1. Introduction
The Hippo pathway, initially identified in
Drosophila as a novel regulator of animal size[
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9], has emerged as a signaling pathway with a central role in diverse biological processes, including tissue homeostasis[
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9], tumorigenesis [
10,
11,
12], immune response [
13], angiogenesis [
14], mechanotransduction [
15], and drug resistance [
16,
17]. Core components of the Hippo pathway encompass two serine/threonine (S/T) kinases (MST, the fly homolog of Hippo, and LATS), two adaptor proteins (MOB1 and SAV), and two transcriptional co-activators (YAP and its paralog TAZ). Upon activation by various stimuli such as cell-cell contact, mechanical force, or nutrient deprivation, MST activates and phosphorylates LATS kinase. Activated LATS, in turn, phosphorylates YAP/TAZ at serine 217 (S127)/S89 residues, preventing their nuclear translocation and transactivation of downstream genes, including CTGF and Cyr61, in collaboration with the transcription factor TEAD [
18,
19,
20,
21,
22].
Dysregulation of the Hippo pathway, marked by the activation of oncogenic YAP/TAZ and loss of the tumor suppressor gene LATS, has been implicated in various human cancers, including breast and lung cancers [
11,
23]. Consequently, targeting the Hippo pathway has emerged as a crucial strategy for cancer therapy [
16,
23,
24].
While the reversible addition (phosphorylation) and removal (dephosphorylation) of phosphate by kinases and phosphatases, respectively, to proteins or lipids is recognized as a pivotal post-translational modification in signal transduction across various cellular processes [
25,
26,
27,
28], existing research predominantly focuses on the roles of S/T kinases (e.g. PI3K, MAPK, TAOKs) and phosphatases (e.g., PP1, PP2A, STRPAK) in regulating the Hippo pathway in tumorigenesis [
29]. The involvement of tyrosine phosphorylation and dephosphorylation in Hippo pathway regulation remains largely unexplored. Recent studies, including our own, have identified the Hippo pathway as a central mediator of receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)-induced tumorigenesis, angiogenesis, immune evasion, and metastasis [
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35]. Although several protein tyrosine kinases (PTPs) such as PTPN14 and PTPN21 have been reported as regulators of the Hippo pathway [
36,
37,
38,
39], the systematic exploration of how regulate the Hippo pathway has been lacking. In this study, we conducted a gain-of-functional screen and identified several novel PTP regulators of the Hippo pathway. Specifically, we validated PTPN12 as a novel negative regulator of Hippo pathway effectors YAP/TAZ, influencing cell proliferation and migration.
2. Results
2.1. Gain-of-functional screening for PTPs regulating the Hippo pathway
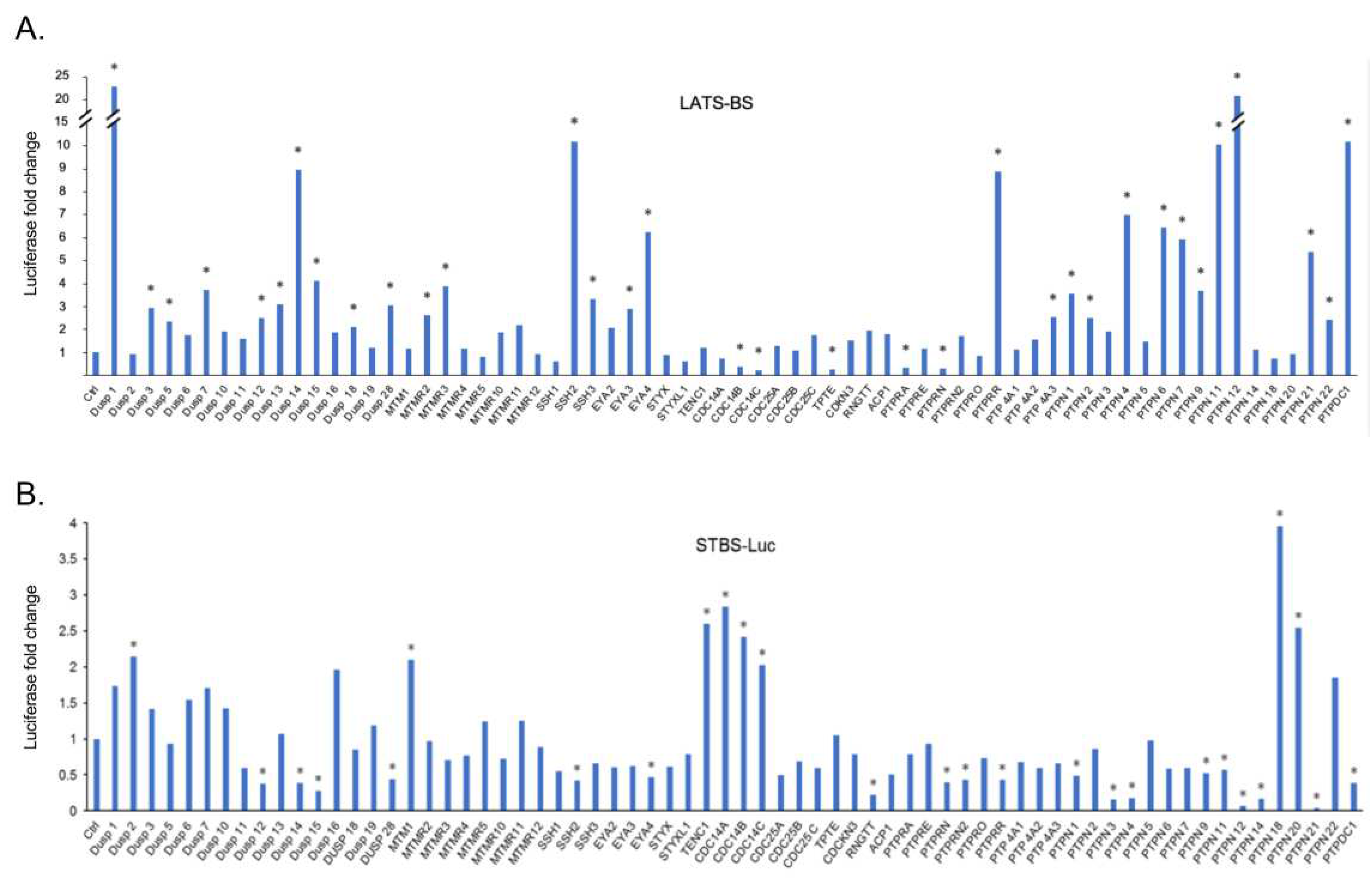
In order to screen for novel phosphatases regulating the Hippo pathway, we cotransfected constructs expressing LATS kinase biosensor (LATS-BS) or YAP/TAZ transcriptional co-activating reporter (STBS-Luc) alone or together with a PTP from a library of 68 PTPs we previously established[
39]. The luciferase activities of the LATS-BS or STBS-Luc reporter were measured. Significantly, 25 PTPs increase LATS-BS activity more than 2.5-fold, while 5 PTPs decrease LATS-BS activity more than 2.5-fold (
Figure 1A). Given the opposing roles of LATS and YAP/TAZ in tumorigenesis[
29], in contrast to the effect of PTPs on LATS-BS, most phosphatases decreased the signal of the reporter compared to the control. 8 PTPs increases STBS-Luc more than 2-fold, whereas 19 PTPs decreases STBS-Luc activity more than 2-fold (
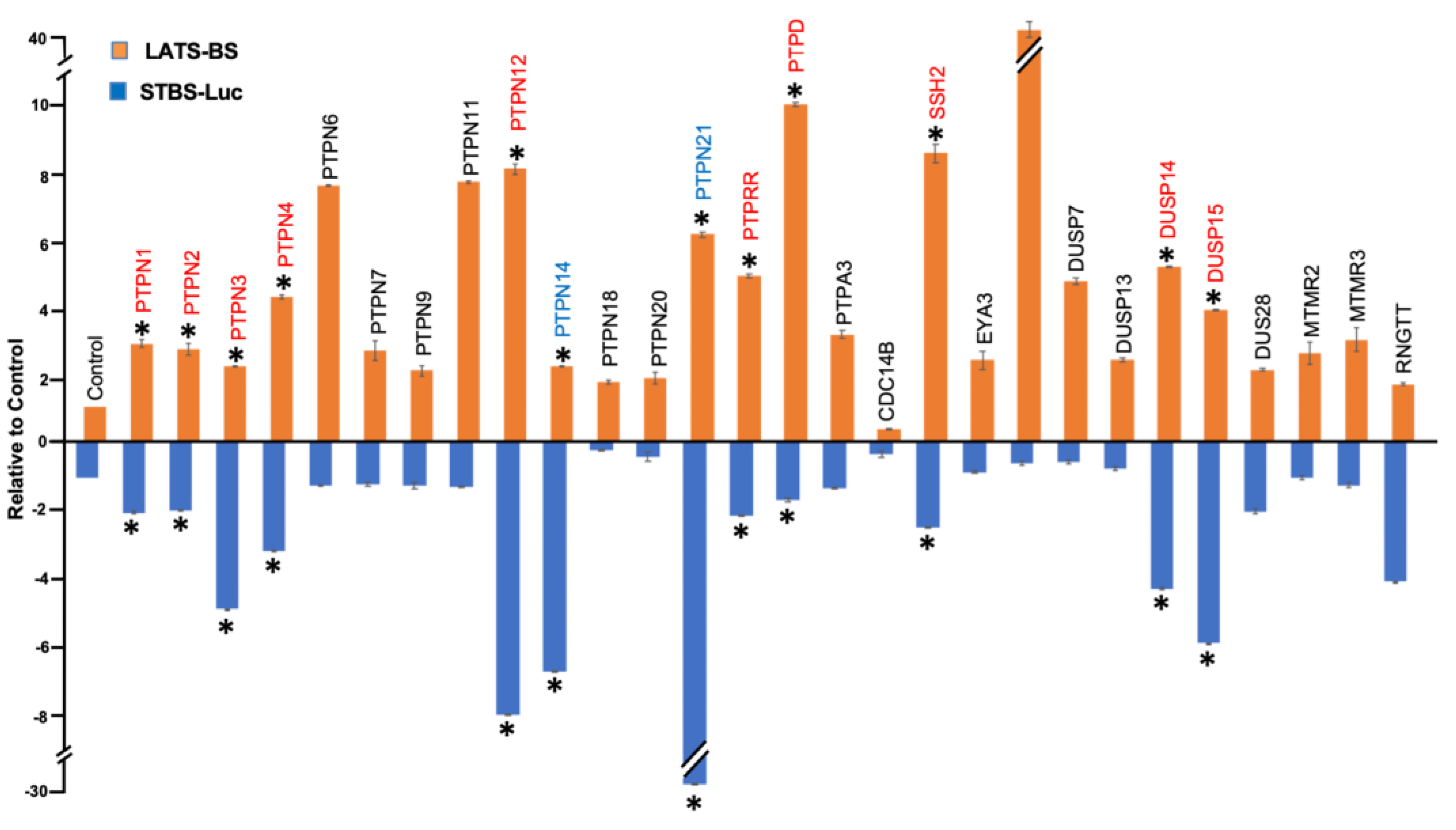
Figure 1B). A total number of 38 PTP candidates were selected for further validation through a triplicate test. All 38 candidates were divided into three different groups. The first group was the PTPs that either increased or decreased the signal of LATS-BS. The second group includes PTPs that have a significant effect on the signal of the STBS-Luc reporter. The third group were phosphatases that have significant opposite effects on the signal of LATS biosensors and YAP/TAZ reporter. Then, a triplicate test was performed to validate the effects of PTPs on the signal of LATS-BS and STBS-Luc (
Figure 2). 25 PTPs are validated for PTPs regulating LATS-BS, whereas 16 PTPs are validated for PTPs regulating STBS-Luc. Of the 28 candidates regulating the signal of LATS-BS or STBS-Luc, several PTPs including PTPN11, PTPN14, PTPN21 and CDC14 were previously shown as PTPs regulating the Hippo pathway [
37,
40,
41,
42,
43,
44,
45], suggesting that the gain-of-function assay worked. Out of 28 validated PTPs, 4 PTPs (PTPN12, PTPDC1, PTPRR and DUSP1) were selected based on the novelty, function and fold change for further experiments.
2.2. Validation of candidate PTPs regulating the Hippo pathway
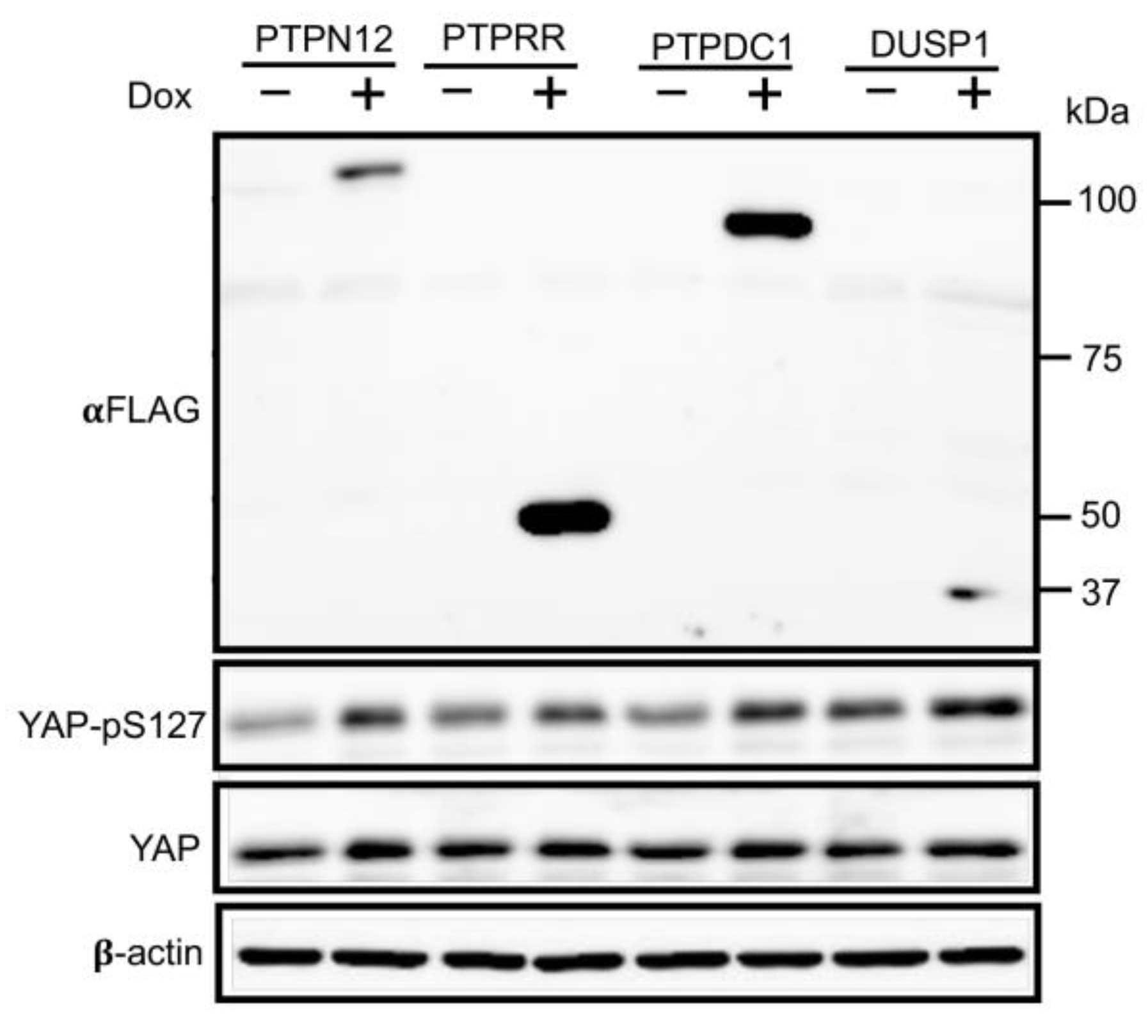
All previous experiments were done on phosphatases regulating the Hippo pathway by using LATS-BS and STBS-Luc. All of the 4 PTPs regulating the Hippo pathway were shown to increase LATS activity (LATS-BS) and decrease YAP/TAZ activity (STBS-Luc reporter). In other words, the phosphatases were associated with increased phosphorylation of YAP and TAZ at S127 and S89, respectively, which leads to the sequestration of YAP/TAZ in the cytoplasm and interaction with 14.3.3 protein. To validate the PTP candidates regulating the Hippo pathway, HEK293T cell lines stably expressing inducible PTPs were first stablished by lentiviral infection. Western blot analysis shows that PTP overexpression after Dox induction causes increased level of YAP phosphorylation on S127 (good TAZ-phospho-S89 is not available) compared to the cells without Dox treatment (
Figure 3), further confirmation that the candidate phosphatase can regulate the Hippo pathway by increasing endogenous YAP phosphorylation and preventing it from translocation to the nucleus.
2.3. Validation of PTPN12 as a novel regulator of the Hippo pathway
2.3.1. Effects of PTPN12 overexpression on the mRNA expression level of Hippo-targeted genes in HEK293T-PTPN12
Of a total number of four candidates, we selected PTPN12 for further experiment and validation because it has been previously shown to play an important role in breast cancer initiation and progression[
46,
47], which is similar to the role of the Hippo pathway in breast cancer[
23]. Since PTPN12 increases the signal of LATS-BS and stimulates phosphorylation of endogenous YAP at S127 (
Figure 3), it may result in the sequestration of YAP into the cytoplasm, which inhibits its transcriptional coactivating function, resulting in downregulation of its target genes such as CTGF and Cyr61.
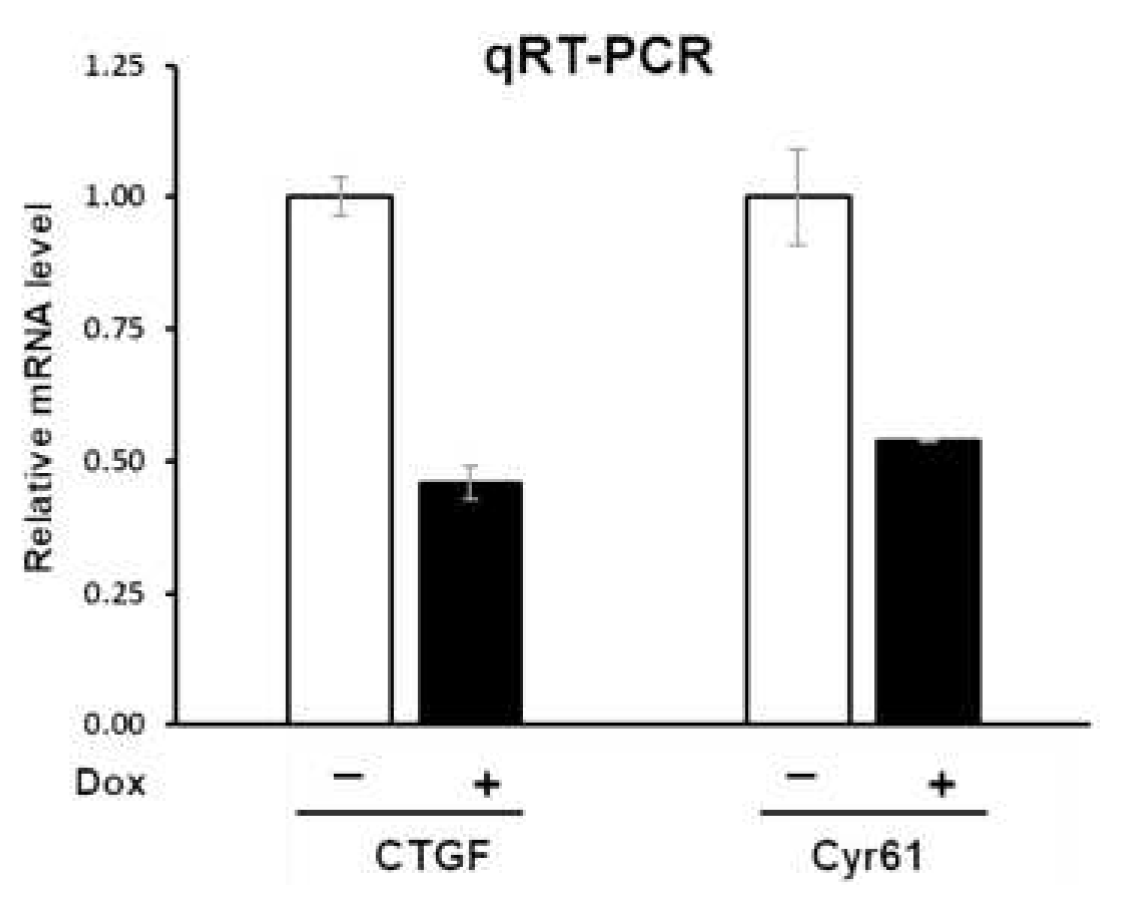
To examine the effects of PTPN12 on the expression level of the downstream genes of the Hippo pathway, the mRNA expression of these genes was assessed using qRT-PCR. Total RNA was extracted from HEK293T-PTPN12 stable cell line with or without Dox treatment. qRT-PCR shows that the mRNA levels of both Cyr61 and CTGF were downregulated around 2-fold by PTPN12, suggesting that PTPN12 is novel regulator of the Hippo signaling pathway (
Figure 4).
2.3.2. Effect of loss-of-PTPN12 on Hippo signaling and cell proliferation in mammary cells
Downregulation and loss-of-function mutations of PTPN12 were shown in a variety of cancers, including breast cancer[
46,
48,
49]. Thus, in this project, we aimed to identify the potential effects of PTPN12 downregulation on tumorigenesis via the Hippo pathway. To further validate the role of PTPN12 in regulating the Hippo pathway in breast cancer, PTPN12 was knocked out in the human mammary epithelial cell line, MCF10A, by the CRISPR system. To improve gene knockout efficiency in mixed cell population, a Dox-inducible system was used[
50]. The Dox-inducible Cas9 endonuclease was first introduced into MCF10A cells by lentiviral infection and geneticin selection. As a green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene is located downstream of the Cas9 promoter, so the expression of GFP induced by Dox is considered as an indicator of the expression of our gene of interest. Therefore, green fluorescent protein (GFP)-high MCF10A-iCas9 cells were sorted after Dox treatment by flow activating cell sorting (FACS). MCF10A-iCas9 was subsequently infected by lentivirus expressing guide RNAs target two different regions of PTPN12 (gPTPN12-1, 2) to establish Dox-inducible MCF10A-PTPN12-KO stable cell lines (
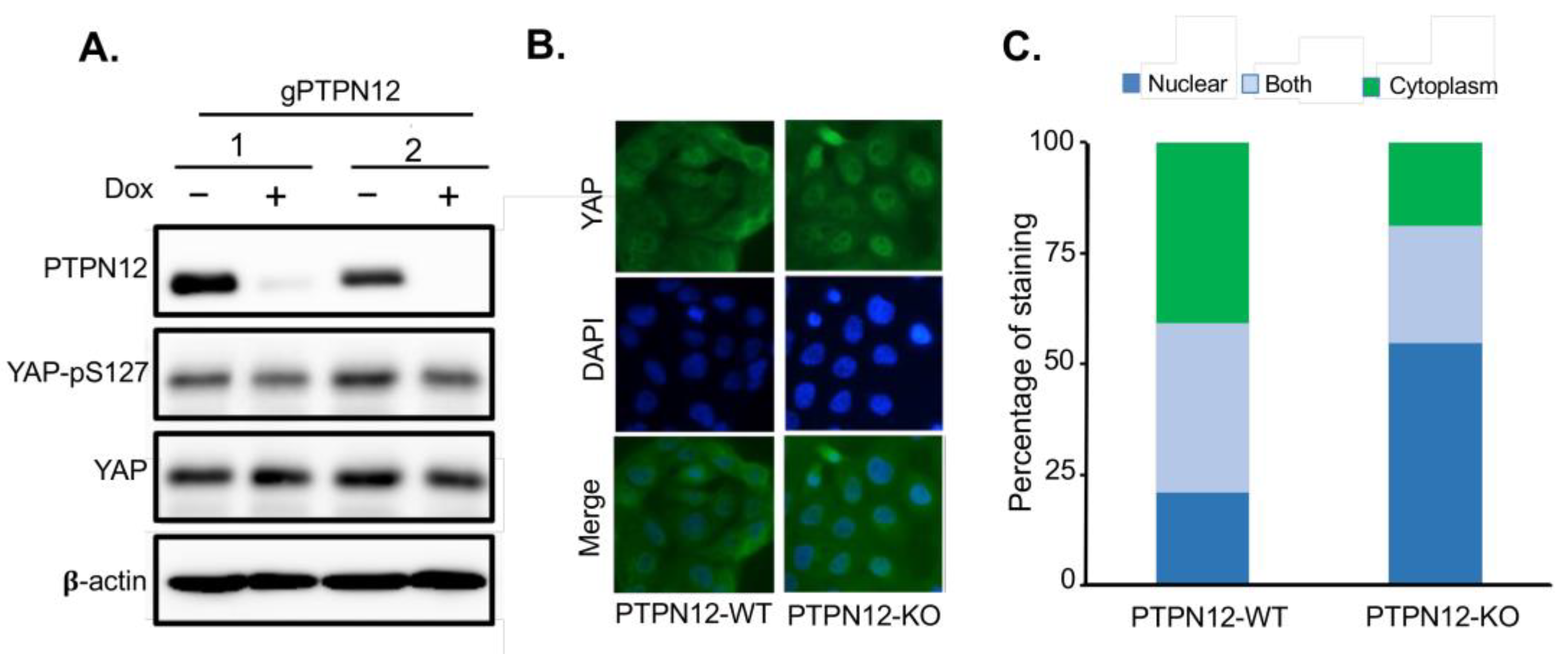
Figure 5). Western blot analysis shows that phosphorylation of YAP at S127 decreased in PTPN12-KO (+Dox) compared to the wild-type (-Dox) MCF10A cells (
Figure 5A), further confirming that PTPN12 regulates the Hippo pathway by stimulating S127 phosphorylation of Hippo major effector protein YAP.
Previous studies show that upon phosphorylation at S127, YAP should be sequestered in the cytoplasm, which prevent it from translocation to the nucleus[
18]. While YAP is localized in both nucleus and cytoplasm in MCF10A-PTPN12-WT cells, it is more localized in the nucleus in the PTPN12-KO cells (
Figure 5B). The quantitative analysis of YAP staining revealed that YAP was localized in the nucleus in more than 50% of MCF10A-PTPN12-KO cell lines, while only less than 25% of WT cell lines showed YAP nuclear localization. Overall, these findings indicate that YAP localization is highly affected by PTPN12, which validates the result of the previous experiment and confirm the potential role of PTPN12 in the regulation of the Hippo pathway.
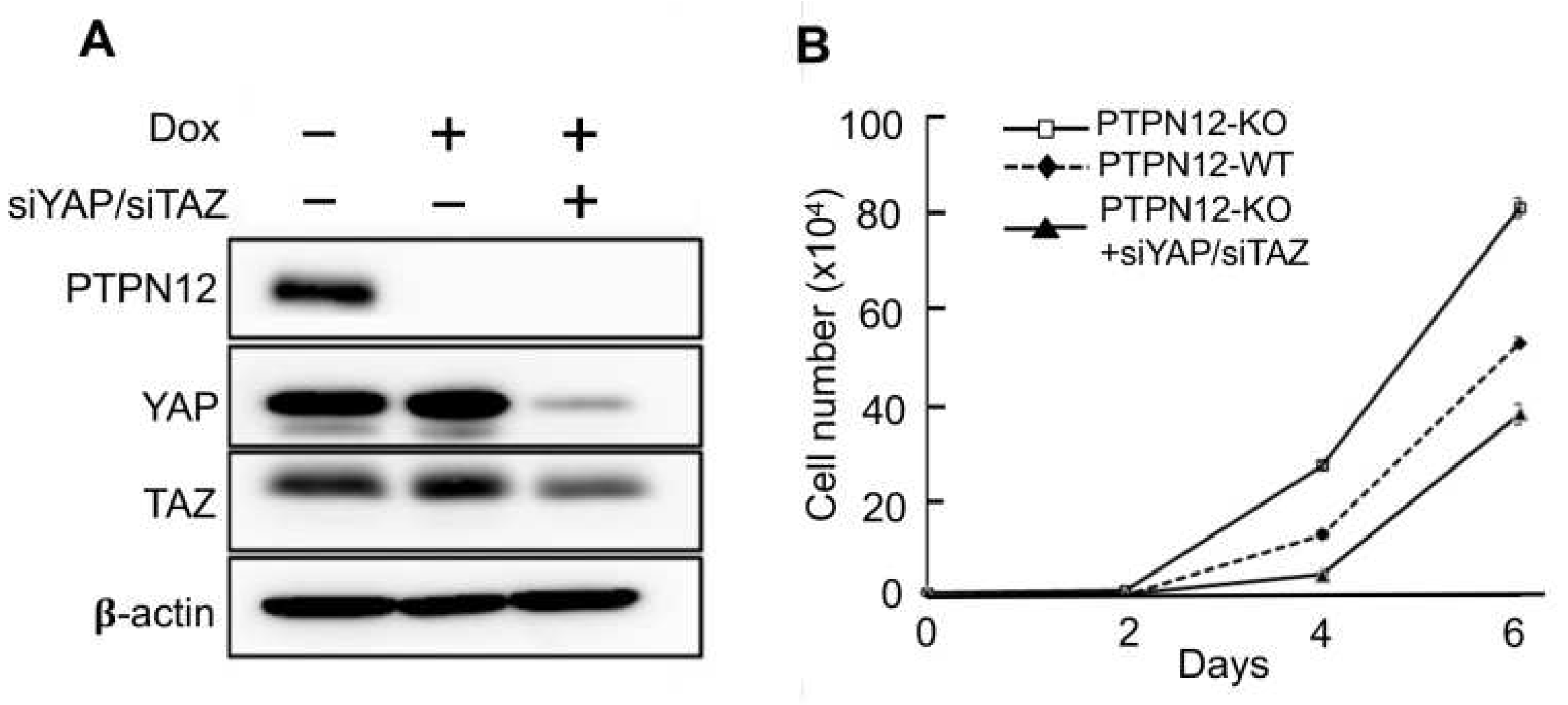
The findings of the present study showed that PTPN12 regulates the Hippo pathway by stimulation of YAP phosphorylation at S127, which prevents it from translocation to the nucleus to transactivate downstream gene transcription. YAP has oncogenic activity in the signaling pathway, and hyperactivation of the transcription coactivator can lead to an increase in cell proliferation. Since PTPN12 KO enhances YAP nuclear localization, it may lead to increased cell proliferation mediated by enhanced activity of YAP. To examine the role of PTPN12 in cell proliferation, MCF10A-PTPN12-KO and WT cells were cultured and counted for several days (
Figure 6B). It is clear that PTPN12-KO causes a more significant increase in cell proliferation compared to the WT. To investigate if the increased cell proliferation in MCF10A-PTPN12-KO was due to activation of YAP and its paralog TAZ, YAP and TAZ were knocked down by siRNAs in MCF10A-gPTPN12 cells (
Figure 6A). Knockdown of YAP and TAZ by siYAP and siTAZ in MCF10A-PTPN12-KO significantly reversed loss-of-PTPN12-induced increased cell proliferation (
Figure 6B). These findings strongly suggest that loss of PTPN12 upregulates cell proliferation by activating the Hippo pathway effectors and oncoproteins YAP and TAZ.
2.3.3. Effect of PTPN12 overexpression on Hippo signaling and cell proliferation and cell migration in mammary cells
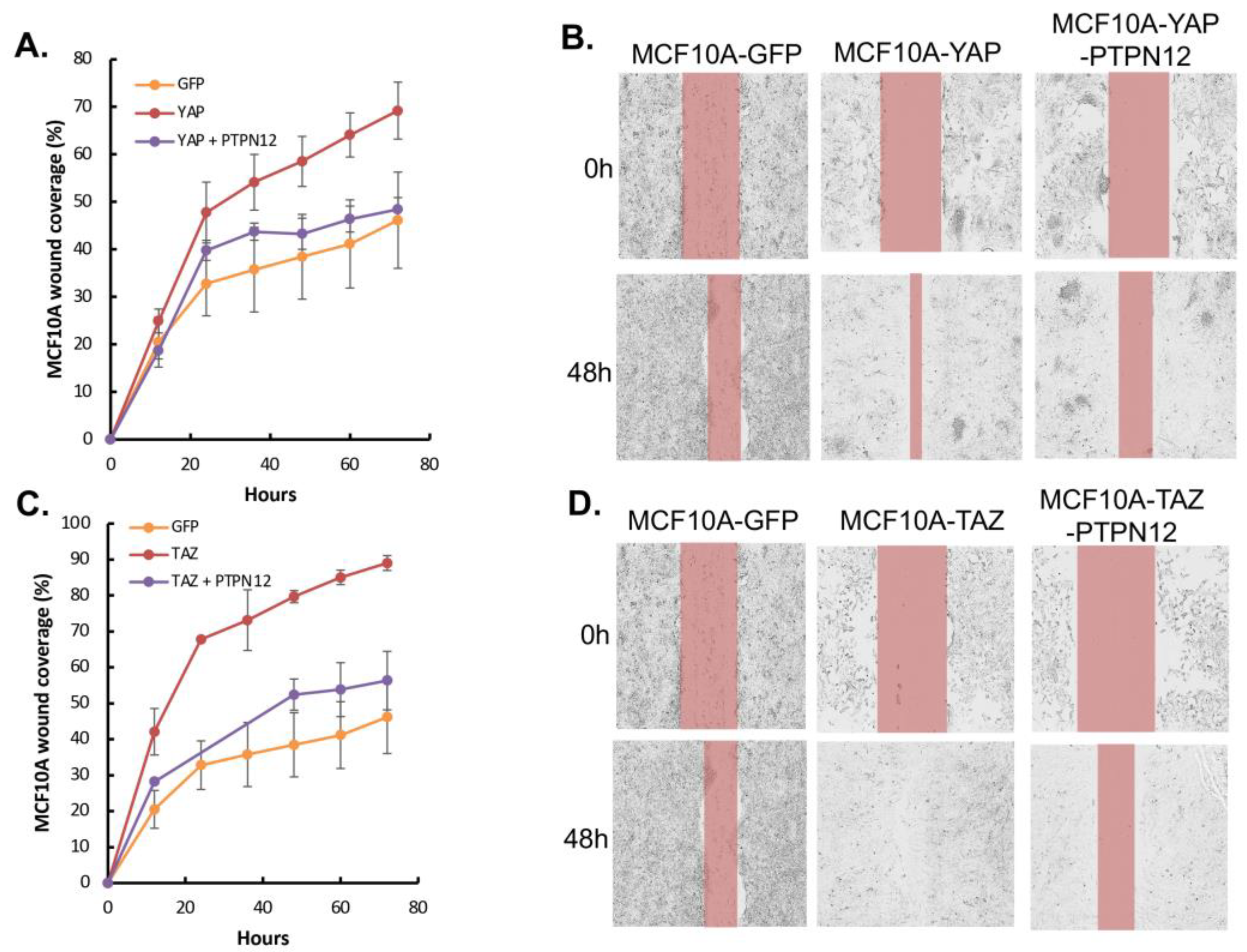
Finally, given PTPN12’s role as a tumor suppressor gene, we aimed to investigate whether its overexpression could mitigate the tumorigenic and metastatic effects induced by the oncoproteins YAP/TAZ, as previously reported [
51,
52]. YAP- or TAZ-overexpressing MCF10A cells were transduced with lentivirus expressing Dox-inducible PTPN12 (
Figure 7). Consistent with results obtained in HEK293T cells (
Figure 3), the overexpression of PTPN12 (+Dox) led to an increase in YAP-pS127 (
Figure 7). Considering that YAP/TAZ overexpression induces tumorigenic and metastatic phenotypes, such as enhanced cell proliferation and migration in MCF10A mammary cells [
18,
30,
53], we evaluated whether PTPN12 could counteract these effects. Remarkably, PTPN12 overexpression resulted in a reduction of YAP/TAZ-induced increased cell proliferation (
Figure 7A,B) and cell migration (
Figure 8A,D) in MCF10A mammary cells.
3. Discussion
3.1. Identification of novel PTP regulating the Hippo pathway
To identify the phosphatases regulating the Hippo pathway, a gain-of-functional screening with 68 PTPs was performed using LATS-BS and STBS-Luc reporter. 28 PTPs candidate were validated to be involved in the regulation of the Hippo pathway as they had significant effects on the signal of STBS-Luc or LATS-BS or both of them. Previous studies demonstrate that PTPN11, PTPN14, PTPN21 and CDC14 are involved in the Hippo pathway regulation[
29]. Thus, in the current study we identified 24 novel PTPs regulating the Hippo pathway through the two parallel screenings. The fold-change in the signal of the LATS biosensor by the PTPs candidates were significantly higher than the fold change in the signal of STBS-Luc, which is mainly because of the high sensitivity of LATS-BS. These screenings suggested that the LATS biosensor and YAP/TAZ reporter used in this study are sensitive tools to identify novel regulators of the Hippo pathway in real time. Based on function and fold change of the signal of biosensor and reporter, PTPRR, DUSP1, PTPDC1, and PTPN12 were selected for further validation.
PTPRR, a transmembrane tyrosine phosphatase, is inactivated in various malignancies, impacting tumorigenesis [
54,
55]. Loss of PTPRR in PTPRR-deficient mice leads to hyperphosphorylation of ERK, affecting MAPK signaling[
56,
57]. PTPRR downregulation is reported in ovarian cancer; its re-expression reduces cell proliferation, inhibiting tumorigenesis[
57,
58]. Studies suggest PTPRR negatively regulates cell proliferation in cancer cells, prompting an intriguing evaluation of its potential role in the Hippo pathway in tumorigenesis.
DUSP1, a dual-specific phosphatase, regulates MAPK by dephosphorylating ERK, contributing to tumorigenesis[
58,
59,
60,
61]. In hepatocellular cancer cells, DUSP1 expression inversely correlates with phosphorylated ERK and cell proliferation[
62,
63]. Downregulation of DUSP1 alters gene expression in various pathways, including metastasis, MAP kinase activity, and RTKs activity[
64]. Despite its oncogenic role in several cancers[
65,
66,
67,
68], the overall function of DUSP1 in tumor progression remains inconclusive. Given its dual role in tumorigenesis, exploring the crosstalk between the Hippo pathway and DUSP1 is intriguing. Considering the tumor suppressor roles of DUSP1 mediated by MAPK, and MAPK’s involvement in the Hippo pathway regulation, DUSP1 may regulate the Hippo pathway either by direct dephosphorylation of the Hippo component or indirectly through MAPK regulation.
PTPDC1 (protein tyrosine phosphatase domain containing 1) is one of the four members of CDC14s phosphatase family [
69]. Until now, there is not any study on the role of PTPDC1 in cancer. As PTPDC1 comprises the critical domains of DSPc (Dual specificity phosphatase, catalytic domain), it is thought that PTPDC1 may be involved in tumorigenesis [
70].
Therefore, it will be interesting to further evaluate how PTPC1, PTPRR, and DUSP1 regulates the Hippo pathway in tumorigenesis and metastasis.
3.2. PTPN12 tumor suppressor function in cancer is mediated by the Hippo pathway
Due to its pivotal roles in breast cancer and its function as a master regulator of RTKs[
46,
47,
71,
72], we investigated how PTPN12 influences tumorigenesis via the Hippo pathway. PTPN12 is implicated in various biological functions such as cell migration, adhesion, immunity, and cell survival[
47,
73,
74]. Dysregulation of the Hippo pathway, through mutation or altered expression of its components, disrupts cell contact inhibition, leading to uncontrolled cell proliferation—a hallmark of oncogenic transformation[
19]. Therefore, assessing the crosstalk between PTPN12 and the Hippo pathway is crucial for understanding the underlying mechanisms of PTPN12 loss in tumorigenesis. In line with this, we demonstrated that the loss of PTPN12 in MCF10A cells increased cell proliferation in a Hippo-dependent manner. This excessive cell proliferation, a critical process in tumorigenesis due to PTPN12 loss, is mediated by the Hippo signaling pathway effectors YAP and TAZ. Furthermore, we provided compelling evidence that PTPN12 exerts its tumor suppressor function through the Hippo pathway by suppressing YAP/TAZ-induced increased cell proliferation and migration. Our findings strongly suggest that the PTPN12-YAP/TAZ signaling axis may play a crucial role in mammary tumorigenesis and metastasis.
While serine phosphorylation, such as phosphorylation of YAP S127, is crucial for regulating the core components of the Hippo pathway, recent studies have highlighted the involvement of tyrosine phosphorylation in Hippo pathway regulation. We have recently show that RTKs, including EGFR, VEGFR, FGFR and RET, play significant roles in modulating the Hippo signaling pathway in cell proliferation, cell migration, and angiogenesis [
30,
34]. In breast cancer, recent findings also indicate that the loss of PTPN12 phosphatase function activates several oncogenic RTKs such as MET, PDGFRb, HER2, and EGFR [
46,
47,
72], positioning PTPN12 as a master regulator of protein tyrosine kinases. PTPN12 phosphatase function is compromised in breast cancer through inactivating mutations, deletions, or loss of expression, leading to the overactivation of multiple RTKs, particularly in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) subsets. Therefore, either restoring PTPN12 expression or employing a combinatorial inhibition of PTPN12-regulated RTKs in PTPN12-deficient TNBC cells inhibits cell proliferation[
46,
72]. As the oncogenic function of RTKs was associated with the increased oncogenic activity of YAP and TAZ through either direct or indirect regulation of YAP/TAZ activity by the tyrosine kinases[
30,
34], further studies need to investigate how PTPN12 is connected to the Hippo pathway. Tyrosine phosphatases such as PTPN12 may either directly regulate YAP and TAZ by dephosphorylation of YAP and TAZ at tyrosine residues or by indirect regulation of YAP and TAZ mediated by RTKs and RTK/MAPK/PI3K. Understanding the underlying molecular mechanism of the Hippo pathway regulation by PTPN12 may provide information about targeting oncogenes that are over-activated upon loss of PTPN12 in cancer treatment.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plasmid construction and purification
pTRIPZ lentiviral vector was used to construct all of the Dox-inducible PTP expression plasmids. For plasmid construction, cDNAs of PTPN12, PTPRR, PTPDC1 and DUSP1 previously constructed by us [
41] were first amplified by Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using gene-specific primers in
Table 1. PCR was performed using PrimeSTAR GXL DNA polymerase (Takara, R050A) according to the manufacturers’ instruction. All PCR products and vector were digested by AgeI and MluI restriction enzymes and was followed by subcloning of the digested PCR product into the AgeI/MluI sites of pTRIPZ vector. Plasmids were purified using the QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
To knock out PTPN12 gene in MCF10A, 2 different guide RNAs (gRNAs) sequences targeting PTPN12 (gPTPN12) were chosen from data set generated by David Root Group in 2016 [
75]. The gRNAs are optimized with maximum on-target effects and minimum off-target activity: gPTPN12-1: forward, 5’-CACCGTTTGTGCCATAGATTATACG–3’ ; reverse, 5′-AAACCGTATAATCTATGG-CACAAAC-3′; gPTPN12-2: forward, 5′-
CACCGAAGAAGGTCCCTCTCCAAGA-3′; reverse, 5′-
AAACTCTTGGAGAGGGACCTTC TTC-3′. BsmBI overhang sequence was added to each of the single-stranded complementary oligoes when they were synthesized. Lentiviral LentiGuide-Puro vector was digested by Esp3I/BsmBI fast digest enzyme (Thermo Fisher, # FD0454). The digested vector was separated on agarose gel and was purified by QIAquick Gel Extraction Kit (Qiagen) and eluted in EB buffer. To anneal and phosphorylate oligos, T4 Polynucleotide Kinase (PNK) (NEB, # M0201S) and10x T4 ligation buffer (NEB, # B0202S) were added to each tube containing gPTPN12-F and gPTPN12-R primers. Following the addition of PNK and buffer, the oligo tubes were put in a thermocycler running at 37°C for 30 min, 95°C for 5 min and then ramp down to 25°C at 5°C per min. Then, ligation reaction was catalyzed by mixing annealed oligos andEsp3I/BsmBI digested LentiGuide-Puro vector with Blunt/TA ligase Master Mix (NEB, # M0367S), followed by a heat shock transformation into Stbl3 competent cell.
4.2. Cell culture
HEK293T (human embryonic kidney; ATTC, Cat# CRL-3216) and HEK293AD (Cell Biolabs, LLC, Cat#AD-100) cell lines were maintained in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM; Sigma-Aldrich, # D6429) medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine essence (FBE) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (P/S) (Invitrogen). MCF10A (human immortalized mammary epithelial) cells expressing inducible Cas9 (iCas9) were cultured in DMEM/Nutrient Mixture F12 Ham without L-Glutamine (Sigma-Aldrich, # D6421) supplemented with 5% horse serum (HS) (Sigma-Aldrich, # H1270), 2.5 mM L-Glutamine (Sigma-Aldrich, # G7513), 10 ng/mL Insulin (Sigma-Aldrich, # I6634), 20 ng/ml human epidermal growth factor (hEGF) (Sigma-Aldrich, # E4269), 100 ng/mL cholera toxin (Sigma-Aldrich, # C8052), 0.5 μg/mL hydrocortisone (Sigma-Aldrich, # H4001) and 1% P/S. All cells were maintained in a 37 oC incubator with 5% CO2.
4.3. Lentivirus production
Plasmid transfection for lentivirus production were performed using Poly-jet transfection reagent according to the manufacturer’s protocol (SignaGen Laboratories). In brief, 1 × HEK293T cells (Passage number lower than 10) were seeded in each 35 mm cell culture plate pre-coated with 250 µl of 0.1 mg/mL poly-L-lysine. The next day, the growth media in each plate was replaced with prewarmed fresh media 30 min prior to transfection. Then, 0.5 µg of each of the pTRIPZ-PTPs, or Lenti-iCas9-neo or gPTPN12 in LentiGuide plasmid was mixed with 0.38 µg of psPAX viral packaging plasmid, 0.13 µg of pMD2G viral envelop plasmid and 3 µl of PolyJet transfection reagent (SignaGen, # SL100688 ) in Serum-free DMEM medium and incubated at room temperature for 15 min. The mixture was added dropwise into medium containing cells. The next day, the medium was replaced with 1ml of DMEM/10%FBS containing 10mM Sodium Butyrate (Santa Cruz, Biotechnology, # sc-202341A). Sodium Butyrate induces gene expression in cells. About 24 hours after treatment of the cells with Sodium Butyrate, the lentivirus-containing media was collected and aliquoted into 250 µl per 1.5 ml Eppendorf tube. After flash-freezing in liquid nitrogen, all virus aliquots were kept at -80 °C.
4.4. Establishment of stable cell lines
To establish HEK293T cells overexpressing PTPs, 3 × 105 HEK293T cells were seeded in each well of a 12-well plate. One day after seeding (~40%-50% confluency), cells were infected with varying amounts of lentivirus (0, 10, 25, 50, 100, 250 µl) expressing doxycycline (Dox)-inducible PTPs or Cas9 in the presence of 8 µg/ml polybrene in 500 µl/well. Twenty-four hours post-infection, cells were subjected to selection with 1.2 µg/mL puromycin.
To establish MCF10A cells expressing Dox-inducible gPTPN12, MCF10A cells were first infected with lentivirus expressing iCas9 as described above, following by selection at 400 µg/mL G481 (neomycin). The established MCF10A-iCas9 cells were further selected by selecting top 15% GFP-positive cells by FACS 2 days after Dox induction of GFP and Cas9.
The sorted cells were subsequently infected with lentivirus expressing gPTPN12, followed by puromycin selection at 2.5 µg/mL. Finally, the stable cell line was treated with 1ug/mL Dox for five days to induce Cas9 expression that leads to PTPN12 KO.
To establish inducible PTPN12 in MCF10A cells overexpressing wild-type YAP or TAZ, previously established YAP/TAZ overexpressing cells[
18,
76] were infected by lentivirus expressing PTPN12 cloned in Dox-inducible vector pTRIPZ, followed by puromycin selection at 1.5 µg/mL.
4.5. Protein extraction and western blot analysis and antibodies
Protein extraction and western blot analysis were as described previously[
18]. The following antibodies were used in our studies (
Table 2).
4.6. RNA extraction and qRT-PCR analysis
RNA extraction and qRT-PCR were carried out as described previously[
77]. Primer sequences for qRT-PCR analysis are: 1) Cyr61: forward, 5′-AATGGAGCCTCGCATCCTATA-3′; reverse, 5′-TTCTTTCACAAGGCGGCA-3′; 2) CTGF: forward, 5′-CCCTCGCGG CTTACCGACTGG-3′; reverse, 5′-CACAGGTCTTGGAACAGGCGC-3′.
4.7. Luciferase assays and gain-of-functional screening
To evaluate the activities of LATS kinase and YAP/TAZ, LATS-BS and STBS-Luc reporter were used, respectively, in luciferase assays. To validate LATS-BS and STBS-Luc, 3 × HEK293T cells were plated in each well of a 12 well plate. One day after cell seeding, 100 ng of LATS-BS and STBS-Luc plasmids were transfected alone or together with LATS2/MST2 or TAZ, respectively, into HEK293AD cells using Polyjet transfection reagent (SignaGen, # SL100688) described in section 2.3. One day after transfection, cells were lysed in 150 µl of Passive Lysis Buffer (PLB, Promega, # E194). Luciferase activity of STBS-Luc reporter was measured by Luciferase Assay Kit (Promega, # E1910) using Turner Biosystems 20/20 luminometer, whereas that of LATS-BS was measured by Nano-Glo® Luciferase Assay System (Promega, #N1110). The fold changes were calculated as the ratio of relative light unit (RLU) of LATS-BS + LATS2/MST2 or STBS-Luc + TAZ to that of LATS-BS or STBS-Luc, respectively. The data is the mean +/- standard deviation (S.D.) of triplicate samples. The experiments were repeated twice.
For gain-of-functional screen, a library including 68 PTPs previously constructed by us [
41]. LATS-BS or STBS-Luc plasmids were either transfected into HEK293AD alone or together with each PTP from the PTP library. To do cotransfection of PTPs and LATS-BS, a total amount of 500 ng plasmids including 100 ng SmBiT-14-3-3, 100 ng Lg-BiT-YAP and 300 ng PTP were transfected into the cells in each well of a 12 well plate. With regard to the cotransfection of PTP and STBS-Luc, 100 ng STBS-Luc plasmid was cotransfected with 400 ng PTP. One day after transfection, cells were lysed in 150 µl of PLB, followed by the luciferase assays described above. Fold change was calculated by the ratio of the RLU of LATS-BS or STBS-Luc plus PTP to that of control (RLU of LATS-BS or STBS-luc alone). The candidate PTPs were further validated by transfection of triplicate samples, followed by luciferase assays as described above.
4.8. Immunostaining
MCF10A-PTPN12-KO and MCHF10A-WT Cells were diluted into 4 × cells per mL and was dispensed 0.5 mL into each well of a 24 well plate. Before seeding the cells, one coverslip (Assistant company) was placed in each well of a 24 well plate. After two days of cell seeding, cell staining was done to evaluate and compare the localization of YAP between MCF10A-PTPN12-KO and MCF10A-WT cell lines. For immunostaining, cells were fixed in 200 µl of a 4% Paraformaldehyde (PFA) at RT for 10 min, followed by cell permeabilization with 200 µl of 0.2% Triton X-100 in 1x PBS at RT for 2 min. After permeabilization, blocking was performed by adding 200 µl of blocking and hybridization solution (BHS; 10% bovine serum albumin and 5% normal goat serum) and incubated on a shaker for 40 min. Cells were incubated in the Alex Fluor 488 conjugated anti-YAP antibody (D8H1X) XP® Rabbit mAb (Cell Signaling, #14074, 1:100) for 1h on a shaker with gentle agitation at RT for 1h in the dark. DAPI was used to stain DNA in cells. Inverted Nikon Eclipse TE 2000U microscope was used to capture Fluorescence fluorescent images.
4.9. Transient knockdown of YAP and TAZ in MCF10A-PTPN12-KO
Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) duplex targeting YAP or TAZ (siYAP or siTAZ) were purchased from Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT). A day before transfection with siRNAs, 4 × cells were seeded in 35 mm plate. MCF10A-PTPN12-KO cells were transfected with 100 nM siYAP and siTAZ using GenMute siRNA transfection reagent (Signagen, SL100568) based on the manufacturer’s protocol. Five hours after transfection, cells were collected for further experiments such as cell proliferation assay. The efficiency of the siRNAs in knocking down of YAP and TAZ was determined by western blot analysis three days after transfection.
4.10. Cell proliferation assay
2 × cells were plated in triplicate into each well of a 24-well plate. Cell counting was performed on days 2, 4, and 6 after cell seeding. The media in each well was refreshed every 3 days by replacing with complete growth media.
4.11. Cell migration assay
Wound healing analysis was used for cell migration assay. In brief, 2×104 cells were seeded into each well of a 96-well plate. Cells were grown until confluent next day. Wounds will be made using a WoundMakerTM (Perkin Elmer). Closure of wounds will be monitored for 72h using a Incycytes Zoom Live Cell Analysis system (Sartorius) at 37 oC in an incubator. Percentage of wound closure was calculated for each time point. The experiments were repeated twice. The means and standard deviations (S.D.) of triplicate samples for each time point were calculated.
5. Conclusions
In summary, this study has uncovered numerous novel PTPs influencing the Hippo pathway through gain-of-function screens. It presents compelling evidence that PTPN12 modulates cell proliferation by affecting the Hippo effector proteins YAP and TAZ, suggesting a potential strategy for treating breast cancer patients with compromised PTPN12. Given PTPN12’s involvement in other cancer types, further exploration of its interactions with the Hippo pathway in diverse cancers is warranted. Validating these findings across various cell lines and cancer types would enhance our understanding of PTPN12’s tumor suppressor role. Deciphering the functional significance of PTPs and the Hippo signaling pathway could yield novel insights into cancer initiation, progression, and development.
The preliminary data from this study can guide future projects, particularly in validating over 10 identified PTP candidates that regulate the Hippo pathway. Investigating the role of these PTPs in Hippo pathway regulation and exploring their impact on tumorigenesis or metastasis represents an intriguing avenue for further research.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Table S1: List of Primers Used for PCR.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.Y.; W.W. methodology, S.SE, A.G., X.Y.; formal analysis, S. SE., A.G..; investigation, S.SE., A.G., D.Z., Y.H., M.L., W.W.; writing—original draft preparation, S.SE, X.Y.; writing—review and editing, X.Y. A.G.; supervision, X.Y.; project administration, X.Y.; funding acquisition, X.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No extra data except the data presented in the manuscript is presented.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Dr. Qin Yan at Yale University School of Medicine for providing the Lenti-iCas9-neo plasmid.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chan, E. H.; Nousiainen, M.; Chalamalasetty, R. B.; Schafer, A.; Nigg, E. A.; Sillje, H. H. , The Ste20-like kinase Mst2 activates the human large tumor suppressor kinase Lats1. Oncogene 2005, 24, 2076–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, S.; Barrera, J.; Matthews, K.; Pan, D. , The Hippo signaling pathway coordinately regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by inactivating Yorkie, the Drosophila Homolog of YAP. Cell 2005, 122, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, K. F.; Pfleger, C. M.; Hariharan, I. K. , The Drosophila Mst ortholog, hippo, restricts growth and cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis. Cell 2003, 114, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udan, R. S.; Kango-Singh, M.; Nolo, R.; Tao, C.; Halder, G. , Hippo promotes proliferation arrest and apoptosis in the Salvador/Warts pathway. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Huang, J.; Dong, J.; Pan, D. , hippo encodes a Ste-20 family protein kinase that restricts cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in conjunction with salvador and warts. Cell 2003, 114, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Feldmann, G.; Huang, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, N.; Comerford, S. A.; Gayyed, M. F.; Anders, R. A.; Maitra, A.; Pan, D. , Elucidation of a universal size-control mechanism in Drosophila and mammals. Cell 2007, 130, 1120–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z. C.; Wei, X.; Shimizu, T.; Ramos, E.; Rohrbaugh, M.; Nikolaidis, N.; Ho, L. L.; Li, Y. , Control of cell proliferation and apoptosis by mob as tumor suppressor, mats. Cell 2005, 120, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapon, N.; Harvey, K. F.; Bell, D. W.; Wahrer, D. C.; Schiripo, T. A.; Haber, D. A.; Hariharan, I. K. , salvador Promotes both cell cycle exit and apoptosis in Drosophila and is mutated in human cancer cell lines. Cell 2002, 110, 467–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Stewart, R. A.; Yu, W. , Identifying tumor suppressors in genetic mosaics: the Drosophila lats gene encodes a putative protein kinase. Development 1995, 121, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.; Chang, M. T.; Vissers, J. H. A.; Dey, A.; Harvey, K. F. , The Hippo Pathway as a Driver of Select Human Cancers. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 781–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, B.; Yu, J.; Yang, X. , Roles of the Hippo pathway in lung development and tumorigenesis. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, S.; Yang, X. , LATS tumor suppressor: A new governor of cellular homeostasis. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 3892–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, Z.; J Janse van Rensburg, H.; Yang, X. , The Hippo pathway: immunity and cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, T. , Ghahremani M., Yang, X., The role of YAP and TAZ in angiogenesis and vascular mimicry. Cells 2019, 8, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, F.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, P.; Gao, J.; Wu, X. , Regulation of Hippo Signaling by Mechanical Signals and the Cytoskeleton. DNA Cell Biol. 2020, 39, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, X. Chapter 8: Targeting the Hippo pathway to improve response to chemotherapy. Tarteting Cell Survival Pathways to Enhance Response to Chemotherapy; Elsevier Publishing Company, 2019; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, X. , The Hippo pathway in chemotherapeutic drug resistance. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 2767–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Chun, A.; Cheung, K.; Rashidi, B.; Yang, X. , Tumor suppressor LATS1 is a negative regulator of oncogene YAP. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 5496–5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wei, X.; Li, W.; Udan, R. S.; Yang, Q.; Kim, J.; Xie, J.; Ikenoue, T.; Yu, J.; Li, L.; Zheng, P.; Ye, K.; Chinnaiyan, A.; Halder, G.; Lai, Z. C.; Guan, K. L. , Inactivation of YAP oncoprotein by the Hippo pathway is involved in cell contact inhibition and tissue growth control. Genes. Dev. 2007, 21, 2747–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Ye, X.; Yu, J.; Li, L.; Li, W.; Li, S.; Yu, J.; Lin, J. D.; Wang, C. Y.; Chinnaiyan, A. M.; Lai, Z. C.; Guan, K. L. , TEAD mediates YAP-dependent gene induction and growth control. Genes. Dev. 2008, 22, 1962–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S. W.; Lim, C. J.; Loo, L. S.; Chong, Y. F.; Huang, C.; Hong, W. , TEADs mediate nuclear retention of TAZ to promote oncogenic transformation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 14347–14358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q. Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, B.; Zha, Z. Y.; Bai, F.; Pei, X. H.; Zhao, S.; Xiong, Y.; Guan, K. L. , TAZ promotes cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition and is inhibited by the hippo pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 2426–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yang, X. , Targeting the Hippo pathway for breast cancer therapy. Cancers 2018, 10, E422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Varelas, X.; Guan, K. L. , Targeting the Hippo pathway in cancer, fibrosis, wound healing and regenerative medicine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 480–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardito, F.; Giuliani, M.; Perrone, D.; Troiano, G.; Lo Muzio, L. , The crucial role of protein phosphorylation in cell signaling and its use as targeted therapy (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, T. , Tyrosine phosphorylation: thirty years and counting. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 140–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmon, M. A.; Schlessinger, J. , Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 2010, 141, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, E. K.; Sosale, N. G.; Lazzara, M. J. , Cell signaling regulation by protein phosphorylation: a multivariate, heterogeneous, and context-dependent process. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 40, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmasti Emami, S.; Zhang, D.; Yang, X. , Interaction of the Hippo Pathway and Phosphatases in Tumorigenesis. Cancers 2020, 12, 2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, T. N. , K; Janse van Rensburg, HJ; Maritan, SM; Wu, L; Hao, Y; Montminy, T; Yu, J; Khanal, K; Mulligan, LM; Yang, X, A gain-of-functional screen identifies the Hippo pathway as a central mediator of receptor tyrosine kinases during tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2020, 39, 334–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuven, N.; Shanzer, M.; Shaul, Y. , Hippo Pathway Regulation by Tyrosine Kinases. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1893, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lamar, J. M.; Xiao, Y.; Norton, E.; Jiang, Z. G.; Gerhard, G. M.; Kooner, S.; Warren, J. S. A.; Hynes, R. O. , SRC tyrosine kinase activates the YAP/TAZ axis and thereby drives tumor growth and metastasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 2302–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, K. A. , T; Lightbody, E; Khanal, P; Nicol, CJ; Yang, X, A kinome-wide screen using a NanoLuc LATS luminescent biosensor identifies ALK as a novel regulator of the Hippo pathway in tumorigenesis and immune evasion. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 12487–12499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, T.; Janse van Rensburg, H. J.; Lightbody, E. D.; Neveu, B.; Champagne, A.; Ghaffari, A.; Kay, V. R.; Hao, Y.; Shen, H.; Yeung, B.; Croy, B. A.; Guan, K. L.; Pouliot, F.; Zhang, J.; Nicol, C. J. B.; Yang, X. , A LATS biosensor functional screen identifies VEGFR as a novel regulator of the Hippo pathway in angiogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Ji, X.; Cao, X.; Dai, X.; Xu, L.; Zhao, H.; Guo, X.; Yan, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, C.; Zhou, Q.; Tang, M.; Xia, Z.; Li, L.; Cong, Y. S.; Ye, S.; Liang, T.; Feng, X. H.; Zhao, B. , Src Inhibits the Hippo Tumor Suppressor Pathway through Tyrosine Phosphorylation of Lats1. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 4868–4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, K. E.; Yang, N.; Mussell, A. L.; Zhang, J. , The Regulatory Role of KIBRA and PTPN14 in Hippo Signaling and Beyond. Genes 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yang, N.; Figel, S. A.; Wilson, K. E.; Morrison, C. D.; Gelman, I. H.; Zhang, J. , PTPN14 interacts with and negatively regulates the oncogenic function of YAP. Oncogene 2013, 32, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaloglou, C.; Lehmann, W.; Martin, T.; Delaunay, C.; Hueber, A.; Barys, L.; Niu, H.; Billy, E.; Wartmann, M.; Ito, M.; Wilson, C. J.; Digan, M. E.; Bauer, A.; Voshol, H.; Christofori, G.; Sellers, W. R.; Hofmann, F.; Schmelzle, T. , The tyrosine phosphatase PTPN14 is a negative regulator of YAP activity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tran, K. M.; Aziz, K. E.; Sorokin, A. V.; Chen, J.; Wang, W. , Defining the Protein-Protein Interaction Network of the Human Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Family. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2016, 15, 3030–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Yuan, J.; Li, X.; Feng, L.; Park, J.-I.; Chen, J. , PTPN14 is required for the density-dependent control of YAP1. Genes. Dev. 2012, 26, 1959–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Tran, K. M.; Aziz, K. E.; Sorokin, A. V.; Chen, J.; Wang, W. , Defining the protein-protein interaction network of the human protein tyrosine phosphatase family. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2016, 15, 3030–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Chen, Y.; Ji, M.; Dong, J. , KIBRA regulates Hippo signaling activity via interactions with large tumor suppressor kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 7788–7796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Chen, Y.; Ji, M.; Volle, D. J.; Lewis, R. E.; Tsai, M.-Y.; Dong, J. , KIBRA protein phosphorylation is regulated by mitotic kinase aurora and protein phosphatase 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 36304–36315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Takahashi-Kanemitsu, A.; Kikuchi, I.; Ben, C.; Hatakeyama, M. , Transcriptional co-activator functions of YAP and TAZ are inversely regulated by tyrosine phosphorylation status of Parafibromin. Iscience 2018, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, R.; Masoudi, M.; Takahashi, A.; Fujii, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Kikuchi, I.; Satou, Y.; Taira, M.; Hatakeyama, M. , YAP and TAZ, Hippo signaling targets, act as a rheostat for nuclear SHP2 function. Dev. Cell 2013, 26, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Aceto, N.; Meerbrey, K. L.; Kessler, J. D.; Zhou, C.; Migliaccio, I.; Nguyen, D. X.; Pavlova, N. N.; Botero, M.; Huang, J.; Bernardi, R. J.; Schmitt, E.; Hu, G.; Li, M. Z.; Dephoure, N.; Gygi, S. P.; Rao, M.; Creighton, C. J.; Hilsenbeck, S. G.; Shaw, C. A.; Muzny, D.; Gibbs, R. A.; Wheeler, D. A.; Osborne, C. K.; Schiff, R.; Bentires-Alj, M.; Elledge, S. J.; Westbrook, T. F. , Activation of multiple proto-oncogenic tyrosine kinases in breast cancer via loss of the PTPN12 phosphatase. Cell 2011, 144, 703–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Davidson, D.; Martins Souza, C.; Zhong, M. C.; Wu, N.; Park, M.; Muller, W. J.; Veillette, A. , Loss of PTPN12 Stimulates Progression of ErbB2-Dependent Breast Cancer by Enhancing Cell Survival, Migration, and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 35, 4069–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Li, L.; Xu, W.; Tian, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Gong, Y.; Ke, J.; Gong, J.; Chang, J.; Zhong, R.; Miao, X. , A missense variant in PTPN12 associated with the risk of colorectal cancer by modifying Ras/MEK/ERK signaling. Cancer Epidemiol. 2019, 59, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y. H.; Wang, Y. N.; Meng, L. B.; Zhang, A. L.; Liu, B. , Progress in the correlation between PTPN12 gene expression and human tumors. Medicine 2020, 99, e20445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wu, L.; Zhang, S. M.; Lu, M.; Cheung, W. K.; Cai, W.; Gale, M.; Xu, Q.; Yan, Q. , An easy and efficient inducible CRISPR/Cas9 platform with improved specificity for multiple gene targeting. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, e149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, M.; Cai, M.; Zhang, C.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Shao, R. , Transcriptional co-activators YAP/TAZ: Potential therapeutic targets for metastatic breast cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, B. J. , YAP/TAZ: Drivers of tumor growth, metastasis, and resistance to therapy. Bioessays 2020, 42, e1900162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S. W.; Lim, C. J.; Guo, K.; Ng, C. P.; Lee, I.; Hunziker, W.; Zeng, Q.; Hong, W. , A role for TAZ in migration, invasion, and tumorigenesis of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2592–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menigatti, M.; Cattaneo, E.; Sabates-Bellver, J.; Ilinsky, V. V.; Went, P.; Buffoli, F.; Marquez, V. E.; Jiricny, J.; Marra, G. , The protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type R gene is an early and frequent target of silencing in human colorectal tumorigenesis. Mol. Cancer 2009, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shen, D.; Parsons, D. W.; Bardelli, A.; Sager, J.; Szabo, S.; Ptak, J.; Silliman, N.; Peters, B. A.; van der Heijden, M. S.; Parmigiani, G.; Yan, H.; Wang, T. L.; Riggins, G.; Powell, S. M.; Willson, J. K.; Markowitz, S.; Kinzler, K. W.; Vogelstein, B.; Velculescu, V. E. , Mutational analysis of the tyrosine phosphatome in colorectal cancers. Science 2004, 304, 1164–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munkley, J.; Lafferty, N. P.; Kalna, G.; Robson, C. N.; Leung, H. Y.; Rajan, P.; Elliott, D. J. , Androgen-regulation of the protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPRR activates ERK1/2 signalling in prostate cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirivi, R. G.; Noordman, Y. E.; Van der Zee, C. E.; Hendriks, W. J. , Altered MAP kinase phosphorylation and impaired motor coordination in PTPRR deficient mice. J. Neurochem. 2007, 101, 829–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, L.; Chen, S.; Hao, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhuang, M.; Yu, Y.; Li, D.; Fan, G. , Protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type R (PTPRR) antagonizes the Wnt signaling pathway in ovarian cancer by dephosphorylating and inactivating β-catenin. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 18306–18323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, D. M.; Keyse, S. M. , Differential regulation of MAP kinase signalling by dual-specificity protein phosphatases. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3203–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krysan, K.; Reckamp, K. L.; Dalwadi, H.; Sharma, S.; Rozengurt, E.; Dohadwala, M.; Dubinett, S. M. , Prostaglandin E2 activates mitogen-activated protein kinase/Erk pathway signaling and cell proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer cells in an epidermal growth factor receptor-independent manner. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6275–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanai, M.; Konda, Y.; Nakajima, T.; Izumi, Y.; Kanda, N.; Nanakin, A.; Kubohara, Y.; Chiba, T. , Differentiation-inducing factor-1 (DIF-1) inhibits STAT3 activity involved in gastric cancer cell proliferation via MEK-ERK-dependent pathway. Oncogene 2003, 22, 548–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keyse, S. M. , Dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatases (MKPs) and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008, 27, 253–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvisi, D. F.; Pinna, F.; Meloni, F.; Ladu, S.; Pellegrino, R.; Sini, M.; Daino, L.; Simile, M. M.; De Miglio, M. R.; Virdis, P.; Frau, M.; Tomasi, M. L.; Seddaiu, M. A.; Muroni, M. R.; Feo, F.; Pascale, R. M. , Dual-specificity phosphatase 1 ubiquitination in extracellular signal-regulated kinase-mediated control of growth in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moncho-Amor, V.; Ibañez de Cáceres, I.; Bandres, E.; Martínez-Poveda, B.; Orgaz, J. L.; Sánchez-Pérez, I.; Zazo, S.; Rovira, A.; Albanell, J.; Jiménez, B.; Rojo, F.; Belda-Iniesta, C.; García-Foncillas, J.; Perona, R. , DUSP1/MKP1 promotes angiogenesis, invasion and metastasis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2011, 30, 668–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magi-Galluzzi, C.; Mishra, R.; Fiorentino, M.; Montironi, R.; Yao, H.; Capodieci, P.; Wishnow, K.; Kaplan, I.; Stork, P. J.; Loda, M. , Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 1 is overexpressed in prostate cancers and is inversely related to apoptosis. Lab. Investig. 1997, 76, 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- Srikanth, S.; Franklin, C. C.; Duke, R. C.; Kraft, R. S. , Human DU145 prostate cancer cells overexpressing mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 are resistant to Fas ligand-induced mitochondrial perturbations and cellular apoptosis. Mol. Cell Biochem. 1999, 199, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loda, M.; Capodieci, P.; Mishra, R.; Yao, H.; Corless, C.; Grigioni, W.; Wang, Y.; Magi-Galluzzi, C.; Stork, P. J. , Expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 in the early phases of human epithelial carcinogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 1996, 149, 1553–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Shen, B.; Liang, Y.; Jin, R.; Liu, X.; Shi, L.; Cai, X. , Role of DUSP1/MKP1 in tumorigenesis, tumor progression and therapy. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 2061–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhore, N.; Wang, B. J.; Chen, Y. W.; Liao, Y. F. Critical Roles of Dual-Specificity Phosphatases in Neuronal Proteostasis and Neurological Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P. P.; Qi, X. W.; Sun, N.; Sun, Y. Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, X. N.; Ding, J.; Han, F.; Zhang, Y. , The emerging roles of dual-specificity phosphatases and their specific characteristics in human cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2021, 1876, 188562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Rhee, I. , Important roles of protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPN12 in tumor progression. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 144, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.; Chung, H. C.; Sun, T.; Tyagi, S.; Dobrolecki, L. E.; Dominguez-Vidana, R.; Kurley, S. J.; Orellana, M.; Renwick, A.; Henke, D. M.; Katsonis, P.; Schmitt, E.; Chan, D. W.; Li, H.; Mao, S.; Petrovic, I.; Creighton, C. J.; Gutierrez, C.; Dubrulle, J.; Stossi, F.; Tyner, J. W.; Lichtarge, O.; Lin, C. Y.; Zhang, B.; Scott, K. L.; Hilsenbeck, S. G.; Sun, J.; Yu, X.; Osborne, C. K.; Schiff, R.; Christensen, J. G.; Shields, D. J.; Rimawi, M. F.; Ellis, M. J.; Shaw, C. A.; Lewis, M. T.; Westbrook, T. F. , Combinatorial inhibition of PTPN12-regulated receptors leads to a broadly effective therapeutic strategy in triple-negative breast cancer. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, I.; Zhong, M. C.; Reizis, B.; Cheong, C.; Veillette, A. , Control of dendritic cell migration, T cell-dependent immunity, and autoimmunity by protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPN12 expressed in dendritic cells. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 34, 888–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, C. M.; Davidson, D.; Rhee, I.; Gratton, J. P.; Davis, E. C.; Veillette, A. , The phosphatase PTP-PEST/PTPN12 regulates endothelial cell migration and adhesion, but not permeability, and controls vascular development and embryonic viability. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 43180–43190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doench, J. G.; Fusi, N.; Sullender, M.; Hegde, M.; Vaimberg, E. W.; Donovan, K. F.; Smith, I.; Tothova, Z.; Wilen, C.; Orchard, R. , Optimized sgRNA design to maximize activity and minimize off-target effects of CRISPR-Cas9. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D.; Ho, K. C.; Hao, Y.; Yang, X. , Taxol resistance in breast cancer cells is mediated by the hippo pathway component TAZ and its downstream transcriptional targets Cyr61 and CTGF. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2728–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janse van Rensburg, H. J.; Azad, T.; Ling, M.; Hao, Y.; Snetsinger, B.; Khanal, P.; Minassian, L. M.; Graham, C. H.; Rauh, M. J.; Yang, X. , The Hippo pathway component TAZ promotes immune evasion in human cancer through PD-L1. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1457–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Parallel screens for PTPs regulating the Hippo pathway by the LATS-BS and STBS-Luc (YAP/TAZ reporter). The ratio of LATS-BS (A) and STBS-Luc reporter (B) signal after cotransfection with phosphatases to that of LATS-BS or STBS-Luc alone was calculated as fold changes. A fold change greater than 2 was considered significant and indicated as “*”.
Figure 1.
Parallel screens for PTPs regulating the Hippo pathway by the LATS-BS and STBS-Luc (YAP/TAZ reporter). The ratio of LATS-BS (A) and STBS-Luc reporter (B) signal after cotransfection with phosphatases to that of LATS-BS or STBS-Luc alone was calculated as fold changes. A fold change greater than 2 was considered significant and indicated as “*”.
Figure 2.
Validation of candidate PTPs regulating the Hippo pathway. A triplicate test was performed to validate the result of the first screening. The fold change of LATS-BS and STBS-Luc reporter was calculated after cotransfection with each phosphatase. “*” represents fold change greater than 2.
Figure 2.
Validation of candidate PTPs regulating the Hippo pathway. A triplicate test was performed to validate the result of the first screening. The fold change of LATS-BS and STBS-Luc reporter was calculated after cotransfection with each phosphatase. “*” represents fold change greater than 2.
Figure 3.
PTPs candidates stimulate phosphorylation of YAP-pS127 endogenously. Western blot analysis of YAP-pS127 after induction of PTPs candidate expression by Dox in HEK293T stable cell line. Without Dox, HEK293T-PTPs stable cell lines do not express PTPs, while Dox treatment induces expression of FLAG-tagged PTPs. Expression of each of the PTPs candidates stimulates phosphorylation of YAP at S127 which validates the result of screening.
Figure 3.
PTPs candidates stimulate phosphorylation of YAP-pS127 endogenously. Western blot analysis of YAP-pS127 after induction of PTPs candidate expression by Dox in HEK293T stable cell line. Without Dox, HEK293T-PTPs stable cell lines do not express PTPs, while Dox treatment induces expression of FLAG-tagged PTPs. Expression of each of the PTPs candidates stimulates phosphorylation of YAP at S127 which validates the result of screening.
Figure 4.
PTPN12 overexpression downregulates mRNA expression of CTGF and Cyr61. qRT-PCR analysis of mRNA levels of CTGF and Cyr61 in HEK293T-PTPN12 stable cell line in the absence (-) and presence (+) of Dox treatment. The relative mRNA levels were calculated based on the ratio of mRNA levels under +/- conditions. The mean +/- S.D. of triplicate samples are shown.
Figure 4.
PTPN12 overexpression downregulates mRNA expression of CTGF and Cyr61. qRT-PCR analysis of mRNA levels of CTGF and Cyr61 in HEK293T-PTPN12 stable cell line in the absence (-) and presence (+) of Dox treatment. The relative mRNA levels were calculated based on the ratio of mRNA levels under +/- conditions. The mean +/- S.D. of triplicate samples are shown.
Figure 5.
Loss of PTPN12 decrease phosphorylation of YAP at S127 and increase YAP nuclear location. A) Decreased phosphorylation of YAP at S127 by PTPN12 in MCF10A-iCas9-gPTPN12-KO mammary cells. MCF10A-iCas9 stably expressing gPTPN12-2 (1) or gPTPN12-3 (2) was untreated (-) or treated (+) with Dox for 5 days, followed by western blot analysis of PTPN12, YAP, S127-phosphorylated YAP (YAP-pS127) using anti-PTPN12, anti-YAP, and anti-pS127-YAP antibodies. B, C) YAP immunostaining in MCF10A-PTPN12-KO and WT cell line. YAP is more localized in the cytoplasm in MCF10A-PTPN12-WT, while nuclear localization of YAP increased in the PTPN12-KO cell line (B). The quantitative analysis of YAP staining showed that in more than 50% of MCF10A-PTPN12-KO cell line YAP is localized in the nucleus, while only less than 25% of WT cell line demonstrated YAP nuclear localization (C).
Figure 5.
Loss of PTPN12 decrease phosphorylation of YAP at S127 and increase YAP nuclear location. A) Decreased phosphorylation of YAP at S127 by PTPN12 in MCF10A-iCas9-gPTPN12-KO mammary cells. MCF10A-iCas9 stably expressing gPTPN12-2 (1) or gPTPN12-3 (2) was untreated (-) or treated (+) with Dox for 5 days, followed by western blot analysis of PTPN12, YAP, S127-phosphorylated YAP (YAP-pS127) using anti-PTPN12, anti-YAP, and anti-pS127-YAP antibodies. B, C) YAP immunostaining in MCF10A-PTPN12-KO and WT cell line. YAP is more localized in the cytoplasm in MCF10A-PTPN12-WT, while nuclear localization of YAP increased in the PTPN12-KO cell line (B). The quantitative analysis of YAP staining showed that in more than 50% of MCF10A-PTPN12-KO cell line YAP is localized in the nucleus, while only less than 25% of WT cell line demonstrated YAP nuclear localization (C).
Figure 6.
PTPN12 regulates cell proliferation which is mediated by the Hippo signaling pathway. (A) Western blot analysis of YAP and TAZ after siYAP/siTAZ transfection into MCF10A-gPTPN12 cells. (B) Cell proliferation assay. Cell proliferation was measured in MCF10A-PTPN12-WT (-Dox, -siYAP/siTAZ), MCF10A-PTPN12-KO (+Dox, -siYAP/siTAZ) and MCF10A-PTPN12-KO-siYAP/siTAZ (+Dox, +siYAP/siTAZ) cells. Cell numbers were counted on days 2, 4 and 6 after seeding.
Figure 6.
PTPN12 regulates cell proliferation which is mediated by the Hippo signaling pathway. (A) Western blot analysis of YAP and TAZ after siYAP/siTAZ transfection into MCF10A-gPTPN12 cells. (B) Cell proliferation assay. Cell proliferation was measured in MCF10A-PTPN12-WT (-Dox, -siYAP/siTAZ), MCF10A-PTPN12-KO (+Dox, -siYAP/siTAZ) and MCF10A-PTPN12-KO-siYAP/siTAZ (+Dox, +siYAP/siTAZ) cells. Cell numbers were counted on days 2, 4 and 6 after seeding.
Figure 7.
Overexpression of PTPN12 suppresses YAP/TAZ-induced increased mammary cell proliferation. A. Inducible expression of PTPN in MCF10A-YAP or –TAZ cells. Dox was added to induce PTPN12 in MCF10A-YAP-PTPN12/pTRIPZ or MCF10A-TAZ-PTPN12/pTRIPZ cells. MCF10A cells expressing WPI lentiviral vector expressing GFP were used as a control. Forty-eight hours after Dox induction, proteins were extracted from cells and subjected to western blot analysis of PTPN12, YAP and TAZ. 𝛃-actin was used as internal control. B. Increased levels of phosphorylated YAP after PTPN12 overexpression. Protein lysates from A. were subjected to western blot analysis of PTPN12, YAP-pS217, and YAP. C. Suppression of YAP-induced increased cell proliferation by PTPN12. MCF10A-GFP (WPI vector) and MCF10A-YAP-PTPN12 in the absence or presence of Dox were subjected to cell proliferation analysis. D. Suppression of TAZ-induced increased cell proliferation by PTPN12. MCF10A-GFP (WPI vector) and MCF10A-TAZ-PTPN12 in the absence or presence of Dox were subjected to cell proliferation analysis. The mean and standard deviation (S.D.) of cell numbers in triplicate samples at each day was shown.
Figure 7.
Overexpression of PTPN12 suppresses YAP/TAZ-induced increased mammary cell proliferation. A. Inducible expression of PTPN in MCF10A-YAP or –TAZ cells. Dox was added to induce PTPN12 in MCF10A-YAP-PTPN12/pTRIPZ or MCF10A-TAZ-PTPN12/pTRIPZ cells. MCF10A cells expressing WPI lentiviral vector expressing GFP were used as a control. Forty-eight hours after Dox induction, proteins were extracted from cells and subjected to western blot analysis of PTPN12, YAP and TAZ. 𝛃-actin was used as internal control. B. Increased levels of phosphorylated YAP after PTPN12 overexpression. Protein lysates from A. were subjected to western blot analysis of PTPN12, YAP-pS217, and YAP. C. Suppression of YAP-induced increased cell proliferation by PTPN12. MCF10A-GFP (WPI vector) and MCF10A-YAP-PTPN12 in the absence or presence of Dox were subjected to cell proliferation analysis. D. Suppression of TAZ-induced increased cell proliferation by PTPN12. MCF10A-GFP (WPI vector) and MCF10A-TAZ-PTPN12 in the absence or presence of Dox were subjected to cell proliferation analysis. The mean and standard deviation (S.D.) of cell numbers in triplicate samples at each day was shown.
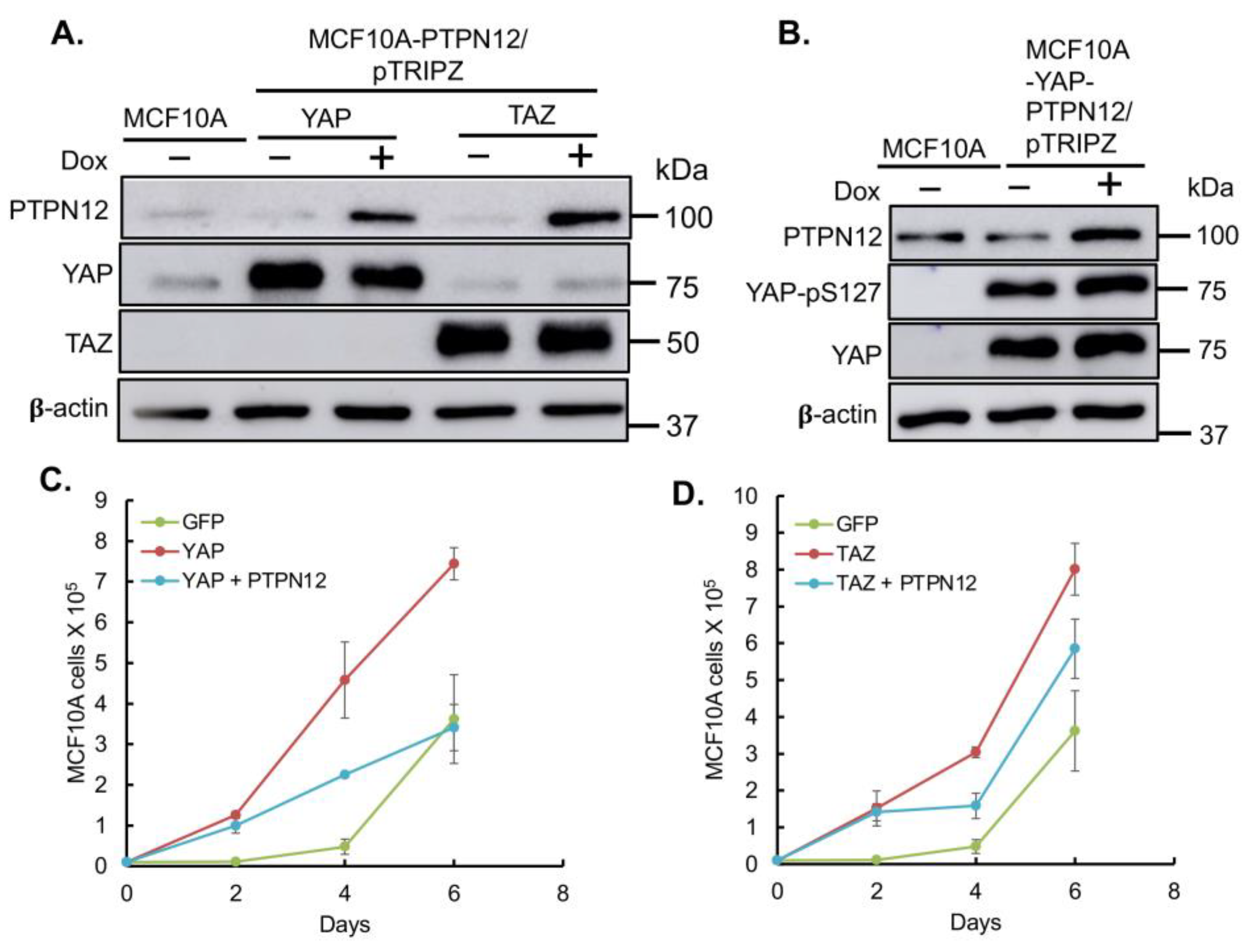
Figure 8.
Inhibition of YAP/TAZ-induced increased cell migration by PTPN12 in MCF10A mammary cells. A. C. Wound healing analysis using Incucyte. MCF10A-GFP (WPI vector), MCF10A-YAP/TAZ expressing Dox-inducible PTPN12 cells in the absence or presence of Dox (+PTPN12) were seeded into 96-wells. After making the wounds, cell migration was monitored as % of wound closure using Incucyte Zoom for 72 h. B. D. Images from A. showing the wound closure at 0h & 48 h. MCF10A-GFP was used as a control for both MCF10A-YAP/PTPN12 and MCF10A-TAZ/PTPN12.
Figure 8.
Inhibition of YAP/TAZ-induced increased cell migration by PTPN12 in MCF10A mammary cells. A. C. Wound healing analysis using Incucyte. MCF10A-GFP (WPI vector), MCF10A-YAP/TAZ expressing Dox-inducible PTPN12 cells in the absence or presence of Dox (+PTPN12) were seeded into 96-wells. After making the wounds, cell migration was monitored as % of wound closure using Incucyte Zoom for 72 h. B. D. Images from A. showing the wound closure at 0h & 48 h. MCF10A-GFP was used as a control for both MCF10A-YAP/PTPN12 and MCF10A-TAZ/PTPN12.
Table 1.
Gene-Specific primers for plasmid construction.
Table 1.
Gene-Specific primers for plasmid construction.
| Construct |
Forward Primer (5′-3′) |
Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
| PTPN12-pTRIPZ |
5’-CGACCGGTGCCACCATGGAAG
ACTACAAAGACGATGACGACAA
GATGGAGCAAGTGGAGATCCTG–3’ |
5’-ACGACGCGTTCATGTCCATTC TGAAGGTG-3’ |
| PTPRR-pTRIPZ |
5’-CGACCGGTGCCACCATGGACTA CAAAGACGATGACGACAAGATGA
TTCTTCACAGATTAAAAGAAAG-3’ |
5’-ACGACGCGTTCACTGGACAGT
CTCTGCTG-3’ |
| DUSP1-pTRIPZ |
5’-CGACCGGTGCCACCATGGACTA CAAAGACGATGACGACAAGATGG TCATGGAAGTGGGCAC-3’ |
5’-ACGACGCGTTCAGCAGCTGGG AGAGGTCGTAATG-3’ |
| PTPDC1-pTRIPZ |
5’-CGACCGGTGCCACCATGGACTA CAAAGACGATGACGACAAGATGG CTGCAGGAGTCTTGCC-3’ |
5’-ACGACGCGTCTAGAGGCCAGG CTTAGGGC-3’
|
Table 2.
Antibodies used for Western blot analysis.
Table 2.
Antibodies used for Western blot analysis.
| Primary or Secondary |
Protein |
Antibody |
Dilution |
Company |
| Primary |
PTPs |
α-FLAG (M2) |
1:1000 |
Sigma-Aldrich |
| Primary |
ꞵ-actin |
α-ꞵ-actin |
1:10000 |
Sigma-Aldrich |
| Primary |
Cas9 |
Cas9 (7A9-3A3) Mouse mAb |
1:1000 |
Cell Signaling |
| Primary |
PTPN12 |
PTP-PEST Rabbit mAb |
1:1000 |
Cell Signaling |
| Primary |
Phospho-YAP |
Phospho-YAP (Ser127)-mAb |
1:1000 |
Cell Signaling |
| Primary |
YAP/TAZ |
YAP/TAZRabbit mAb |
1:1000 |
Cell Signaling |
| Secondary |
--- |
HRP goat α-mouse |
1:10000 |
Cell Signaling |
| Secondary |
--- |
HRP goat α-rabbit |
1:10000 |
Cell Signaling |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).