Submitted:
16 January 2024
Posted:
17 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Source and preparation of PLR decoction
2.2. Animals and experimental design
2.3. Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) experiment
2.5. RNA-seq analysis
2.6. Gene expression analysis
2.7. Protein expression and biochemical analysis
2.8. FD-4 permeability experiment
2.9. Imaging of intestinal inflammation in vivo
2.10. Histological staining and analysis
2.11. Immunofluorescence
2.12. Statistical analysis
3. Results
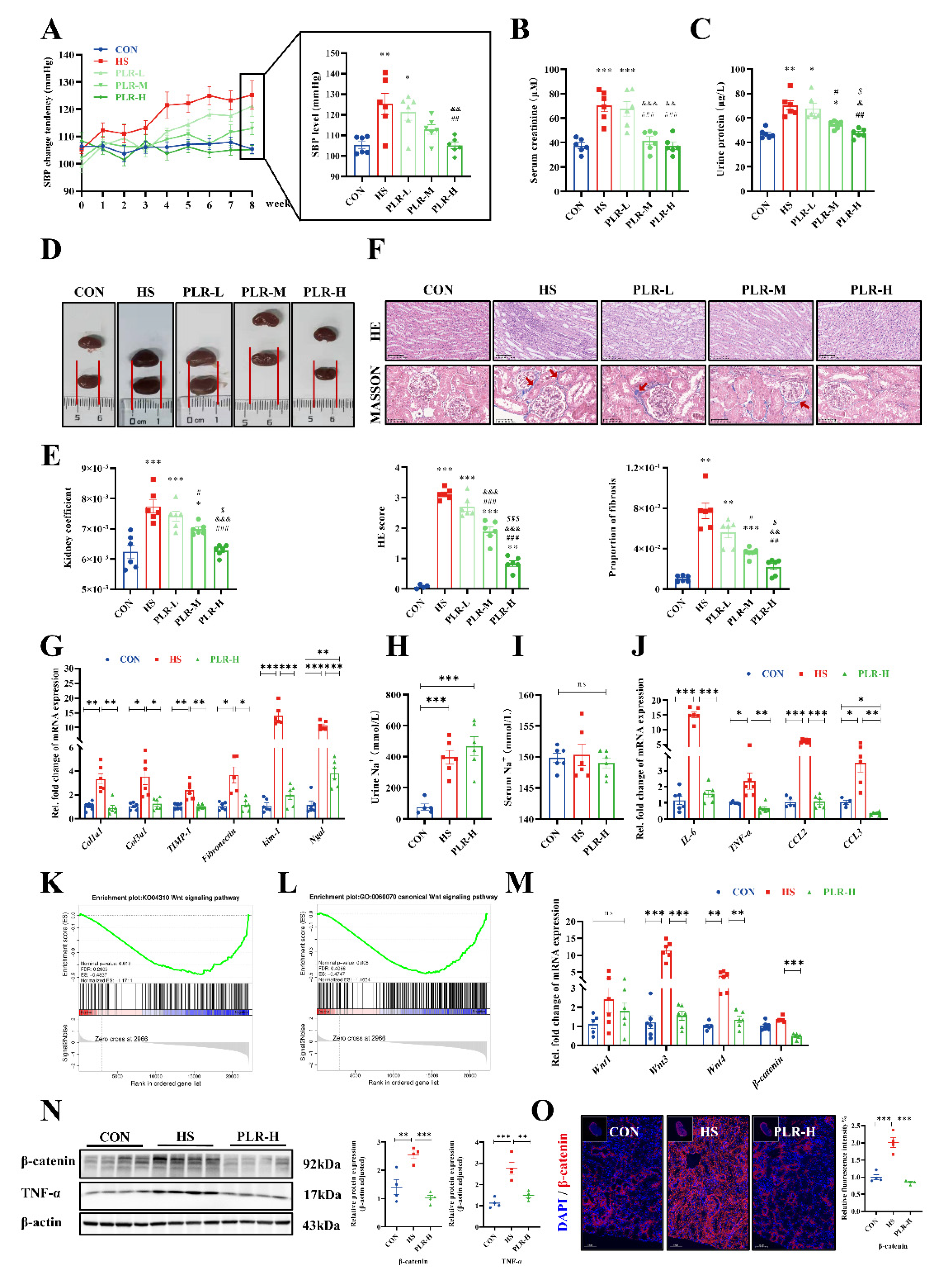
3.1. PLR alleviated CKD and renal fibrosis induced by high salt diet
3.2. PLR mitigated inflammatory response and down-regulated the Wnt / β-catenin pathway in kidney
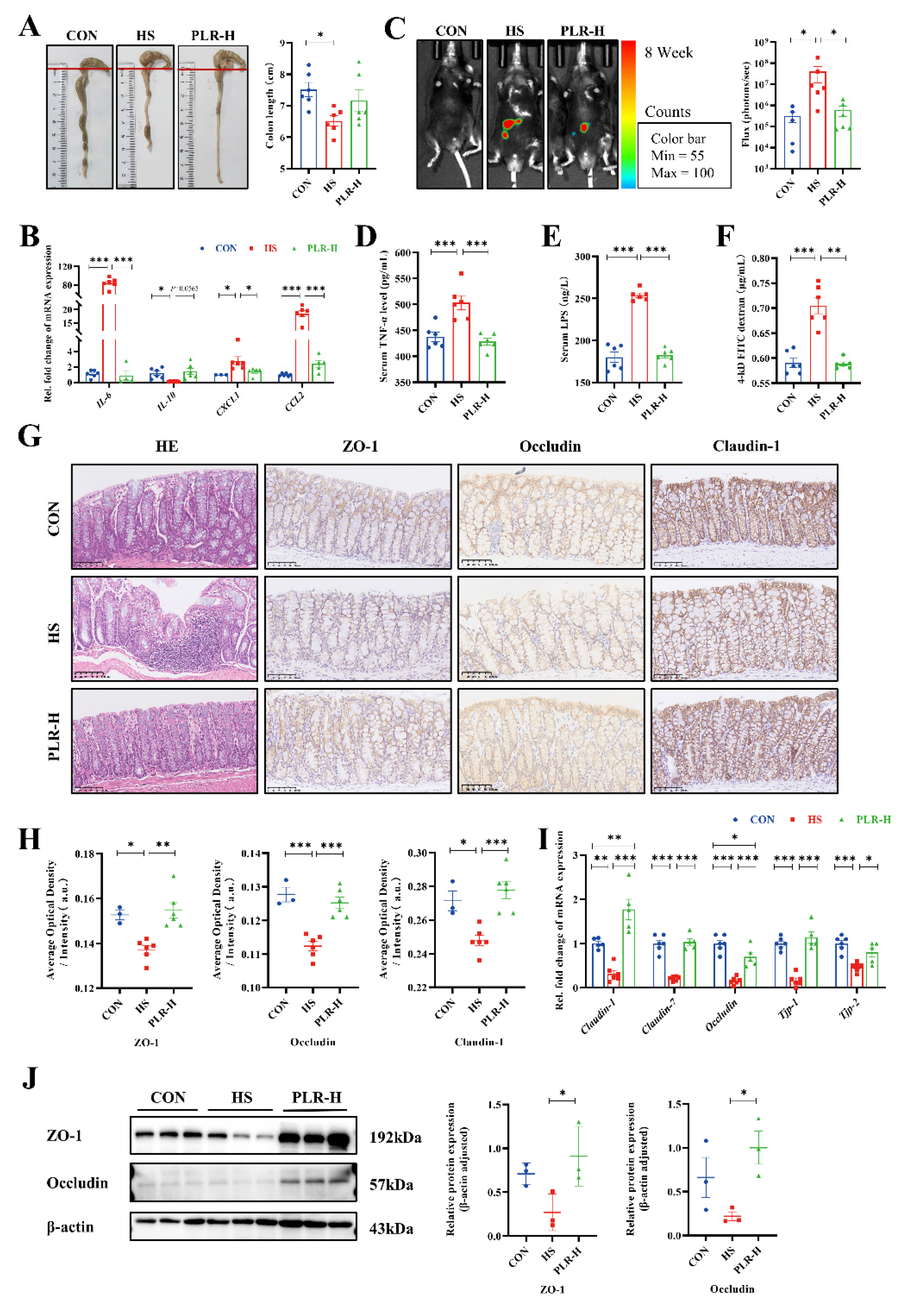
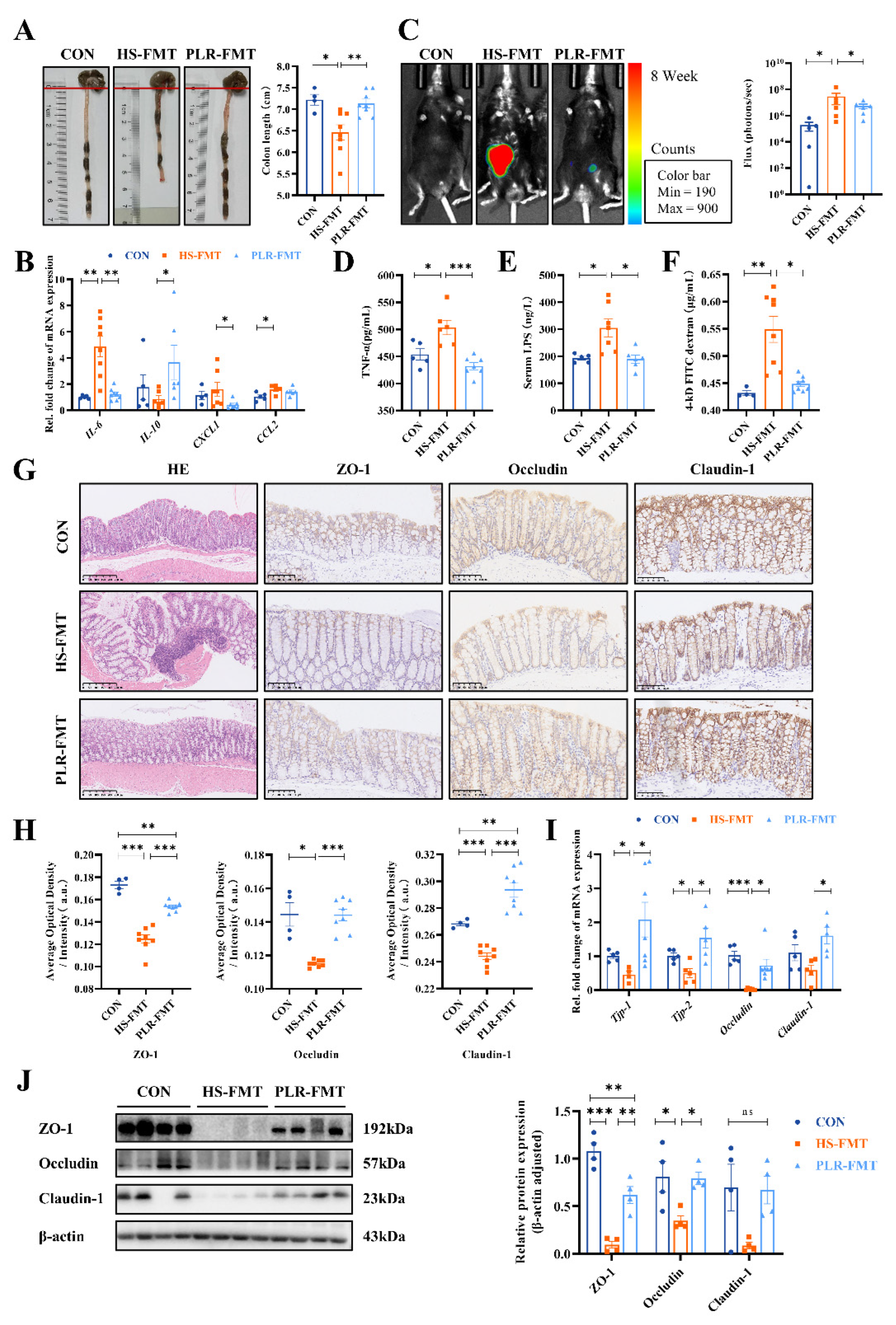
3.3. PLR reduced intestinal inflammation and protected against intestinal barrier damage
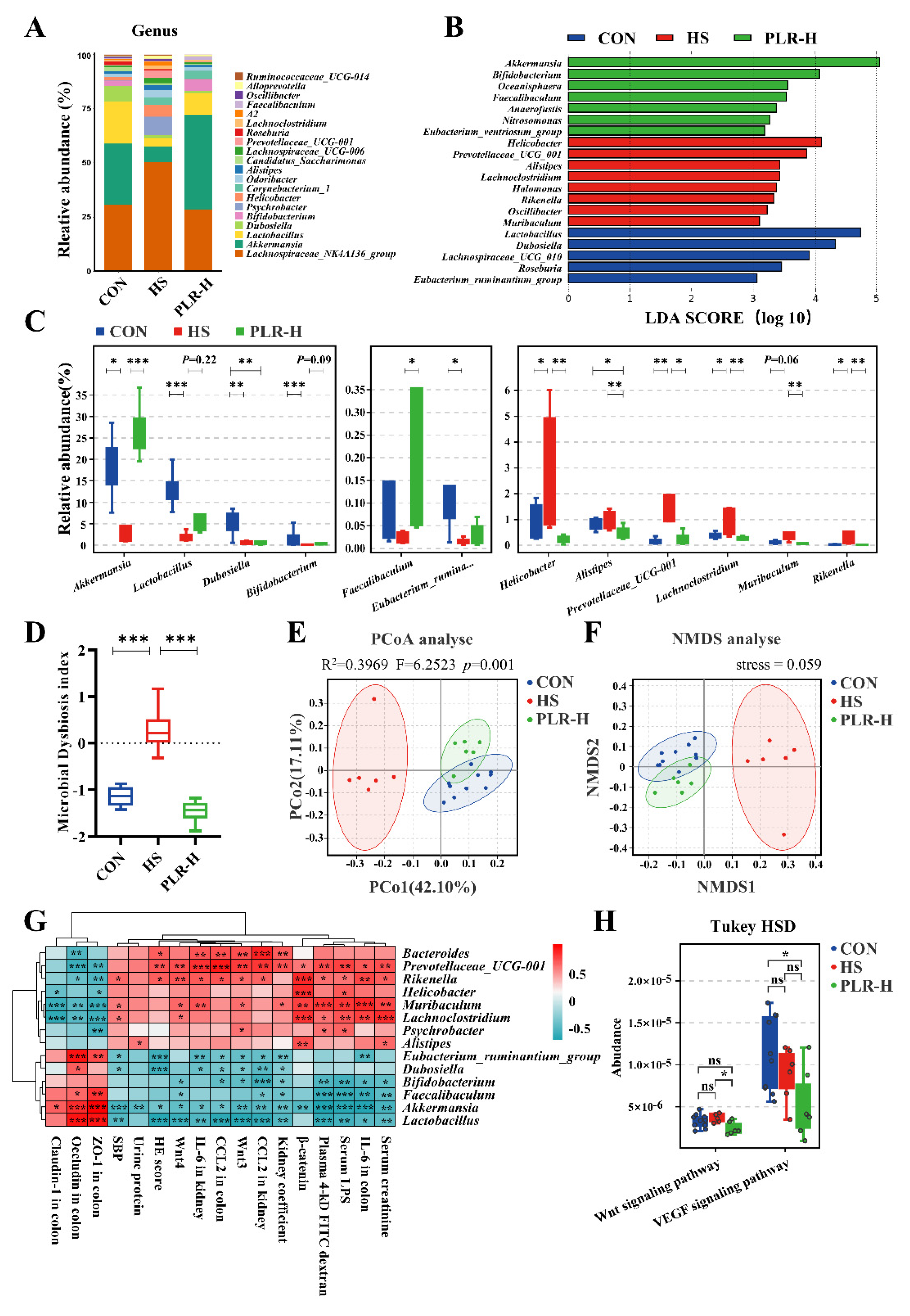
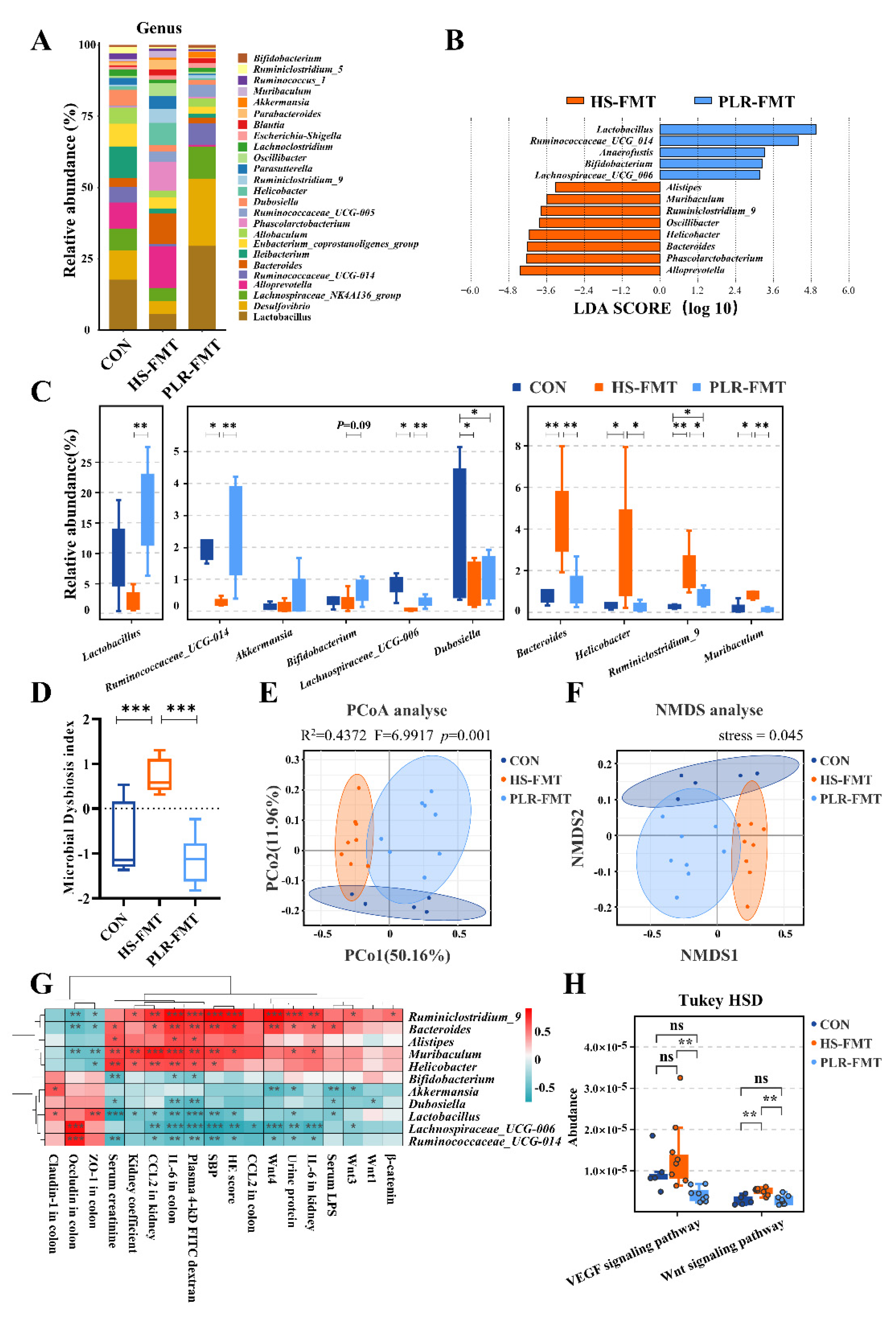
3.4. PLR reversed gut microbial dysbiosis and increased the relative abundance of beneficial bacteria
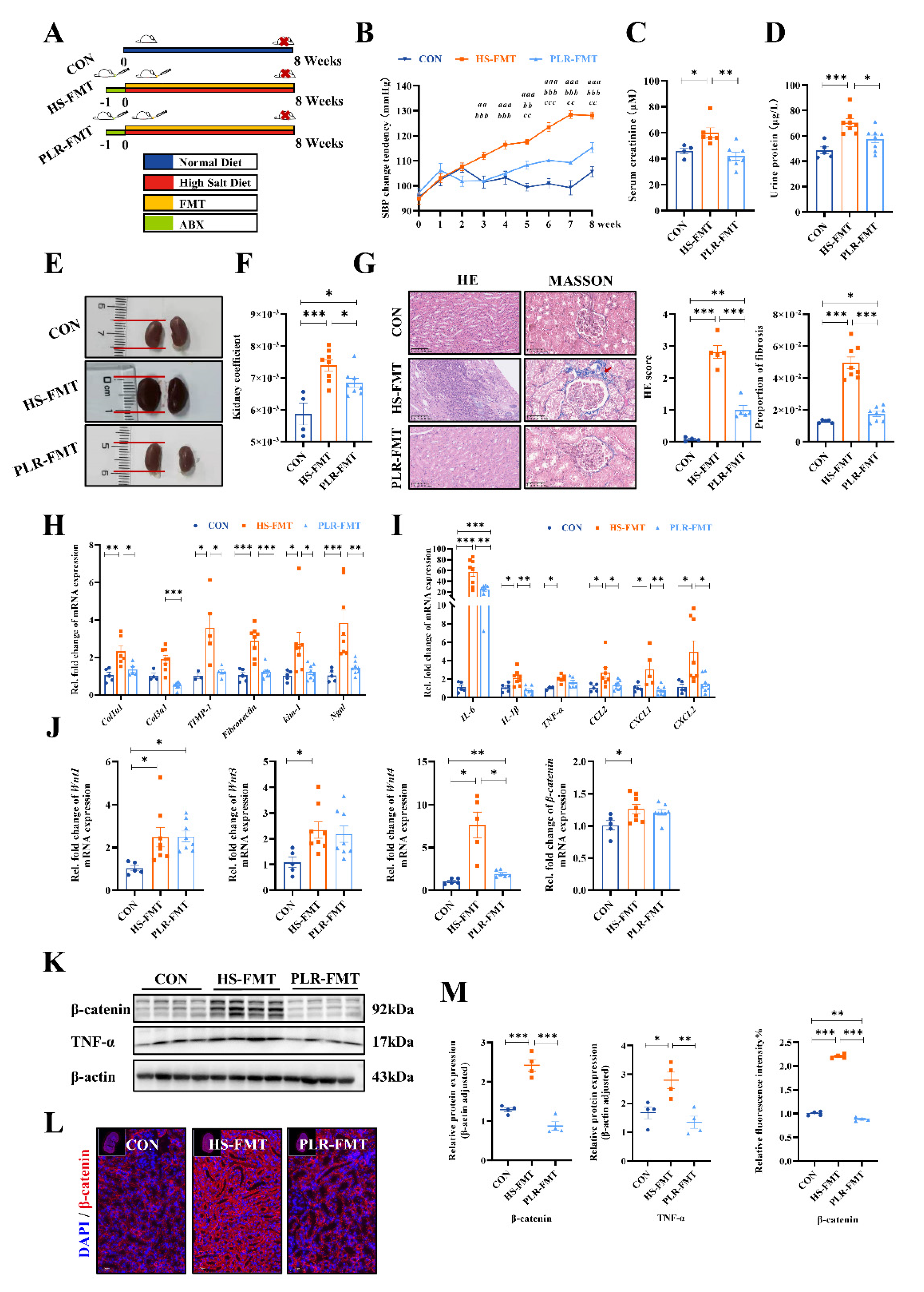
3.5. Gut microbiota reestablished by PLR reduced renal tissue fibrosis and intestinal epithelial barrier impairment
3.6. Gut microbiota rebuilt by PLR promoted intestinal homeostasis in CKD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cockwell, P.; Fisher, L.-A. The Global Burden of Chronic Kidney Disease. Lancet 2020, 395, 662–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, C.; Borrelli, S.; Provenzano, M.; De Stefano, T.; Vita, C.; Chiodini, P.; Minutolo, R.; De Nicola, L.; Conte, G. Dietary Salt Restriction in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2018, 10, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Jung, J.Y. Nutritional Management in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Korean J Intern Med 2020, 35, 1279–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppelaar, J.J.; Vogt, L. Body Fluid-Independent Effects of Dietary Salt Consumption in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.C.; Burrell, L.M.; Black, M.J.; Wu, L.L.; Dilley, R.J.; Cooper, M.E.; Johnston, C.I. Salt Induces Myocardial and Renal Fibrosis in Normotensive and Hypertensive Rats. Circulation 1998, 98, 2621–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Liu, Y.; Kahn, M.; Ann, D.K.; Han, A.; Wang, H.; Nguyen, C.; Flodby, P.; Zhong, Q.; Krishnaveni, M.S.; et al. Interactions between β-Catenin and Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling Pathways Mediate Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Are Dependent on the Transcriptional Co-Activator cAMP-Response Element-Binding Protein (CREB)-Binding Protein (CBP). The Journal of Biological Chemistry 2012, 287, 7026–7038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmora, N.; Suez, J.; Elinav, E. You Are What You Eat: Diet, Health and the Gut Microbiota. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019, 16, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.J.; Tan, M.; Ma, Y.; MacGregor, G.A. Salt Reduction to Prevent Hypertension and Cardiovascular Disease: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J Am Coll Cardiol 2020, 75, 632–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, P.M.; De Palma, G.; Serkis, V.; Lu, J.; Louis-Auguste, M.P.; McCarville, J.L.; Verdu, E.F.; Collins, S.M.; Bercik, P. High Salt Diet Exacerbates Colitis in Mice by Decreasing Lactobacillus Levels and Butyrate Production. Microbiome 2018, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Jin, J.; Su, X.; Yin, X.; Gao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Bu, P.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Intestinal Flora Modulates Blood Pressure by Regulating the Synthesis of Intestinal-Derived Corticosterone in High Salt-Induced Hypertension. Circ Res 2020, 126, 839–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Luo, H.; Wang, J.; Tang, W.; Lu, J.; Wu, S.; Xiong, Z.; Yang, G.; Chen, Z.; Lan, T.; et al. Enteric Dysbiosis-Linked Gut Barrier Disruption Triggers Early Renal Injury Induced by Chronic High Salt Feeding in Mice. Exp Mol Med 2017, 49, e370–e370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-B.; Xu, M.-L.; Xu, X.-D.; Tang, Y.-Y.; Jiang, H.-L.; Li, L.; Xia, W.-J.; Cui, N.; Bai, J.; Dai, Z.-M.; et al. Faecalibacterium Prausnitzii Attenuates CKD via Butyrate-Renal GPR43 Axis. Circ. Res. 2022, 131, e120–e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Liu, Z.; Wu, P.; Yue, X.; Lian, Z.; He, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, R.; Zhao, J. Puerariae Lobatae Radix Alleviates Pre-Eclampsia by Remodeling Gut Microbiota and Protecting the Gut and Placental Barriers. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, W.; Feng, Y.; Hou, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, Q.; Luo, Y.; Ouyang, H.; et al. Radix Puerariae Thomsonii Polysaccharide (RPP) Improves Inflammation and Lipid Peroxidation in Alcohol and High-Fat Diet Mice by Regulating Gut Microbiota. Int J Biol Macromol 2022, 209, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.-S.; Zhang, N.-N.; Guo, S.; Liu, S.-J.; Hou, Y.-F.; Li, S.; Ho, C.-T.; Bai, N.-S. Glycosides and Flavonoids from the Extract of Pueraria Thomsonii Benth Leaf Alleviate Type 2 Diabetes in High-Fat Diet plus Streptozotocin-Induced Mice by Modulating the Gut Microbiota. Food Funct 2022, 13, 3931–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Wu, P.; Cai, Z.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Lasanajak, Y.; Tang, L.; Ye, L.; Hou, C.; Zhao, J. Puerariae Lobatae Radix with Chuanxiong Rhizoma for Treatment of Cerebral Ischemic Stroke by Remodeling Gut Microbiota to Regulate the Brain-Gut Barriers. J Nutr Biochem 2019, 65, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila-Carrasco, L.; García-Mayorga, E.A.; Díaz-Avila, D.L.; Garza-Veloz, I.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L.; González-Mateo, G.T. Potential Therapeutic Effects of Natural Plant Compounds in Kidney Disease. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2021, 26, 6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Li, K.; Sun, Q.; Xie, M.; Huang, P.; Yu, Y.; Wang, B.; Xue, J.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Unraveling the Impact of Lactobacillus Spp. and Other Urinary Microorganisms on the Efficacy of Mirabegron in Female Patients with Overactive Bladder. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1030315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, C.; Xie, M.; Huang, P.; Sun, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Li, B.; Zhao, J.; Wu, P. Deciphering the Influence of Urinary Microbiota on FoxP3+ Regulatory T Cell Infiltration and Prognosis in Chinese Patients with Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Human Cell 2022, 35, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME Allows Analysis of High-Throughput Community Sequencing Data. Nat Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic Biomarker Discovery and Explanation. Genome Biol 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aßhauer, K.P.; Wemheuer, B.; Daniel, R.; Meinicke, P. Tax4Fun: Predicting Functional Profiles from Metagenomic 16S rRNA Data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2882–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis: A Knowledge-Based Approach for Interpreting Genome-Wide Expression Profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirtz, S.; Popp, V.; Kindermann, M.; Gerlach, K.; Weigmann, B.; Fichtner-Feigl, S.; Neurath, M.F. Chemically Induced Mouse Models of Acute and Chronic Intestinal Inflammation. Nat Protoc 2017, 12, 1295–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manabe, E.; Ito, S.; Ohno, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Naito, Y.; Sasaki, N.; Asakura, M.; Masuyama, T.; Ishihara, M.; Tsujino, T. Reduced Lifespan of Erythrocytes in Dahl/Salt Sensitive Rats Is the Cause of the Renal Proximal Tubule Damage. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 22023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, A.W.; Fouts, D.E.; Brandl, J.; Stärkel, P.; Torralba, M.; Schott, E.; Tsukamoto, H.; Nelson, K.E.; Brenner, D.A.; Schnabl, B. Enteric Dysbiosis Associated with a Mouse Model of Alcoholic Liver Disease. Hepatology 2011, 53, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.C.-H.; Shih, Y.-A.; Wu, L.-L.; Lin, Y.-D.; Kuo, W.-T.; Peng, W.-H.; Lu, K.-S.; Wei, S.-C.; Turner, J.R.; Ni, Y.-H. Enteric Dysbiosis Promotes Antibiotic-Resistant Bacterial Infection: Systemic Dissemination of Resistant and Commensal Bacteria through Epithelial Transcytosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2014, 307, G824–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Zhu, X.; Wei, X.; Long, M.; Jiang, L.; Li, C.; Jin, D.; Du, Y. Pro- and Anti-Fibrotic Effects of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Chronic Kidney Diseases. Ren Fail 2022, 44, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosohata, K. Biomarkers of High Salt Intake. Adv Clin Chem 2021, 104, 71–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favero, C.; Giordano, L.; Mihaila, S.M.; Masereeuw, R.; Ortiz, A.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D. Postbiotics and Kidney Disease. Toxins (Basel) 2022, 14, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Jafar, T.H.; Nitsch, D.; Neuen, B.L.; Perkovic, V. Chronic Kidney Disease. Lancet 2021, 398, 786–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belzer, C.; de Vos, W.M. Microbes Inside--from Diversity to Function: The Case of Akkermansia. The ISME journal 2012, 6, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Siles, M.; Enrich-Capó, N.; Aldeguer, X.; Sabat-Mir, M.; Duncan, S.H.; Garcia-Gil, L.J.; Martinez-Medina, M. Alterations in the Abundance and Co-Occurrence of Akkermansia Muciniphila and Faecalibacterium Prausnitzii in the Colonic Mucosa of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Subjects. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, H.; Pan, K.; Duan, Q.; Kaluzny, S.; Pandey, E.; Fatumoju, L.; Saraswathi, V.; Wu, R.; Harris, E.N.; Su, Q. Akkermansia Muciniphila and Its Membrane Protein Ameliorates Intestinal Inflammatory Stress and Promotes Epithelial Wound Healing via CREBH and miR-143/145. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 30, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y. Alterations to the Gut Microbiota and Their Correlation With Inflammatory Factors in Chronic Kidney Disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2019, 9, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Li, W.; Liu, Y. Astragalus Membranaceus and Salvia Miltiorrhiza Ameliorates Cyclosporin A-Induced Chronic Nephrotoxicity through the “Gut-Kidney Axis. ” J Ethnopharmacol 2021, 269, 113768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshavarz Azizi Raftar, S.; Ashrafian, F.; Yadegar, A.; Lari, A.; Moradi, H.R.; Shahriary, A.; Azimirad, M.; Alavifard, H.; Mohsenifar, Z.; Davari, M.; et al. The Protective Effects of Live and Pasteurized Akkermansia Muciniphila and Its Extracellular Vesicles against HFD/CCl4-Induced Liver Injury. Microbiol Spectr 2021, 9, e0048421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, T.; Hu, R.; Wang, F.; Yang, S.; Feng, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yan, S.; Ju, L.; He, Z.; et al. Akkermansia Muciniphila Ameliorates Chronic Kidney Disease Interstitial Fibrosis via the Gut-Renal Axis. Microb Pathog 2023, 174, 105891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; He, P.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, J. Gut Microbiota-Derived Melatonin from Puerariae Lobatae Radix-Resistant Starch Supplementation Attenuates Ischemic Stroke Injury via a Positive Microbial Co-Occurrence Pattern. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 190, 106714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarao, L.K.; Arora, M. Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Microencapsulation: A Review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2017, 57, 344–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engevik, M.A.; Luk, B.; Chang-Graham, A.L.; Hall, A.; Herrmann, B.; Ruan, W.; Endres, B.T.; Shi, Z.; Garey, K.W.; Hyser, J.M.; et al. Bifidobacterium Dentium Fortifies the Intestinal Mucus Layer via Autophagy and Calcium Signaling Pathways. mBio 2019, 10, e01087–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ji, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y. Probiotic Lactobacillus Plantarum Promotes Intestinal Barrier Function by Strengthening the Epithelium and Modulating Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B, W.; X, C.; Z, C.; H, X.; J, D.; Y, L.; X, Z.; J, L.; G, W.; S, F.; et al. Stable Colonization of Akkermansia Muciniphila Educates Host Intestinal Microecology and Immunity to Battle against Inflammatory Intestinal Diseases. Experimental & molecular medicine 2023, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, A.; Vergalito, F.; Tremonte, P.; Iorizzo, M.; Lombardi, S.J.; Sorrentino, E.; Luongo, D.; Coppola, R.; Di Marco, R.; Succi, M. Preliminary Evaluation of the Safety and Probiotic Potential of Akkermansia Muciniphila DSM 22959 in Comparison with Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Li, S.; Zhao, L.; Hao, Y.; Qin, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Bian, W.; Zuo, L.; et al. Aberrant Gut Microbiota Alters Host Metabolome and Impacts Renal Failure in Humans and Rodents. Gut 2020, 69, 2131–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, N.; Li, L.; Ng, J.K.-C.; Li, P.K.-T. The Potential Benefits and Controversies of Probiotics Use in Patients at Different Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrović, M.; Stanković-Popović, V.; Tolinački, M.; Golić, N.; Soković Bajić, S.; Veljović, K.; Nastasijević, B.; Soldatović, I.; Svorcan, P.; Dimković, N. The Impact of Synbiotic Treatment on the Levels of Gut-Derived Uremic Toxins, Inflammation, and Gut Microbiome of Chronic Kidney Disease Patients-A Randomized Trial. J Ren Nutr 2022, S1051-2276(22)00152-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.-Y.; Zhou, R.-R.; Nan, T.-G.; Huang, L.-Q.; Yuan, Y. [Comparison of Major Chemical Components in Puerariae Thomsonii Radix and Puerariae Lobatae Radix]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi = Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi = China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica 2022, 47, 2689–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, P.M.; De Palma, G.; Serkis, V.; Lu, J.; Louis-Auguste, M.P.; McCarville, J.L.; Verdu, E.F.; Collins, S.M.; Bercik, P. High Salt Diet Exacerbates Colitis in Mice by Decreasing Lactobacillus Levels and Butyrate Production. Microbiome 2018, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Zhai, Q. The Role of Mucin and Oligosaccharides via Cross-Feeding Activities by Bifidobacterium: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, S.; Li, T.; Li, N.; Han, D.; Zhang, B.; Xu, Z.Z.; Zhang, S.; Pang, J.; Wang, S.; et al. Gut Microbiota from Green Tea Polyphenol-Dosed Mice Improves Intestinal Epithelial Homeostasis and Ameliorates Experimental Colitis. Microbiome 2021, 9, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Xu, Y.; Wu, P.; Zhou, H.; Lasanajak, Y.; Fang, Y.; Tang, L.; Ye, L.; Li, X.; Cai, Z.; et al. Transplantation of Fecal Microbiota Rich in Short Chain Fatty Acids and Butyric Acid Treat Cerebral Ischemic Stroke by Regulating Gut Microbiota. Pharmacol Res 2019, 148, 104403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; d’Aigle, J.; Atadja, L.; Quaicoe, V.; Honarpisheh, P.; Ganesh, B.P.; Hassan, A.; Graf, J.; Petrosino, J.; Putluri, N.; et al. Gut Microbiota-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids Promote Poststroke Recovery in Aged Mice. Circ Res 2020, 127, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Ren, J.; Gui, Y.; Wei, W.; Shu, B.; Lu, Q.; Xue, X.; Sun, X.; He, W.; Yang, J.; et al. Wnt/β-Catenin-Promoted Macrophage Alternative Activation Contributes to Kidney Fibrosis. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology: JASN 2018, 29, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunk, S.J.; Floege, J.; Fliser, D.; Speer, T. WNT-β-Catenin Signalling - a Versatile Player in Kidney Injury and Repair. Nat Rev Nephrol 2021, 17, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Takahashi-Yanaga, F.; Arioka, M.; Igawa, K.; Tomooka, K.; Yamaura, K.; Sasaguri, T. Cardiac and Renal Protective Effects of 2,5-Dimethylcelecoxib in Angiotensin II and High-Salt-Induced Hypertension Model Mice. J Hypertens 2021, 39, 892–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, J.A.; Shah, S.S.; Nikolic, A.; Henshall, T.L.; Khew-Goodall, Y.; Kumar, S. The Ubiquitin Ligase NEDD4-2/NEDD4L Regulates Both Sodium Homeostasis and Fibrotic Signaling to Prevent End-Stage Renal Disease. Cell Death Dis 2021, 12, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benito, I.; Encío, I.J.; Milagro, F.I.; Alfaro, M.; Martínez-Peñuela, A.; Barajas, M.; Marzo, F. Microencapsulated Bifidobacterium Bifidum and Lactobacillus Gasseri in Combination with Quercetin Inhibit Colorectal Cancer Development in ApcMin/+ Mice. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.-R.; Wei, S.-J.; Huang, Y.-Q.; Xing, W.; Wang, L.-Y.; Liang, L.-L. Mechanism of Combined Use of Vitamin D and Puerarin in Anti-Hepatic Fibrosis by Regulating the Wnt/β-Catenin Signalling Pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2018, 24, 4178–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiyama, A.; Yokoyama, K.; Nukaga, T.; Sakai, D.; Mochida, J. A Complex Interaction between Wnt Signaling and TNF-α in Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Arthritis Res Ther 2013, 15, R189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Hong, X.; Miao, J.; Liao, Y.; Hou, F.F.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Y. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Mediates Both Heart and Kidney Injury in Type 2 Cardiorenal Syndrome. Kidney Int 2019, 95, 815–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, B.; Zhang, H.; Hong, Y.; Ma, M.; Wan, X.; Cao, C. Indoleamine-2,3-Dioxygenase Activates Wnt/β-Catenin Inducing Kidney Fibrosis after Acute Kidney Injury. Gerontology 2021, 67, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Xu, B.; Zhou, L.; Tan, R.J.; Zhou, D.; Fu, H.; Li, A.; Hou, F.F.; Liu, Y. Wnt/β-Catenin Regulates Blood Pressure and Kidney Injury in Rats. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2019, 1865, 1313–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelfand, B.D.; Meller, J.; Pryor, A.W.; Kahn, M.; Bortz, P.D.S.; Wamhoff, B.R.; Blackman, B.R. Hemodynamic Activation of Beta-Catenin and T-Cell-Specific Transcription Factor Signaling in Vascular Endothelium Regulates Fibronectin Expression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2011, 31, 1625–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, F.-L.; Fang, M.; Yutzey, K.E. Loss of β-Catenin in Resident Cardiac Fibroblasts Attenuates Fibrosis Induced by Pressure Overload in Mice. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Dong, M.-Q.; Liu, Z.-M.; Xu, M.; Huang, Z.-H.; Liu, H.-J.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, W.-J. A Strategy of Vascular-Targeted Therapy for Liver Fibrosis. Hepatology 2022, 76, 660–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Shi, L.; Xiao, T.; Xue, J.; Li, J.; Wang, P.; Wu, L.; Dai, X.; Ni, X.; Liu, Q. microRNA-21, via the HIF-1α/VEGF Signaling Pathway, Is Involved in Arsenite-Induced Hepatic Fibrosis through Aberrant Cross-Talk of Hepatocytes and Hepatic Stellate Cells. Chemosphere 2021, 266, 129177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Yin, M.; Wei, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Niu, C.; Kang, X.; Xu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, S.; et al. Bach1 Represses Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling and Angiogenesis. Circ Res 2015, 117, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, S.W.; Zhang, R.; Tan, Z.; Chung, J.P.W.; Zhang, T.; Wang, C.C. Pharmaceuticals Targeting Signaling Pathways of Endometriosis as Potential New Medical Treatment: A Review. Med Res Rev 2021, 41, 2489–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.; Hong, J.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, D.; Xu, B.; Yu, X.; Sheng, L. Chronic Exposure to Nanoparticulate TiO2 Causes Renal Fibrosis Involving Activation of the Wnt Pathway in Mouse Kidney. J Agric Food Chem 2015, 63, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Parsons, C.J.; Stefanovic, B. Gene Expression Profile of Quiescent and Activated Rat Hepatic Stellate Cells Implicates Wnt Signaling Pathway in Activation. J Hepatol 2006, 45, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaton, H.; Andrews, D.; Parsons, M.; Murphy, M.; Gaffney, A.; Kavanagh, D.; McKay, G.J.; Maxwell, A.P.; Taylor, C.T.; Cummins, E.P.; et al. Wnt6 Regulates Epithelial Cell Differentiation and Is Dysregulated in Renal Fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2016, 311, F35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




