Submitted:
08 January 2024
Posted:
09 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
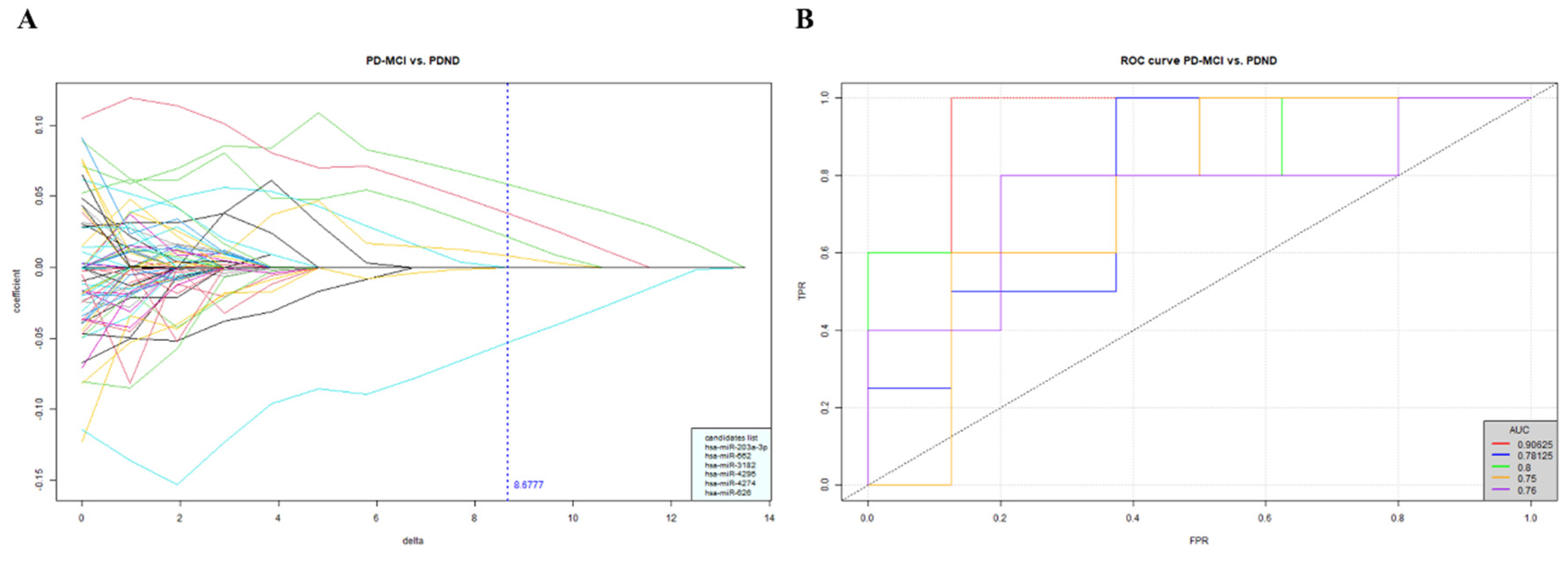
2.1. Using small RNA-seq to explore the potential miRNA cluster that may allow for differentiation of PD with or without cognitive impairment
Analyzing miRNA candidates from the NGS profiling in the discovery cohort
2.2. Validation of the miRNA candidates in another PwP cohort
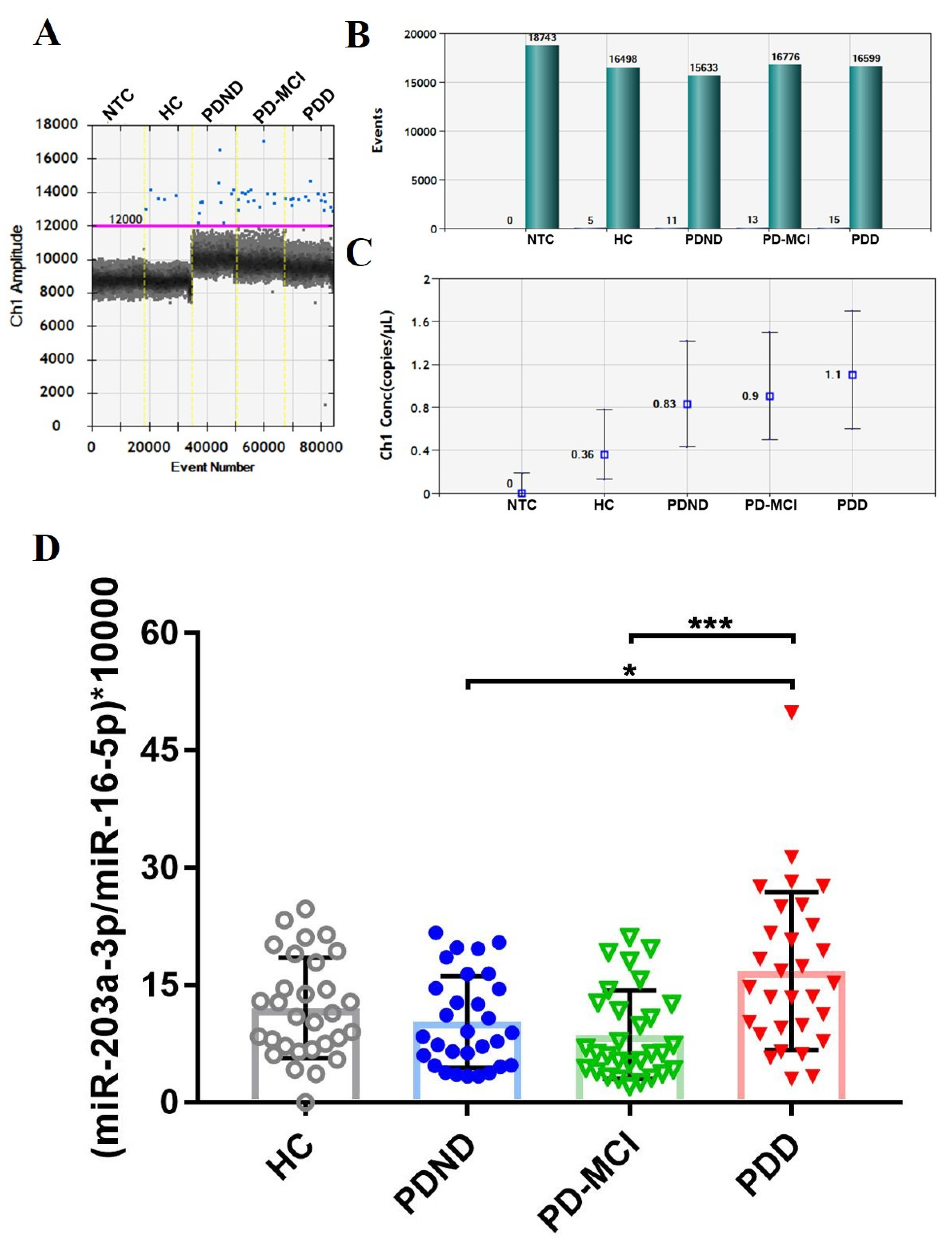
2.2.1. Measurement of the selected miRNA candidates
2.2.2. Motor function deterioration was associated with poor cognitive status
2.3. The expression level of plasma miR-203a-3p/miR-16-5p validated using ddPCR
2.4. Correlation of miRNA expression and cognitive performance
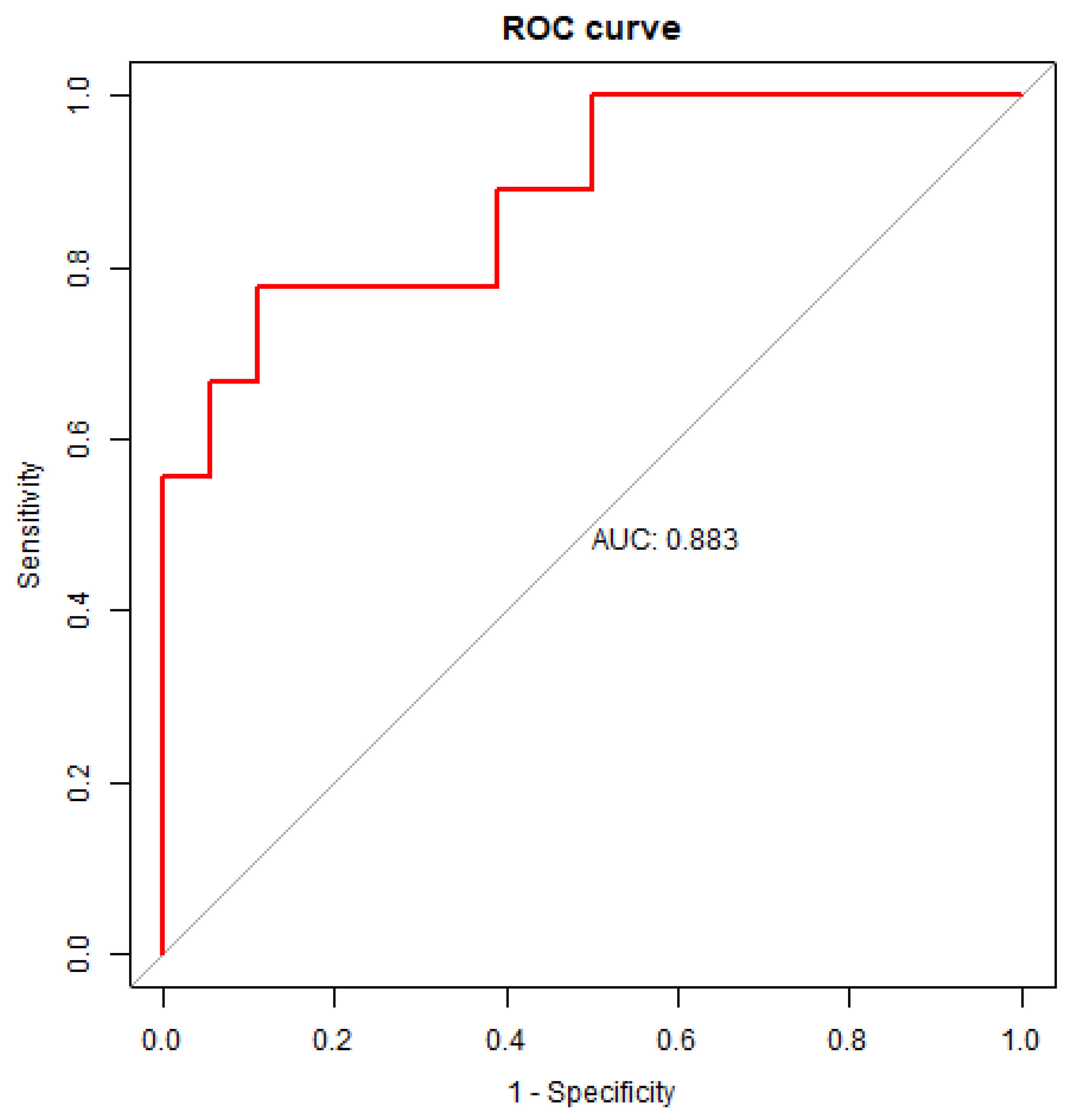
2.5. Using the ratio of miR-203a-3p/miR-16-5p as variable for building regression model
2.6. MiR-203a-3p associated with cognition-related KEGG pathways
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plasma miRNA profiling in the discovery cohort
4.1.1. Recruitment of participants
4.1.2. Plasma collection
4.1.3. Plasma miRNA sequencing
4.1.4. BOLD Selector included data analytic scheme
4.2. Validating plasma miRNA candidates in new PD cohort
4.2.1. Sample size estimation
4.2.2. Recruitment of participants
4.2.3. Cognitive assessments
4.2.4. Plasma collection
4.2.5. RNA extraction
4.2.6. Droplet digital PCR
4.2.7. Pathway prediction
4.2.8. Statistical analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aarsland, D.; Batzu, L.; Halliday, G.M.; Geurtsen, G.J.; Ballard, C.; Ray Chaudhuri, K.; Weintraub, D. Parkinson disease-associated cognitive impairment. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Okun, M.S. Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson Disease: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.L.; Wu, R.M.; Tai, C.H.; Lin, C.H.; Cheng, T.W.; Hua, M.S. Neuropsychological profile in patients with early stage of Parkinson's disease in Taiwan. Park. Relat. Disord. 2012, 18, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litvan, I.; Goldman, J.G.; Troster, A.I.; Schmand, B.A.; Weintraub, D.; Petersen, R.C.; Mollenhauer, B.; Adler, C.H.; Marder, K.; Williams-Gray, C.H.; et al. Diagnostic criteria for mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease: Movement Disorder Society Task Force guidelines. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Åström, D.O.; Simonsen, J.; Raket, L.L.; Sgarbi, S.; Hellsten, J.; Hagell, P.; Norlin, J.M.; Kellerborg, K.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Odin, P. High risk of developing dementia in Parkinson's disease: A Swedish registry-based study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, D.J.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Parkinson's disease dementia: Convergence of alpha-synuclein, tau and amyloid-beta pathologies. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorsey, E.R.; Bloem, B.R. The Parkinson Pandemic-A Call to Action. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkouzi, A.; Vedam-Mai, V.; Eisinger, R.S.; Okun, M.S. Emerging therapies in Parkinson disease - repurposed drugs and new approaches. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 204–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, Y.H.; Hsu, C.C.; Yang, Y.H. A Nationwide Survey of Dementia Prevalence in Long-Term Care Facilities in Taiwan. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-Y.; Huang, C.-S. Aging in Taiwan: Building a Society for Active Aging and Aging in Place. Gerontol. 2015, 56, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huertas, I.; Jesús, S.; García-Gómez, F.J.; Lojo, J.A.; Bernal-Bernal, I.; Bonilla-Toribio, M.; Martín-Rodriguez, J.F.; García-Solís, D.; Gómez-Garre, P.; Mir, P. Genetic factors influencing frontostriatal dysfunction and the development of dementia in Parkinson's disease. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanskey, J.H.; McColgan, P.; Schrag, A.E.; Acosta-Cabronero, J.; Rees, G.; Morris, H.R.; Weil, R.S. Can neuroimaging predict dementia in Parkinson's disease? Brain 2018, 141, 2545–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, B.; Burn, D.; Goetz, C.; Aarsland, D.; Brown, R.G.; Broe, G.A.; Dickson, D.; Duyckaerts, C.; Cummings, J.; Gauthier, S.; et al. Diagnostic procedures for Parkinson's disease dementia: Recommendations from the movement disorder society task force. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 2314–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Htike, T.T.; Mishra, S.; Kumar, S.; Padmanabhan, P.; Gulyas, B. Peripheral Biomarkers for Early Detection of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 2256–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, M.C.; Liu, S.C.; Hsu, Y.F.; Wu, R.M. The role of noncoding RNAs in Parkinson's disease: Biomarkers and associations with pathogenic pathways. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 28, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, J.A.; Baxter, D.H.; Zhang, S.; Huang, D.Y.; Huang, K.H.; Lee, M.J.; Galas, D.J.; Wang, K. The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Yang, J.; Lu, J.; Cao, S.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, Z. Identification of aberrant circulating miRNAs in Parkinson's disease plasma samples. Brain Behav. 2018, 8, e00941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, A.R.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Saperi, A.A.; Jamal, R.; Mohamed Ibrahim, N.; Abdul Murad, N.A. MicroRNAs and Target Genes As Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Early Onset of Parkinson Disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batistela, M.S.; Josviak, N.D.; Sulzbach, C.D.; de Souza, R.L. An overview of circulating cell-free microRNAs as putative biomarkers in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Diseases. Int. J. Neurosci. 2017, 127, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, P.Y.; Yang, F.C.; Chiu, M.J.; Lin, W.C.; Lu, C.H.; Yang, S.Y. Relevance of plasma biomarkers to pathologies in Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and frontotemporal dementia. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.S.; Liu, S.C.; Wu, R.M. Alpha-Synuclein and Cognitive Decline in Parkinson Disease. Life (Basel Switz. ) 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, C.C.; Cheng, H.H.; Tewari, M. MicroRNA profiling: Approaches and considerations. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindson, C.M.; Chevillet, J.R.; Briggs, H.A.; Gallichotte, E.N.; Ruf, I.K.; Hindson, B.J.; Vessella, R.L.; Tewari, M. Absolute quantification by droplet digital PCR versus analog real-time PCR. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1003–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraldi, M.; Gomarasca, M.; Banfi, G.; Lombardi, G. Free Circulating miRNAs Measurement in Clinical Settings: The Still Unsolved Issue of the Normalization. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2018, 87, 113–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehlmann, T.; Lehallier, B.; Schaum, N.; Hahn, O.; Kahraman, M.; Li, Y.; Grammes, N.; Geffers, L.; Backes, C.; Balling, R.; et al. Common diseases alter the physiological age-related blood microRNA profile. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanidis, S.; Bougea, A.; Papagiannakis, N.; Maniati, M.; Koros, C.; Simitsi, A.M.; Bozi, M.; Pachi, I.; Stamelou, M.; Paraskevas, G.P.; et al. Circulating Brain-enriched MicroRNAs for detection and discrimination of idiopathic and genetic Parkinson's disease. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, T.M.; Kuiperij, H.B.; Bruinsma, I.B.; van Rumund, A.; Aerts, M.B.; Esselink, R.A.J.; Bloem, B.R.; Verbeek, M.M. MicroRNAs in Cerebrospinal Fluid as Potential Biomarkers for Parkinson's Disease and Multiple System Atrophy. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 7736–7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, S.; Yuan, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, K. Relationship between the plasma levels of neurodegenerative proteins and motor subtypes of Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2017, 124, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.; Chung, C.C.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Wu, R.M.; Hong, C.T. Plasma extracellular vesicle tau, beta-amyloid, and alpha-synuclein and the progression of Parkinson's disease: A follow-up study. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2023, 16, 17562864221150329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, T.; Sun, J. Serum NFL discriminates Parkinson disease from essential tremor and reflect motor and cognition severity. BMC Neurol. 2022, 22, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.T.; Shaw, J.S.; Cheng, F.Y.; Chen, P.H. Plasma total tau predicts executive dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2022, 145, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coughlin, D.G.; Irwin, D.J. Fluid and Biopsy Based Biomarkers in Parkinson's Disease. Neurother. : J. Am. Soc. Exp. NeuroTherapeutics 2023, 20, 932–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoporis, J.N.; Ektesabi, A.M.; Gupta, S.; Izhar, S.; Salpeas, V.; Rizos, I.K.; Kympouropoulos, S.P.; Dos Santos, C.C.; Parker, T.G.; Rizos, E. A longitudinal study of alterations of circulating DJ-1 and miR203a-3p in association to olanzapine medication in a sample of first episode patients with schizophrenia. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2022, 146, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antipova, D.; Bandopadhyay, R. Expression of DJ-1 in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1037, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biosa, A.; Sandrelli, F.; Beltramini, M.; Greggio, E.; Bubacco, L.; Bisaglia, M. Recent findings on the physiological function of DJ-1: Beyond Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2017, 108, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Li, Z.; Yang, M.; Yu, W.; Luo, R.; Zhou, J.; He, J.; Chen, Q.; Song, Z.; Cheng, S. Non-Coding RNA in Microglia Activation and Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's Disease. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 4165–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swarup, V.; Hinz, F.I.; Rexach, J.E.; Noguchi, K.I.; Toyoshiba, H.; Oda, A.; Hirai, K.; Sarkar, A.; Seyfried, N.T.; Cheng, C.; et al. Identification of evolutionarily conserved gene networks mediating neurodegenerative dementia. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, D.; Botta-Orfila, T.; Cirillo, D.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Livi, C.M.; Fernández-Santiago, R.; Ezquerra, M.; Martí, M.J.; Bechara, E.; Tartaglia, G.G. Discovering the 3' UTR-mediated regulation of alpha-synuclein. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 12888–12903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nies, Y.H.; Mohamad Najib, N.H.; Lim, W.L.; Kamaruzzaman, M.A.; Yahaya, M.F.; Teoh, S.L. MicroRNA Dysregulation in Parkinson's Disease: A Narrative Review. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 660379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phongpreecha, T.; Cholerton, B.; Mata, I.F.; Zabetian, C.P.; Poston, K.L.; Aghaeepour, N.; Tian, L.; Quinn, J.F.; Chung, K.A.; Hiller, A.L.; et al. Multivariate prediction of dementia in Parkinson's disease. NPJ Park. Dis. 2020, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auclair-Ouellet, N.; Lieberman, P.; Monchi, O. Contribution of language studies to the understanding of cognitive impairment and its progression over time in Parkinson's disease. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 80, 657–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Liang, X.; Song, C.; Zou, Y. miR-203, fine-tunning neuroinflammation by juggling different components of NF-kappaB signaling. J. Neuroinflammation 2022, 19, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, H.S.; Ahn, J.H.; Oh, J.K.; Chang, I.B.; Song, J.H.; Wee, J.H.; Min, C.Y.; Yoo, D.M.; Choi, H.G. Association Between Thyroid Diseases and Parkinson's Disease: A Nested Case-Control Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort. J. Park. Dis. 2021, 11, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iadecola, C. The Neurovascular Unit Coming of Age: A Journey through Neurovascular Coupling in Health and Disease. Neuron 2017, 96, 17–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, A.; Chaker, L.; Darweesh, S.K.; Korevaar, T.I.; Mattace-Raso, F.U.; Dehghan, A.; Franco, O.H.; van der Geest, J.N.; Ikram, M.A.; Peeters, R.P. Gait patterns associated with thyroid function: The Rotterdam Study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnen, N.I.; Albin, R.L. The cholinergic system and Parkinson disease. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 221, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjari Moghaddam, H.; Zare-Shahabadi, A.; Rahmani, F.; Rezaei, N. Neurotransmission systems in Parkinson's disease. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 28, 509–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnen, N.I.; Yarnall, A.J.; Weil, R.S.; Moro, E.; Moehle, M.S.; Borghammer, P.; Bedard, M.A.; Albin, R.L. Cholinergic system changes in Parkinson's disease: Emerging therapeutic approaches. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colloby, S.J.; Nathan, P.J.; Bakker, G.; Lawson, R.A.; Yarnall, A.J.; Burn, D.J.; O'Brien, J.T.; Taylor, J.P. Spatial Covariance of Cholinergic Muscarinic M(1) /M(4) Receptors in Parkinson's Disease. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 1879–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Mesulam, M.M.; Cuello, A.C.; Farlow, M.R.; Giacobini, E.; Grossberg, G.T.; Khachaturian, A.S.; Vergallo, A.; Cavedo, E.; Snyder, P.J.; et al. The cholinergic system in the pathophysiology and treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Brain 2018, 141, 1917–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandiah, N.; Pai, M.C.; Senanarong, V.; Looi, I.; Ampil, E.; Park, K.W.; Karanam, A.K.; Christopher, S. Rivastigmine: The advantages of dual inhibition of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase and its role in subcortical vascular dementia and Parkinson's disease dementia. Clin. Interv. Aging 2017, 12, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvan, I.; Kieburtz, K.; Troster, A.I.; Aarsland, D. Strengths and challenges in conducting clinical trials in Parkinson's disease mild cognitive impairment. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boel, J.A.; de Bie, R.M.A.; Schmand, B.A.; Dalrymple-Alford, J.C.; Marras, C.; Adler, C.H.; Goldman, J.G.; Troster, A.I.; Burn, D.J.; Litvan, I.; et al. Level I PD-MCI Using Global Cognitive Tests and the Risk for Parkinson's Disease Dementia. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pr. 2022, 9, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Corbett, A.L.; Taatizadeh, E.; Tasnim, N.; Little, J.P.; Garnis, C.; Daugaard, M.; Guns, E.; Hoorfar, M.; Li, I.T.S. Challenges and opportunities in exosome research-Perspectives from biology, engineering, and cancer therapy. APL Bioeng. 2019, 3, 011503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.W.; Lin, Y.H.; Phoa, F.K.H.; Lin, S.P.; Tsai, Y.T.; Kuo, M.C.; Ueda, K.; Wu, R.M. Differentiating Patient Group across Parkinsonism Spectrum via the Biomedical Oriented Logistic Dantzig Selector (BOLD Selector). (manuscript in submission).
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.G. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, S.T.; Kaldenbach, M.A.; Antonini, A.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Timmermann, L.; Odin, P.; Katzenschlager, R.; Borgohain, R.; Fasano, A.; Stocchi, F.; et al. Levodopa Dose Equivalency in Parkinson's Disease: Updated Systematic Review and Proposals. Mov. Disord. 2023, 38, 1236–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M. Toward understanding the origin and evolution of cellular organisms. Protein Sci. : A Publ. Protein Soc. 2019, 28, 1947–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehl, T.; Kern, F.; Backes, C.; Fehlmann, T.; Stöckel, D.; Meese, E.; Lenhof, H.P.; Keller, A. miRPathDB 2.0: A novel release of the miRNA Pathway Dictionary Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D142–d147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.C.; Müller, M. pROC: An open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M. Building Predictive Models in R Using the caret Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 28, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| HC (n=40) |
PDND (n=37) |
PD-MCI (n=23) |
PDD (n=23) |
p-value* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, % male | 40.00% | 54.05% | 73.91% | 52.17% | ns |
| Age, year | 69.08 ± 6.05 | 64.78 ± 12.51 | 67.70 ± 7.15 | 72.00 ± 5.52 | ns |
| HC (n=30) |
PDND (n=30) |
PD-MCI (n=30) |
PDD (n=30) |
p-value* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, % male | 56.67% | 56.67% | 53.33% | 46.67% | - |
| Age, year | 66.67 ± 5.14 | 69.67 ± 7.03 | 70.13 ± 6.75 | 75.20 ± 6.92 | <0.0001 |
| MoCA† | 28.00 ± 2.00 | 28.00 ± 1.25 | 23.00 ± 1.00 | 17.50 ± 7.00 | <0.0001 |
| Education, year | 14.13 ± 4.13 | 14.13 ± 2.79 | 11.47 ± 4.75 | 10.73 ± 4.64 | 0.0049 |
| Onset age, year | - | 63.53 ± 7.96 | 64.13 ± 7.96 | 67.37 ± 8.71 | ns |
| Duration, year | - | 7.10 ± 3.91 | 6.90 ± 3.07 | 7.23 ± 4.75 | ns |
| Hoehn–Yahr stage† | - | 2.00 ± 1.00 | 2.00 ± 1.00 | 3.00 ± 2.00 | <0.0001 |
| UPDRS III† | - | 13.00 ± 12.00 | 18.50 ± 9.00 | 27.00 ± 22.00 | <0.0001 |
| LEDD | - | 682.54 ± 438.75 | 747.78 ± 398.03 | 765.82 ± 419.36 | ns |
| Cognitive domains of MoCA | Spearman r | p-value |
|---|---|---|
| Total score* | -0.237 | 0.024 |
| Visuospatial* | -0.207 | 0.050 |
| Naming | -0.117 | 0.272 |
| Attention | -0.112 | 0.292 |
| Language* | -0.208 | 0.049 |
| Abstract | -0.124 | 0.246 |
| Memory | -0.205 | 0.052 |
| Orientation* | -0.220 | 0.037 |
| Comparison groups | AUC (95% CI) |
Specificity (95% CI) |
Sensitivity (95% CI) |
Accuracy (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PD-MCI/PDD | 0.7160 (0.4321-0.9506) |
0.5556 (0.2222-0.8889) |
1.0000 (1.0000-1.0000) |
0.7778 (0.6111-0.9444) |
| PD-MCI/PDND | 0.5309 (0.2469-0.8025) |
0.8889 (0.6667-1.0000) |
0.4444 (0.1111-0.7778) |
0.6667 (0.4444-0.8333) |
| PDD/PDND | 0.7407 (0.4815-0.9506) |
0.5556 (0.2222-0.8889) |
1.0000 (1.0000-1.0000) |
0.7778 (0.6111-0.9444) |
| PDD/HC | 0.6420 (0.3333-0.9259) |
0.6667 (0.3333-1.0000) |
0.7778 (0.4444-1.0000) |
0.7222 (0.5000-0.8889) |
| PD-MCI/HC | 0.6667 (0.3824-0.9136) |
0.8889 (0.6667-1.0000) |
0.5556 (0.2222-0.8889) |
0.7222 (0.5556-0.8889) |
| PDND/HC | 0.7160 (0.4318-0.9383) |
0.8889 (0.6667-1.0000) |
0.6667 (0.3333-1.0000) |
0.7778 (0.6111-0.9444) |
| Database | Pathway | p-value | Targets |
|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG | Dopaminergic synapse | 3.00E-04 | AKT2,CLOCK,CREB1,GNAS,GSK3B,KIF5B,MAPK8,MAPK9,PPP1CB,PRKACB,PRKCA |
| KEGG | Apoptosis | 0.011 | AKT2, ATM,MYD88,PIK3CA,PRKACB,TNF |
| KEGG | Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | 0.014 | AKT2, GSK3B,PIK3CA,PRKACB,PRKCA,SRC,STAT1 |
| KEGG | Cholinergic synapse | 0.027 | AKT2, CREB1,KCNJ2,PIK3CA,PRKACB,PRKCA |
| KEGG | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | 0.041 | ATM, CXCL8,MYD88,SYK,TNF |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





