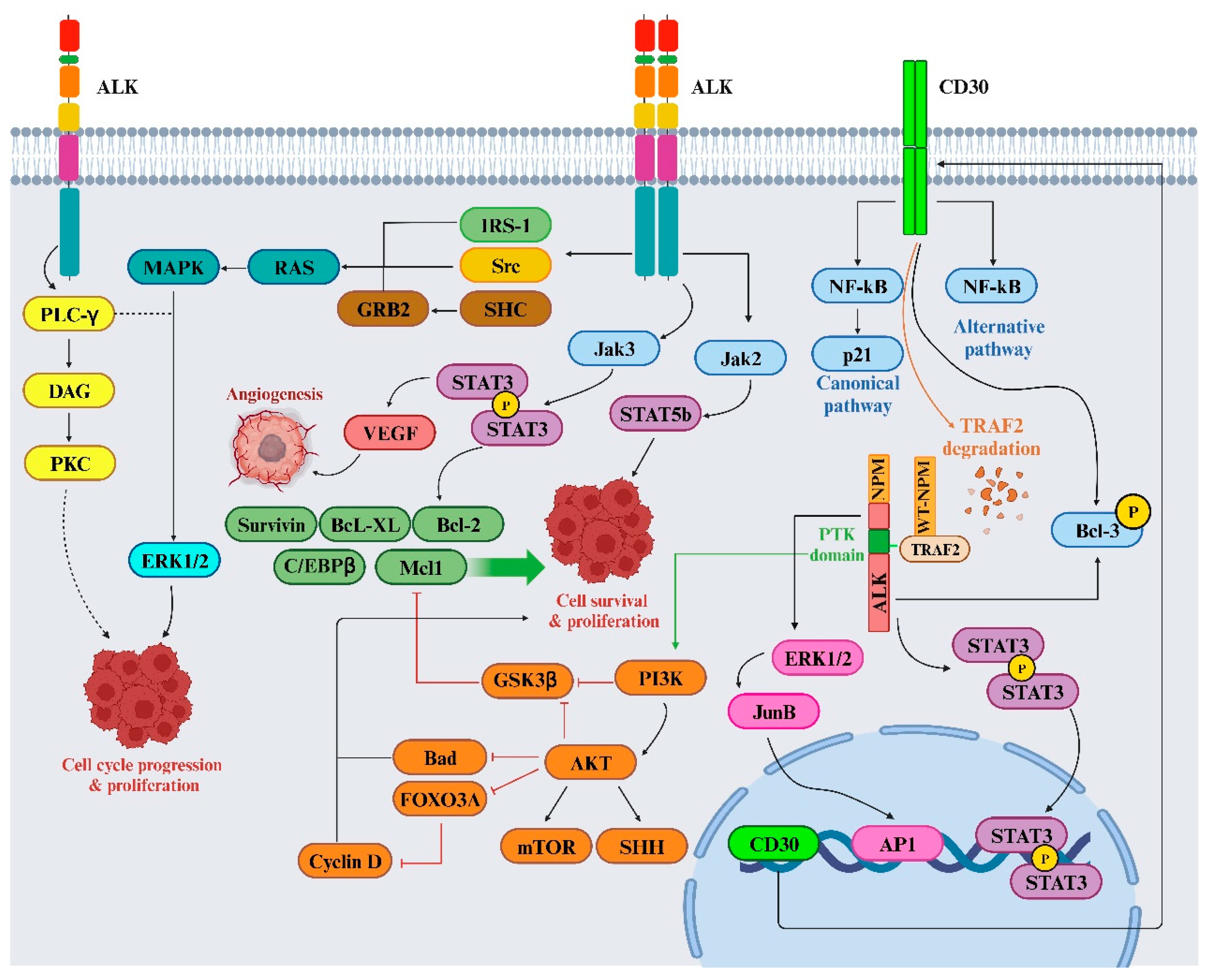
4. ALK signaling and TKI resistance
5. FDA-approved ALK inhibitors
6. ALK-targeted therapy and future directions
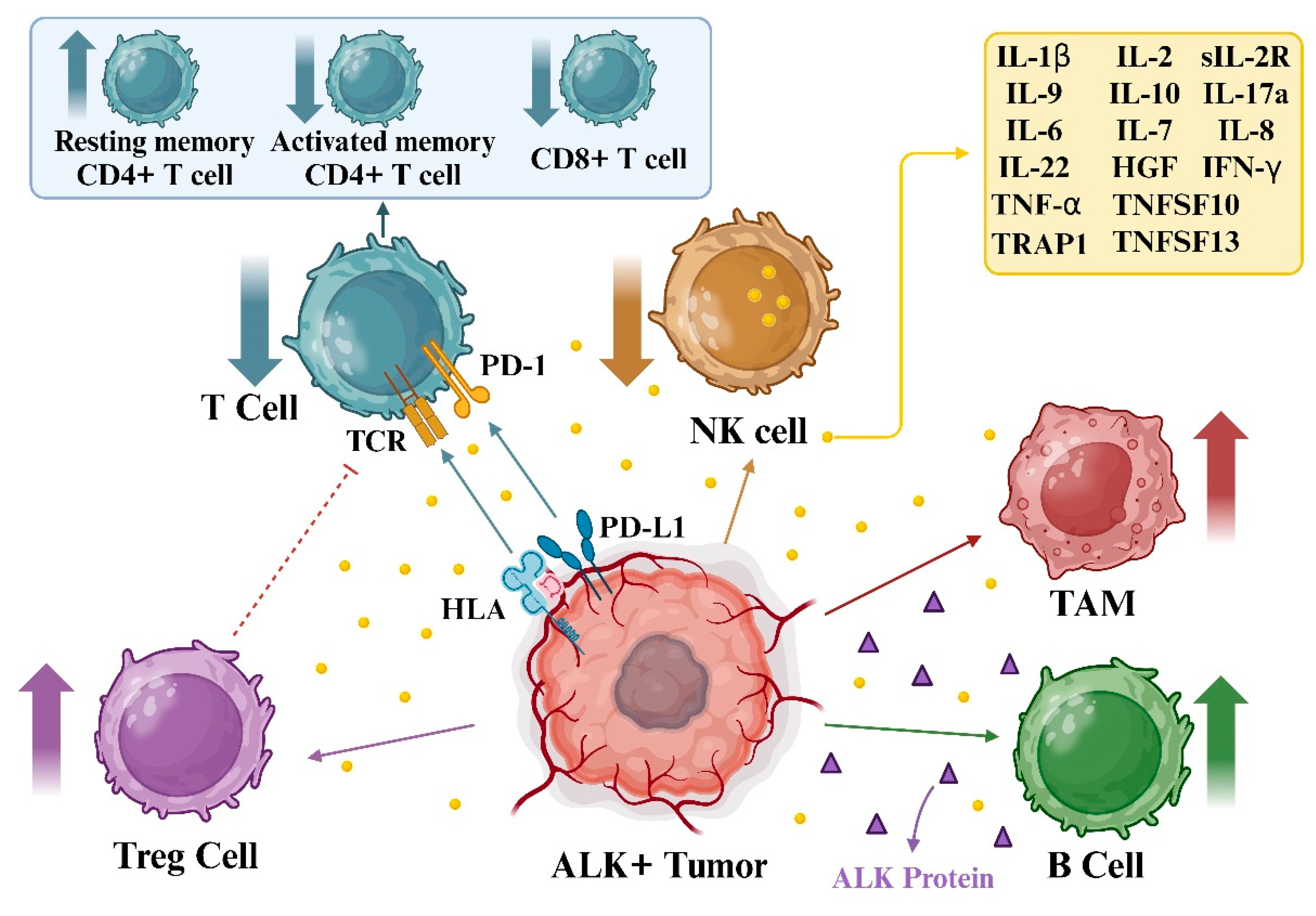
6.1. ALK and immunotherapy
6.2. ALK-innovative approaches
7. Concluding remarks
Funding
CRediT Author Statement
Data Availability
Conflict of Interests
Acknowledgments
Abbreviations
| Akt | Protein Kinase B |
| ALCL | Anaplastic large cell lymphoma |
| ALK | Anaplastic lymphoma kinase |
| CDK | Cyclin-dependent kinase |
| c-MET | Mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor |
| ECD | Extracellular domain |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| EML4 | Echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 4 |
| ERK | Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| GRB2 | Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 |
| GRD | Glycine-rich domain |
| ICI | Immune checkpoint inhibitor |
| LDLa | Low-density lipoprotein receptor class A |
| MAM | Meprin, A5 protein and receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase mu |
| MMP-9 | Matrix metallopeptidase 9 |
| NPM | Nucleolar phosphoprotein |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| ORR | Objective response rate |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PD-1 | Programmed cell death 1 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase |
| PTK | Protein tyrosine kinase |
| RAS | Rat sarcoma viral oncogene |
| STAT | Signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| TKI | Tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Hallberg, B.; Palmer, R.H. Mechanistic Insight into ALK Receptor Tyrosine Kinase in Human Cancer Biology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, J.D.; Lee, J.K.H.; Bacani, J.T.C.; Lai, R.; Ingham, R.J. NPM-ALK: The Prototypic Member of a Family of Oncogenic Fusion Tyrosine Kinases. J. Signal Transduct. 2012, 2012, 123253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reshetnyak, A.V.; Rossi, P.; Myasnikov, A.G.; Sowaileh, M.; Mohanty, J.; Nourse, A.; Miller, D.J.; Lax, I.; Schlessinger, J.; Kalodimos, C.G. Mechanism for the Activation of the Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Receptor. Nature 2021, 600, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Receptor Tyrosine Kinase: A Catalytic Receptor with Many Faces. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andraos, E.; Dignac, J.; Meggetto, F. NPM-ALK: A Driver of Lymphoma Pathogenesis and a Therapeutic Target. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, K.; Nagrath, S.; Ramnath, N. Immunotherapy for ALK-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Challenges Inform Promising Approaches. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, L.B.; Hitchen, N.; Chandran, E.; Morris, T.; Manser, R.; Solomon, B.J.; Jordan, V. Targeted Therapy for Advanced Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (<I>ALK</I>)-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cochrane database Syst. Rev. 2022, 1, CD013453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, J. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Special Immunity and Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 908894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotidis, E. The Role of Positron Computed Tomography (PET/CT) in Lung Cancer Staging. Hell. J. Nucl. Med. 2023, 26 Suppl, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soda, M.; Choi, Y.L.; Enomoto, M.; Takada, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Ishikawa, S.; Fujiwara, S.; Watanabe, H.; Kurashina, K.; Hatanaka, H.; et al. Identification of the Transforming EML4-ALK Fusion Gene in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Nature 2007, 448, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Huang, T.; Liu, M.; He, W.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, L.; Long, Y.; Zong, D.; Zeng, H.; Liu, Y.; et al. The Genomic Characteristics of ALK Fusion Positive Tumors in Chinese NSCLC Patients. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Yeap, B.Y.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Costa, D.B.; Heist, R.S.; Solomon, B.; Stubbs, H.; Admane, S.; McDermott, U.; et al. Clinical Features and Outcome of Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Who Harbor EML4-ALK. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4247–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, P.L.; Mitchell, P.; Dobrovic, A.; John, T. Prevalence and Natural History of ALK Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and the Clinical Impact of Targeted Therapy with ALK Inhibitors. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 6, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.-H.I.; Lee, A.T.M.; Nagasaka, M. From Preclinical Efficacy to 2022 (36.7 Months Median Follow -up) Updated CROWN Trial, Lorlatinib Is the Preferred 1st-Line Treatment of Advanced ALK+ NSCLC. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2023, 187, 104019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Mok, T.; Kim, D.-W.; Wu, Y.-L.; Nakagawa, K.; Mekhail, T.; Felip, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Paolini, J.; Usari, T.; et al. First-Line Crizotinib versus Chemotherapy in ALK-Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Kim, T.M.; Crinò, L.; Gridelli, C.; Kiura, K.; Liu, G.; Novello, S.; Bearz, A.; Gautschi, O.; Mok, T.; et al. Ceritinib versus Chemotherapy in Patients with ALK-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Previously given Chemotherapy and Crizotinib (ASCEND-5): A Randomised, Controlled, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet. Oncol. 2017, 18, 874–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadgeel, S.M.; Gandhi, L.; Riely, G.J.; Chiappori, A.A.; West, H.L.; Azada, M.C.; Morcos, P.N.; Lee, R.-M.; Garcia, L.; Yu, L.; et al. Safety and Activity of Alectinib against Systemic Disease and Brain Metastases in Patients with Crizotinib-Resistant ALK-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (AF-002JG): Results from the Dose-Finding Portion of a Phase 1/2 Study. Lancet. Oncol. 2014, 15, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, S.-H.I.; Ahn, J.S.; DePetris, L.; Govindan, R.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Hughes, B.; Lena, H.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Bearz, A.; Ramirez, S.V.; et al. Alectinib in Crizotinib-Refractory ALK-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase II Global Study. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novello, S.; Mazières, J.; Oh, I.-J.; deCastro, J.; Migliorino, M.R.; Helland, Å.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Griesinger, F.; Kotb, A.; Zeaiter, A.; et al. Alectinib versus Chemotherapy in Crizotinib-Pretreated Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK)-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results from the Phase III ALUR Study. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-W.; Tiseo, M.; Ahn, M.-J.; Reckamp, K.L.; Hansen, K.H.; Kim, S.-W.; Huber, R.M.; West, H.L.; Groen, H.J.M.; Hochmair, M.J.; et al. Brigatinib in Patients With Crizotinib-Refractory Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Randomized, Multicenter Phase II Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2490–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanzeb, M.; Lin, H.M.; Pan, X.; Yin, Y.; Baumann, P.; Langer, C.J. Immunotherapy Treatment Patterns and Outcomes Among ALK-Positive Patients With Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2021, 22, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazieres, J.; Drilon, A.; Lusque, A.; Mhanna, L.; Cortot, A.B.; Mezquita, L.; Thai, A.A.; Mascaux, C.; Couraud, S.; Veillon, R.; et al. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Patients with Advanced Lung Cancer and Oncogenic Driver Alterations: Results from the IMMUNOTARGET Registry. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Chen, N.; Fang, W.; Zhan, J.; Liu, Q.; Kang, S.; He, X.; Liu, L.; Zhou, T.; Huang, J.; et al. Upregulation of PD-L1 by EML4-ALK Fusion Protein Mediates the Immune Escape in ALK Positive NSCLC: Implication for Optional Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Immune Therapy for ALK-TKIs Sensitive and Resistant NSCLC Patients. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1094598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigel, D.R.; Reynolds, C.; Waterhouse, D.; Garon, E.B.; Chandler, J.; Babu, S.; Thurmes, P.; Spira, A.; Jotte, R.; Zhu, J.; et al. Phase 1/2 Study of the Safety and Tolerability of Nivolumab Plus Crizotinib for the First-Line Treatment of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Translocation - Positive Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (CheckMate 370). J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2018, 13, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Jabbour, S.K.; Malhotra, J. ALK Inhibitors and Checkpoint Blockade: A Cautionary Tale of Mixing Oil with Water? J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S2198–S2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, R.H.; Vernersson, E.; Grabbe, C.; Hallberg, B. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase: Signalling in Development and Disease. Biochem. J. 2009, 420, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Stayrook, S.E.; Tsutsui, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Proffitt, A.; Krimmer, S.G.; Ahmed, M.; Belliveau, O.; et al. Structural Basis for Ligand Reception by Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase. Nature 2021, 600, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, J.; Umapathy, G.; Yamazaki, Y.; Wolfstetter, G.; Mendoza, P.; Pfeifer, K.; Mohammed, A.; Hugosson, F.; Zhang, H.; Hsu, A.W.; et al. FAM150A and FAM150B Are Activating Ligands for Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase. Elife 2015, 4, e09811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reshetnyak, A.V.; Murray, P.B.; Shi, X.; Mo, E.S.; Mohanty, J.; Tome, F.; Bai, H.; Gunel, M.; Lax, I.; Schlessinger, J. Augmentor α and β (FAM150) Are Ligands of the Receptor Tyrosine Kinases ALK and LTK: Hierarchy and Specificity of Ligand-Receptor Interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2015, 112, 15862–15867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossi, R.T.; Saccardo, M.B.; Ardini, E.; Menichincheri, M.; Rusconi, L.; Magnaghi, P.; Orsini, P.; Avanzi, N.; Borgia, A.L.; Nesi, M.; et al. Crystal Structures of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase in Complex with ATP Competitive Inhibitors. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 6813–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.J.; Tran-Dubé, M.; Shen, H.; Nambu, M.; Kung, P.-P.; Pairish, M.; Jia, L.; Meng, J.; Funk, L.; Botrous, I.; et al. Structure Based Drug Design of Crizotinib (PF-02341066), a Potent and Selective Dual Inhibitor of Mesenchymal-Epithelial Transition Factor (c-MET) Kinase and Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK). J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 6342–6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Johnson, T.W.; Bailey, S.; Brooun, A.; Bunker, K.D.; Burke, B.J.; Collins, M.R.; Cook, A.S.; Cui, J.J.; Dack, K.N.; et al. Design of Potent and Selective Inhibitors to Overcome Clinical Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Mutations Resistant to Crizotinib. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 1170–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornev, A.P.; Taylor, S.S. Dynamics-Driven Allostery in Protein Kinases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 40, 628–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donella-Deana, A.; Marin, O.; Cesaro, L.; Gunby, R.H.; Ferrarese, A.; Coluccia, A.M.L.; Tartari, C.J.; Mologni, L.; Scapozza, L.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; et al. Unique Substrate Specificity of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK): Development of Phosphoacceptor Peptides for the Assay of ALK Activity. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 8533–8542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartari, C.J.; Gunby, R.H.; Coluccia, A.M.L.; Sottocornola, R.; Cimbro, B.; Scapozza, L.; Donella-Deana, A.; Pinna, L.A.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C. Characterization of Some Molecular Mechanisms Governing Autoactivation of the Catalytic Domain of the Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 3743–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wu, F.; Zhang, J.; McMullen, T.; Young, L.C.; Ingham, R.J.; Li, L.; Lai, R. Serine Phosphorylation of NPM-ALK, Which Is Dependent on the Auto-Activation of the Kinase Activation Loop, Contributes to Its Oncogenic Potential. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallberg, B.; Palmer, R.H. The Role of the ALK Receptor in Cancer Biology. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2016, 27 Suppl 3, iii4–iii15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loong, H.H.; Mok, K.; Leung, L.K.S.; Mok, T.S.K. Crizotinib in the Management of Advanced-Stage Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Future Oncol. 2015, 11, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Friboulet, L.; Leshchiner, I.; Gainor, J.F.; Bergqvist, S.; Brooun, A.; Burke, B.J.; Deng, Y.-L.; Liu, W.; Dardaei, L.; et al. Resensitization to Crizotinib by the Lorlatinib ALK Resistance Mutation L1198F. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazandjian, D.; Blumenthal, G.M.; Chen, H.-Y.; He, K.; Patel, M.; Justice, R.; Keegan, P.; Pazdur, R. FDA Approval Summary: Crizotinib for the Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Rearrangements. Oncologist 2014, 19, e5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X. The Potential Role of HGF-MET Signaling and Autophagy in the War of Alectinib versus Crizotinib against ALK-Positive NSCLC. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, S.W.; Naeve, C.; Mathew, P.; James, P.L.; Kirstein, M.N.; Cui, X.; Witte, D.P. ALK, the Chromosome 2 Gene Locus Altered by the t(2;5) in Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, Encodes a Novel Neural Receptor Tyrosine Kinase That Is Highly Related to Leukocyte Tyrosine Kinase (LTK). Oncogene 1997, 14, 2175–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degoutin, J.; Brunet-de Carvalho, N.; Cifuentes-Diaz, C.; Vigny, M. ALK (Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase) Expression in DRG Neurons and Its Involvement in Neuron-Schwann Cells Interaction. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazot, P.; Cazes, A.; Boutterin, M.C.; Figueiredo, A.; Raynal, V.; Combaret, V.; Hallberg, B.; Palmer, R.H.; Delattre, O.; Janoueix-Lerosey, I.; et al. The Constitutive Activity of the ALK Mutated at Positions F1174 or R1275 Impairs Receptor Trafficking. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2017–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazot, P.; Cazes, A.; Dingli, F.; Degoutin, J.; Irinopoulou, T.; Boutterin, M.-C.; Lombard, B.; Loew, D.; Hallberg, B.; Palmer, R.H.; et al. Internalization and Down-Regulation of the ALK Receptor in Neuroblastoma Cell Lines upon Monoclonal Antibodies Treatment. PLoS One 2012, 7, e33581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pischedda, F.; Ghirelli, A.; Tripathi, V.; Piccoli, G. Negr1-Derived Peptides Trigger ALK Degradation and Halt Neuroblastoma Progression In Vitro and In Vivo. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkannagari, H.; Kasper, J.M.; Misra, A.; Rush, S.A.; Fan, S.; Lee, H.; Sun, H.; Seshadrinathan, S.; Machius, M.; Hommel, J.D.; et al. Highly Conserved Molecular Features in IgLONs Contrast Their Distinct Structural and Biological Outcomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 5287–5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moog-Lutz, C.; Degoutin, J.; Gouzi, J.Y.; Frobert, Y.; Brunet-de Carvalho, N.; Bureau, J.; Créminon, C.; Vigny, M. Activation and Inhibition of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Receptor Tyrosine Kinase by Monoclonal Antibodies and Absence of Agonist Activity of Pleiotrophin. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 26039–26048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Gont, A.; Kee, L.; Dries, R.; Pfeifer, K.; Sharma, B.; Debruyne, D.N.; Harlow, M.; Sengupta, S.; Guan, J.; et al. Extracellular Domain Shedding of the ALK Receptor Mediates Neuroblastoma Cell Migration. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DelGrosso, F.; DeMariano, M.; Passoni, L.; Luksch, R.; Tonini, G.P.; Longo, L. Inhibition of N-Linked Glycosylation Impairs ALK Phosphorylation and Disrupts pro-Survival Signaling in Neuroblastoma Cell Lines. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contessa, J.N.; Bhojani, M.S.; Freeze, H.H.; Rehemtulla, A.; Lawrence, T.S. Inhibition of N-Linked Glycosylation Disrupts Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling in Tumor Cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 3803–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedoni, S.; Scherma, M.; Camoglio, C.; Siddi, C.; Fratta, W.; Fadda, P. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Receptor: Possible Involvement in Anorexia Nervosa. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.-J.; Pan, W.-W.; Liu, S.-B.; Shen, Z.-F.; Xu, Y.; Hu, L.-L. ERK/MAPK Signalling Pathway and Tumorigenesis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducray, S.P.; Natarajan, K.; Garland, G.D.; Turner, S.D.; Egger, G. The Transcriptional Roles of ALK Fusion Proteins in Tumorigenesis. Cancers (Basel). 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.; Fang, W.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Wang, C.; Huang, Q.; Huang, M.; Zhuang, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, L. Impact of STAT1 Polymorphisms on Crizotinib-Induced Hepatotoxicity in ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 147, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreca, A.; Lasorsa, E.; Riera, L.; Machiorlatti, R.; Piva, R.; Ponzoni, M.; Kwee, I.; Bertoni, F.; Piccaluga, P.P.; Pileri, S.A.; et al. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase in Human Cancer. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 47, R11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unno, K.; Chalmers, Z.R.; Pamarthy, S.; Vatapalli, R.; Rodriguez, Y.; Lysy, B.; Mok, H.; Sagar, V.; Han, H.; Yoo, Y.A.; et al. Activated ALK Cooperates with N-Myc via Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling to Induce Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 2157–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilling, A.B.; Kim, J.; Estrada-Bernal, A.; Zhou, Q.; Le, A.T.; Singleton, K.R.; Heasley, L.E.; Tan, A.C.; DeGregori, J.; Doebele, R.C. ALK Is a Critical Regulator of the MYC-Signaling Axis in ALK Positive Lung Cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 8823–8835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, R.; Sasaki, T.; Minami, Y.; Hibino, Y.; Okumura, S.; Sado, M.; Miyokawa, N.; Hayashi, S.; Kitada, M.; Ohsaki, Y. Activation of Src Signaling Mediates Acquired Resistance to ALK Inhibition in Lung Cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lu, S.; Jian, H. AZD0530 Sensitizes Drug-Resistant ALK-Positive Lung Cancer Cells by Inhibiting SRC Signaling. FEBS Open Bio 2017, 7, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimura, K.; Yamada, T.; Horinaka, M.; Katayama, Y.; Fukui, S.; Morimoto, K.; Nakano, T.; Tokuda, S.; Morimoto, Y.; Iwasaku, M.; et al. Inhibition of C-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Signaling Increased Apoptosis and Prevented the Emergence of ALK-TKI-Tolerant Cells in ALK-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2021, 522, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanizaki, J.; Okamoto, I.; Okabe, T.; Sakai, K.; Tanaka, K.; Hayashi, H.; Kaneda, H.; Takezawa, K.; Kuwata, K.; Yamaguchi, H.; et al. Activation of HER Family Signaling as a Mechanism of Acquired Resistance to ALK Inhibitors in EML4-ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. cancer Res. an Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 6219–6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Meng, Y.; Wang, K.; Gao, M.; Du, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Zuo, D.; Wu, Y. EML4-ALK G1202R Mutation Induces EMT and Confers Resistance to Ceritinib in NSCLC Cells via Activation of STAT3/Slug Signaling. Cell. Signal. 2022, 92, 110264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanizaki, J.; Okamoto, I.; Takezawa, K.; Sakai, K.; Azuma, K.; Kuwata, K.; Yamaguchi, H.; Hatashita, E.; Nishio, K.; Janne, P.A.; et al. Combined Effect of ALK and MEK Inhibitors in EML4-ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Deng, X.; Yoshioka, Y.; Vougiouklakis, T.; Park, J.-H.; Suzuki, T.; Dohmae, N.; Ueda, K.; Hamamoto, R.; Nakamura, Y. Effects of SMYD2-Mediated EML4-ALK Methylation on the Signaling Pathway and Growth in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Hung, P.-S.; Chih-Hsin Yang, J. Potential Therapeutic Strategy for EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer With Concomitant EML4-ALK Rearrangement-Combination of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and ALK Inhibitors. JTO Clin. Res. reports 2022, 3, 100405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gou, W.; Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Shen, J.; Guo, M.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhai, X.; Zuo, D. ZX-29, a Novel ALK Inhibitor, Induces Apoptosis via ER Stress in ALK Rearrangement NSCLC Cells and Overcomes Cell Resistance Caused by an ALK Mutation. Biochim. Biophys. acta. Mol. cell Res. 2020, 1867, 118712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Fan, Z.; Zhu, S.-J.; Huang, X.; Zhuang, Z.; Li, Y.; Deng, Z.; Gao, L.; Hong, X.; Zhang, T.; et al. A New ALK Inhibitor Overcomes Resistance to First- and Second-Generation Inhibitors in NSCLC. EMBO Mol. Med. 2022, 14, e14296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-T.; Chiang, C.-L.; Hung, J.-Y.; Lee, M.-H.; Su, W.-C.; Wu, S.-Y.; Wei, Y.-F.; Lee, K.-Y.; Tseng, Y.-H.; Su, J.; et al. Resistance Profiles of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Multicenter Study Using Targeted next-Generation Sequencing. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 156, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.-Y.; Chen, M.-K.; Wei, Y.; Lee, H.-H.; Xia, W.; Wang, Y.-N.; Yam, C.; Hsu, J.L.; Wang, H.-L.; Chang, W.-C.; et al. Targeting the ALK-CDK9-Tyr19 Kinase Cascade Sensitizes Ovarian and Breast Tumors to PARP Inhibition via Destabilization of the P-TEFb Complex. Nat. cancer 2022, 3, 1211–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Yu, B.; Xu, Y.; Du, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, L.A.; Chen, R.; Ma, F.; et al. Discovery of Selective and Potent Macrocyclic CDK9 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Osimertinib-Resistant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 15340–15361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Knoll, S.; Bocharova, I.; Tang, W.; Signorovitch, J. Comparative Efficacy of First-Line Ceritinib and Crizotinib in Advanced or Metastatic Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: An Adjusted Indirect Comparison with External Controls. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2019, 35, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Lu, S.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Shi, Y.-K.; Sriuranpong, V.; Ho, J.C.M.; Ong, C.K.; Tsai, C.-M.; Chung, C.-H.; et al. Results of PROFILE 1029, a Phase III Comparison of First-Line Crizotinib versus Chemotherapy in East Asian Patients with ALK-Positive Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2018, 13, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Gadgeel, S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, D.-W.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Pérol, M.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus Crizotinib in Untreated ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadgeel, S.; Peters, S.; Mok, T.; Shaw, A.T.; Kim, D.W.; Ou, S.I.; Pérol, M.; Wrona, A.; Novello, S.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus Crizotinib in Treatment-Naive Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive (ALK+) Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: CNS Efficacy Results from the ALEX Study. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2018, 29, 2214–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziadziuszko, R.; Peters, S.; Mok, T.; Camidge, D.R.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Konopa, K.; Noé, J.; Nowicka, M.; Bordogna, W.; et al. Circulating Cell-Free DNA as a Prognostic Biomarker in Patients with Advanced ALK+ Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in the Global Phase III ALEX Trial. Clin. cancer Res. an Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 1800–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.; Peters, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Noé, J.; Gadgeel, S.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Kim, D.-W.; Konopa, K.; Pozzi, E.; Liu, T.; et al. Outcomes According to ALK Status Determined by Central Immunohistochemistry or Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization in Patients With ALK-Positive NSCLC Enrolled in the Phase 3 ALEX Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2021, 16, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérol, M.; Pavlakis, N.; Levchenko, E.; Platania, M.; Oliveira, J.; Novello, S.; Chiari, R.; Moran, T.; Mitry, E.; Nüesch, E.; et al. Patient-Reported Outcomes from the Randomized Phase III ALEX Study of Alectinib versus Crizotinib in Patients with ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2019, 138, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Kim, H.R.; Ahn, M.-J.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Han, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-S.; Hochmair, M.J.; Li, J.Y.-C.; Chang, G.-C.; Lee, K.H.; et al. Brigatinib versus Crizotinib in ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camidge, D.R.; Kim, H.R.; Ahn, M.-J.; Yang, J.C.H.; Han, J.-Y.; Hochmair, M.J.; Lee, K.H.; Delmonte, A.; García Campelo, M.R.; Kim, D.-W.; et al. Brigatinib Versus Crizotinib in Advanced ALK Inhibitor-Naive ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Second Interim Analysis of the Phase III ALTA-1L Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3592–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Kim, H.R.; Ahn, M.-J.; Yang, J.C.H.; Han, J.-Y.; Hochmair, M.J.; Lee, K.H.; Delmonte, A.; Garcia Campelo, M.R.; Kim, D.-W.; et al. Brigatinib Versus Crizotinib in ALK Inhibitor-Naive Advanced ALK-Positive NSCLC: Final Results of Phase 3 ALTA-1L Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2021, 16, 2091–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.L.; Narasimhan, N.; Gupta, N.; Venkatakrishnan, K.; Kerstein, D.; Camidge, D.R. Early-Onset Pulmonary Events Associated With Brigatinib Use in Advanced NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2020, 15, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popat, S.; Liu, G.; Lu, S.; Song, G.; Ma, X.; Yang, J.C.-H. Brigatinib vs Alectinib in Crizotinib-Resistant Advanced Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (ALTA-3). Future Oncol. 2021, 17, 4237–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.-C.; Tan, D.S.W.; Chiari, R.; Wu, Y.-L.; Paz-Ares, L.; Wolf, J.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Cortinovis, D.; Yu, C.-J.; et al. First-Line Ceritinib versus Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Advanced ALK-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (ASCEND-4): A Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Study. Lancet (London, England) 2017, 389, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiura, K.; Imamura, F.; Kagamu, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Hida, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Satouchi, M.; Okamoto, I.; Takenoyama, M.; Fujisaka, Y.; et al. Phase 3 Study of Ceritinib vs Chemotherapy in ALK-Rearranged NSCLC Patients Previously Treated with Chemotherapy and Crizotinib (ASCEND-5): Japanese Subset. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 48, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Bauer, T.M.; deMarinis, F.; Felip, E.; Goto, Y.; Liu, G.; Mazieres, J.; Kim, D.-W.; Mok, T.; Polli, A.; et al. First-Line Lorlatinib or Crizotinib in Advanced ALK-Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2018–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazieres, J.; Iadeluca, L.; Shaw, A.T.; Solomon, B.J.; Bauer, T.M.; deMarinis, F.; Felip, E.; Goto, Y.; Kim, D.-W.; Mok, T.; et al. Patient-Reported Outcomes from the Randomized Phase 3 CROWN Study of First-Line Lorlatinib versus Crizotinib in Advanced ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2022, 174, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Patra, R.; Behzadi, P.; Masotti, A.; Paolini, A.; Sarshar, M. Toll-like Receptor-Guided Therapeutic Intervention of Human Cancers: Molecular and Immunological Perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1244345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janik, J.E.; Morris, J.C.; Pittaluga, S.; McDonald, K.; Raffeld, M.; Jaffe, E.S.; Grant, N.; Gutierrez, M.; Waldmann, T.A.; Wilson, W.H. Elevated Serum-Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptor Levels in Patients with Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2004, 104, 3355–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, H.; Suzuki, H.I.; Nishimori, H.; Noguchi, M.; Yao, T.; Komatsu, N.; Mano, H.; Sugimoto, K.; Miyazono, K. MiR-135b Mediates NPM-ALK-Driven Oncogenicity and Renders IL-17-Producing Immunophenotype to Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2011, 118, 6881–6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knörr, F.; Damm-Welk, C.; Ruf, S.; Singh, V.K.; Zimmermann, M.; Reiter, A.; Woessmann, W. Blood Cytokine Concentrations in Pediatric Patients with Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Haematologica 2018, 103, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeles, A.K.; Janke, F.; Daum, A.-K.; Reck, M.; Schneider, M.A.; Thomas, M.; Christopoulos, P.; Sültmann, H. Integrated Circulating Tumour DNA and Cytokine Analysis for Therapy Monitoring of ALK-Rearranged Lung Adenocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 129, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zeng, H.; Wei, Q.; Tian, P. High PD-L1 Expression Correlates with an Immunosuppressive Tumour Immune Microenvironment and Worse Prognosis in ALK-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Biomolecules 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbarzadeh Kaboli, P.; Shabani, S.; Sharma, S.; Partovi Nasr, M.; Yamaguchi, H.; Hung, M.-C. Shedding Light on Triple-Negative Breast Cancer with Trop2-Targeted Antibody-Drug Conjugates. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2022, 12, 1671–1685. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Guo, J.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, J.; Kaboli, P.J.; Xiang, S.; Du, F.; Wu, X.; Li, M.; Wan, L.; et al. Comprehensive Assessment of PD-L1 and PD-L2 Dysregulation in Gastrointestinal Cancers. Epigenomics 2020, 12, 2155–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riudavets, M.; Auclin, E.; Mosteiro, M.; Dempsey, N.; Majem, M.; Lobefaro, R.; López-Castro, R.; Bosch-Barrera, J.; Pilotto, S.; Escalera, E.; et al. Durvalumab Consolidation in Patients with Unresectable Stage III Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Driver Genomic Alterations. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 167, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, K.; Azuma, K.; Kawahara, A.; Hattori, S.; Iwama, E.; Tanizaki, J.; Harada, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Takayama, K.; Takamori, S.; et al. Induction of PD-L1 Expression by the EML4-ALK Oncoprotein and Downstream Signaling Pathways in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. cancer Res. an Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4014–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghaei, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Steins, M.; Ready, N.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Vokes, E.E.; Felip, E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldacci, S.; Grégoire, V.; Patrucco, E.; Chiarle, R.; Jamme, P.; Wasielewski, E.; Descarpentries, C.; Copin, M.-C.; Awad, M.M.; Cortot, A.B. Complete and Prolonged Response to Anti-PD1 Therapy in an ALK Rearranged Lung Adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2020, 146, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebart, H.; Lang, P.; Woessmann, W. Nivolumab for Refractory Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: A Case Report. Ann. Intern. Med. 2016, 165, 607–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigaud, C.; Abbou, S.; Minard-Colin, V.; Geoerger, B.; Scoazec, J.Y.; Vassal, G.; Jaff, N.; Heuberger, L.; Valteau-Couanet, D.; Brugieres, L. Efficacy of Nivolumab in a Patient with Systemic Refractory ALK+ Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-W.; Gadgeel, S.; Gettinger, S.N.; Riely, G.J.; Oxnard, G.R.; Mekhail, T.; Schmid, P.; Dowlati, A.; Heist, R.S.; Wozniak, A.J.; et al. Brief Report: Safety and Antitumor Activity of Alectinib Plus Atezolizumab From a Phase 1b Study in Advanced ALK-Positive NSCLC. JTO Clin. Res. reports 2022, 3, 100367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Luo, L.; Jia, K.; Shao, C.; Mao, S.; Qiu, T.; et al. Association of PD-L1 Expression with Efficacy of Alectinib in Advanced NSCLC Patients with ALK Fusion. Lung Cancer 2023, 181, 107233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socinski, M.A.; Jotte, R.M.; Cappuzzo, F.; Orlandi, F.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Nogami, N.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Thomas, C.A.; Barlesi, F.; et al. Atezolizumab for First-Line Treatment of Metastatic Nonsquamous NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2288–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hack, S.P.; Zhu, A.X.; Wang, Y. Augmenting Anticancer Immunity Through Combined Targeting of Angiogenic and PD-1/PD-L1 Pathways: Challenges and Opportunities. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 598877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, K.-H.; Lim, S.M.; Park, C.-W.; Jo, H.-N.; Kim, J.H.; Yun, M.-R.; Kim, D.; Xin, C.-F.; Lee, W.; Gheorghiu, B.; et al. Comprehensive Analyses of Immunodynamics and Immunoreactivity in Response to Treatment in ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Immunother. cancer 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, D.F.; Huseni, M.A.; Atkins, M.B.; Motzer, R.J.; Rini, B.I.; Escudier, B.; Fong, L.; Joseph, R.W.; Pal, S.K.; Reeves, J.A.; et al. Clinical Activity and Molecular Correlates of Response to Atezolizumab Alone or in Combination with Bevacizumab versus Sunitinib in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, N.J.; Young, R.J.; Sellitti, M.; Miller, A.; Drilon, A. Lorlatinib and Bevacizumab Activity in ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancers After Lorlatinib Progression. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2020, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Chiarle, R.; Martinengo, C.; Mastini, C.; Ambrogio, C.; D’Escamard, V.; Forni, G.; Inghirami, G. The Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Is an Effective Oncoantigen for Lymphoma Vaccination. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voena, C.; Menotti, M.; Mastini, C.; DiGiacomo, F.; Longo, D.L.; Castella, B.; Merlo, M.E.B.; Ambrogio, C.; Wang, Q.; Minero, V.G.; et al. Efficacy of a Cancer Vaccine against ALK-Rearranged Lung Tumors. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codony-Servat, J.; García-Roman, S.; Molina-Vila, M.Á.; Bertran-Alamillo, J.; Viteri, S.; d’Hondt, E.; Rosell, R. Anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Vaccine Antibodies Increase the Antitumor Activity of Kinase Inhibitors in ALK and RET Rearranged Lung Cancer Cells. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 100887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, K.; Azad, T.; Lightbody, E.; Khanal, P.; Nicol, C.J.; Yang, X. A Kinome-Wide Screen Using a NanoLuc LATS Luminescent Biosensor Identifies ALK as a Novel Regulator of the Hippo Pathway in Tumorigenesis and Immune Evasion. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2019, 33, 12487–12499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutmair, S.; Erlacher, M.; Andrieux, G.; Istvanffy, R.; Mueller-Rudorf, A.; Zwick, M.; Rückert, T.; Pantic, M.; Poggio, T.; Shoumariyeh, K.; et al. Loss of the Fanconi Anemia-Associated Protein NIPA Causes Bone Marrow Failure. J. Clin. Invest. 2020, 130, 2827–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutmair, S.; Lippert, L.J.; Klingeberg, C.; Albers-Leischner, C.; Yacob, S.; Shlyakhto, V.; Mueller, T.; Mueller-Rudorf, A.; Yu, C.; Gorantla, S.P.; et al. NIPA (Nuclear Interaction Partner of ALK) Is Crucial for Effective NPM-ALK Mediated Lymphomagenesis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 875117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, L.; Yi, H.; Zou, L.; Mo, J.; Xue, F.; Zheng, J.; Huang, Y.; Lu, H.; Wu, H.; et al. Inhibiting ALK-TOPK Signaling Pathway Promotes Cell Apoptosis of ALK-Positive NSCLC. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X. Prognostic Value of PDZ-Binding Kinase/T-LAK Cell-Originated Protein Kinase (PBK/TOPK) in Patients with Cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, Y.; Park, J.-H.; Miyamoto, T.; Takamatsu, N.; Kato, T.; Iwasa, A.; Okabe, S.; Imai, Y.; Fujiwara, K.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. T-LAK Cell-Originated Protein Kinase (TOPK) as a Prognostic Factor and a Potential Therapeutic Target in Ovarian Cancer. Clin. cancer Res. an Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 6110–6117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlobec, I.; Molinari, F.; Kovac, M.; Bihl, M.P.; Altermatt, H.J.; Diebold, J.; Frick, H.; Germer, M.; Horcic, M.; Montani, M.; et al. Prognostic and Predictive Value of TOPK Stratified by KRAS and BRAF Gene Alterations in Sporadic, Hereditary and Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Patients. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, T.; Komatsu, S.; Ichikawa, D.; Miyamae, M.; Okajima, W.; Imamura, T.; Kiuchi, J.; Kosuga, T.; Konishi, H.; Shiozaki, A.; et al. Overexpression of PBK/TOPK Relates to Tumour Malignant Potential and Poor Outcome of Gastric Carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




